A New Method to Assess Fine-Scale Outdoor Thermal Comfort for Urban Agglomerations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The UrbClim Model
2.2. Outdoor WBGT Calculation
2.3. Experiment Setup
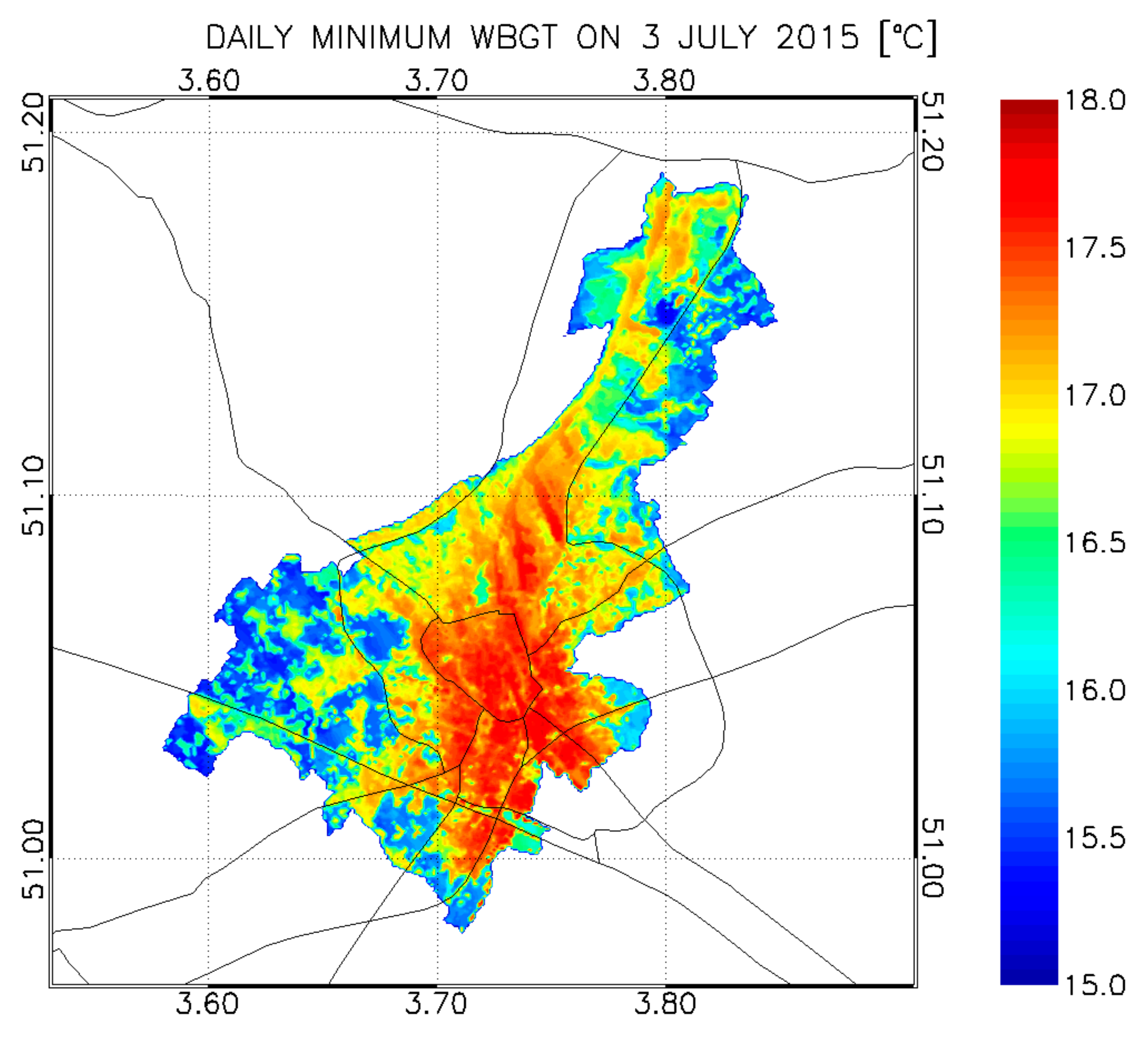
3. Results
3.1. Model Evaluation
3.2. Effect of Green and Blue Areas on Air Temperatures
3.3. Effect of Green and Blue Areas on Thermal Comfort
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenzweig, C.C.; Solecki, W.W.; Romero-Lankao, P.P.; Mehrotra, S.; Dhakal, S.S.; Bowman, T.T.; Ali Ibrahim, S. ARC3.2 Summary for City Leaders. Urban Climate Change Research Network; Columbia University: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lemonsu, A.A.; Viguié, V.V.; Daniel, M.M.; Masson, V.V. Vulnerability to heat waves: Impact of urban expansion scenarios on urban heat island and heat stress in Paris (France). Urban Clim. 2015, 14, 586–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, T.R.R.; Johnson, G.T.T.; Steyn, D.G.G.; Watson, I.D. Simulation of surface urban heat islands under ‘‘ideal’’ conditions at night. Part 2: Diagnosis of causation. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1991, 56, 339–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, V. Urban surface modeling and the meso-scale impact of cities. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2006, 84, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, B.H.H.; Carlson, T.N.N.; Rosenzweig, C.; Goldberg, R.; Druyan, L.; Cox, J.; Gaffin, S.; Parshall, L.; Civerolo, K. A modification to the NOAH LSM to simulate heat mitigation strategies in the New York City Metropolitan Area. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2009, 48, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, K.M.A.A.; Endlicher, W.R. Urban and rural mortality rates during heat waves in Berlin and Brandenburg, Germany. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2044–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dousset, B.B.; Gourmelon, F.F.; Laaidi, K.K.; Zeghnoun, A.A.; Giraudet, E.E.; Bretin, P.P.; Maurid, E.E.; Vandentorren, S. Satellite monitoring of summer heat waves in the Paris metropolitan area. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 31, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwood, S.C.C.; Huber, M. An adaptability limit to climate change due to heat stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, G.S.S.; Baccini, M.M.; De Ridder, K.K.; Hooyberghs, H.H.; Lefebvre, W.W.; Kendrovski, V.V.; Scott, K.K.; Spasenovska, M. Projected heat-related mortality under climate change in the metropolitan area of Skopje. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouters, H.; De Ridder, K.K.; Willems, P.P.; Poelmans, L.; Hosseinzadehtalaei, P.P.; Tabari, H.H.; Brouwers, J.J.; Vanden Broucke, S.S.; van Lipzig, N.P.M.M.; Demuzere, M. Heat stress increase towards the mid-21st century is twice as large for cities compared to rural areas. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 8997–9007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demuzere, M.M.; Orru, K.K.; Heidrich, O.O.; Olazabal, E.E.; Geneletti, D.D.; Orru, H.H.; Faehnle, M. Mitigating and adapting to climate change: Multi-functional and multi-scale assessment of green urban infrastructure. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 146, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.Z.; Ka-Lun Lau, K.K.; Ng, E. Urban tree design approaches for mitigating daytime urban heat island effects in a high-density urban environment. Energy Build. 2016, 114, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.L.; Lau, K.K.K.; Yuan, C.C.; Chen, Y.Y.; Xu, Y.Y.; Ren, C. Regulation of outdoor thermal comfort by trees in Hong Kong. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 31, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowler, D.E.E.; Buyung-Ali, L.L.; Knight, T.M.M.; Pullin, A.S. Urban greening to cool towns and cities: A systematic review of the empirical evidence. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2010, 97, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armson, D.D.; Stringer, P.P.; Ennos, A.R. The effect of tree shade and grass on surface and globe temperatures in an urban area. Urban For. Urban Green. 2012, 11, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamei, E.E.; Rajagopalan, P.P.; Seyedmahmoudian, M.M.; Jamei, Y. Review on the impact of urban geometry and pedestrian level greening on outdoor thermal comfort. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 54, 1002–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upmanis, H.H.; Chen, D. Influence of geographical factors and meteorological variables on nocturnal urban-park temperature differences—A case study of summer 1995 in Göteborg, Sweden. Clim. Res. 1999, 13, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.R.R.; Li, M.H.H.; Chang, S.D. A preliminary study on the local cool-island intensity of Taipei city parks. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 80, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutts, A.M.M.; Tapper, N.J.J.; Beringer, J.J.; Loughnan, M.M.; Demuzere, M. Watering our cities: The capacity for Water Sensitive Urban Design to support urban cooling and improve human thermal comfort in the Australian context. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2012, 37, 2–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.Z.; Zhao, L.L.; Meng, Q. Field measurements on microclimate in residential community in Guangzhou, China. Front. Archit. Civ. Eng. China 2009, 3, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaroni, H.H.; Ziv, B. The impact of a small lake on heat stress in a Mediterranean urban park: The case of Tel Aviv, Israel. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2003, 47, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakawa, S.S.; Sekine, T.T.; Narita, K.I.I.; Nishina, D. Study of the effects of a river on the thermal environment in an urban area. Energy Build. 1991, 16, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steeneveld, G.J.J.; Koopmans, S.S.; Heusinkveld, B.G.G.; Theeuwes, N.E. Refreshing the role of open water surfaces on mitigating the maximum urban heat island effect. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 121, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höppe, P. The physiological equivalent temperature—A universal index for the biometeorological assessment of the thermal environment. Int. J. Biometeorol. 1999, 43, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzan, J.R.R.; Oleson, K.K.; Huber, M. Implementation and comparison of a suite of heat stress metrics within the Community Land Model version 4.5. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 151–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzarakis, A.A.; Rutz, F.F.; Mayer, H. Modelling radiation fluxes in simple and complex environments—Application of the RayMan model. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2007, 51, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, E.E.; Chen, L.L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Yuan, C. A study on the cooling effects of greening in a high-density city: An experience from Hong Kong. Build. Environ. 2012, 47, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashua-Bar, L.L.; Pearlmutter, D.D.; Erell, E. The influence of trees and grass on outdoor thermal comfort in a hot-arid environment. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 31, 1498–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coccolo, S.S.; Pearlmutter, D.D.; Kämpf, J.J.; Scartezzini, J.-L. Thermal Comfort Maps to estimate the impact of urban greening on the outdoor human comfort. Urban For. Urban Green. 2018, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhart, C.C.; Dogan, T.T.; Jakubiec, J.J.; Rakha, T.T.; Sang, A. UMI—An urban simulation environment for building energy use, daylighting and walkability. In Proceedings of the BS 2013: 13th Conference of the International Building Performance Simulation Association, Chambery, France, 26–28 August 2013; Available online: http://www.ibpsa.org/proceedings/BS2013/p_1404.pdf (accessed on 5 January 2020).
- De Ridder, K.K.; Lauwaet, D.D.; Maiheu, B. UrbClim—A fast urban boundary layer climate model. Urban Clim. 2015, 12, 21–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO. Hot Environments—Estimation of the Heat Stress on Working Man, Based on the WBGT-Index (Wet Bulb Globe Temperature); ISO Standard 7243; International Standards Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- De Ridder, K.K.; Schayes, G. The IAGL Land Surface Model. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1997, 36, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, M.M.; Kanega, M.M.; Kawai, T.T.; Moriwaki, R.R.; Sugawara, H. Roughness lengths for momentum and heat derived from outdoor urban-scale models. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2007, 46, 1067–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ridder, K.K.; Bertrand, C.C.; Casanova, G.G.; Lefebvre, W. Exploring a new method for the retrieval of urban thermophysical properties using thermal infrared remote sensing and deterministic modelling. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.R.; Engelen, G.G.; Uljee, I. Modeling Cities and Regions as Complex Systems; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; p. 330. [Google Scholar]
- Gutman, G.G.; Ignatov, A. Derivation of green vegetation fraction from NOAA/AVHRR for use in weather prediction models. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 1533–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielson, J.J.J.; Gesch, D.B. Global Multi-Resolution Terrain Elevation Data 2010 (GMTED2010); 2011-1073; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, WV, USA, 2011; p. 26.
- García-Díez, M.M.; Lauwaet, D.D.; Hooyberghs, H.H.; Ballester, J.J.; De Ridder, K.K.; Rodó, X. Advantages of using a fast urban boundary layer model as compared to a full mesoscale model to simulate the urban heat island of Barcelona. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 4439–4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauwaet, D.D.; Hooyberghs, H.H.; Maiheu, B.B.; Lefebvre, W.W.; Driesen, G.G.; Van Looy, S.S.; De Ridder, K. Detailed Urban Heat Island projections for cities worldwide: Dynamical downscaling CMIP5 global climate models. Climate 2015, 3, 391–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauwaet, D.D.; De Ridder, K.; Saeed, S.; Brisson, E.; Chatterjee, F.; van Lipzig, N.P.M.; Maiheu, B.; Hooyberghs, H. Assessing the current and future urban heat island of Brussels. Urban Clim. 2016, 15, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Lauwaet, D.; Hooyberghs, H.; De Ridder, K.; Kropp, J.P.; Rybski, D. Assessing seasonality in the surface urban heat island of London. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2016, 55, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ridder, K. Testing Brutsaert’s temperature roughness parameterization for representing urban surfaces in atmospheric models. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooyberghs, H.; Verbeke, S.; Lauwaet, D.; Costa, H.; Floater, G.; De Ridder, K. Influence of climate change on summer cooling costs and heat stress in urban office buildings. Clim. Change 2017, 144, 721–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liljegren, J.C.; Carhart, R.A.; Lawday, P.; Tschopp, S.; Sharp, R. Modeling the Wet Bulb Globe Temperature Using Standard Meteorological Measurements. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2008, 5, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemke, B.; Kjellstrom, T. Calculating Workplace WBGT from Meteorological Data: A Tool for Climate Change Assessment. Ind. Health 2012, 50, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conrad, O.; Bechtel, B.; Bock, M.; Dietrich, H.; Fischer, E.; Gerlitz, L.; Wehberg, J.; Wichmann, V.; Boehner, J. System for Automated Geoscientific Analyses (SAGA) v. 2.1.4. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 1991–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ridder, K. Radiative transfer in the IAGL land surface model. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1997, 36, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boënne, W.; Desmet, N.; Van Looy, S.; Seuntjens, P. Use of online water quality monitoring for assessing the effects of WWTP overflows in rivers. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2014, 16, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Changnon, S.A.; Kunkel, K.E.; Reinke, B.C. Impacts and responses to the 1995 heat wave: A call to action. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughnan, M.; Nicholls, N.; Tapper, N.J. Mapping Heat Health Risks in Urban Areas. Int. J. Popul. Res. 2012, e518687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Lau, S.S.; Qian, F. Thermal comfort effects of urban design strategies in high-rise urban environments in a sub-tropical climate. Archit. Sci. Rev. 2011, 54, 285–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Land Use | Model | Measurements | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean [°C] | SD [°C] | Mean [°C] | SD [°C] | |
| Urban | 30.2 | 0.26 | 30.0 | 0.45 |
| Park | 30.0 | 0.28 | 29.9 | 0.85 |
| Rural | 30.1 | 0.29 | 29.0 | 0.36 |
| Water | 28.4 | 0.43 | 28.4 | 0.32 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lauwaet, D.; Maiheu, B.; De Ridder, K.; Boënne, W.; Hooyberghs, H.; Demuzere, M.; Verdonck, M.-L. A New Method to Assess Fine-Scale Outdoor Thermal Comfort for Urban Agglomerations. Climate 2020, 8, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli8010006
Lauwaet D, Maiheu B, De Ridder K, Boënne W, Hooyberghs H, Demuzere M, Verdonck M-L. A New Method to Assess Fine-Scale Outdoor Thermal Comfort for Urban Agglomerations. Climate. 2020; 8(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli8010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleLauwaet, Dirk, Bino Maiheu, Koen De Ridder, Wesley Boënne, Hans Hooyberghs, Matthias Demuzere, and Marie-Leen Verdonck. 2020. "A New Method to Assess Fine-Scale Outdoor Thermal Comfort for Urban Agglomerations" Climate 8, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli8010006
APA StyleLauwaet, D., Maiheu, B., De Ridder, K., Boënne, W., Hooyberghs, H., Demuzere, M., & Verdonck, M.-L. (2020). A New Method to Assess Fine-Scale Outdoor Thermal Comfort for Urban Agglomerations. Climate, 8(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli8010006





