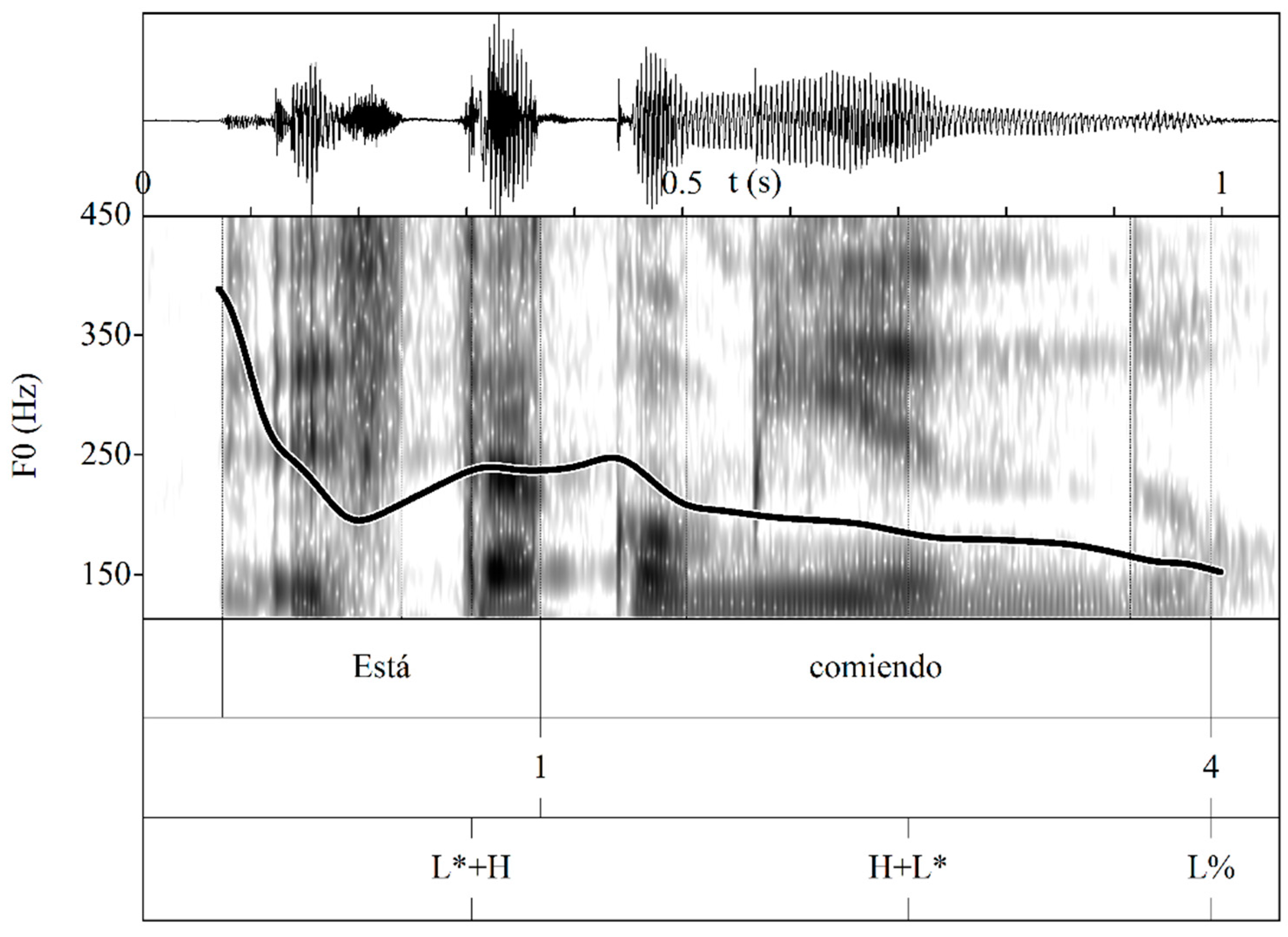
Figure 1.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the broad focus statement Está comiendo ‘She is eating’, produced with an H + L* L% final configuration by a 36-year-old female from Lalín.
Figure 1.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the broad focus statement Está comiendo ‘She is eating’, produced with an H + L* L% final configuration by a 36-year-old female from Lalín.
Figure 2.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the broad focus statement Salgo un momento a merendar ‘I am going out for a moment for snack’, produced with an H + L* L% final configuration by a 22-year-old male from Santiago.
Figure 2.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the broad focus statement Salgo un momento a merendar ‘I am going out for a moment for snack’, produced with an H + L* L% final configuration by a 22-year-old male from Santiago.
Figure 3.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the broad focus statement
Pues la niña se está bebiendo una limonada ‘Well the girl is drinking lemonade’, produced by a 21-year-old male from A Coruña with an upstepped L + ¡H*
3 final accent followed by L%.
Figure 3.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the broad focus statement
Pues la niña se está bebiendo una limonada ‘Well the girl is drinking lemonade’, produced by a 21-year-old male from A Coruña with an upstepped L + ¡H*
3 final accent followed by L%.
Figure 4.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the broad focus statement Está bebiendo un refresco ‘She is drinking soda’, produced with an L + H* H% final configuration by a 22-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 4.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the broad focus statement Está bebiendo un refresco ‘She is drinking soda’, produced with an L + H* H% final configuration by a 22-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 5.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the narrow focus statement No, no, de limones, limones ‘No, no, of lemons, lemons’, produced with an L + ¡H* L% final configuration by a 34-year-old female from A Coruña.
Figure 5.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the narrow focus statement No, no, de limones, limones ‘No, no, of lemons, lemons’, produced with an L + ¡H* L% final configuration by a 34-year-old female from A Coruña.
Figure 6.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the narrow focus statement No, de limones ‘No, of lemons’, produced with an L + ¡H* L% final configuration by a 22-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 6.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the narrow focus statement No, de limones ‘No, of lemons’, produced with an L + ¡H* L% final configuration by a 22-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 7.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the contradiction statement Yo estoy convencido de que van a Lima ‘I am convinced that they are going to Lima’, produced with an L + H* L% final configuration by a 52-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 7.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the contradiction statement Yo estoy convencido de que van a Lima ‘I am convinced that they are going to Lima’, produced with an L + H* L% final configuration by a 52-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 8.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the exclamative statement ¡Qué bien huele! ‘How well it smells!’, produced with an L* L% final configuration by a 64-year-old male from Santiago.
Figure 8.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the exclamative statement ¡Qué bien huele! ‘How well it smells!’, produced with an L* L% final configuration by a 64-year-old male from Santiago.
Figure 9.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the uncertainty statement ¿Cómo no lo sabes? De Guillermo ‘How do you not know this? It’s Guillermo’s!’, produced with an L + H* L% final configuration by a 19-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 9.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the uncertainty statement ¿Cómo no lo sabes? De Guillermo ‘How do you not know this? It’s Guillermo’s!’, produced with an L + H* L% final configuration by a 19-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 10.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the uncertainty statement No estoy muy seguro de que le vaya a gustar este regalo ‘I am not really sure that s/he is going to like this present’, produced with an L + ¡H* L% final configuration by an 18-year-old female from A Coruña.
Figure 10.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the uncertainty statement No estoy muy seguro de que le vaya a gustar este regalo ‘I am not really sure that s/he is going to like this present’, produced with an L + ¡H* L% final configuration by an 18-year-old female from A Coruña.
Figure 11.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the information-seeking yes–no question ¿Tienes mermelada? ‘Do you have any jam?’, produced with an H + L* L% final configuration by an 18-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 11.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the information-seeking yes–no question ¿Tienes mermelada? ‘Do you have any jam?’, produced with an H + L* L% final configuration by an 18-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 12.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the information-seeking yes–no question ¿Tienes mermelada? ‘Do you have any jam?’, produced with an L + H* H% final configuration by an 18-year-old female from A Coruña.
Figure 12.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the information-seeking yes–no question ¿Tienes mermelada? ‘Do you have any jam?’, produced with an L + H* H% final configuration by an 18-year-old female from A Coruña.
Figure 13.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the disjunctive yes–no question ¿Qué preferís? ¿Melón o helado? ‘What do you prefer? Melon or ice cream?’, produced with an H + L* L% final configuration by a 22-year-old male from Santiago.
Figure 13.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the disjunctive yes–no question ¿Qué preferís? ¿Melón o helado? ‘What do you prefer? Melon or ice cream?’, produced with an H + L* L% final configuration by a 22-year-old male from Santiago.
Figure 14.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the echo yes–no question ¿Pero tienes frío? ‘But are you cold?’, produced with an L + ¡H* final accent followed by an L% boundary tone by a 26-year-old female from Santiago.
Figure 14.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the echo yes–no question ¿Pero tienes frío? ‘But are you cold?’, produced with an L + ¡H* final accent followed by an L% boundary tone by a 26-year-old female from Santiago.
Figure 15.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the counter expectational echo yes–no question ¿Aún no llegó el electricista? ‘The electrician has still not arrived?’, produced with an H + L* H% final configuration by a 22-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 15.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the counter expectational echo yes–no question ¿Aún no llegó el electricista? ‘The electrician has still not arrived?’, produced with an H + L* H% final configuration by a 22-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 16.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the imperative yes–no question ¿Queréis callaros? ‘Would you be quiet?’ produced with an H + L* !H% final configuration by a 26-year-old female from Santiago.
Figure 16.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the imperative yes–no question ¿Queréis callaros? ‘Would you be quiet?’ produced with an H + L* !H% final configuration by a 26-year-old female from Santiago.
Figure 17.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the invitation yes–no question ¿Te apetece una limonada? ‘Would you like a lemonade?’, produced with an H + L* L% final configuration by a 52-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 17.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the invitation yes–no question ¿Te apetece una limonada? ‘Would you like a lemonade?’, produced with an H + L* L% final configuration by a 52-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 18.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the invitation yes–no question ¿Quieres venir a la fiesta? ‘Would you like to come to the party?’, produced with an L + H* H% final configuration by a 39-year-old female from Santiago.
Figure 18.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the invitation yes–no question ¿Quieres venir a la fiesta? ‘Would you like to come to the party?’, produced with an L + H* H% final configuration by a 39-year-old female from Santiago.
Figure 19.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the confirmation yes–no question ¿Tienes frío? ‘Are you cold?’, produced with an H + L* L% final configuration by an 18-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 19.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the confirmation yes–no question ¿Tienes frío? ‘Are you cold?’, produced with an H + L* L% final configuration by an 18-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 20.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the confirmation yes–no question
Por fin vienes hoy, ¿no? ‘You are finally coming today, right?’, produced with an L + ¡H* H% final configuration
5 by a 57-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 20.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the confirmation yes–no question
Por fin vienes hoy, ¿no? ‘You are finally coming today, right?’, produced with an L + ¡H* H% final configuration
5 by a 57-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 21.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the information-seeking wh- question Mira Mario, ¿quién trajo este paquete? ‘Look Mario, who brought this parcel?’, produced with an L* L% final configuration by a 22-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 21.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the information-seeking wh- question Mira Mario, ¿quién trajo este paquete? ‘Look Mario, who brought this parcel?’, produced with an L* L% final configuration by a 22-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 22.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the information-seeking wh- question ¿Quién ha traído esto? ‘Who brought this?’, produced with an L + ¡H* H% final configuration by a 41-year-old female from A Coruña.
Figure 22.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the information-seeking wh- question ¿Quién ha traído esto? ‘Who brought this?’, produced with an L + ¡H* H% final configuration by a 41-year-old female from A Coruña.
Figure 23.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the echo wh- question ¿Me preguntaste dónde voy y cuándo vuelvo? ‘Did you ask me where I’m going and when I’m coming back?’, produced with an H + L* H% final configuration by a 26-year-old female from Santiago.
Figure 23.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the echo wh- question ¿Me preguntaste dónde voy y cuándo vuelvo? ‘Did you ask me where I’m going and when I’m coming back?’, produced with an H + L* H% final configuration by a 26-year-old female from Santiago.
Figure 24.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the emphatic and dubitative wh- question ¿Quién será a estas horas? ‘Who might be at this time?’, produced with an H + L* L% final configuration by a 26-year-old female from Santiago.
Figure 24.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the emphatic and dubitative wh- question ¿Quién será a estas horas? ‘Who might be at this time?’, produced with an H + L* L% final configuration by a 26-year-old female from Santiago.
Figure 25.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the imperative wh- question ¿Qué quieres? ‘What do you want?’, produced with an H + L* L% final configuration by an 18-year-old female from A Coruña.
Figure 25.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the imperative wh- question ¿Qué quieres? ‘What do you want?’, produced with an H + L* L% final configuration by an 18-year-old female from A Coruña.
Figure 26.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the rhetorical wh- question ¿Qué haríais sin mí? ‘What would you do without me?’, produced with an L* L% final configuration by a 19-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 26.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the rhetorical wh- question ¿Qué haríais sin mí? ‘What would you do without me?’, produced with an L* L% final configuration by a 19-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 27.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the command María, vente aquí ya ‘Maria, come here right now’, produced with an H + L* L% final configuration by a 21-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 27.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the command María, vente aquí ya ‘Maria, come here right now’, produced with an H + L* L% final configuration by a 21-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 28.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the request Tenéis que rellenar un formulario ‘You need to fill in a form’, produced with an H + L* L% final configuration by a 49-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 28.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the request Tenéis que rellenar un formulario ‘You need to fill in a form’, produced with an H + L* L% final configuration by a 49-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 29.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the request Venga, vente al cine ‘Come on, come to the movies’, produced with an L + H* L% final configuration by a 21-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 29.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the request Venga, vente al cine ‘Come on, come to the movies’, produced with an L + H* L% final configuration by a 21-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 30.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the vocative ¡Bobi!, produced by a 22-year-old male from A Coruña with an L + H* final accent followed by an HL% boundary tone.
Figure 30.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the vocative ¡Bobi!, produced by a 22-year-old male from A Coruña with an L + H* final accent followed by an HL% boundary tone.
Figure 31.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the vocative ¡Marina!, produced with an L + ¡H* H% final configuration by a 49-year-old male from A Coruña.
Figure 31.
Waveform, spectrogram, and F0 trace for the vocative ¡Marina!, produced with an L + ¡H* H% final configuration by a 49-year-old male from A Coruña.
Table 1.
Pitch accents and boundary tones in the corpus.
Table 2.
Pitch accents associated with the penultimate stressed syllable in broad focus statements (N = 227).
Table 2.
Pitch accents associated with the penultimate stressed syllable in broad focus statements (N = 227).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| L* + H | 74 | 32.6 |
| L + H* | 42 | 18.5 |
| H* | 36 | 15.9 |
| H + L* | 31 | 13.7 |
| L + <H* | 26 | 11.4 |
| L* | 15 | 6.6 |
| H* + L | 3 | 1.3 |
| Total | 227 | |
Table 3.
Final pitch accents in broad focus statements (N = 237).
Table 3.
Final pitch accents in broad focus statements (N = 237).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| L* | 83 | 35.0 |
| L + H* | 69 | 29.1 |
| L + ¡H* | 37 | 15.6 |
| H + L* | 35 | 14.8 |
| H* | 5 | 2.1 |
| ¡H* | 4 | 1.7 |
| H* + L | 3 | 1.3 |
| L* + H | 1 | 0.4 |
| Total | 237 | |
Table 4.
Boundary tones in broad focus statements (N = 237)
4.
Table 4.
Boundary tones in broad focus statements (N = 237)
4.
| Tone | N | % |
|---|
| L% | 113 | 47.6 |
| H% | 62 | 26.2 |
| HL% | 18 | 7.6 |
| !H% | 17 | 7.2 |
| L!H% | 16 | 6.7 |
| LH% | 5 | 2.1 |
| H!H% | 3 | 1.3 |
| LHL% | 3 | 1.3 |
| Total | 237 | |
Table 5.
Pitch accents for contrastive statements in the corpus (N = 25).
Table 5.
Pitch accents for contrastive statements in the corpus (N = 25).
| | ‘No’ (Initial Position) | ‘Limones’ (Final Position) |
|---|
| Accent | N | % | N | % |
|---|
| L* + H | 12 | 48 | | |
| H + L* | 8 | 32 | 2 | 8 |
| L + H* | 5 | 20 | 5 | 20 |
| L + ¡H* | | | 9 | 36 |
| L* | | | 9 | 36 |
| Total | 25 | | 25 | |
Table 6.
Pitch accents for the word ‘Lima’ in contradictory statements (N = 26).
Table 6.
Pitch accents for the word ‘Lima’ in contradictory statements (N = 26).
| | ‘Lima’ (Mid-Sentence) | ‘Lima’ (Sentence-Final) |
|---|
| Accent | N | % | N | % |
|---|
| L* + H | 2 | 25.0 | | |
| H + L* | | | 7 | 38.9 |
| L + H* | 2 | 25.0 | 3 | 16.6 |
| L + ¡H* | | | 1 | 5.6 |
| L* | 3 | 37.5 | 6 | 33.3 |
| H* | 1 | 12.5 | | |
| ¡H* | | | 1 | 5.6 |
| Total | 8 | | 18 | |
Table 7.
Boundary tones for narrow focus statements (N = 51).
Table 7.
Boundary tones for narrow focus statements (N = 51).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| L% | 37 | 72.5 |
| !H% | 5 | 9.8 |
| H% | 3 | 5.9 |
| LH% | 3 | 5.9 |
| L!H% | 3 | 5.9 |
| Total | 51 | |
Table 8.
Pitch accents associated with the penultimate stressed syllable in exclamative statements (N = 65).
Table 8.
Pitch accents associated with the penultimate stressed syllable in exclamative statements (N = 65).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| L* + H | 23 | 35.4 |
| L + H* | 11 | 17.0 |
| H + L* | 11 | 17.0 |
| L + <H* | 8 | 12.3 |
| H* | 7 | 10.7 |
| L* | 3 | 4.6 |
| H* + L | 2 | 3.0 |
| Total | 65 | |
Table 9.
Final pitch accents in exclamative statements (N = 69).
Table 9.
Final pitch accents in exclamative statements (N = 69).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| L + H* | 26 | 37.8 |
| L* | 23 | 33.3 |
| H + L* | 7 | 10.1 |
| L + ¡H* | 6 | 8.7 |
| ¡H* | 3 | 4.3 |
| H* | 2 | 2.9 |
| H* + L | 2 | 2.9 |
| Total | 69 | |
Table 10.
Boundary tones in exclamative statements (N = 69).
Table 10.
Boundary tones in exclamative statements (N = 69).
| Tone | N | % |
|---|
| L% | 33 | 47.8 |
| H% | 14 | 20.3 |
| L!H% | 8 | 11.6 |
| HL% | 7 | 10.1 |
| !H% | 5 | 7.2 |
| LH% | 1 | 1.5 |
| LHL% | 1 | 1.5 |
| Total | 69 | |
Table 11.
Pitch accents associated with the word Guillermo (N = 24).
Table 11.
Pitch accents associated with the word Guillermo (N = 24).
| | Guillermo (Mid-Sentence) | Guillermo (Sentence-Final) |
|---|
| Accent | N | % | N | % |
|---|
| L + H* | 9 | 81.8 | 9 | 69.2 |
| L + ¡H* | | | 4 | 30.8 |
| L* + H | 2 | 18.2 | | |
| Total | 11 | | 13 | |
Table 12.
Boundary tones in statements of the obvious (N = 24).
Table 12.
Boundary tones in statements of the obvious (N = 24).
| Tone | N | % |
|---|
| L% | 13 | 54.2 |
| HL% | 4 | 16.7 |
| L!H% | 3 | 12.5 |
| H% | 2 | 8.3 |
| !H% | 2 | 8.3 |
| Total | 24 | |
Table 13.
Pitch accents associated with the penultimate stressed syllable in uncertainty statements (N = 23).
Table 13.
Pitch accents associated with the penultimate stressed syllable in uncertainty statements (N = 23).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| L* + H | 6 | 26.1 |
| H* | 6 | 26.1 |
| L + H* | 5 | 21.7 |
| H + L* | 5 | 21.7 |
| H* + L | 1 | 4.4 |
| Total | 23 | |
Table 14.
Final pitch accents in uncertainty statements (N = 23).
Table 14.
Final pitch accents in uncertainty statements (N = 23).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| L + H* | 8 | 34.8 |
| L* | 8 | 34.8 |
| L + ¡H* | 6 | 26.1 |
| H + L* | 1 | 4.3 |
| Total | 23 | |
Table 15.
Boundary tones in uncertainty statements (N = 23).
Table 15.
Boundary tones in uncertainty statements (N = 23).
| Tone | N | % |
|---|
| L% | 10 | 43.5 |
| H% | 6 | 26.1 |
| HL% | 3 | 13.1 |
| !H% | 2 | 8.7 |
| H!H% | 1 | 4.3 |
| L!H% | 1 | 4.3 |
| Total | 23 | |
Table 16.
Pitch accents associated with the penultimate stressed syllable in yes–no questions (N = 244).
Table 16.
Pitch accents associated with the penultimate stressed syllable in yes–no questions (N = 244).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| L* + H | 75 | 30.7 |
| L + H* | 51 | 20.9 |
| L + <H* | 41 | 16.8 |
| H* | 26 | 10.7 |
| H + L* | 26 | 10.7 |
| L* | 21 | 8.6 |
| H* + L | 4 | 1.6 |
| Total | 244 | |
Table 17.
Final pitch accents in yes–no questions (N = 258).
Table 17.
Final pitch accents in yes–no questions (N = 258).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| H + L* | 145 | 56.2 |
| L + H* | 47 | 18.2 |
| L* | 47 | 18.2 |
| L + ¡H* | 17 | 6.6 |
| ¡H* | 2 | 0.8 |
| Total | 258 | |
Table 18.
Boundary tones in yes–no questions (N = 258).
Table 18.
Boundary tones in yes–no questions (N = 258).
| Tone | N | % |
|---|
| L% | 131 | 50.8 |
| H% | 62 | 24.0 |
| !H% | 25 | 9.7 |
| L!H% | 15 | 5.8 |
| HL% | 12 | 4.6 |
| H!H% | 10 | 3.9 |
| LH% | 3 | 1.2 |
| Total | 258 | |
Table 19.
Pitch accents associated with the penultimate stressed syllable in echo yes–no questions (N = 157).
Table 19.
Pitch accents associated with the penultimate stressed syllable in echo yes–no questions (N = 157).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| H* | 41 | 26.2 |
| L* + H | 35 | 22.3 |
| L + H* | 31 | 19.7 |
| L + <H* | 25 | 15.9 |
| H + L* | 23 | 14.6 |
| L* | 2 | 1.3 |
| Total | 157 | |
Table 20.
Final pitch accents in echo yes–no questions (N = 181).
Table 20.
Final pitch accents in echo yes–no questions (N = 181).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| H + L* | 106 | 58.6 |
| L + ¡H* | 36 | 19.9 |
| L + H* | 28 | 15.4 |
| L* | 11 | 6.1 |
| Total | 181 | |
Table 21.
Boundary tones in echo yes–no questions (N = 181).
Table 21.
Boundary tones in echo yes–no questions (N = 181).
| Tone | N | % |
|---|
| L% | 93 | 51.4 |
| H% | 35 | 19.3 |
| !H% | 12 | 6.6 |
| L!H% | 23 | 12.7 |
| HL% | 13 | 7.2 |
| LH% | 4 | 2.2 |
| H!H% | 1 | 0.6 |
| Total | 181 | |
Table 22.
Pitch accents associated with the penultimate stressed syllable in imperative yes–no questions (N = 85).
Table 22.
Pitch accents associated with the penultimate stressed syllable in imperative yes–no questions (N = 85).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| L* + H | 35 | 41.2 |
| H* | 16 | 18.8 |
| L + <H* | 14 | 16.5 |
| H + L* | 10 | 11.8 |
| L + H* | 7 | 8.2 |
| L* | 3 | 3.5 |
| Total | 85 | |
Table 23.
Final pitch accents in imperative yes–no questions (N = 99).
Table 23.
Final pitch accents in imperative yes–no questions (N = 99).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| H + L* | 63 | 63.6 |
| L + ¡H* | 15 | 15.2 |
| L + H* | 14 | 14.1 |
| L* | 4 | 4.1 |
| ¡H* | 2 | 2.0 |
| H* | 1 | 1.0 |
| Total | 99 | |
Table 24.
Boundary tones in imperative yes–no questions (N = 99).
Table 24.
Boundary tones in imperative yes–no questions (N = 99).
| Tone | N | % |
|---|
| L% | 55 | 55.6 |
| H% | 19 | 19.2 |
| !H% | 8 | 8.1 |
| HL% | 7 | 7.1 |
| L!H% | 5 | 5.0 |
| H!H% | 3 | 3.0 |
| LH% | 1 | 1.0 |
| LHL% | 1 | 1.0 |
| Total | 99 | |
Table 25.
Pitch accents associated with the penultimate stressed syllable in confirmation yes–no questions (N = 64).
Table 25.
Pitch accents associated with the penultimate stressed syllable in confirmation yes–no questions (N = 64).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| L* + H | 18 | 28.1 |
| H + L* | 16 | 25.0 |
| L + <H* | 15 | 23.5 |
| L + H* | 8 | 12.5 |
| H* | 7 | 10.9 |
| Total | 64 | |
Table 26.
Final pitch accents in confirmation yes–no questions (N = 81).
Table 26.
Final pitch accents in confirmation yes–no questions (N = 81).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| H + L* | 41 | 50.6 |
| L + ¡H* | 16 | 19.8 |
| L + H* | 14 | 17.3 |
| L* | 10 | 12.3 |
| Total | 81 | |
Table 27.
Boundary tones in confirmation yes–no questions (N = 81).
Table 27.
Boundary tones in confirmation yes–no questions (N = 81).
| Tone | N | % |
|---|
| L% | 48 | 59.3 |
| H% | 19 | 23.4 |
| !H% | 3 | 3.7 |
| L!H% | 5 | 6.2 |
| HL% | 5 | 6.2 |
| H!H% | 1 | 1.2 |
| Total | 81 | |
Table 28.
Pitch accents on wh- words in neutral interrogatives (N = 156).
Table 28.
Pitch accents on wh- words in neutral interrogatives (N = 156).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| L + H* | 66 | 42.3 |
| H + L* | 38 | 24.4 |
| L* + H | 20 | 12.8 |
| H* | 16 | 10.3 |
| L + <H* | 8 | 5.1 |
| L* | 7 | 4.5 |
| L + ¡H* | 1 | 0.6 |
| Total | 156 | |
Table 29.
Final pitch accents in neutral partial interrogatives (N = 156).
Table 29.
Final pitch accents in neutral partial interrogatives (N = 156).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| L* | 64 | 41.0 |
| H + L* | 46 | 29.5 |
| L + H* | 32 | 20.5 |
| L + ¡H* | 9 | 5.8 |
| ¡H* | 5 | 3.2 |
| Total | 156 | |
Table 30.
Boundary tones in neutral partial interrogatives (N = 156).
Table 30.
Boundary tones in neutral partial interrogatives (N = 156).
| Tone | N | % |
|---|
| L% | 82 | 52.6 |
| H% | 43 | 27.6 |
| !H% | 17 | 10.9 |
| HL% | 6 | 3.8 |
| L!H% | 5 | 3.2 |
| LH% | 2 | 1.3 |
| H!H% | 1 | 0.6 |
| Total | 156 | |
Table 31.
Pitch accents associated with the focal wh- element in echo wh- questions (N = 140
6).
Table 31.
Pitch accents associated with the focal wh- element in echo wh- questions (N = 140
6).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| L* + H | 37 | 26.9 |
| L + H* | 33 | 23.9 |
| H* | 22 | 15.9 |
| H + L* | 17 | 12.3 |
| L + <H* | 16 | 11.6 |
| L* | 13 | 9.4 |
| Total | 138 | |
Table 32.
Final pitch accents in echo wh- questions (N = 105).
Table 32.
Final pitch accents in echo wh- questions (N = 105).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| L* | 37 | 35.2 |
| H + L* | 30 | 28.6 |
| L + H* | 24 | 22.9 |
| L + ¡H* | 10 | 9.5 |
| H* | 3 | 2.9 |
| ¡H* | 1 | 0.9 |
| Total | 105 | |
Table 33.
Boundary tones in echo wh- questions (N = 105).
Table 33.
Boundary tones in echo wh- questions (N = 105).
| Tone | N | % |
|---|
| L% | 55 | 52.4 |
| H% | 22 | 21.0 |
| HL% | 14 | 13.3 |
| L!H% | 8 | 7.6 |
| !H% | 4 | 3.8 |
| H!H% | 2 | 1.9 |
| Total | 105 | |
Table 34.
Pitch accents associated with the focal wh- element in emphasis and uncertainty wh- questions (N = 49).
Table 34.
Pitch accents associated with the focal wh- element in emphasis and uncertainty wh- questions (N = 49).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| L* + H | 17 | 34.7 |
| H + L* | 14 | 28.6 |
| L + H* | 12 | 24.5 |
| H* | 4 | 8.2 |
| L + <H* | 1 | 2.0 |
| L* | 1 | 2.0 |
| Total | 49 | |
Table 35.
Final pitch accents in emphasis and uncertainty wh- questions (N = 49).
Table 35.
Final pitch accents in emphasis and uncertainty wh- questions (N = 49).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| L* | 19 | 38.8 |
| H + L* | 13 | 26.5 |
| L + H* | 8 | 16.3 |
| L + ¡H* | 7 | 14.3 |
| H* | 2 | 4.1 |
| Total | 49 | |
Table 36.
Boundary tones in emphasis and uncertainty wh- questions (N = 49).
Table 36.
Boundary tones in emphasis and uncertainty wh- questions (N = 49).
| Tone | N | |
|---|
| L% | 27 | 55.1 |
| H% | 12 | 24.5 |
| !H% | 5 | 10.2 |
| HL% | 3 | 6.1 |
| H!H% | 2 | 4.1 |
| Total | 49 | |
Table 37.
Pitch accents associated with the focal wh- element in imperative wh- questions (N = 51).
Table 37.
Pitch accents associated with the focal wh- element in imperative wh- questions (N = 51).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| L* + H | 15 | 29.4 |
| H + L* | 12 | 23.5 |
| L + H* | 11 | 21.7 |
| H* | 4 | 7.8 |
| L* | 4 | 7.8 |
| L + <H* | 3 | 5.9 |
| H* + L | 2 | 3.9 |
| Total | 51 | |
Table 38.
Final pitch accents in imperative wh- questions (N = 51).
Table 38.
Final pitch accents in imperative wh- questions (N = 51).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| H + L* | 21 | 41.2 |
| L + H* | 14 | 27.4 |
| L* | 11 | 21.6 |
| L + ¡H* | 3 | 5.9 |
| ¡H* | 2 | 3.9 |
| Total | 51 | |
Table 39.
Boundary tones in imperative wh- questions (N = 51).
Table 39.
Boundary tones in imperative wh- questions (N = 51).
| Tone | N | % |
|---|
| L% | 33 | 64.7 |
| H% | 10 | 19.6 |
| LH% | 3 | 5.9 |
| !H% | 2 | 3.9 |
| L!H% | 2 | 3.9 |
| HL% | 1 | 2.0 |
| Total | 51 | |
Table 40.
Pitch accents associated with the wh- element in rhetorical wh- questions (N = 19).
Table 40.
Pitch accents associated with the wh- element in rhetorical wh- questions (N = 19).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| H + L* | 6 | 31.6 |
| L* + H | 3 | 15.8 |
| L* | 3 | 15.8 |
| L + H* | 3 | 15.8 |
| H* | 3 | 15.8 |
| L + <H* | 1 | 5.2 |
| Total | 19 | |
Table 41.
Final pitch accents in rhetorical wh- questions (N = 41).
Table 41.
Final pitch accents in rhetorical wh- questions (N = 41).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| L* | 10 | 52.7 |
| H + L* | 5 | 26.3 |
| L + H* | 2 | 10.5 |
| H* | 2 | 10.5 |
| Total | 19 | |
Table 42.
Boundary tones in rhetorical wh- questions (N = 42).
Table 42.
Boundary tones in rhetorical wh- questions (N = 42).
| Tone | N | % |
|---|
| L% | 9 | 47.4 |
| H% | 7 | 36.7 |
| !H% | 1 | 5.3 |
| L!H% | 1 | 5.3 |
| HL% | 1 | 5.3 |
| Total | 19 | |
Table 43.
Pitch accents associated with the penultimate stressed syllable in commands (N = 135).
Table 43.
Pitch accents associated with the penultimate stressed syllable in commands (N = 135).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| L* + H | 40 | 29.7 |
| L + H* | 34 | 25.2 |
| L + <H* | 18 | 13.3 |
| H* | 18 | 13.3 |
| H + L* | 15 | 11.1 |
| L* | 8 | 5.9 |
| H* + L | 2 | 1.5 |
| Total | 135 | |
Table 44.
Final pitch accents in commands (N = 145).
Table 44.
Final pitch accents in commands (N = 145).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| H + L* | 59 | 40.7 |
| L + H* | 37 | 25.5 |
| L* | 24 | 16.6 |
| L + ¡H* | 17 | 11.7 |
| ¡H* | 8 | 5.5 |
| Total | 145 | |
Table 45.
Boundary tones in commands (N = 145).
Table 45.
Boundary tones in commands (N = 145).
| Tone | N | % |
|---|
| L% | 84 | 57.9 |
| H% | 32 | 22.1 |
| HL% | 13 | 8.9 |
| L!H% | 8 | 5.5 |
| !H% | 3 | 2.1 |
| LH% | 3 | 2.1 |
| H!H% | 2 | 1.4 |
| Total | 145 | |
Table 46.
Pitch accents associated with the penultimate stressed syllable in requests (N = 117).
Table 46.
Pitch accents associated with the penultimate stressed syllable in requests (N = 117).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| L* + H | 37 | 31.6 |
| L + H* | 23 | 19.7 |
| H* | 19 | 16.2 |
| H + L* | 16 | 13.7 |
| L* | 11 | 9.4 |
| L + <H* | 6 | 5.1 |
| H* + L | 5 | 4.3 |
| Total | 117 | |
Table 47.
Final pitch accents in requests (N = 118).
Table 47.
Final pitch accents in requests (N = 118).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| H + L* | 42 | 35.6 |
| L + H* | 29 | 24.6 |
| L + ¡H* | 21 | 17.8 |
| L* | 14 | 11.8 |
| ¡H* | 6 | 5.1 |
| H* | 6 | 5.1 |
| Total | 118 | |
Table 48.
Boundary tones in requests (N = 118).
Table 48.
Boundary tones in requests (N = 118).
| Tone | N | % |
|---|
| L% | 79 | 66.9 |
| !H% | 13 | 11.0 |
| HL% | 12 | 10.2 |
| H% | 5 | 4.2 |
| L!H% | 5 | 4.2 |
| ¡HL% | 2 | 1.7 |
| LH% | 1 | 0.9 |
| ¡H!H% | 1 | 0.9 |
| Total | 118 | |
Table 49.
Final pitch accents in vocatives (N = 44).
Table 49.
Final pitch accents in vocatives (N = 44).
| Accent | N | % |
|---|
| L + ¡H* | 22 | 50.0 |
| L + H* | 21 | 47.7 |
| L* | 1 | 2.3 |
| Total | 44 | |
Table 50.
Boundary tones in vocatives (N = 44).
Table 50.
Boundary tones in vocatives (N = 44).
| Tone | N | % |
|---|
| H% | 14 | 31.8 |
| HL% | 12 | 27.3 |
| L% | 11 | 25.0 |
| !H% | 6 | 13.6 |
| LH% | 1 | 2.3 |
| Total | 44 | |