Abstract
In the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic, the need for efficient and reliable disease diagnosis in smart cities has become increasingly serious. In this study, we introduce a novel blockchain-based federated learning framework tailored specifically for the diagnosis of pandemic diseases in smart cities, called BFLPD, with a focus on COVID-19 as a case study. The proposed BFLPD takes advantage of the decentralized nature of blockchain technology to design collaborative intelligence for automated diagnosis without violating trustworthiness metrics, such as privacy, security, and data sharing, which are encountered in healthcare systems of smart cities. Cheon–Kim–Kim–Song (CKKS) encryption is intelligently redesigned in BFLPD to ensure the secure sharing of learning updates during the training process. The proposed BFLPD presents a decentralized secure aggregation method that safeguards the integrity of the global model against adversarial attacks, thereby improving the overall efficiency and trustworthiness of our system. Extensive experiments and evaluations using a case study of COVID-19 ultrasound data demonstrate that BFLPD can reliably improve diagnostic accuracy while preserving data privacy, making it a promising tool with which smart cities can enhance their pandemic disease diagnosis capabilities.
Keywords:
blockchain; federated learning; pandemic disease; smart cities; COVID-19; privacy-preserving; decentralized computing; Internet of Things (IoT); timely response to outbreaks MSC:
68-04; 68Uxx; 68Vxx; 68Wxx
1. Introduction
The swift pace of urbanization and the rise of smart cities have transformed urban landscapes internationally. With the advent of advanced technologies and the Internet of Things (IoT), cities have become more interconnected, integrating various digital infrastructures to improve efficiency, sustainability, and quality of life [1]. This, in turn, has led to the propagation of data sources generating vast quantities of valued information [2]. Furthermore, the interconnected nature of smart cities enables seamless sharing and collaboration among different entities, fostering an environment conducive to the development of innovative solutions to societal challenges [3]. In this context, the challenge of pandemic disease diagnosis in smart cities encompasses several key aspects that need to be addressed in order to effectively alleviate the outbreak of infectious diseases [2,3,4]. These challenges stem from the unique characteristics of smart cities, such as their high population density, complex mobility patterns, and diverse sources of data. Timely identification and containment of outbreaks are crucial for preventing the rapid spread of infectious diseases and minimizing their impact on public health. Precise diagnosis not only supports the operative treatment and management of diseased individuals, but also enables proactive measures to be taken, such as resource allocation, targeted interventions, and public awareness campaigns [5]. Smart cities possess the capacity to transform pandemic disease diagnosis through the utilization of IoT and AI technologies, facilitating timely and evidence-based decision-making that can have life-saving implications and safeguard communities [3,4,5].
Unfortunately, the existing centralized approaches to pandemic disease diagnosis in smart cities face several challenges and limitations. First, they rely on centralized data repositories where sensitive health information is collected and saved in a single location, which poses noteworthy concerns concerning data privacy and security. Additionally, the sheer volume and velocity of data generated in smart cities can overwhelm centralized systems, causing delays and inefficiencies in diagnosis and replies to efforts [4,5]. Moreover, centralized approaches may encounter regulatory and governance matters, such as data ownership and access rights, impeding operative collaboration and information exchange among diverse stakeholders. Accordingly, smart cities are facing a pressing need for innovative solutions that leverage decentralized and privacy-preserving approaches to enhance the accuracy, efficiency, and security of pandemic disease diagnosis in smart cities [6,7].
Federated learning (FL) is a distributed AI mechanism that enables collaborative model training across multiple devices or entities without the need for centralized data aggregation [8,9]. In FL, instead of sending raw data to a central server, local models are trained on individual devices or entities, and only the model updates or aggregated parameters are shared. This decentralized approach ensures data privacy and security, as sensitive data remain on the local devices. Furthermore, FL leverages the collective intelligence of diverse data sources, allowing models to be trained on a more representative and inclusive dataset [9,10,11]. By involving various entities, such as healthcare providers, research institutions, and government agencies, in the collaborative training process, FL encourages knowledge sharing, cross-institutional cooperation, and the integration of diverse perspectives. This collaborative nature enhances the robustness and generalizability of the trained models, enabling more accurate and comprehensive pandemic disease diagnosis in smart cities. Moreover, FL empowers resource-constrained IoT devices to participate in the model training process, democratizing access to advanced AI techniques and fostering inclusivity in the healthcare and research domains [12].
The integration of federated learning and blockchain technology holds tremendous significance in the context of smart cities. The inherent properties of blockchains, such as decentralization, immutability, and transparency, offer a compelling solution for enhancing the security and trustworthiness of data sharing and storage in smart city environments [13]. By leveraging blockchains, smart cities can establish robust and tamper-resistant infrastructure that ensures the integrity and provenance of shared data, thereby addressing concerns related to data privacy, trust, and accountability. Furthermore, the collaborative nature of federated learning aligns perfectly with the distributed and interconnected nature of smart cities [14]. The significance of blockchains and federated learning in smart cities goes beyond data privacy and accuracy to promote inclusivity and equity, ensuring that all stakeholders have equal opportunities to participate in the diagnosis process [15,16,17,18]. This inclusiveness empowers communities, healthcare providers, and researchers, enabling them to collectively contribute to the identification, tracking, and containment of pandemic diseases.
The objectives of this study are twofold: first, to propose a new blockchain-based federated learning model that is personalized for the diagnosis of pandemic diseases in smart cities, hence named BFLPD; and second, to introduce an all-inclusive case study focusing on COVID-19 as an exemplar of our framework’s applicability. Our proposed BFLPD aims to address the challenges of trustworthiness and scalability in the context of pandemic disease diagnosis while leveraging cooperative intelligence among distributed entities in smart cities. In this view, the contributions of this study can be summarized as follows:
- We introduce a pioneering framework that combines the decentralized and immutable nature of blockchain technology with the collaborative and privacy-preserving capabilities of FL, providing a secure and transparent environment for pandemic disease diagnosis in smart cities.
- A decentralized and secure aggregation method is presented to empower the global model to be unaffected by malicious updates from unknown clients in smart cities, which is aimed to improve the overall efficiency and trustworthiness of our system.
- We demonstrate the practicality and effectiveness of our framework through a rigorous case study on COVID-19, showcasing its potential to improve diagnostic accuracy and efficiency compared to traditional centralized approaches.
- We address critical considerations such as data privacy, security, and regulatory compliance within the smart city context, proposing mechanisms such as consensus algorithms, data aggregation techniques, and privacy-preserving mechanisms to overcome associated challenges.
2. Related Works
In this section, we review the existing literature and research labors that have investigated several aspects of blockchain, FL, and their applications in the context of smart city healthcare and pandemic management.
2.1. Pandemic Management in Smart Cities
In this section, we review and analyze a selection of literature studies that have examined the function of smart cities in managing and dealing with pandemics. These studies shed light on the innovative approaches, technological interventions, and governance strategies employed by smart cities worldwide to effectively tackle the challenges posed by public health emergencies. For instance, Hassankhani et al. [1] studied the crucial role of smart city technologies and their potential to effectively respond to and manage crisis situations. They explored the key lessons and insights gained from the COVID-19 pandemic, emphasizing the value of data-driven decision-making, real-time monitoring, and the integration of various technological solutions within a smart city framework. They offered valuable recommendations and guidelines for policymakers, urban planners, and stakeholders to use to enhance crisis management strategies and to build resilient smart cities capable of effectively addressing future pandemics or similar crises. In addition, Strielkowski et al. [2] contributed to the understanding of how to manage smart and sustainable cities in the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic. They examined the lessons learned from the pandemic and explored its implications for the management of cities striving to be smart and sustainable. They shed light on the importance of integrating technological advancements, such as IoT, big data analytics, and artificial intelligence, with sustainable urban planning and governance practices. The study emphasized the need for resilient infrastructure, citizen engagement, and effective decision-making processes to foster sustainable development in cities.
Das and Zhang [3] investigated the functions of technology and society in managing the COVID-19 pandemic in Singapore, a renowned smart city. They focused on Singapore’s innovative approach to pandemic management, leveraging technology-driven solutions and societal cooperation. The authors also detailed the key technological interventions implemented by the government, including contact tracing apps, data analytics, and digital tools for remote work and learning. The study emphasized the critical role of societal factors, such as public trust, citizen compliance, and community engagement, in the successful deployment of these technological solutions. Kim et al. [4] explored the necessary adaptations to the structures of smart cities to effectively predict and overcome pandemics. They examined the roles of smart city technologies and infrastructure in enhancing preparedness and response to pandemic outbreaks. Through an in-depth analysis, they identified key areas where structural adjustments are needed, such as data collection and analysis, communication networks, healthcare systems, and urban planning. Furthermore, Costa et al. [5] provided a comprehensive review of smart city initiatives aimed at addressing the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic. The research examined different technological solutions and strategies implemented by smart cities worldwide to combat the spread of the virus and mitigate its impacts. They studied key initiatives such as contact tracing applications, data analytics, remote healthcare services, and intelligent urban management systems, and highlighted the importance of leveraging smart city infrastructure and capabilities to enhance surveillance, early detection, and responses to new outbreaks.
2.2. Federated Learning in Smart Cities
In this subsection, we delve into the existing literature studies that focus on the application of FL in the context of smart cities, which is a collaborative and privacy-preserving ML paradigm, making it particularly relevant for the data-rich ecosystems found within smart cities. Zheng et al. [9] provided a comprehensive overview of the taxonomy of and the recent advances and open challenges in the application of federated learning in smart cities. They explored the potential of FL, as a distributed ML approach, to address privacy concerns and data limitations while enabling collaborative and efficient data analysis in smart city environments. They also classified and categorized the various applications of FL in smart cities, including traffic management, energy optimization, healthcare, and public safety. They emphasized the advantages and challenges associated with FL in smart city contexts and recognized significant research directions for future improvements. In [10], the authors surveyed the FL approaches that could leverage data from distributed sensors in a smart city environment while addressing data privacy and security concerns. They identified and discussed the key challenges associated with FL in smart city sensing, such as communication and coordination among sensors, data heterogeneity, and ensuring privacy-preserving mechanisms. The authors of [11] explored the concept of integrating FL techniques with digital twin technology, which designs virtual representations of physical resources and systems in smart cities. They discussed the ideas and theories related to FL-enabled digital twins, highlighting their potential applications in various domains of smart cities, including urban planning, infrastructure management, and resource optimization. They also discussed the advances in the field, such as FL algorithms, communication protocols, and privacy-preserving mechanisms. In [12], Rasha et al. studied the challenges and potential solutions for preserving privacy and ensuring data security when implementing federated learning in the context of smart cities. They investigated different aspects related to privacy and security, including data protection, secure communication protocols, privacy-preserving machine learning algorithms, and secure model aggregation. They debated the existing privacy and security issues in FL for smart cities and presented an overview of the state-of-the-art privacy and security mechanisms and techniques that have been proposed and implemented. Pandya et al. [13] surveyed the applications of FL that could address the unique challenges and requirements of smart city environments, such as data privacy, scalability, and resource-constrained devices. They explored various aspects of FL in smart cities, incorporating the architecture, algorithms, communication protocols, and their practical implementations in different sectors of smart cities, such as energy management, transportation, and healthcare.
2.3. Blockchain in Smart Cities
This section provides an overview of the existing research and literature related to the application of blockchain technology in the context of smart cities. This section aims to highlight the advancements, challenges, and potential opportunities offered by blockchains in various domains of smart city development. In [14], the authors offered a comprehensive review of the applications of blockchain technology in smart cities through the analysis of blockchain architectures, integration trends, and potential future research directions in the context of smart city development. They explored various aspects related to blockchain technology, such as consensus mechanisms, scalability, interoperability, and security. They studied the existing architectures and integration approaches of blockchains in smart cities and discussed the benefits and challenges associated with their implementation. In [15], the authors surveyed the application of blockchain technology in smart cities by analyzing the research issues and challenges associated with the implementation of blockchains in the context of smart city development. The authors explored various aspects related to blockchain technology, including its architecture, consensus mechanisms, privacy, security, scalability, and interoperability. Additionally, they discussed the challenges and open research issues that need to be addressed for the successful implementation of blockchain technology in smart cities. In [16], the authors focused on the application of blockchain technology in IoT-based smart cities though investigating the recent advances in blockchain technology and exploring its requirements and challenges in the context of smart cities. They examined the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) systems and blockchains and discussed the benefits and potential use cases of this combination in smart city environments. They also addressed the key requirements for implementing blockchains in IoT-based smart cities, such as scalability, interoperability, privacy, and security. Hakak et al. [17] studied the application of blockchain technology for enhancing the security of smart cities by examining the architecture, requirements, and challenges associated with securing smart cities using blockchain technology. They explored the potential of blockchain to address security vulnerabilities and risks in various domains of smart cities, including transportation, energy, healthcare, and public safety. They discussed the essential architectural components and requirements for implementing blockchains into smart cities, such as decentralized consensus, data integrity, privacy, and identity management. Furthermore, Kim et al. [18] presented a system of blockchain-based personal health records, which not only used an on-chain, off-chain system to regulate the consensus data of the patients, but also investigated the definite user experience based on a conducted questionnaire. Furthermore, Fiore et al. [19] reviewed the application of blockchains to tackle the supply chain challenges in healthcare, precisely for drugs, medical devices, lifeblood, and tissues. They conducted the review based on the PRISMA guidelines and an investigation of English studies in the PubMed and Proquest databases.
The prevailing literature on blockchain application in smart cities has made notable contributions in different parts. Nevertheless, a critical analysis reveals certain gaps that motivate the development of our proposed solution. Firstly, previous studies have primarily focused on the application of blockchains in smart cities without fully addressing the specific challenges and requirements of FL for pandemic diagnosis. Secondly, while some works have explored the integration of blockchains and FL, they regularly oversee the crucial facet of secure aggregation to alleviate the risks of malicious updates and preserve the integrity of the global model. These gaps in the present literature underline the requirement for our proposed framework, which not only fills these research voids, but also offers a healthy and protected solution for the cooperative analysis of distributed healthcare data in smart cities.
3. Methodology
In this section, we present a detailed discussion of the methodology of designing our proposed BFLPD framework for pandemic disease diagnosis in smart cities. Through the delineation of BFLPD methodology, we offer transparency and reproducibility, enabling researchers and practitioners to comprehend and replicate our framework in their own smart city healthcare systems.
3.1. System Model
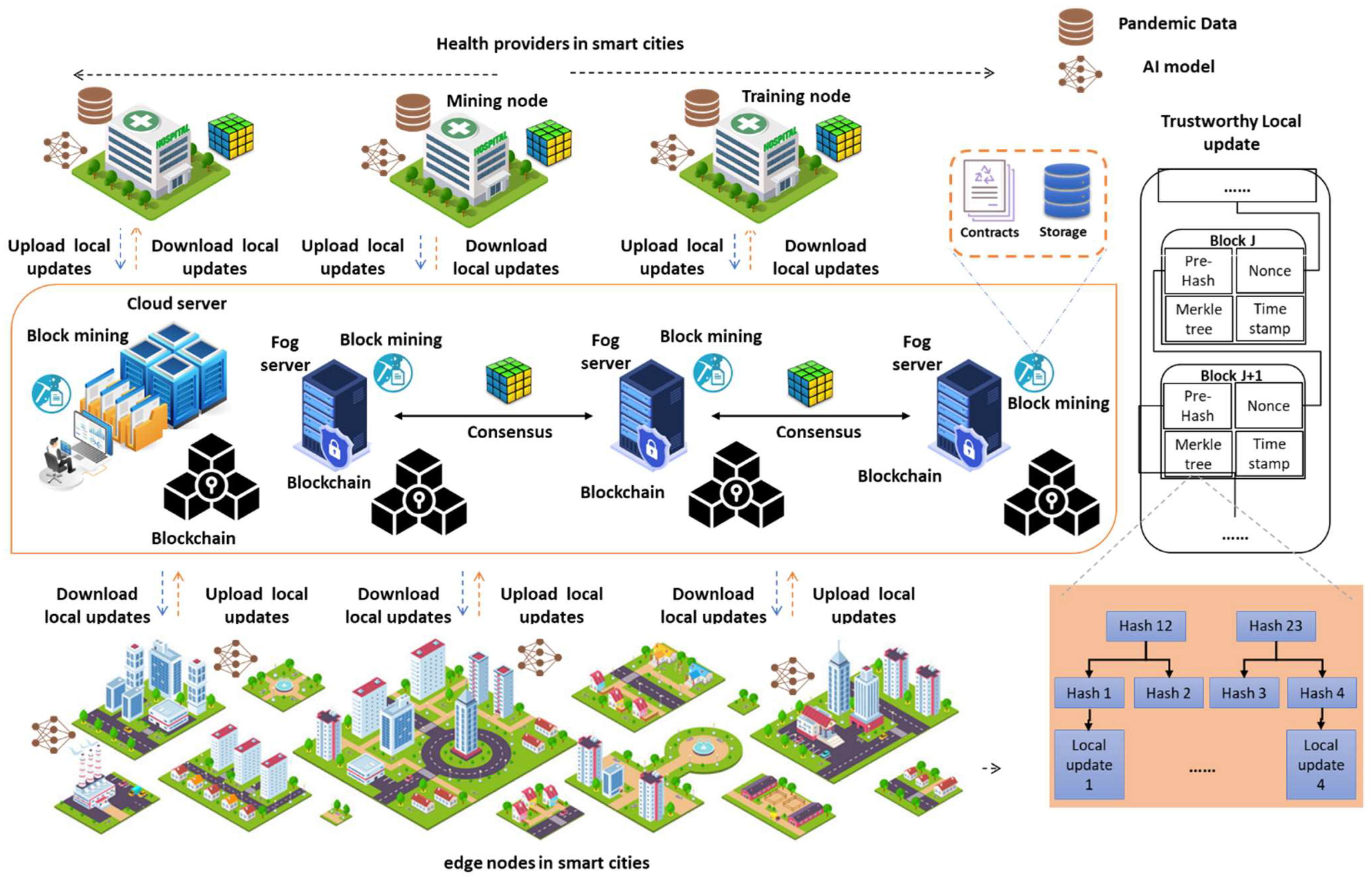
Herein, we present the system model intended for the proposed BFLPD, providing inclusive details on each system component and its role in the diagnosis of pandemic diseases in smart cities. Figure 1 visualizes the architecture of the proposed system model, which is composed of several fundamental components that work together to enable the effective and secure federated diagnosis of pandemic diseases in a smart city environment. These components include the following.
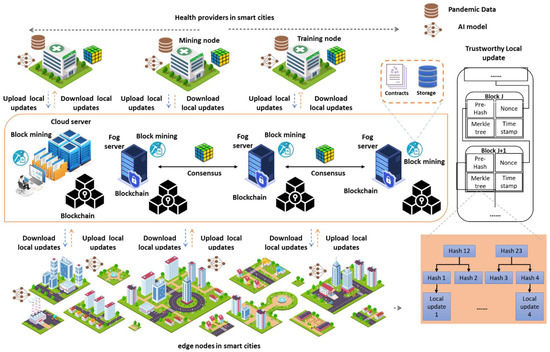
Figure 1.
Visualization of our BFLPD system design for pandemic disease diagnosis in smart cities.
Data Sources: The BFLPD acknowledges the diverse nature of pandemic data and the requirement to gather information from diverse devices and sources. Pandemic data can take different formats, incorporating medical records, diagnostic test results, symptom reports, medical images, contact tracing data, health records, and environmental data. These data can originate from a variety of devices and systems, such as healthcare databases, wearable devices, IoT sensors, mobile applications, and social media platforms. The BFLPD highlights the integration and harmonization of different data types, guaranteeing interoperability among diverse systems and devices.
Edge Devices: These devices are distributed throughout the city and are equipped with sensors and data collection capabilities. They are in charge of collecting real-time data related to the health statuses of individuals, such as vital signs, symptoms, and potential exposure to the disease. They act as the frontline data sources, capturing valuable information directly from the individuals within the smart city environment. The distributed nature of the edge devices guarantees the obtainability of varied and up-to-date data, enhancing the accuracy and reliability of the pandemic disease’s diagnosis and control. Furthermore, the inclusion of edge devices in BFLPD helps to minimize latency in data transmission and enables real-time monitoring, prompt replies, and control measures in the event of a pandemic outbreak.
Blockchain Network: This is a crucial component of our system model in which we incorporate the use of the hyperledger fabric blockchain network to ensure secure and transparent data management for pandemic diagnosis in smart cities. It is a kind of permissioned blockchain framework that provides a robust infrastructure for enterprise-grade applications. It consists of several key conditions and modules, which include the following. (1) We have the Peer Nodes, which are responsible for maintaining the distributed ledger and executing chain codes. These peer nodes are permitted, meaning that they require authentication and authorization to participate in the network. (2) The ordering service guarantees the consensus and order of transactions within the network. (3) The channel enables the segregation of network participants into distinct subgroups, allowing for privacy and confidentiality between different stakeholders through the promotion of selective sharing of data and transactions, thus guaranteeing that only authorized participants can access and authenticate specific information related to the pandemic diagnosis. The implementation of channels in hyperledger fabric includes the following common steps. First, we set up a rudimentary network by installing orderers, certificate authorities, and peers for each participant. Then, a consortium was created and participants were added to it. Then, the channel was defined and configured by specifying its name, the participation, and other parameters in the configuration file. Next, the genesis block was generated, and each organization joined the channel by signing and sending the channel configuration to the ordering service. Anchor peers are designated for cross-organization communication. Finally, participants can invoke transactions on the channel, which are endorsed, ordered, and committed to update the ledger’s state.
Given that we are targeting pandemic disease diagnosis, the choice of the consensus method is crucial to guaranteeing the reliability, scalability, and security of the network. To accommodate these requirements in the BFLPD framework, the practical Byzantine fault tolerance (PBFT) is used for a high level of fault tolerance and Byzantine fault resistance, making it appropriate for serious and sensitive applications such as pandemic disease diagnosis. Unlike Proof of Work (PoW), which necessitates extensive computing power and the ingestion of energy for the purpose of resolving intricate puzzles, PBFT does not depend on resource-intensive mining actions. The PBFT algorithm’s consensus mechanism is dependent on voting and a replication scheme, through which nodes can reach agreement on the validity of transactions. Unlike Proof of Stake (PoS), where block creation is limited to a select group of validators based on their stake, PBFT allows all participating nodes to contribute to the consensus procedure. This makes PBFT well-suited for a smart city environment with a large population and numerous nodes. It ensures that the consensus protocol can accommodate the computational demands of federated learning in a pandemic diagnosis scenario.
PBFT is derived according to a network of nodes, a predefined number of nodes of which are labeled as validators accountable for realizing a consensus on the order of transactions. In our case, the validators were designated as trusted nodes from various smart cities or healthcare institutions participating in the framework. The PBFT consensus method confirms that transactions are agreed upon by the utmost of the validators prior to being committed to the blockchain. PBFT provides a high degree of finality and reduces the risk of fraudulent or malicious activities in the network. Hence, it offers a fast consensus process, acknowledging high transaction throughput, which is decisive in scenarios involving large-scale pandemic diagnosis data and regular updates to the model, and has low energy consumption, which is beneficial in resource-constrained environments.
3.2. Methodological Design
The section outlines the step-by-step process followed in our study to implement the BFLPD framework for pandemic diagnosis. This section provides a thorough overview of the key stages involved in our methodology, including system initialization, local model updates, model aggregation, etc.
Initialization: In this phase of the BFLPD framework, the Key Management Center (KMC) was used to configure a pair of public/private keys for each client node in the system. Additionally, another pair of public/private keys was configured for the validator.
Once the key pairs had been adopted to perform homomorphic encryption computations, the original global model was uploaded to the blockchain, which was started by setting up an exclusive channel for each federated pandemic diagnosis within the network. This was followed by the addition of organization members, peer nodes, and ordered nodes to their respective channels, as well as the deployment of smart contracts.
Meanwhile, keys and certificates were issued by the Hyperledger Fabric Certificate Authority (CA) for each approved node joining the channel.
Finally, a genesis block was created for each channel, and the block that contained the original global model was stored on the blockchain. This arrangement enabled the execution of each FL-based diagnosis model through the participating nodes on their respective blockchain channels.
Local update: During this phase of the BFLPD framework, a client who wished to participate in an FL-based diagnosis was required to initiate a cycle of local training. In order to accomplish this, the client downloaded the most recent round’s global model from the blockchain via the peer nodes. The global model was then decrypted by the client using their private key, , resulting in the local model , which served as the starting point for the new round of training. The client then conducted the local model training utilizing a differentially private stochastic gradient descent (DP-SGD) procedure that optimized the loss function , which was defined on a batch size of b using sample . was a subset of the client’s local dataset .
where denotes an instance of local pandemic data, and denotes the relevant loss function. Thus, we obtained the local gradient, as follows:
Then, we injected Laplace noise according to the following:
where is the sensitivity of the model, which represents the maximum change in the gradient due to the inclusion or exclusion of any single data point, and is the privacy budget or privacy parameter that determines the level of privacy protection. This was then used to implement local upgrades, as follows:
By following this local update procedure, each participating client downloaded the newest global model, decoded it using their private key, performed local model training using their local dataset, and communicated the updated local model back to the local edge device.
To achieve this, the proposed BFLPD framework utilized the fully homomorphic CKKS (Cheon–Kim–Kim–Song) encryption scheme. This encryption scheme enabled the establishment of both floating-point addition and multiplication functions for complex or real numbers. During the encryption process and at each layer, the local updates were transformed into vectors, which were encrypted layer by layer. If a vector surpassed the pre-defined maximum length limit, it was divided into many vectors and encrypted separately. The local model was encrypted using the client’s public key and the validator’s public key resulting in the encrypted versions, and , respectively.
Subsequently, the client uploaded the encrypted editions, and to the blockchain like a transaction. At the same time, was dispatched to the resolver to guarantee that the updated model was securely saved in the blockchain and could be accessed by other participants for FL-based diagnosis.
Secure aggregation: Upon receiving the local updates from all clients, the validator utilized a model-averaging approach to aggregate these local updates:
However, it is crucial to address potential malicious activities where certain clients intentionally transmit incorrect local updates to disrupt the aggregation process, leading to an invalid aggregation result and failure of the entire training process. Furthermore, there is concern regarding the privacy of client data, as the “sincere” but “probing” server may attempt to infer sensitive information from the model parameters. Therefore, it becomes essential to mitigate the opposing impacts of poisoning attacks and safeguard the privacy of client data. Consequently, we must consider incorporating mechanisms to ensure secure aggregation, which can be expressed as follows:
To this end, we present an updated version of the Multi-Krum aggregation algorithm to carry out global model aggregation in the BFLPD framework, which allows for robust aggregation of the local updates from the participating clients to form a more accurate and trustworthy global model. Similarly to the Multi-Krum algorithm, our aggregation scheme is based on selecting a subset of clients’ models that are deemed reliable and consistent based on their resemblances. It considers the divergence between the models and their gradients to identify the most agreeable models. The algorithm aims to exclude potential malicious or faulty models while aggregating the contributions from trustworthy clients. This, in turn, is advantageous for pandemic diagnosis models that have undergone the local training process, since it guarantees that the final global model represents a consensus among the participating clients, providing a dependable and accurate diagnosis of a pandemic disease. Rather than using Euclidean distance, we used total variation distance to estimate the similarity between local updates of two clients.
Thus, for each client , the Krum distance was computed as the sum of distances between and each of its next neighbors ,
where is the number of models to be chosen for aggregation. Then, the threshold value was calculated as the sum of the smallest Krum distances () among all of the clients’ models. It denotes the maximum acceptable distance for a model to be considered reliable.
At this point, we selected the reliable local updates for aggregation, as follows:
The final global model was obtained by aggregating the reliable models contributed by the clients in set . |S| denotes the number of clients in set .
4. Case Study and Setup
In this section, we describe the experimental setup used to evaluate the performance and effectiveness of the proposed BFLPD for pandemic disease diagnosis in smart cities. We outline the dataset which was utilized, including its sources and preprocessing steps, to ensure the reliability and representativeness of our experimental results. Moreover, we debate the hardware and software infrastructure which we deployed, providing details on the computing resources and tools leveraged for model training and evaluation.
For our experimental setup, we built a multi-source dataset based in three publicly available ultrasound datasets, namely, the POCUS [6], ICLUS-DB [7], and COVIDx-US datasets [8]. The combined dataset was built to train and evaluate our proposed method for pandemic disease diagnosis in smart cities.
The POCUS dataset encompassed a total of 261 recordings, comprising 59 images and 202 videos. These recordings were captured from 216 individuals using either linear or convex probes. It is worth noting that linear probes offer a higher frequency, resulting in superior resolution for examining irregularities near the pleural line. However, they may present challenges in distinguishing between B-line artifacts and hidden tissue due to their reduced penetration of lung tissue. This aspect emphasizes the importance of accurate diagnosis in distinguishing between different lung conditions. For curating the POCUS dataset, the images and videos were aggregated from diverse sources, including academic scientific publications, hospitals, ultrasound courses, health-tech corporations, and public medical repositories. Further details regarding the specific sources of data can be found in [20]. The COVID-19 cases included in the dataset were confirmed using RT-PCR testing, ensuring the inclusion of reliable and accurate samples. The videos in the dataset exhibited varying lengths (ranging from 160 to 144 frames) and were recorded at frame rates between 25 and 10 Hz, which added diversity to the dataset and simulated real-world scenarios. To ensure the quality and accuracy of the dataset, all samples were carefully reviewed and confirmed by a single medical expert possessing over 10 years of clinical experience and expertise as an academic instructor.
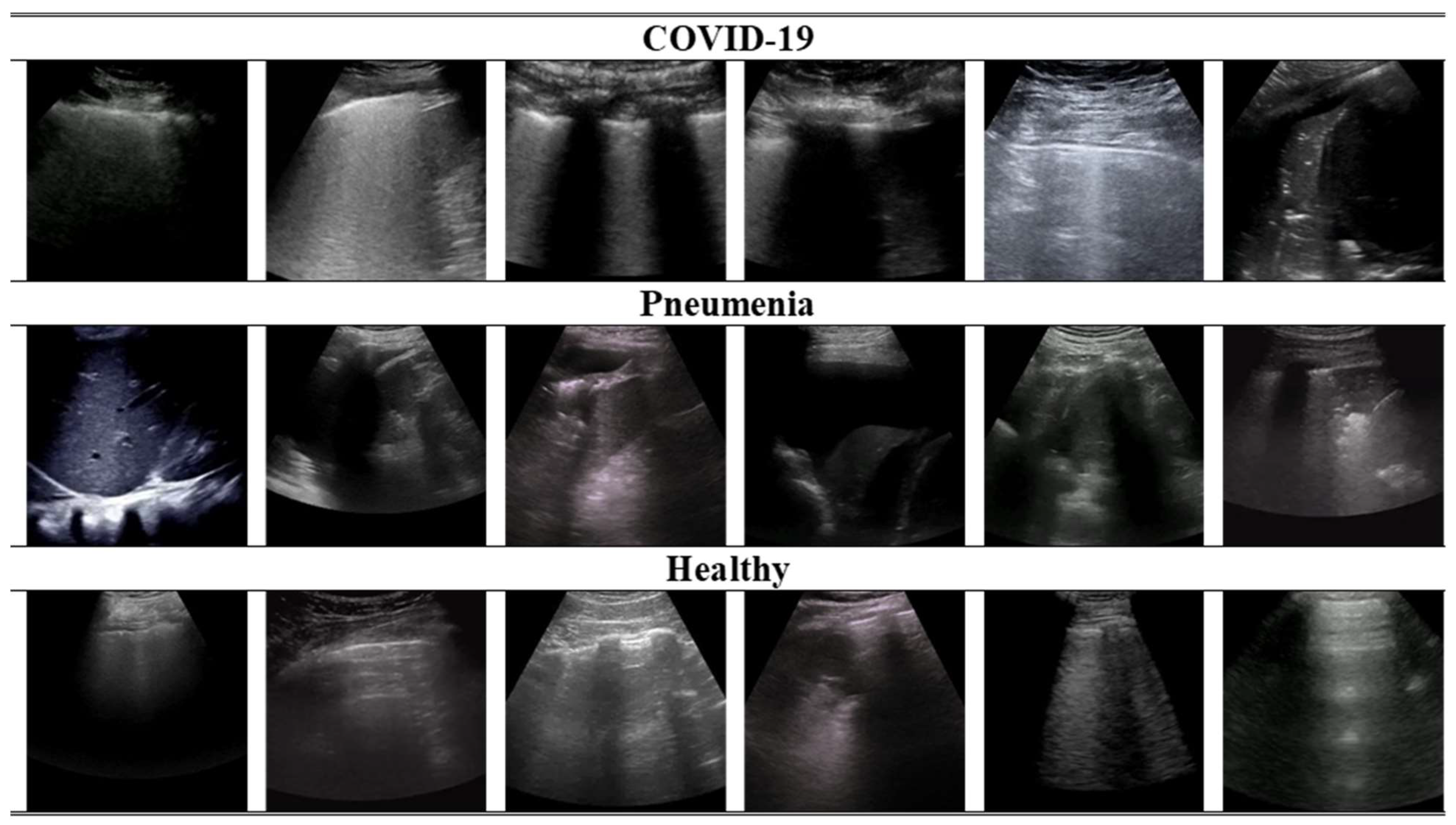
Second, ICLUS-DB [2] was composed of 277 lung ultrasound (LUS) videos from 35 patients, conforming to 58,924 frames. The data were aggregated from clinical centers using a diverse range of ultrasound scanners. Both linear and convex probes were utilized, depending on which was needed. The data were collected from a total of 35 patients, comprising 17 individuals with confirmed cases of COVID-19, 4 individuals suspected of having COVID-19, and 14 healthy individuals. Furthermore, COVIDx-US [3] consisted of 242 lung ultrasound videos comprising 29,651 processed images obtained from patients diagnosed with COVID-19 infection or pneumonia, healthy individuals, and patients with other lung diseases/conditions. It also encompasses a standardized and integrated lung ultrasound score per video file, allowing for better analysis while supporting other research opportunities, such as severity judgment. The dataset was systematically managed and authorized explicitly for the intent of creating and assessing AI models. Table 1 summarizes the class distribution in the combined dataset. In Figure 2, some instances of 2D ultrasound frames of healthy, pneumonia, and COVID-19 patients are displayed in the datasets.

Table 1.
The class distribution of our combined dataset.
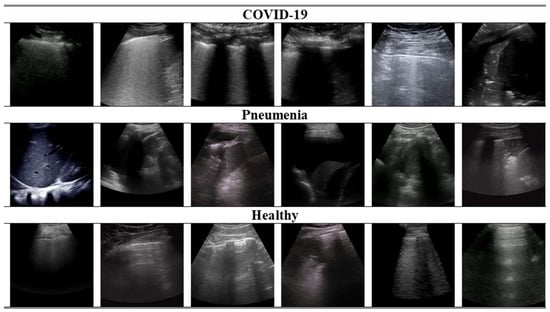
Figure 2.
Visualization of randomly selected ultrasound frames from the combined dataset used in this study.
As a crucial step in the process of developing an ML solution, the data underwent pre-processing before being utilized for training purposes. During the experiments, convex ultrasound probes were employed to train the models. Nevertheless, the viral pneumonia class had a limited number of samples available (only three convex videos), which led us to pre-process the data by removing this class from the training set. Consequently, the training process solely utilized the data from the remaining three classes: healthy, pneumonia, and COVID-19 individuals. To facilitate the training process, all convex ultrasound samples were subjected to physical pre-processing. This involved dividing the videos into individual images at a frame rate of 3 Hz, resulting in a maximum of 30 frames per video. Subsequently, the generated image samples underwent cropping to remove artifacts, ratio bars, and text, ensuring that the focus was solely on the relevant content. The images were then resized to dimensions of pixels, facilitating uniformity and compatibility during the training process. In this work, the reported results were obtained by applying a five-fold cross-validation technique which was bedded according to the number of examples in each class. The image samples were separated at the patient level to ensure that frames from a single video were present in only one of the five folds. Furthermore, the distribution of videos across classes was approximately equal for all folds, ensuring a balanced representation during model training and evaluation. All models were trained to classify images into three categories: healthy, pneumonia, and/or COVID-19. To enhance the robustness of the models and mitigate overfitting, data augmentation techniques were applied. Following the common augmentation practices, image flipping, rotations within the range of −45° to +45°, and translations of up to 10% were applied to introduce variations in the data, differentiating the training samples and preventing the models from solely relying on specific patterns or features [19,21]. By undertaking these data preparation steps, we aimed to optimize the quality and suitability of the dataset for training our models, ensuring their robustness, generalization capability, and ability to accurately classify pandemic disease-related images in smart city environments.
In the process of evaluating the performance of our proposed BFLPD for pandemic disease diagnosis in smart cities, we employed several key evaluation metrics to assess its effectiveness and efficiency. These metrics included diagnostic Accuracy, Precision, Recall, and F1-score:
To conduct simulations and evaluate the performance of our proposed BFLPD for pandemic disease diagnosis in smart cities, we implemented the framework using a combination of software tools, programming languages, and hardware resources. The blockchain infrastructure was developed using Ethereum, a widely adopted platform for creating decentralized applications. Smart contracts were written in Solidity, a programming language specifically designed for Ethereum smart contract development. We leveraged PyTorch to code the FL algorithms and train the models, which were run on Python 3.8.0 environment. The simulations were conducted in a controlled experimental environment (equipped with a powerful NVIDIA RTX GPU, multiple processors, and 128 GB RAM) with standardized settings and parameters. The specific configuration details, including the network architecture, hyperparameters, learning rate, batch size, and optimization algorithms, were carefully selected based on empirical studies and best practices in the field. By stating constant experimental settings across simulations, we guaranteed fair comparisons and consistent evaluations of our proposed framework’s performance.
Since we focused on COVID-19 detection as a case study for our work, we chose common computer vision models (Shufflenet v2 [20], Mobilevit [22], Levit [23]) to be deployed as AI models in our BFLPD.
5. Results and Discussion
In this section, we present the results obtained from the evaluation of our proposed BFLPD, with a specific focus on the case study of COVID-19. We analyze and interpret the quantitative and qualitative outcomes of our experiments, shedding light on the performance indicators and the privacy preservation achieved by our framework. Furthermore, we discuss the implications of these results in the context of smart city healthcare and pandemic management, addressing the potential aids, confines, and future directions. Also, we provide visions into the efficacy and practicality of BFLPD, providing valuable perspectives for researchers, policymakers, and stakeholders involved in improving pandemic disease diagnosis in smart cities.
In order to assess the classification performance of the BFLPD framework for pandemic disease diagnosis in smart cities, we compared it against state-of-the-art models [24,25,26,27,28,29]. The results of this comparative analysis are presented in Table 2, showcasing the performance metrics obtained from the evaluation. Our framework exhibited highly promising results, outperforming existing state-of-the-art models in terms of diagnostic accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score. The classification accuracy achieved by BFLPD (95.14%) surpassed the benchmark set by the state-of-the-art distributed models, demonstrating its greater competence in accurately classifying diverse classes of infection, including in COVID-19, pneumonia, and healthy individuals. Furthermore, the BFLPD framework demonstrated notable precision and recall values (95.26%, 95.77%) across all classes, reflecting its capacity to reduce false positives and false negatives. The high F1 score (95.52%) further indicated the balanced performance and effectiveness of our BFLPD framework in terms of pandemic disease diagnosis.

Table 2.
Comparison of the performance of BFLPD against cutting-edge FL models.
To determine the statistical significance of the comparative results presented in Table 2, we conducted appropriate statistical tests to validate the observed differences in performance between the BFLPD framework and the state-of-the-art models. The statistical significance test we employed depended on the nature of the data and the evaluation metrics being compared. To demonstrate the classification performance, we utilized the Wilcoxon signed-rank test, depending on the distributional assumptions and the size of the samples. This test examines whether the medians of two paired samples differ significantly. By examining the p-values in Table 3, we can determine the statistical significance of the results. It could be noted that the reported p-value was less than the specified significance level (typically 0.05), which signifies that the perceived differences are statistically significant; thus, we can reject the null hypothesis. This, in turn, enables us to raw confident conclusions about the superiority of our BFLPD framework and its statistically substantial improvements to pandemic disease diagnosis within smart city environments. The superiority of the BFLPD framework can be attributed to the innovative combination of blockchain technology and FL, which supports privacy-preserving and cooperative model training using distributed data sources. By leveraging the strengths of these two technologies, our framework effectively overcomes the limitations of centralized approaches, such as data privacy concerns and scalability issues, while achieving exceptional classification performance. With superior classification performance, along with its ability to preserve privacy and leverage distributed data sources, the BFLPD framework can be regarded as a compelling solution for accurate and efficient disease diagnosis in real-world scenarios.

Table 3.
The p-values resulting from the Wilcoxon signed-rank test.
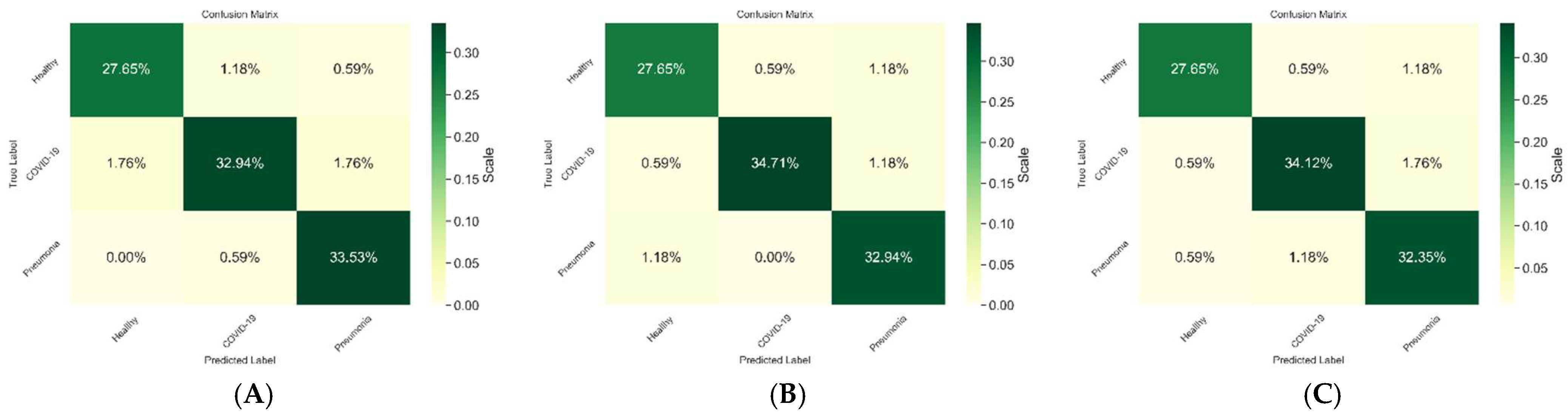
As shown in Figure 3, we evaluated the performance of the BFLPD framework using different classifiers to assess its effectiveness in pandemic diagnosis, and we presented the confusion matrix of each experiment to provide a visual representation of the classifier. Our results consistently demonstrated high detection performance across all classifiers. The confusion matrix illustrated the ability of the framework to correctly classify instances of both COVID-19 and non-COVID-19 cases. The high detection performance indicated the robustness and accuracy of BFLPD framework in identifying potential cases of the pandemic, which is crucial for effective diagnosis and mitigation strategies. This further highlights the potential BFLPD framework for real-world applications in pandemic management.
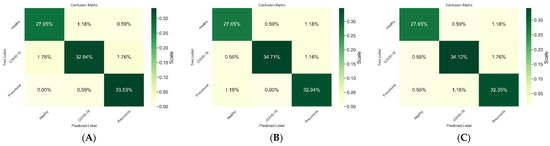
Figure 3.
Comparison between the performance of the BFLPD framework under different classifiers. (A) Shufflenet v2 [20], (B) Mobilevit [22], (C) Levit [23].
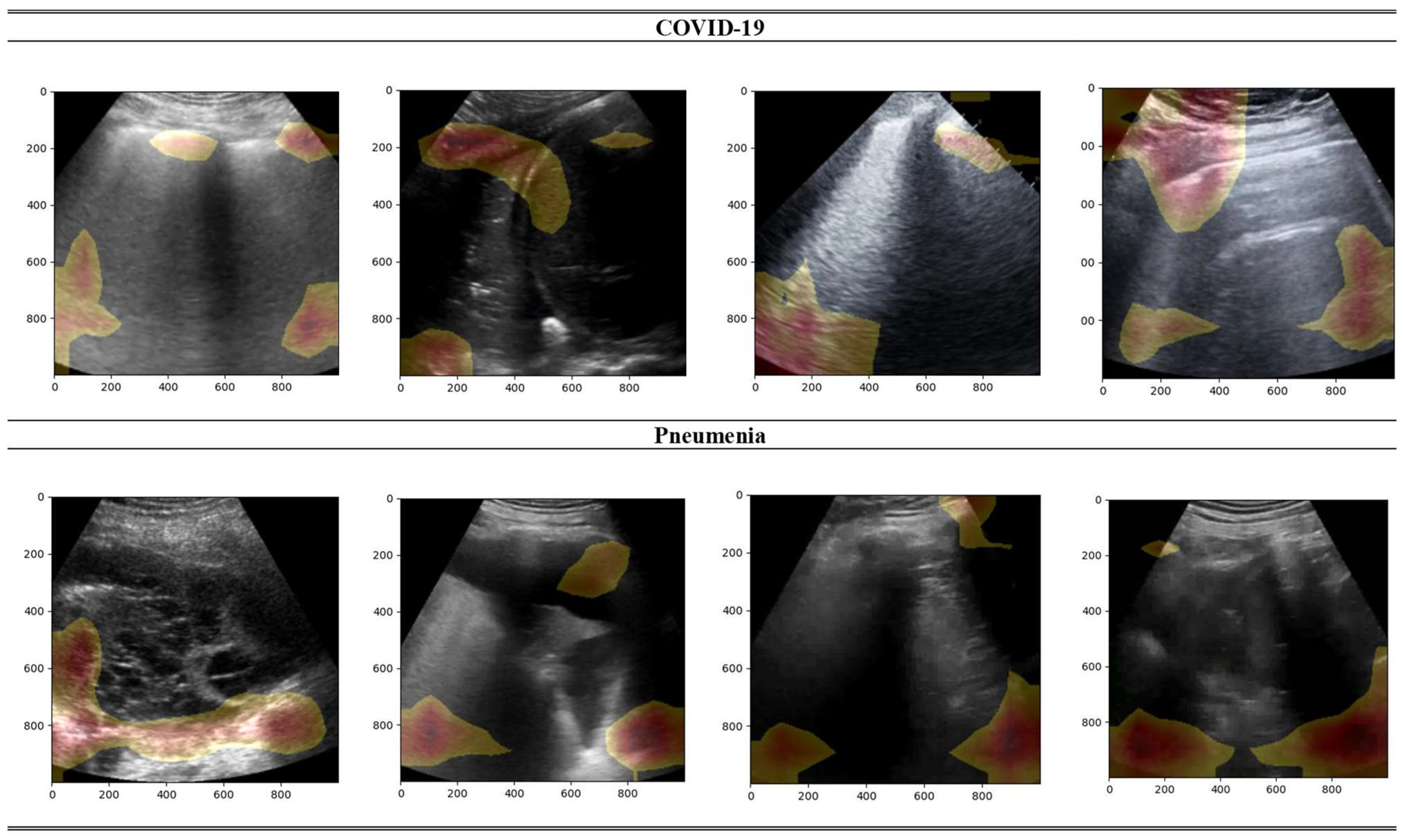
In Figure 4, a heatmap visualization of the predictions of BFLPD framework is portrayed on randomly chosen samples from the test set. This heatmap specifies valuable insights into the regions of attention and relevance that contributed to the model’s classification decisions. By overlapping the heat map with the ultrasound images, we were able to visually identify the regions that played significant roles in the classification process. Intense and bright colors suggest higher activation and importance, while cooler colors represent regions of lower importance. This visualization technique allowed us to understand which specific features or patterns captured by the ultrasound images influenced the prediction of the BFLPD framework. It can be observed that the BFLPD focused on certain areas that were revealing of COVID-19 or pneumonia conditions. These areas may include specific lung regions, lesions, or characteristic patterns associated with distinctive diseases. This interpretability enhances the trustworthiness of the model’s predictions, granting medical specialists and researchers the chance to gain deeper insights into the diagnostic process.
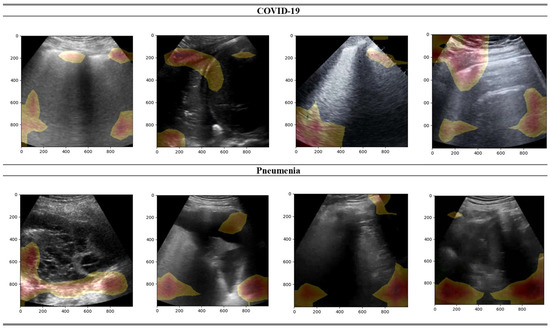
Figure 4.
Visualization of gradient heatmaps for explaining the predictions of the BFLPD framework on samples from the test set.
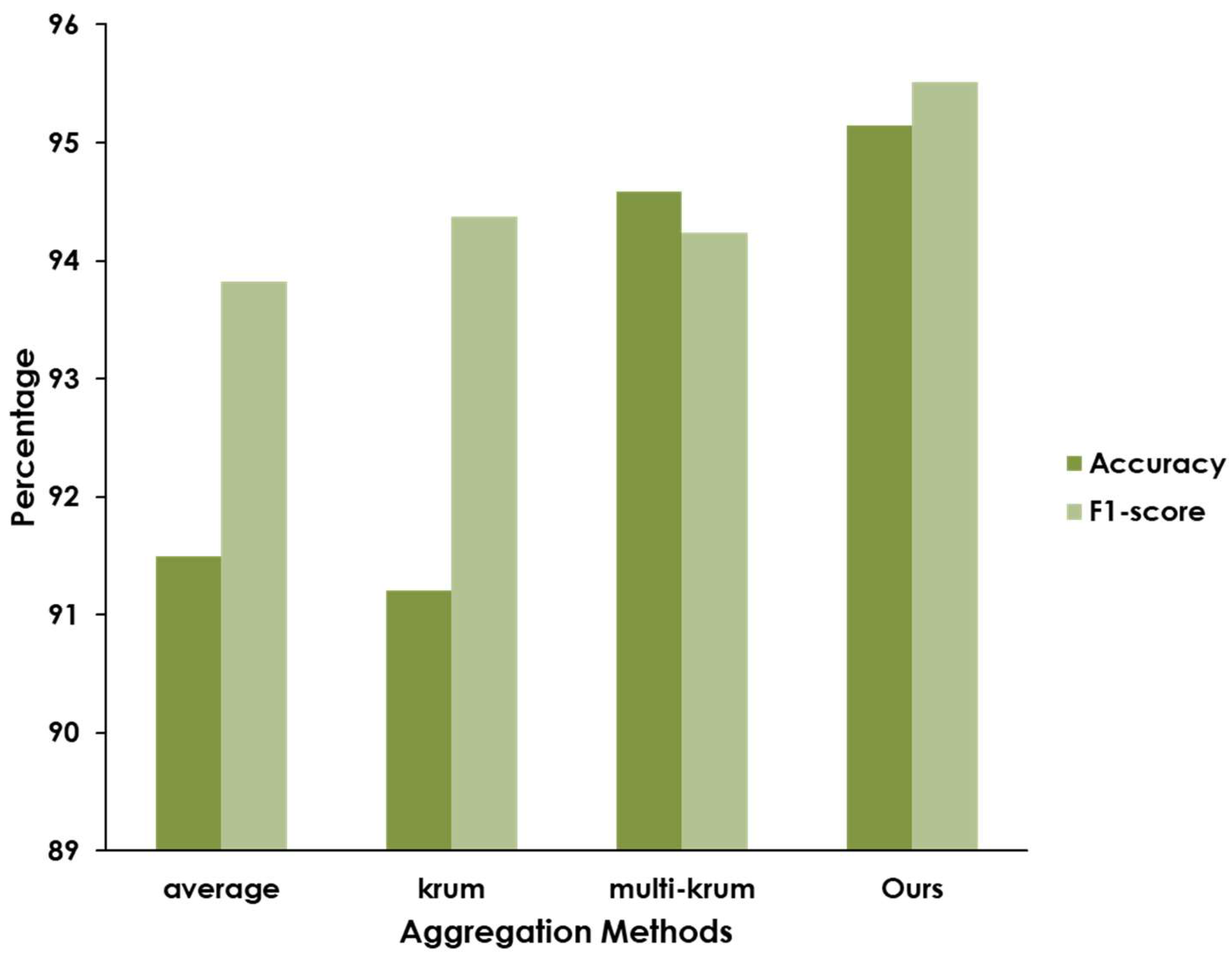
Furthermore, we compared the detection performance of our BFLPD framework under different aggregation methods, e.g., model averaging, Krum, and Multi-Krum (see Figure 5). In the case of the averaging approach, we observed that this method yielded a satisfactory detection performance, but it was susceptible to the presence of malicious clients who intentionally sent incorrect models, compromising the aggregation process and potentially leading to inaccurate results. On the other hand, we can observe that the Krum and Multi-Krum aggregation algorithms were able to mitigate the impact of malicious clients. This algorithm considered the consensus among a subset of clients, discarding outliers and focusing on the models that demonstrated the highest agreement. Interestingly, our modified aggregation algorithm significantly improved the robustness of the aggregation process and enhanced the detection performance, overcoming the influence of malicious clients and becoming a more accurate and reliable global model than Multi-Krum aggregation.
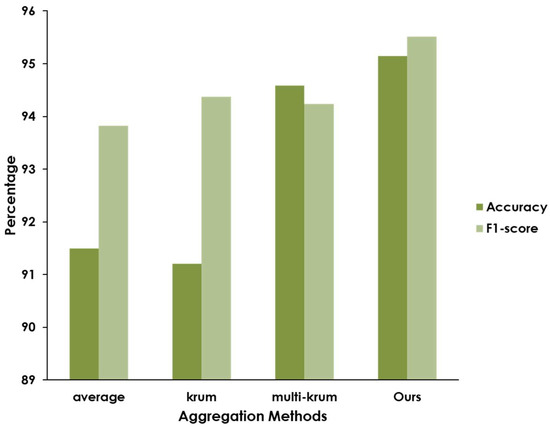
Figure 5.
Comparison of the detection performance of the BFLPD framework according to different aggregation methods.
6. Conclusions
This study presents a robust blockchain-based FL framework that integrates blockchain and federated intelligence to improve pandemic disease diagnosis in smart cities while retaining the privacy and security of sensitive user data. Our framework demonstrates high detection performance amid a secure aggregation scheme, ensuring the accurate and reliable identification of pandemic diseases. The experimental results of a case study of COVID-19 validated the effectiveness of our framework in achieving an accurate and reliable pandemic diagnosis. The high detection performance achieved consistently across different classifiers underscores the robustness and generalizability of our approach. The thriving functioning of our framework holds great promise for improving the efficiency and effectiveness of pandemic management systems and participating in improved public health outcomes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A.-B., I.A., H.H., K.S. and I.A.H.; Methodology, M.A.-B., H.H., I.A. and K.S.; Software, M.A.-B., H.H. and K.S.; Validation, M.A.-B., I.A., H.H., K.S. and I.A.H.; Formal analysis, M.A.-B., I.A., H.H., K.S. and I.A.H.; Investigation, M.A.-B.; Resources, M.A.-B. and I.A.H.; Writing—original draft, M.A.-B., I.A., H.H. and K.S.; Writing—review & editing, M.A.-B., I.A., H.H., K.S. and I.A.H.; Supervision, I.A. and K.S.; Funding acquisition, I.A.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deputyship for Research & Innovation, Ministry of Education Saudi Arabia, for funding this research work through the project number 223202.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset used in this paper is available upon request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest to declare in the research.
References
- Hassankhani, M.; Alidadi, M.; Sharifi, A.; Azhdari, A. Smart city and crisis management: Lessons for the COVID-19 pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strielkowski, W.; Zenchenko, S.; Tarasova, A.; Radyukova, Y. Management of Smart and Sustainable Cities in the Post-COVID-19 Era: Lessons and Implications. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das; Zhang, J.J. Pandemic in a smart city: Singapore’s COVID-19 management through technology & society. Urban Geogr. 2020, 42, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.Y. How Should the Structure of Smart Cities Change to Predict and Overcome a Pandemic? Sustainability 2022, 14, 2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.G.; Peixoto, J.P.J. COVID-19 pandemic: A review of smart cities initiatives to face new outbreaks. ET Smart Cities 2020, 2, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Born, J.; Wiedemann, N.; Cossio, M.; Buhre, C.; Brändle, G.; Leidermann, K.; Goulet, J.; Aujayeb, A.; Moor, M.; Rieck, B.; et al. Accelerating detection of lung pathologies with explainable ultrasound image analysis. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Menapace, W.; Oei, S.; Luijten, B.; Fini, E.; Saltori, C.; Huijben, I.; Chennakeshava, N.; Mento, F.; Sentelli, A.; et al. Deep Learning for Classification and Localization of COVID-19 Markers in Point-of-Care Lung Ultrasound. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 2676–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebadi, A.; Xi, P.; MacLean, A.; Florea, A.; Tremblay, S.; Kohli, S.; Wong, A. COVIDx-US: An Open-Access Benchmark Dataset of Ultrasound Imaging Data for AI-Driven COVID-19 Analytics. Front. Biosci. 2022, 27, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, B.; Li, K. Applications of federated learning in smart cities: Recent advances, taxonomy, and open challenges. Connect. Sci. 2022, 34, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.C.; Kantarci, B.; Oktug, S.; Soyata, T. Federated learning in smart city sensing: Challenges and opportunities. Sensors 2020, 20, 6230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramu, S.P.; Boopalan, P.; Pham, Q.-V.; Maddikunta, P.K.R.; Huynh-The, T.; Alazab, M.; Nguyen, T.T.; Gadekallu, T.R. Federated learning enabled digital twins for smart cities: Concepts, recent advances, and future directions. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 79, 103663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasha, A.H.; Li, T.; Huang, W.; Gu, J.; Li, C. Federated learning in smart cities: Privacy and security survey. Inf. Sci. 2023, 632, 833–857. [Google Scholar]
- Pandya, S.; Srivastava, G.; Jhaveri, R.; Babu, M.R.; Bhattacharya, S.; Maddikunta, P.K.R.; Mastorakis, S.; Piran, J.; Gadekallu, T.R. Federated learning for smart cities: A comprehensive survey. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2023, 55, 102987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B.; Khamparia, A.; Sagayam, K.M.; Sharma, S.K.; Ahad, M.A.; Debnath, N.C. Blockchain for smart cities: A review of architectures, integration trends and future research directions. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 61, 102360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Tang, H.; Huang, T.; Yu, F.R.; Xie, R.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y. A survey of blockchain technology applied to smart cities: Research issues and challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2019, 21, 2794–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, U.; Khan, L.U.; Yaqoob, I.; Kazmi, S.A.; Salah, K.; Hong, C.S. Blockchain for IoT-based smart cities: Recent advances, requirements, and future challenges. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2021, 181, 103007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakak, S.; Khan, W.Z.; Gilkar, G.A.; Imran, M.; Guizani, N. Securing smart cities through blockchain technology: Architecture, requirements, and challenges. IEEE Netw. 2020, 34, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Kim, S.J.; Cha, W.C.; Kim, T. A blockchain-applied personal health record application: Development and user experience. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, M.; Capodici, A.; Rucci, P.; Bianconi, A.; Longo, G.; Ricci, M.; Sanmarchi, F.; Golinelli, D. Blockchain for the healthcare supply chain: A systematic literature review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.T.; Sun, J. Shufflenet v2: Practical guidelines for efficient cnn architecture design. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 116–131. [Google Scholar]
- Hejazi, H.D.; Khamees, A.A. Employees Motivational Factors toward Knowledge Sharing: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Adv. Appl. Comput. Intell. 2022, 1, 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, S.; Rastegari, M. Mobilevit: Light-weight, general-purpose, and mobile-friendly vision transformer. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.02178. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, B.; El-Nouby, A.; Touvron, H.; Stock, P.; Joulin, A.; Jégou, H.; Douze, M. Levit: A vision transformer in convnet’s clothing for faster inference. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 12259–12269. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, T.; Lu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhu, C.; Sun, H.; Wang, Z.; Lo, S.K.; Wang, F.-Y. Dynamic-fusion-based federated learning for COVID-19 detection. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 15884–15891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feki, I.; Ammar, S.; Kessentini, Y.; Muhammad, K. Federated learning for COVID-19 screening from Chest X-ray images. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 106, 107330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Khan, A.A.; Kumar, J.; Zakria, A.; Golilarz, N.A.; Zhang, S.; Ting, Y.; Zheng, C.; Wang, W. Blockchain-federated-learning and deep learning models for COVID-19 detection using CT imaging. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 16301–16314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, H.; Naeem, A.; Naqvi, R.A.; Loh, W.K. DMFL_Net: A Federated Learning-Based Framework for the Classification of COVID-19 from Multiple Chest Diseases Using X-rays. Sensors 2023, 23, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, G.; Qu, W.; Shao, B. Blockchain-Based Trusted Federated Learning with Pre-Trained Models for COVID-19 Detection. Electronics 2023, 12, 2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wibawa, F.; Catak, F.O.; Kuzlu, M.; Sarp, S.; Cali, U. Homomorphic encryption and federated learning based privacy-preserving cnn training: COVID-19 detection use-case. In Proceedings of the 2022 European Interdisciplinary Cybersecurity Conference, Barcelona, Spain, 15–16 June 2022; pp. 85–90. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).