Hybrid Entropy-Based Metrics for k-Hop Environment Analysis in Complex Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Previous and Related Work
3. Notation and Conventions
3.1. Basic Definitions
3.2. Mixed Degree and Convex Parameter
- If , both and are set to 0;
- If , then and by definition.
4. Formal Definitions and Properties
Basic Properties
5. Proofs
5.1. Proof of Theorem (Range of EWR)
5.2. Proof of Theorem (Range and Upper Bound Monotonicity of NED)
5.3. Proof of Lemma (Isomorphism Invariance)
5.4. Auxiliary Facts on Extreme Cases
- If and , then for every v, is a clique. With local degrees, is uniform, hence and , so and .
- If and , then for the center v: , while with global degrees is uniform so ; thus and . For a leaf w: and , hence both metrics are 0.
5.5. Stability Bounds Under Local Edits
5.6. Non-Monotonicity Examples in k
6. Topology Analysis
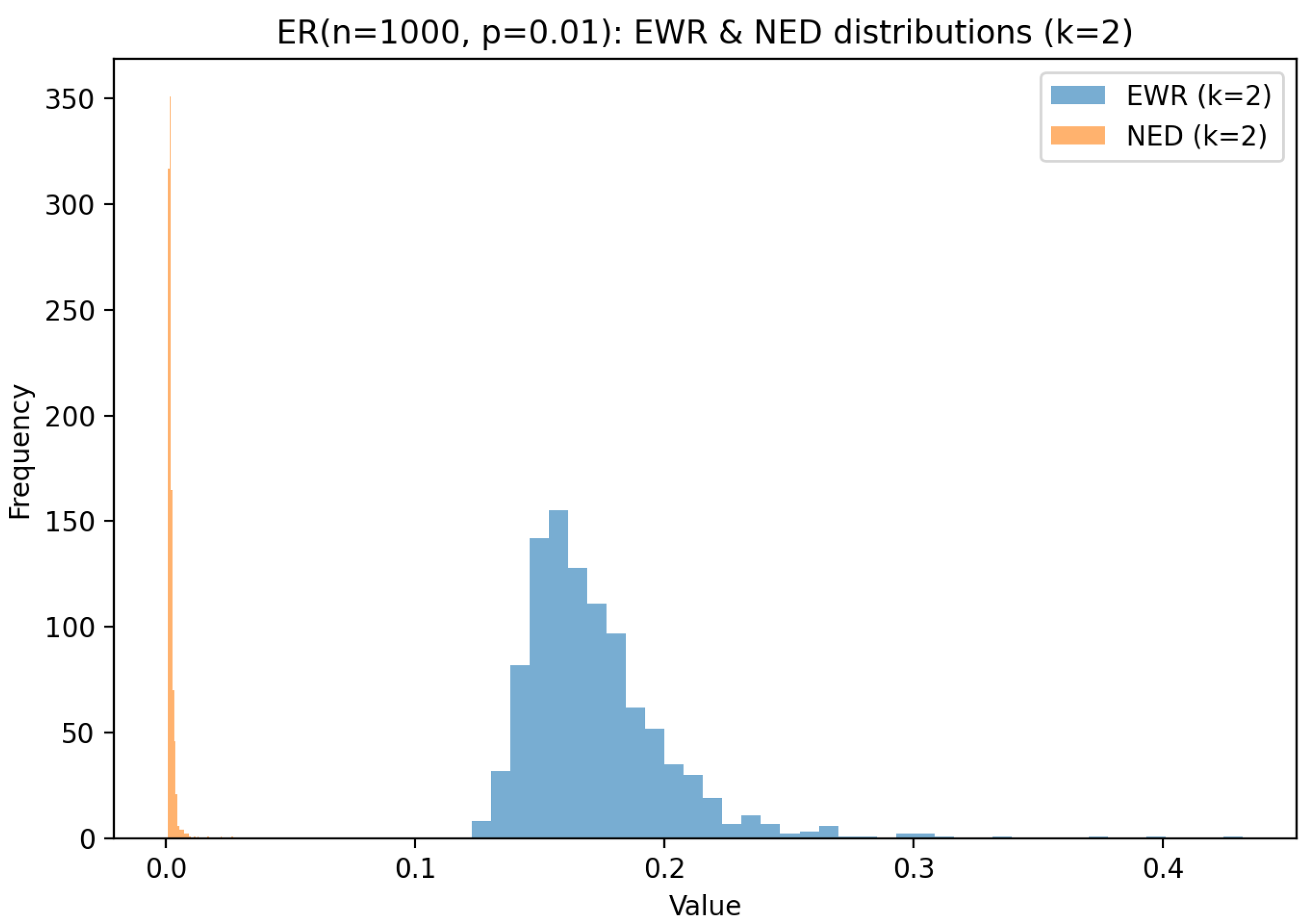
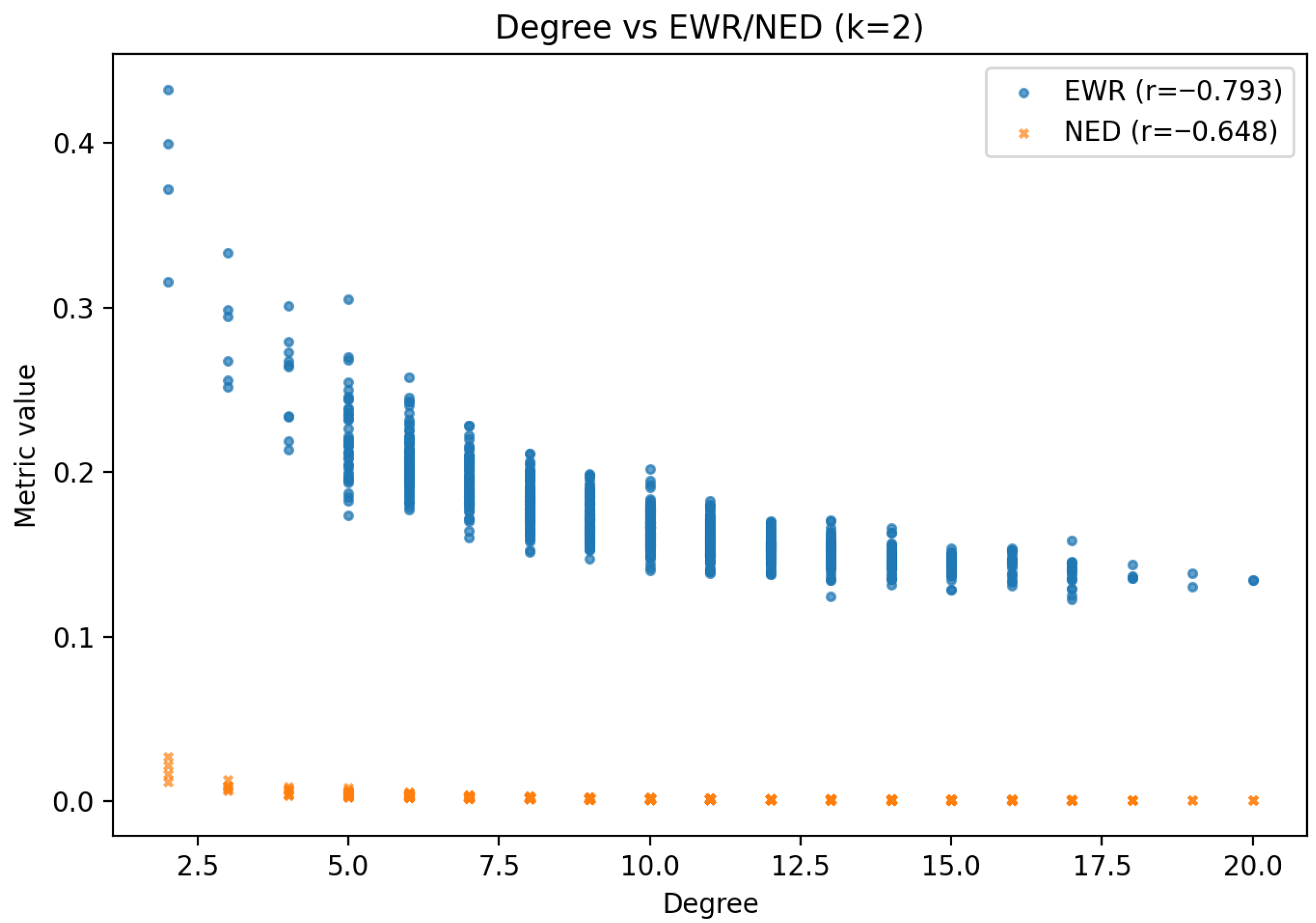
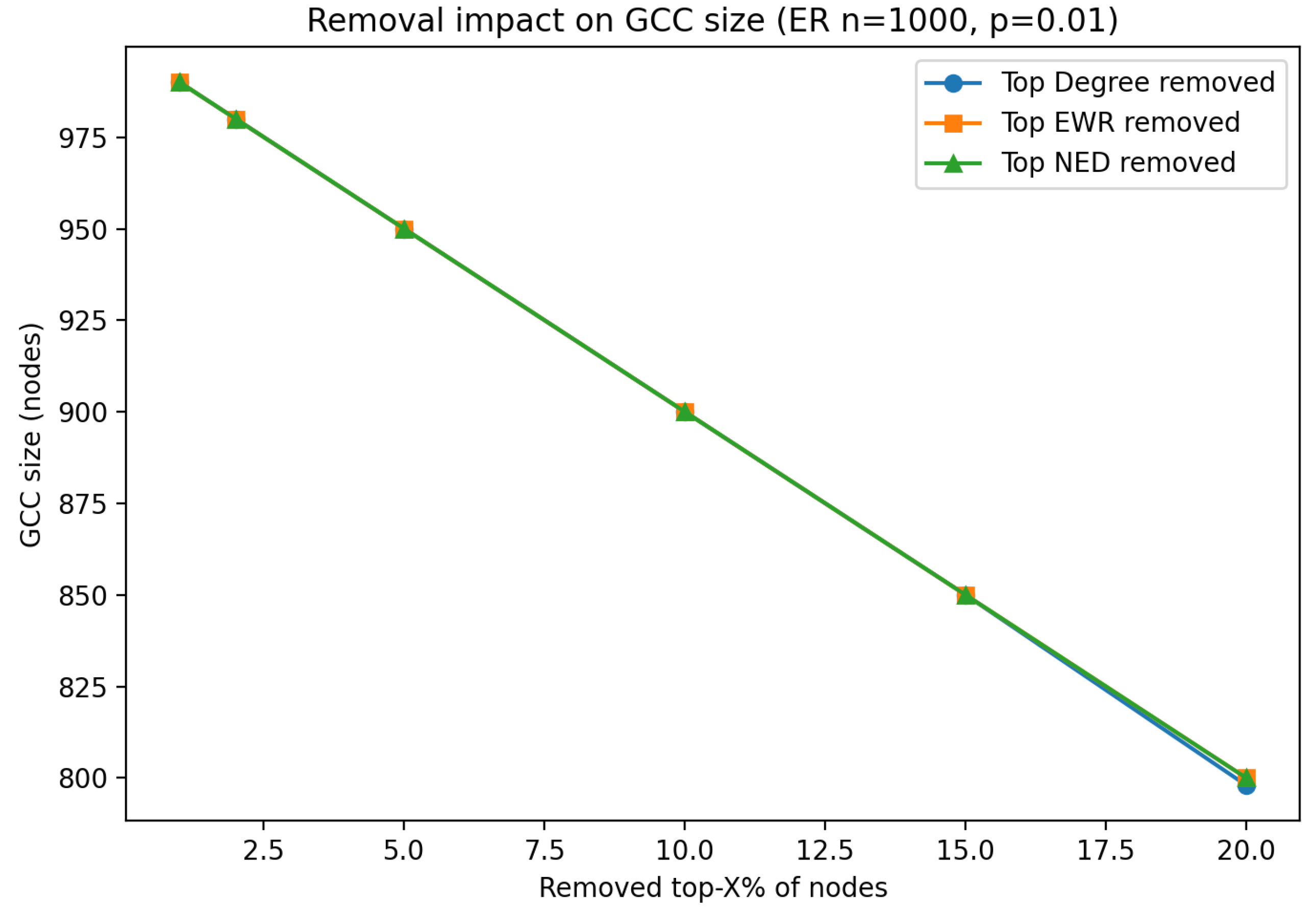
6.1. Erdős–Rényi Random Graph Analysis
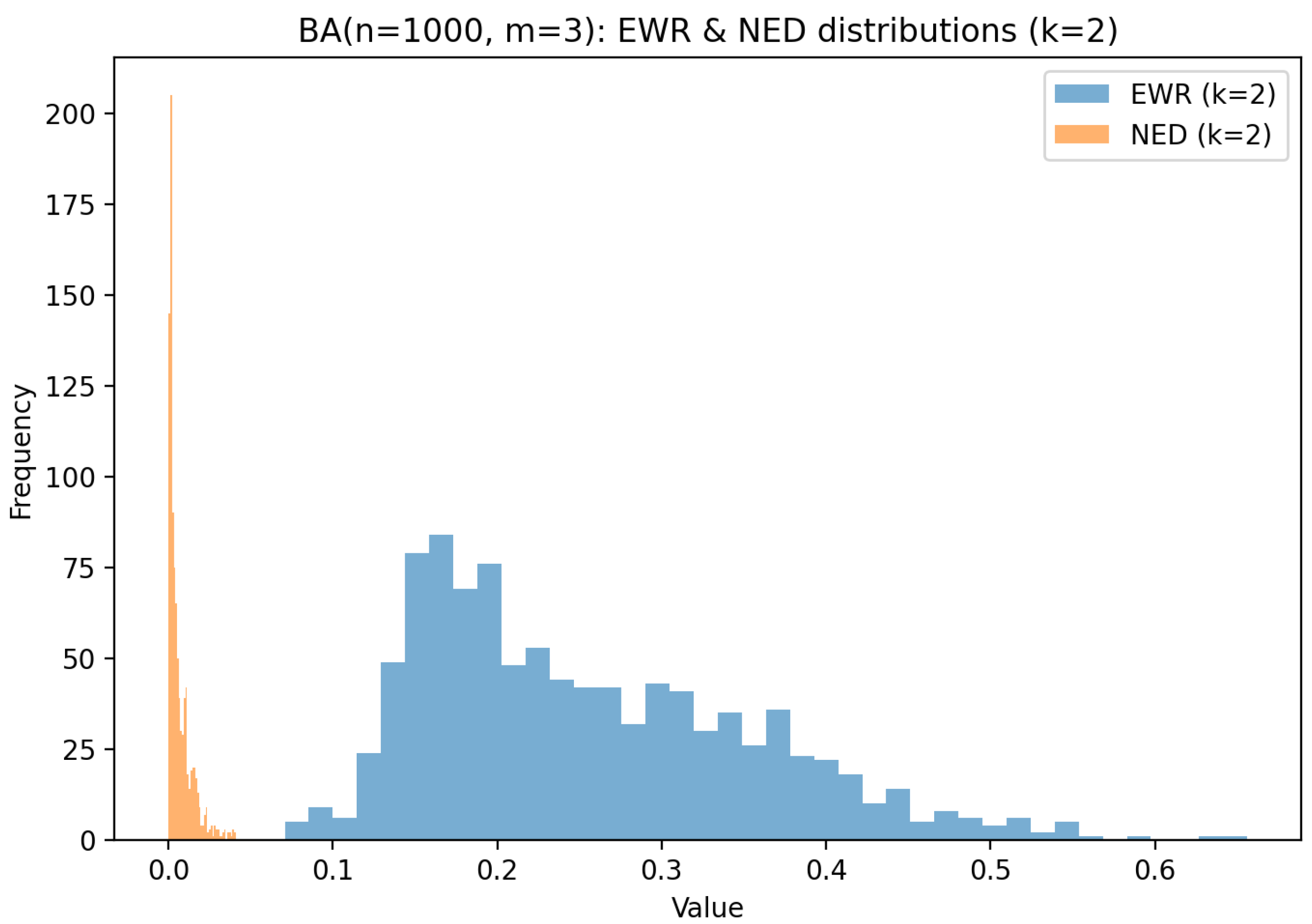
6.2. Barabási–Albert Graph Analysis
6.3. Watts–Strogatz Small-World Graph Analysis
Random Geometric Graph Analysis
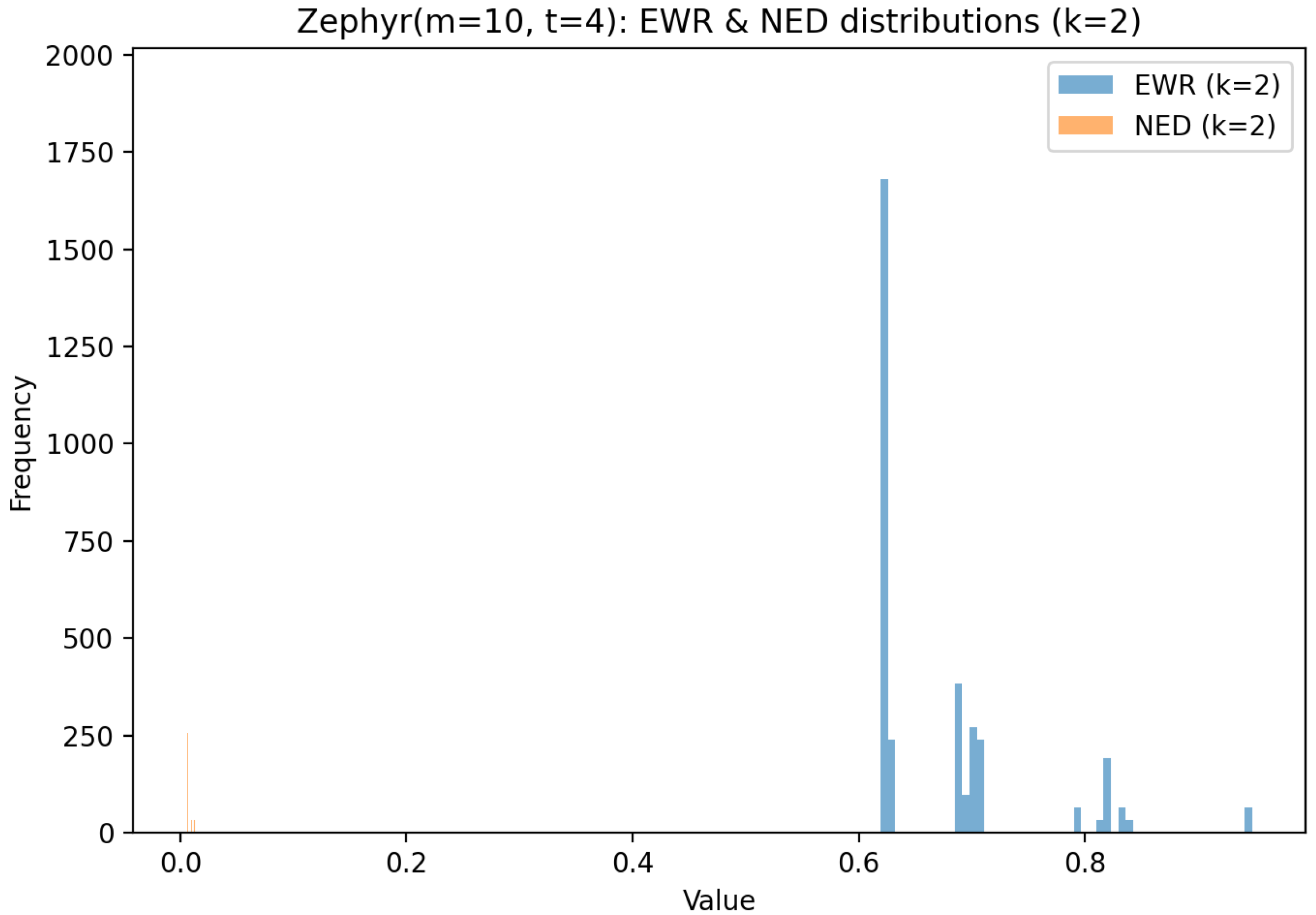
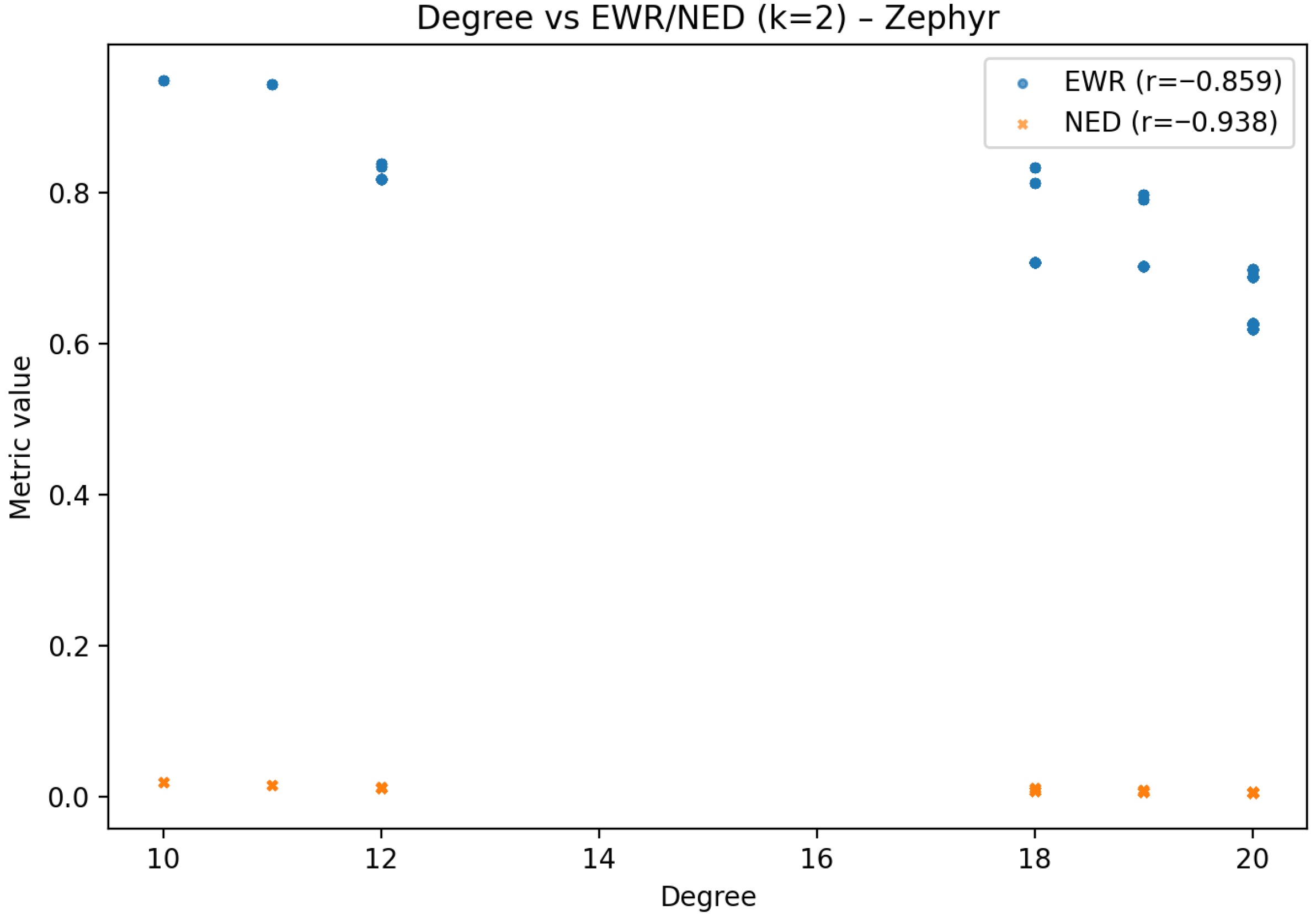
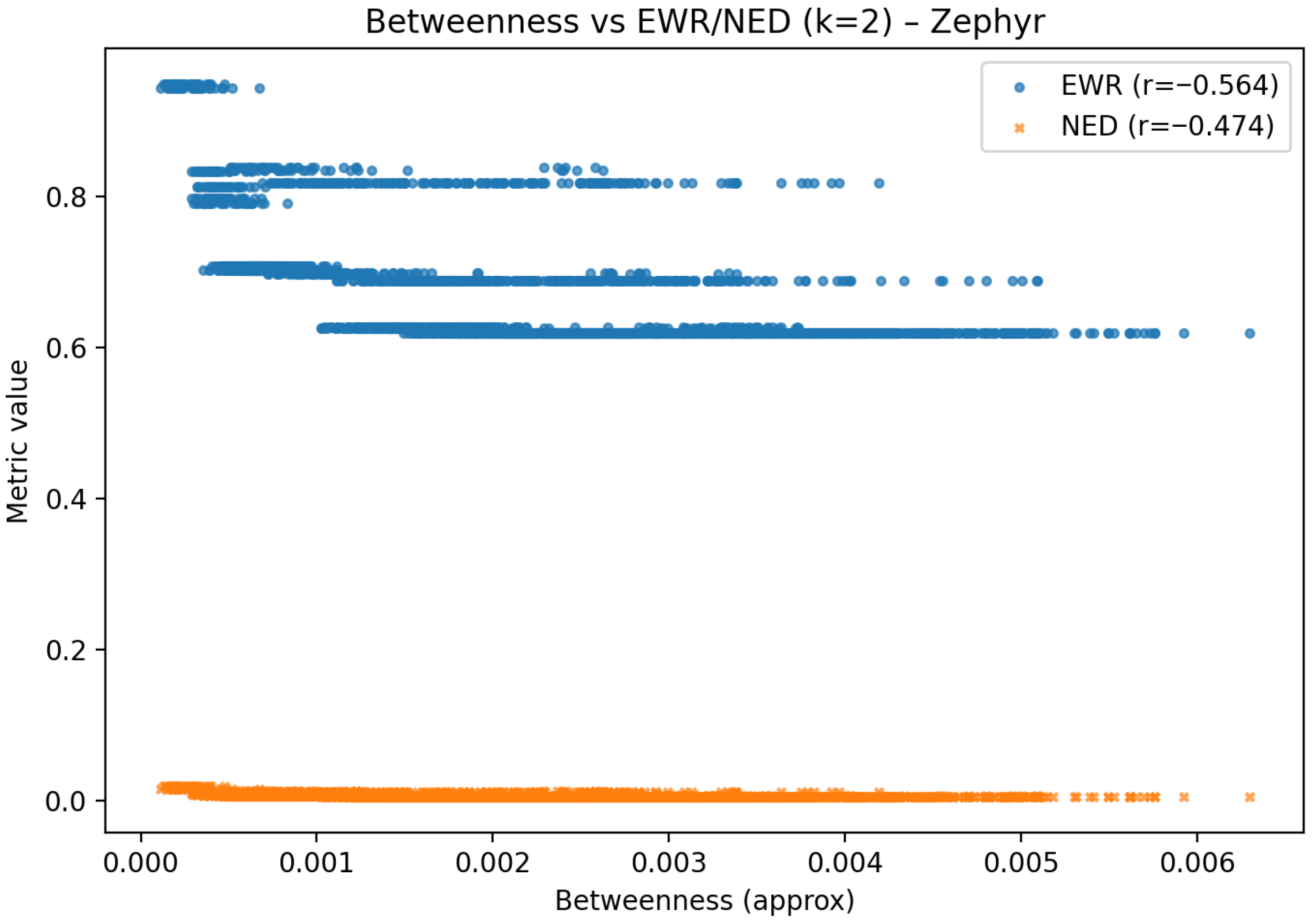
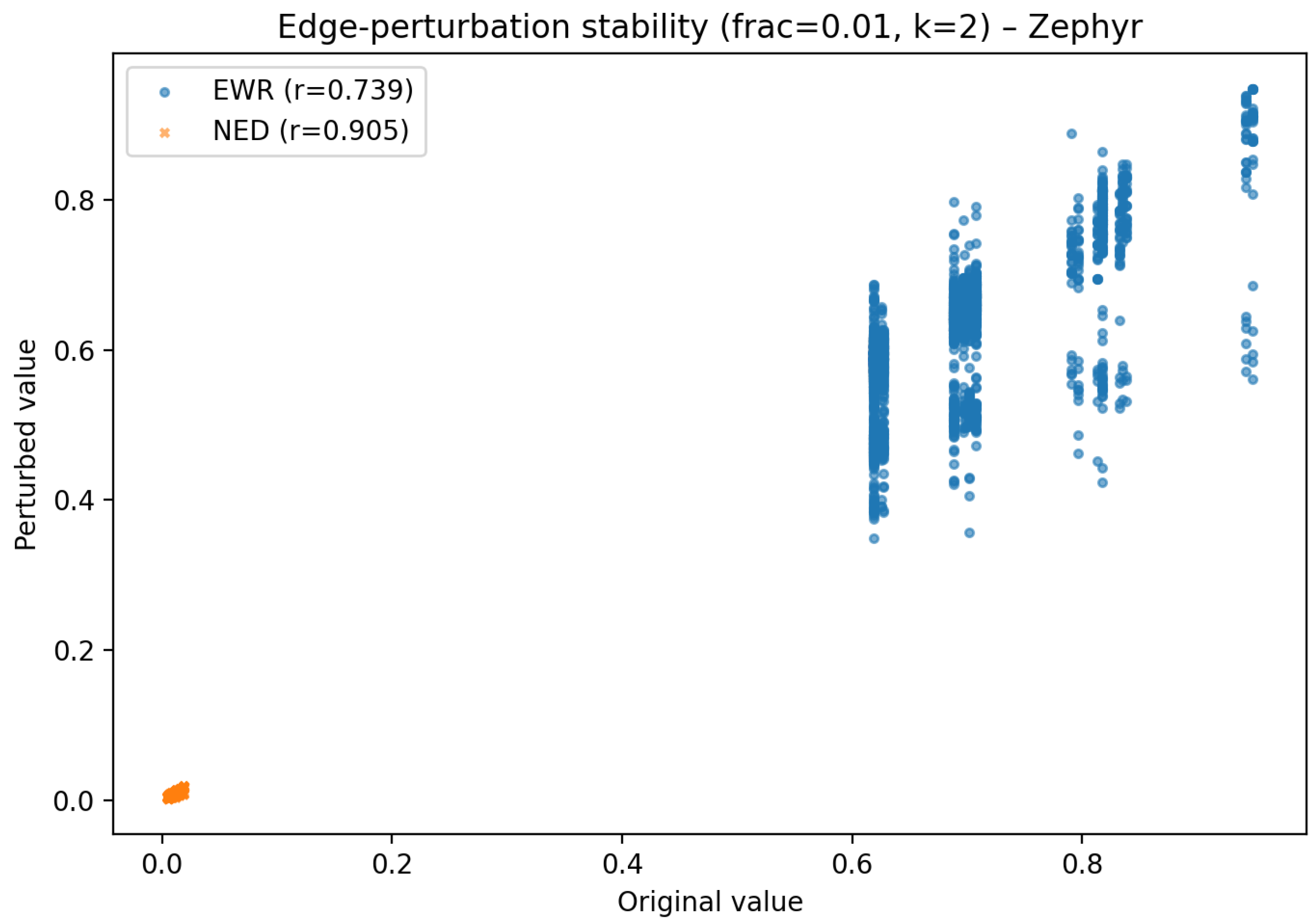
6.4. Zephyr Graph Analysis
6.5. Comparative Summary Across Network Topologies
6.5.1. On the Negative Correlations with Degree
6.5.2. Comparative Perspective
7. Algorithms, Complexity, and Code Availability
7.1. Algorithms
| Algorithm 1: BFS_UpToK (returns without v) |
| Require: Graph as adjacency lists; source ; hop radius |
Ensure:
Set
|
| Algorithm 2: EWR/NED on k-hop neighborhoods (all vertices) |
| Require: Graph ; hop radius k |
Ensure:
Arrays ,
|
7.2. Computational Complexity
7.3. Code Availability
8. Conclusions and Future Work
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anand, K.; Bianconi, G. Entropy measures for networks: Toward an information theory of complex topologies. Phys. Rev. E—Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2009, 80, 045102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Wu, W.; Wang, H.; Xiong, M.; Wang, W. Symmetry-based structure entropy of complex networks. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2008, 387, 2611–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowshowitz, A.; Dehmer, M. Entropy and the complexity of graphs revisited. Entropy 2012, 14, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passerini, F.; Severini, S. The von Neumann entropy of networks. arXiv 2008, arXiv:0812.2597v2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Escolano, F.; Hancock, E.R.; Wilson, R.C. Graph characterizations from von Neumann entropy. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2012, 33, 1958–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; He, J.; Hu, H.; Shi, Y. Fast computation of von Neumann entropy for large-scale graphs via quadratic approximations. Linear Algebra Its Appl. 2020, 585, 127–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-Y.; Wu, L.; Liu, S.; Rajapakse, I. Fast incremental von Neumann graph entropy computation: Theory, algorithm, and applications. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning-PMLR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; Volume 97, pp. 1091–1101. Available online: http://proceedings.mlr.press/v97/chen19j/chen19j.pdf (accessed on 9 August 2025).
- Paton, J.; Hartle, H.; Stepanyants, H.; van der Hoorn, P.; Krioukov, D. Entropy of labeled versus unlabeled networks. Phys. Rev. E 2022, 106, 054308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhao, B.; Chen, L.; Gao, T.; Li, J. Identifying important nodes in complex networks based on node propagation entropy. Entropy 2022, 24, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, S.; Hric, D. Community detection in networks: A user guide. Phys. Rep. 2016, 659, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, Y.M.; Plapper, P. A survey of information entropy metrics for complex networks. Entropy 2020, 22, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidis, G.; Ioannidis, E.; Makris, G.; Antoniou, I.; Varsakelis, N. Competitive Conditions in Global Value Chain Networks: An Assessment Using Entropy and Network Analysis. Entropy 2020, 22, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, X. Node Importance Ranking of Complex Networks with Entropy Variation. Entropy 2017, 19, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Gao, H. The Structure Entropy-Based Node Importance Ranking Method for Graph Data. Entropy 2023, 25, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, B.; Chu, S.-H.; Parhi, K.K. Ranking Regions, Edges and Classifying Tasks in Functional Brain Graphs by Sub-Graph Entropy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, E. Complex networks in the Euclidean space of communicability distances. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 85, 066122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M. Networks, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018; ISBN 9780198805090. [Google Scholar]
- Boothby, T.; King, A.D.; Roy, A. Fast clique minor generation in Chimera qubit connectivity graphs. Quantum Inf. Process. 2016, 15, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dattani, N.S.; Szalay, S.; Chancellor, N. Pegasus: The second connectivity graph for large-scale quantum annealing hardware. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.07636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Macready, W.G.; Roy, A. A practical heuristic for finding graph minors. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelofske, E.; Hahn, G.; Djidjev, H. Decomposition algorithms for solving NP-hard problems on a quantum annealer. J. Signal Process. Syst. 2022, 93, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biamonte, J.; Wittek, P.; Pancotti, N.; Rebentrost, P.; Wiebe, N.; Lloyd, S. Quantum machine learning. Nature 2017, 549, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biró, C.; Kusper, G. Some k-Hop Based Graph Metrics and Node Ranking in Wireless Sensor Networks. Ann. Math. Informaticae 2019, 50, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biró, C. Analysis of D-Wave Topologies with Classical Graph Metrics. Int. J. Math. Comput. Sci. 2024, 19, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar]
- Biró, C.; Kusper, G. Analysis of D-Wave Topologies with k-Hop-Based Graph Metrics. Quantum Rep. 2025, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biró, C. Structural Sensitivity in Graphs: An Entropy-Based k-Hop Metric and its Applications. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE 19th International Symposium on Applied Computational Intelligence and Informatics (SACI), Budapest, Hungary, and Timişoara, Romania, 19–24 May 2025; pp. 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdős, P.; Rényi, A. On the evolution of random graphs. A Magyar Tudományos Akadémia Matematikai Kutató Intézetének Közleményei 1959, 5, 17–61. [Google Scholar]
- Barabási, A.-L.; Albert, R. Emergence of scaling in random networks. Science 1999, 286, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, D.J.; Strogatz, S.H. Collective dynamics of ’small-world’ networks. Nature 1998, 393, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penrose, M. Random Geometric Graphs; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2003; ISBN 9780191545030. [Google Scholar]
- Boothby, K.; King, D.A.; Raymond, J. Zephyr Topology of D-Wave Quantum Processors. D-Wave Technical Report. 2021. Available online: https://www.dwavequantum.com/media/2uznec4s/14-1056a-a_zephyr_topology_of_d-wave_quantum_processors.pdf (accessed on 9 August 2025).


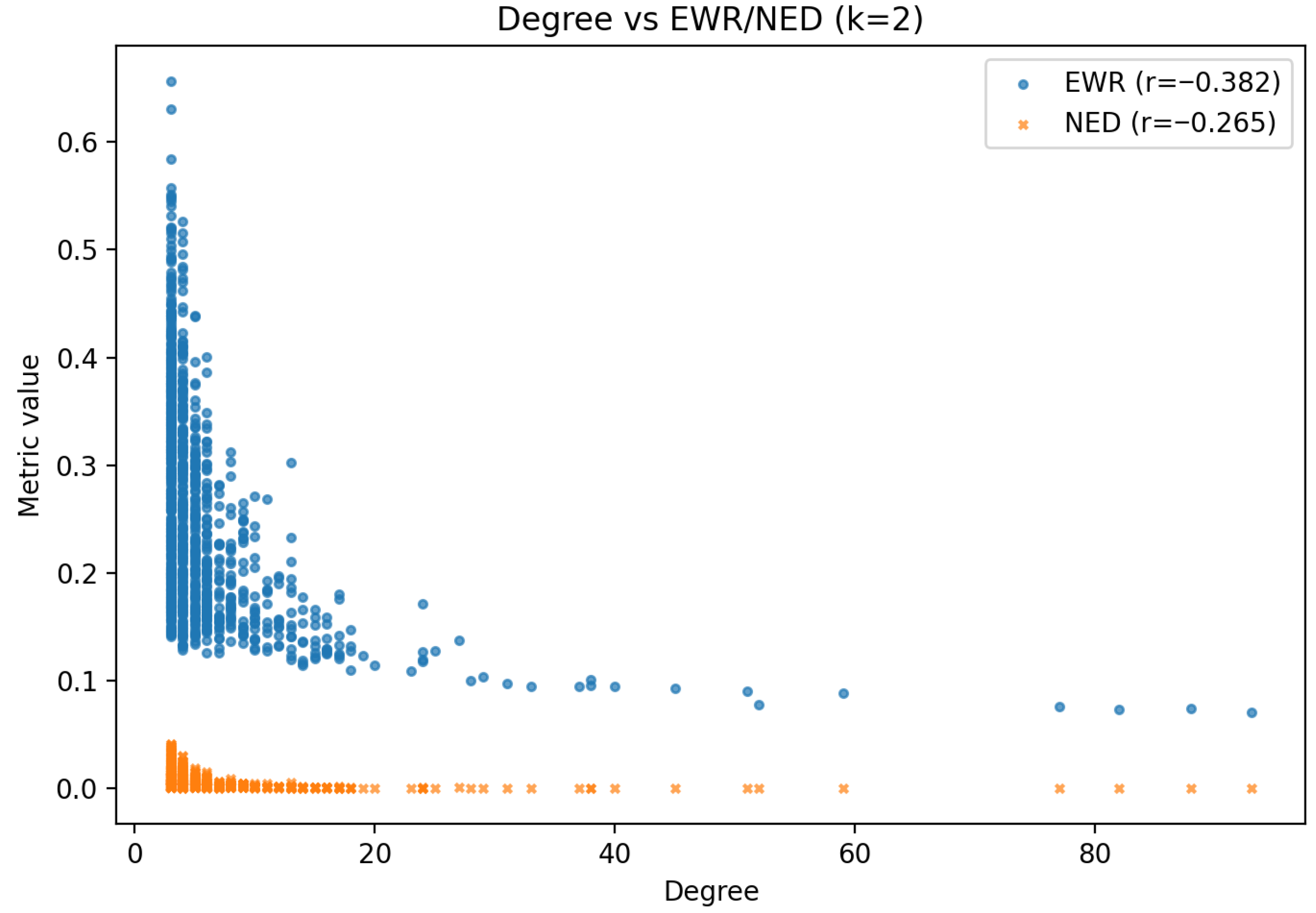
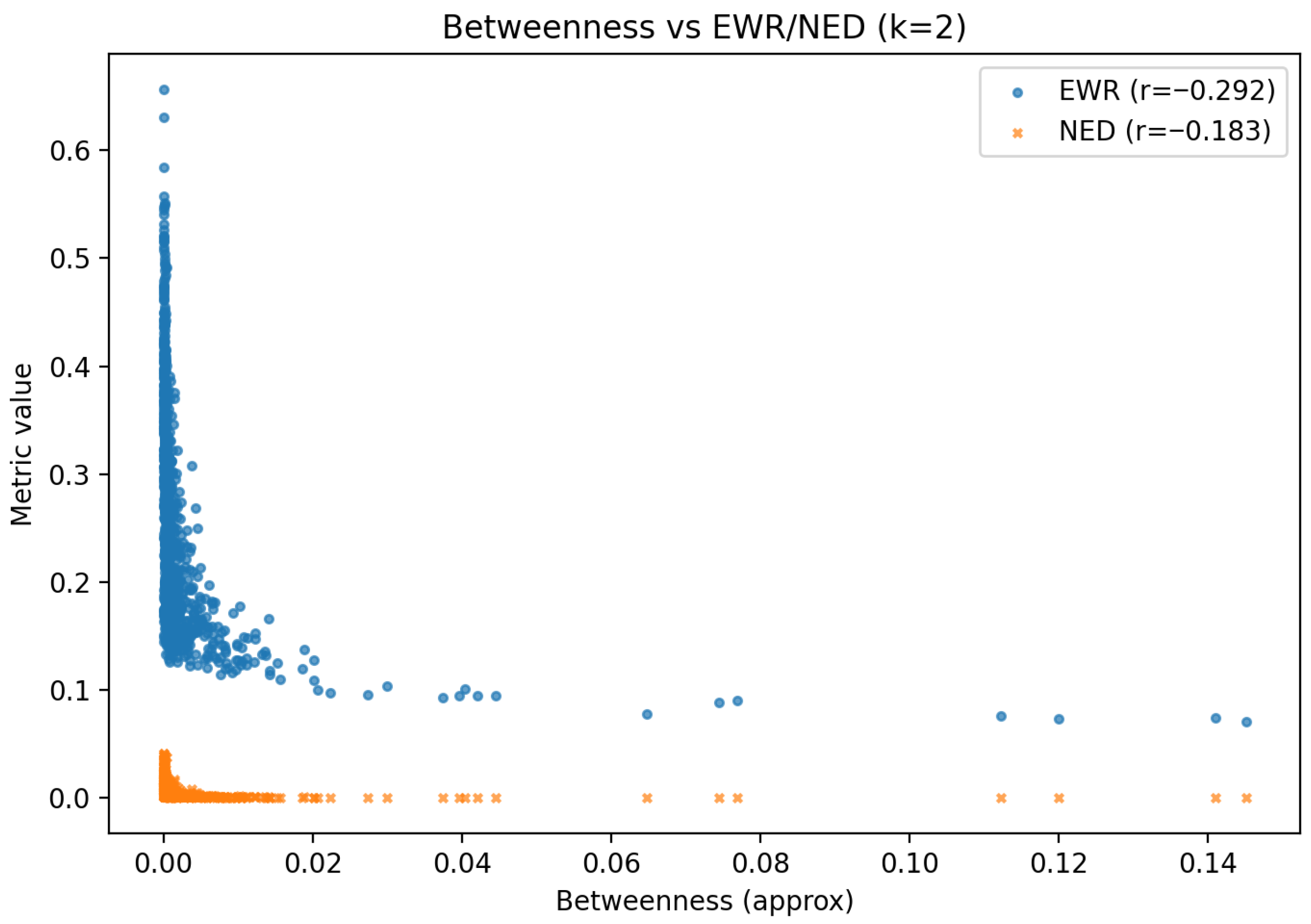
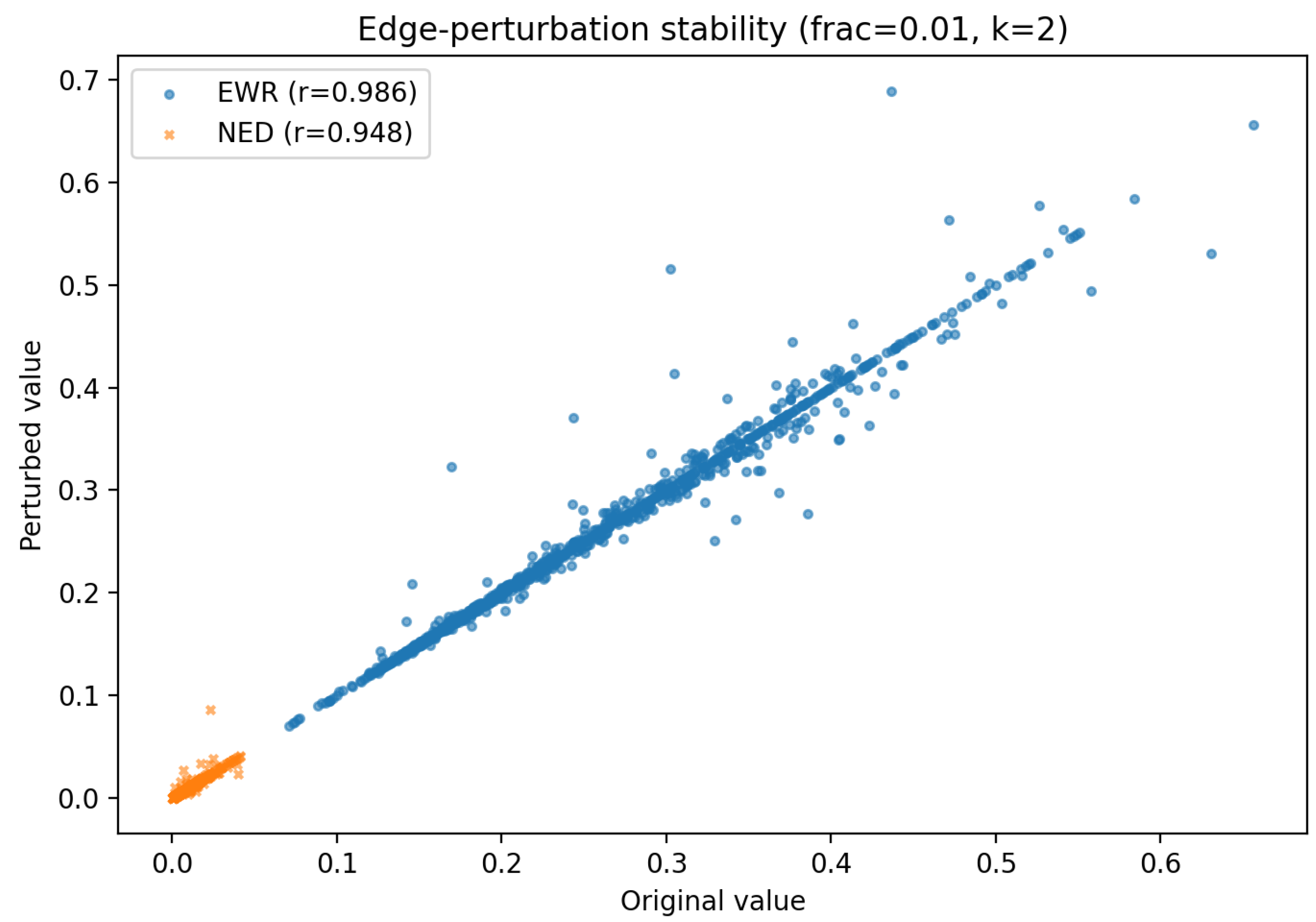
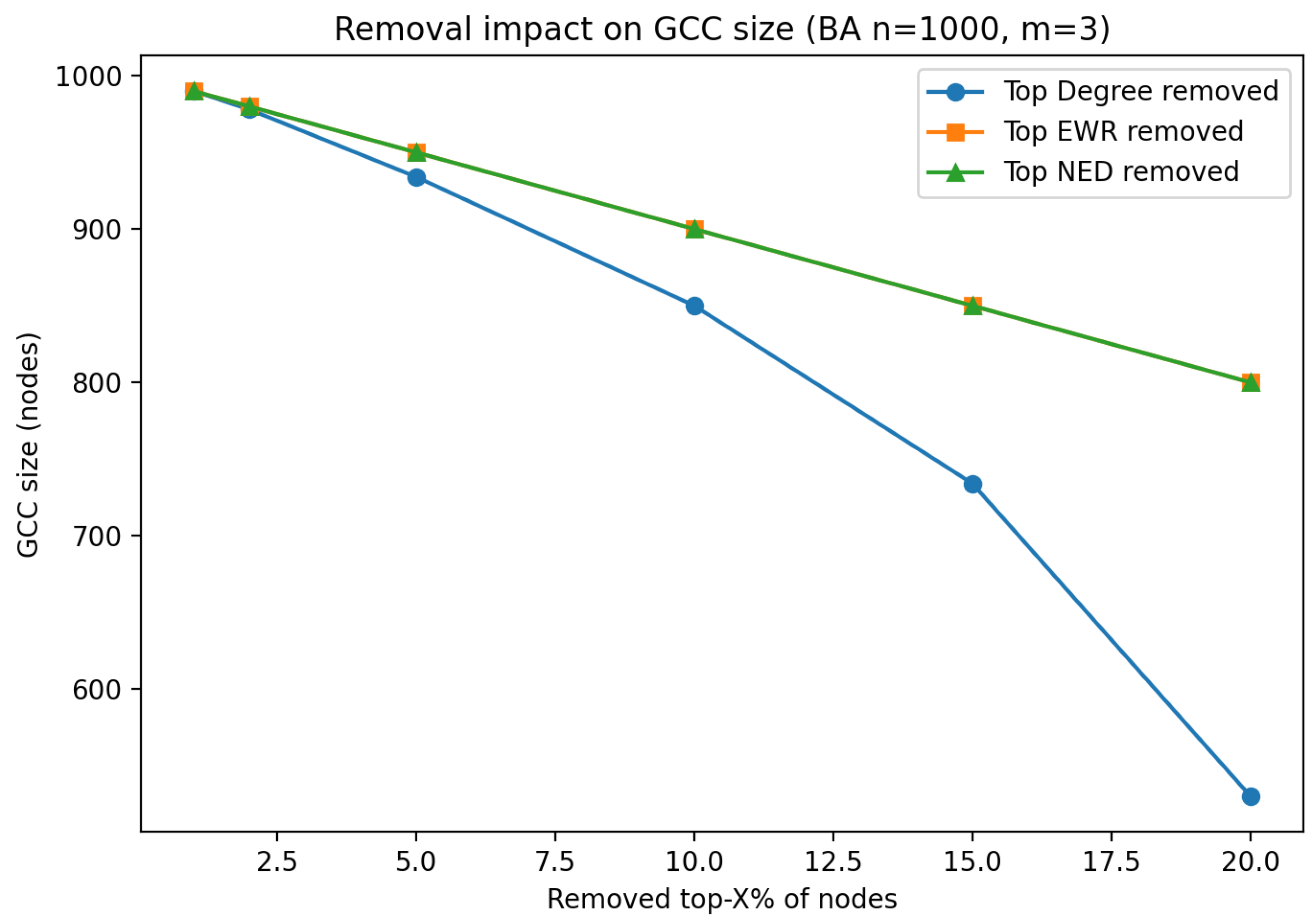
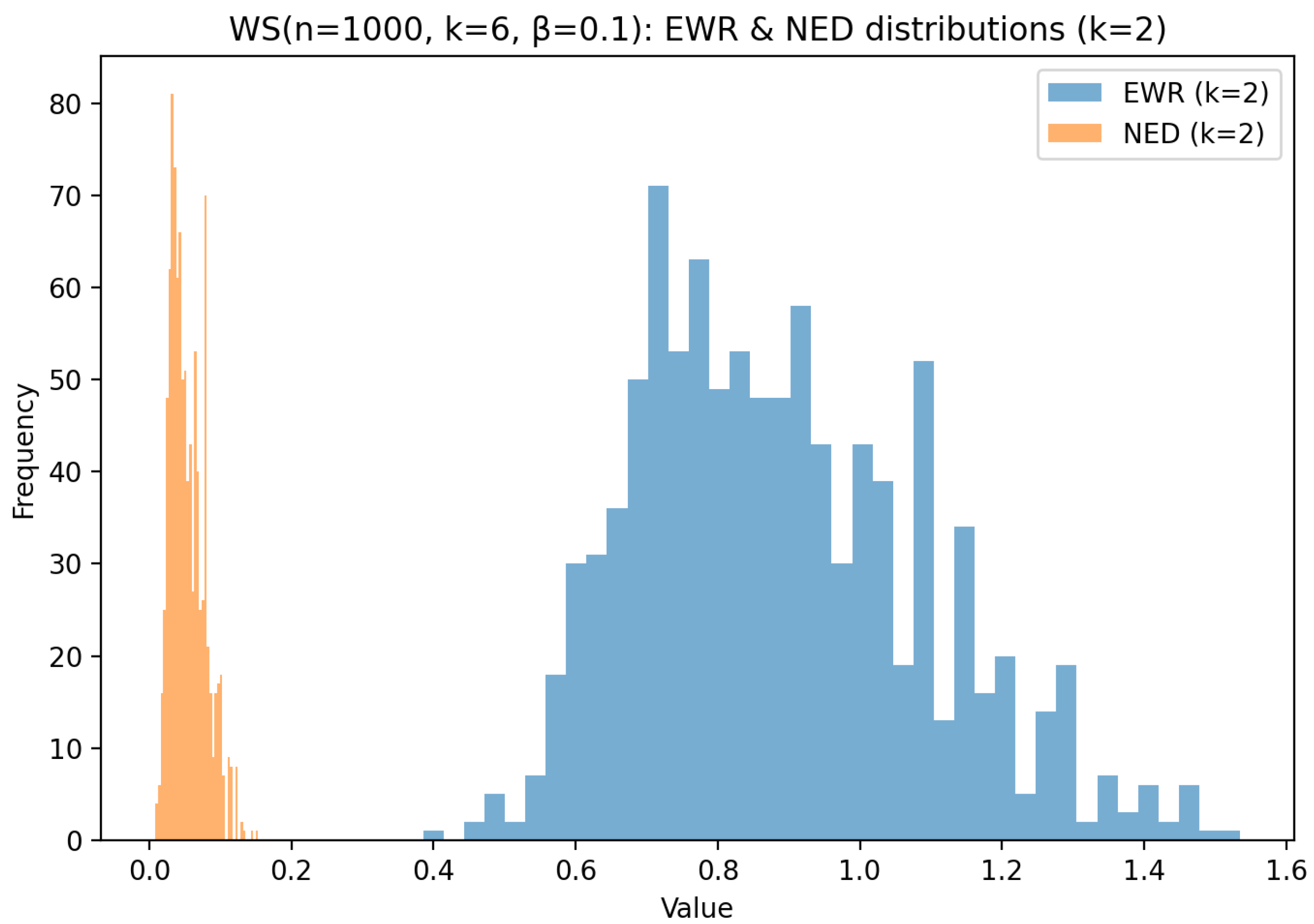

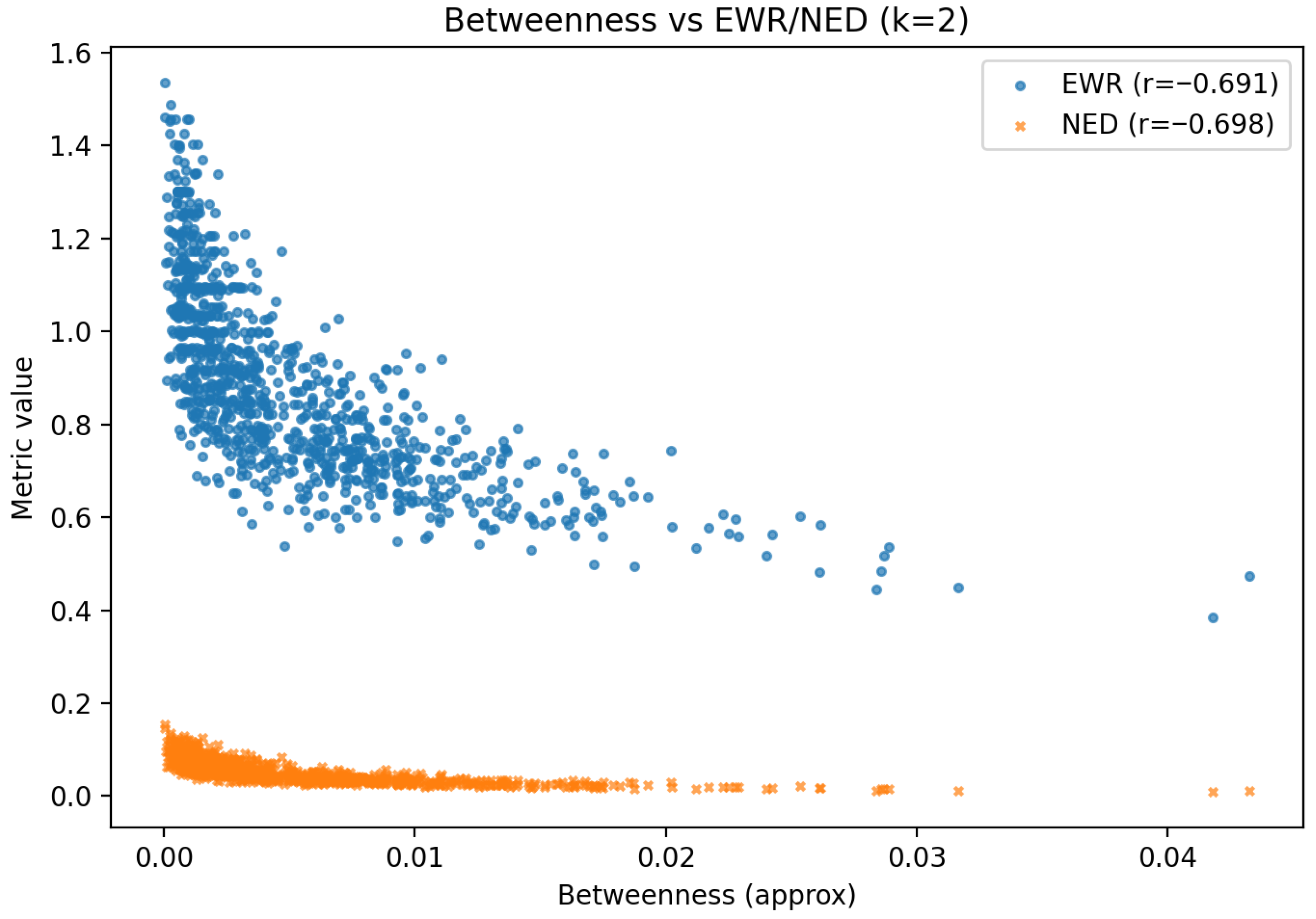
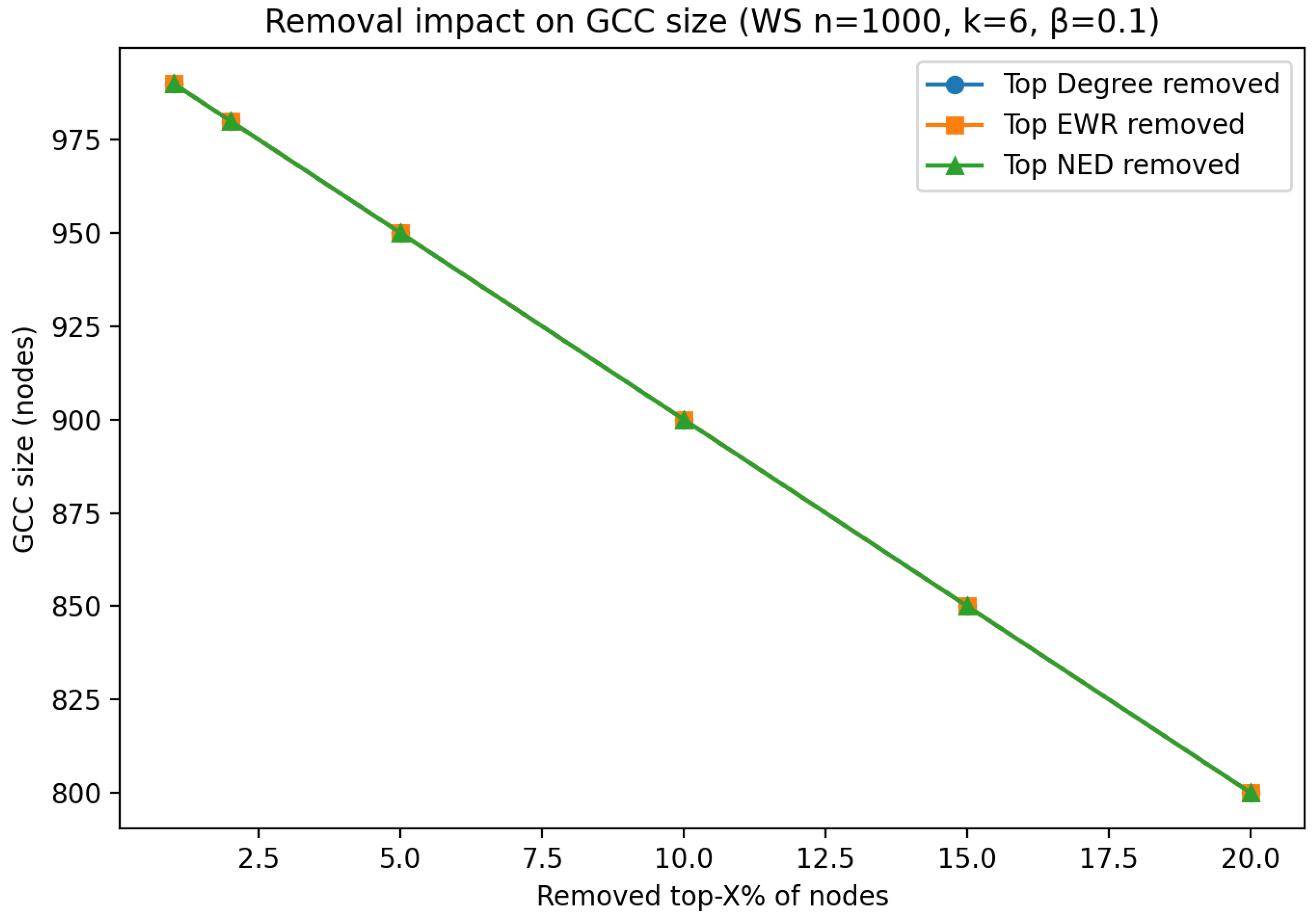
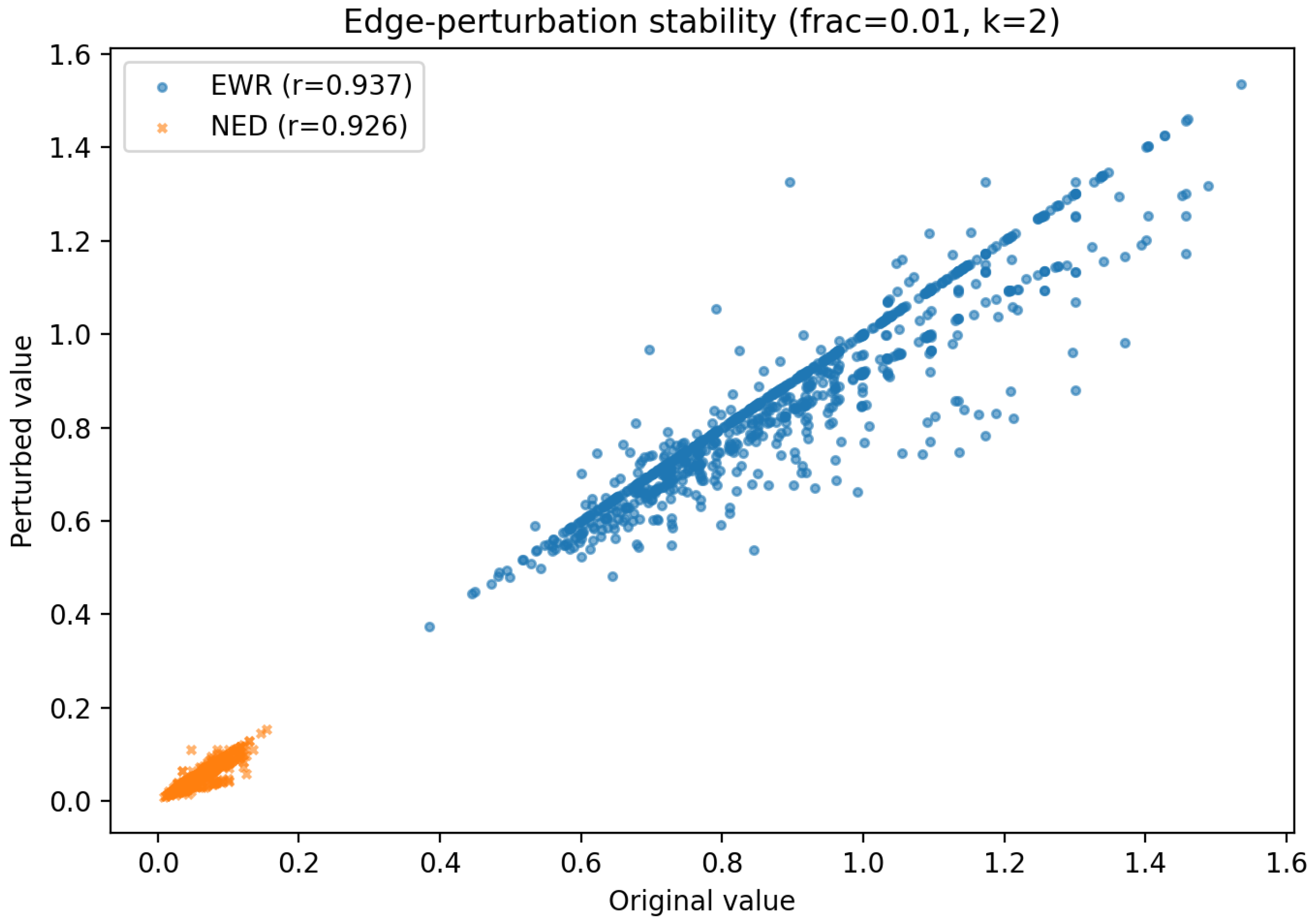
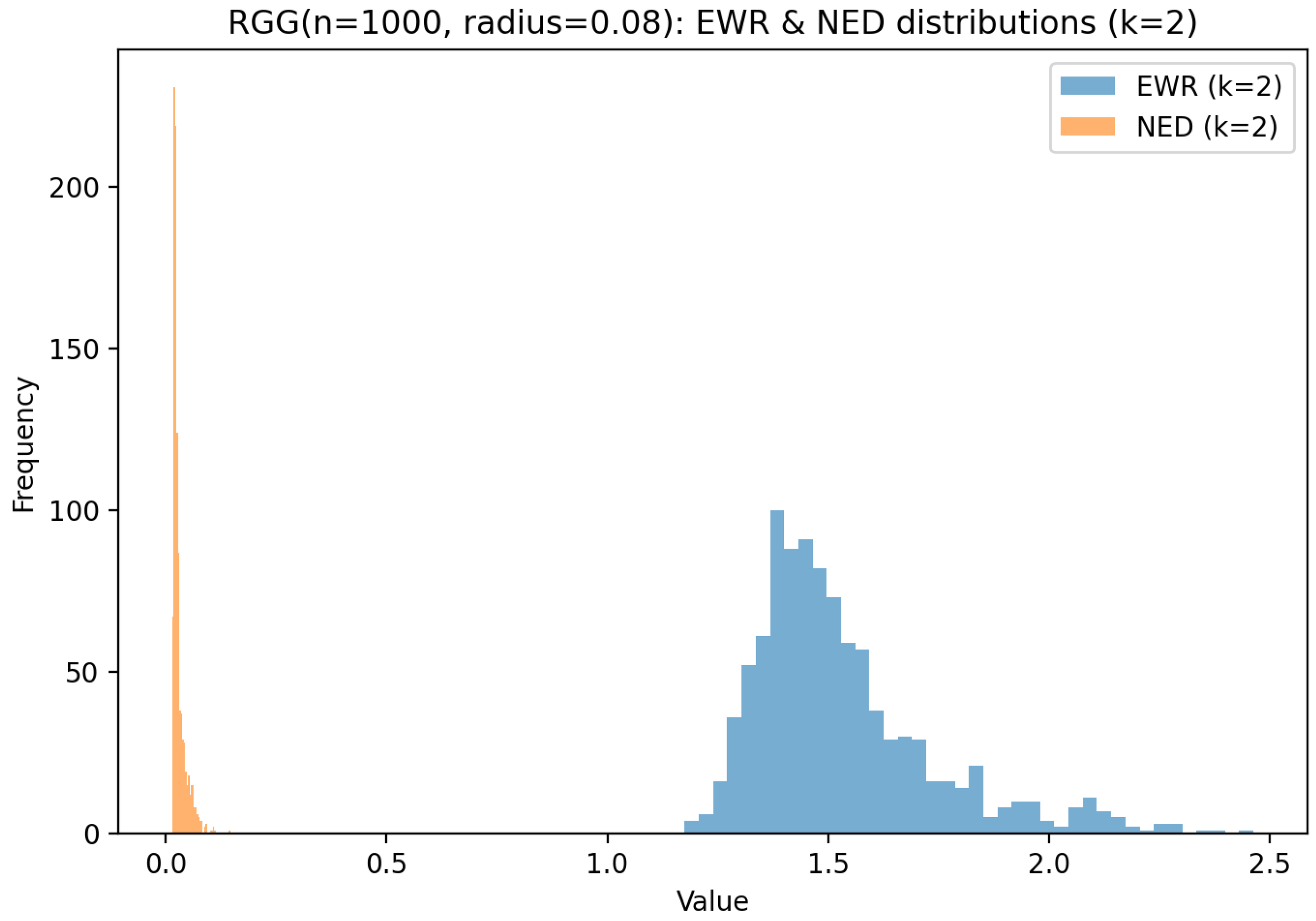
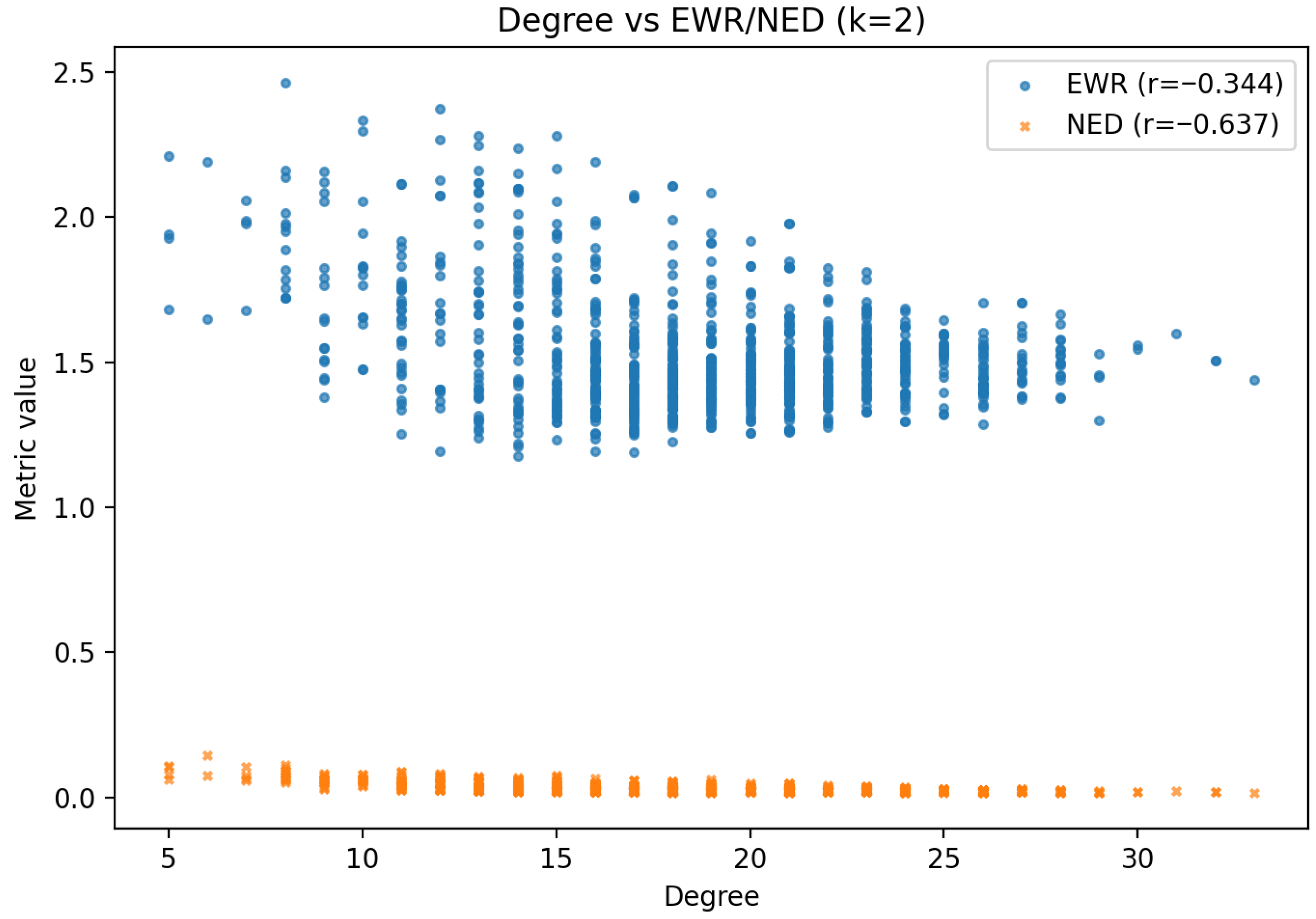
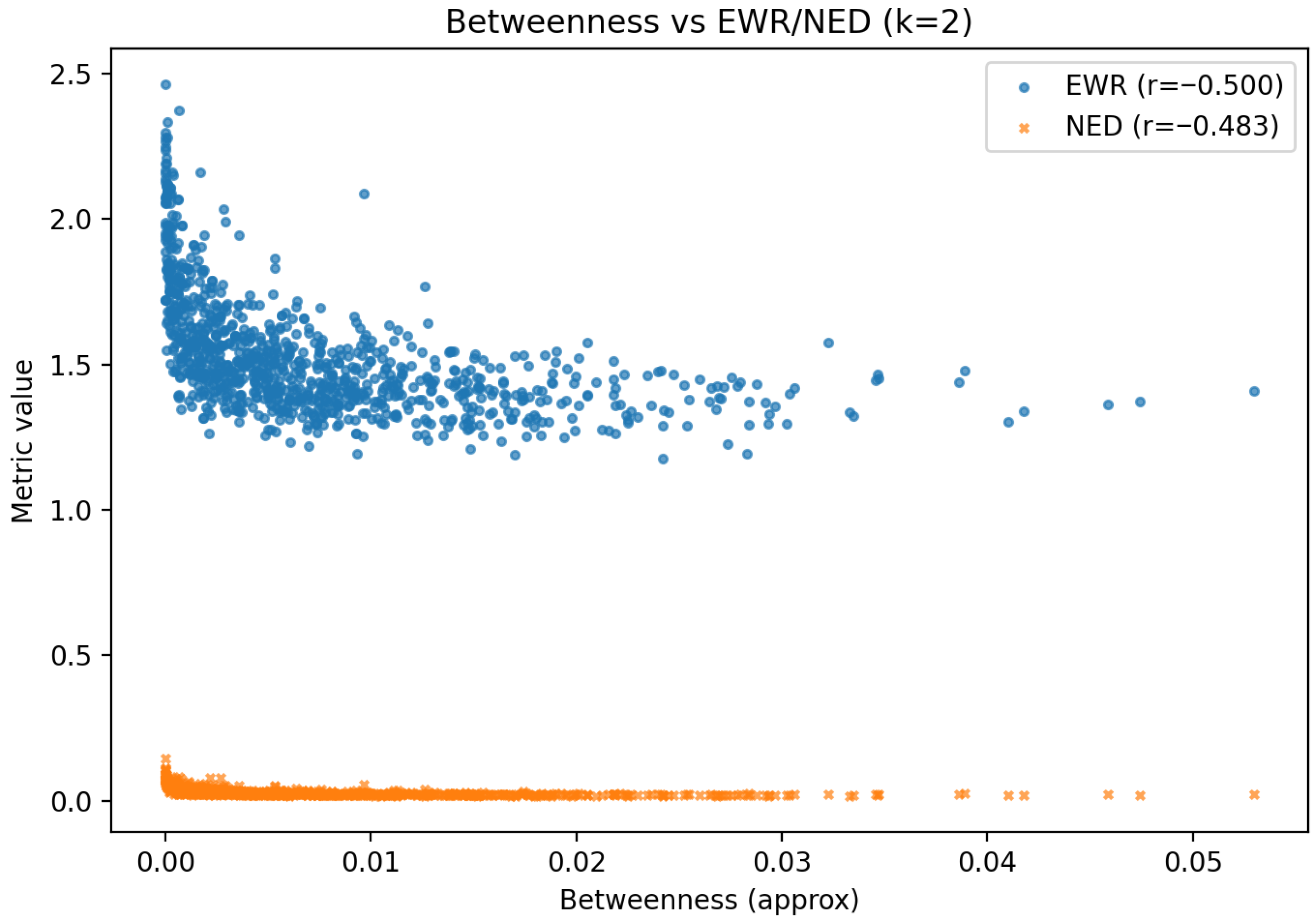
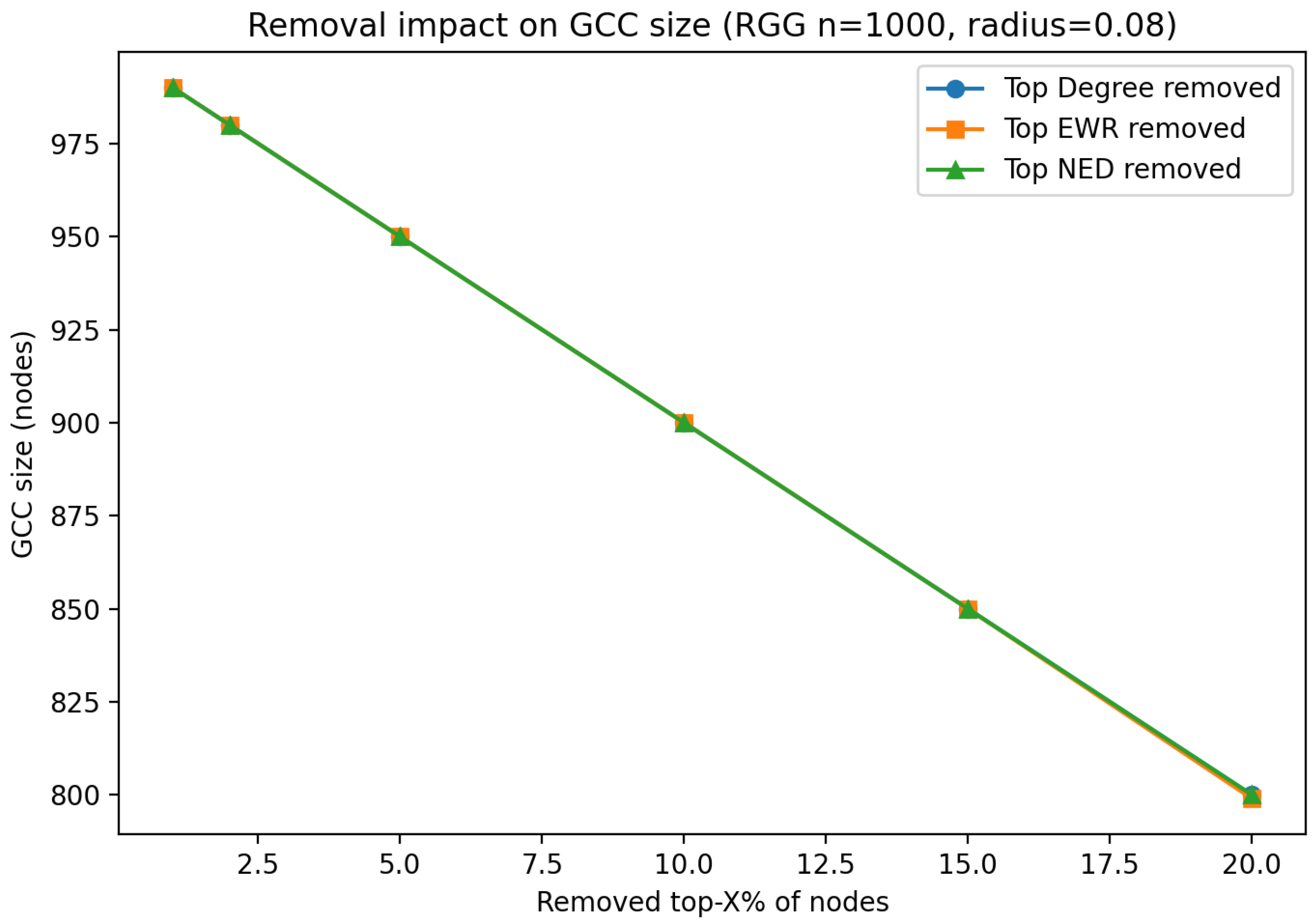


| Topology | EWR Distribution | NED Distribution | Degree Corr. (EWR/NED) | Betweenness Corr. (EWR/NED) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ER | Broad, unimodal | Broad, unimodal | / | / |
| BA | Right-skewed, hubs dominate | Right-skewed, hubs dominate | / | / |
| WS | Narrow, peaked | Narrow, peaked | / | / |
| RGG | Narrow, moderate spread | Narrow, low spread | / | / |
| Zephyr | Discrete peaks (0.6–0.9) | Near-zero cluster | / | / |
| Topology | Perturb. Stability (EWR/NED) | Removal Effect |
|---|---|---|
| ER | / | Metrics outperform degree slightly |
| BA | / | Metrics ≈ degree targeting |
| WS | / | Metrics ≈ degree targeting |
| RGG | / | Slight metric advantage over degree |
| Zephyr | / | Metrics ≈ degree targeting |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biró, C. Hybrid Entropy-Based Metrics for k-Hop Environment Analysis in Complex Networks. Mathematics 2025, 13, 2902. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13172902
Biró C. Hybrid Entropy-Based Metrics for k-Hop Environment Analysis in Complex Networks. Mathematics. 2025; 13(17):2902. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13172902
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiró, Csaba. 2025. "Hybrid Entropy-Based Metrics for k-Hop Environment Analysis in Complex Networks" Mathematics 13, no. 17: 2902. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13172902
APA StyleBiró, C. (2025). Hybrid Entropy-Based Metrics for k-Hop Environment Analysis in Complex Networks. Mathematics, 13(17), 2902. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13172902





