Fluorescence Detection of 4-Hydroxy-2,5-dimethyl-3(2H)-furanone Based on Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer and Competitive Host–Guest Recognition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
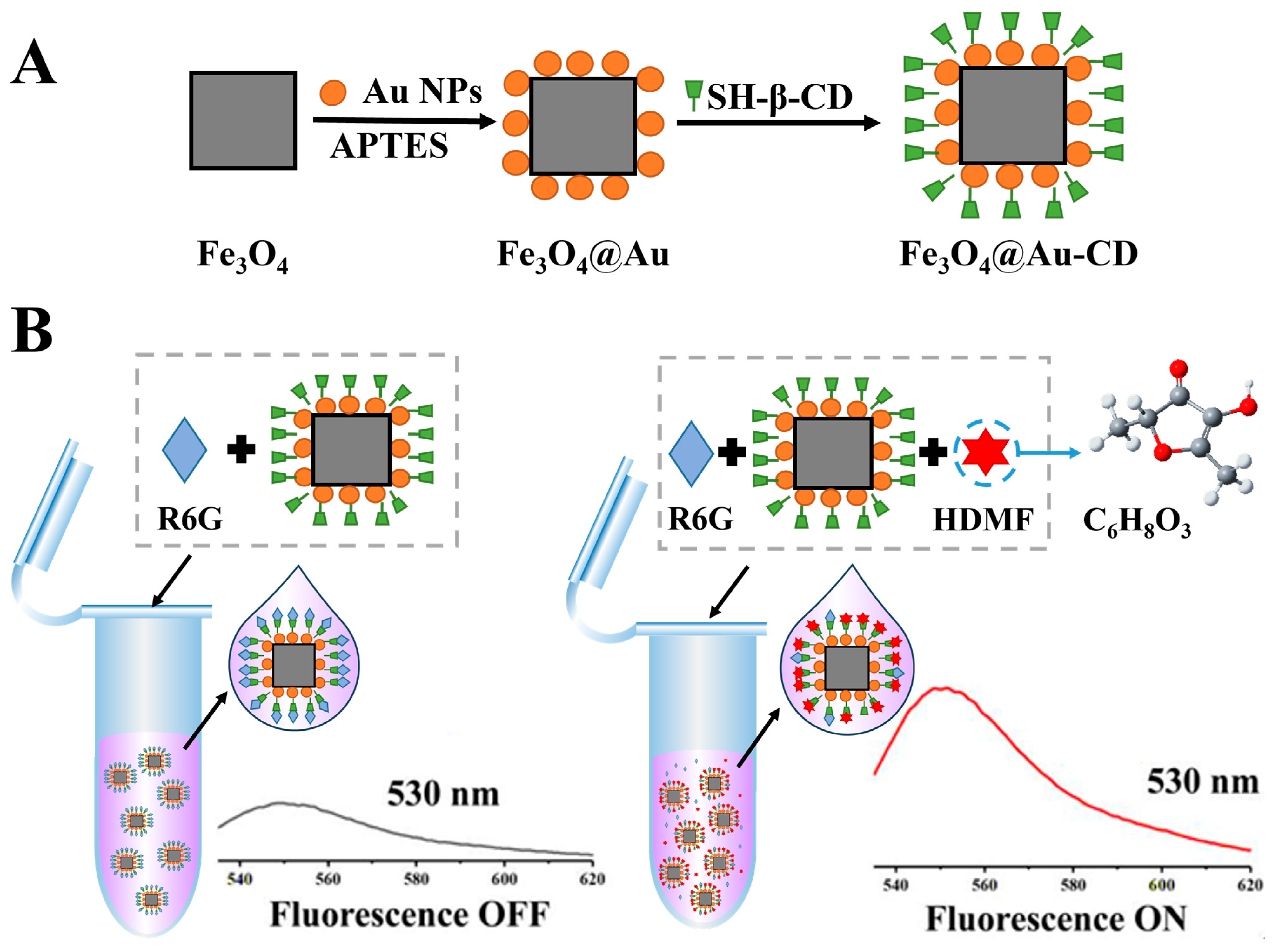
2.1. Preparation of Fe3O4@Au-CD
2.2. Fluorescence Detection of HDMF
2.3. HDMF Detection in Real Samples
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Fe3O4@Au-CD
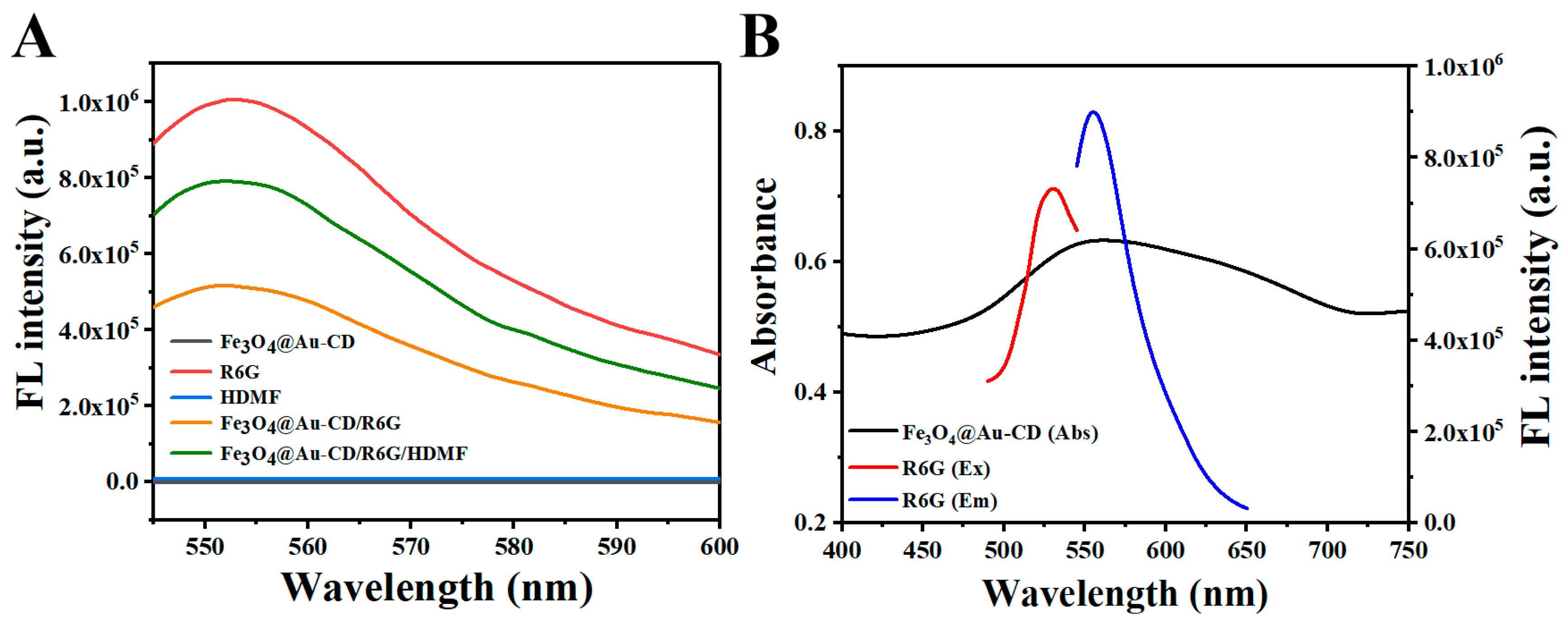
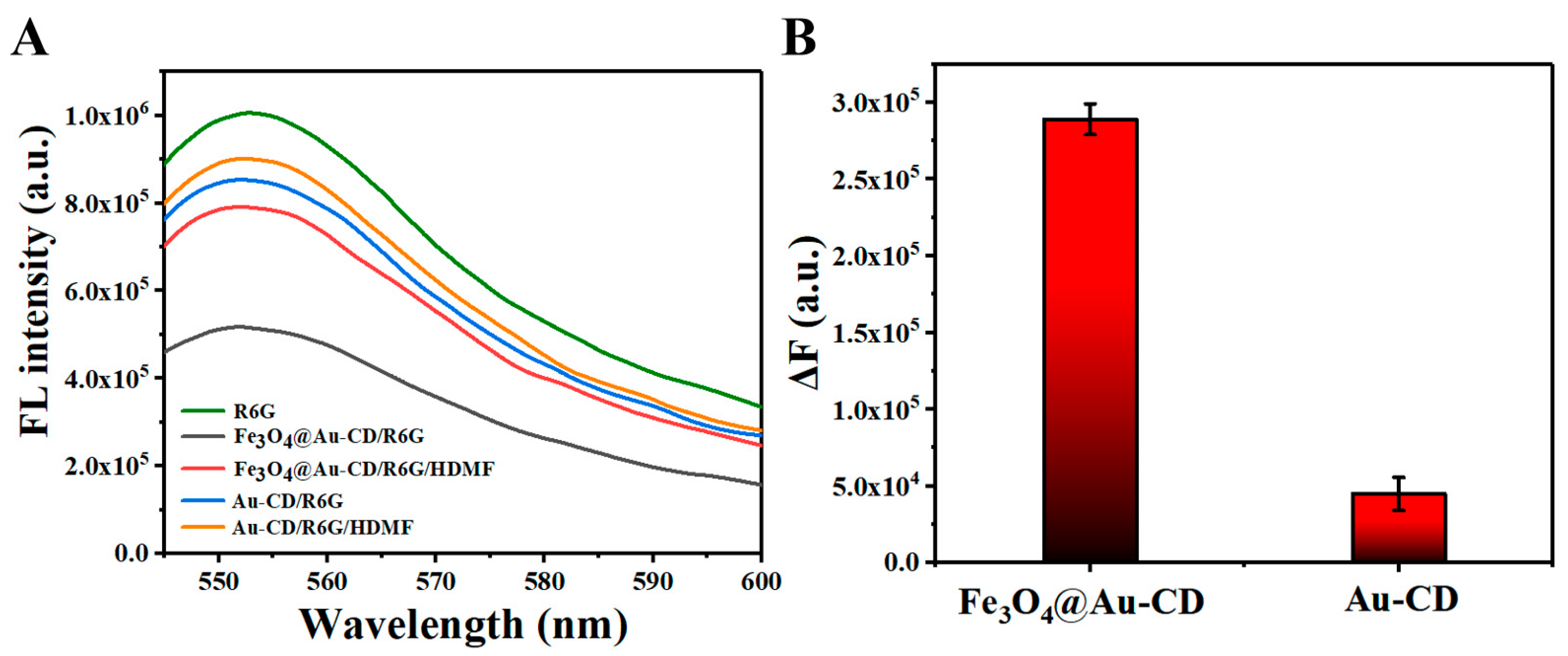
3.2. Feasibility of Detecting HDMF
3.3. Optimization of HDMF Detection
3.4. HDMF Detection
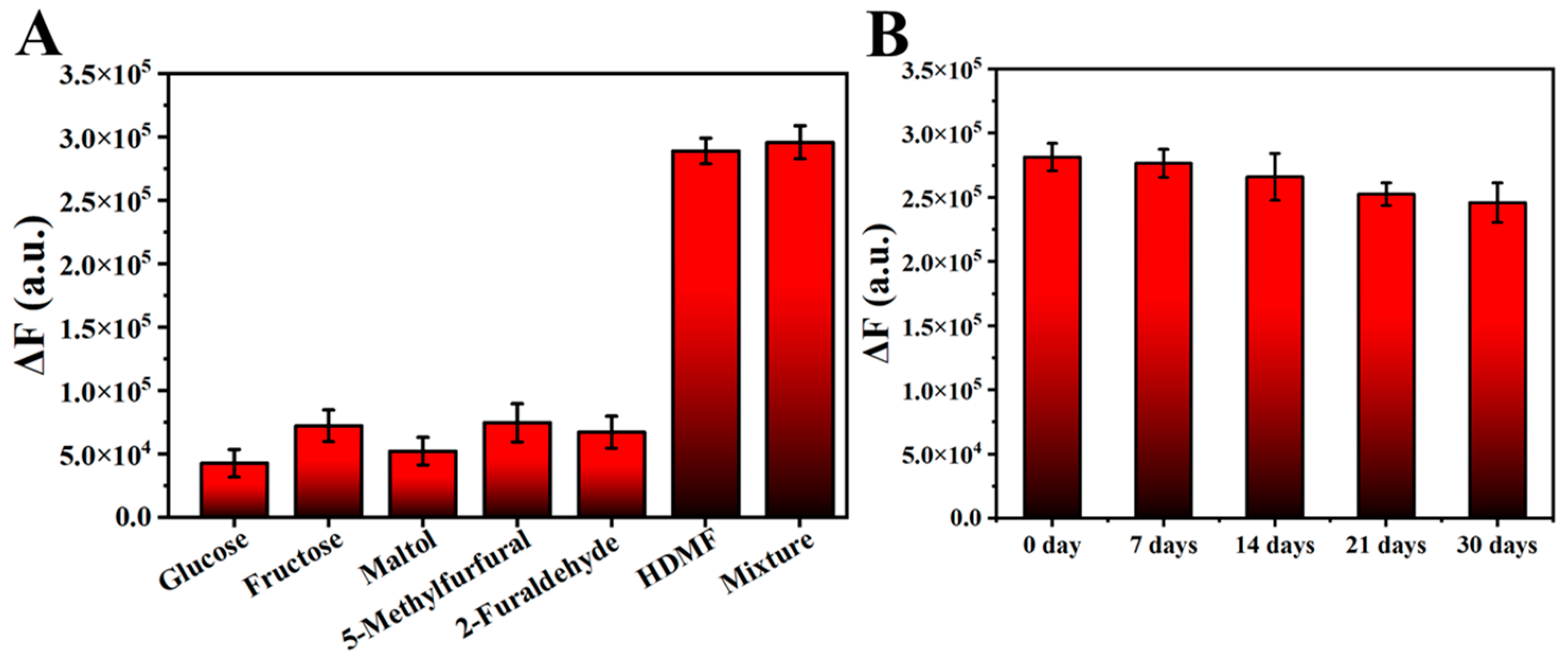
3.5. Selectivity and Stability of the HDMF Detection
3.6. Application of the HDMF Detection in Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haynes, A.; Winnall, W.R.; Brennan, E.; Dunstone, K.; Benowitz, N.L.; Ashley, D.L.; Samet, J.M.; Hatsukami, D.K.; Wakefield, M.A. Tobacco constituents, flavorants, and paper permeability of factory-made and roll-your-own cigarettes on the Australian market. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2024, 26, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talhout, R.; Opperhuizen, A.; van Amsterdam, J.G.C. Sugars as tobacco ingredient: Effects on mainstream smoke composition. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2006, 44, 1789–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Cardenas, R.B.; Watson, C. An isotope dilution ultra high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous determination of sugars and humectants in tobacco products. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1514, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Liang, L.; Cai, Y.; Mou, S. Determination of sugars and alditols in tobacco with high performance anion-exchange chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2007, 30, 2160–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.; de Oliveira, R.B.; dos Santos, G.L.A.A.; de Oliveira, K.M.; Reis, A.S.; Furlanetto, R.H.; Júnior, L.A.Y.B.; Coelho, F.S.; Nanniet, M.R. Rapid quantification of alkaloids, sugar and yield of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) varieties by using Vis–NIR–SWIR spectroradiometry. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 274, 121082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.R.; Bishop, L.J. The pyrolysis of tobacco ingredients. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2004, 71, 223–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Pan, S.; Liu, X.; Tan, M.; Zheng, X.; Du, W.; Wu, M.; Song, Y. Profiling the major aroma-active compounds of microwave-dried jujube slices through molecular sensory science approaches. Foods 2023, 12, 3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Guo, X.; Gao, T.; Zhang, N.; Wan, X.; Schwab, W.; Song, C. UGT74AF3 enzymes specifically catalyze the glucosylation of 4-hydroxy-2,5-dimethylfuran-3(2H)-one, an important volatile compound in Camellia sinensis. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwab, W. Natural 4-hydroxy-2,5-dimethyl-3(2H)-furanone (Furaneol®). Molecules 2013, 18, 6936–6951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rögner, N.S.; Mall, V.; Steinhaus, M. Impact of malt extract addition on odorants in wheat bread crust and crumb. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 13586–13595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Y. Volatile aroma compounds in wines from Chinese wild/hybrid species. J. Food Biochem. 2018, 43, e12684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Xie, Z.; Huang, M.; Tong, X.; Hou, S.; Tin, H.; Zhao, M. Decoding temperature-driven microbial community changes and flavor regulation mechanism during winter fermentation of soy sauce. Food Res. Int. 2024, 117, 113756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, V.; Aznar, M.; López, R.; Cacho, C. Quantitative gas chromatography–olfactometry carried out at different dilutions of an extract. Key differences in the odor profiles of four high-quality Spanish aged red wines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 4818–4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Guo, M.; Meng, Q.; Song, H. Characterization of key odor-active compounds in high quality high-salt liquid-state soy sauces. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 117, 105148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Hernandez, M.; Zhu, H.; Shao, S. An efficient method for the determination of furan derivatives in apple cider and wine by solid phase extraction and high performance liquid chromatography—Diode array detector. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1284, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Cadwallader, K.R. Identification of characterizing aroma components of roasted chicory “coffee” brews. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13848–13859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Zeng, D.; Wang, J.; Zhao, M.; Feng, Y. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) for the determination of soy sauce aroma compounds. Food Control 2023, 152, 109838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dein, M.; Moore, A.; Ricketts, C.; Huynh, C.; Munafo, J.P., Jr. Characterization of odorants in chardonnay marc skins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 12262–12269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prata, R.; Petrarca, M.H.; Filho, J.T.; Godoy, H.T. Simultaneous determination of furfural, 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and 4-hydroxy-2,5-dimethyl-3(2H)-furanone in baby foods available in the Brazilian market. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 99, 103874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Tang, Z.; Xie, X.; Chen, Q.; Cao, H.; Yu, X.; Liu, X.; Hammock, B.D. Fluonanobody-based nanosensor via fluorescence resonance energy transfer for ultrasensitive detection of ochratoxin A. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 422, 126838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Cai, J.; Liu, F.; Yang, H.; Lin, Y.; Li, S.; Huang, X.; Lin, L. Construction of a turn off-on fluorescent nanosensor for cholesterol based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer and competitive host-guest recognition. Talanta 2019, 201, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Atwater, M.; Wang, J.; Huo, Q. Extinction coefficient of gold nanoparticles with different sizes and different capping ligands. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2007, 58, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, H.; Lv, M.; Liu, X.; Chen, G.; Zhang, N.; Cao, Y.; Wang, H.; Ma, R.; Qiu, G. Activating hematite nanoplates via partial reduction for electrocatalytic oxygen reduction reaction. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 11841–11849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wu, C.; Liu, H.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; Ai, H.; Gao, J. Surface and interfacial engineering of iron oxide nanoplates for highly efficient magnetic resonance angiography. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3012–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beiranvand, M.; Farhadi, S.; Mohammadi-Gholami, A. Adsorptive removal of tetracycline and ciprofloxacin drugs from water by using a magnetic rod-like hydroxyapatite and MIL-101(Fe) metal–organic framework nanocomposite. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 34438–34453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, S.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, W.; Ren, S.; Liu, B.; Gao, Z. Dual-responsive amplification strategy for ultrasensitive detection of norovirus in food samples: Combining magnetic relaxation switching and fluorescence assay. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 396, 134573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, G.; Wang, Z.; Ma, J.; Jia, Q. Fe3O4@Au@cyclodextrin-molecularly imprinted polymers labeled with SERS nanotags for ultrasensitive detection of transferrin. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 361, 131669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Rong, S.; Cen, Y.; Xu, G.; Xie, Z.; Yang, J.; Sun, Y.; Hu, Q.; Wei, F. A facile fluorescent sensor based on carbon dots and Fe3O4 nanoplates for the detection of hyaluronidase activity. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 346, 130434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Gong, C.; Chu, J.; Wang, X.; Yan, C.; Qian, S.; Wang, Y.; Rao, G.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; et al. Ultrabroadband photodetectors up to 10.6 µm based on 2D Fe3O4 Nanosheets. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2002237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gao, L.; Wang, J.; Dai, H. Dual-signal amplification sensing platform based on competitive host-guest cycling recognition process for ultrasensitive detection of thyroglobulin. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 405, 135036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, C.B.; Kwant, R.L.; MacDonald, J.I.; Rao, M.; Francis, M.B. Capture and recycling of sortase a through site-specific labeling with lithocholic acid. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 8585–8589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X.; Ma, H.; Wei, Y. Fluorescence detection of amantadine based on competitive β-Cyclodextrin host-guest inclusion process. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 681, 132801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Shen, H.; Huo, B.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Z. A novel bionic magnetic SERS aptasensor for the ultrasensitive detection of deoxynivalenol based on “dual antennae” nano-silver. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 211, 114383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, G.S.; Shin, J.R.; Hur, J.U.; Oh, A.H.; Kim, B.; Jung, Y.; Choi, S. Fabrication of core-shell structured Fe3O4@Au nanoparticle via self-assembly method based on positively charged surface silylation/polymerization. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 798, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Goswami, N.; Yao, Q.; Chen, T.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, D.; Lu, J.; Xie, J. Cyclodextrin–gold nanocluster decorated TiO2 enhances photocatalytic decomposition of organic pollutants. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 1102–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Gan, N.; Li, T.; Cao, Y.; Hu, F.; Chen, Y. An ultrasensitive fluorescence aptasensor for chloramphenicol based on FRET between quantum dots as donor and the magnetic SiO2@Au NPs probe as acceptor with exonuclease-assisted target recycling. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 222, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Hou, Y.; Sun, S. Magnetic core/shell Fe3O4/Au and Fe3O4/Au/Ag nanoparticles with tunable plasmonic properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 8698–8699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Zhang, X.; Qi, Y.; Ding, S.; Cao, S.; Zhu, A.; Shi, G. Pb2+-modified graphene quantum dots as a fluorescent probe for biological aminothiols mediated by an inner filter effect. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 235, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Xie, Z.; Qu, D.; Li, D.; Du, P.; Jing, X.; Sun, Z. On-off-on fluorescent carbon dot nanosensor for recognition of chromium(VI) and ascorbic acid based on the inner filter effect. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 13242–13247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Huang, P.; Wei, G.; Cao, Y.; Wu, F. Visualization and quantification of Hg2+ based on anti-aggregation of label-free gold nanoparticles in the presence of 2-mercaptobenzothiazole. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 233, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Han, L. Displaying of acetylcholinesterase mutants on surface of yeast for ultra-trace fluorescence detection of organophosphate pesticides with gold nanoclusters. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 148, 111825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douaki, A.; Abera, B.D.; Cantarella, G.; Shkodra, B.; Mushtaq, A.; Ibba, P.; Inam, A.K.M.S.; Petti, L.; Lugli, P. Flexible Screen Printed Aptasensor for Rapid Detection of Furaneol: A Comparison of CNTs and AgNPs Effect on Aptasensor Performance. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Samples | Found (M) | Added (M) | Found (M) | Recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beverage | Not found | 5 × 10−7 | 4.93 × 10−7 | 98.7 | 6.6 |
| 5 × 10−6 | 5.53 × 10−6 | 110.6 | 5.6 | ||
| 5 × 10−5 | 4.56 × 10−5 | 91.2 | 5.5 | ||
| Cigarette | Not found | 5 × 10−7 | 4.96 × 10−7 | 99.1 | 7.0 |
| 5 × 10−6 | 4.69 × 10−6 | 93.9 | 3.2 | ||
| 5 × 10−5 | 5.23 × 10−5 | 104.6 | 7.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, P.; Sun, S.; Wei, W. Fluorescence Detection of 4-Hydroxy-2,5-dimethyl-3(2H)-furanone Based on Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer and Competitive Host–Guest Recognition. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13030110
Zhang X, Wang C, Zhuang Y, Wang D, Li P, Sun S, Wei W. Fluorescence Detection of 4-Hydroxy-2,5-dimethyl-3(2H)-furanone Based on Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer and Competitive Host–Guest Recognition. Chemosensors. 2025; 13(3):110. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13030110
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaowan, Chenchen Wang, Yurong Zhuang, Dingzhong Wang, Peng Li, Shihao Sun, and Wei Wei. 2025. "Fluorescence Detection of 4-Hydroxy-2,5-dimethyl-3(2H)-furanone Based on Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer and Competitive Host–Guest Recognition" Chemosensors 13, no. 3: 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13030110
APA StyleZhang, X., Wang, C., Zhuang, Y., Wang, D., Li, P., Sun, S., & Wei, W. (2025). Fluorescence Detection of 4-Hydroxy-2,5-dimethyl-3(2H)-furanone Based on Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer and Competitive Host–Guest Recognition. Chemosensors, 13(3), 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13030110





