Abstract
Background/Objectives: A bidirectional association between inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and periodontitis has been observed, yet their causal relationship remains unclear. This study aimed to investigate the potential causal links between these two inflammatory conditions through comprehensive genetic and molecular analyses. Methods: We conducted a bidirectional Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis integrated with bioinformatics approaches. The causal relationships were primarily evaluated using inverse variance weighting (IVW), complemented by multiple sensitivity analyses to assess the robustness of the findings. Additionally, we performed differential gene expression analysis using RNA sequencing data to identify co-expressed genes and shared inflammatory mediators between IBD and periodontitis, followed by pathway enrichment analysis. Results: Bidirectional MR analysis revealed significant causal associations between IBD and periodontitis (p-value < 0.05). Sensitivity analyses demonstrated the consistency of these findings, with no evidence of significant heterogeneity or horizontal pleiotropy (p-value > 0.05). Integrated bioinformatics analysis identified key immune regulators, particularly interleukin 1 beta (IL1B) and C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4), and inflammatory signaling pathways, including tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) and interleukin 17 (IL17), as potential molecular mechanisms underlying the bidirectional relationship between these conditions. Conclusions: Our findings provide genetic evidence supporting a bidirectional causal relationship between IBD and periodontitis. Transcriptomic analysis revealed shared pathological mechanisms and identified crucial immune regulatory factors common to both diseases. These insights enhance our understanding of the molecular interplay between IBD and periodontitis, potentially informing new therapeutic strategies for both conditions.
1. Introduction
Periodontal disease is a highly prevalent chronic inflammatory disorder of the oral cavity, with approximately 1.1 billion prevalent cases of severe periodontitis globally in 2019, and has been implicated in numerous systemic pathologies [1,2]. The pathogenesis of this condition is fundamentally linked to perturbations in the oral microbiome composition, wherein pathogenic organisms trigger host immune responses, culminating in tissue inflammation [3]. During this pathological process, a complex network of inflammatory mediators, including cytokines, chemokines, and adenylate cyclase, orchestrates the inflammatory cascade. These molecular mediators not only regulate local inflammatory responses but can also exert systemic effects through hematogenous dissemination. For example, factors like tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) and interleukin 1 beta (IL1B) not only promote the recruitment and activation of inflammatory cells but may also trigger immune responses in distant tissues, potentially underlying the connection between periodontal disease and systemic illnesses like cardiovascular diseases [4], diabetes [5], and other diseases related to systemic immunity [6]. Moreover, periodontal pathogens and their associated toxins trigger a cascade of inflammatory responses, engaging both innate and adaptive immune mechanisms [7,8]. The resultant inflammatory mediators and immune cells can disseminate systemically through the circulation, extending beyond the confines of the oral cavity to influence distant organ systems [9]. This systemic inflammatory burden, initiated by periodontal disease, may serve as a mechanistic link to various systemic pathologies through sustained immune dysregulation and chronic inflammation.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), including Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), is another chronic inflammatory condition that impacts gastrointestinal health worldwide, with a global age-standardized prevalence rate of 84.3 per 100,000 population in 2017 [10,11]. These disorders are characterized by persistent inflammation of the intestinal mucosa, resulting in significant gastrointestinal dysfunction. Analogous to periodontal disease, the pathogenesis of IBD involves aberrant immune system activation [12], with pro-inflammatory mediators, including TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, orchestrating the immune microenvironment and driving disease progression [13,14,15]. Furthermore, alterations in gut microbiota-mediated metabolism may significantly influence IBD pathophysiology [16,17], potentially contributing to malignant transformation [18]. Given the shared features of dysregulated inflammatory and immune responses in both periodontal disease and IBD, we have reason to believe that there are underlying pathophysiological connections between these conditions [19,20,21,22]. Beyond the role of inflammatory mediators [23], periodontal pathogens and their associated toxins may directly modulate intestinal inflammation through systemic circulation [24,25]. Moreover, periodontal disease-induced alterations in the oral microbiome may precipitate changes in gut microbiota composition and functionality [26], representing potential mechanistic links between these disorders. Although these conditions differ in their anatomical localization and clinical manifestations, the similarities in their inflammatory and immune response mechanisms provide a theoretical framework for their potential bidirectional interaction. Multiple meta-analyses based on observational studies have confirmed a significant association between periodontitis and IBD [27,28,29,30,31]. However, several recent Mendelian randomization (MR) analyses have reported inconsistent findings [32,33,34,35], making the precise causal relationship between these diseases still elusive. Therefore, further research is needed to clarify the underlying mechanisms linking periodontal disease and IBD, which remains crucial for understanding the precise causal relationship between these conditions.
MR analysis uses genetic variants as instrumental variables (IVs) to reduce the confounding effects common in observational studies, thereby facilitating more robust causal inferences [36,37]. We employed a dual approach to elucidate the relationship between IBD and periodontitis. First, we performed a bidirectional MR analysis to assess potential causal associations based on genetic variation. Second, we conducted transcriptomic analyses of RNA sequencing data from both conditions to identify shared differentially expressed genes (DEGs). Through systematic analysis of gene interaction networks and biological pathway enrichment, we unveiled potential molecular mechanisms underlying the relationship between these conditions. This integrative approach provides novel insights into the molecular interplay between IBD and periodontitis.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Source
This study incorporated parallel MR and bioinformatics analyses. The MR analysis was conducted in accordance with the Strengthening the Reporting of Mendelian Randomization Studies (STROBE-MR) guidelines [38]. For genome-wide association study (GWAS) data acquisition, we downloaded IBD data [39] (GWAS number: ieu-a-31, Ncase/Ncontrol: 12,882/21,770) and its major subtypes, CD (GWAS number: ieu-a-30, Ncase/Ncontrol: 5956/14,927) and UC (GWAS number: ieu-a-32, Ncase/Ncontrol: 6968/20,464), from the OpenGWAS database (https://gwas.mrcieu.ac.uk/, accessed on 15 October 2024). Chronic periodontitis data (GWAS number: finn-b-K11_PERIODON_CHRON, Ncase/Ncontrol: 3046/195,395) were obtained from the Finngen database (https://www.finngen.fi/, accessed on 15 October 2024) [40]. All datasets comprised large-scale cohorts from distinct geographical regions within the same ethnic population, minimizing potential sample overlap bias.
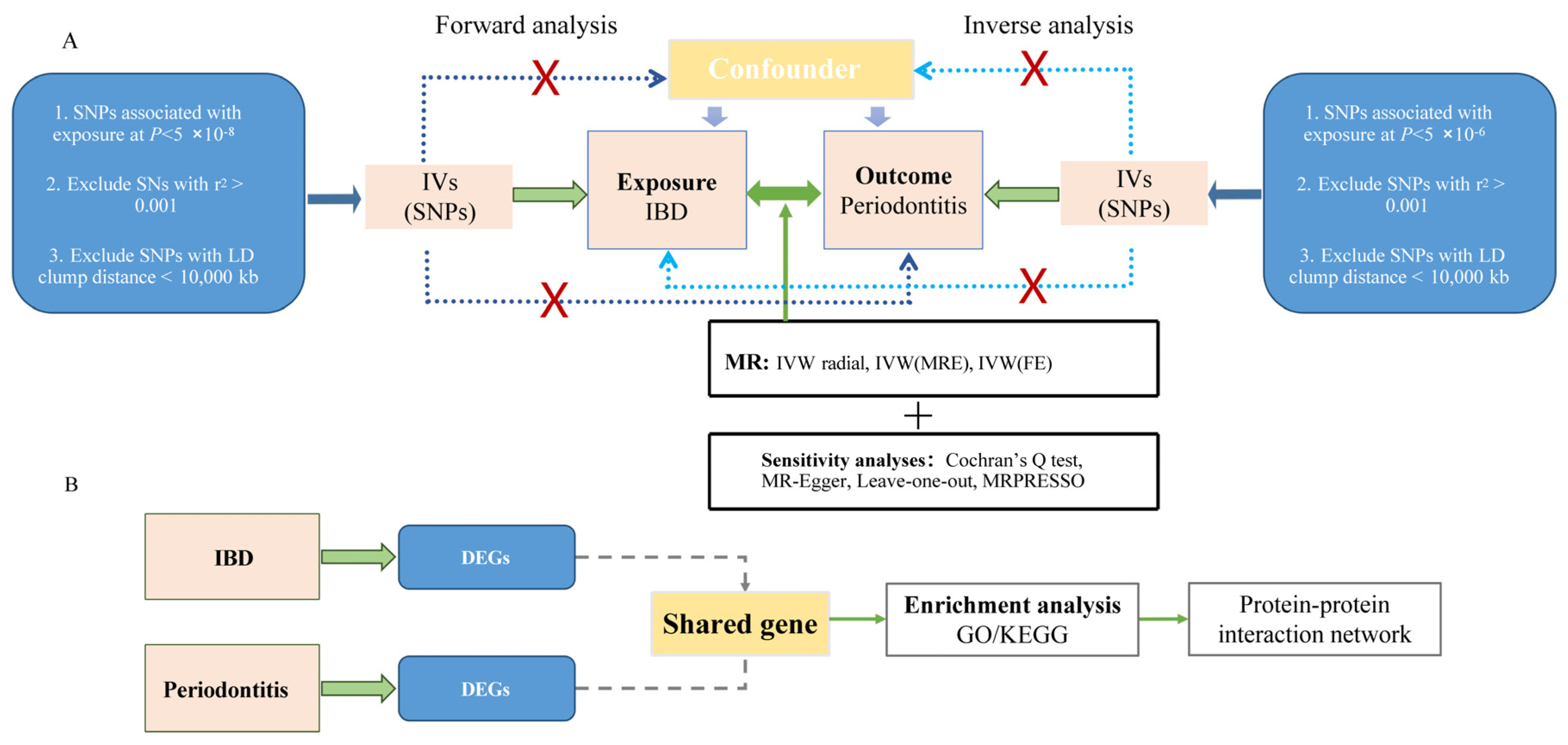
We performed bidirectional MR analysis. The forward analysis evaluated IBD, CD, and UC as exposure variables with chronic periodontitis as the outcome, while the reverse analysis assessed chronic periodontitis as the exposure with IBD, CD, and UC as outcomes. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with exposure variables were selected as IVs, adhering to three fundamental MR assumptions [36,41]: (1) robust association between IVs and exposure variables; (2) independence of IVs from potential confounding factors affecting both exposure and outcomes; and (3) exclusive influence of IVs on outcomes through exposure pathways. As this study utilized publicly available GWAS summary statistics, additional ethical approval and informed consent were not required. Figure 1 shows the analytical workflow, including GWAS details, sample data, SNP metrics, IV selection, and IV counts.
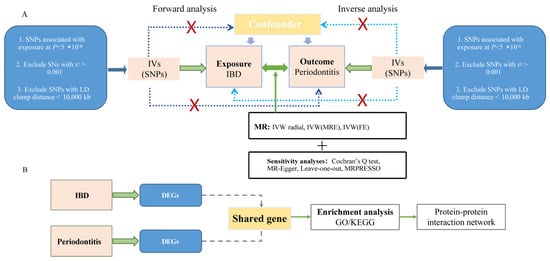
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of the study design and analytical workflow. (A) Pipeline for Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis demonstrating the systematic evaluation of bidirectional causal relationships between inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and chronic periodontitis. (B) Bioinformatics analysis framework illustrating the integrated transcriptomic and enrichment analyses. LD, linkage disequilibrium; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; IVW, inverse-variance weighted; MRE, model of random effect; FE, model of fixed effect; DEGs, differentially expressed genes; KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; GO, gene ontology.
The bioinformatics analysis encompassed systematic investigation of biological processes and molecular regulatory pathways associated with shared differential genes between chronic periodontitis and IBD. This analysis comprised differential gene expression analysis followed by biological process and pathway enrichment analyses. This integrative approach elucidated the immunological mechanisms linking IBD and chronic periodontitis while identifying molecular interactions and pathway convergence points.
2.2. Data Cleaning for MR Analysis
The data preprocessing pipeline comprised several sequential steps: Initially, SNPs associated with exposure variables were extracted using the “TwoSampleMR” R package (version 0.6.6) [42,43]. Disease-specific p-value thresholds were implemented, 5 × 10−8 for IBD-related analyses and 5 × 10−6 for periodontitis, accounting for variations in sample size and SNP availability. Subsequently, we eliminated SNPs exhibiting linkage disequilibrium (LD) using stringent parameters (r2 = 0.001, window size = 10,000 kb) [44,45]. Instrument strength was assessed through F-statistics, calculated as (Beta2/SE2) [46], with a minimum threshold of 10 [47,48]. To ensure IV validity, we utilized the LDLink database (https://ldlink.nih.gov/?tab=ldtrait, accessed on 15 October 2024) [49] to identify and exclude potential pleiotropic variants associated with outcome variables in both analytical directions. This systematic approach ensured adherence to core MR assumptions [50]. Identical preprocessing protocols were applied in both forward and reverse analyses to maintain methodological consistency and result comparability.
2.3. MR Analysis
The primary MR analysis was conducted using the inverse variance-weighted (IVW)–radial method [51,52], complemented by multiple analytical approaches including IVW with the model of random effects (MRE), IVW with the model of fixed effects (FE), MR-Egger, and weighted median (WM) estimators. To validate the robustness of our findings, we implemented comprehensive sensitivity analyses. Specifically, MR-Egger regression was employed to detect and adjust for potential pleiotropy through intercept testing [53], while the MR-PRESSO method was utilized for outlier detection [54,55]. We conducted leave-one-out analyses to evaluate the influence of individual SNPs on the overall causal estimates [45,56]. Heterogeneity among genetic instruments was assessed using Cochrane’s Q test [37]. All analyses were performed using two-sided tests in R software (version 4.3.3) with the “TwoSampleMR” (version 0.6.6) and “MR-PRESSO” packages (version 1.0). Statistical significance was defined as p-value < 0.05 [56].
2.4. Obtaining RNA Sequencing Data and Identifying Differential Expressed Genes (DEGs)
The GEO database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gds, accessed on 20 September 2024) was used for retrieving the RNA sequencing data with the data type set to “Expression profiling by array”, the keywords set to “inflammatory bowel disease” and “periodontitis”, and the species set to “Homo sapiens” [57]. Finally, sequencing data from intestinal mucosa of IBD patients (GSE59071 [58]) and periodontitis patients (GSE16434 [59]) were included in the analysis. Then, using the “limma” R package(version 3.54.2) [60,61] independently, we compared each of these disease-related transcriptomic datasets to their healthy control groups in order to find DEGs. A volcano plot and heatmap will be presented as a display of these differential analyses [62]. The criteria for selecting DEGs were logFC > 1 and p-value < 0.01 [63].
2.5. Enrichment Analysis and Interaction Network Construction of Co-Expressed DEGs
A visual Venn diagram was drawn and the co-expressed DEGs were extracted for enrichment analysis and interaction network construction. We performed Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analyses utilizing the “clusterProfiler” package (version 4.6.2) [64]. The GO analysis was conducted across three categories: biological process (BP), Cellular Component (CC), and Molecular Function (MF) [65]. Subsequently, we applied a significance threshold of adjusted p-value < 0.05 to filter the results of both GO and KEGG analyses [66]. The visualization of the outcomes included the presentation of the top 5 GO terms with the most significant p-values and the top 10 pathways in the KEGG pathway enrichment analysis with the most significant p-values. Finally, the “STRING” database (https://string-db.org/, accessed on 25 October 2024) was utilized to conduct protein–protein interaction (PPI) analysis on the identified co-expressed DEGs [67]. Using “Cytoscape” software (version 3.10.2), we extracted signal strengths and interaction patterns among these co-expressed DEGs by focusing on “Degree” [68].
3. Results
3.1. The Casual Relationship Between IBD and Chronic Periodontitis
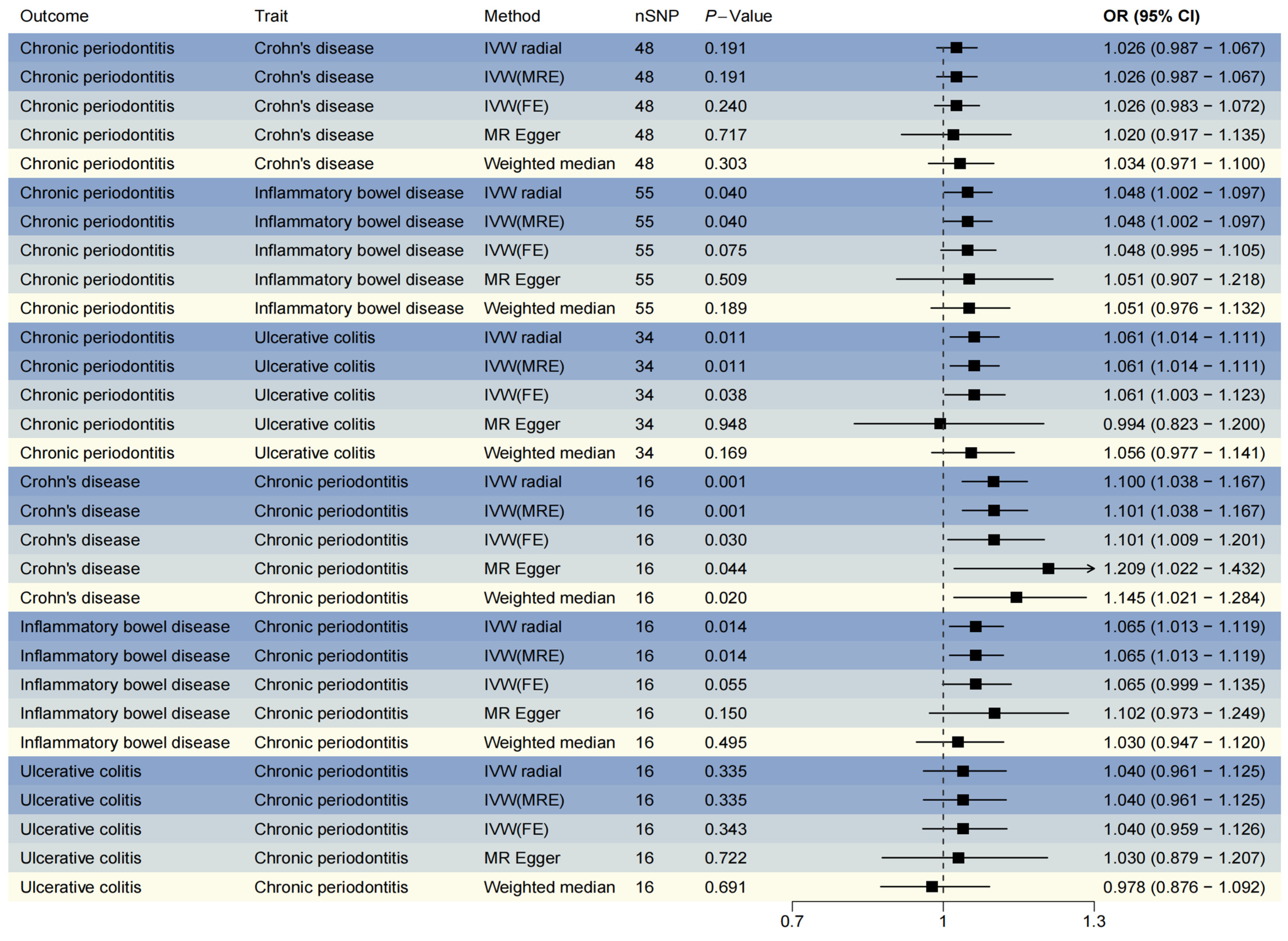
In the forward analysis, we identified 55, 48, and 34 IVs associated with IBD, CD, and UC, respectively (Table S1). The reverse analysis yielded 48 IVs associated with chronic periodontitis (Table S1). Following confounder elimination and outcome matching, all identified IVs were incorporated into the bidirectional MR analyses (Table S2). The bidirectional MR analyses revealed significant causal associations through both IVW–radial and IVW-MRE methods between IBD and chronic periodontitis, particularly for UC (Figure 2, OR > 1, PIVW-radial < 0.05). However, no significant causal relationship was detected between CD and chronic periodontitis in the forward analysis (Figure 2, OR > 1, PIVW-radial > 0.05). In the reverse analysis, all five methods (IVW–radial, IVW-MRE, IVW-FE, MR-Egger, and WM) consistently demonstrated a significant positive causal effect of chronic periodontitis on CD (Figure 2, OR > 1, p-value < 0.05). While IVW–radial and IVW-MRE methods indicated a significant causal relationship between chronic periodontitis and IBD (Figure 2, OR > 1, PIVW-radial < 0.05), no significant association was observed between chronic periodontitis and UC (Figure 2, OR > 1, PIVW-radial > 0.05).
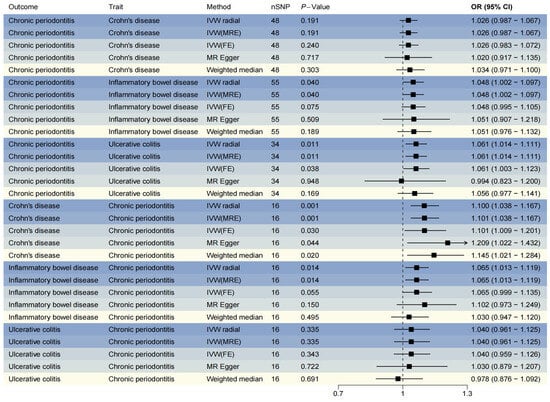
Figure 2.
Forest plot for Mendelian randomization (MR) results. IVW, inverse variance-weighted (IVW); MRE, model of random effects; FE, model of fixed effects; nSNP, number of single nucleotide polymorphism; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval. The gradient blue hues symbolize the diverse magnetic resonance (MR) methodologies employed across various analytical dimensions.
3.2. Sensitivity Analysis
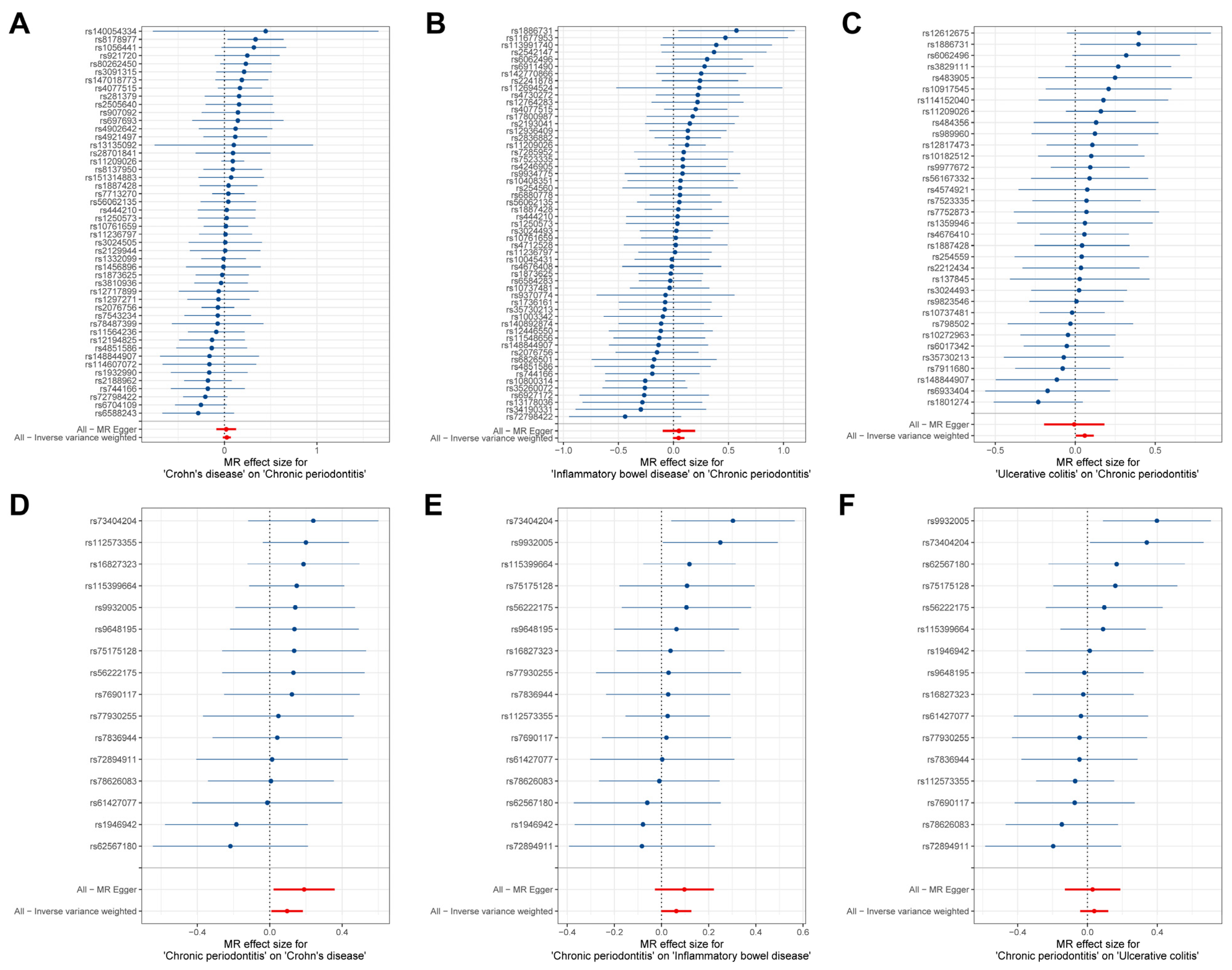
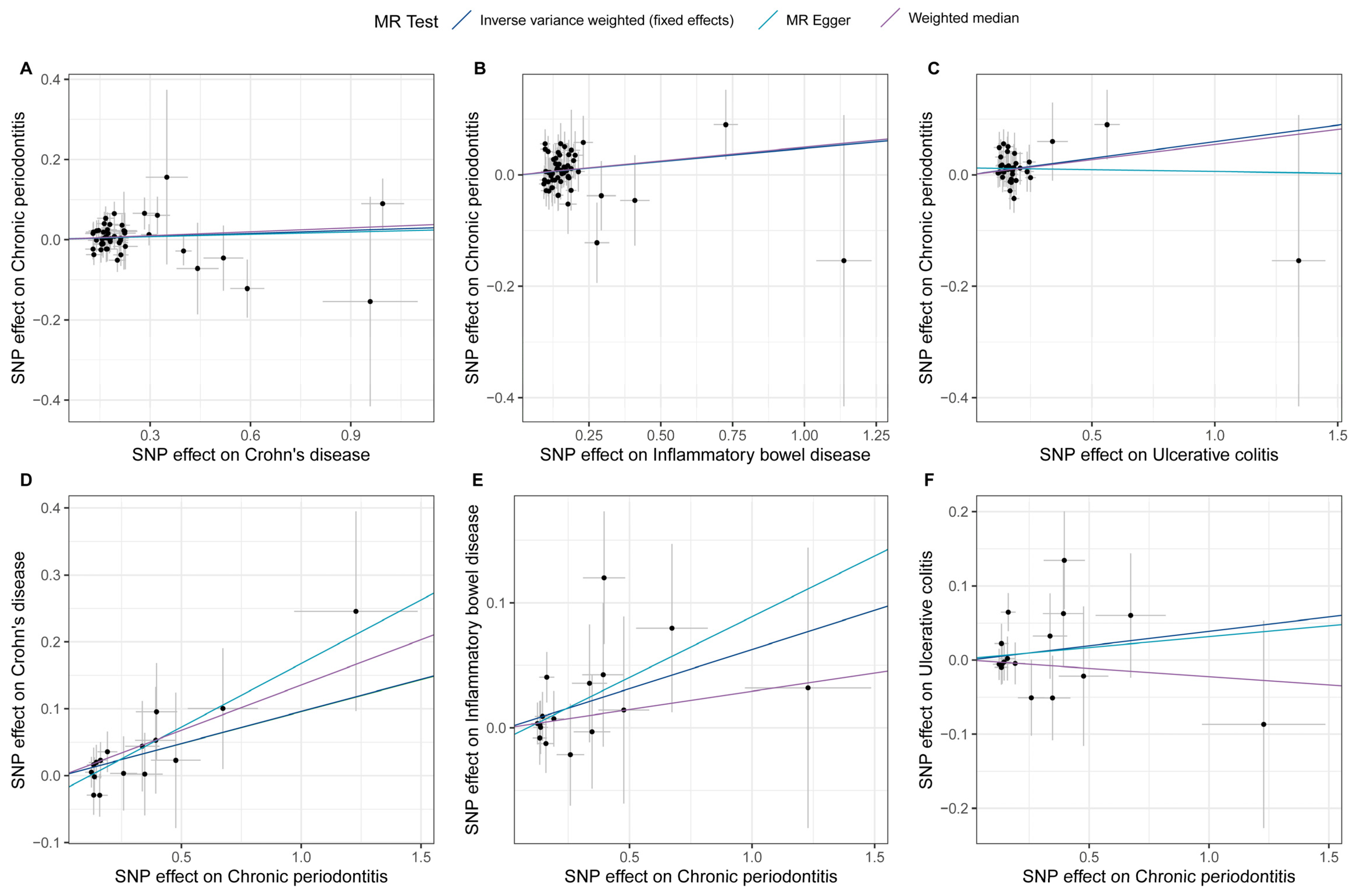
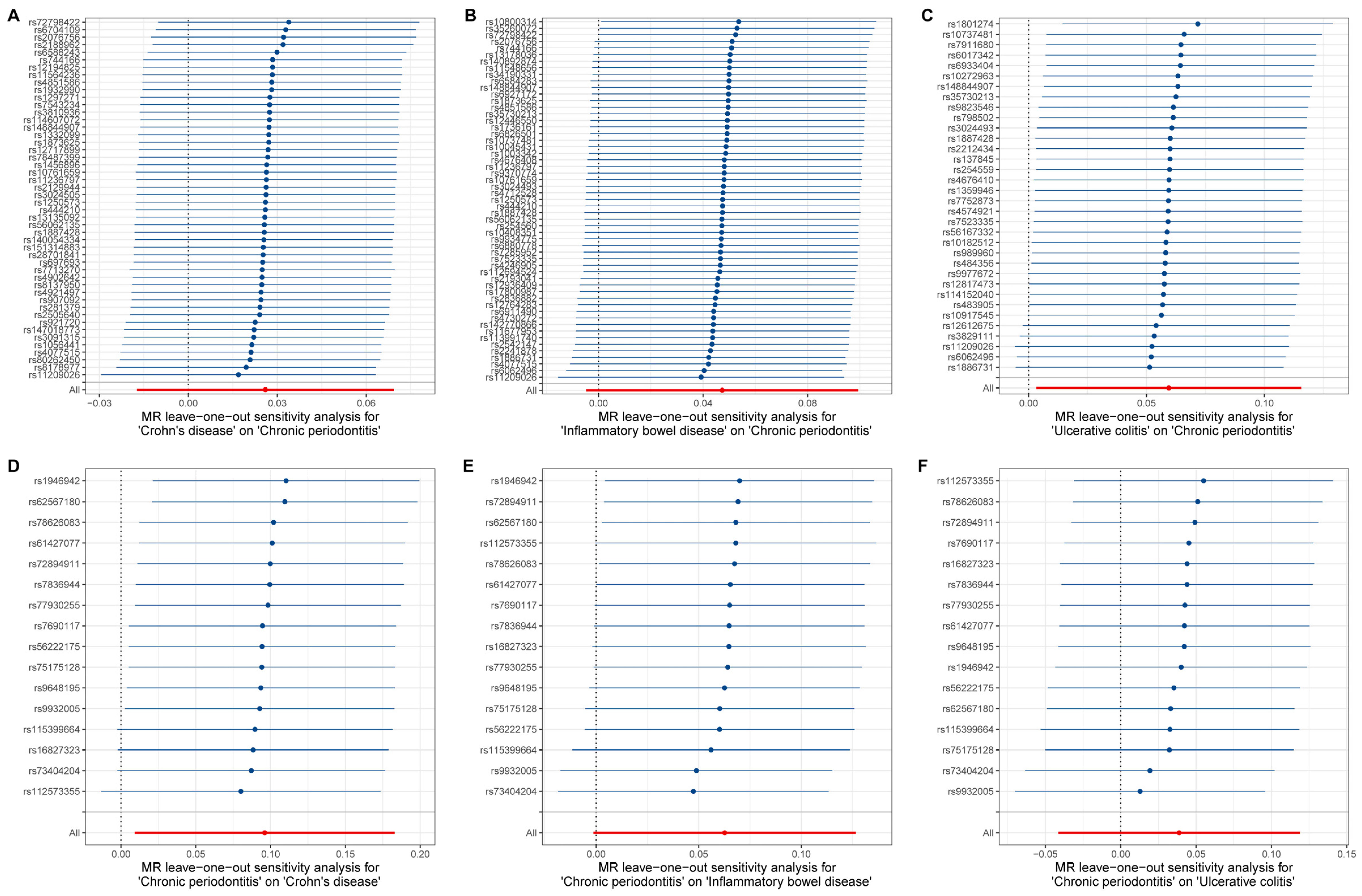
The estimates of causal effects for each SNP are inconsistent (Figure 3), with some SNPs exhibiting significantly different estimated values than the majority of SNPs or overall MR analysis results, such as rs8178977 (Figure 3A, CD on CP), rs1886731 (Figure 3B, IBD on CP, Figure 3C, UC on CP), rs73404204 (Figure 3D, CP on IDB), rs9932005, and rs73404204 (Figure 3F, CP on UC). Scatter plots of the causal effect estimates of individual SNPs on outcomes for each analysis direction suggested potential outlier distributions (Figure 4). In the leave-one-out analysis test, we found that when removing individual SNPs and repeating the MR analysis, substantial differences were observed in the estimated causal effects (Figure 5), for example, rs10800314 and rs35620072 (Figure 5B, IBD on CP), rs9977672 (Figure 5C, UC on CP), rs115399664 (Figure 5D, CP on CD), rs1986942, rs72894911, rs62567180, and rs78626083 (Figure 5E, CP on IBD); when these SNPs are removed, there will be a significant statistically significant change in the overall causal effect estimation. Notably, despite the fact that there is potential heterogeneity in this analysis from the perspective of a single SNP, no definitive outliers were detected after assessing for outliers using MR-PRESSO (Table S3). Furthermore, evaluations of heterogeneity using Cochrane’s Q test (Table S4) and horizontal pleiotropy using the MR-Egger method (Table S5) did not reveal results with significant statistical evidence (p-value > 0.05), indicating that the IVs included in the current bidirectional MR analysis were homogeneous and exhibited no pleiotropy, and all the MR results are robust and reliable.
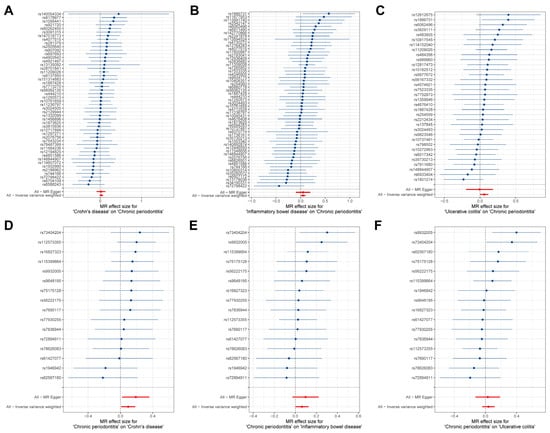
Figure 3.
Forest plot for the causal effects estimates of each SNP on outcomes. (A–F) represent each SNP results for different analytical directions, respectively (with the title description at the bottom of each figure). The blue horizontal line represents the distribution range of the estimated effect value for current SNP, and the blue dots represent the size of the estimated effect value. The vertical line at coordinate 0 is the reference line. The red dots signify the overall causal effect based on MR Egger and inverse variance weighted methods, with the red lines passing through these dots delineating the range of variation in the causal effect.
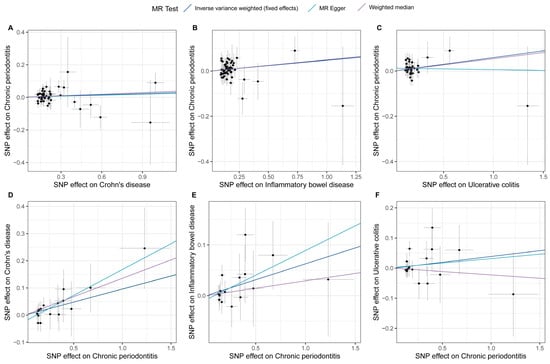
Figure 4.
Scatter plots for effects of genetic liability to exposure on outcomes in this bidirectional MR analysis. A to F represent different analytical directions, respectively. Specifically, A-C denote the analyses from Crohn’s disease (A), inflammatory bowel disease (B), and ulcerative colitis (C) to periodontitis; while D-F represent the analyses from periodontitis to Crohn’s disease (D), inflammatory bowel disease (E), and ulcerative colitis (F). Each point represents an included SNP, and the color of the lines corresponds to the methods described in the legend.
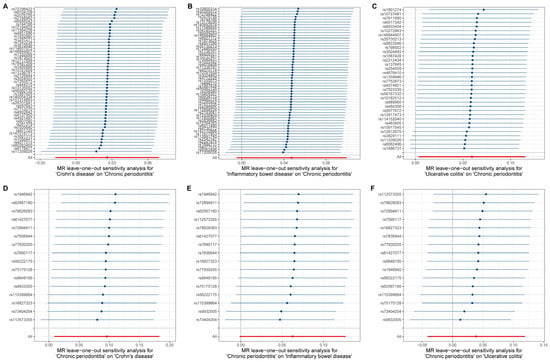
Figure 5.
Leave-one-out tests were conducted to evaluate the effects of excluding individual SNPs on the results of MR analysis. (A–F) represent the leave-one-out analysis results for different analytical directions, respectively (with the title description at the bottom of each figure). The horizontal blue line represents the distribution range of the estimated effect value after removing current single nucleotide polymorphism, and the blue dots represent the size of the estimated effect value. The vertical line at coordinate 0 is the reference line. The red dots signify the overall causal effect, with the red lines passing through these dots delineating the range of variation in the causal effect.
3.3. DEGs in Patients with IBD or Periodontitis
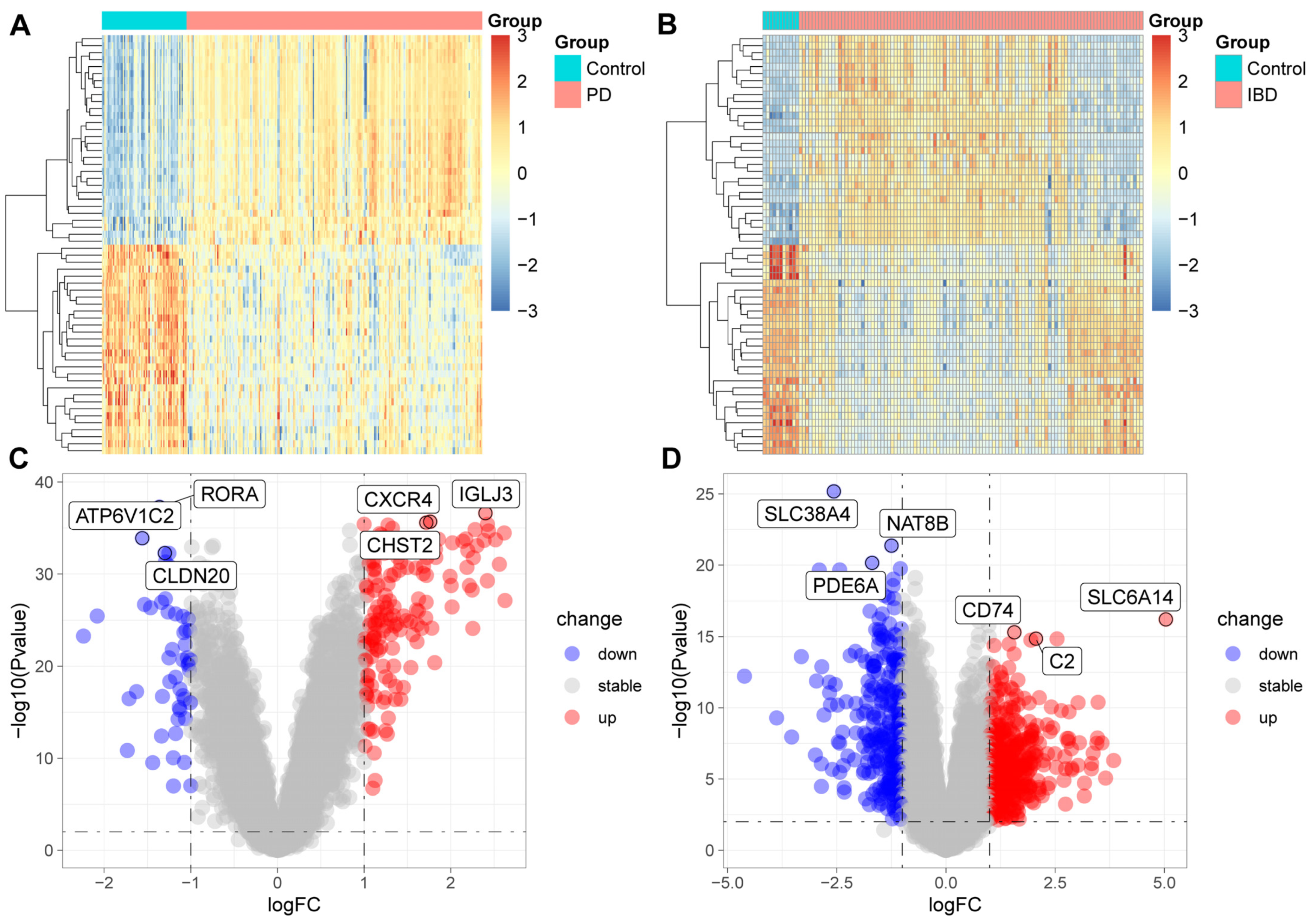
We extracted RNA sequencing data for IBD and periodontitis patients from the GEO database, with each dataset including samples from healthy controls. Differential analysis between the disease cohorts and the healthy controls revealed significant gene expression alterations in patients with periodontitis (Figure 6A,C) and IBD (see Figure 6B,D), predominantly involving genes associated with the immune and inflammatory responses, such as immunoglobulin lambda joining 3 (IGLJ3), C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4), CD74 molecule (CD74), complement C2 (C2), among others. These alterations suggest that changes in the expression levels of genes related to immune and inflammatory responses may play a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of periodontitis and IBD, affecting immune cell activity, cytokine release, and immune regulation. This could be a key factor exacerbating the progression of these diseases, implying the potential of these genes as targets for future therapeutic interventions.
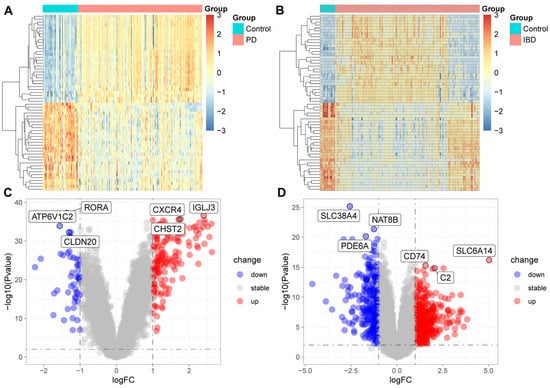
Figure 6.
Differential gene expression in patients with periodontitis (A,C) and IBD (B,D). PD, chronic periodontitis; down, down-regulated genes, up, up-regulated genes; stable, genes whose expression has no significance between disease and healthy tissues.
3.4. Enrichment Analysis and PPI Network of Co-DEGs
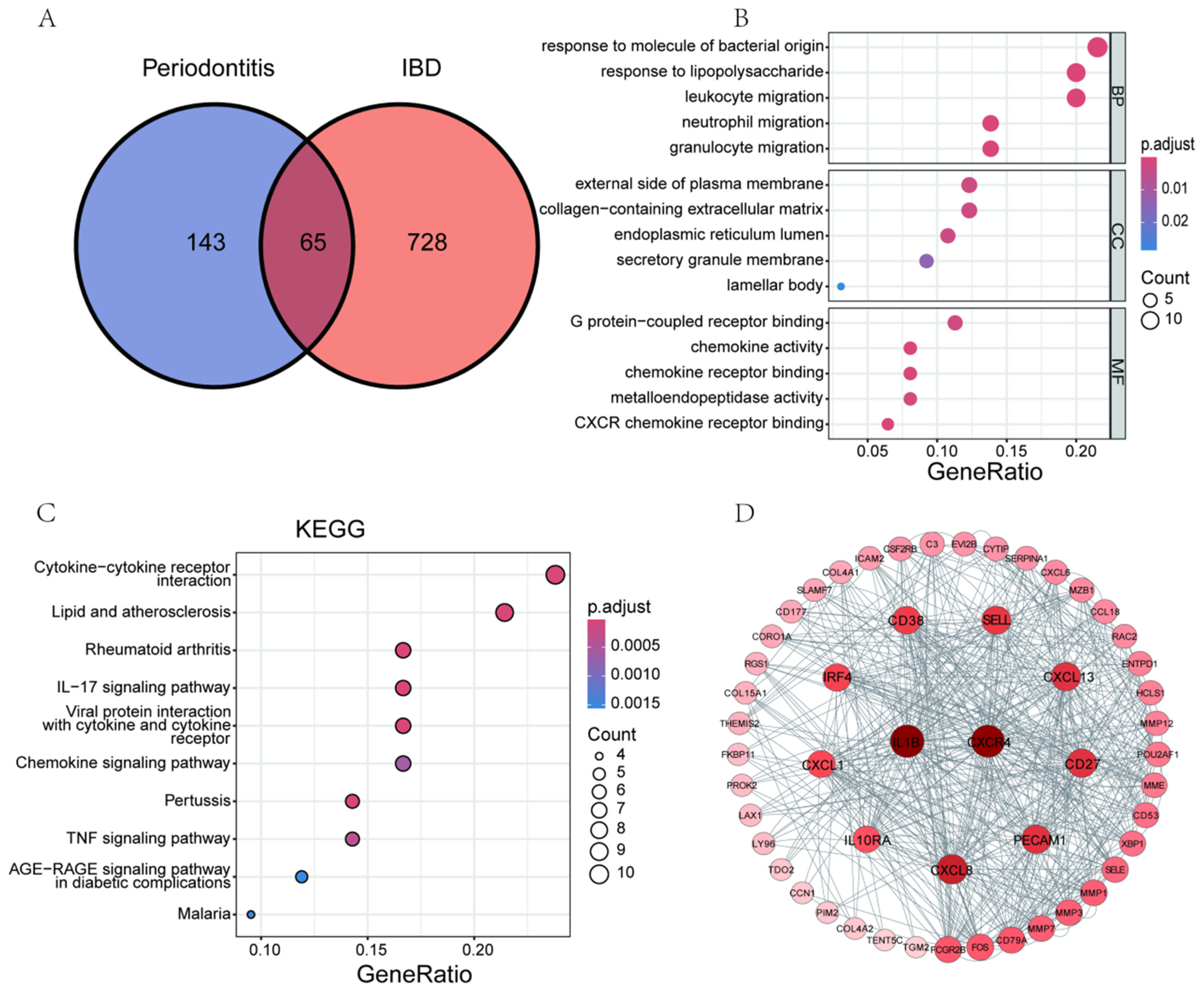
In the periodontitis group, a total of 208 DEGs were identified (Table S6), while in the IBD group, 793 DEGs were determined (Table S7). From these, we screened out 65 co-expressed DEGs (Figure 7A). GO analysis revealed that these co-expressed DEGs are mainly located in secretory organelles (GO term: CC), and their MF largely involves the regulation of cytokine activity. Biologically, they are primarily associated with the migration of immune cells (GO term: BP, Figure 7B). Further enrichment analysis of the KEGG signaling pathways confirmed (Figure 7C) that these co-expressed DEGs are significantly enriched in cytokine receptor interactions, interleukin-17 (IL-17), and TNF signaling pathways. The molecular interaction analysis of these DEGs revealed an extensive network of inflammation-related factors centered around IL1B and CXCR4 (Figure 7D). This evidence suggests that these molecular interactions could be key in regulating inflammatory responses and pathological processes. They may represent a common pathological characteristic of periodontitis and IBD, potentially providing a basis for a common therapeutic target for these diseases.
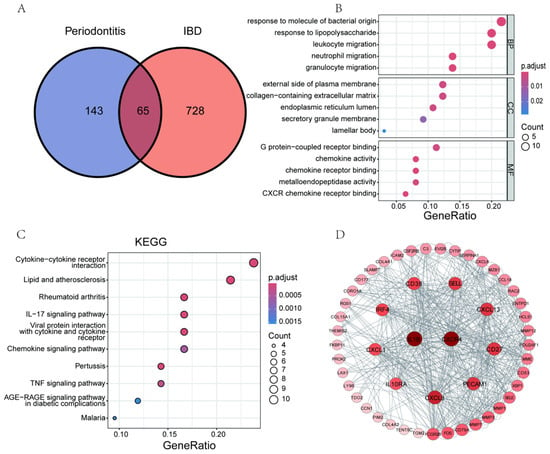
Figure 7.
The results of enrichment analysis and protein-protein interaction (PPI) network of Co-DEGs. (A) displays a Venn diagram illustrating the distribution of shared and unique differentially expressed genes between periodontitis and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). (B–D) present the Gene Ontology(GO) analysis (B), KEGG pathway enrichment analysis (C), and PPI network results (D) for the 65 shared genes between periodontitis and IBD.
4. Discussion
The intricate relationship between IBD and chronic periodontitis represents a critical focus in contemporary medical research. Through bidirectional two-sample MR analysis, our study has provided valuable evidence for the mechanistic interplay between these conditions while offering novel therapeutic insights. The MR analysis demonstrated a significant bidirectional causal relationship, indicating that individuals with IBD exhibit increased susceptibility to chronic periodontitis and, conversely, suggesting shared pathogenic mechanisms. To elucidate the molecular basis of this bidirectional relationship, we conducted transcriptomic analyses, which revealed common differentially expressed genes between these conditions. This molecular-level evidence illuminated shared regulatory networks underlying the pathogenesis of both diseases. Subsequent bioinformatics analyses highlighted the central role of immune-related signaling cascades, particularly the IL-17, cytokine, and TNF pathways, in disease progression. Notably, protein–protein interaction analyses identified IL1B and CXCR4 as key immune modulators potentially orchestrating the bidirectional relationship between these conditions. Based on these findings, therapeutic strategies targeting these immune pathways—especially IL-17, TNF, and IL1B—could hold promise for the development of treatments that simultaneously address both IBD and chronic periodontitis, offering a more integrated approach to managing these co-occurring diseases. These findings not only substantiate the hypothesized interaction between IBD and chronic periodontitis but also present novel therapeutic targets. The identification of shared molecular mechanisms and pathological processes offers unprecedented opportunities for developing targeted interventions. This enhanced understanding of the molecular landscape governing both conditions may facilitate more effective, pathway-specific therapeutic strategies, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
IL1B and CXCR4 are key regulators of inflammation and immune responses [69,70], garnering widespread attention for their roles in diseases like IBD and chronic periodontitis in recent years. IL1B is a potent pro-inflammatory cytokine that activates various immune cells and induces the production of other cytokines [71,72]. In IBD, increased expression of IL1B is closely associated with intestinal mucosal inflammation, stimulating intestinal epithelial cells and macrophages to produce inflammatory mediators like prostaglandins and leukotrienes, thereby exacerbating intestinal inflammation [73,74,75]. Additionally, IL1B can promote the infiltration of inflammatory cells, aggravating tissue damage [76]. Similarly, in periodontitis, IL1B plays a crucial role, and it considered one of the primary inflammatory mediators in the disease’s pathogenesis [77,78]. It promotes inflammatory responses in gingival tissues, leading to tissue destruction and bone resorption. CXCR4 is significant in cell migration and immune responses, especially within the inflammatory environments of IBD and chronic periodontitis [79,80,81]. Increased expression of CXCR4 and its ligand CXCL12 in IBD patients aids in the recruitment and activation of inflammatory cells [82,83]. CXCR4 is also involved in maintaining the intestinal epithelial barrier, with its aberrant expression linked to impaired barrier function [84]. In periodontitis, CXCR4 regulates the migration and activation of inflammatory cells in periodontal tissues, influencing disease progression and the extent of tissue damage [83,85].
Apart from IL1B and CXCR4, various other immune-related cytokines play significant roles in the onset and development of IBD and periodontitis. These cytokines regulate inflammation processes through related signaling pathways, such as TNF-α and the IL17 signaling pathway, impacting the clinical manifestations and treatment outcomes of these diseases. TNF-α, a key pro-inflammatory factor, not only enhances the activation of inflammatory cells but also promotes the production and release of cytokines, exacerbating tissue damage [86,87]. The level of TNF is significantly elevated in IBD, correlating with the severity of intestinal inflammation [88]. TNF inhibitors have become an important part of IBD treatment [89,90]. Similarly, in periodontitis, TNF is involved in regulating inflammatory responses and tissue destruction, becoming a potential treatment target [91,92]. IL-17, produced by Th17 cells, is crucial for maintaining the integrity of mucosal barriers [93,94]. In IBD, IL-17 helps enhance mucosal defense, but excessive IL-17 response can exacerbate inflammation [95,96]. In periodontitis, increased IL-17 is also associated with ongoing inflammation and tissue damage [97,98]. Corroborating our findings, recent empirical evidence has demonstrated that periodontal pathogens can exacerbate colitis through modulation of the gut microbiota–metabolite–Th17/Treg axis, further substantiating the mechanistic link between periodontal disease and IBD pathogenesis through immune-mediated pathways [99]. The complex interaction network of these cytokines forms the immunopathological foundation of IBD and periodontitis. Additionally, other interleukin family members, such as interleukin-6 (IL-6)-related pathways, have been reported to be closely associated with inflammation responses in IBD and periodontitis [100,101,102,103]. Understanding the mechanisms of these factors in diseases not only helps to delve deeper into the pathology of IBD and chronic periodontitis but also provides potential targets for developing new treatment methods.
Our findings have several important clinical implications. First, the established bidirectional causal relationship between IBD and chronic periodontitis suggests that clinicians should implement comprehensive screening protocols for both conditions when either is diagnosed, enabling early intervention and improved patient outcomes. Second, the identification of shared molecular pathways, particularly IL-17 and TNF signaling cascades [104,105,106,107], suggests that targeting these pathways could offer a potential avenue for dual-action treatments. Although dual-target therapies have been explored in other contexts, such as in autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis, their application in managing both IBD and chronic periodontitis remains an area for further investigation. Third, the revelation of key immune regulators, including IL1B and CXCR4 [108], provides new opportunities for developing biomarker-based diagnostic approaches and personalized therapeutic strategies tailored to individual patient profiles.
In comparison to previous studies [19,20,28,31,109,110,111], while several reports have explored the association between IBD and periodontitis, our study provided valuable evidence of a bidirectional causal relationship through the use of MR analysis. Previous research has mostly been observational, often showing correlation rather than causality, and has been limited by confounding factors. Moreover, many studies, including several previously published MR analyses [32,33,34,35], have focused on either the periodontal or gastrointestinal aspects, without investigating the underlying shared molecular mechanisms. By addressing this gap, our research provides a clearer understanding of the interplay between IBD and periodontitis, with a focus on common immune-related signaling pathways. This distinction highlights the need for further investigation into integrated therapeutic strategies targeting these shared mechanisms, which could offer more effective treatment approaches for patients suffering from both conditions simultaneously.
While this study provides valuable insights, several limitations should be acknowledged. First, the MR analysis predominantly focused on European populations, potentially limiting the generalizability of our findings across different ethnic groups due to variations in genetic backgrounds and lifestyle factors [112]. Second, given the systemic nature of IBD, our analysis may not have captured all relevant genetic variations involved in disease pathogenesis, potentially affecting the comprehensiveness of our findings. Third, despite rigorous methodological controls, residual confounding factors may persist, warranting cautious interpretation of the results [113]. Future studies should encompass diverse populations and more extensive genetic analyses to enhance the robustness and applicability of these findings.
5. Conclusions
Through MR analysis, this study established a bidirectional causal relationship between IBD and periodontitis, demonstrating increased susceptibility to chronic periodontitis among IBD patients and, conversely, heightened IBD risk in individuals with periodontal disease. Transcriptomic analyses revealed shared differentially expressed genes between these conditions, illuminating common pathogenic mechanisms. Notably, key immune regulators, particularly IL1B and CXCR4, emerged as central mediators in the pathogenesis of both diseases. Furthermore, our findings highlighted the crucial involvement of specific cytokine signaling cascades, especially the IL-17 and TNF pathways, in disease progression. These molecular insights provide a robust scientific framework for the diagnosis and therapeutic management of both conditions, emphasizing the clinical importance of considering their bidirectional relationship in treatment strategies.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biomedicines13020476/s1, Figure S1: Funnel plot for the study; Table S1: All IVs used in the study; Table S2: The results of MR analysis data; Table S3: MR PRESSO result for MR analysis; Table S4: Heterogeneity results for MR analysis; Table S5: Pleiotropy result for MR analysis; Table S6: GSE16134 DEGs; Table S7: GSE59071 DEGs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.L. and M.Z.; methodology, Z.F. and S.L.; software, Z.F. and Z.C.; validation, Z.F. and X.W.; formal analysis, Z.F.; investigation, Z.F. and X.W. resources, Z.F. and Z.C.; data curation, Z.F., Z.C. and X.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.F.; writing—review and editing, M.Z. and S.L.; visualization, Z.F. and Z.C.; supervision, S.L. and M.Z.; project administration, S.L. and M.Z.; funding acquisition, M.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number: 82473564).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study utilized publicly available GWAS summary statistics from the OpenGWAS database, derived from studies that obtained appropriate institutional review board approval and participant informed consent. No additional ethical approval was required for the analysis of these publicly accessible summary-level data.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available in the ieu open GWAS project (https://gwas.mrcieu.ac.uk/, accessed on 15 October 2024) and the GEO database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gds, accessed on 20 September 2024).
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the OpenGWAS, UK Biobank, and GEO database consortia for providing access to their comprehensive datasets. We extend our appreciation to all investigators who contributed to the generation and sharing of these valuable genetic and transcriptomic resources. This research would not have been possible without their commitment to open science and data accessibility.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, W.; Cao, Y.; Dong, L.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Lv, Z.; Iheozor-Ejiofor, Z.; Li, C. Periodontal therapy for primary or secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease in people with periodontitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 12, CD009197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, S.Q.; Zhao, L.; Ren, Z.H.; Hu, C.Y. Global, regional, and national burden of periodontitis from 1990 to 2019: Results from the Global Burden of Disease study 2019. J. Periodontol. 2022, 93, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutsopoulos, N.M.; Konkel, J.E. Tissue-Specific Immunity at the Oral Mucosal Barrier. Trends Immunol. 2018, 39, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global report published on links between periodontal and cardiovascular diseases. BDJ Team 2020, 7, 6. [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Preshaw, P.M.; Bissett, S.M. Periodontitis and diabetes. BDJ Team 2020, 7, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajishengallis, G.; Chavakis, T. Local and systemic mechanisms linking periodontal disease and inflammatory comorbidities. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 426–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajishengallis, G. Toll gates to periodontal host modulation and vaccine therapy. Periodontol. 2000 2009, 51, 181–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Han, D.; Choi, B.K. Proteome and immune responses of extracellular vesicles derived from macrophages infected with the periodontal pathogen Tannerella forsythia. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2023, 12, e12381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahoumi, L.A.; Saleh, M.H.A.; Meghil, M.M. Virulence Factors of the Periodontal Pathogens: Tools to Evade the Host Immune Response and Promote Carcinogenesis. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, N.; Pantazi, E.; Pavlidis, P.; Tsakmaki, A.; Li, K.; Yang, F.; Parker, A.; Pin, C.; Cozzetto, D.; Minns, D.; et al. Interleukin-22 orchestrates a pathological endoplasmic reticulum stress response transcriptional programme in colonic epithelial cells. Gut 2020, 69, 578–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2017 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Collaborators. The global, regional, and national burden of inflammatory bowel disease in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Hou, L. Diminished Immune Response and Elevated Abundance in Gut Microbe Dubosiella in Mouse Models of Chronic Colitis with GBP5 Deficiency. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seegert, D.; Rosenstiel, P.; Pfahler, H.; Pfefferkorn, P.; Nikolaus, S.; Schreiber, S. Increased expression of IL-16 in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2001, 48, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Viennois, E.; Prasad, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Han, M.K.; Xiao, B.; Xu, C.; Srinivasan, S.; et al. Edible ginger-derived nanoparticles: A novel therapeutic approach for the prevention and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease and colitis-associated cancer. Biomaterials 2016, 101, 321–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.J.; Tang, B.; Wang, F.C.; Tang, L.; Lei, Y.Y.; Luo, Y.; Huang, S.J.; Yang, M.; Wu, L.Y.; Wang, W.; et al. Parthenolide ameliorates colon inflammation through regulating Treg/Th17 balance in a gut microbiota-dependent manner. Theranostics 2020, 10, 5225–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spathakis, M.; Dovrolis, N.; Filidou, E.; Kandilogiannakis, L.; Tarapatzi, G.; Valatas, V.; Drygiannakis, I.; Paspaliaris, V.; Arvanitidis, K.; Manolopoulos, V.G.; et al. Exploring Microbial Metabolite Receptors in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: An In Silico Analysis of Their Potential Role in Inflammation and Fibrosis. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tursi, A.; D’Avino, A.; Brandimarte, G.; Mocci, G.; Pellegrino, R.; Savarino, E.V.; Gravina, A.G.; Hericium-Uc Study Group. Enhancing Oral 5-ASA Effectiveness in Mild-to-Moderate Ulcerative Colitis through an H. erinaceus-Based Nutraceutical Add-on Multi-Compound: The “HERICIUM-UC” Two-Arm Multicentre Retrospective Study. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chacon-Millan, P.; Lama, S.; Del Gaudio, N.; Gravina, A.G.; Federico, A.; Pellegrino, R.; Luce, A.; Altucci, L.; Facchiano, A.; Caraglia, M.; et al. A Combination of Microarray-Based Profiling and Biocomputational Analysis Identified miR331-3p and hsa-let-7d-5p as Potential Biomarkers of Ulcerative Colitis Progression to Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, K.L.; Kamada, N. Pathogenic associations between oral and gastrointestinal diseases. Trends Mol. Med. 2022, 28, 1030–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, K.; Kamada, N. Exploring the oral-gut linkage: Interrelationship between oral and systemic diseases. Mucosal Immunol. 2024, 17, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zilberstein, N.F.; Engen, P.A.; Swanson, G.R.; Naqib, A.; Post, Z.; Alutto, J.; Green, S.J.; Shaikh, M.; Lawrence, K.; Adnan, D.; et al. The Bidirectional Effects of Periodontal Disease and Oral Dysbiosis on Gut Inflammation in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2024, jjae162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Xu, W.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, C.; Li, H.; Chao, Y.; Sun, Y.; A, L. The effect of the “Oral-Gut” axis on periodontitis in inflammatory bowel disease: A review of microbe and immune mechanism associations. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1132420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamoto, S.; Kamada, N. Periodontal connection with intestinal inflammation: Microbiological and immunological mechanisms. Periodontol. 2000 2022, 89, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haznedaroglu, E.; Polat, E. Dental Caries, Dental Erosion and Periodontal Disease in Children with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 20, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, E.; Curtis, M.A.; Neves, J.F. The role of oral bacteria in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, W.; Li, J.; Cao, Z.; Lin, S.; Pan, C.; Pang, Y.; Liu, J. Decorating Bacteria with a Therapeutic Nanocoating for Synergistically Enhanced Biotherapy. Small 2021, 17, e2101810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domokos, Z.; Uhrin, E.; Szabó, B.; Czumbel, M.L.; Dembrovszky, F.; Kerémi, B.; Varga, G.; Hegyi, P.; Hermann, P.; Németh, O. Patients with inflammatory bowel disease have a higher chance of developing periodontitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 1020126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-Pouso, A.I.; Castelo-Baz, P.; Rodriguez-Zorrilla, S.; Pérez-Sayáns, M.; Vega, P. Association between periodontal disease and inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2021, 79, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, S.N.; Hagner, M.; Nogueira, A.V.; Franke, A.; Jäger, A.; Deschner, J. Inflammatory bowel disease and oral health: Systematic review and a meta-analysis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Y.Y.; Kong, X.B.; Ge, Y.P.; Liu, Z.Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Jiang, J.W.; Jiang, H.B.; Fang, S.L. Periodontitis and inflammatory bowel disease: A meta-analysis. BMC Oral. Health 2020, 20, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Qiao, D.; Chen, R.; Zhu, F.; Gong, J.; Yan, F. The Association between Periodontitis and Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6692420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhong, Z.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L.; Fang, S.; Jiang, T.; Luo, X.; Yang, Y.; Song, G.; et al. Causal Association Analysis of Periodontitis and Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2024, 30, 1251–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Gong, J.; Ding, C. Genetic evidence for the oral-gut axis between periodontitis and inflammatory bowel disease. J. Dent. Sci. 2023, 18, 1904–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Tan, D.; Abudourexiti, W.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Ding, C.; Gong, J. Association between inflammatory bowel disease and periodontitis: A bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2023, 50, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Yang, Y.; Wu, D.; Chang, M.; Han, C.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; He, D. Deciphering genetic causality between inflammatory bowel disease and periodontitis through bi-directional two-sample Mendelian randomization. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawlor, D.A.; Harbord, R.M.; Sterne, J.A.; Timpson, N.; Davey Smith, G. Mendelian randomization: Using genes as instruments for making causal inferences in epidemiology. Stat. Med. 2008, 27, 1133–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.; Davey Smith, G.; Davies, N.M.; Dudbridge, F.; Gill, D.; Glymour, M.M.; Hartwig, F.P.; Kutalik, Z.; Holmes, M.V.; Minelli, C.; et al. Guidelines for performing Mendelian randomization investigations: Update for summer 2023. Wellcome Open Res. 2019, 4, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrivankova, V.W.; Richmond, R.C.; Woolf, B.A.R.; Yarmolinsky, J.; Davies, N.M.; Swanson, S.A.; VanderWeele, T.J.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Timpson, N.J.; Dimou, N.; et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology Using Mendelian Randomization: The STROBE-MR Statement. JAMA 2021, 326, 1614–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.Z.; van Sommeren, S.; Huang, H.; Ng, S.C.; Alberts, R.; Takahashi, A.; Ripke, S.; Lee, J.C.; Jostins, L.; Shah, T.; et al. Association analyses identify 38 susceptibility loci for inflammatory bowel disease and highlight shared genetic risk across populations. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurki, M.I.; Karjalainen, J.; Palta, P.; Sipilä, T.P.; Kristiansson, K.; Donner, K.M.; Reeve, M.P.; Laivuori, H.; Aavikko, M.; Kaunisto, M.A.; et al. FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population. Nature 2023, 613, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Qin, Z.; Cai, Z.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.-L.; Yin, X.; Yin, Y.; Peng, X.; Zhang, B. Evaluating the Causal Association between Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Risk of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: Univariable and Multivariable Mendelian Randomization Study. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemani, G.; Zheng, J.; Elsworth, B.; Wade, K.H.; Haberland, V.; Baird, D.; Laurin, C.; Burgess, S.; Bowden, J.; Langdon, R.; et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. eLife 2018, 7, e34408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Hu, C.; Wu, X.; Qi, H.; Lin, L.; Xu, M.; Xu, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, Y.; et al. Evaluating the Effects of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Inflammatory Bowel Disease via Circulating Metabolites: A Mediation Mendelian Randomization Study. Metabolites 2023, 13, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.; Shi, M.; Zhong, Z.; Hu, H.; Sang, H.; Zhou, M.; Feng, Z. Causal Relationship between Aging and Anorexia Nervosa: A White-Matter-Microstructure-Mediated Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Z.; Liao, J.; Liu, H.; Zhou, M. Exploring the Causal Effects of Mineral Metabolism Disorders on Telomere and Mitochondrial DNA: A Bidirectional Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Feng, Z.; Xu, B. Metabolic Characteristics of Gut Microbiota and Insomnia: Evidence from a Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G. Avoiding bias from weak instruments in Mendelian randomization studies. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 755–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G. Bias in causal estimates from Mendelian randomization studies with weak instruments. Stat. Med. 2011, 30, 1312–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machiela, M.J.; Chanock, S.J. LDlink: A web-based application for exploring population-specific haplotype structure and linking correlated alleles of possible functional variants. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3555–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Yang, P.; Li, Y.; Liu, T.; Zha, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Feng, Z.; Li, M. New insights from bidirectional Mendelian randomization: Causal relationships between telomere length and mitochondrial DNA copy number in aging biomarkers. Aging 2024, 16, 7387–7404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Butterworth, A.; Thompson, S.G. Mendelian randomization analysis with multiple genetic variants using summarized data. Genet. Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Deng, Y.; Liu, H.; Fu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Feng, Z. Causal Relationship between Meat Intake and Biological Aging: Evidence from Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 32, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbanck, M.; Chen, C.Y.; Neale, B.; Do, R. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, R.; Xie, H.; Gao, H.; Xie, C.; Yuan, H.; Feng, Z. Mitochondrial proteins as therapeutic targets in diabetic ketoacidosis: Evidence from Mendelian randomization analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1448505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Lian, P.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Feng, Z. Causal Associations between Gut Microbiota and Different Types of Dyslipidemia: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Qiao, R.; Ren, Z.; Hou, X.; Feng, J.; He, X.; Chen, D. Could CTSK and COL4A2 be specific biomarkers of poor prognosis for patients with gastric cancer in Asia?-a microarray analysis based on regional population. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2020, 11, 386–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhove, W.; Peeters, P.M.; Staelens, D.; Schraenen, A.; Van der Goten, J.; Cleynen, I.; De Schepper, S.; Van Lommel, L.; Reynaert, N.L.; Schuit, F.; et al. Strong Upregulation of AIM2 and IFI16 Inflammasomes in the Mucosa of Patients with Active Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 2673–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.H.; Singh, P.; Chen, C.W.; Thomas, J.; Weber, J.; Mauch-Mani, B.; Zimmerli, L. Priming for enhanced defence responses by specific inhibition of the Arabidopsis response to coronatine. Plant J. 2011, 65, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phipson, B.; Lee, S.; Majewski, I.J.; Alexander, W.S.; Smyth, G.K. Robust hyperparameter estimation protects against hypervariable genes and improves power to detect differential expression. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2016, 10, 946–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Gao, L.; Lu, Y.; He, X.; Xie, J. The potential contribution of aberrant cathepsin K expression to gastric cancer pathogenesis. Discover. Oncol. 2024, 15, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Feng, Z.; Zhou, M.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y. Bioinformatic Evidence Reveals that Cell Cycle Correlated Genes Drive the Communication between Tumor Cells and the Tumor Microenvironment and Impact the Outcomes of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 4092635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consortium, T.G.O. Expansion of the Gene Ontology knowledgebase and resources. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D331–D338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Li, X.; Ren, Z.; Feng, J.; He, X.; You, C. Prognostic and Predictive Value of Cadherin 11 for Patients with Gastric Cancer and Its Correlation with Tumor Microenvironment: Results from Microarray Analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 8107478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING database in 2023: Protein-protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.L.; Ding, R.; Jia, X.M.; Huang, J.J.; Yu, S.; Chan, H.T.; Li, W.; Mao, L.L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.Y.; et al. Correlation of Moraxella catarrhalis macrolide susceptibility with the ability to adhere and invade human respiratory epithelial cells. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 2055–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eislmayr, K.; Bestehorn, A.; Morelli, L.; Borroni, M.; Vande Walle, L.; Lamkanfi, M.; Kovarik, P. Nonredundancy of IL-1α and IL-1β is defined by distinct regulation of tissues orchestrating resistance versus tolerance to infection. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabj7293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimaz, R.; Cazalis, M.A.; Reynaud, C.; Gerloni, V.; Zulian, F.; Biggioggero, M.; Martini, G.; Pontikaki, I.; Fantini, F.; Mougin, B.; et al. IL1 and TNF gene polymorphisms in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis treated with TNF inhibitors. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007, 66, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teramoto, K.; Tsurekawa, Y.; Suico, M.A.; Kaseda, S.; Omachi, K.; Yokota, T.; Kamura, M.; Piruzyan, M.; Kondo, T.; Shuto, T.; et al. Mild electrical stimulation with heat shock attenuates renal pathology in adriamycin-induced nephrotic syndrome mouse model. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aschenbrenner, D.; Quaranta, M.; Banerjee, S.; Ilott, N.; Jansen, J.; Steere, B.; Chen, Y.H.; Ho, S.; Cox, K.; Arancibia-Cárcamo, C.V.; et al. Deconvolution of monocyte responses in inflammatory bowel disease reveals an IL-1 cytokine network that regulates IL-23 in genetic and acquired IL-10 resistance. Gut 2021, 70, 1023–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, C.; Duewell, P.; Mayer, C.; Lehr, H.A.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Dauer, M.; Tschopp, J.; Endres, S.; Latz, E.; Schnurr, M. Colitis induced in mice with dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) is mediated by the NLRP3 inflammasome. Gut 2010, 59, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.V.; Leonardi, I.; Putzel, G.G.; Semon, A.; Fiers, W.D.; Kusakabe, T.; Lin, W.Y.; Gao, I.H.; Doron, I.; Gutierrez-Guerrero, A.; et al. Immune regulation by fungal strain diversity in inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 2022, 603, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Lai, X.; Liu, X.; Yan, H.; Wu, C. Pyroptosis in glioblastoma: A crucial regulator of the tumour immune microenvironment and a predictor of prognosis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 1579–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, R.; Wu, Z.; Li, M.; Shao, M.; Hu, T. Interleukin-1β is a potential therapeutic target for periodontitis: A narrative review. Int. J. Oral. Sci. 2020, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.P.; Huang, J.; Chan, K.W.Y.; Leung, W.K.; Goto, T.; Ho, Y.S.; Chang, R.C. IL-1β and TNF-α play an important role in modulating the risk of periodontitis and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keppler, S.J.; Burbage, M.; Gasparrini, F.; Hartjes, L.; Aggarwal, S.; Massaad, M.J.; Geha, R.S.; Bruckbauer, A.; Batista, F.D. The Lack of WIP Binding to Actin Results in Impaired B Cell Migration and Altered Humoral Immune Responses. Cell Rep. 2018, 24, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, A.; Fujimoto, J.; Miyata, H.; Stumm, R.; Narazaki, M.; Schulz, S.; Baba, Y.; Kumanogoh, A.; Suzuki, K. The COMMD3/8 complex determines GRK6 specificity for chemoattractant receptors. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 1630–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Otsuka, A.; Ishida, Y.; Wong, L.S.; Seidel, J.A.; Nonomura, Y.; Nakashima, C.; Nakajima, S.; Kitoh, A.; Nomura, T.; et al. Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide promotes cutaneous dendritic cell functions in contact hypersensitivity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 858–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckner, C.M.; Moir, S.; Kardava, L.; Ho, J.; Santich, B.H.; Kim, L.J.; Funk, E.K.; Nelson, A.K.; Winckler, B.; Chairez, C.L.; et al. CXCR4/IgG-expressing plasma cells are associated with human gastrointestinal tissue inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 1676–1685.e1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, F.; Ma, S.; Heng, B.C.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xu, M.; He, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. Cell Membrane Vesicles with Enriched CXCR4 Display Enhances Their Targeted Delivery as Drug Carriers to Inflammatory Sites. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, e2101562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, L.; Guzner-Gur, H.; Dotan, I. Involvement of CXCR4/CXCR7/CXCL12 Interactions in Inflammatory bowel disease. Theranostics 2013, 3, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Chen, D.; Li, R.; Li, R.; Teng, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zou, X.; Wang, W.; Zhou, C. Genetically engineered CXCR4-modified exosomes for delivery of miR-126 mimics to macrophages alleviate periodontitis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Feng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ma, S.; Hu, Z.; Yang, P.; Chai, Y.; Xie, X. Discovery of Novel Ligands for TNF-α and TNF Receptor-1 through Structure-Based Virtual Screening and Biological Assay. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57, 1101–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Fu, Y.; Mei, K.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Ren, F.; Jiang, C.; Meng, L.; Lu, S.; et al. A shedding soluble form of interleukin-17 receptor D exacerbates collagen-induced arthritis through facilitating TNF-α-dependent receptor clustering. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 1883–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, J.M.; de Zoete, M.R.; Palm, N.W.; Laenen, Y.; Bright, R.; Mallette, M.; Bu, K.; Bielecka, A.A.; Xu, F.; Hurtado-Lorenzo, A.; et al. Immunoglobulin A Targets a Unique Subset of the Microbiota in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 83–93.e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Haens, G.R.; van Deventer, S. 25 years of anti-TNF treatment for inflammatory bowel disease: Lessons from the past and a look to the future. Gut 2021, 70, 1396–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Kim, H.; Jang, H.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, S.H.; Yang, Y. Oral TNF-α siRNA delivery via milk-derived exosomes for effective treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 34, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, Y.; Fukuda, T.; Zhang, Q.; Sanui, T.; Shinjo, T.; Kou, X.; Chen, C.; Liu, D.; Watanabe, Y.; Hayashi, C.; et al. Exosomes from TNF-α-treated human gingiva-derived MSCs enhance M2 macrophage polarization and inhibit periodontal bone loss. Acta Biomater. 2021, 122, 306–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purnamasari, D.; Khumaedi, A.I.; Soeroso, Y.; Marhamah, S. The influence of diabetes and or periodontitis on inflammation and adiponectin level. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2019, 13, 2176–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Itakura, E.; Nelson, G.M.; Sheng, M.; Laurent, P.; Fenk, L.A.; Butcher, R.A.; Hegde, R.S.; de Bono, M. IL-17 is a neuromodulator of Caenorhabditis elegans sensory responses. Nature 2017, 542, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huangfu, L.; Li, R.; Huang, Y.; Wang, S. The IL-17 family in diseases: From bench to bedside. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujino, S.; Andoh, A.; Bamba, S.; Ogawa, A.; Hata, K.; Araki, Y.; Bamba, T.; Fujiyama, Y. Increased expression of interleukin 17 in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 2003, 52, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Tang, Z.; Ma, X.; Sun, K.; Fan, L.; Fang, J.; Pan, J.; Wang, X.; An, H.; Zhou, J. TAOK1 negatively regulates IL-17-mediated signaling and inflammation. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 15, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaffen, S.L.; Moutsopoulos, N.M. Regulation of host-microbe interactions at oral mucosal barriers by type 17 immunity. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eaau4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, E.; Mattos, M.; Vieira, G.H.A.; Chen, S.; Corrêa, J.D.; Wu, Y.; Albiero, M.L.; Bittinger, K.; Graves, D.T. Diabetes Enhances IL-17 Expression and Alters the Oral Microbiome to Increase Its Pathogenicity. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 120–128.e124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, L.; Fu, J.; Du, J.; Luo, Z.; Guo, L.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y. Porphyromonas gingivalis aggravates colitis via a gut microbiota-linoleic acid metabolism-Th17/Treg cell balance axis. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, L.H.; Rose-John, S. IL-6 biology: Implications for clinical targeting in rheumatic disease. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2014, 10, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraldez, M.D.; Carneros, D.; Garbers, C.; Rose-John, S.; Bustos, M. New insights into IL-6 family cytokines in metabolism, hepatology and gastroenterology. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 787–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose-John, S.; Jenkins, B.J.; Garbers, C.; Moll, J.M.; Scheller, J. Targeting IL-6 trans-signalling: Past, present and future prospects. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 666–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, S.; Aden, K.; Bernardes, J.P.; Conrad, C.; Tran, F.; Höper, H.; Volk, V.; Mishra, N.; Blase, J.I.; Nikolaus, S.; et al. Therapeutic Interleukin-6 Trans-signaling Inhibition by Olamkicept (sgp130Fc) in Patients With Active Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 2354–2366.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Mello-Neto, J.M.; Ervolino, E.; Elangovan, G.; Toro, L.F.; Lee, J.; Gustafsson, A.; Figueredo, C. The Resolution of Periodontal Inflammation Promotes Changes in Cytokine Expression in the Intestine and Gingival Tissues of Aged Rats with DSS-Induced Colitis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasiakos, S.; Gwack, Y.; Kang, M.; Nishimura, I. Calcium Signaling in T Cells and Chronic Inflammatory Disorders of the Oral Cavity. J. Dent. Res. 2021, 100, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menegat, J.S.; Lira-Junior, R.; Siqueira, M.A.; Brito, F.; Carvalho, A.T.; Fischer, R.G.; Figueredo, C.M. Cytokine expression in gingival and intestinal tissues of patients with periodontitis and inflammatory bowel disease: An exploratory study. Arch. Oral. Biol. 2016, 66, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, S.; Reichert, S.; Streetz, K.; Trautwein, C.; Reichert, Y.; Gläser, C.; Schaller, H.G.; Stein, J.M. Tumor necrosis factor-α and oral inflammation in patients with Crohn disease. J. Periodontol. 2014, 85, 1424–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, C.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, Y.; Huang, S.; Lin, Z.; He, F.; Song, Z. Exploration of the shared gene signatures and molecular mechanisms between periodontitis and inflammatory bowel disease: Evidence from transcriptome data. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2023, 11, goad041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, K.M.; Gulati, A.S. The “Gum-Gut” Axis in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Hypothesis-Driven Review of Associations and Advances. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 620124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, J.; Ichikawa, H.; Kitamoto, S.; Golob, J.L.; Kaneko, M.; Nagata, J.; Takahashi, M.; Gillilland, M.G., III; Tanaka, R.; Nagao-Kitamoto, H.; et al. A potential pathogenic association between periodontal disease and Crohn’s disease. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e148543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, J. Editorial: Unravelling the relationship between periodontal disease and inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 58, 1232–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, A. Use of race in clinical algorithms. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadd2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Leeuw, C.; Savage, J.; Bucur, I.G.; Heskes, T.; Posthuma, D. Understanding the assumptions underlying Mendelian randomization. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2022, 30, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).