Treatment of Rare Mutations in Patients with Lung Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Rare LC Mutations
2.1. ROS1 Gene
2.1.1. Description
2.1.2. Detection Methods
2.1.3. Pharmaceutical Agents
2.1.4. Role of Immunotherapy
2.1.5. Mechanisms of Resistance
2.2. RET Gene
2.2.1. Description
2.2.2. Detection Methods
2.2.3. Pharmaceutical Agents
2.2.4. Role of Immunotherapy
2.2.5. Mechanisms of Resistance
2.3. BRAF Gene
2.3.1. Description
2.3.2. Detection Methods
2.3.3. Pharmaceutical Agents
2.3.4. Role of Immunotherapy
2.3.5. Mechanisms of Resistance
2.4. NTRK Gene
2.4.1. Description
2.4.2. Detection Methods
2.4.3. Pharmaceutical Agents
2.4.4. Role of Immunotherapy
2.4.5. Mechanisms of Resistance
2.5. MET Gene
2.5.1. Description
2.5.2. Detection Methods
2.5.3. Pharmaceutical Agents
2.5.4. Role of Immunotherapy
2.5.5. Mechanisms of Resistance
2.6. HER2 Gene
2.6.1. Description
2.6.2. Detection Methods
2.6.3. Pharmaceutical Agents
2.6.4. Role of Immunotherapy
2.6.5. Mechanisms of Resistance
3. Discussion and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, C.S.D.; Tanoue, L.T.; Matthay, R.A. Lung Cancer: Epidemiology, Etiology, and Prevention. Clin. Chest Med. 2011, 32, 605–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2017—SEER Statistics. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/cr/1975_2017/ (accessed on 29 March 2021).
- Peters, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Shaw, A.T.; Gadgeel, S.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, D.-W.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Pérol, M.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Rosell, R.; et al. Alectinib versus Crizotinib in Untreated ALK-Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenfeld, A.; Arbour, K.; Rizvi, H.; Iqbal, A.; Gadgeel, S.; Girshman, J.; Kris, M.; Riely, G.; Yu, H.; Hellmann, M. Severe immune-related adverse events are common with sequential PD-(L)1 blockade and osimertinib. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, P.T.; Vyse, S.; Huang, P.H. Rare epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 61, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, I.; Planchard, D. ALKinhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: The latest evidence and developments. Ther. Adv. Med Oncol. 2015, 8, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.J.; Shaw, A.T. Recent Advances in Targeting ROS1 in Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1611–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergethon, K.; Shaw, A.T.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Katayama, R.; Lovly, C.M.; McDonald, N.T.; Massion, P.P.; Siwak-Tapp, C.; Gonzalez, A.; Fang, R.; et al. ROS1 Rearrangements Define a Unique Molecular Class of Lung Cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeuchi, K.; Soda, M.; Togashi, Y.; Suzuki, R.; Sakata, S.; Hatano, S.; Asaka, R.; Hamanaka, W.; Ninomiya, H.; Uehara, H.; et al. RET, ROS1 and ALK fusions in lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, C.S.; Zeng, L.; Jiang, Y.; Sadowski, H.B.; Wang, L.-H. Stat3 Plays an Important Role in Oncogenic Ros- and Insulin-like Growth Factor I Receptor-induced Anchorage-independent Growth. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 28065–28072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, K.T.; Zong, C.S.; Uttamsingh, S.; Sachdev, P.; Bhanot, M.; Le, M.-T.; Chan, J.L.-K.; Wang, L.-H. The Role of Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase, Rho Family GTPases, and STAT3 in Ros-induced Cell Transformation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 11107–11115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patil, T.; Smith, D.E.; Bunn, P.A.; Aisner, D.L.; Le, A.T.; Hancock, M.; Purcell, W.T.; Bowles, D.W.; Camidge, D.R.; Doebele, R.C. The Incidence of Brain Metastases in Stage IV ROS1-Rearranged Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer and Rate of Central Nervous System Progression on Crizotinib. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1717–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaw, A.T.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Bang, Y.-J.; Camidge, D.R.; Solomon, B.J.; Salgia, R.; Riely, G.J.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Shapiro, G.I.; Costa, D.B.; et al. Crizotinib in ROS1-Rearranged Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1963–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.-L.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Kim, D.-W.; Lu, S.; Zhou, J.; Seto, T.; Yang, J.-J.; Yamamoto, N.; Ahn, M.-J.; Takahashi, T.; et al. Phase II Study of Crizotinib in East Asian Patients With ROS1-Positive Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1405–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazières, J.; Zalcman, G.; Crinò, L.; Biondani, P.; Barlesi, F.; Filleron, T.; Dingemans, A.-M.C.; Léna, H.; Monnet, I.; Rothschild, S.I.; et al. Crizotinib Therapy for Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma and a ROS1 Rearrangement: Results From the EUROS1 Cohort. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.M.; Kim, H.R.; Lee, J.-S.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, Y.-G.; Min, Y.J.; Cho, E.K.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, B.-S.; Choi, M.Y.; et al. Open-Label, Multicenter, Phase II Study of Ceritinib in Patients With Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Harboring ROS1 Rearrangement. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2613–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolfo, C.; Ruiz, R.; Giovannetti, E.; Gil-Bazo, I.; Russo, A.; Passiglia, F.; Giallombardo, M.; Peeters, M.; Raez, L. Entrectinib: A potent new TRK, ROS1, and ALK inhibitor. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2015, 24, 1493–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Siena, S.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Barlesi, F.; Krebs, M.G.; Shaw, A.T.; de Braud, F.; Rolfo, C.; Ahn, M.-J.; Wolf, J.; et al. Entrectinib in ROS1 fusion-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Integrated analysis of three phase 1–2 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlesi, F.; Drilon, A.; De Braud, F.; Cho, B.; Ahn, M.; Siena, S.; Krebs, M.; Lin, C.; John, T.; Tan, D.; et al. Entrectinib in locally advanced or metastatic ROS1 fusion-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Integrated analysis of ALKA-372-001, STARTRK-1 and STARTRK-2. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, ii48–ii49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Solomon, B.J.; Chiari, R.; Riely, G.J.; Besse, B.; Soo, A.R.; Kao, S.; Lin, C.-C.; Bauer, T.M.; Clancy, J.S.; et al. Lorlatinib in advanced ROS1-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: A multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 1–2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1691–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, K.; Patell, R.; Rangachari, D.; Costa, D.B. Targeting ROS1 rearrangements in non-small cell lung cancer with crizotinib and other kinase inhibitors. Transl. Cancer Res. 2018, 7, S779–S786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazieres, J.; Drilon, A.; Lusque, A.; Mhanna, L.; Cortot, A.; Mezquita, L.; Thai, A.; Mascaux, C.; Couraud, S.; Veillon, R.; et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitors for patients with advanced lung cancer and oncogenic driver alterations: Results from the IMMUNOTARGET registry. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Ahn, B.-C.; Lim, S.W.; Sun, J.-M.; Kim, H.R.; Hong, M.H.; Lee, S.-H.; Ahn, J.S.; Park, K.; La Choi, Y.; et al. Characteristics and Outcome of ROS1-Positive Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients in Routine Clinical Practice. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yue, D.; Qian, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, B.; Chen, P.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C. Short-term response to immune-chemotherapy and immune features of a ceritinib-resistant patient with ROS1-rearranged lung adenocarcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e001967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gainor, J.F.; Tseng, D.; Yoda, S.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; Friboulet, L.; Lin, J.J.; Hubbeling, H.G.; Dardaei, L.; Farago, A.F.; Schultz, K.R.; et al. Patterns of Metastatic Spread and Mechanisms of Resistance to Crizotinib in ROS1-Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2017, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulligan, L.M. GDNF and the RET Receptor in Cancer: New Insights and Therapeutic Potential. Front. Physiol. 2019, 9, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosten, M.; Pützer, B.M. Mechanisms of Disease: Cancer targeting and the impact of oncogenic RET for medullary thyroid carcinoma therapy. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 2006, 3, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, T.; Ichikawa, H.; Totoki, Y.; Yasuda, K.; Hiramoto, M.; Nammo, T.; Sakamoto, H.; Tsuta, K.; Furuta, K.; Shimada, Y.; et al. KIF5B-RET fusions in lung adenocarcinoma. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leighl, N.B.; Page, R.D.; Raymond, V.M.; Daniel, D.B.; Divers, S.G.; Reckamp, K.L.; Villalona-Calero, M.A.; Dix, D.; Odegaard, J.I.; Lanman, R.B.; et al. Clinical Utility of Comprehensive Cell-free DNA Analysis to Identify Genomic Biomarkers in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Metastatic Non–small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4691–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drilon, A.; Rekhtman, N.; Arcila, M.; Wang, L.; Ni, A.; Albano, M.; Van Voorthuysen, M.; Somwar, R.; Smith, R.S.; Montecalvo, J.; et al. Cabozantinib in patients with advanced RET -rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer: An open-label, single-centre, phase 2, single-arm trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drilon, A.; Fu, S.; Patel, M.R.; Fakih, M.; Wang, D.; Olszanski, A.J.; Morgensztern, D.; Liu, S.V.; Cho, B.C.; Bazhenova, L.; et al. A Phase I/Ib Trial of the VEGFR-Sparing Multikinase RET Inhibitor RXDX-105. Cancer Discov. 2018, 9, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hida, T.; Velcheti, V.; Reckamp, K.L.; Nokihara, H.; Sachdev, P.; Kubota, T.; Nakada, T.; Dutcus, C.E.; Ren, M.; Tamura, T. A phase 2 study of lenvatinib in patients with RET fusion-positive lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 2019, 138, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subbiah, V.; Velcheti, V.; Tuch, B.; Ebata, K.; Busaidy, N.; Cabanillas, M.; Wirth, L.; Stock, S.; Smith, S.; Lauriault, V.; et al. Selective RET kinase inhibition for patients with RET-altered cancers. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1869–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainor, J.F.; Lee, D.H.; Curigliano, G.; Doebele, R.C.; Kim, D.-W.; Baik, C.S.; Tan, D.S.-W.; Lopes, G.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Cassier, P.A.; et al. Clinical activity and tolerability of BLU-667, a highly potent and selective RET inhibitor, in patients (pts) with advanced RET-fusion+ non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 9008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Oxnard, G.R.; Tan, D.S.; Loong, H.H.; Johnson, M.; Gainor, J.; McCoach, C.E.; Gautschi, O.; Besse, B.; Cho, B.C.; et al. Efficacy of Selpercatinib in RET Fusion–Positive Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, A.; Andreev-Drakhlin, A.Y.; Roszik, J.; Huang, L.; Liu, S.; Hess, K.; Cabanillas, M.; Hu, M.I.; Busaidy, N.L.; Sherman, S.I.; et al. Responsiveness to immune checkpoint inhibitors versus other systemic therapies in RET-aberrant malignancies. ESMO Open 2020, 5, e000799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisier, F.; Dubos-Arvis, C.; Viñas, F.; Doubre, H.; Ricordel, C.; Ropert, S.; Janicot, H.; Bernardi, M.; Fournel, P.; Lamy, R.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Anti–PD-1 Immunotherapy in Patients With Advanced NSCLC With BRAF, HER2, or MET Mutations or RET Translocation: GFPC 01-2018. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, T.; Pu, X.; Wang, L.; Yu, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, X.; Chen, H.; Xu, C.; Song, Z.; et al. Association between RET Fusions and Efficacy of Pemetrexed-based Chemotherapy for Patients With Advanced NSCLC in China: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. Clin. Lung Cancer 2020, 21, e349–e354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson-Taylor, S.K.; Le, A.T.; Yoo, M.; Schubert, L.; Mishall, K.M.; Doak, A.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Tan, A.-C.; Doebele, R.C. Resistance to RET-Inhibition in RET-Rearranged NSCLC Is Mediated By Reactivation of RAS/MAPK Signaling. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 1623–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Shen, T.; Mooers, B.H.M.; Hilberg, F.; Wu, J. Drug resistance profiles of mutations in the RET kinase domain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 3504–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Solomon, B.J.; Tan, L.; Lin, J.J.; Wong, S.Q.; Hollizeck, S.; Ebata, K.; Tuch, B.B.; Yoda, S.; Gainor, J.F.; Sequist, L.V.; et al. RET Solvent Front Mutations Mediate Acquired Resistance to Selective RET Inhibition in RET-Driven Malignancies. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.; Liu, S.; McCoach, C.; Zhu, V.; Tan, A.; Yoda, S.; Peterson, J.; Do, A.; Prutisto-Chang, K.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; et al. Mechanisms of resistance to selective RET tyrosine kinase inhibitors in RET fusion-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1725–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, T.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Su, B.; Zhou, C. Clinicopathologic characteristics and outcomes of Chinese patients with non-small-cell lung cancer andBRAFmutation. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, A.; Felicioni, L.; Malatesta, S.; Sciarrotta, M.G.; Guetti, L.; Chella, A.; Viola, P.; Pullara, C.; Mucilli, F.; Buttitta, F. Clinical Features and Outcome of Patients With Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Harboring BRAF Mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3574–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchard, D.; Kim, T.M.; Mazieres, J.; Quoix, E.; Riely, G.; Barlesi, F.; Souquet, P.-J.; Smit, E.F.; Groen, H.J.M.; Kelly, R.J.; et al. Dabrafenib in patients with BRAFV600E-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A single-arm, multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baik, C.S.; Myall, N.J.; Wakelee, H.A. Targeting BRAF-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: From Molecular Profiling to Rationally Designed Therapy. Oncologist 2017, 22, 786–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roviello, G.; D’Angelo, A.; Sirico, M.; Pittacolo, M.; Conter, F.U.; Sobhani, N. Advances in anti-BRAF therapies for lung cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2021, 39, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissot, C.; Couraud, S.; Tanguy, R.; Bringuier, P.-P.; Girard, N.; Souquet, P.-J. Clinical characteristics and outcome of patients with lung cancer harboring BRAF mutations. Lung Cancer 2016, 91, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardarella, S.; Ogino, A.; Nishino, M.; Butaney, M.; Shen, J.; Lydon, C.; Yeap, B.Y.; Sholl, L.M.; Johnson, B.E.; Jänne, P.A. Clinical, Pathologic, and Biologic Features Associated with BRAF Mutations in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4532–4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, G.; Liu, D.; Li, W.; Fu, X.; Liang, Y.; Li, Y.; Shi, W.; Chen, X.; Zhao, S. A meta-analysis of the association between BRAF mutation and nonsmall cell lung cancer. Medicine 2017, 96, e6552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.B.; Menzies, A.M.; Zimmer, L.; Eroglu, Z.; Ye, F.; Zhao, S.; Rizos, H.; Sucker, A.; Scolyer, R.A.; Gutzmer, R.; et al. Acquired BRAF inhibitor resistance: A multicenter meta-analysis of the spectrum and frequencies, clinical behaviour, and phenotypic associations of resistance mechanisms. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 2792–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marusiak, A.A.; Edwards, Z.C.; Hugo, W.; Trotter, E.W.; Girotti, M.R.; Stephenson, N.L.; Kong, X.; Gartside, M.G.; Fawdar, S.; Hudson, A.; et al. Mixed lineage kinases activate MEK independently of RAF to mediate resistance to RAF inhibitors. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchard, D.; Besse, B.; Groen, H.J.M.; Souquet, P.-J.; Quoix, E.; Baik, C.S.; Barlesi, F.; Kim, T.M.; Mazieres, J.; Novello, S.; et al. Dabrafenib plus trametinib in patients with previously treated BRAFV600E-mutant metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: An open-label, multicentre phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Planchard, D.; Smit, E.F.; Groen, H.J.M.; Mazieres, J.; Besse, B.; Helland, Å.; Giannone, V.; D’Amelio, A.M., Jr.; Zhang, P.; Mookerjee, B.; et al. Dabrafenib plus trametinib in patients with previously untreated BRAFV600E-mutant metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: An open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudnik, E.; Peled, N.; Nechushtan, H.; Wollner, M.; Onn, A.; Agbarya, A.; Moskovitz, M.; Keren, S.; Popovits-Hadari, N.; Urban, D.; et al. BRAF Mutant Lung Cancer: Programmed Death Ligand 1 Expression, Tumor Mutational Burden, Microsatellite Instability Status, and Response to Immune Check-Point Inhibitors. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rihawi, K.; Giannarelli, D.; Galetta, D.; Delmonte, A.; Giavarra, M.; Turci, D.; Garassino, M.; Tiseo, M.; Barbieri, F.; Panni, S.; et al. BRAF Mutant NSCLC and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Results From a Real-World Experience. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, e57–e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Offin, M.; Pak, T.; Mondaca, S.; Montecalvo, J.; Rekhtman, N.; Halpenny, D.; Wu, S.; Kris, M.; Paik, P.; Riely, G.; et al. P1.04-39 Molecular Characteristics, Immunophenotype, and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Response in BRAF Non-V600 Mutant Lung Cancers. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, S455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okimoto, R.A.; Lin, L.; Olivas, V.; Chan, E.; Markegard, E.; Rymar, A.; Neel, D.; Chen, X.; Hemmati, G.; Bollag, G.; et al. Preclinical efficacy of a RAF inhibitor that evades paradoxical MAPK pathway activation in protein kinaseBRAF-mutant lung cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 13456–13461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Passiglia, F.; Caparica, R.; Giovannetti, E.; Giallombardo, M.; Listi, A.; Diana, P.; Cirrincione, G.; Caglevic, C.; Raez, L.E.; Russo, A.; et al. The potential of neurotrophic tyrosine kinase (NTRK) inhibitors for treating lung cancer. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2016, 25, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaishnavi, A.; Capelletti, M.; Le, A.T.; Kako, S.; Butaney, M.; Ercan, D.; Mahale, S.; Davies, K.D.; Aisner, D.L.; Pilling, A.B.; et al. Oncogenic and drug-sensitive NTRK1 rearrangements in lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1469–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gatalica, Z.; Xiu, J.; Swensen, J.; Vranic, S. Molecular characterization of cancers with NTRK gene fusions. Mod. Pathol. 2019, 32, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Xue, X.; Ding, H.; Ou, Q.; Wu, X.; Nagasaka, M.; Shao, Y.W.; Hu, X.; Ou, S.-H.I. Evidence of NTRK1 Fusion as Resistance Mechanism to EGFR TKI in EGFR+ NSCLC: Results From a Large-Scale Survey of NTRK1 Fusions in Chinese Patients with Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2020, 21, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farago, A.F.; Taylor, M.S.; Doebele, R.C.; Zhu, V.W.; Kummar, S.; Spira, A.I.; Boyle, T.A.; Haura, E.B.; Arcila, M.E.; Benayed, R.; et al. Clinicopathologic Features of Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Harboring an NTRK Gene Fusion. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.S.; DuBois, S.G.; Kummar, S.; Farago, A.F.; Albert, C.M.; Rohrberg, K.S.; van Tilburg, C.M.; Nagasubramanian, R.; Berlin, J.D.; Federman, N.; et al. Larotrectinib in patients with TRK fusion-positive solid tumours: A pooled analysis of three phase 1/2 clinical trials. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolfo, C.D.; De Braud, F.G.; Doebele, R.C.; Drilon, A.E.; Siena, S.; Patel, M.; Cho, B.C.; Liu, S.V.; Ahn, M.-J.; Chiu, C.-H.; et al. Efficacy and safety of entrectinib in patients (pts) with NTRK-fusion positive (NTRK-fp) solid tumors: An updated integrated analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, D.S.; Wong, M.; Mayoh, C.; Kumar, A.; Tsoli, M.; Mould, E.; Tyrrell, V.; Khuong-Quang, D.-A.; Pinese, M.; Gayevskiy, V.; et al. Brief Report: Potent clinical and radiological response to larotrectinib in TRK fusion-driven high-grade glioma. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 693–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skoulidis, F.; Goldberg, M.E.; Greenawalt, D.M.; Hellmann, M.D.; Awad, M.M.; Gainor, J.F.; Schrock, A.B.; Hartmaier, R.J.; Trabucco, S.E.; Gay, L.; et al. STK11/LKB1 Mutations and PD-1 Inhibitor Resistance in KRAS-Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuse, M.J.; Okada, K.; Oh-Hara, T.; Ogura, H.; Fujita, N.; Katayama, R. Mechanisms of Resistance to NTRK Inhibitors and Therapeutic Strategies in NTRK1-Rearranged Cancers. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 2130–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weir, B.A.; Woo, M.S.; Getz, G.; Perner, S.; Ding, L.; Beroukhim, R.; Lin, W.M.; Province, M.A.; Kraja, A.; Johnson, L.A.; et al. Characterizing the cancer genome in lung adenocarcinoma. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 450, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Newton, R.C.; Scherle, P.A. Developing c-MET pathway inhibitors for cancer therapy: Progress and challenges. Trends Mol. Med. 2010, 16, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 511, 543–550. [CrossRef]
- Frampton, G.M.; Ali, S.M.; Rosenzweig, M.; Chmielecki, J.; Lu, X.; Bauer, T.M.; Akimov, M.; Bufill, J.A.; Lee, C.; Jentz, D.; et al. Activation of MET via Diverse Exon 14 Splicing Alterations Occurs in Multiple Tumor Types and Confers Clinical Sensitivity to MET Inhibitors. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schrock, A.B.; Frampton, G.M.; Suh, J.; Chalmers, Z.R.; Rosenzweig, M.; Erlich, R.L.; Halmos, B.; Goldman, J.; Forde, P.; Leuenberger, K.; et al. Characterization of 298 Patients with Lung Cancer Harboring MET Exon 14 Skipping Alterations. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 1493–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Awad, M.M.; Oxnard, G.R.; Jackman, D.M.; Savukoski, D.O.; Hall, D.; Shivdasani, P.; Heng, J.C.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Jänne, P.A.; Verma, S.; et al. MET Exon 14 Mutations in Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Are Associated With Advanced Age and Stage-Dependent MET Genomic Amplification and c-Met Overexpression. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Awad, M.M.; Leonardi, G.C.; Kravets, S.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Drilon, A.; Noonan, S.A.; Camidge, D.R.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Costa, D.B.; Gadgeel, S.M.; et al. Impact of MET inhibitors on survival among patients with non-small cell lung cancer harboring MET exon 14 mutations: A retrospective analysis. Lung Cancer 2019, 133, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camidge, D.R.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Shapiro, G.; Otterson, G.A.; Villaruz, L.C.; Villalona-Calero, M.A.; Iafrate, A.J.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Dacic, S.; Cardarella, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of crizotinib in patients with advanced c-MET-amplified non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 8001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.E.; Camidge, D.R.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Clark, J.W.; Socinski, M.A.; Weiss, J.; Riely, G.J.; Winter, M.; Wang, S.C.; Monti, K.; et al. Efficacy and safety of crizotinib in patients (pts) with advanced MET exon 14-altered non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, M.; Berardi, R.; Lim, W.-T.; de Jonge, M.; Bauer, T.; Azaro, A.; Gottfried, M.; Han, J.-Y.; Lee, D.; Wollner, M.; et al. Molecular correlates of response to capmatinib in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Clinical and biomarker results from a phase I trial. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J.; Seto, T.; Han, J.-Y.; Reguart, N.; Garon, E.B.; Groen, H.J.; Tan, D.S.; Hida, T.; de Jonge, M.; Orlov, S.V.; et al. Capmatinib inMETExon 14–Mutated orMET-Amplified Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 944–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabari, J.; Leonardi, G.; Shu, C.; Umeton, R.; Montecalvo, J.; Ni, A.; Chen, R.; Dienstag, J.; Mrad, C.; Bergagnini, I.; et al. PD-L1 expression, tumor mutational burden, and response to immunotherapy in patients with MET exon 14 altered lung cancers. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 2085–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffmann-Guerrero, D.; Tufman, A.; Kahnert, K.; Bollmann, B.A.; Reu, S.; Syunyaeva, Z.; Schneider, C.; Manapov, F.; Huber, R.M.; Golpon, H. Response to Checkpoint Inhibition in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Molecular Driver Alterations. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2020, 43, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayenga, M.; Assié, J.-B.; Monnet, I.; Massiani, M.-A.; Tabeze, L.; Friard, S.; Fraboulet, S.; Métivier, A.-C.; Chouaïd, C.; Zemoura, L.; et al. Durable responses to immunotherapy of non-small cell lung cancers harboring MET exon-14–skipping mutation: A series of 6 cases. Lung Cancer 2020, 150, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recondo, G.; Bahcall, M.; Spurr, L.F.; Che, J.; Ricciuti, B.; Leonardi, G.C.; Lo, Y.-C.; Li, Y.Y.; Lamberti, G.; Nguyen, T.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Acquired Resistance to MET Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Patients with MET Exon 14–Mutant NSCLC. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2615–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.; Alex, D.; Xu, Z. MET Exon 14 Skipping Alterations in Non-small Cell Lung Carcinoma—Current Understanding and Therapeutic Advances. Oncol. Hematol. Rev. (US) 2021, 16, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamme, P.; Fernandes, M.; Copin, M.-C.; Descarpentries, C.; Escande, F.; Morabito, A.; Grégoire, V.; Jamme, M.; Baldacci, S.; Tulasne, D.; et al. Alterations in the PI3K Pathway Drive Resistance to MET Inhibitors in NSCLC Harboring MET Exon 14 Skipping Mutations. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Shao, X.; Gao, W.; Bai, J.; Wang, R.; Huang, P.; Yin, Y.; Liu, P.; Shu, Y. The Role of Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 as a Prognostic Factor in Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis of Published Data. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 1922–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, B.T.; Ross, D.S.; Aisner, D.L.; Chaft, J.E.; Hsu, M.; Kako, S.L.; Kris, M.G.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Arcila, M.E. HER2 Amplification and HER2 Mutation Are Distinct Molecular Targets in Lung Cancers. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Sun, Y.; Fang, R.; Han, X.; Luo, X.; Wang, R.; Pan, Y.; Hu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Pao, W.; et al. Lung Adenocarcinomas with HER2-Activating Mutations Are Associated with Distinct Clinical Features and HER2/EGFR Copy Number Gains. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pillai, R.N.; Behera, M.; Berry, L.D.; Rossi, M.R.; Kris, M.G.; Johnson, B.E.; Bunn, P.A.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Khuri, F.R. HER2 mutations in lung adenocarcinomas: A report from the Lung Cancer Mutation Consortium. Cancer 2017, 123, 4099–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kris, M.G.; Camidge, D.R.; Giaccone, G.; Hida, T.; Li, B.T.; O’Connell, J.; Taylor, I.; Zhang, H.; Arcila, M.E.; Goldberg, Z.; et al. Targeting HER2 aberrations as actionable drivers in lung cancers: Phase II trial of the pan-HER tyrosine kinase inhibitor dacomitinib in patients with HER2-mutant or amplified tumors. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1421–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Grève, J.; Moran, T.; Graas, M.-P.; Galdermans, D.; Vuylsteke, P.; Canon, J.-L.; Schallier, D.; Decoster, L.; Teugels, E.; Massey, D.; et al. Phase II study of afatinib, an irreversible ErbB family blocker, in demographically and genotypically defined lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer 2015, 88, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazières, J.; Barlesi, F.; Filleron, T.; Besse, B.; Monnet, I.; Beau-Faller, M.; Peters, S.; Dansin, E.; Früh, M.; Pless, M.; et al. Lung cancer patients with HER2 mutations treated with chemotherapy and HER2-targeted drugs: Results from the European EUHER2 cohort. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.T.; Shen, R.; Buonocore, D.; Olah, Z.T.; Ni, A.; Ginsberg, M.S.; Ulaner, G.A.; Offin, M.; Feldman, D.; Hembrough, T.; et al. Ado-Trastuzumab Emtansine for Patients With HER2-Mutant Lung Cancers: Results from a Phase II Basket Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2532–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Gao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Shu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Fang, J.; et al. Pyrotinib in HER2-Mutant Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma After Platinum-Based Chemotherapy: A Multicenter, Open-Label, Single-Arm, Phase II Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2753–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socinski, M.; Cornelissen, R.; Garassino, M.; Clarke, J.; Tchekmedyian, N.; Molina, J.; Goldman, J.; Bhat, G.; Lebel, F.; Le, X. LBA60 ZENITH20, a multinational, multi-cohort phase II study of poziotinib in NSCLC patients with EGFR or HER2 exon 20 insertion mutations. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, S1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, W.-C.V.; Feldman, D.L.; Buonocore, D.J.; Brzostowski, E.B.; Rizvi, H.; Plodkowski, A.J.; Ni, A.; Sabari, J.K.; Offin, M.D.; Kris, M.G.; et al. PD-L1 expression, tumor mutation burden and response to immune checkpoint blockade in patients with HER2-mutant lung cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 9060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulidis, F.; Heymach, J.V. Co-occurring genomic alterations in non-small-cell lung cancer biology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearden, S.; Stevens, J.; Wu, Y.-L.; Blowers, D. Mutation incidence and coincidence in non small-cell lung cancer: Meta-analyses by ethnicity and histology (mutMap). Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2371–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, S.; Shen, R.; Ang, D.C.; Johnson, M.L.; D’Angelo, S.P.; Paik, P.K.; Brzostowski, E.B.; Riely, G.J.; Kris, M.G.; Zakowski, M.F.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology of EGFR and KRAS Mutations in 3,026 Lung Adenocarcinomas: Higher Susceptibility of Women to Smoking-Related KRAS-Mutant Cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 6169–6177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrer, I.; Zugazagoitia, J.; Herbertz, S.; John, W.; Paz-Ares, L.; Schmid-Bindert, G. KRAS-Mutant non-small cell lung cancer: From biology to therapy. Lung Cancer 2018, 124, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, D.S.; Fakih, M.G.; Strickler, J.H.; Desai, J.; Durm, G.A.; Shapiro, G.I.; Falchook, G.S.; Price, T.J.; Sacher, A.; Denlinger, C.S.; et al. KRASG12C Inhibition with Sotorasib in Advanced Solid Tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
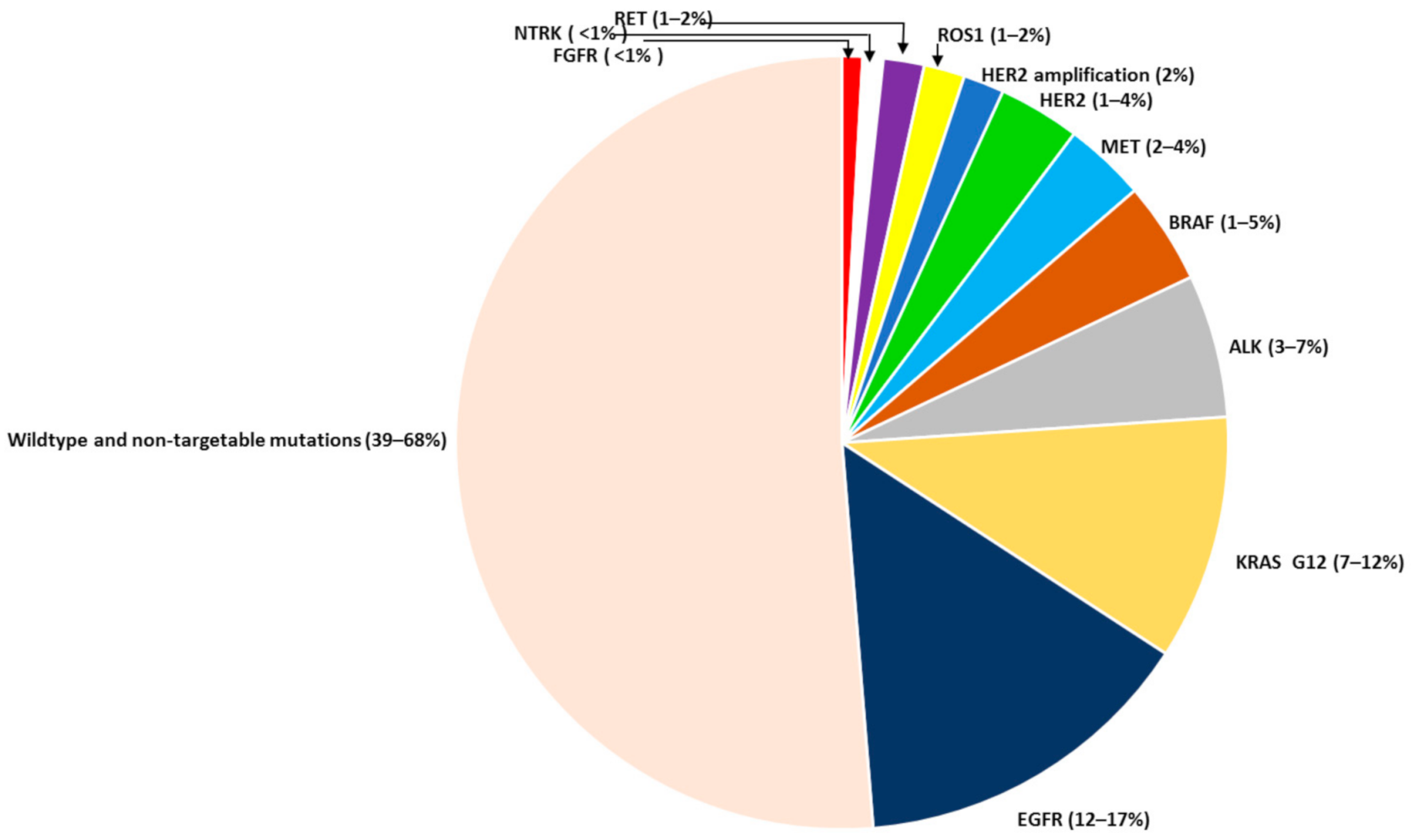
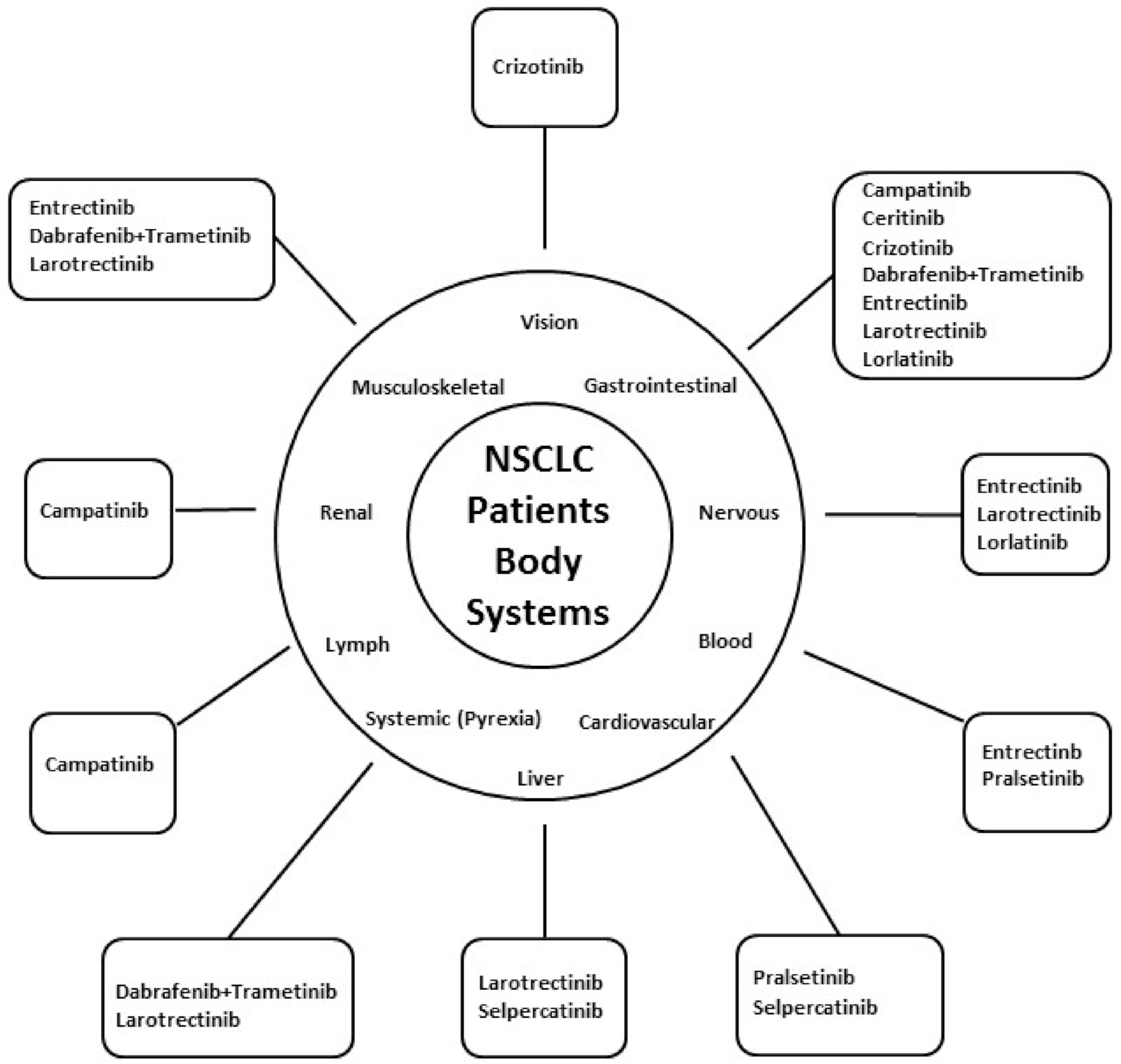
| Agent | Target | Approved for | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ceritinib | ALK | ROS1 rearranged | 2014 |
| Crizotinib | ALK, MET | ROS1 rearranged, MET mutated | 2016 |
| Entrectinib | TRK, ROS, ALK | ROS1 rearranged, NTRK fused | 2019 |
| Dabrafenib | BRAF | BRAF mutated (In combination with trametinib) | 2015 |
| Trametinib | MEK1/2 | BRAF mutated (In combination with dabrafenib) | 2015 |
| Larotrectinib | NTRK | NTRK fused | 2018 |
| Capmatinib | MET | MET mutated | 2020 |
| Selpercatinib | RET | RET mutated | 2020 |
| Pralsetinib | RET | RET mutated | 2020 |
| Cabozantinib | VEGFR2, PDGFR, KIT | RET mutated | 2020 |
| Lorlatinib | ALK, ROS1 | ROS1 rearranged | 2018 |
| Gene Alterations | Pharmaceutical Agent | Clinical Trial No. |
|---|---|---|
| ROS1 | Lorlatinib | NCT01970865 |
| Entrectinib | NCT02568267 | |
| Cabozantinib | NCT01639508 | |
| DS-6051b | NCT02279433 | |
| TPX-0005 | NCT03093116 | |
| RET | Cabozantinib | NCT01639508, NCT04131543 |
| Alectinib | NCT03445000, NCT03178552, NCT02183883 | |
| TPX-0046 | NCT04161391 | |
| BOS172738 | NCT03780517 | |
| BRAF | Dabrafenib + Trametinib Vemurafenib Encorafenib + Binimetinib | NCT03543306, NCT01336634 NCT04302025 NCT04526782 |
| NTRK | Cabozantinib | NCT01639508 |
| LOXO-195 | NCT03215511 | |
| Repotrectinib | NCT03093116 | |
| DS-6051b | NCT02675491 | |
| PLX7486 | NCT01804530 | |
| Merestinib | NCT02920996 | |
| VMD-928 | NCT03556228 | |
| MGCD516 | NCT02219711 | |
| ONO-7579 | NCT03182257 | |
| MET | Crizotinib | NCT00585195, NCT02465060, NCT02499614, NCT02664935, NCT01121575, NCT00965731 |
| Cabozantinib | NCT00596648, NCT03911193, NCT01639508, NCT02132598, NCT03468985 | |
| Merestinib | NCT02920996 | |
| Glesatinib | NCT02954991, NCT02544633 | |
| Foretinib | NCT02034097 | |
| Capmatinib | NCT03693339, NCT02750215, NCT02468661, NCT03647488, NCT02414139, NCT01911507, NCT02323126, NCT02335944, NCT02276027 | |
| Tepotinib | NCT01982955. NCT02864992, NCT03940703 | |
| Savolitinib | NCT03944772, NCT03778229, NCT02117167, NCT02897479, NCT02143466, NCT02374645 | |
| Tivantinib | NCT01251796, NCT01069757 | |
| SAR125844 | NCT02435121 | |
| Onartuzumab | NCT02031744, NCT01519804, NCT01496742, NCT01887886 | |
| Telisotuzumab | NCT03574753 | |
| JNJ-61186372 | NCT02609776 | |
| Ficlatuzumab | NCT01039948 | |
| HER2 | Trastuzumab-deruxtecan | NCT04644237 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taha, T.; Khoury, R.; Brenner, R.; Nasrallah, H.; Shofaniyeh, I.; Yousef, S.; Agbarya, A. Treatment of Rare Mutations in Patients with Lung Cancer. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9050534
Taha T, Khoury R, Brenner R, Nasrallah H, Shofaniyeh I, Yousef S, Agbarya A. Treatment of Rare Mutations in Patients with Lung Cancer. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(5):534. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9050534
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaha, Tarek, Rasha Khoury, Ronen Brenner, Haitam Nasrallah, Irena Shofaniyeh, Samih Yousef, and Abed Agbarya. 2021. "Treatment of Rare Mutations in Patients with Lung Cancer" Biomedicines 9, no. 5: 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9050534







