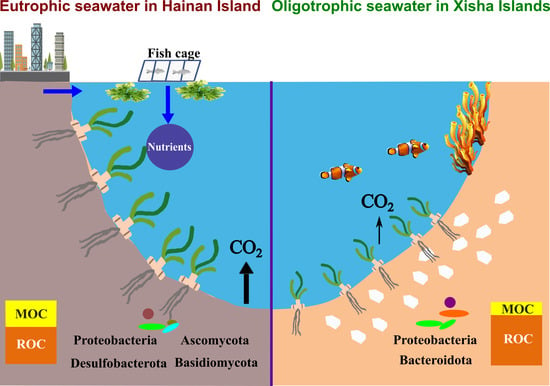
Sediment Carbon Sequestration and Driving Factors in Seagrass Beds from Hainan Island and the Xisha Islands
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Regions
2.2. Sampling and Sample Preparation
2.3. Determination of Seawater Nutrients, Sediment Characteristics and Carbon Stocks
2.4. Analysis of Microbial Enzymes
2.5. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification
2.6. Bioinformatics Analyses
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Seawater Nutrients
3.2. Sediment Characteristics and Carbon Stocks
3.3. Seagrass Biomass and Biochemical Properties
3.4. Sediment Enzyme Activities
3.5. Microbial Community Diversities, Compositions and Distributions
3.6. Bacterial Putative Metabolic Functions Involved in Carbon Cycle
3.7. The Key Environmental Drivers of Sediment Cstocks
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duarte, C.M. The future of seagrass meadows. Environ. Conserv. 2002, 29, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.L.; Lin, W.J.; Liu, P.J.; Shao, K.T.; Lin, H.J. Highly productive tropical seagrass beds support diverse consumers and a large organic carbon pool in the sediments. Diversity 2021, 13, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrish, J.D. Fish communities of interacting shallow-water habitats in tropical oceanic regions. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1989, 58, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, R.; Jenkins, G.; Loneragan, N. Seagrass dynamics and fisheries sustainability. In Seagrass in Australia; Strategic Review and Development of an R&D Plan; Butler, A., Jernakoff, P., Eds.; CSIRO Publishing: Sydney, Australia, 1999; pp. 25–62. [Google Scholar]
- Orth, R.J.; Carruthers, T.J.B.; Dennison, W.C.; Duarte, C.M.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Heck, K.L., Jr.; Hughes, A.R.; Kendrick, G.A.; Kenworthy, W.J.; Olyarnik, S.; et al. A global crisis for seagrass ecosystems. BioScience 2006, 56, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrinao, S.; Chiara, F.; Antonia, M. Sedimentation rates and erosion processes in the lagoon of Venice. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casal-Porras, I.; de los Santos, C.B.; Martins, M.; Santos, R.; Pérez-Lloréns, J.L.; Brun, F.G. Sedimentary organic carbon and nitrogen stocks of intertidal seagrass meadows in a dynamic and impacted wetland: Effects of coastal infrastructure constructions and meadow establishment time. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 322, 115841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.J.; Li, L.L.; Fang, Y.; Lin, J.Z.; Liu, S.L.; Wu, Y.C.; Huang, X.P. Eutrophication reduced the release of dissolved organic carbon from tropical seagrass roots through exudation and decomposition. Mar. Environ. Res. 2022, 179, 105703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nellemann, C.; Corcoran, E.; Duarte, C.M.; Valdes, L.; De Young, C.; Fonseca, L.; Grimsditch, G. Blue Carbon: The Role of Healthy Oceans in Binding Carbon. A Rapid Response Assessment; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya; GRID-Arendal: Arendal, Norway, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Garrard, S.L.; Beaumont, N.J. The effect of ocean acidification on carbon storage and sequestration in seagrass beds; a global and UK context. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 86, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, H.; Beggins, J.; Duarte, C.M.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Holmer, M.; Marbà, N.; Middelburg, J.J. Seagrass sediments as a global carbon sink: Isotopic constraints. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2010, 24, 6696–6705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, E.; Chmura, G.L.; Bouillon, S.; Salm, R.; Björk, M.; Duarte, C.M.; Lovelock, C.E.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Silliman, B.R. A blueprint for blue carbon: Toward an improved understanding of the role of vegetated coastal habitats in sequestering CO2. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 9, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M.; Losada, I.J.; Hendriks, I.E.; Mazarrasa, I.; Marbà, N. The role of coastal plant communities for climate change mitigation and adaptation. Nat. Clim. Chang 2013, 3, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, J.; Sutton-Grier, A.; Herr, D.; Kleypas, J.; Landis, E.; Mcleod, E. Clarifying the role of coastal and marine systems in climate mitigation. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2017, 15, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourqurean, J.W.; Duarte, C.M.; Kennedy, H.; Marbà, N.; Holmer, M.; Mateo, M.A.; Apostolaki, E.T.; Kendrick, G.A.; Krause-Jensen, D.; McGlathery, K.J.; et al. Seagrass ecosystems as a globally significant carbon stock. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M.; Kennedy, H.; Marbà, N.; Hendriks, I. Assessing the capacity of seagrass meadows for carbon burial: Current limitations and future strategies. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2013, 83, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Lee, C.L.; Chung, C.Y.; Hsiao, S.C.; Lin, H.J. Carbon budgets of multispecies seagrass beds at Dongsha Island in the South China Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 106, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, M.A.C.; Raymond, D.W.; Chris, B.J. Environmental drivers of sediment carbon storage in temperate seagrass meadows. Hydrobiologia 2020, 847, 1773–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuellar-Martinez, T.; Ruiz-Fernández, A.C.; Sanchez-Cabeza, J.A.; Pérez-Bernal, L.H.; Sandoval-Gil, J. Relevance of carbon burial and storage in two contrasting blue carbon ecosystems of a north-east Pacific coastal lagoon. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 675, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potouroglou, M.; Whitlock, D.; Milatovic, L.; MacKinnon, G.; Kennedy, H.; Diele, K.; Huxham, M. The sediment carbon stocks of intertidal seagrass meadows in Scotland. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 258, 107442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, J.D.; Chambers, P.A.; James, W.F.; Koch, E.W.; Westlake, D.F. The interaction between water movement, sediment dynamics and submersed macrophytes. Hydrobiologia 2001, 444, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacia, E.; Duarte, C.M.; Middelburg, J.J. Carbon and nutrient deposition in the Mediterranean seagrass (Posidonia oceanica). Limnol. Oceanogr. 2002, 47, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoni, V.; Vela, A.; Pasqualini, V.; Pergent-Martini, C.; Pergent, G. Effects of experimental reduction of light and nutrient enrichments (N and P) on seagrasses: A review. Aquat. Conserv. 2008, 18, 202–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Huang, X.; Zhang, J. Effect of nitrate enrichment and salinity reduction on the seagrass Thalassia hemprichii previously grown in low light. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2013, 443, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, M.; Deyanova, D.; Gütschow, S.; Asplund, M.E.; Lyimo, L.D.; Karamfilov, V.; Santos, R.; Björk, M.; Gullström, M. Sediment properties as important predictors of carbon storage in Zostera marina meadows: A comparison of four european areas. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaine, S.; Mariotti, A.; Abbadie, L. The priming effect of organic matter: A question of microbial competition? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carney, K.M.; Hungate, B.A.; Drake, B.G.; Megonigal, J.P. Altered soil microbial community at elevated CO2 leads to loss of soil carbon. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4990–4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, O.; Ricart, A.M.; Lavery, P.S.; Mateo, M.A.; Arias-Ortiz, A.; Masque, P.; Steven, A.; Duarte, C.M. Key biogeochemical factors affecting soil carbon storage in Posidonia meadows. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 4581–4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samper-Villarreal, J.; Mumby, P.J.; Saunders, M.I.; Roelfsema, C.; Lovelock, C.E. Seagrass organic carbon stocks show minimal variation over short time scales in a heterogenous subtropical seascape. Estuar. Coast. 2018, 41, 1732–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, L.G.; Guevara, R.; Boyer, J.N.; Troxler, T.G.; Davis, S.E. Effects of salinity and inundation on microbial community structure and function in a mangrove peat soil. Wetlands 2016, 36, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.J.; Li, A.; Yang, Y.F.; Li, G.H.; Zhang, F. Soil organic carbon stability under natural and anthropogenic-induced perturbations. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 205, 103199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca, A.; Cetin, S.C.; Turgay, O.C.; Kizilkaya, R. Soil enzymes as indication of soil quality. In Soil Enzymology; Shukla, G., Varma, A.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 119–148. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Hou, L.; Liu, M.; Lin, X.; Li, Y.; Li, S. Primary effects of extracellular enzyme activity and microbial community on carbon and nitrogen mineralization in estuarine and tidal wetlands. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 2895–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, W.B.; Cifuentes, L.A.; Kaldy, J.E. Stable carbon isotope evidence for coupling between sedimentary bacteria and seagrasses in a sub-tropical lagoon. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 255, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmer, M.; Duarte, C.M.; Boschker, H.T.S. Carbon cycling and bacterial carbon sources in pristine and impacted Mediterranean seagrass sediments. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 36, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, W.; Folman, L.B.; Summerbell, R.C.; Boddy, L. Living in a fungal world: Impact of fungi on soil bacterial niche development. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 795–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.J.; Liu, S.L.; Zhang, J.P.; Zhao, C.Y.; Wu, Y.C.; Yua, S.; Zhanga, X.; Huangd, C.; Huang, X.P.; Kumare, M. Newly discovered seagrass beds and their potential for blue carbon in the coastal seas of Hainan Island, South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 125, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.J.; Zhao, C.Y.; Yu, S.; Liu, S.L.; Cui, L.J.; Wu, Y.C.; Fang, Y.; Huang, X.P. Contrasting root length, nutrient content and carbon sequestration of seagrass growing in offshore carbonate and onshore terrigenous sediments in the South China Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.J.; Chen, S.Q.; Cai, Z.F.; Shen, J.; Luo, L.Z.; Wang, D.R. Distribution and restoration of seagrass beds in Hainan Island. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2021, 40, 542–549. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xing, F.W.; Li, Z.X.; Ye, H.G.; Chen, B.H.; Wu, D.L. Floristic geography of Xisha Islands in China. Trop. Geogr. 1993, 13, 250–257. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Howard, J.; Hoyt, S.; Isensee, K.; Telszewski, M.; Pidgeon, E. Coastal Blue Carbon: Methods for Assessing Carbon Stocks and Emissions Factors in Mangroves, Tidal Salt Marshes, and Seagrasses; Conservation International: Arlington, VA, USA; Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Paris, France; International Union for Conservation of Nature: Gland, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.; Ryden, J.C.; Whitchead, D.C. Some relationships between denitrification potential and fractions of organic carbon in air-dried and field-moist soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1988, 20, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, G.J.; Lefroy, R.D.B.; Lisle, L. Soil carbon fractions based on their degree of oxidation, and the development of a carbon management index for agricultural systems. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1995, 46, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Deng, H.; Wang, H.L.; Zhang, B. Vegetation type affects soil enzyme activities and microbial functional diversity following re-vegetation of a severely eroded red soil in sub-tropical China. Catena 2014, 115, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.X.; Yang, W.Y.; Wu, M. Seasonal dynamics of soil labile organic carbon and enzyme activities in relation to vegetation types in Hangzhou Bay tidal flat wetland. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Han, Q.Y.; Shi, Y.F. Phosphorus forms in the sediment of seagrass meadows affected mainly by fungi rather than bacteria: A preliminary study based on 31P-NMR and high-throughput sequencing. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. St. 2020, 49, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.N.; Park, J.M.; Im, S.O.; Jawad, L.A. Influences of diel and tidal cycles on fish assemblage in eelgrass (Zostera marina) bed of southern Korea during autumn. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2018, 37, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.L.; Jiang, Z.J.; Wu, Y.C.; Deng, Y.Q.; Chen, Q.M.; Zhao, C.Y.; Cui, L.J.; Huang, X.P. Macroalgae bloom decay decreases the sediment organic carbon sequestration potential in tropical seagrass meadows of the South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 138, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louca, S.; Parfrey, L.W.; Doebeli, M. Decoupling function and taxonomy in the global ocean microbiome. Science 2016, 353, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullström, M.; Lyimo, L.D.; Dahl, M.; Samuelsson, G.S.; Eggertsen, M.; Anderberg, E.; Rasmusson, L.M.; Linderholm, H.W.; Knudby, A.; Bandeira, S.; et al. Blue carbon storage in tropical seagrass meadows relates to carbonate stock dynamics, plant-sediment processes, and landscape context: Insights from the western indian ocean. Ecosystems 2018, 21, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevathan-Tackett, S.M.; Kelleway, J.J.; Macreadie, P.I.; Beardall, J.; Ralph, P.; Bellgrove, A. Comparison of marine macrophytes for their contributions to blue carbon sequestration. Ecology 2016, 96, 3034–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macreadie, P.I.; Allen, K.; Kelaher, B.P.; Ralph, P.J.; Skilbeck, C.G. Paleoreconstruction of estuarine sediments reveal human-induced weakening of coastal carbon sink. Glob. Change Biol. 2012, 8, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.J.; Liu, S.L.; Zhang, J.P.; Wu, Y.C.; Zhao, C.Y.; Lian, Z.L.; Huang, X.P. Eutrophication indirectly reduced carbon sequestration in a tropical seagrass bed. Plant Soil 2018, 426, 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.E.; Lacey, E.A.; Decker, R.A.; Crooks, S.; Fourqurean, J.W. Carbon storage in seagrass beds of Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. Estuar. Coasts 2015, 38, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, A.R.; Fourqurean, J.W. Carbon storage in seagrass soils: Long-term nutrient history exceeds the effects of near-term nutrient enrichment. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.P.; Huang, X.P.; Jiang, Z.J. Physiological responses of the seagrass Thalassia hemprichii (Ehrenb.) Aschers as indicators of nutrient loading. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 83, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Invers, O.; Kraemer, G.P.; Perez, M.; Romero, J. Effects of nitrogen addition on nitrogen metabolism and carbon reserves in the temperate seagrass Posidonia oceanica. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 303, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazarrasa, I.; Samper-Villarreal, J.; Serrano, O.; Lavery, P.S.; Lovelock, C.E.; Marba, N.; Duarte, C.M. Habitat characteristics provide insights of carbon storage in seagrass meadows. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 134, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avena, M.J.; Koopal, L.K. Kinetics of humic acids adsorption at solid-water interfaces. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 2739–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.Z. Environmental hydrologic features of the Xisha Archipelago. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Sunyatseni 1996, S1, 19–25. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Enriquez, S.; Duarte, C.M.; Sand-Jensen, K. Patterns in decomposition rates among photosynthetic organisms: The importance of detritus C:N:P content. Oecologia 1993, 94, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M. Carbon Storage in the Seagrass Sediments of Guangxi, China. Master’s Thesis, Guangxi Normal University, Guangxi, China, 2018. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Neff, J.C.; Townsend, A.R.; Gleixner, G.; Lehman, S.J.; Turnbull, J.; Bowman, W.D. Variable effects of nitrogen additions on the stability and turnover of soil carbon. Nature 2002, 419, 915–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Lauber, C.L.; Ramirez, K.S.; Zaneveld, J.; Bradford, M.A.; Knight, R. Comparative metagenomics, phylogenetic, and physiological analyses of soil microbial communities across nitrogen gradients. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenlord, S.D.; Freedman, Z.; Zak, D.R.; Xue, K.; He, Z.; Zhou, J.Z. Microbial mechanisms mediating increased soil C storage under elevated atmospheric N deposition. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldrop, M.P.; Zak, D.R.; Sinsabaugh, R.L. Microbial community response to nitrogen deposition in northern forest ecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2004, 36, 1443–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.; Anderson, I.C.; Singh, B.K. Microbial modulators of soil carbon storage: Integrating genomic an metabolic knowledge for global prediction. Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Xu, J.; Li, X.F.; Li, R.H.; Li, Q. Links of extracellular enzyme activities, microbial metabolism, and community composition in the river-impacted coastal waters. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeo. 2019, 124, 3507–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, M.; Okuyama, M.; Tanzawa, F.; Mori, H.; Kitago, Y.; Watanabe, N.; Kimura, A.; Tanaka, I.; Yao, M. Structural and functional analysis of a glycoside hydrolase family 97 enzyme from Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 36328–36337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raskin, L.; Rittmann, B.E.; Stahl, D.A. Competition and coexistence of sulfate-reducing and methanogenic populations in anaerobic biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 3847–3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.D.; Fang, J.; Zhu, X.S.; Spencer, R.G.M.; Álvarez-Salgado, X.A.; Deng, Y.C.; Huang, T.; Yang, H.; Huang, C.C. Properties of sediment dissolved organic matter respond to eutrophication and interact with bacterial communities in a plateau lake. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 301, 118996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macreadie, P.I.; Atwood, T.B.; Seymour, J.R.; Schmitz Fontes, M.L.; Sanderman, J.; Nielsen, D.A.; Connolly, R.M. Vulnerability of seagrass blue carbon to microbial attack following exposure to warming and oxygen. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, M.S.; Rousk, J. Considering fungal: Bacterial dominance in soils-methods, controls, and ecosystem implications. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1385–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Heijden, M.G.A.; Bardgett, R.D.; van Straalen, N.M. The unseen majority: Soil microbes as drivers of plant diversity and productivity in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, A.D.M.; Boddy, L. Wood Decomposition: Its Biology and Ecology; John Wiley: Chichester, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Worrall, J.J.; Anagnost, S.E.; Zabel, R.D. Comparison of wood decay among diverse lignicolous fungi. Mycologia 1997, 89, 199–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynd, L.R.; Weimer, P.J.; van Zyl, W.H.; Pretorius, I.S. Microbial cellulose utilization: Fundamentals and biotechnology. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2002, 66, 506–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güsewell, S.; Gessner, M.O. N:P ratios influence litter decomposition and colonization by fungi and bacteria in microcosms. Funct. Ecol. 2009, 23, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Guo, X.H.; Zheng, P.F.; Zou, S.B.; Li, G.H.; Gong, J. Distinct seasonality of chytrid-dominated benthic fungal communities in the neritic oceans (Bohai Sea and North Yellow Sea). Fungal Ecol. 2017, 30, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagami, M.; Miki, T.; Takimoto, G. Mycoloop: Chytrids in aquatic food webs. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, F.H.; Kagami, M.; Lefevre, E.; Sime-Ngando, T. The ecology of chytrids in aquatic ecosystems: Roles in food web dynamics. Fung. Biol. Rev. 2008, 22, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurber, R.V.; Willner-Hall, D.; Rodriguez-Mueller, B.; Desnues, C.; Edwards, R.A.; Angly, F.; Dinsdale, E.; Kelly, L.; Rohwer, F. Metagenomic analysis of stressed coral holobionts. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 2148–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Góes-Neto, A.; Marcelino, V.R.; Verbruggen, H.; da Silva, F.F.; Badotti, F. Biodiversity of endolithic fungi in coral skeletons and other reef substrates revealed with 18S rDNA metabarcoding. Coral. Reefs 2020, 39, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| NO3−-N (μmol/L) | NO2−-N (μmol/L) | NH4+-N (μmol/L) | DIN (μmol/L) | DIP (μmol/L) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study site | ||||||
| Hainan Island | Li’an Port | 5.83 ± 0.77 b | 0.08 ± 0.03 bd | 2.96 ± 0.16 b | 8.87 ± 0.87 b | 0.13 ± 0.01 b |
| Long Bay | 20.80 ± 1.46 a | 2.00 ± 0.17 a | 4.72 ± 0.60 b | 27.52 ± 0.96 a | 0.74 ± 0.06 a | |
| Tanmen Port | 12.68 ± 1.31 c | 0.37 ± 0.05 c | 3.73 ± 0.03 b | 16.78 ± 1.28 c | 1.35 ± 0.20 a | |
| Xincun Bay | 14.53 ± 2.18 c | 0.17 ± 0.01 bc | 12.16 ± 1.13 a | 26.87 ± 1.87 a | 1.08 ± 0.10 a | |
| Dongzhai Harbor | 14.36 ± 0.53 c | 0.39 ± 0.06 c | 3.06 ± 0.50 b | 17.81 ± 0.68 c | 1.20 ± 0.28 a | |
| Xiaohai | 22.24 ± 3.89 a | 2.20 ± 0.65 a | 3.06 ± 0.34 b | 27.49 ± 3.88 a | 0.82 ± 0.03 a | |
| Xisha Islands | 1.28 ± 0.03 d | 0.06 ± 0.00 d | 1.06 ± 0.06 c | 2.40 ± 0.06 d | 0.34 ± 0.02 c | |
| Seagrass species | ||||||
| E. acodoides | 13.10 ± 2.25 | 0.816 ± 0.302 A | 3.80 ± 0.31 A | 17.72 ± 2.75 A | 0.74 ± 0.19 | |
| Halophila sp. | 4.31 ± 1.24 | 0.284 ± 0.119 B | 1.56 ± 0.15 B | 6.16 ± 1.45 B | 0.42 ± 0.06 | |
| T. hemprichii | 2.44 ± 0.64 | 0.069 ± 0.007 B | 1.86 ± 0.54 B | 4.37 ± 1.16 B | 0.43 ± 0.04 | |
| OTUs | Shannon | Chao 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study region | ||||
| Bacteria | Hainan Island | 3570.89 ± 65.01 | 6.74 ± 0.04 | 5329.50 ± 107.42 |
| Xisha Islands | 3577.09 ± 108.60 | 6.31 ± 0.17 | 5237.62 ± 139.58 | |
| Fungi | Hainan Island | 341.22 ± 67.37 a | 3.44 ± 0.45 | 356.89 ± 68.29 a |
| Xisha Islands | 111.47 ± 3.57 b | 2.84 ± 0.10 | 120.02 ± 4.00 b | |
| Seagrass species | ||||
| Bacteria | E. acodoides | 3737.22 ± 72.30 | 6.74 ± 0.07 | 5591.00 ± 113.48 |
| Halophila sp. | 3405.57 ± 178.76 | 6.13 ± 0.30 | 5048.95 ± 228.21 | |
| T. hemprichii | 3697.75 ± 60.41 | 6.60 ± 0.05 | 5369.04 ± 98.15 | |
| Fungi | E. acodoides | 206.44 ± 35.07 AB | 2.32 ± 0.58 | 218.26 ± 35.18 AB |
| Halophila sp. | 215.17 ± 45.94 A | 3.22 ± 0.23 | 226.85 ± 46.65 A | |
| T. hemprichii | 117.03 ± 5.54 B | 2.96 ± 0.13 | 125.30 ± 5.76 B | |
| MOC | DOC | Corg | Cstocks | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sediment | MOC | – | – | 0.490 ** | 0.418 ** |
| DOC | – | – | −0.036 | −0.049 | |
| TN | 0.276 ** | −0.032 | 0.449 ** | 0.409 ** | |
| Alkaline phosphatase | 0.178 | 0.015 | −0.008 | −0.035 | |
| Urease | 0.055 | 0.091 | −0.03 | −0.012 | |
| Invertase | −0.032 | 0.067 | −0.181 | −0.223 * | |
| Cellulose | −0.188 | 0.163 | −0.075 | −0.089 | |
| Polyphenol Oxidase | 0.105 | 0.008 | −0.044 | −0.042 | |
| pH | −0.689 ** | 0.147 | −0.347 ** | −0.449 ** | |
| Grain sizes | −0.578 ** | −0.044 | −0.278 ** | −0.306 ** | |
| DBD | −0.068 | −0.046 | −0.308 ** | 0.012 | |
| Seawater | NO3-N | 0.585 ** | −0.184 | −0.015 | −0.018 |
| NH4+-N | 0.234 * | 0.01 | −0.256 * | −0.208 | |
| DIN | 0.553 ** | −0.149 | −0.071 | −0.066 | |
| DIP | 0.253 * | −0.208 | 0.007 | 0.092 | |
| Seagrass above-ground tissue | C | 0.135 | −0.054 | 0.038 | 0.015 |
| N | 0.206 | −0.012 | −0.02 | −0.047 | |
| C/N ratio | −0.109 | −0.024 | 0.059 | 0.054 | |
| Seagrass below-ground tissue | C | 0.051 | −0.094 | 0.017 | −0.03 |
| N | 0.342 ** | −0.108 | −0.089 | −0.095 | |
| C/N ratio | −0.285 * | 0.048 | 0.09 | 0.055 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Q.; Qiu, C.; Zeng, W.; Chen, S.; Zhao, M.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, X. Sediment Carbon Sequestration and Driving Factors in Seagrass Beds from Hainan Island and the Xisha Islands. Processes 2023, 11, 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11020456
Han Q, Qiu C, Zeng W, Chen S, Zhao M, Shi Y, Zhang X. Sediment Carbon Sequestration and Driving Factors in Seagrass Beds from Hainan Island and the Xisha Islands. Processes. 2023; 11(2):456. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11020456
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Qiuying, Chongyu Qiu, Wenxuan Zeng, Shiquan Chen, Muqiu Zhao, Yunfeng Shi, and Xiaoli Zhang. 2023. "Sediment Carbon Sequestration and Driving Factors in Seagrass Beds from Hainan Island and the Xisha Islands" Processes 11, no. 2: 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11020456
APA StyleHan, Q., Qiu, C., Zeng, W., Chen, S., Zhao, M., Shi, Y., & Zhang, X. (2023). Sediment Carbon Sequestration and Driving Factors in Seagrass Beds from Hainan Island and the Xisha Islands. Processes, 11(2), 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11020456