Abstract
In the past, hydrogen was mostly produced from fossil fuels, causing a certain degree of energy and environmental problems. With the development of low-carbon energy systems, renewable energy hydrogen production technology has developed rapidly and become one of the focuses of research in recent years. However, the existing work is still limited by small-scale hydrogen production systems, and there is a lack of comprehensive research on the whole production-storage-transportation-utilization hydrogen system (PSTUH2S), especially on the modeling of different hydrogen transportation modes and various hydrogen loads in different fields. To make up for these deficiencies, the specific physical and mathematical models of the PSTUH2S are firstly described in this paper, with a full account of large-scale water-electrolytic hydrogen production from renewable power curtailment and grid power, various hydrogen storage and transportation modes, and multi-field hydrogen consumption paths. Furthermore, to achieve the maximum economic, energy, and environmental benefits from the PSTUH2S, a multi-objective nonlinear optimization model is also presented herein and then solved by the hybrid method combining the nonlinear processing method, the CPLEX solver and the piecewise time series production simulation method. Lastly, case studies are conducted against the background of a region in northwest China, where hydrogen consumption capacity in various years is accurately assessed and the potential advantages of the PSTUH2S are demonstrated. As the simulation results show, the power curtailment of renewable energy generation can be reduced by 3.61/11.87/14.72 billion kW·h in 2025/2030/2035, respectively, thus contributing to a 4.98%~10.09% increase in the renewable energy consumption rate and millions of tons of carbon emission reduction in these years. In terms of the total equivalent economic benefits, the proposed method is able to bring about a cost saving of USD 190.44 million, USD 634.66 million, and USD 865.87 million for 2025, 2030, and 2035, respectively.
1. Introduction
Against the background of the transformation of low-carbon energy systems, hydrogen energy is considered to be an important carrier of sustainable development and an important direction of the world’s energy development [1,2]. However, most hydrogen was produced from fossil fuels in the past, causing a certain degree of energy and environmental problems. With advances in renewable energy hydrogen production technology, more and more hydrogen has been produced from wind and solar power in recent years, which plays an important role in economy, energy and environment [3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. Generally, using renewable energy instead of fossil fuels to produce hydrogen can reduce carbon emissions and, thus, bring good energy and environmental benefits. At the same time, the utilization efficiency and consumption level of renewable energy can be improved through the utilization of wind and solar curtailment to produce hydrogen. When deploying renewable energy hydrogen production as a flexible regulating resource in the power grid, it can also smooth the fluctuations of renewable energy output, assist in grid regulation, and improve system reliability and power quality.
According to the relevant literature and reports, Chen et al. [6] demonstrated that 86% of greenhouse gas emissions could be reduced with the introduction of hydrogen production and methanol synthesis from renewable energy sources in a coal-based chemical hybrid energy system. Also, this system was approved as being practical for nations with heavy coal usage and could greatly decrease carbon emissions within the next 5 to 15 years. Samara et al. [7] pointed out that if 300 MW·h of the surplus electricity from wind farms was used for hydrogen production, not only can the produced hydrogen be sent to meet the hydrogen demand of the other cities but CNY 1.4 bn of revenue can also be anticipated. Bao et al. [8] showed that renewable energy hydrogen production could raise the renewable energy consumption rate from 89.51% to 96.40% in this region of northwest China. In addition, the power curtailment of the system was reduced from 65.18 billion kW·h to 22.40 billion kW·h, bringing the equivalent economic benefit of CNY 11.10 billion to the system. Brey et al. [9] mentioned that it could allow 7.27 TW·h of renewable energy to be reused and 2.54 million tons of CO2 emissions to be reduced when using the existing natural gas network in Spain to store hydrogen and generating power through hydrogen gas turbines. In reality, the Mainz Energy Project, the world’s first mega-watt-level electric hydrogen production project, completed in 2016, converted renewable energy to hydrogen and further utilized and stored it, thus effectively alleviating the fluctuations caused by the integration of renewable energy systems into the grid [10].
Up to now, many scholars at home and abroad have conducted various research studies on hydrogen energy systems based on renewable energy and have successfully applied their research results to practical engineering demonstration projects [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. However, the existing work is still in the preliminary exploration stage, is limited to small-scale hydrogen systems, and lacks comprehensive studies of the entire large-scale production-storage-transportation-utilization hydrogen system (PSTUH2S). For example, Yin et al. [16] presented a modeling framework of the main integrated renewables-based green hydrogen production subsystems, which consisted of a power grid, wind farms, PV arrays, pumped hydro storage, and electrolyzers. On this basis, the optimal layout of wind farms and the best configurations of the PV array and pumped hydro storage can be determined through the co-design optimization of integrated renewables with the power grid. However, it should be pointed out that only hydrogen production and storage were discussed in this system. In addition, Le et al. [17] focused on hydrogen storage systems and conducted a quantitative risk assessment to investigate the effects of design parameters such as storage size, pressure, temperature, and mass flow rate on system safety. Lin et al. [18] introduced a small-scale hydrogen energy industry chain in an industrial park-integrated energy system and investigated the optimal planning of such a system. The optimization results indicated that the system could lead to an increase in economic benefit and a reduction in carbon emissions and power curtailment. Noh et al. [19] focused on offshore hydrogen supply chains and assessed their environmental impact and energy efficiency through the life cycle assessment method, especially the effect of ship transportation to hydrogen supply chains, in terms of the supplied electrical energy sources and the transport distances. In this system, hydrogen was produced on an offshore platform using offshore wind power and converted to compressed gaseous hydrogen (CGH2), liquefied hydrogen, liquid organic hydrogen carriers, or ammonia, then transported by ships and converted back to CGH2 for storage at an onshore plant located in a port. In their research, the offshore hydrogen system was investigated considering the links of hydrogen production, storage, and transportation, but hydrogen applications in various fields were not covered. Zhang et al. [20] took account of different application scenarios and influencing factors of hydrogen energy, but they mainly focused on the medium- and long-term forecasting of hydrogen energy demand for the fields of industry, power, heat, and transportation, based on hydrogen load prediction functions and a rolling grey prediction method containing an original data test. The forecast results showed that the hydrogen load would grow rapidly to about 2200 Mt by 2035, and the carbon emissions of the system would be 15,583.9 Mt when utilizing hydrogen energy in that year.
In this paper, the specific physical and mathematical models of the PSTUH2S are first presented, with a full account of large-scale water-electrolytic hydrogen production with renewable power curtailment, various hydrogen storage and transportation modes, and multi-field hydrogen consumption paths. Then, a multi-objective nonlinear optimization model is put forward to achieve the maximum economic, energy, and environmental benefits from the PSTUH2S, which is further solved by combining a nonlinear processing method, CPLEX solver, and piecewise time series production simulation method. Lastly, case studies are conducted against the background of a region in northwest China, where multi-field hydrogen consumption capacity in different years is accurately assessed and the potential benefit advantages of the PSTUH2S are demonstrated. Overall, the novelty and contributions of this work can be summarized in the following three points: (1) proposing an entire model framework containing hydrogen production, hydrogen storage, hydrogen transportation, and hydrogen utilization; (2) realizing a quantitative assessment of the consumption capacity of hydrogen energy in different scenarios; (3) illustrating the positive benefits of the PSTUH2S in promoting renewable energy consumption, reducing carbon emissions, and improving the economy.
2. Modeling the Whole Hydrogen System
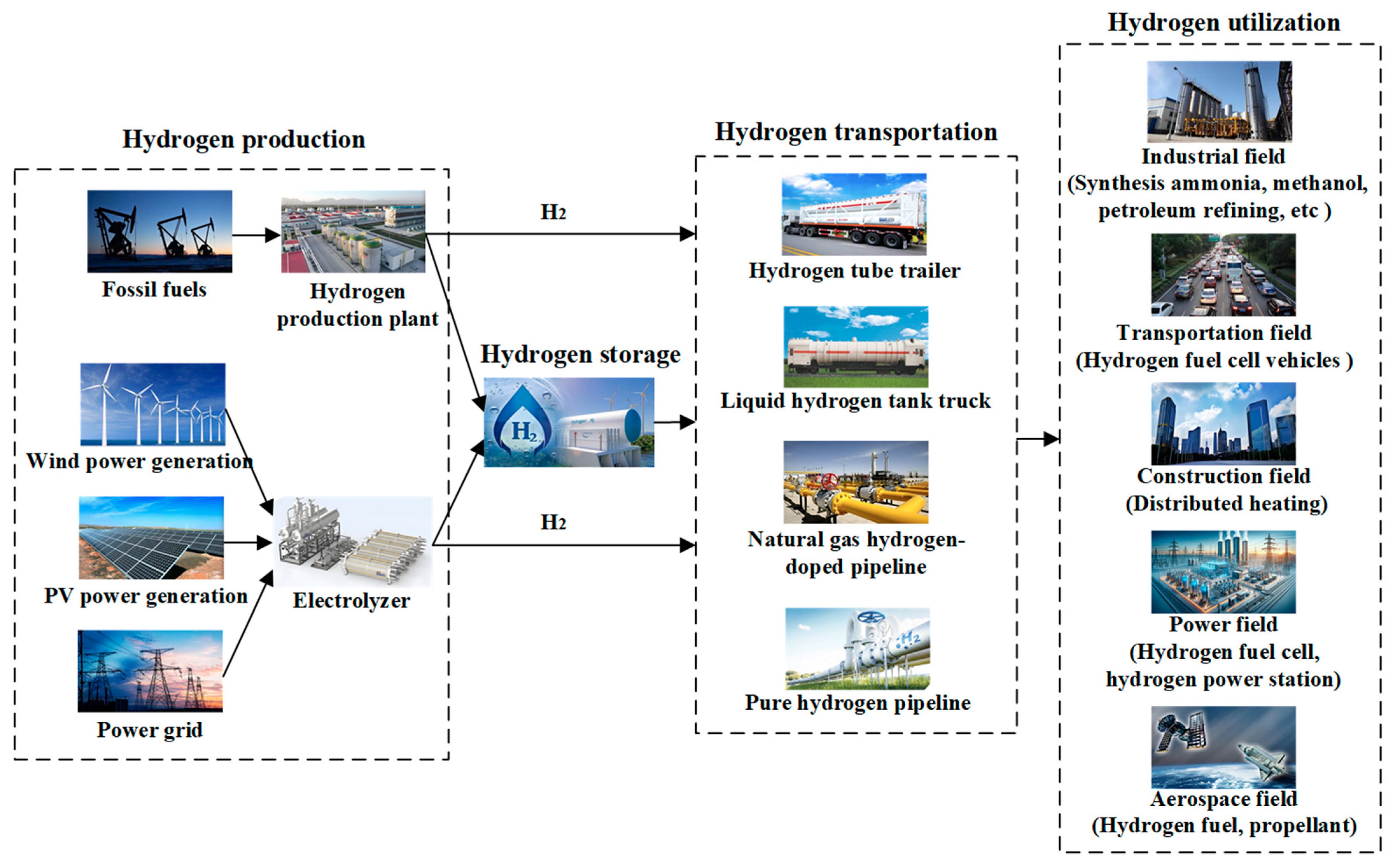
As shown in Figure 1, the proposed PSTUH2S system mainly includes four parts: hydrogen production, hydrogen storage, hydrogen transportation, and hydrogen utilization. Specifically, hydrogen is simultaneously produced from fossil fuels and renewable energy sources in the system. On the one hand, coal, oil, and natural gas can be converted to hydrogen through a hydrogen production plant. On the other hand, renewable power curtailment or grid power can be fully used to produce hydrogen with electrolyzers. After being produced, hydrogen can be stored in the storage devices or transported to the user terminal through multiple modes such as a hydrogen tube trailer, liquid hydrogen tank truck, natural gas hydrogen-doped pipelines, and pure hydrogen pipelines. From an application point of view, hydrogen can be widely used in various fields, mainly involving industry, transportation, power, construction, and aerospace. In the field of industry, hydrogen can be utilized for ammonia synthesis, methanol production, petroleum refining, and so on. In the field of transportation, hydrogen is mainly used for the combustion of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. In the power field, hydrogen can be converted into electricity through hydrogen fuel cells or hydrogen power stations to smooth renewable energy fluctuations, assist grid regulation, and maintain power balance. The utilization of hydrogen energy in the construction field is mainly reflected in distributed heating through the combustion of natural gas mixed with hydrogen. In the field of aerospace, hydrogen can be used as a fuel or propellant for aircraft, rockets, and spacecraft. From the mathematical modeling perspective, the PSTUH2S system can mainly be described according to the following aspects: (1) the basic principles of four hydrogen links, namely, production, storage, transportation, and utilization; (2) energy conversion relationships; (3) the input and output of the equipment or subsystem. In addition, it should be pointed out that some hydrogen devices, such as hydrogen filtration systems, are assumed to meet the requirements of stable operation and hydrogen quality in the modeling process, which would not affect the study on the optimization and evaluation of the hydrogen system.
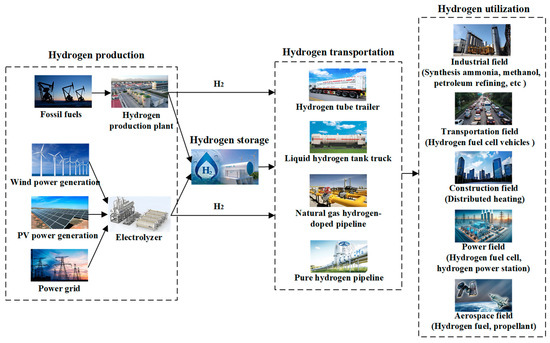
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the PSTUH2S system.
2.1. Hydrogen Production from Renewable Energy
Renewable energy hydrogen production involves the processes of converting wind energy or solar energy into electricity and then into hydrogen energy, whereby an electrolyzer is needed to realize the electrolysis of water to produce hydrogen. When modeling an electrolyzer, the following assumptions are made: (1) a semi-empirical model is used to describe the electrolyzer, and the small diffusion voltage is ignored; (2) the operating temperature of the electrolyzer is set to 80 °C and the proton exchange membrane maintains a stable structure at this temperature. Therefore, the voltage of the electrolyzer is composed of reversible voltage, ohmic overvoltage, and polarization overvoltage, and its voltage-current formula [21] can be expressed as follows:
where is the voltage of the electrolyzer; is the reversible voltage; and are the parameters of the electrolyte ohmic resistance; and are pressure coefficients; is the temperature of the electrolyte; p is pressure; A is the area of the electrolyte module; is the electrolysis current; s, , , and are the overvoltage coefficients of the electrolyte module.
The amount of hydrogen produced by the electrolyzer per unit of time can be expressed as follows:
where is the quantity of hydrogen produced in the electrolyzer; is the Faraday efficiency of the electrolyzer; is the Faraday constant; is the current density; , , and are the Faraday efficiency coefficients.
The electric power consumed by the electrolyzer can be obtained according to the volt–current formula of the electrolyzer, and the energy contained in hydrogen output per unit of time can be obtained based on the present density of the electrolyzer. The efficiency of the electrolyzer can then be expressed as the ratio of the energy contained in the output hydrogen per unit of time to the input power of the electrolyzer, and the amount of hydrogen production is the product of the power input to the electrolyzer and the electrolyzer efficiency. Therefore, the hydrogen production models can be formulated as follows:
where is the electrolyzer efficiency; is the energy output of hydrogen per unit of time from the electrolyzer; is the power of the electrolyzer; is the higher heating value of hydrogen; is the amount of hydrogen production; is the conversion factor between electricity and equal-energy hydrogen, equal to 39.65 kW·h/kg.
2.2. Hydrogen Production from Fossil Fuels
Hydrogen production from fossil fuels is a process that produces hydrogen through the processing of fossil fuels, usually involving chemical reactions and fossil fuel gasification technology. Since this is a traditional hydrogen production method, it is usually accompanied by high carbon emissions and requires complex gas treatment steps to reduce environmental pollution. In this paper, the hydrogen production cost of fossil fuel hydrogen production technology and its carbon emissions are focused on; the mathematical model of fossil fuel hydrogen production can be expressed as:
where and are, respectively, the cost and carbon emissions; and are, respectively, the cost coefficient and carbon emission coefficient; is the amount of hydrogen production at time t.
2.3. Hydrogen Storage
Hydrogen storage devices are considered critical components within the hydrogen system. They enable the bridging of temporal gaps between hydrogen generation and demand, facilitating peak shaving and valley filling, thereby enhancing system stability [22]. Due to the low energy loss found in compressed gaseous hydrogen storage, a hydrogen storage tank is utilized in this paper. The hydrogen storage capacity of the hydrogen storage tank at time t can be determined by the hydrogen storage capacity at time t − 1, the hydrogen charge capacity, and the hydrogen discharge capacity of the hydrogen storage tank. The internal pressure of the hydrogen storage tank is calculated as follows:
where is the hydrogen storage capacity at time t; and are, respectively, the amount of hydrogen charged and discharged from the hydrogen storage tank at time t; and are, respectively, the efficiency of hydrogen storage and discharge; and T are, respectively, the volume, pressure, and temperature of hydrogen inside the tank; R is the ideal gas constant.
2.4. Hydrogen Fuel Cell
Hydrogen fuel cells can be used to combine electricity, hydrogen, and heat, allowing chemical energy to be converted directly into electrical and thermal energy. The PEM fuel cell was selected because of its high efficiency and relatively mature development. In it, hydrogen is catalyzed and split into protons and electrons at the anode, and the electrons pass through an external load circuit to the cathode side of the membrane electrode assembly to generate the current output of the fuel cell. Similarly, in order to ascertain the efficiency of hydrogen fuel cells, a mathematical model of hydrogen fuel cells is established [23]. The polarization overvoltage of hydrogen fuel cells is mainly composed of activation overvoltage, ohmic overvoltage, and concentration overvoltage. Its output voltage expressions can be described as follows:
where is the theoretical output voltage of the fuel cell, determined by the temperature hydrogen partial pressure and oxygen partial pressure ; is the current of the fuel cell; is the activation overvoltage, determined by the oxygen concentration and the current of the fuel cell; ξ is an empirical parameter; is Ohmic overvoltage; is the equivalent resistance parameters of the fuel cell; is concentration overvoltage; is the maximum allowable current of the fuel cell.
The amount of hydrogen consumed per unit of time in a hydrogen fuel cell can be expressed as follows:
As an analogy to the cell efficiency model, hydrogen fuel cell efficiency can be expressed as the ratio of the value of the output electric power to the energy contained in the input hydrogen, and is shown as follows:
where is the fuel cell efficiency; is the energy input of hydrogen per unit of time from the fuel cell; is the power output of the fuel cell; is the higher heating value of hydrogen; is hydrogen consumption for fuel cells.
2.5. Hydrogen Transportation
The hydrogen thus produced can be transported to a local region or to other places through a variety of transportation modes, such as hydrogen tube trailers, liquid hydrogen tank trucks, natural gas hydrogen-doped pipelines, and pure hydrogen pipelines, simultaneously meeting the demand for nearby consumption and the delivery consumption demand of hydrogen.
- (1)
- Hydrogen tube trailer and liquid hydrogen tank truck
The amount of hydrogen transported by a hydrogen tube trailer or by a liquid hydrogen tank truck is limited by the capacity of the vehicles and can be calculated by:
where and are, respectively, the total amount of hydrogen transported through hydrogen tube trailers and liquid hydrogen tank trucks within the time period T; and are, respectively, the hydrogen transportation quantity by a single vehicle at time t; and are, respectively, the total number of hydrogen tube trailers and liquid hydrogen tank trucks.
- (2)
- Pure hydrogen pipeline
Power would be consumed to provide the driving force when transporting hydrogen in pure hydrogen pipelines [24], and the required power can be modeled by:
where is the power consumed by the pure hydrogen pipeline for providing propulsion; is the total amount of hydrogen transported by the pure hydrogen pipeline at time t; is the hydrogen pressure in the pure hydrogen pipeline at time t; is the hydrogen pressure at the destination of the pure hydrogen pipeline.
- (3)
- Natural gas hydrogen-doped pipeline
The feasibility of incorporating hydrogen into natural gas pipelines has been proven in recent years. For example, with the development of the west–east gas transmission project in China, construction of the natural gas infrastructure in its western region is relatively complete, and the realistic conditions for the hydrogen transportation of natural gas have been met in this western region. Therefore, a natural gas hydrogen-doped pipeline is regarded as an important way to achieve large-scale hydrogen delivery from one place to another and can be modeled as follows:
where is the hydrogen-blending ratio in natural gas hydrogen-doped pipelines, defined as the volume fraction of hydrogen to the total gas volume in the pipeline; is the amount of hydrogen blended in natural gas hydrogen-doped pipelines at time t; is the total gas volume in natural gas hydrogen-doped pipelines at time t; is the quantity of natural gas present within the pipeline at time t.
2.6. Hydrogen Utilization
Hydrogen has a wide range of applications in various fields, mainly involving industry, transportation, power, construction, and aerospace. Generally, hydrogen loads in these fields could be calculated through different prediction methods according to the historical situation and future development policies of regional energy utilization.
- (1)
- Hydrogen load in the field of industry
Hydrogen is widely used in petroleum refining, ammonia synthesis, methanol synthesis, and other industries, which makes it difficult to grasp the distribution law and change trend of the actual hydrogen load. According to grey theory, the medium- and long-term hydrogen load in industry can be forecast through the grey forecasting method based on the grey model GM(1,1) [25]. The specific prediction methodology unfolds as detailed below:
(1) Input data inspection
In order to ensure the practicability of the GM(1,1) model of grey prediction, the stage ratio test of the hydrogen load sequence in the original industrial sector is carried out first. The sequence ratio is then calculated. When all the calculated step ratios fall within the overlayable interval, the step ratio test is passed, and a GM (1,1) model can be established for sequence .
The level ratio formula of the sequence is expressed as:
The coverage interval X is:
(2) The establishment of the GM (1,1) model
The original hydrogen load data is accumulated to generate the cumulative series . After that, the adjacent mean series is generated, and the generation process can be represented by:
The differential formula GM (1,1) about k is established for the hydrogen load generation series according to the grey system theory, and the development coefficient a reflecting the change trend of and the grey action quantity b reflecting the change relationship of the data are obtained. Thus, the GM (1,1) model can be established as follows:
The restore model is:
(3) Predicted data inspection
Residual inspection is carried out on the predicted value of hydrogen load, and the relative residual value and average residual value of the predicted value are calculated by Equation (26). If the average residual is less than 20%, the predicted value meets the requirements:
(4) Hydrogen load prediction based on the GM(1,1) model
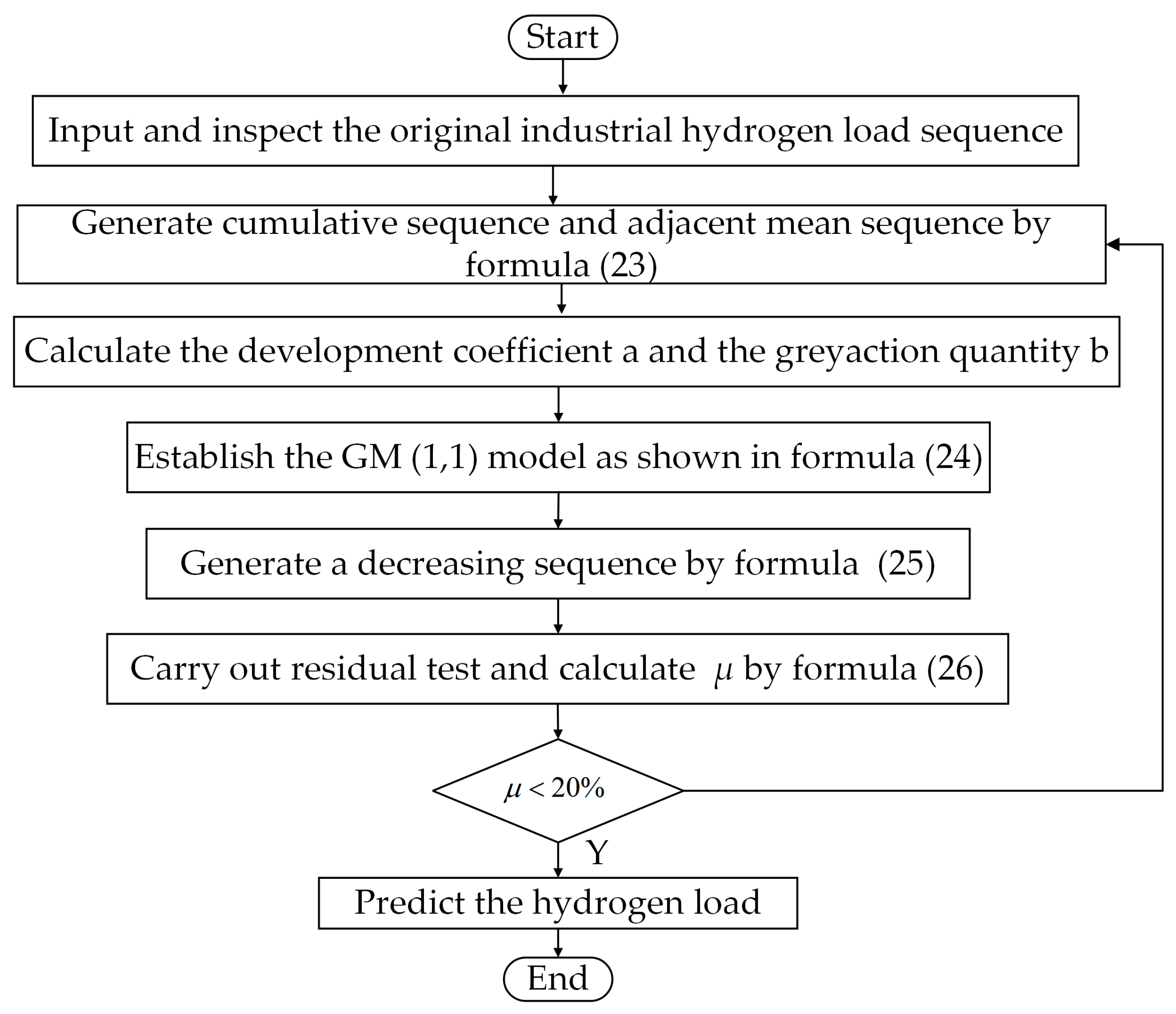
If the predicted value is qualified, the obtained GM(1,1) model is used to predict the hydrogen load in an industrial sector. Otherwise, the grey prediction model fails in terms of its use in modeling. Furthermore, it is necessary to go back to Step 2 to re-model. A hydrogen load prediction based on GM(1,1) is shown in Figure 2.
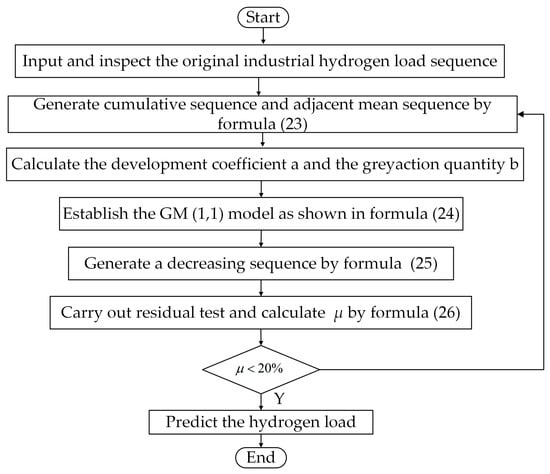
Figure 2.
Hydrogen load prediction method based on GM(1,1).
- (2)
- Hydrogen load in the field of power
The application of hydrogen in the power field is still in its preliminary exploration stage at present. As a new type of energy storage with great potential, hydrogen can be converted into electricity through hydrogen fuel cells or hydrogen power stations, to deal with the fluctuation problems of renewable energy generation and, thus, play an important role in the power grid, such as peak clipping, valley filling, frequency modulation, voltage regulation, improving power quality, enhancing reliability and flexibility, etc. Assuming that hydrogen is used to smooth the fluctuations of renewable energy generation in the power grid, the total hydrogen load in the power sector could be calculated by the product of the smoothing output coefficient and the renewable energy output smoothing demand, which could be represented by:
where is the over-limit indication of renewable energy output at time t; and are, respectively, the output of renewable energy sources at time t + 1 and t; R is the limit value for fluctuations; is the smoothing output coefficient; is the power output of fuel cell at time t; is the hydrogen load in the power field at time t.
- (3)
- Hydrogen load in the transportation sector
In the field of transportation, hydrogen is mainly used for the combustion of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. According to the relevant data and statistical analysis, the annual hydrogen consumption of a single hydrogen fuel cell vehicle can be calculated based on the following assumptions: (1) each hydrogen fuel cell vehicle travels an average of 200 km per day and the attendance rate reaches 90% throughout the year. (2) Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles consume an average of 7 kg of hydrogen per 100 km. Therefore, the total annual hydrogen load in the transportation sector can be predicted by the product of the number of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles and the annual hydrogen consumption of a single vehicle, which could be represented by:
where is the annual hydrogen load in the transportation field; is the daily hydrogen consumption of a hydrogen fuel cell vehicle; is the hydrogen fuel cell vehicle ownership planned in that region.
- (4)
- Hydrogen load in the construction sector
According to the national energy development plan, the application of hydrogen energy in the construction field is mainly reflected in the distributed heating through the combustion of civil natural gas mixed with hydrogen. That is, hydrogen would be injected into the natural gas pipeline in a certain proportion to replace part of the natural gas used for combustion heating in the intended buildings. According to the actual data of natural gas load in the construction field in previous years, the historical annual growth rate of natural gas load can be statistically obtained. In this paper, it is assumed that the annual growth rate of natural gas load remains roughly constant over the next few years; then, the amount of natural gas used in a given year can be predicted according to the historical natural gas load. Thus, the annual hydrogen load in the construction field could be forecast by the product of the hydrogen-blending ratio of natural gas pipelines and the annual utilization amount of natural gas, which can be represented by:
where is the annual hydrogen load in the construction field; is the hydrogen-blending ratio of natural gas pipelines; is the annual natural gas utilization in the construction field.
- (5)
- Hydrogen load in the field of aerospace
In the aerospace sector, hydrogen can be used as a fuel or propellant for aircraft, rockets, and spacecraft, and has been used mainly for rockets in recent years. Due to the difficulty of obtaining historical hydrogen load data in the aerospace field, we firstly extrapolate the rocket launch frequency and the hydrogen consumption per rocket launch in a future year, according to the historical reports and the development plans of the aerospace field, and then use the product of these calculations to predict the annual hydrogen load in the aerospace field, which can be represented by:
where is the annual hydrogen load in the aerospace field; is the annual rocket launch frequency, assumed to be 25; is the hydrogen consumption per rocket launch, assumed to be 4 tons.
3. Multi-Objective Optimization Model of the Hydrogen System
To accurately assess the hydrogen consumption space and capacity in different fields and to achieve optimal performance throughout the whole production-storage-transportation-utilization hydrogen system, a multi-objective nonlinear optimization model is presented here, with the objectives of maximizing economic benefit, maximizing renewable energy consumption, and minimizing carbon emissions while satisfying various equality and inequality constraints.
3.1. Optimization Objectives
- (1)
- The goal of maximizing economic benefit
The economic benefit of the whole hydrogen system mainly encompasses three parts: (1) operational and maintenance costs; (2) the costs associated with producing hydrogen from renewable resources, the power grid, and fossil fuels; (3) the revenue from selling hydrogen. Thus, the objective function of economic benefit can be represented by:
where is the maintenance cost of the system; is the total cost of hydrogen production; is the revenue from selling hydrogen by the system; and are, respectively, the maintenance cost per unit power and the rated power of the equipment k; and are, respectively, the per unit volume and total volume of hydrogen storage tank; and are, respectively, the unit cost of hydrogen production from renewable power curtailment and power grid;, and are, respectively, the amount of hydrogen production from renewable power curtailment, the power grid, and fossil fuels at time t; is the hydrogen price; is the hydrogen consumption in each field S at time t; is the hydrogen delivered at time t.
- (2)
- The goal of maximizing renewable energy consumption
Given that hydrogen production leverages power curtailment from renewable energy sources, the amount of renewable energy that is utilized can be gauged by the power curtailment of the system. The minimum renewable power curtailment indicates that the capacity for consuming renewable energy is at its maximum, which can be represented by:
where is the renewable power curtailment at time t.
- (3)
- The goal of minimizing carbon emissions
Carbon emissions from the hydrogen system are predominantly attributable to two points: one is hydrogen production from fossil fuels; the other is the electrolysis of water to produce hydrogen, wherein the electricity consumption is from the power grid rather than renewable power curtailment. The objective function on carbon emissions can be represented by:
where and are, respectively, the carbon emission coefficient and hydrogen amount for water-electrolytic hydrogen production from renewable power curtailment at time t; and are, respectively, the carbon emission coefficient and the hydrogen amount for hydrogen production from the power grid at time t; and are, respectively, the carbon emission coefficient and the hydrogen amount for hydrogen production from fossil fuels at time t.
3.2. Constraints
The equality relations represented by Equations (1)–(20) should be satisfied in the multi-objective nonlinear optimization model to describe the hydrogen system. The relevant energy balance constraints, operational constraints, and technical constraints of the system also need to be met to ensure safety and stability, which can be represented as follows:
- (1)
- Hydrogen quantity constraint
- (2)
- Hydrogen delivery capacity constraints
- (3)
- Annual green hydrogen production constraint
- (4)
- Hydrogen production and reserve constraints, based on fossil fuels
- (5)
- Hydrogen storage constraints
- (6)
- Power constraints
- (7)
- Electrolyzer capacity constraint
4. Solution Method
4.1. Nonlinear Processing Method
According to the proposed models represented by Equations (1)–(4) and (8)–(14), it can be observed that the relationships between efficiency and power for the electrolyzer and hydrogen fuel cell are nonlinear, which leads to difficulties in solving the models. Therefore, the piecewise linearization technique is employed to linearize the efficiency; subsequently, this problem is transformed into a mixed integer linear optimization problem. First, the efficiency of the electrolyzer and the hydrogen fuel cell is divided into L segments, and each segment is represented by the average value . Then, the variable with a value from 0 to 1 is introduced. The power interval is determined by the input power of the device, and the variable corresponding to the power interval is assigned as 1, as shown in Equation (44). For variables (), it should be guaranteed that only one variable is 1 and the others are 0, as expressed by Equation (45). Finally, the total efficiency of the equipment is expressed as Equation (46), and the piecewise linearization of the equipment efficiency can be realized through the above linearization process [26]:
where is the rated power of the device; is the power per unit value corresponding to segment l.
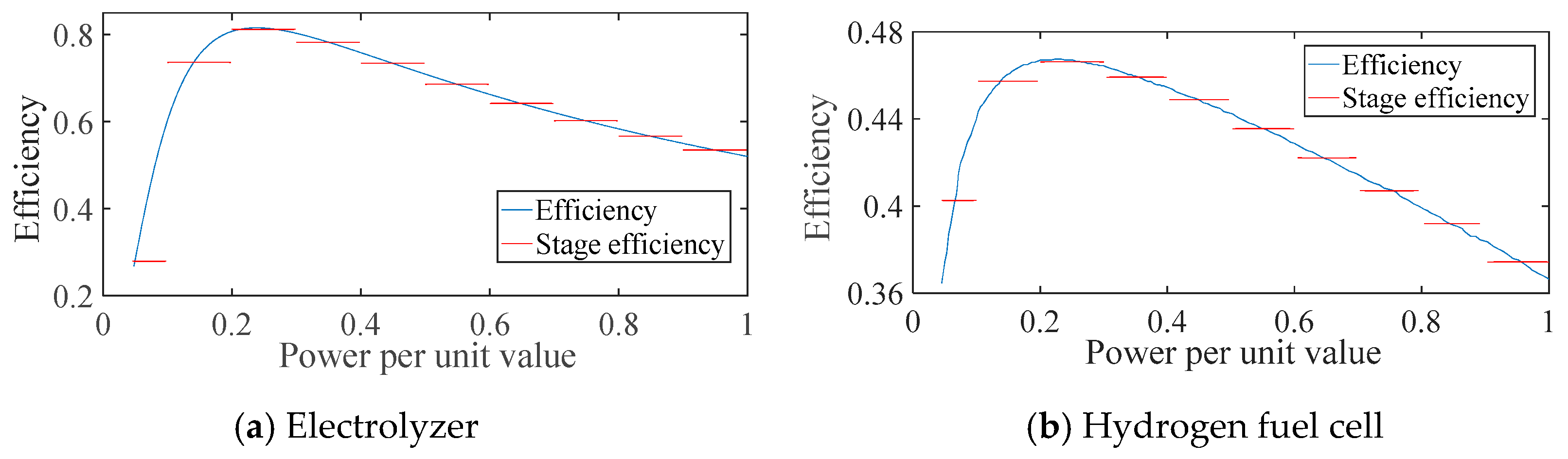
According to the piecewise linearization of equipment efficiency, the power-efficiency curves of the electrolyzer and hydrogen fuel cell can be depicted as in Figure 3. It can be seen that the curve shape of the two devices is similar. The efficiency of the equipment increases rapidly with the increase in power, reaching its maximum values at 25% and 22% of the rated power, which are 80% and 47%, respectively. After that, with the further increase of power, a slow decline in the efficiency of the two devices is evident, and the efficiency at the rated power is 55% and 37%, respectively. Furthermore, the above nonlinear processing method can be applied to the piecewise linearization of the curve, as shown by the red line in the figure. For example, at 10% to 20% of the rated power, the cell efficiency is simplified to 73%, and the fuel cell efficiency is simplified to 46%. The efficiency of the two devices is simplified to 80% and 47%, respectively, at 20%~30% of rated power, thus achieving a simplified solution for the model.
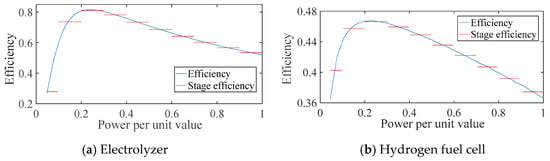
Figure 3.
Efficiency curves of the electrolyzer and hydrogen fuel cell.
4.2. Piecewise Time Series Production Simulation Method
In the energy sector, the times series production simulation method is widely used when evaluating the consumption capacity of renewable energy. It can simulate the specific operation process and, thus, reflect the actual situation under the guarantee of various energy balances at all times and in all operating boundary conditions [27]. Similarly, it can also be applied in an analysis of the consumption space and capacity of the hydrogen system. Specifically, hydrogen production quantity and various hydrogen loads are firstly regarded as time series variables, and then the operational simulation is conducted for each period at hourly intervals. The operational limitations encompass all the constraints related to the electrolyzer, power balance, hydrogen storage tanks, hydrogen quantity balance, and hydrogen transportation capacity. During the simulation phase, the comprehensive hydrogen energy system’s balance optimization model is resolved by utilizing the version 12.8.0 of CPLEX solver via the MATLAB R2016a simulation environment. Given the potential impact on optimization outcomes from the direct invocation of the solver across the entire span of 8760 h of annual operational data, the system’s overarching optimization challenge is segmented into optimization subproblems for each period, applying the strategy of a piecewise solution. The 8760 h are averaged into 365 time periods, with 24 values for each time period; that is, the one-dimensional time series T is divided into the multidimensional time series M with the dimensions 365 × 24 on average, as shown in Equation (48). These 365 time periods are solved separately, then the overall optimization problem is transformed into M small-scale sub-optimization problems.
5. Case Studies
The main work in this paper focuses on the specific modeling, global optimization, and quantitative evaluation of the whole hydrogen system. In the simulation studies, the developing hydrogen system of a region in northwest China is taken as a case study to assess multi-field hydrogen consumption capacity in different years, as well as the positive benefits of promoting renewable energy consumption, reducing carbon emissions, and improving economy.
5.1. Parameter Settings and Boundary Conditions
The detailed parameter settings in the case studies are given based on those used in [28,29,30,31,32], as shown in Table 1. Three scenarios with different boundary conditions are also set up in the case studies, according to the regional hydrogen energy development plan [33,34,35], which can be described as follows.

Table 1.
Parameter settings.
Scenario 1 (in 2025): The installed capacity of renewable energy generation is 36.95 GW. The number of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles is 200. The planned quantities of hydrogen production from renewable energy and fossil fuels are set, respectively, at 100 thousand tons and 30 thousand tons. Hydrogen is mainly transported in a gaseous state through a hydrogen tube trailer and a pure hydrogen pipeline.
Scenario 2 (in 2030): The installed capacity of renewable energy generation is 60 GW. The number of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles is 500. The planned quantities of hydrogen production from renewable energy and fossil fuels are set, respectively, at 500 thousand tons and 150 thousand tons. The large-scale transportation of liquid hydrogen is realized, and the transportation mode is composed of a hydrogen tube trailer, a liquid hydrogen tank truck, and a pure hydrogen pipeline.
Scenario 3 (in 2035): The installed capacity of renewable energy generation is 92.67 GW. The number of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles is 1000. The planned quantities of hydrogen production from renewable energy and fossil fuels are set, respectively, at 2 million tons and 600 thousand tons. The hydrogen transportation mode using large-scale natural gas hydrogen-doped pipelines is realized, and all four modes of hydrogen transportation are used.
5.2. Prediction Results of Renewable Energy Generation and Hydrogen Loads
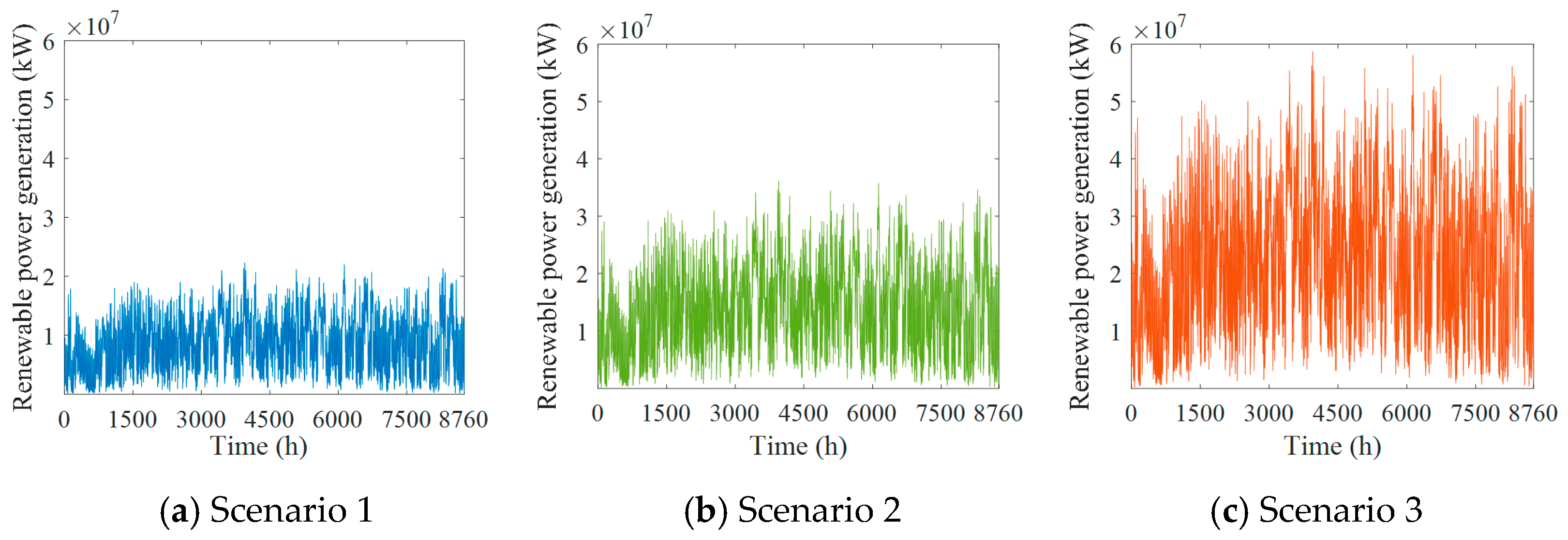
Renewable energy exhibits strong volatility and randomness. Since most hydrogen is produced from renewable energy using water-electrolytic hydrogen production technology in the proposed hydrogen system, the fluctuations of renewable energy also eventually influence the fluctuations of hydrogen production and storage. To describe these fluctuations and to provide input data for hydrogen prediction and consumption capacity assessment in the subsequent simulation experiments, the hourly forecast data of renewable power generation for the three scenarios are predicted by the linear growth method, calculated according to the historical data and installed renewable power capacity, which are shown in Figure 4.
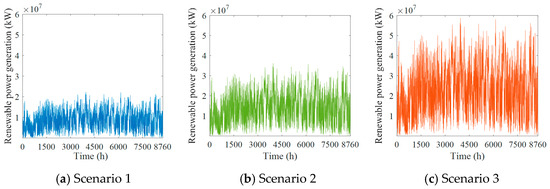
Figure 4.
Prediction results for renewable power generation in three different scenarios.
The annual hydrogen load in different fields can be predicted by the proposed methods and is shown in Table 2. In 2025, there will be 71,500.42 tons of hydrogen used in industry, while the total hydrogen load used for power, construction, transportation, and aerospace will be 2148.44 tons, 149.39 tons, 919.07 tons, and 100.00 tons, respectively. Along with further development in society, the hydrogen load in the various fields grows rapidly. The hydrogen used in the industrial sector will increase by nearly 10 times from 2025 to 2035, while the hydrogen load in the other sectors will increase by around 2 to 6 times. Comparing the proportion of hydrogen load used in each field, it can be seen that the hydrogen load in the industrial field is far higher than that used in other fields, which focuses a lot of attention on the use of hydrogen in industry, both at home and abroad. In addition, hydrogen is also increasingly being used in other sectors, especially in the power sector. Therefore, hydrogen application in other fields has also attracted attention in recent years.

Table 2.
The annual local hydrogen load in different fields.
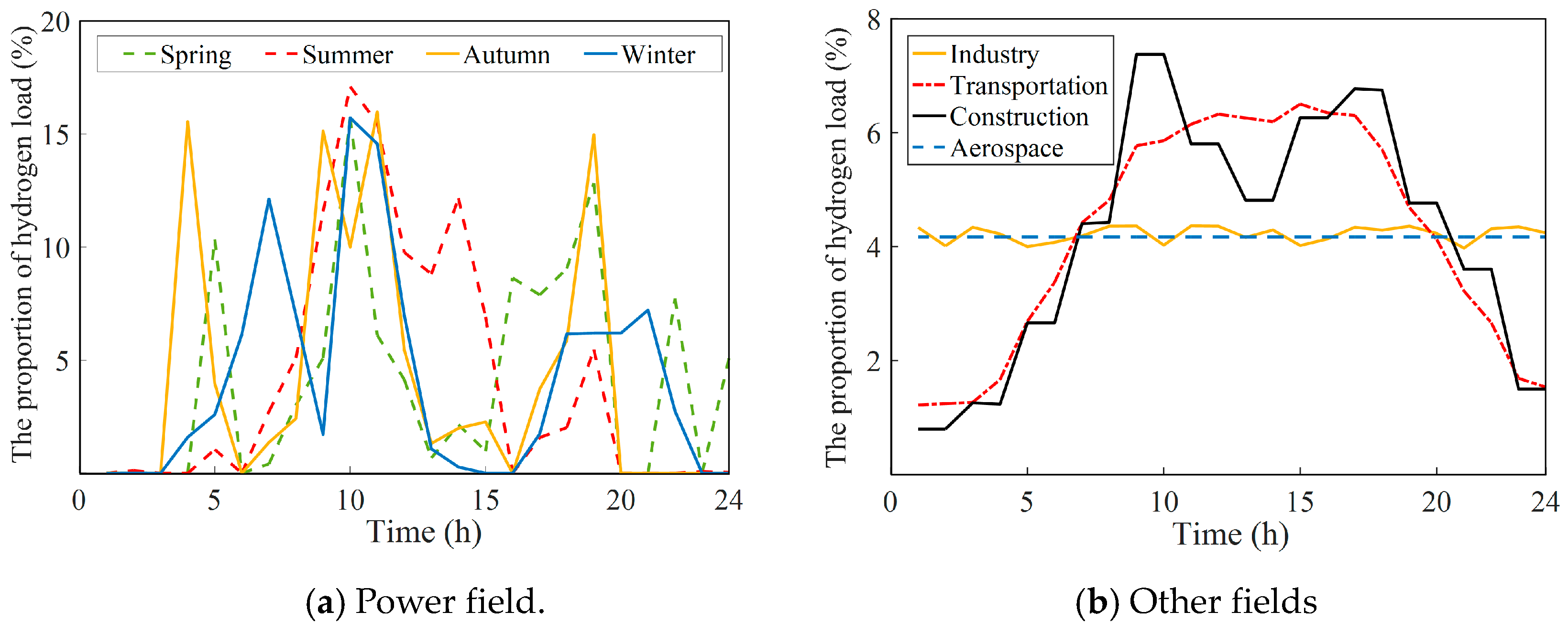
Figure 5 also shows the hourly hydrogen load of a typical day in different fields. In the field of power, it is necessary to predict the different hydrogen load for four typical days in spring, summer, autumn, and winter because hydrogen is usually used to smooth fluctuations in the power grid, and the corresponding hydrogen load would vary greatly with renewable energy generation from season to season, as shown in Figure 5a. For the hourly hydrogen load in other fields, this can be obtained using the product of the daily hydrogen load on a typical day and the load ratio per hour, where the daily hydrogen load is assumed to be equal to the annual hydrogen load, divided by 365. Generally, the hourly hydrogen load ratio follows a certain variation law and can be set according to Reference [15]. Considering the diversity of hydrogen loads in different fields and for ease of comparison and display, the corresponding proportion of the hourly hydrogen load is used to show the variations over time, as depicted in Figure 5b. It can be seen that the hydrogen load in the industrial sector is characterized by stable consumption with little variation over time. In the transportation and construction fields, hydrogen load is related to people’s daily activities and travel, showing a law of high load during the day and low load at night. For the hydrogen load in the aerospace sector, it can be assumed to be the same at all times of the day because its hydrogen consumption is always determined in advance, according to the rocket launch plan.
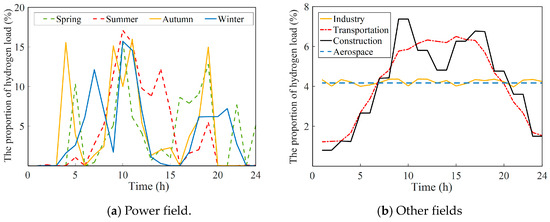
Figure 5.
Hourly hydrogen load of a typical day in different sectors.
5.3. Optimization and Evaluation Results of the Whole Hydrogen System
- (1)
- Hourly optimization results and hydrogen consumption space
According to the simulation studies, the hourly optimization results of the specific production, storage, transportation, and utilization of hydrogen energy can be obtained. For ease of understanding, we take a typical day in 2025 as an example for analysis. The results of other periods are similar and will not be described here.
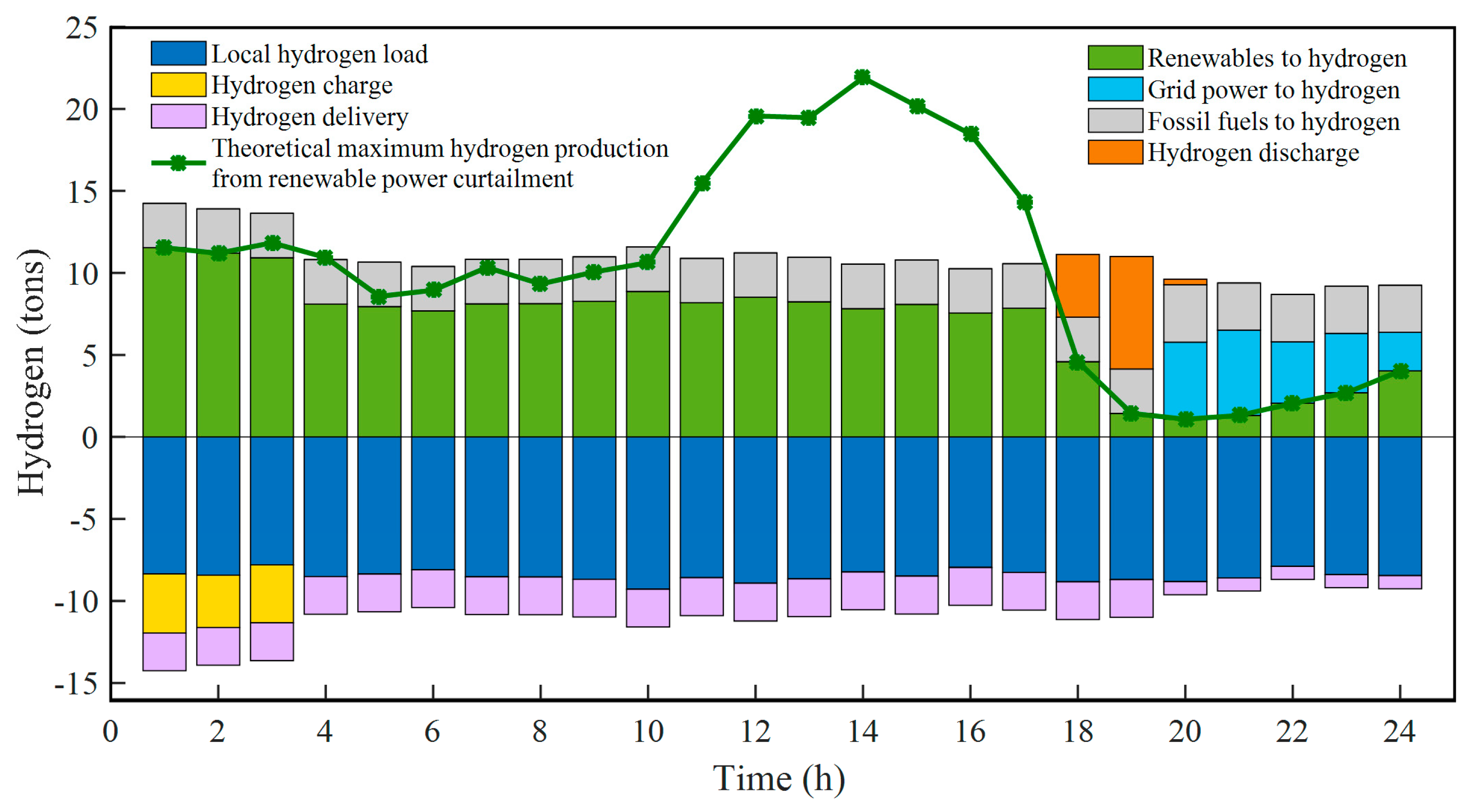
As shown in Figure 6, various hydrogen sources and hydrogen consumptions are plotted with bars above and below the horizontal coordinate, respectively. Hydrogen sources in the system include water-electrolytic hydrogen production from renewable power curtailment and grid power, hydrogen production from fossil fuels, and hydrogen discharge from storage devices, while hydrogen consumption not only includes the local hydrogen load but also includes the hydrogen charge of storage devices and hydrogen delivery to other places. The green curve represents the theoretical maximum hydrogen production from renewable power curtailment. It can be seen that the hourly hydrogen load changes slightly at around 9 tons. The change is small because most of the hydrogen load is composed of stable hydrogen demand from industry, while hydrogen demand in other fields is relatively much lower. In addition, it can be seen that the fluctuation of renewable energy influences the fluctuation of the hydrogen system because most hydrogen is produced from stochastic renewable energy via water-electrolytic hydrogen production technology in the proposed hydrogen system. From 1:00 to 17:00, renewables-based hydrogen production fluctuates at around 9.5 tons, much greater than the hydrogen production from fossil fuels. Especially between 1:00 and 3:00, there are still about 11.03 tons of surplus hydrogen that are stored in hydrogen storage tanks for backup after meeting the required hydrogen loads and maximum hydrogen delivery capacity. For those areas with abundant wind and solar energy, such as in northwest China, the abandonment of renewable energy power generation is usually a serious matter. The full use of renewable power curtailment to produce hydrogen can improve the renewable energy consumption rate and reduce carbon emissions, to a certain extent. From 18:00 to 24:00, however, the output of renewable energy power generation is small, resulting in less than 5 tons of renewables-based hydrogen production. At this time of day, most hydrogen loads would be satisfied by hydrogen production from fossil fuels and grid power, as well as the hydrogen discharge of storage tanks. As at 18:00–20:00, the hydrogen in the storage tanks would be released to cover the hydrogen shortage. At 20:00–24:00, since the stored hydrogen has been used up, hydrogen would be produced by purchasing electricity from the grid to meet the hydrogen requirements and the hydrogen delivery quantity would also be cut down. In addition, it should be pointed out that to ensure the reliable supply of hydrogen and the stability of the hydrogen system, it is necessary to use fossil fuels to produce hydrogen at any given moment; thus, a minimum level of hydrogen production from fossil fuels is set (such as at 2.71 tons in this scenario).
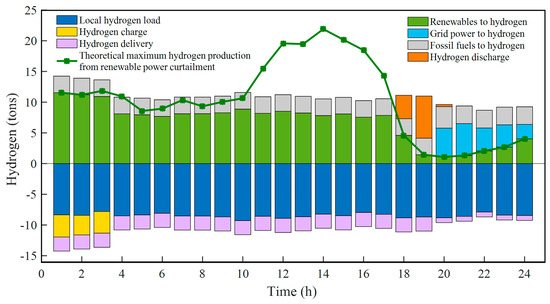
Figure 6.
Hourly optimization results for the entire hydrogen system.
Here are some factors to explain how exactly minimum hydrogen production from fossil fuels ensures reliable hydrogen supply and system stability: (1) by stipulating a minimum level of hydrogen production from fossil fuels, the system gains a consistent and controllable hydrogen source that can be used to stabilize fluctuations in hydrogen production from renewable sources. This minimizes the risk of sudden hydrogen imbalances and helps maintain system stability. (2) Hydrogen production from fossil fuels provides a reliable hydrogen backup. This ensures that the hydrogen system can consistently meet demand, especially during times of low renewable energy production. (3) Hydrogen production from fossil fuels can serve as a baseload hydrogen provider, offering a constant level of hydrogen production to meet the minimum demand of the system. This complements the fluctuation of hydrogen production from renewable sources and helps maintain a stable baseline supply.
To sum up, hydrogen sources can meet the needs of all the hydrogen consumption fields, which ensures the real-time hydrogen balance of the hydrogen system.
- (2)
- Annual optimization results and benefits evaluation
To illustrate the development and positive benefits of the hydrogen system in the next few years, the annual optimization and evaluation results were obtained by the proposed method and can be described as follows.
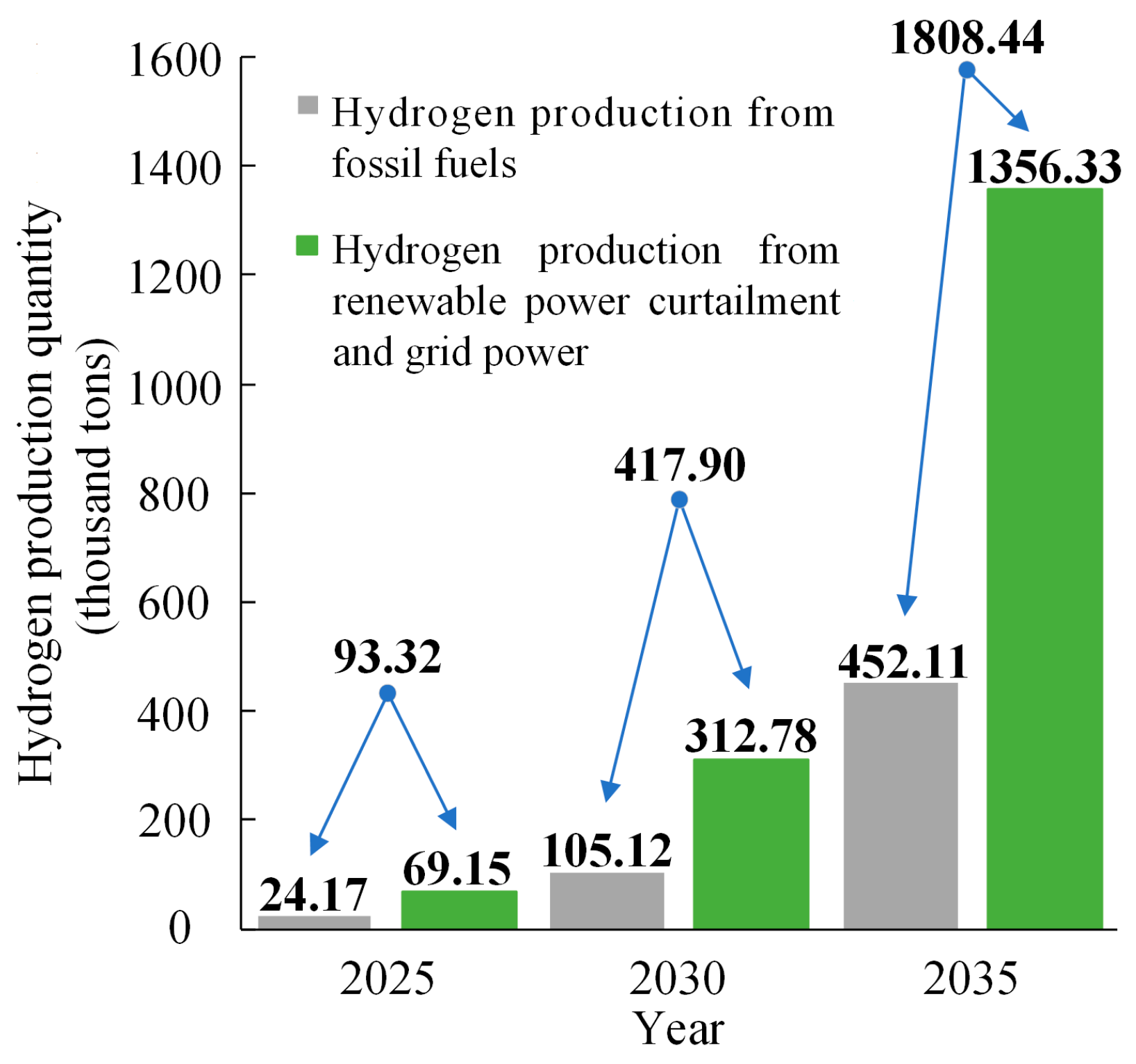
Figure 7 shows the annual hydrogen production in 2025, 2030, and 2035. It can be seen that there will be 93.32 thousand tons of hydrogen produced in 2025, wherein 69.15 thousand tons of hydrogen are produced from renewable power curtailment and grid power, far more than the 24.17 thousand tons of hydrogen production from fossil fuels. With the progress of technology and the increase in hydrogen demand, the amount of hydrogen production will increase significantly. The total hydrogen production in 2030 and 2035 will reach 417.90 thousand tons and 1808.44 thousand tons, respectively, an increase of about 3.5 times and 18.4 times compared with 2025. From the proportion of hydrogen production, it can be seen that about 75% of total hydrogen can be produced from renewable power curtailment and grid power, which is much higher than the hydrogen production from fossil fuels. That is, a large amount of hydrogen production from fossil fuels can be replaced by hydrogen production from renewable energy in the future, thereby alleviating energy and environmental problems.
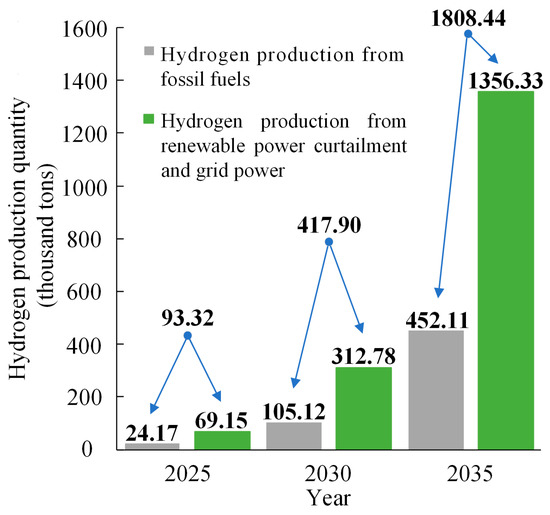
Figure 7.
Annual hydrogen production.
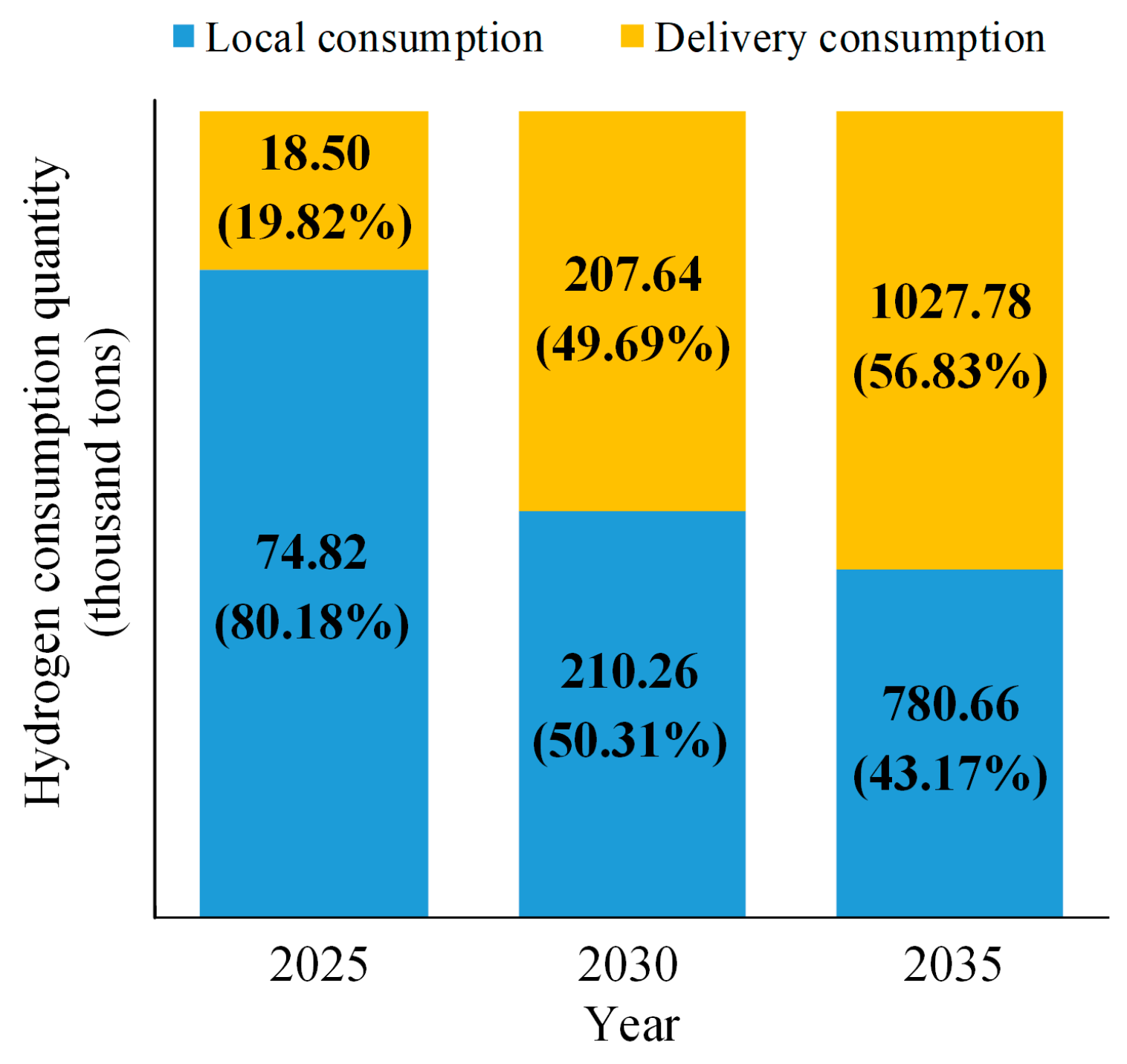
Figure 8 shows the local consumption and delivery consumption of hydrogen energy in different years. It can be seen that 74.82 thousand tons of hydrogen will be consumed in local regions in 2025, accounting for 80.18% of the total annual hydrogen consumption. With the further development of society, the demand for hydrogen energy in various fields is increasing year by year. Local hydrogen consumption will reach 210.26 thousand tons and 780.66 thousand tons by 2030 and 2035, respectively. At the same time, more and more hydrogen can be delivered to other places with the improvement of long-distance hydrogen transportation technology. In addition to hydrogen tube trailers and liquid hydrogen tank trucks, natural gas hydrogen-doped pipelines and pure hydrogen pipelines will also be planned and put into use in the next few years. It can be observed that the annual hydrogen delivery consumption will reach 207.64 thousand tons and 1027.78 thousand tons in 2030 and 2035, respectively, which is about 11.2 times and 55.6 times that of 2025. Comparing local consumption and the delivery consumption of hydrogen energy, it can be seen that the proportion of local hydrogen consumption will be declining due to the limitations of the local hydrogen market, while the proportion of delivery consumption will gradually increase from 19.82% in 2025 to 56.83% in 2035 and will occupy a dominant position.
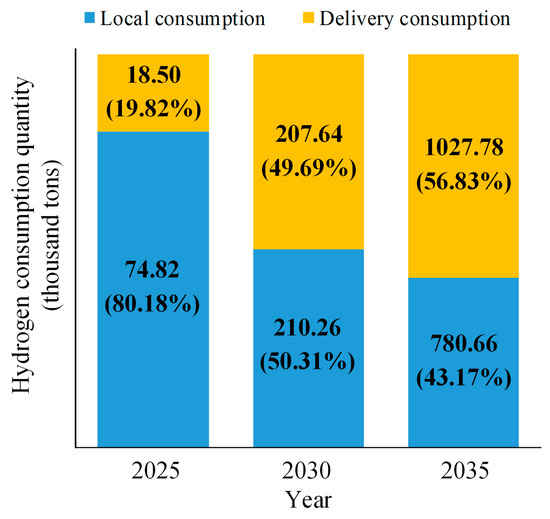
Figure 8.
Annual hydrogen consumption.
To verify the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed system, an in-depth comparative simulation study was also conducted to compare it against the traditional hydrogen system. The comparison results are shown in Table 3 and Table 4. In these tables, the abbreviation “HPfRE” in the table represents “hydrogen production from renewable energy”, and the expressions “With HPfRE” and “Without HPfRE” represent the proposed system and the traditional hydrogen system, respectively. From Table 3, it can be seen that there will be 72.51 billion kW·h of electricity generated from renewable energy in the region in 2025. If using a traditional hydrogen system (without HPfRE), the renewable energy consumption rate would be 89.53% according to the regional grid development plan; thus, 7.59 billion kW·h of renewable power curtailment occurs. Through the full use of large-scale renewable power curtailment to produce hydrogen (with HPfRE), the consumption rate of renewable energy can be significantly improved to 94.51%, which will yield a good energy benefit. In the next few years, renewable power curtailment can be even more marked due to the rapid growth of the installed capacity for renewable energy generation, restrictions to grid access, excess power supply, and a lack of storage capacity and transmission infrastructure. This usually happens when there is high wind or solar availability but there is low electricity consumption, such as in northwest China. Thus, the renewable energy consumption rate without HPfRE in 2030 is assumed to be 86.50%, which is lower than that in 2025, leading to 15.89 billion kW·h of renewable power curtailment. Employing HPfRE can reduce the power curtailment by nearly three-quarters and further improve the renewable energy consumption rate to 96.59%. As time goes on, renewable power curtailment can be alleviated when improvements are made in terms of grid infrastructure, storage capabilities, and regulatory policies to better accommodate and utilize renewable energy. Assuming that the renewable energy consumption rate without HPfRE in 2035 is 91.00%, there would be 17.21 billion kW·h of renewable power curtailment. If HPfRE is taken into account, the renewable energy consumption rate can be further increased to 98.70%.

Table 3.
Evaluation results for promoting renewable energy consumption in the hydrogen system.

Table 4.
Energy, environmental, and economic benefits of the hydrogen system.
Table 4 further shows the energy, environmental, and economic benefits of the hydrogen system. It can be seen that more and more renewable energy consumption can be promoted with the increasing hydrogen production from renewable power curtailment. From 2025 to 2035, renewable energy consumption promotion will increase from 3.61 billion kW·h to 14.72 billion kW·h, an increase of nearly three times. If this sector of renewable energy generation is converted into coal-fired power generation and the benchmark electricity price for coal burning is 0.0502 USD/kW·h, it will lead to an economic cost of USD 181.27 million in 2025. Similarly, the corresponding economic costs of USD 596.35 million and USD 738.53 million will be incurred in 2030 and 2035. From the point of view of environmental benefit, 1.11 million tons of carbon emissions can be reduced in 2025 because large amounts of hydrogen production from fossil fuels are replaced by hydrogen production from renewable power curtailment and grid power, which is equivalent to saving USD 9.17 million of economic costs according to the current average level of carbon market prices (USD 8.2853/ton). By 2030, both the reduction in carbon emissions and the corresponding economic benefits will be more than three times greater than in 2025. That is, the carbon emissions of the system can be reduced by 4.62 million tons, bringing equivalent economic benefits of USD 38.31 million. By 2035, the positive benefits of the hydrogen system will be even more pronounced. Among them, 15.37 million tons of carbon emissions reduction can save economic costs of USD 127.34 million, an increase of nearly 13 times compared with 2025. In total, the equivalent economic benefits of renewable energy consumption promotion and carbon emissions reduction are USD 190.44 million, USD 634.66 million, and USD 865.87 million for 2025, 2030, and 2035, respectively.
6. Conclusions
The modeling, optimization, and assessment of a large-scale renewables-based hydrogen system are conducted with full consideration of the various transportation modes and multi-field hydrogen loads. According to the proposed model and method, simulation studies are undertaken in detail and the results demonstrate the following major findings:
- (1)
- For those areas with abundant wind and solar energy, the abandonment of renewable energy power generation is usually a serious matter. By utilizing renewable power curtailment to produce hydrogen, the consumption rate of renewable energy can be increased to 94.51% in 2025, 96.59% in 2030, and 98.70% in 2035, which is about 5–10% higher than the traditional hydrogen system based on fossil fuels. Since the fluctuation of renewable energy influences the fluctuation of hydrogen production, it is necessary to set a minimum level of hydrogen production from fossil fuels to ensure the reliable supply of hydrogen and the stability of the hydrogen system.
- (2)
- The real-time hydrogen balance of the whole system and the quantitative assessment of regional hydrogen consumption capacity in different years can be realized through the proposed method. With the further development of society, the total amount of annual hydrogen consumption will increase significantly from 93.32 thousand tons in 2025 to 1808.44 thousand tons in 2035, about an 18-fold increase. In this scenario, about 75% of hydrogen would be produced from renewable power curtailment and grid power, a much higher percentage than hydrogen production from fossil fuels. Due to the limitations of the local hydrogen market and the improvement of long-distance hydrogen transportation technology, the proportion of local hydrogen consumption will decline from 80.18% in 2025 to 43.17% in 2035, while the proportion of hydrogen delivery consumption will increase from 19.82% in 2025 to 56.83% in 2035 and will occupy a dominant position.
- (3)
- By utilizing renewable energy instead of fossil fuels to produce hydrogen, this could reduce carbon emissions by 1.11 million tons in 2025, 4.62 million tons in 2030, and 15.37 million tons in 2035, which represents a good environmental benefit. In terms of the equivalent economic benefits of renewable energy consumption promotion and carbon emissions reduction, this will save USD 190.44 million in 2025, USD 634.66 million in 2030, and USD 865.87 million in 2035.
In addition, it should be pointed out that this work makes some simplifications and assumptions in the modeling of the hydrogen system, which leads to a certain level of error compared to the actual situation. In follow-up work, the whole hydrogen system will be further improved with more realistic models and more complete system components (such as hydrogen filtration). At the same time, an in-depth parameter sensitivity analysis and some fluctuation control strategies, along with the consideration of more operating conditions (such as the load, speed, and purity of water input) will be studied to improve the system’s performance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.T. and L.H.; methodology, Y.T., Q.Z. and L.S.; software, Q.Z., Y.T. and D.L.; validation, L.H., Y.T. and Q.Z.; formal analysis, Y.T., Q.Z., D.L. and L.S.; investigation, Q.Z., Y.X. and T.L.; resources, D.L., L.S., Y.X. and Y.T.; data curation, Y.T., L.H. and Q.Z.; writing—original draft, Y.T., Q.Z., L.H., L.S. and D.L.; writing—review and editing, Y.T., Y.X., Q.Z. and T.L.; visualization, Y.X. and T.L.; supervision, L.H. and Y.T.; project administration, L.H., D.L. and Y.T.; funding acquisition, L.H. and Y.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by the Scientific and Technological Project of the State Grid Gansu Electric Power Company Jiuquan Power Supply Company (W23KJ2706018).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Liu Hong, Deqi Liu, Lei Shi and Yujin Xiang were employed by the State Grid Gansu Electric Power Company Jiuquan Power Supply Company. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, F.; Harindintwali, J.D.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, M.; Wang, F.; Li, S.; Yin, Z.; Huang, L.; Fu, Y.; Li, L.; et al. Technologies and perspectives for achieving carbon neutrality. Innovation 2021, 2, 100180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Energy Administration. Medium and Long-Term Planning of Hydrogen Energy Industry Development (2021–2035). Available online: http://zfxxgk.nea.gov.cn/2022-03/23/c_1310525630.htm (accessed on 23 October 2022).
- Pan, G.; Gu, W.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, Y. Electricity and hydrogen energy system towards accommodation of high proportion of renewable energy. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2020, 44, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, F.; Guo, T.; Chen, K.; Jin, X.L.; Zhang, L.; Yang, J.H.; Yin, A.M. Progress and development prospect of coupled wind and hydrogen systems. Proc. CSEE 2021, 41, 2187–2200. [Google Scholar]
- Ruhani, B.; Moghaddas, S.A.; Kheradmand, A. Hydrogen production via renewable-based energy system: Thermoeconomic assessment and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) optimization approach. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 52, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Lv, M.; Gu, Y.; Yang, X.; Tang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, M. Hybrid energy system for a coal-based chemical industry. Joule 2018, 2, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samara, E.; Andronikidis, A.; Komninos, N.; Bakouros, Y.; Katsoras, E. The role of digital technologies for regional development: A system dynamics analysis. J. Knowl. Econ. 2022, 14, 2215–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Mao, J.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, Q. Modeling, optimization and evaluation of production-storage-utilization hydrogen system based on renewable energy. In Proceedings of the 2023 3rd International Conference on Intelligent Power and Systems (ICIPS), Shenzhen, China, 20–22 October 2023; pp. 832–838. [Google Scholar]
- Brey, J.J. Use of hydrogen as a seasonal energy storage system to manage renewable power deployment in Spain by 2030. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 17447–17457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. The status quo and trend of producing hydrogen from new energy. Chem. Ind. 2018, 36, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, D.; Aziz, M. Perspective of staged hydrogen economy in Japan: A case study based on the data-driven method. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 189, 113907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Wang, D.; Chen, Q.; Tang, Z. Techno-economic analysis of green methanol plant with optimal design of renewable hydrogen production: A case study in China. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 5085–5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den, R.B.; Smit, M.A. Determining the future business case for small-scale hydrogen storage of renewable energy for autonomous residential applications. Acad. Res. Community Publ. 2018, 1, 423–429. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, D.; Aziz, M. Flexible operation strategy of an integrated renewable multi-generation system for electricity, hydrogen, ammonia, and heating. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 253, 115166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Yang, D.; Sun, C.; Yuan, T.; Liu, Y. Capacity planning of hydrogen production and storage system based on hydrogen load demand. Electr. Power 2023, 56, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, X.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, W. Ensemble prediction aided multi-objective co-design optimizations of grid-connected integrated renewables for green hydrogen production. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 425, 138585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, S.T.; Nguyen, T.N.; Linforth, S.; Ngo, T.D. Safety investigation of hydrogen energy storage systems using quantitative risk assessment. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 2861–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Cai, R. Optimal planning for industrial park-integrated energy system with hydrogen energy industry chain. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 19046–19059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, H.; Kang, K.; Seo, Y. Environmental and energy efficiency assessments of offshore hydrogen supply chains utilizing compressed gaseous hydrogen, liquefied hydrogen, liquid organic hydrogen carriers and ammonia. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 7515–7532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yuan, T.; Tan, J. Medium and long-term forecast of hydrogen load in unified energy system. Proc. CSEE 2021, 41, 3364–3372, 3662. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Gómez, Á.; Ramirez, V.; Guilbert, D. Investigation of PEM electrolyzer modeling: Electrical domain, efficiency, and specific energy consumption. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 14625–14639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Cheng, J. Multi-agent coordination and optimization of vpps-p2h based on carbon capture. Acta Energiae Solaris Sin. 2023, 44, 92–101. [Google Scholar]
- Asl, S.M.S.; Rowshanzamir, S.; Eikani, M.H. Modelling and simulation of the steady-state and dynamic behaviour of a PEM fuel cell. Energy 2010, 35, 1633–1646. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, S.; Xu, X.; Yan, Z.; Wang, H.; Han, P. Multi-stage robust optimal scheduling of coupled electricity-hydrogen system based on multiple affine decision rules. Autom. Electr. Power Syst. 2023, 47, 42–52. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Luo, X.; Duan, H. A novel nonlinear multivariable Verhulst grey prediction model: A case study of oil consumption forecasting in China. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 3424–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhi, Y.; Jia, H.; Hou, K.; Zhang, S.; Du, W.; Wang, X.; Fang, M. Optimal scheduling strategy of district integrated heat and power system with wind power and multiple energy stations considering thermal inertia of buildings under different heating regulation modes. Appl. Energy 2019, 240, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Feng, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, X. Multiple time-scale production simulation of power system with large-scale renewable energy. Proc. CSEE 2020, 40, 6103–6113. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, J. The Evaluation of Economic, Energy, Environment and Social Comprehensive Benefits of Different Hydrogen Production Technologies; Shanxi University of Finance & Economics: Xi’an, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H. Potential advantages of hydrogen in transformation of energy resources. Distrib. Energy 2020, 5, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Cost Analysis and Development Forecast of Electric Hydrogen Production. Available online: https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1779738798875117732&wfr=spider&for=pc (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Yu, J.; Fang, J.; Kong, L.; Wang, Y. Rational utilization and development of Shaoxing industrial by-product hydrogen. Mod. Ind. Econ. Informationization 2023, 13, 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Miao, S.; Yuan, T. Prediction of hydrogen demand in transportation field based on system dynamics. Electr. Power Autom. Equip. 2024, 44, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Jiuquan Municipal People’s Government Office. “14th Five-Year” Energy Development Plan in Jiuquan City. Available online: https://www.jiuquan.gov.cn/jiuquan/c102145g/202208/4d151a36b8b14b7d8c5dc0301b60766b.shtml?eqid=ef6e7378002e097800000003644800c5 (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Jiuquan Municipal People’s Government Office. Hydrogen Energy Industry Development Implementation Plan in Jiuquan City (2022–2025). Available online: https://www.jiuquan.gov.cn/jiuquan/c100039/202206/4cdeff606ef4444a955c899d98daaa78.shtml (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Jiuquan Municipal People’s Government Office. Medium and Long-Term Planning of Hydrogen Industry Development in Jiuquan City (2022–2035). Available online: http://www.jiuquan.gov.cn/jiuquan/c102145g/202210/69f4336cb7354fe6a040bc1dcdccc49e.shtml (accessed on 10 January 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).