Abstract
Previous studies have linked the electron-shuttling properties of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) species to antiviral efficacy. This study explores the antiviral potential of Cassia obtusifolia seeds through electrochemical analyses using microbial fuel cells (MFCs) and cyclic voltammetry (CV) complemented by in silico methods. The phytochemical contents and antioxidant activity of Cassia seed extracts were assessed and correlated with bioenergy generation and electrochemical stability. A principal component analysis (PCA) indicated that phytochemical and antioxidant activity influence Cassia’s power-generating potential. The MFC study revealed a 1.87-fold power amplification in unprocessed Cassia seed water extract (CTS-W), while CV analysis demonstrated enhanced electrochemical stability and reversibility due to the presence of electron-shuttling (ES) species. In silico analyses, including network pharmacology and molecular docking, provided supporting evidence for the antiviral potential of bioactive metabolites in Cassia seeds, particularly in targeting Hepatitis B virus-related genes. Furthermore, a mathematical model highlighted the superior therapeutic efficacy of electron-shuttling (ES) species compared to antioxidants in disease treatment. These findings demonstrate a strong correlation between the electron-shuttling properties and the antiviral potential of C. obtusifolia seed extracts, suggesting that bioenergy-mediated mechanisms may play a crucial role in the development of effective antiviral therapies.
1. Introduction
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has been extensively utilized for thousands of years, serving as a fundamental component of traditional healthcare systems across Asia. Despite the rapid advancements in modern pharmacotherapy, TCM remains integral to disease prevention and treatment due to its holistic approach and the synergistic interactions of its multi-component formulations. Herbal medicines constitute the core of TCM, encompassing a vast array of plant species with well-documented therapeutic effects. These medicinal plants have demonstrated efficacy in managing a broad spectrum of conditions, including metabolic disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and infectious diseases. Over the years, TCM has been increasingly studied using modern scientific methodologies to elucidate its pharmacological mechanisms. One emerging area of interest is the role of bio-electrochemical properties in modulating disease treatment efficacy. Recent studies have highlighted the potential of electron-shuttling compounds (ESs) in facilitating pharmacological effects through electrochemical catalysis [1]. Tsai et al. [1] suggested that bio-electrochemical assessments provide a scientific foundation for understanding the antiviral potential of TCM, particularly in the context of COVID-19. The electrochemical catalysis of ESs enhances synergistic interactions among herbal compounds, thereby potentiating antiviral, immunomodulatory, and neuroprotective effects. Given the multi-component nature of TCM formulations, its effectiveness against viral infections may be strongly correlated with such electrochemical interactions, warranting further exploration [2,3,4]. Even TCM and many plant species have been popularly used for many thousands of years, scientific Deciphering in depth still remained not completed very likely due to lack of precise and delicate instruments. In particular, medicinal herbs contained diverse compositions for medical purposes. Thus, MOA associated with combined and complicated interactions for disease treatment may still be inevitably required to have wide-ranging applications. That is, TCM’s own power of compounded medication that “single drug to single disease”-based Western medicine cannot simply address. In particular, environmental conditions have gradually worsened over the past two decades, even leading to the emergence of more diseases. TCM’s broad therapeutic capabilities will likely be the most promising treatment approach, at least for the coming decades and beyond. Due to these reasons, this work intends to provide a new perspective coupled with electrochemical methodology to elucidate the MOA of herbal medication via redox mediation (or electron transfer). This is the significance of this novel work.
The therapeutic effects of TCM formulations are attributed to their complex chemical compositions, comprising phenolics, flavonoids, alkaloids, anthraquinones, terpenoids, and polysaccharides, among others. These bioactive constituents exhibit diverse pharmacological activities, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, antibacterial, and anticancer properties [5,6,7,8]. Notably, polyphenolic compounds have been extensively studied for their redox-modulating capabilities, which are crucial for mediating their biological effects. Recent research has underscored the distinction between traditional antioxidants and electron-shuttling compounds. While antioxidants neutralize free radicals through transient electron donation, ESs provide sustained bioelectric power, thereby prolonging therapeutic effects [1]. The presence of ortho- and para-dihydroxyl substituents in these compounds is essential for their redox-mediated interactions, making them highly relevant to antiviral therapy and immunomodulation. Furthermore, flavonoids with such electron-transfer properties exhibit synergistic effects when combined with other phenolic metabolites, significantly enhancing their pharmacological efficacy.
The bio-electrochemical activity of phenolic metabolites is intrinsically linked to their structural features, particularly their capability to facilitate electron transfer. Polyphenols bearing ortho-dihydroxyl groups exhibit remarkable redox-mediating capabilities, which have been associated with antiviral, neuroprotective, and anti-inflammatory characteristics [1]. These redox-mediating compounds have demonstrated the potential to stimulate bioelectricity generation, an essential factor in mediating their electrochemical interactions with biological systems. That is why we were first study group to correlate such a nature in terms of bioelectric capability to identify whether phenolic compounds in plant species own redox-mediating or antioxidant-bearing nature for the above-mentioned characteristics. This model platform provided economically feasible and technically promising means to screen among the test plant species for the next follow-up step and toward FDA testing. Furthermore, the electron-shuttling nature of certain phenolic compounds has been linked to their modulation of cellular signaling pathways, including those involved in oxidative stress, mitochondrial function, and immune responses. Specifically, anthraquinones, a class of polyphenolic secondary metabolites, have been identified as promising electroactive compounds with bioenergy-enhancing properties. Given their electron-donating capacity, anthraquinones such as chrysophanol, emodin, aloe-emodin, and rhein are of particular interest in antiviral drug development [5,6,9,10,11]. ES as an electrochemical catalyst is a new concept to link with herbal medication. In particular, for at least two decades, polyphenolic compounds have been misinterpreted as antioxidants in the literature. This “misunderstanding” has limited the potential of phenolic-based medications, reducing them to merely non-sustainable reactants for disease treatment. However, with the COVID-19 pandemic, we have clarified the true significance of ES, explaining why and how ES-bearing herbal medicines have been so effective in treating COVID-19.The genus Cassia consists of several medicinally significant species, among which Cassia obtusifolia (C. obtusifolia) is widely utilized in TCM. The dried seeds of this plant, referred to as Cassia seeds, have been traditionally consumed as herbal teas or health supplements. In TCM, C. obtusifolia is prescribed for vision disorders [10,12], dizziness [13], constipation [9,12,13,14], hypertension [12], and hyperlipidemia [13]. In addition to its conventional applications, Cassia seed extracts have demonstrated broad pharmacological potential, including anticancer [5,6,9,14], neuroprotective [5,6,7,9,14], antibacterial [13,15], and anti-inflammatory properties [9,12,14,16]. However, limited studies have explored their antiviral potential, necessitating further investigation into their mechanisms of action (MOA) and therapeutic feasibility.
Recent research has identified several anthraquinone derivatives in C. obtusifolia seeds, including chrysophanol, emodin, aloe-emodin, rhein, gluco-obtusifolin, gluco-aurantioobtusin, glucochrysoobtusin, and questin [5,6,9,10]. These compounds exhibit potent electron-shuttling capabilities, which contribute to their bioenergy-enhancing and antiviral effects. Notably, the electrochemical properties of anthraquinones have been correlated with their ability to amplify electron transfer, making them valuable candidates for antiviral research. Despite growing evidence supporting the therapeutic potential of C. obtusifolia, the antiviral capabilities of its bioactive constituents remain largely unexplored. Given the emerging role of electron-shuttling mechanisms in antiviral pharmacology, this study aims to investigate the bioelectrochemical properties of C. obtusifolia seed extracts to establish their pharmacological feasibility.
This study is based on the hypothesis that the electron-shuttling nature of anthraquinones plays a crucial role in electrochemical catalysis, which is possibly related to their antiviral efficacy., offering a novel MOA distinct from conventional antioxidant mechanisms. To test this hypothesis, this study employed the following: (1) microbial fuel cells (MFCs) and cyclic voltammetry (CV) analyses to assess the bioenergy-stimulating capabilities of C. obtusifolia extracts; (2) Network Pharmacology (NP) to analyze the potential interactions between anthraquinone compounds and biological pathways associated with viral infections; (3) Molecular Dynamics (MD) simulations to establish protein–ligand binding relationships, elucidating the structural determinants of antiviral activity; and (4) an integrative model combining phytochemical, electrochemical, NP, and MD approaches to propose a hypothesized comprehensive mechanistic understanding of anthraquinone compounds in antiviral therapy.
By systematically evaluating the electrochemical, biochemical, and pharmacological attributes of C. obtusifolia, this study aims to bridge the gap between traditional knowledge and modern pharmacological research. The findings will offer valuable insights into the therapeutic implications of electron-shuttling mechanisms, paving the way for the development of novel bioelectrochemical antiviral strategies based on TCM. The most important insight is to provide the revolutionary concept of “electron shuttling” to redefine how and why many redox-mediating herbal medicines or/and drugs were so powerful as to efficaciously treat diseases (e.g., COVID-19).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
Samples of C. obtusifolia seeds were purchased from a Traditional Chinese Medicine store in Tainan City, Taiwan (a voucher specimen #CJCU-CO-001 of C. obtusifolia was deposited at the Department of Medical Science Industries, Chang Jung Christian University, Taiwan).
2.2. Sample Preparation of Processing C. obtusifolia Seeds
In total, 200 g of sample C. obtusifolia seeds were processed by stir-frying using an induction cooker (950–1150 W) until a burnt yellow color was observed. Meanwhile, approximately 100 g of raw and processed C. obtusifolia seeds were accurately weighed and grinded prior to extraction. At the ratio of 1:20 (sample: solvent), the samples were extracted using water and ethanol. For the ethanol solvent, reflux extraction (2 h, 65 °C) was applied. While the water extraction (decoction) was implemented by using a traditional Chinese decoction pot until 200 mL of the extract was obtained. The resulting solutions were vacuum-filtered, and the excess solvent was evaporated using a rotary evaporator. Residual water from the samples was removed via freeze-drying. All samples were then prepared in a microcentrifuge tube by dissolving 10 mg of each of the dried extracts in 1 mL of ethanol, except for the aqueous extract, which was prepared using distilled and deionized water for phytochemical content analysis and antioxidant evaluation.
2.3. Phytochemical Analyses
2.3.1. Determination of Total Polyphenol Content (TPC)
The determination of TPC was adopted as described elsewhere [1]. The sample solution was prepared by diluting 10 mg/mL of the crude extract with ethanol to obtain 1 mg/mL of the sample. In total, 250 µL of sample was treated with 250 µL of Folin–Ciocalteu reagent, followed by the addition of 500 µL of saturated Na2CO3 solution. The sample was diluted with 4 mL using distilled water. Meanwhile, stock solution A was prepared by dissolving 10 mg of gallic acid with 1 mL of ethanol. In addition, stock solution B was prepared by diluting 50 µL of stock A to 1 mL. Serial dilution with 1000 µL of ethanol was performed to obtain different standard concentrations. Similarly to the sample solution, 250 µL of the standard solution was treated with 250 µL of Folin–Ciocalteu reagent, followed by adding 500 µL of saturated Na2CO3 and then diluting it with DI water. The resulting solutions were incubated for 30 min prior to analysis. After the incubation, 200 µL of the test solutions were transferred to an ELISA microplate reader in triplicate, and the absorbances of the solutions were analyzed at a wavelength of 600 nm.
2.3.2. Determination of Total Flavonoid Content (TFC)
The TFC of the samples was determined using protocols from the literature [1]. In preparing the sample solution, 1 mg/mL was obtained by diluting the 10 mg/mL of the crude extracted with ethanol. Meanwhile, the standard stock solution was prepared by dissolving 5 mg of quercetin with 1 mL of ethanol. Using the standard stock solution, a series of standards with varying concentrations were made by serial dilution using ethanol. The sample and standard solutions were treated with 2% AlCl3 solution in methanol (1 mL sample:1 mL AlCl3) and incubated for 1 h in a dark room. The solutions were transferred in a microplate reader in triplicate before analyzing in the UV-Vis spectrophotometer at a wavelength of 430 nm [17].
2.3.3. Determination of Total Condensed Tannin Content (TCTC)
This study also examined the total condensed tannins based on previously mentioned procedures [1]. The first standard stock solution was made by dissolving 5 mg of catechin in 1 mL of ethanol. The second stock solution was obtained by taking 32 μL of the previously prepared solution and diluting it to 1000 μL with ethanol. From here, the second stock solution was serially diluted twice to create seven standard solutions (160, 80, 40, 20, 10, 5.0, and 2.5 μg/mL). Regarding the sample, 1 mL of ethanol was used to dissolve 10 mg of extract. After that, an aliquot of 50 μL was made and diluted with 250 μL of ethanol. Following that, 600 μL of vanillin was added. To guarantee the repeatability of the data, each solution preparation step was completed in triplicate. The absorbance of the solutions was measured using an ELISA microplate reader at 530 nm.
2.3.4. HPLC Analysis
The major compound was separated and identified in the extracts using liquid chromatography (LC-2050C 3D; Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan) for verification through a Hypersil ™ BDS C18 column (250 4.6 mm, 5 m, Thermo Fischer Scientific Inc., Taipei, Taiwan) kept at 40 °C. An amount of 10 mg/mL of crude extracts dissolved in water or ethanol was filtered in a 0.45 μm syringe filter and injected into the column. Chromatography runs were performed with mobile phases of water (eluent A) and ACN (eluent B). The implemented gradient program was 5–100% B (0–60 min) [18].
2.4. Antioxidant Activity
2.4.1. Determination of DPPH Free Radical Scavenging Activity
All procedures for the DPPH assay were based on the protocols mentioned in the literature [1]. The environment was kept dark to prevent the breakdown of light-sensitive reagents during the DPPH experiment. The stock solution was made by dissolving 5 mg of ascorbic acid in 1 mL of deionized (DI) water before making the standard solutions. A set of standards with varying concentrations was generated from the stock solution by serial dilution with ethanol. In a microplate, 100 µL of the sample, standards, control (ethanol), and blank solutions were transferred and treated with 150 µL of DPPH solution. After resting for 30 min, the solution was examined at a wavelength of 517 nm. Meanwhile, the solution presented below was used to determine the radical scavenging activity (%RSA) of the sample. In addition, a linear regression analysis was implemented to determine the 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) at 50% RSA.
2.4.2. Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power (FRAP) Assay
The procedure concerning the FRAP assay was made following previous work [1]. To obtain a final concentration of 1000 μg/mL, 500 μg/mL of Trolox stock solution was diluted with 500 μL of ethanol:double-distilled (DD) water (2:3) mixture to create a standard stock solution. Using ethanol, 100 μL of the standard stock solution was further diluted to 1000 μL. Through serial dilution, a range of standard concentrations were created. In a microplate, 1450 μL of FRAP solution was added to 50 microliters (50 μL) of extract, standard solution, and blank. Each solution was made in triplicate to find the quantitation limit, and 24 blanks were tested. The absorbance of each test solution was then measured at 593 nm using an ELISA microplate reader for analysis.
2.5. Cyclic Voltammetry
Cyclic Voltammetry (CV) is an electrochemical technique used to study redox reactions by applying a cyclic potential sweep to a system and measuring the resulting current. It utilizes a three-electrode setup (working, reference, and counter electrodes) and an electrolyte to facilitate electron transfer. As the potential is cycled, oxidation and reduction currents are recorded, revealing redox potentials, reaction kinetics, and electrochemical stability. Reversible reactions show symmetric anodic and cathodic peaks, while irreversible reactions display single peaks.
The same concentration of plant extracts (2000 ppm) was prepared to determine and compare its electrochemical properties. The CV studies followed the protocol indicated in a previous work [17]. Using an electrochemical workstation (CHI-627A, CH Instruments Inc., USA), the electrochemical reversible stability of the samples was tested with a scan rate of 10 mV/s for 50 cycles. Before the analysis, the sample was flushed with nitrogen gas for 15 min. The electrodes used were a glassy carbon electrode (WE, 0.07 cm2), platinum electrode (AE, 6.08 cm2), and Hg/Hg2Cl2 electrode with saturated KCl (aq) (RE). The glassy carbon electrode (ID = 3 mm; model CHI-104, CH Instruments Inc., USA) was first cleaned using 0.05 mm alumina polish and was washed with deionized water before the study.
2.6. Power Density Assessment Via DC-MFC Platform
The theory of power density assessment Via a DC-MFC (Direct Current Microbial Fuel Cell) platform explores how bioelectrochemical systems generate power density by converting chemical energy from organic matter into electrical energy through the microbial metabolism. In MFCs, microorganisms oxidize substrates at the anode, releasing electrons that flow to the cathode through an external circuit, generating direct current (DC). Power density, a key metric for evaluating MFC efficiency, depends on factors such as electron transfer rates, substrate utilization, internal resistance, and the electrochemical properties of electron shuttles.
2.6.1. MFC Operation and Microbial Cultures
For the microbial growth medium, LB broth medium (Difco LB Broth, Miller; Luria–Bertani) containing 10 g/L tryptone, 5 g/L yeast extract, and 10 g/L NaCl was used for batch cultures. The electroactive bacterium—Aeromonas hydrophilia (NIU01)—was precultured in a sterile LB broth for 12 h in a shaker water bath at 30 °C. Afterward, subcultures were prepared by adding 1% (v/v) of the preculture broth into a freshly prepared LB broth solution. The resulting solutions were incubated for another 12 h. Consequently, the electrolyte solution for the cathode chamber was prepared by dissolving a mixture of 6.38 g K3[Fe(CN)6] and 17.42 g K2HPO4 in 200 mL of distilled deionized water.
For the double chamber MFC operation, the graphite anode and cathode soaking areas were approximately 0.001649 m2, and the chambers of the MFC were isolated using a proton exchange membrane (DuPont Nafion NR-212). Both anode and cathode chambers consist of 200 mL working solutions. For the quantitative evaluation of the bioelectricity-generating performance, the herbal extract was then placed in the anodic chamber in a double-chamber MFC (OD600~2.0–2.2). MFC experiments were performed at room temperature. All procedures were performed according to previous studies [1].
2.6.2. Power-Generating Determination
Using a D/A system (DAS 5020, Jiehan Tech. Corp., Taiwan), the power generation of the MFC was determined. The D/A system allowed for the determination of electric current (IMFC) and voltage (VMFC). An external resistance of 1 KΩ was employed in the system to have a consistent comparison. The following equations were utilized to calculate the power and current densities. The VMFC and IMFC were obtained by performing the linear sweep voltammetry feature of the electrochemical analysis workstation. The concentrations of extracts supplemented for MFCs are 500, 1000, 1500, and 2000 ppm. The calculations were adapted from prior studies [1].
2.7. Network Pharmacology
The principle of network pharmacology integrates systems biology and bioinformatics to explore the complex interactions between drugs, targets, and biological networks, offering a holistic approach to drug discovery and disease treatment. Unlike traditional pharmacology, which often focuses on single-target drugs, network pharmacology emphasizes multi-target multi-pathway mechanisms by analyzing molecular networks and their biological pathways. This approach identifies key nodes and interactions within these networks, elucidating drug effects at the systems level. By mapping the connections between compounds, targets, and diseases, network pharmacology provides insights into synergistic effects, drug repositioning, and precision medicine, making it especially relevant for complex diseases and herbal medicine.
2.7.1. Screening of Bioactive Compounds from C. obtusifolia
The bioactive compounds in Cassia seed extracts were retrieved using the SymMap webserver (http://www.symmap.org/, accessed on 6 November 2023). This database combines TCM with modern medicine, using symptom mapping and molecular mechanisms to establish correlations between compounds and targets [19]. Only anthraquinone species were taken into consideration in order to reduce the total number of chemicals collected.
2.7.2. Identification of Target Proteins
The protein targets of the bioactive compounds were identified using the “Target” function in SymMap. Meanwhile, the GeneCards database (https://www.genecards.org/, accessed on 6 November 2023) was used to look for genes associated with the Hepatitis B virus and viral cell replication. Using the intersection of the genes linked to Hepatitis B, viral cell replication, and the protein targets of the bioactive chemicals in the Venn diagram constructed using Venny (https://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny/, accessed on 6 November 2023), the primary target genes were identified.
2.7.3. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network Construction
Protein–protein interactions were predicted by utilizing the genes associated with Hepatitis B and the bioactive compounds of Cassia in STRING (https://string-db.org/, accessed on 8 November 2023). The network that was established was imported into Cytoscape 3.10.1. The cytoHubba plugin in Cytoscape determined the degree, MCC, and centrality based on the betweenness and closeness of the network nodes to determine the top ten hub genes in this network. The genes commonly appearing in each of the four computed criteria are referred to as the hub genes [20].
2.7.4. Pathway Enrichment Analysis—KEGG and Gene Ontology
The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) and Gene Ontology (GO) databases were used with the ShinyGO 0.77 web server (http://bioinformatics.sdstate.edu/go/, accessed on 6 November 2023). The discovered target and disease-related proteins were subjected to separate functional and pathway analyses in these databases. The fundamental characteristics and abilities of the genes are listed in the GO database. Consequently, distinct data regarding the genes and the pathways connected to them can be found in the KEGG pathway database [20].
2.8. Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Studies
Molecular docking and molecular dynamics (MD) studies are computational techniques used to investigate ligand–target interactions, predict binding affinities, and explore the stability of molecular complexes. Docking predicts the preferred orientation of a ligand when binding to a target, scoring potential binding poses based on shape complementarity, hydrogen bonding, and other interactions, aiding in drug discovery by screening compounds and identifying binding modes. MD simulations analyze the time-dependent behavior of molecules, providing insights into the stability, flexibility, and dynamic interactions of ligand–target complexes in realistic conditions. Together, these methods offer a comprehensive approach to understanding molecular mechanisms and guiding rational drug design.
The molecular docking study was conducted using the CB-Dock2 online server to ascertain the interactions between the compounds and selected proteins. After obtaining the target protein’s structure from the Protein Data Bank, it was immediately imported onto the CB-Dock2 site. On the other hand, the docking ligands were uploaded to CB-Dock2 after being retrieved in 3D configuration from PubChem. A blind docking study was conducted to evaluate the binding energy of the selected ligands to the target protein. In the meantime, the CABS-flex 2.0 web server was used to examine the deformability of the protein–ligand complexes obtained from the docking study to determine their stability and binding modes.
2.9. Statistical Analysis and PCA
The principal component analysis statistical method was used to assess the relationships between the components TPC, TFC, TCTC, DPPH, and PD [21]. The IBM SPSS software (version 25) was used for all statistical data treatment, PCA, and factor analysis to show the multivariate data clusters connecting the mentioned variables. All calculations for p-values were performed using Microsoft Excel.
3. Results
3.1. Phytochemical Analyses
Table 1 presents the phytochemical composition of different Cassia extracts, including total polyphenol content (TPC), total flavonoid content (TFC), and total condensed tannin content (TCTC). The results indicate significant differences in bioactive compound levels depending on the extraction method and processing conditions. Among the extracts, the processed ethanol extract (PCTS-E) exhibited the highest bioactive compound concentrations, with TPC at 35.109 ± 1.254 mg/g, TFC at 58.803 ± 0.157 mg/g, and TCTC at 19.814 ± 0.394 mg/g. In contrast, the unprocessed water extract (CTS-W) had the lowest values across all phytochemical categories, with TPC at 12.149 ± 0.224 mg/g, TFC at 13.890 ± 0.600 mg/g, and TCTC at 3.430 ± 0.180 mg/g. The statistical analysis revealed highly significant differences (p < 0.001) among the extract groups, particularly between processed ethanol extract (PCTS-E) and unprocessed water extract (CTS-W). Furthermore, the comparison between processed (PCTS-W, PCTS-E) and unprocessed (CTS-W, CTS-E) extracts demonstrated that processing (stir-frying) and ethanol extraction greatly enhanced the yield of polyphenols, flavonoids, and tannins. The results indicate that ethanol extraction combined with processing (stir-frying) is the most effective method for maximizing the extraction of bioactive compounds from Cassia. These findings emphasize the importance of both solvent selection and thermal processing in optimizing the phytochemical yield, which may further enhance the functional and therapeutic potential of Cassia extracts.

Table 1.
Phytochemical content analysis on water and ethanol extracts of Cassia: unprocessed water extract (CTS-W), unprocessed ethanol extract (CTS-E), processed water extract (PCTS-W), and processed ethanol extract (PCTS-E).
The HPLC spectra in Supplementary Figure S6 compare the chemical fingerprints of unprocessed (CTS-W, CTS-E) and processed (PCTS-W, PCTS-E) Cassia extracts, along with a chrysophanol standard. The extracts (A–D) show varying chromatographic peaks, indicating different phytochemical profiles influenced by processing and solvents. The chrysophanol standard (E) confirms the presence of a key compound in these extracts. The results highlight that processing and ethanol extraction enhance the phytochemical diversity and concentration of Cassia extracts.
3.2. Antioxidant Activity Evaluation
Table 2 presents the antioxidant activity evaluation of different Cassia extracts, categorized as unprocessed (CTS-W, CTS-E) and processed (PCTS-W, PCTS-E). The antioxidant potential was assessed using the DPPH radical scavenging assay (IC50 values) and the FRAP assay (Trolox equivalents, mg/g). In the DPPH assay, which measures radical scavenging activity, the processed water extract (PCTS-W) exhibited the strongest antioxidant activity, indicated by the lowest IC50 value (2.848 ± 0.087 mg/mL), followed by the processed ethanol extract (PCTS-E) (3.621 ± 0.028 mg/mL). Among the unprocessed extracts, CTS-E (4.555 ± 0.028 mg/mL) demonstrated greater antioxidant capacity than CTS-W (8.392 ± 0.090 mg/mL), which had the weakest activity. The FRAP assay, which evaluates the ferric-reducing antioxidant power, further confirmed the superior activity of processed extracts. PCTS-E exhibited the highest antioxidant activity (39.592 ± 0.397 mg/g), followed closely by PCTS-W (38.294 ± 0.583 mg/g). In contrast, CTS-E (30.533 ± 0.128 mg/g) and CTS-W (9.190 ± 0.376 mg/g) showed significantly lower reducing power. Statistical analysis indicated significant differences among all of the extracts (p < 0.05), with distinct letter notations in Table 2 confirming the statistical separation of means. The enhanced antioxidant properties of processed extracts align with phytochemical findings, which suggest that thermal processing (stir-frying) and ethanol as a solvent enhance phenolic compound extraction, thereby boosting antioxidant activity. These results highlight the therapeutic potential of processed Cassia extracts, particularly PCTS-W and PCTS-E, for applications in bioactive compound enrichment, antiviral efficacy, and bioenergy production, where strong antioxidant properties are beneficial.

Table 2.
Antioxidant activity of water and ethanol extracts of Cassia: unprocessed water extract (CTS-W), unprocessed ethanol extract (CTS-E), processed water extract (PCTS-W), and processed ethanol extract (PCTS-E).
3.3. Power Density Assessment
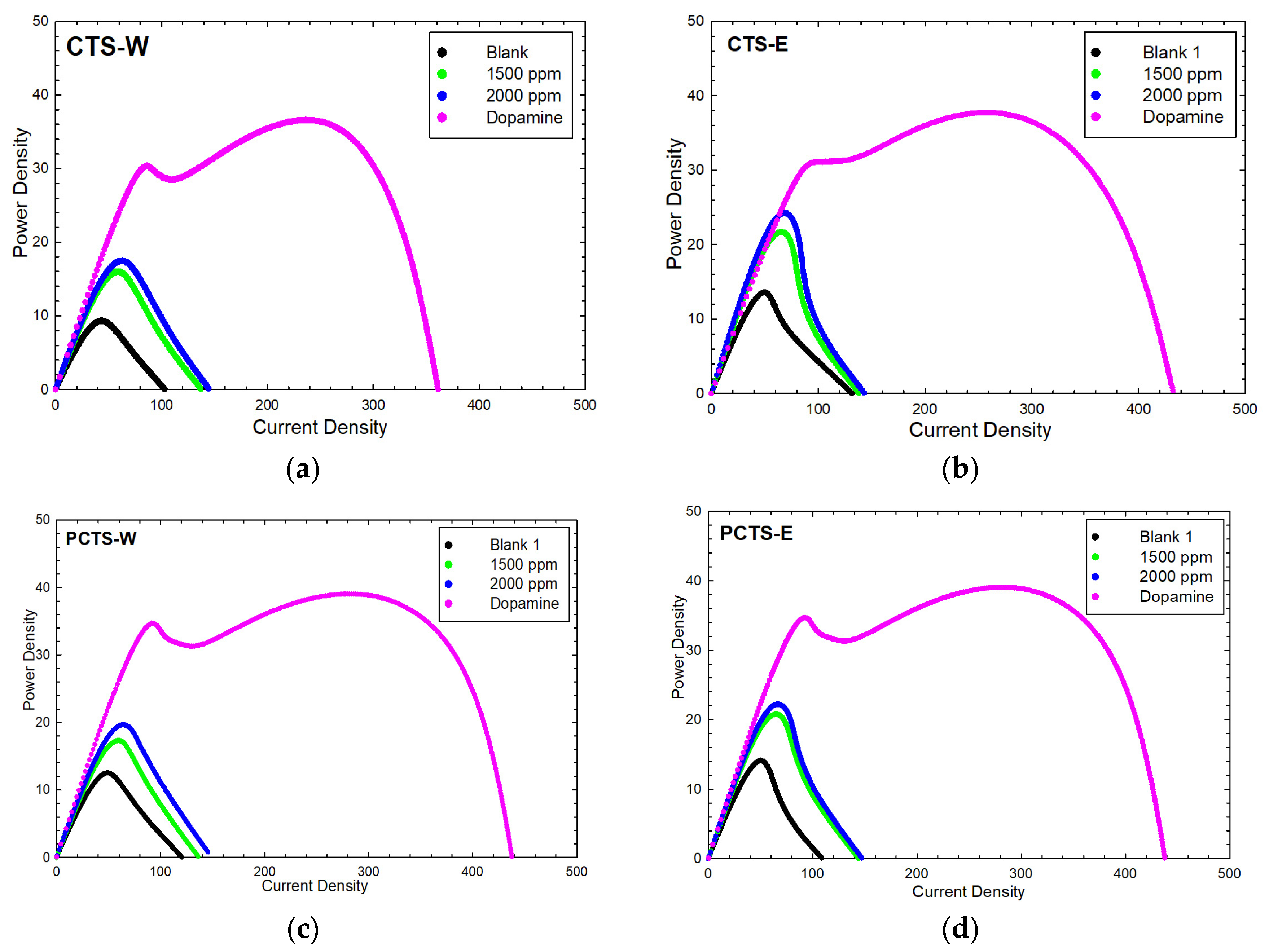
The power density profiles of the extracts used in the DC-MFC experiment in comparison with the blank (negative control) and dopamine (positive control) are presented in Figure 1, and the corresponding amplification factors are shown in Table 3. The most promising power density was obtained for the unprocessed water extract, while the lowest power density resulted from the processed water extract. The amplification factor for power density with respect to the blank in increasing order for C. obtusifolia seed extracts was shown as PCTS-W (1.5735 ± 0.5745) < PCTS-E (1.5772 ± 0.4747) < CTS-E (1.7844 ± 0.5308) < CTS-W (1.8759 ± 0.5911). These results suggest that unprocessed samples could more favorably amplify the power generation of MFCs compared to processed samples (i.e., stir-fried samples). In contrast to the results of phytochemical analyses and antioxidant activity evaluations, the processed samples (i.e., PCTS-E and PCTS-W) showed promising phenolic content and antioxidant activity. These findings suggest that these extracts would provide the highest amplified power in DC-MFC studies; however, the results show otherwise. The processed samples (i.e., PCTS-E and PCTS-W) showed the least power amplification among the test samples, 1.5735 ± 0.5745 and 1.5772 ± 0.4747, for PCTS-W and PCTS-E, respectively. The bioenergy–energy expression was compared to the positive control, dopamine, which exhibits an amplification factor of ca. 3.5–4.0-fold. Prior studies have revealed that the use of neurotransmitters as electron shuttles has successfully presented over-expressed bioenergy generation in MFCs.
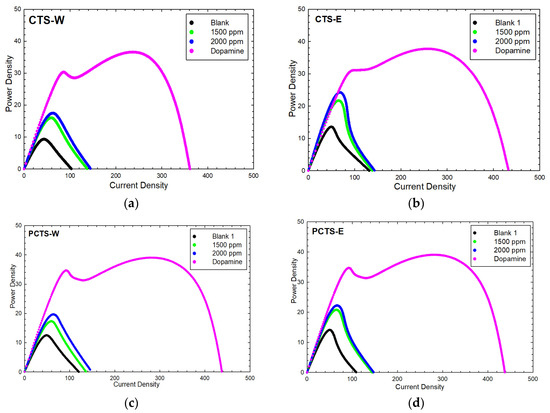
Figure 1.
Power density profiles of Cassia seed extracts compared to blank and dopamine. CTS-W showed the highest PD amplification ratio (ca. 1.87-fold) among all of the extracts. (a) Power density profile of CTS-W; (b) power density profile of CTS-E; (c) power density profile of PCTS-W; (d) power density profile of PCTS-E.

Table 3.
Comparative list of power-generating performance (AF) for water and ethanol extracts of Cassia seeds: unprocessed water extract (CTS-W), unprocessed ethanol extract (CTS-E), processed water extract (PCTS-W), and processed ethanol extract (PCTS-E) at 2000 ppm.
3.4. Cyclic Voltammetry
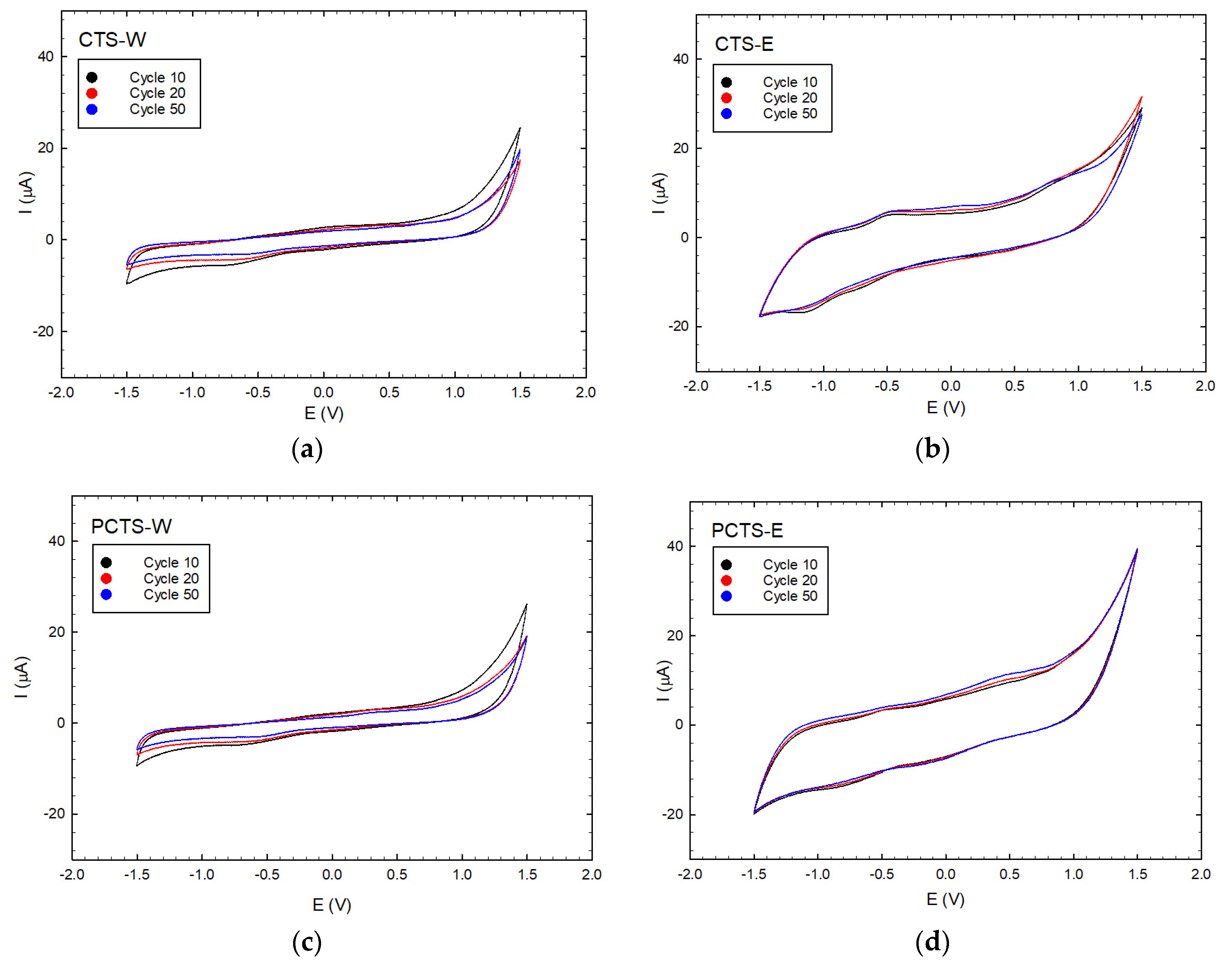
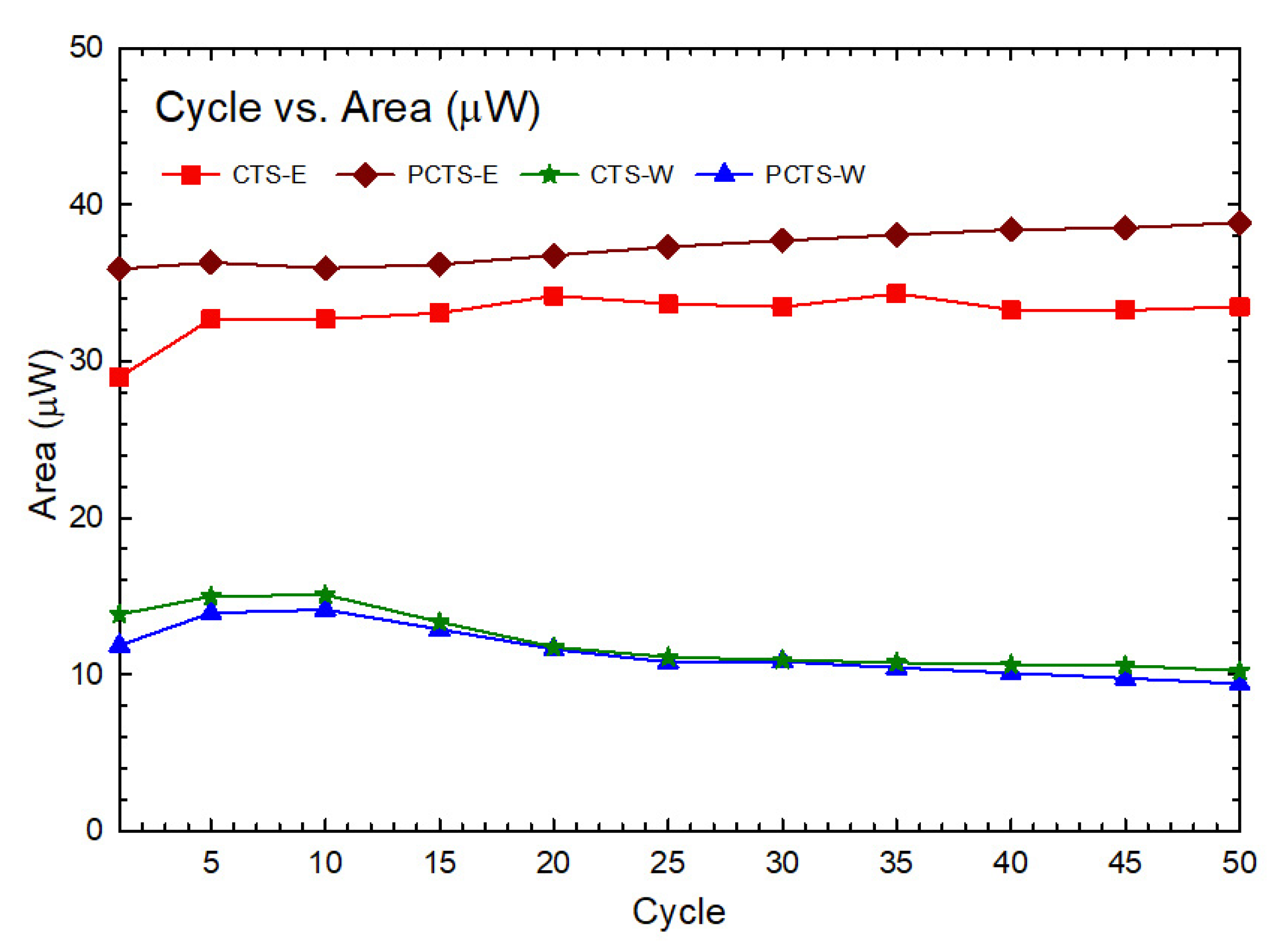
To assess the electrochemical activities of Cassia seed extracts, studies using cyclic voltammetry (CV) were conducted. As the literature [1] discusses, CV is a valuable tool in determining the electroactive contents of electron-shuttling compounds and antioxidants based on their electrochemical stability and reversible electron transfer characteristics. The cyclic voltametric profiles can be used to assess the presence of electrochemical catalysts by exhibiting both reduction and oxidation potential peaks. In contrast, antioxidant-dominated species only exhibit significant oxidation peaks. The presence of ES species can be associated with their capability to resist electrochemical attenuation even after being exposed to repeated redox cycles, indicating their potential for electroactive sustainability. However, no potential peaks were revealed in Cassia seeds’ CV profiles (Figure 2), indicating that such samples were not antioxidant, antireductant, ES, or that the measure conditions were not able to achieve such peak(s). Aside from the reduction and oxidation peaks, the areas enclosed within the CV loops could exhibit electrochemical contents in the samples. Figure 3 shows the closed-loop area curve of different cycle numbers for the extracts analyzed in this study (see Table S3 for the numerical values of the area). While there is an insignificant change observed with the enclosed loop areas of the Cassia seed extracts, clearly indicating the electrochemical stability of the samples [17], the actual measure of the area must be accounted for, since the abundance of easily decomposed or/and converted electroactive compounds in the extracts can be supported by the presence of larger area in the enclosed CV loops. This factor would considerably influence bioelectricity-generating performance (PD).
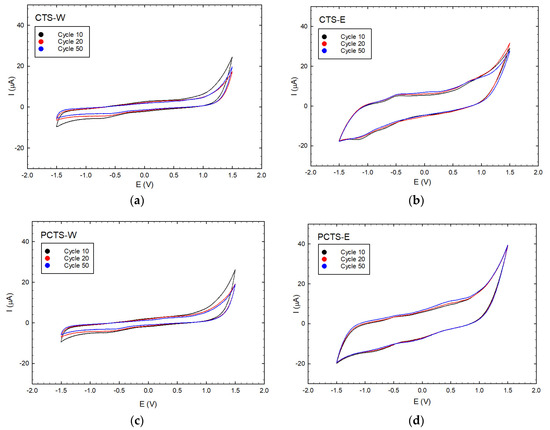
Figure 2.
Cyclic voltammogram (CV) profiles of Cassia seed extracts at 10, 20, and 50 cycles exhibit the electrochemical stability of the samples, suggesting the presence of ES species that are not easily degraded after electrochemical attenuation; (a) CV profile of CTS-W; (b) CV profile of CTS-E; (c) CV profile of PCTS-W; and (d) CV profile of PCTS-E.
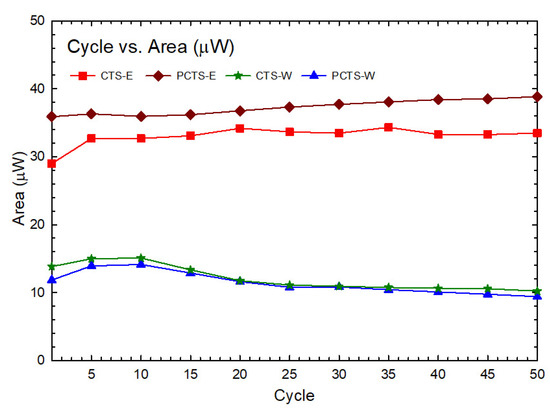
Figure 3.
Comparison of closed-loop areas of CV profiles for C. obtusifolia seed extracts showed that PCTS-E has the most significant area among all sample extracts, suggesting that it contains the most amount of electroactive species that should be reflected in the PD amplification ratio of the extracts.
3.5. Network Pharmacology
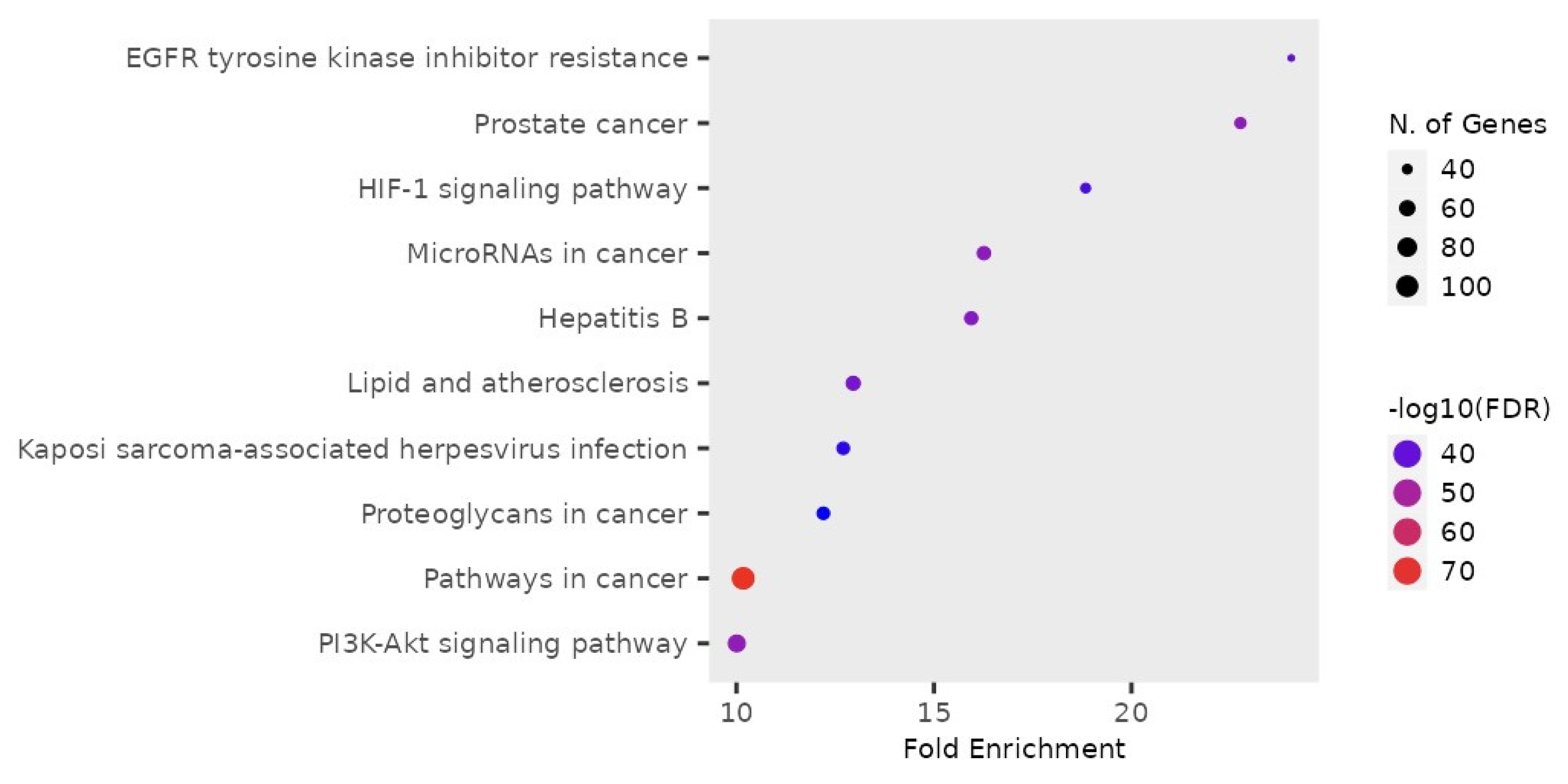
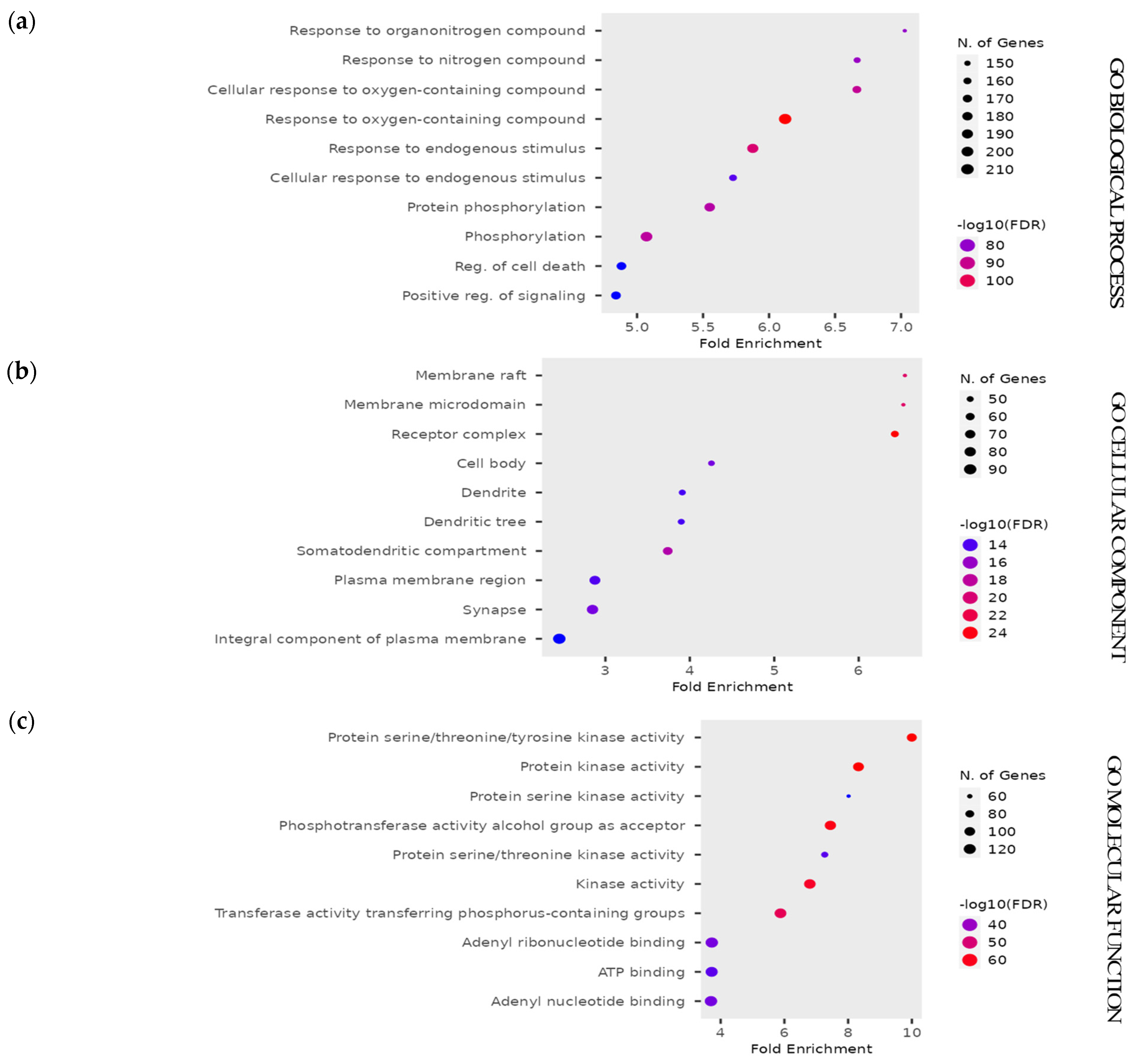
Using the SymMap web server, the active ingredients of C. obtusifolia were collected and narrowed down by selecting only the anthraquinone species obtained from the search. In this screening criterion, 243 compounds were identified from the database, and only 16 compounds were selected after duplicates were removed and anthraquinone species were selected (Table S1). From the selected compounds, the “Target” function in SymMap was utilized to determine the protein targets of the bioactive compounds. Using the targets predicted using the bioactive components, the analysis of the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway showed the appearance of Hepatitis B virus (HBV) in the pathways considerably associated with these bioactive compounds (Figure 4). Based on the false discovery rate (FDR) on the KEGG pathway, the appearance of HBV is significant to the bioactive compounds of C. obtusifolia. The lower FDR values indicate the confidence of the appearance of disease in the pathway associated with the bioactive compounds. Thus, the Hepatitis B virus was selected herein to assess the antiviral potential of Cassia seeds. The Gene Ontology (Figure 5) analysis showed different biological processes re-lated to the pathways associated with Cassia seeds.
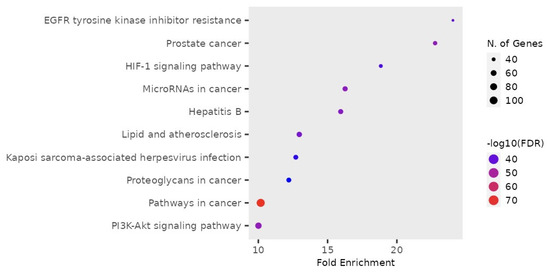
Figure 4.
KEGG pathway enrichment analysis exhibited that the bioactive components of C. obtusifolia target pathways associated with cancer, herpes virus, and Hepatitis B virus. The false discovery rate (FDR) suggests the significance of the diseases in the pathways associated with the bioactive metabolites, and lower FDR values suggest a high significance of the disease in the pathways. Thus, Hepatitis B virus was selected as the disease target due to a low FDR value.
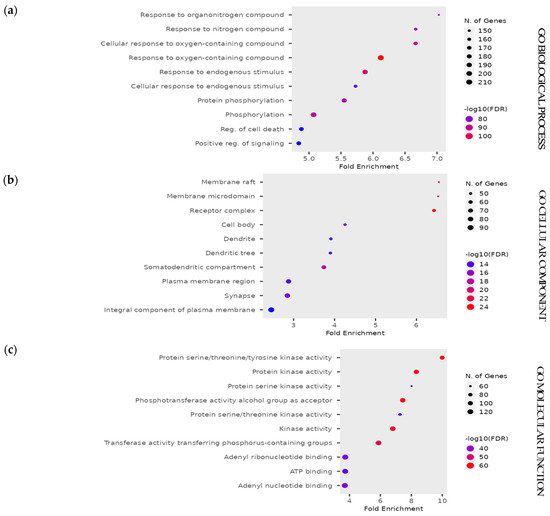
Figure 5.
Bubble plots for gene ontology (GO) for (a) biological process, (b) cellular component, and (c) molecular function exhibiting signaling pathways that are relevant to the disease treatment potential of bioactive metabolites extracted from Cassia seeds.
Consequently, the GeneCards database searched for genes related to Hepatitis B virus and viral cell replication. The identified targets were narrowed down by removing duplicates and overlapping genes common in the targets of the bioactive metabolites and HBV, and a total of 473 targets were obtained (Figure S1). Using these genes, the protein–protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed by submitting it to the STRING database (Figure S2).
3.6. Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics
To validate the results of network pharmacology (Table 4), molecular docking assessments between selected compounds from C. obtusifolia and the identified genes of the Hepatitis B virus were performed. The docking scores (kcal/mol) presented in Table 4 were used to select the optimal docked ligand with the most negative binding affinity. Based on the molecular docking simulation results, emodin has the most promising result for TNF (−6.6 kcal/mol), and emodin and rhein were selected for TP53 (−8.1 kcal/mol). Moreover, in comparison with the control—entecavir, a drug commonly used to treat hepatitis B virus—all of the selected ligands have higher binding scores (i.e., −5.2 and −6.6 for TNF and TP53, respectively), clearly suggesting their promising capabilities of inhibiting Hepatitis B virus.

Table 4.
List of binding affinities (kcal/mol) of selected bioactive compounds from C. obtusifolia, control, and key targets.
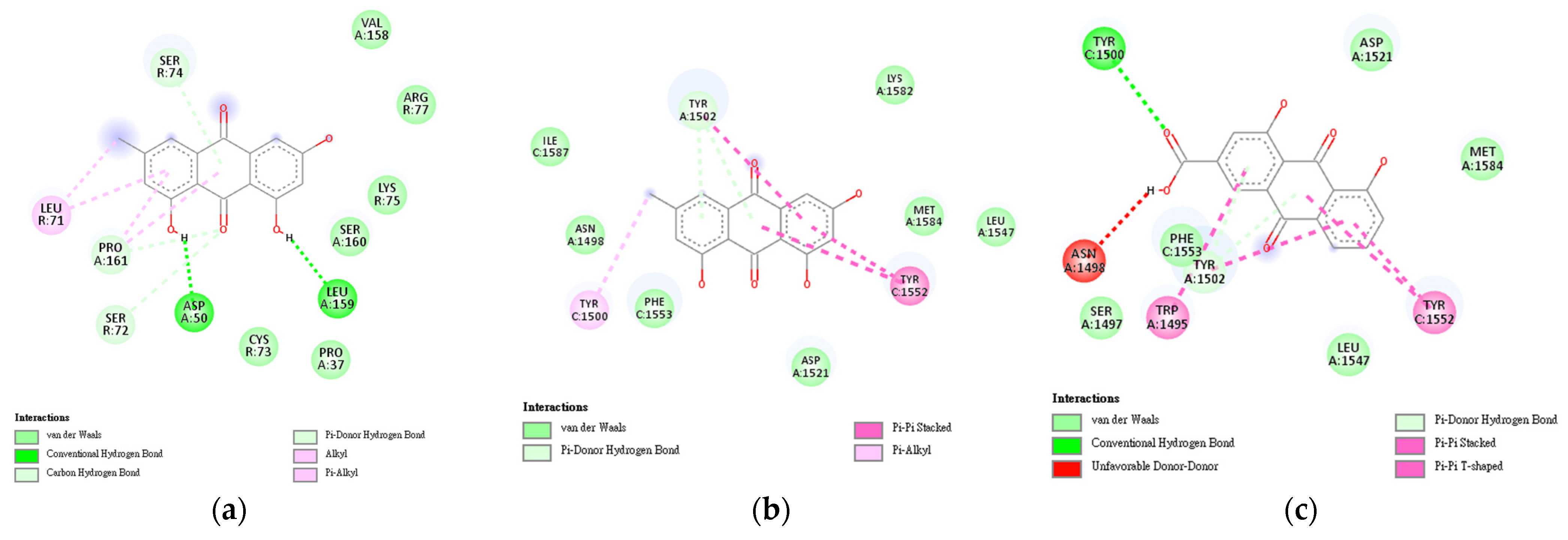
Meanwhile, to identify the interactions present in the protein–ligand complexes, BIOVIA 2021 was used (Figure 6). It was evident in the results of the molecular docking simulations that there are various interactions between the protein–ligand binding (Table 5). These interactions contribute to the stabilization of the protein–ligand complexes. This is supported by the conformations observed in the molecular dynamics simulation performed on these protein–ligand complexes (Figure 6).
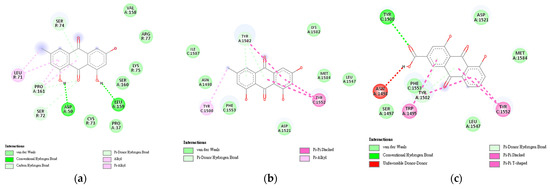
Figure 6.
Two-dimensional representation of interactions in protein–ligand complexes for HBV showing the interactions that contribute to the stability of the formed complex. (a) Emodin–TNF complex; (b) Emodin–TP53 complex; (c) Rhein–TP53 complex.

Table 5.
Protein–ligand interactions for selected bioactive metabolites of C. obtusifolia and Hepatitis B-related proteins.
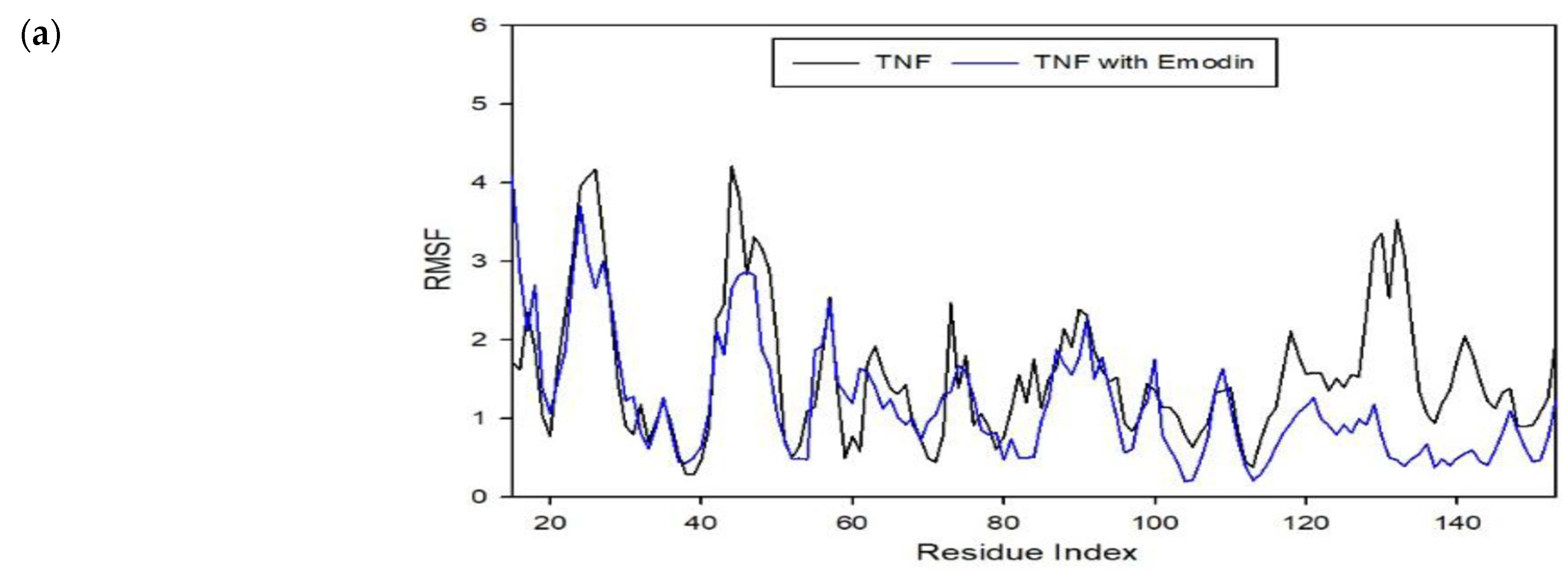
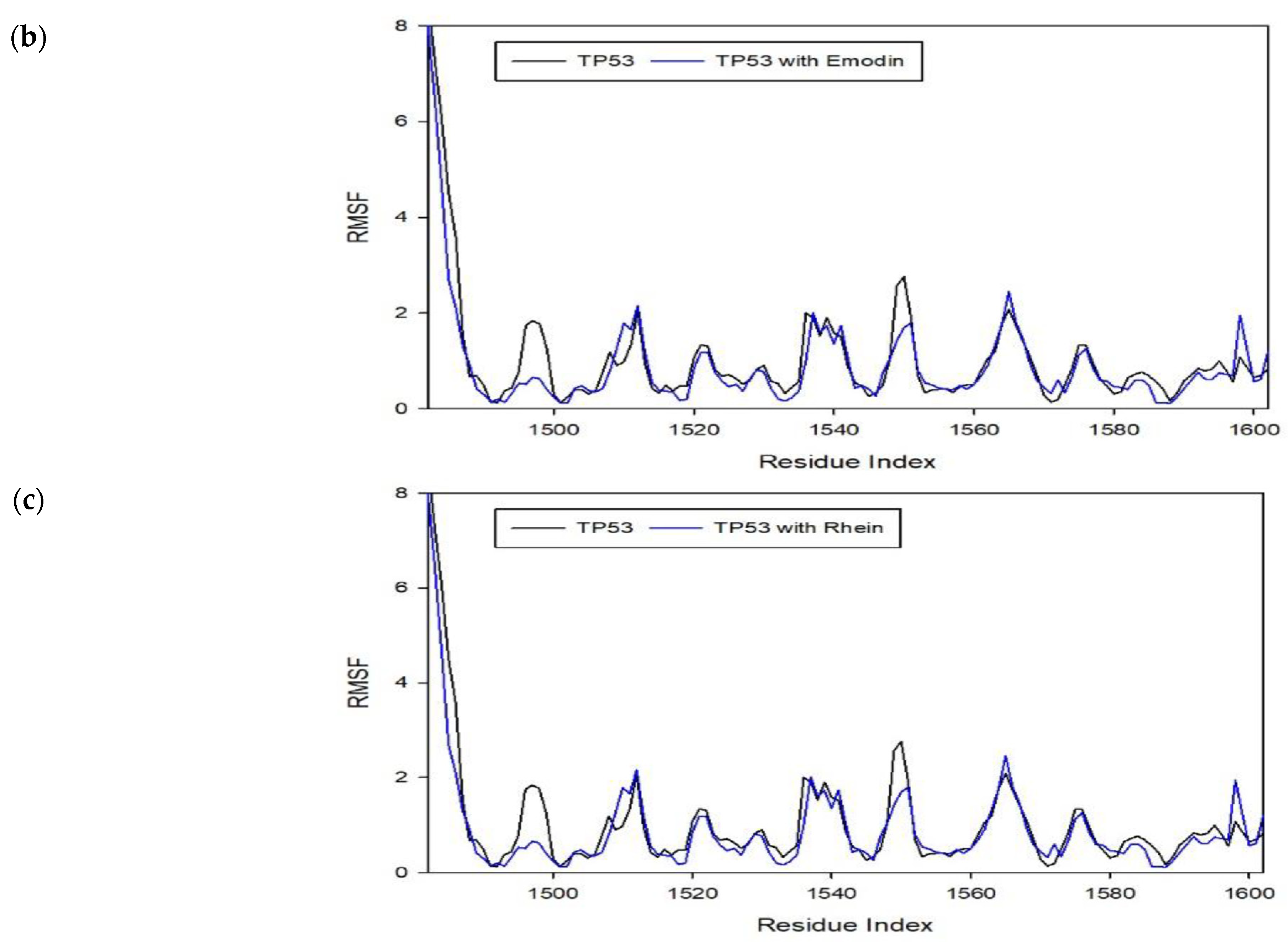
To assess the effect of molecular interactions in protein–ligand complexes, molecular dynamics simulations were performed using the CABS-Flex 2.0 web server. The molecular interactions in the protein–ligand complexes account for the changes and stabilization in the protein structures. Figure 7 shows the different root mean square fluctuation (RMSF) plots for different protein–ligand complexes compared to the protein unbounded to the ligand. As observed in the plots, stiffer peaks were formed due to the stabilization of the molecule. In addition, stiffer peaks are caused by stronger intermolecular interactions between the protein–ligand complexes. The stabilization brought by the binding of the ligand to the protein allows it to reduce the motion of the protein after the binding [22]. Thus, the ligand used for this study (i.e., emodin and rhein) shows potential antiviral activity by stabilizing these proteins and establishing a MOA similar to the literature [23].
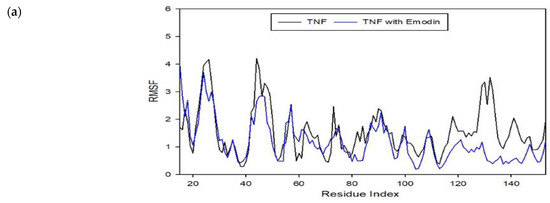
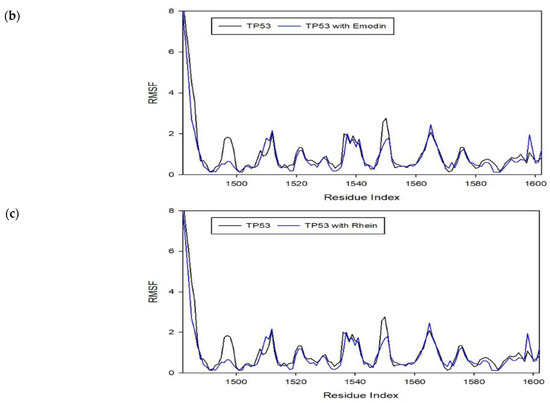
Figure 7.
RMSF plot for protein–ligand complexes from a molecular dynamics simulation showing the deformations and conformational changes that occurred within the complex compared to the protein alone. (a) RMSF plot for TNF–Emodin complex in comparison to TNF protein; (b) RMSF plot for TP53–Emodin complex in comparison to TP53 protein; (c) RMSF plot for TP53-Rhein complex in comparison to TP53 protein.
3.7. Principal Component Analysis
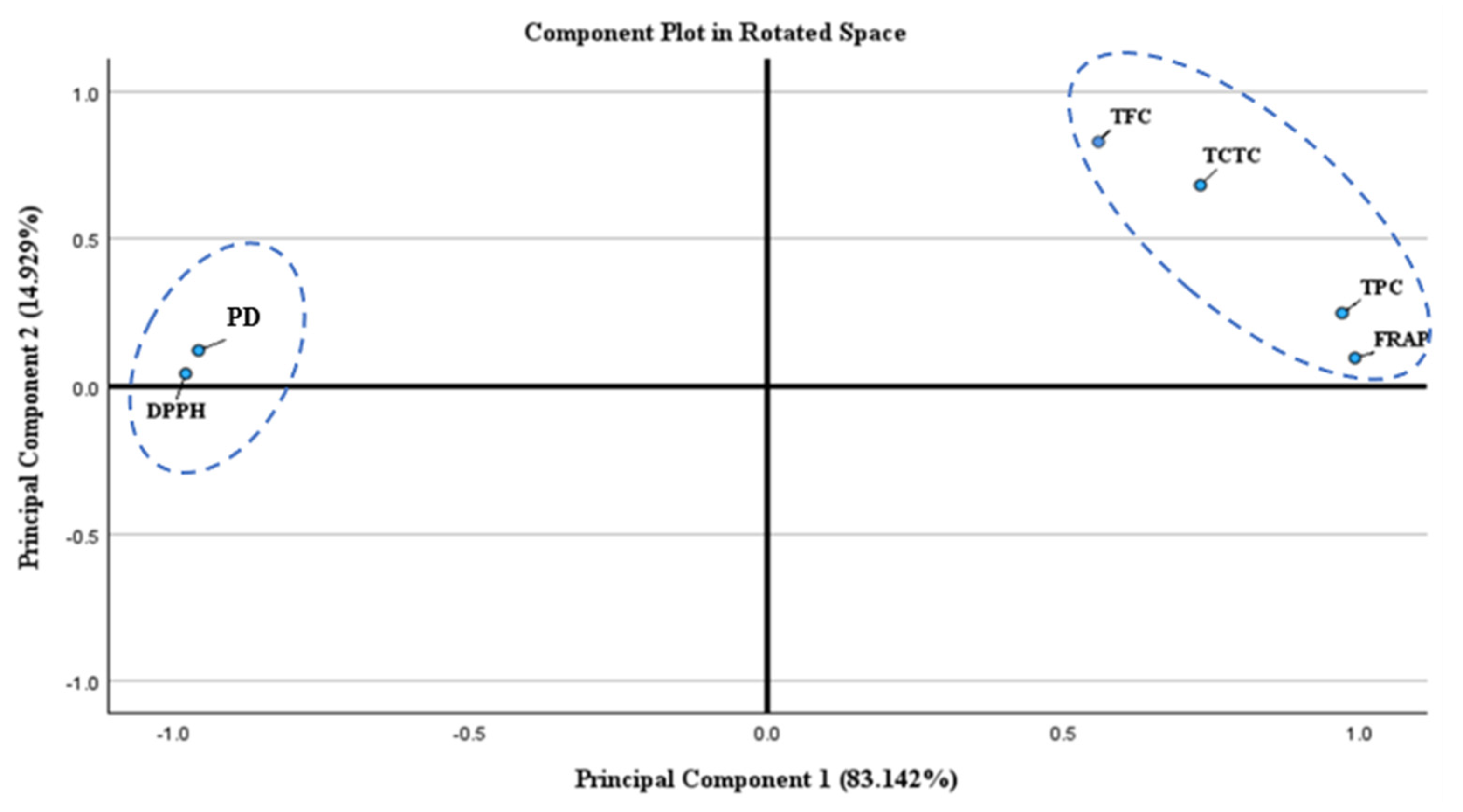
PCA was implemented to provide conclusive remarks and exhibit correlations among these six variables (i.e., TPC, TFC, TCTC, DPPH, FRAP, and PD). It reveals that PC1 captures 83% of the total variance while PC2 captures ~15% of the total variance of these variables. The component plot shows a positive association between FRAP, TPC, TCTC, and TFC towards PC1, while PC2 positively correlates with all of the variables. The spatial rearrangements of the variables shown in Figure 8 towards PC2 highlight the correlation between DPPH and PD with TPC, TFC, TCTC, and FRAP, suggesting a positive association among these variables in the y-axis. These associations are indications that the phytochemical content of C. obtusifolia seed extracts influence its antioxidant activity in terms of the FRAP assay, as indicated by the positive correlation established with PC1.
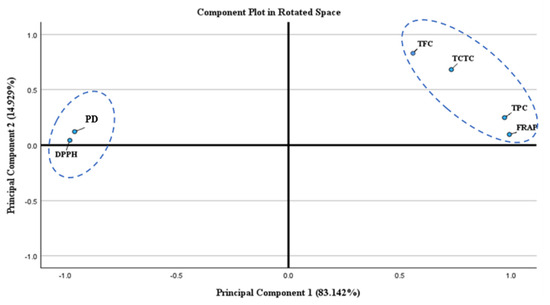
Figure 8.
Principal component analysis for correlation of variables (TPC, TFC, TCTC, DPPH, FRAP, and PD). The PCA indicates that DPPH and PD were correlated and that TFC, TCTC, TPC, and FRAP were more associated with being located in the first quadrant.
4. Discussion
As Tsai et al. [1,17] indicate, the characteristics of antiviral TCM to treat COVID-19 were strongly associated with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and bioelectricity-stimulating activities. These findings show that the antiviral characteristics of herbal medicine are redox-mediating and electron transfer-steering; that is, disclosing the electrochemical activities of test herbal extract would be the primary rationale for selecting feasible virus-resisting medicinal herbs. Of course, measurements of such capabilities are essential to determine whether TCM can treat multiple-spectrum virus-related diseases. Thus, a phytochemical analysis and an antioxidant activity evaluation for the phytoconstituents were employed to select the appropriate extraction method. Moreover, as mentioned, bioelectricity-generating potentials were possibly influenced by the extraction strategies and methods utilized. As a recent study [1] suggested, the electron-mediating properties of electrochemical catalysts may improve the disease-treating efficacy of herbal medicine. Moreover, biomass energy-amplifying and electron transfer-stimulating medications, in particular, have been shown to own the potential to treat not only brain-related disorders, but also virus-caused infections. The functioning of neurotransmitters and virus receptors could be electrochemically manipulated by redox-mediating compositions (e.g., ESs). This is why determining whether there is a significant correlation between the processing method, bioenergy production, and the potential viral activity of C. obtusifolia is a top priority issue for this feasibility study.
In these phytochemical analyses (e.g., TPC, TFC, and TCTC), the maximal yield of phenolics resulted from the processed ethanol extract (i.e., PCTS-E). TPC analysis showed that PCTS-E had the highest phenolic content (35.109 ± 1.254 mg/g), while CTS-W was the lowest (12.149 ± 0.0.224 mg/g). Similarly, PCTS-E had the highest amount of flavonoids (58.803 ± 0.157 mg/g), as indicated by TFC analysis, with CTS-W still being the lowest (13.890 ± 0.600 mg/g). Moreover, TCTC analyses exhibited a similar trend as in prior analyses, with CTS-W being the lowest (3.430 ± 0.180 mg/g) and PCTS-E being the highest (19.814 ± 0.394 mg/g). Thus, the most appropriate extraction of polyphenolic compounds to induce the maximal yield of phytochemical activities was stir-frying using ethanol as a solvent. The reference [24] showed that roasting temperature and duration affect the total polyphenol content of Cassia seeds. The results show that roasting significantly increased total polyphenol content compared to raw seeds, with the highest levels recorded at 200 °C for 10 min (12.69 mg TAE/g) and 225 °C for 10 min (13.01 mg TAE/g). However, prolonged roasting at 250 °C for 10 min caused a drastic reduction in polyphenol content (2.30 mg TAE/g), indicating the thermal degradation of bioactive compounds. The results align with the literature that highlights ethanol as a superior solvent for extracting polyphenols, owing to its ability to dissolve both hydrophilic and lipophilic compounds. Additionally, thermal processing (such as roasting or stir-frying) can enhance the release of bound polyphenols by breaking down cell walls, increasing bioavailability [24].
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, much attention has been paid to the pharmacological activities (e.g., antiviral, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial) of phenolic compounds for disease treatment. As a matter of fact, phenolic compounds hold strong antioxidant power that makes them capable of neutralizing free radicals. Due to these promising therapeutic potentials, compounds with phenolic groups (e.g., polyphenols, flavonoids, tannins) have been thus selected as candidate chemical species for drug discovery [25]. Furthermore, phytochemical content analysis was a prescreening criterion for the evaluation of the bio-electrochemical generation of C. obtusifolia seeds that is considered to be a function of its disease treatment capability.
Phytochemical analyses were also conducted to determine which solvent and processing method were appropriate for the maximal recovery of phytochemicals in C. obtusifolia seeds. Regarding processing procedures, the most promising extraction and processing methods would be selected to optimize the performance of bioenergy production and possible antiviral efficacy. Here, the phenolic compounds present in the extracts were quantified in terms of gallic acid (TPC), rutin (TFC), and catechin (TCTC), as shown in Table 1. The findings clearly show the comparative ranking of the processing method, and the superior phytochemical yields of PCTS-E suggest that it is the optimal method for maximizing phenolic, flavonoid, and tannin content, thereby enhancing the bioelectrochemical and potential therapeutic activities of Cassia extracts. This validates the role of ethanol as a solvent and processing techniques in optimizing the medicinal potential of Cassia seeds. In addition, the yield of extracted phytochemicals could likely indicate the therapeutic potential of the sample (e.g., virus resistance) and its bioenergy-stimulating capability, since such capability was strongly associated with antiviral characteristics, as prior studies mention [17].
According to the Taiwan Herbal Pharmacopoeia, CTS must contain Chrysophanol at levels exceeding 0.12% to be considered a qualified traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) (https://reurl.cc/yQNx0D, accessed on 28 January 2025). Analysis of Supplementary Figure S6 indicates that CTS-W and PCTS-W do not contain any anthraquinone compounds, while CTS-E and PCTS-E contain the marker compound Chrysophanol. However, Aloe–Emodin, Emodin, and Rhein were absent across all extracts. Notably, the most significant finding is that the processing of CTS resulted in an increased Chrysophanol content.
The antioxidant activity of Cassia extracts and seeds was significantly influenced by the processing methods, including thermal treatment (stir-frying or roasting) and solvent selection. Table 2 demonstrates that the processed extracts (PCTS-W and PCTS-E) exhibited superior antioxidant capacities compared to the unprocessed ones, as indicated by lower IC50 values in the DPPH assay and higher ferric-reducing antioxidant power (FRAP values). This suggests that thermal processing and ethanol extraction enhance phenolic compound availability, thereby boosting antioxidant activity. Similarly, Yen et al. indicated that roasting positively affected the antioxidant ability of Cassia seeds, with their electron-donating ability increasing with roasting time. However, seeds roasted for 5 min at lower temperatures (175 °C: 80.61%, 200 °C: 80.75%) exhibited higher antioxidant potential compared to those roasted at higher temperatures (225 °C: 76.26%, 250 °C: 77.35%) [24]. These findings highlight that controlled thermal processing optimizes antioxidant activity, but excessive heating may degrade bioactive compounds. Thus, stir-frying with ethanol extraction and moderate roasting temperatures are optimal strategies for maximizing the bioactive potential of Cassia extracts and seeds, making them valuable for applications in bioactive compound enrichment, antiviral efficacy, and bioenergy production.
Antioxidants are substances that delay or prevent the oxidation of the target substrate. Since the antioxidant activity was assessed via free-radical-scavenging capabilities, the different natures of free radicals apparently could significantly influence the activity measured. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) can be prevented by a variety of techniques, one of which is the production of natural radical scavengers (e.g., antioxidants), which can scavenge ROS by single-electron transfer (SET) and hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) [26,27]. Due to this, the DPPH assay, which assesses antioxidant activity via HAT, and the FRAP assay, which measures activity via SET, were employed herein. Theoretically, higher antioxidant and electron-shuttling activities are probed indicators of persistent reversible electrochemical catalysis of the constituents, resulting in prolonged biological activities (e.g., anti-virus) [26]. Thus, the antioxidant activities help to assess the biological activities of the plant extracts.
In fact, the distinction between ES and antioxidants does matter in assessing the performance of bioelectricity generation and disease treatment. To uncover such phenomena, we proposed some basic rationale of enzyme kinetics for mathematical modeling to elucidate these mysteries. As indicated in mathematical derivation (see Supplementary Information—Mathematical Derivation Section), there is a clear distinction between the use of phenolic compounds, designated as compound E, as catalyst (i.e., electron shuttle) and a reactant (i.e., antioxidant). A phenolic compound designated as a catalyst can move the reaction forward (e.g., virus resistance) more effectively than the reactant. For herbal medication to be used in antiviral disease treatment, it should have a nearly maximal reaction rate to be the most efficacious. When the characteristics of the electrochemical catalyst ES were expressed for disease treatment, the maximal rate could be guaranteed, since the concentration of E remained fixed as the initial concentration Eo to persist the power of catalysis for the reaction (e.g., antioxidant or antiviral characteristics). However, if E behaved as an antioxidant (or reactant), its concentration would be gradually consumed, and the reaction rate would be steadily attenuated as time passed. This automatically reduced the capabilities to resist viruses and/or remove antioxidants. That is, ES would be more promising than antioxidants for efficacious disease treatment from the perspective of reaction engineering.
Since bioelectricity-stimulating characteristics are of great significance to determine whether a redox-mediating disease-treating nature is present, assessing the bioenergy stimulation and biocompatibility of Cassia seed extracts toward receptor microbes via dual-chamber microbial fuel cells (DC-MFC) were implemented. Electron-transporting characteristics are associated with power-generating performance and virus-resisting capabilities [28]. In addition, it was revealed that polyphenolics-bearing chemicals available in different medicinal herbs contain crucial electrochemical steering capabilities for bioenergy generation. Furthermore, as Chen et al. [28] mentioned, phytochemicals extracted from herbal sources possess low levels of biotoxicity, influencing power generation in MFCs. Thus, this study uncovers the bioenergy-generating potential of Cassia seed extracts to establish a correlation between disease-treating potential and electron-shuttling characteristics.
As suggested by the study conducted by Xu et al. [29], aromatic compounds from medicinal plant extracts used for bioenergy generation in MFCs can act as redox mediators (RMs). These RMs could allow for the reversible interconversion of reduced and oxidized forms of intermediates, resulting in an enhanced electron transfer. It was proposed in the literature [29] that the MFC system works similarly to the electron transport chain (ETC), as shown in Supplementary Figure S5. The supplementation of RMs to the microorganism system allows for the efficient utilization of carbon and energy sources in the MFCs, producing more of the desired products. Similarly to ATP production in cells, MFCs utilize the proton gradient from the flow of electrons to produce energy in the system. The increased concentration of ATP in MFCs can be stipulated to be caused by the stimulation of energy extraction brought by the presence of RMs from the extracts added to the MFCs. The proposed mechanism suggests that redox mediators in the system could lead to a means of enhanced electron transport, resulting in amplified power generation.
The DC-MFC results are indicators of the possible antiviral potential of the unprocessed samples, as expressed by their bioenergy-stimulating capability. The power amplification observed in CTS-W (ca. 1.87-fold) suggests that the chemical constituents of the plant extract have electron-mediating characteristics that result in bioenergy generation. It is crucial to establish the electron-mediating character of the species under investigation, as it indicates the electrochemical catalytic nature of the suspected ES found in these extracts [1]. In addition, as the literature mentions [1], when there is a significant amplification observed, which is approximately an 87% increase in the case of CTS-W with respect to the blank, an appropriate level of electron transfer is attained to consider antiviral capabilities. Therefore, in this study, the unprocessed water extract (CTS-W) holds the most promising antiviral potential.
To assess the electrochemical activities of Cassia seed extracts, studies of cyclic voltammetry (CV) were conducted. As the literature [1] mentions, CV is a valuable tool in determining the electroactive contents of electron-shuttling compounds and antioxidants based on their electrochemical stability and reversible electron transfer characteristics. The cyclic voltametric profiles can be used to assess the presence of electrochemical catalysts by exhibiting both reduction and oxidation potential peaks. In contrast, antioxidant-dominated species only exhibit significant oxidation peaks. The presence of ES species can be associated with their capability to resist electrochemical attenuation even after being exposed to repeated redox cycles, indicating their potential for electroactive sustainability. However, no potential peaks were revealed in Cassia seeds’ CV profiles (Figure 2), indicating that such samples were not antioxidant, antireductant, ES, or that the measured conditions were not to achieve such peak(s). Aside from reduction and oxidation peaks, the areas enclosed within the CV loops could exhibit electrochemical contents in the samples. Figure 3 shows the close-loop-area curve of different cycle numbers for the extracts analyzed in this study (see Table S3 for the numerical values of the area). While there is an insignificant change observed with the enclosed loop areas of the Cassia seed extracts that clearly indicates the electrochemical stability of the samples [17], the actual measure of the area must be accounted for, since the abundance of easily decomposed or/and converted electroactive compounds in the extracts can be supported by the presence of larger areas in the enclosed CV loops. This factor would considerably influence bioelectricity-generating performance (PD).
The CV results show that the lowest areas were observed with the water extracts (CTS-W and PCTS-W), while the most prominent areas were with ethanol extracts (CTS-E and PCTS-E). In fact, the electrochemical stability observed in the CV profiles of Cassia seed extracts suggests that electroactive ES species are abundant in these plant extracts, allowing for bioelectricity generation stimulated by electron transfer. The literature reveals that the antiviral characteristics of medicinal herbs have been linked to their electrochemical potential [28]. Furthermore, it has been suggested that electrochemical catalysis experienced by the polyphenolic antioxidants extracted from TCMs contributes to their disease-treating potential by enhancing electron-mediating performance [1]. Thus, these results indicate that Cassia seed extracts may have antiviral disease treatment potential due to electrochemical stability influenced by ES species that stimulate electron transport.
The implementation of CV studies is crucial in assessing the electrochemical characteristics of these plant extracts. Particularly, the electrochemical reversibility and stability observed under prolonged exposure to repeated oxidation and reduction cycles are important factors to determine the electron-shuttling character of the species under investigation [30]. The electrochemical stability and reversible nature of the species examined through CV investigations demonstrated high correlations with antiviral potentials in the recently published studies [1]. Therefore, the potential for sustained disease-treating activity of putative ES-bearing species might be established using electrochemical analyses. In fact, ethanol extracts should have the largest PD amplification ratio (i.e., the maximum bioelectricity-stimulating potential) based on the known area–power amplification relationship. However, a distinct situation was shown by the MFC result for the amplification factor: CTS-W > CTS-E > PCTS-E > PCTS-W. According to the data, ethanol extracts should include the greatest number of electroactive species; nevertheless, more prevalent inhibitory components appeared to have an impact on the sample’s ability to generate bioelectricity, resulting in reduced power amplification. In other words, the bioenergy-expression of the reporter bacteria NIU01 (i.e., Aeromonas hydrophilia) in MFCs may have been suppressed by the inhibitory chemicals found in the broth.
TCM plays a key role in treating a variety of illnesses, as the literature suggests [20,31]. However, the MOA behind medicinal herbs’ efficacy is unclear due to the species and quantities of several chemicals that provide distinct therapeutic effects. Therefore, a new method is unavoidably needed to comprehend how and why its mechanism has been produced. A new science called Network Pharmacology (NP) combines pharmacology, bioinformatics, and network analysis to offer a dependable and effective method of comprehending the MOA behind TCM’s effectiveness in treating a range of illnesses [17]. To identify the illnesses and biological processes that the suspected ES species in C. obtusifolia were targeting, network pharmacology was used.
Aside from the Hepatitis B virus, several cancer-related pathways were associated with the bioactive metabolites of Cassia, as indicated by the KEGG pathway analysis (Figure 4). The association of cancer-related pathways indicates the multitude of biological activities targeted by the bioactive compounds of Cassia. Cancer affects multiple body organs and cells, allowing it to target various pathways. Similarly, herpes virus infection was also significant in the pathway associated with the bioactive metabolites from Cassia (Figure 6). It was evident that bioactive compounds from C. obtusifolia can exhibit antiviral activity by targeting the genes related to the pathways shown.
The Gene Ontology (Figure 5) analysis showed different biological processes related to the pathways associated with Cassia seeds. It is apparent that different responses to stimuli (GO0071495, GO0009719) were enriched in the pathway. Similarly, phosphorylation pathways (GO0016310, GO0006468) were also enriched in the biological process pathway together with positive regulation of the biological process (GO0023056). These enriched pathways are associated with the regulation of diseases in the body. Furthermore, these pathways suggest the body’s positive response towards the changes brought by the bioactive compounds of Cassia seeds. The cellular component pathways showed that most genes are found around the plasma membrane, while molecular function pathways revealed the association of the genes with cellular binding.
As [10,16] indicate, Cassia seed extracts are abundant in Aloe–Emodin, Chrysophanol, Emodin, and Rhein. Thus, these compounds were selected when performing molecular docking studies. In the CB-Dock2 web server, a blind docking analysis was performed to identify the target site for the selected proteins, TNF and TP53. The identified protein targets are markers used in identifying the proliferation of chronic HBV in the host’s body. Particularly, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) was identified to be a potent target in treating inflammatory diseases [32], such that liver inflammation caused by Hepatitis proliferation in the body could be addressed by drugs that targets this protein. Moreover, tumor suppressor p53 (TP53) has recently been associated as a suitable target towards inhibiting HBV cell replication in the body [33]. To be specific, mutated TP53 are suitable targets towards inhibiting HBV cell replication [21]. Thus, this indicates that TNF and TP53 are appropriate targets to prevent the proliferation of HBV.
Meanwhile, to identify the interactions present in the protein–ligand complexes, BIOVIA 2021 was used (Figure 6). It is evident from the results of the molecular docking simulations that there are various interactions between the protein–ligand bindings (Table 5). These interactions contribute to the stabilization of the protein–ligand complexes. This is supported by the conformations observed in the molecular dynamics simulation performed on these protein–ligand complexes (Figure 7).
This study tends to correlate the MFC performance of Cassia seed extracts with its antiviral activity. The novelty presents phytochemical analyses of C. obtusifolia seeds utilizing various extraction solvents through antioxidant and ES capabilities, pharmacological potential, and antiviral efficacy measures. Furthermore, the overall bioenergy-stimulating capacities of the extracts will be assessed by power-generating capability Via dual chamber-microbial fuel cells. If the antiviral activity would be strongly associated with bioelectricity-stimulating activities, using the MFC platform to pre-screen high bioenergy content of medicinal herbs and agricultural wastes for possible virus-resisting or inhibiting biomaterials would be electrochemically encouraging for various applications. To grasp in-depth schematics of disease-treating capabilities, a molecular docking study was implemented to determine the potential of compounds found in the extract to inhibit several virus-related diseases. In MD studies, the marker substances obtained from Cassia seed extracts suspected of electron-shuttling capabilities were utilized as test compounds for antiviral activities. Molecular dynamics were utilized to determine the stability of the protein–ligand complexes obtained from MD simulations.
Consequently, the emergence of NP paved the way for a new strategy for understanding the mechanisms underlying TCM by creating networks that evaluate the relationship between targets and proteins. NP is a multidisciplinary field focusing on the interactions of pharmaceuticals and biological systems on a network level by combining principles from pharmacology, bioinformatics, systems biology, and network science [17]. NP aims to understand the complex relationships between medicines, their targets, and the biological pathways and networks they regulate [17]. Thus, NP was implemented herein to determine the MOA of TCM towards disease treatment. To the best of our knowledge, this pharmacological assessment could even find new methodologies to treat disease(s) that have never been mentioned before. In particular, using ES chemicals as key composition(s) for disease treatment would be a novel exploration for herbal medication.
The established relationships showed that electron-shuttling capabilities strongly correlate with bioenergy-stimulating characteristics, similar to the literature described elsewhere [26]. Chen et al. [26,27] suggested that electron-shuttling capabilities are vital because of their association with the antioxidant characteristics of the test samples. The significant association of TFC, TPC, and TCTC towards FRAP directly reflected whether the antioxidant power of Cassia seed extract is highly influenced by its phenolic content. Similarly, the power-generating characteristics of the extracts are also affected by their antioxidant activity, as indicated by the DPPH assay, which is also driven by polyphenolic contents. Thus, the positive association of the variables in terms of PC2 is supported. As previously mentioned, the bioenergy generation of plant extracts indicates electron-shuttling characteristics made possible by the presence of polyphenolic substances [28]. These correlations suggest that Cassia seed extract’s phytochemical content significantly contributes to its electron-shuttling potential based on the associations between power generation and antioxidant activities.
Significance of This Study
Antioxidant activity was significantly boosted by the anthraquinone-rich Cassia seed extracts, which demonstrated promising phytochemical contents in terms of TPC, TFC, and TCTC. The processed ethanol extract (i.e., PCTS-E) exhibited the highest phenolic content, and both processed samples (i.e., PCTS-E and PCTS-W) showed the most promising antioxidant activities. Stir-frying and ethanol extraction together proved to be the most effective extraction technique. Its electrochemical stability and bioenergy-generating potential have also been discovered to be significantly influenced by these activities, which is suggestive of the presence of ES species in the extracts. The antiviral activity of Cassia seed extract was ascertained by the use of in silico investigations, specifically network pharmacology and molecular docking, in addition to the findings of MFC and CV tests. The production of bioenergy in the MFCs served as an indicator for ES’s electrochemical catalytic properties, which were known to be closely linked to its antiviral capabilities. The HPLC analysis of Supplementary Figure S6 reveals that PCTS-E contained a higher Chrysophanol content compared to CTS-E after undergoing the processing method. The lower PD value observed in PCTS-E compared to CTS-E can be attributed to the increased Chrysophanol content, which is known to reduce PD values and influence antioxidant activity [18]. The electrochemical stability and reversibility of the compounds under investigation, which are used as indicators of the electron-mediating character and catalytic nature of ESs that were found to have a significant impact on their disease-treating potential, also demonstrated the ES nature in the CV study results. Furthermore, these in silico analyses suggest the potential antiviral effects of bioactive compounds in C. obtusifolia based on their hypothesized mechanisms of action. Specifically, network pharmacology and molecular docking identified the suitable disease targets and biological pathways associated with these bioactive chemicals, indicating their possible role in antiviral activity. The pathway enrichment analysis suggested a correlation between these compounds and genes linked to Hepatitis B virus (HBV)-associated biological pathways. Similarly, molecular docking simulations implied the potential inhibitory effects of these compounds on key proliferative markers of HBV in the body. According to the literature, the selected ligands—Rhein, Emodin, Aloe–Emodin, and Chrysophanol—were found to interact with target genes related to HBV, supporting their potential role in modulating viral activity. While the findings presented here suggest an association between these compounds and HBV-related targets, they also highlight the differences in the electrochemical reaction capacities of antioxidants and electron shuttles, providing insights into their distinct biochemical roles.
5. Conclusions
This study systematically explored the phytochemical, electrochemical, and pharmacological properties of C. obtusifolia seed extracts, emphasizing their bioenergy-mediated antiviral potential. The findings reveal that the antiviral efficacy of the extracts is strongly associated with redox-mediated and electron transfer-driven mechanisms, highlighting the critical role of bioelectricity-stimulating compounds in disease treatment. Phytochemical analyses showed that PCTS-E contains the highest phenolic, flavonoid, and tannin contents, while CTS-W exhibits the highest bioenergy-stimulating capability (1.87-fold amplification), demonstrating the impact of processing and extraction methods. Chrysophanol, found in higher concentrations in PCTS-E, contributed to lower power density (PD) values while influencing antioxidant activity. PCA confirmed strong correlations between phenolic content, antioxidant capacity, and bioenergy production, while CV validated the extracts’ electrochemical stability. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analyses suggest that rhein and emodin have the potential to inhibit HBV proliferation based on their hypothesized mechanisms of action. Additionally, kinetic modeling indicates that electron shuttles may exhibit superior therapeutic potential compared to antioxidants in disease treatment. Collectively, these findings imply the possible therapeutic significance of C. obtusifolia extracts, supporting their potential role in bioenergy-driven antiviral strategies.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pr13020458/s1, Table S1. Bioactive compounds present in Cassia obtusifolia seeds extracted from Symmap webserver; Table S2. Protein-ligand Interactions; Table S3. Cycle vs Area of CV profiles; Figure S1. Venn diagram for the genes relating to Hepatitis B virus and the target genes of the bioactive metabolites of Cassia obtusifolia seed; Figure S2. Protein-protein Network Interaction for Hepatitis B and genes related to Cassia obtusifolia; Figure S3. Identified hub-genes from PPI network construction for HBV and Cassia seed metabolites; Figure S4. Structures of anthraquinones considered for molecular docking simulations; Figure S5. Proposed schematic diagram for the mechanism of redox mediators and electroactive bacteria in MFCs by Xu et al. [29]; Figure S6. HPLC fingerprint of (A) CTS-W, (B) PCTS-W, (C) CTS-E, (D) PCTS-E and (E) Chrysophanol standard. (A-D sample concentration at 10 mg/mL, wavelength at 254 nm, E sample concentration at 0.1 mg/mL, wavelength at 254 nm).
Author Contributions
S.C.M.T.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing. B.-Y.C.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing. C.-C.H.: Data curation, Formal Analysis and Conceptualization. K.A.D.C.-C.: Data curation, Writing—review and editing. Y.L.: Data curation, Formal Analysis. P.-W.T.: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors sincerely appreciate financial support (NSTC 113-2221-E-197-001-MY2, NSTC 112-2221-E-197-004-MY3, 112-2221-E-019-074, MOST 109-2221-E-197-016-MY3, MOST 110-2221-E-197-008, and MOST 111-2221-E-197-001) from Taiwan’s National Science and Technology Council and 112-113 TEEP@AsiaPlus Program from Taiwan’s Ministry of Education.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge all support from National Ilan University, National Taiwan Ocean University, and Mapúa University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Tsai, P.-W.; Hsieh, C.-Y.; Ting, J.U.; Ciou, Y.-R.; Lee, C.-J.; Hsieh, C.-L.; Lien, T.-K.; Hsueh, C.-C.; Chen, B.-Y. Synergistic Deciphering of Bioenergy Production and Electron Transport Characteristics to Screen Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) for COVID-19 Drug Development. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2022, 135, 104365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrell, S.N.; Li, Y.-C.; Yamaguchi, H.; Chen, H.-F.; Hung, M.-C. Herbal Compounds Dauricine and Isoliensinine Impede SARS-CoV-2 Viral Entry. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, R.L.; Andurkar, S.V. A Review of Natural Products, Their Effects on SARS-CoV-2 and Their Utility as Lead Compounds in the Discovery of Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19. Med. Chem. Res. 2022, 31, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, Y.S.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, W.C.; Huang, C.C.; Chang, J.S. Unraveling the Molecular Mechanism of Traditional Chinese Medicine: Formulas Against Acute Airway Viral Infections as Examples. Molecules 2019, 24, 3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, B.; Ding, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Tian, X.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Han, L. Investigation on the Stability in Plant Metabolomics with a Special Focus on Freeze-Thaw Cycles: LC–MS and NMR Analysis to Cassiae Semen (Cassia Obtusifolia L.) Seeds A Case Study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 204, 114243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-H.; Li, H.-B.; Li, G.-L.; Lv, N.; Qi, Y.-J. Metabolite Identification of Gut Microflora-Cassia Seed Interactions Using Uplc-Qtof/Ms. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 3305–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, R. Neuroprotective Role of Traditional Chinese Plant Extracts on Parkinson’s Disease; a Comprehensive Preclinical Review. Pharmacol. Res.-Mod. Chin. Med. 2025, 14, 100573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parham, S.; Kharazi, A.Z.; Bakhsheshi-Rad, H.R.; Nur, H.; Ismail, A.F.; Sharif, S.; RamaKrishna, S.; Berto, F. Antioxidant, Antimicrobial and Antiviral Properties of Herbal Materials. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Zhou, S.; Wang, W.; Huo, L.; Zhang, L.; Fang, X.; Yang, Z. Water Availability Effects on Plant Growth, Seed Yield, Seed Quality in Cassia Obtusifolia L., a Medicinal Plant. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 195, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sob, S.V.T.; Wabo, H.K.; Tchinda, A.T.; Tane, P.; Ngadjui, B.T.; Ye, Y. Anthraquinones, Sterols, Triterpenoids and Xanthones from Cassia Obtusifolia. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2010, 38, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-X.; Yang, S.-S.; Pang, J.-W.; He, L.; Zang, Y.-N.; Ding, L.; Ren, N.-Q.; Ding, J. Anthraquinones-Based Photocatalysis: A Comprehensive Review. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2024, 22, 100449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, M.; Zhang, X.; Dong, Q.; Yao, J.; Liu, Q.; Ding, K. Isolation and Structural Characterization of the Water-Extractable Polysaccharides from Cassia Obtusifolia Seeds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.Y.; Park, S.; Chang, M. Phytochemistry, Ethnopharmacological Uses, Biological Activities, and Therapeutic Applications of Cassia Obtusifolia L.: A Comprehensive Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-Y.; Liao, W.-L.; Liu, Y.-H.; Kuo, C.-L.; Lung, F.-W.; Hsieh, C.-L. Oral Administration of Processed Cassia Obtusifolia L. Seed Powder May Reduce Body Weight and Cholesterol in Overweight Patients with Schizophrenia: A 36-Week Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Trial of High and Low Doses. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 292, 115111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moglad, E.H.; Hamad, A.M.; Fatima, F.; Devanathadesikan Seshadri, V.; Naz, M. Antimicrobial and Wound Healing Activities of Certain Sudanese Medicinal Plants. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 1766–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakulpanich, A.; Gritsanapan, W. Extraction Method for High Content of Anthraquinones from Cassia Fistula Pods. J. Health Res. 2008, 22, 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, P.-W.; Tayo, L.L.; Ting, J.U.; Hsieh, C.-Y.; Lee, C.-J.; Chen, C.-L.; Yang, H.-C.; Tsai, H.-Y.; Hsueh, C.-C.; Chen, B.-Y. Interactive Deciphering Electron-Shuttling Characteristics of Coffea Arabica Leaves and Potential Bioenergy-Steered Anti-SARS-CoV-2 RdRp Inhibitor via Microbial Fuel Cells. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 191, 115944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, P.-W.; Chen, B.-Y.; Yang, L.-L. Interactive Deciphering Electron-Mediating Characteristics of Rheum Species and Potential Bioenergy-Steered Anti-COVID-19 RdRp Inhibitor. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2023, 151, 105124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yang, K.; Fang, S.; Bu, D.; Li, H.; Sun, L.; Hu, H.; Gao, K.; Wang, W. SymMap: An Integrative Database of Traditional Chinese Medicine Enhanced by Symptom Mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D1110–D1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Xiao, S.; Yang, L.; Ma, K.; Shang, H.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, F.; Xiang, R. Systematic Analysis of the Mechanism of Xiaochaihu Decoction in Hepatitis B Treatment via Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 138, 104894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galy, O.; Chemin, I.; Le Roux, E.; Villar, S.; Le Calvez-Kelm, F.; Lereau, M.; Gouas, D.; Vieco, B.; Suarez, I.; Navas, M.-C. Mutations in TP53 and CTNNB1 in Relation to Hepatitis B and C Infections in Hepatocellular Carcinomas from Thailand. Hepat. Res. Treat. 2011, 2011, 697162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünberg, R.; Nilges, M.; Leckner, J. Flexibility and Conformational Entropy in Protein-Protein Binding. Structure 2006, 14, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardal, S.K.; Waechter, J.E.; Martin, D.S.; Bardal, S.K.; Waechter, J.E.; Martin, D.S. Pharmacokinetics-Chapter 2. In Applied Pharmacology; Saunders Elsevier: London, UK, 2011; pp. 17–34. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, G.-C.; Chuang, D.-Y. Antioxidant Properties of Water Extracts from Cassia Tora L. in Relation to the Degree of Roasting. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 2760–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loaiza-Cano, V.; Monsalve-Escudero, L.M.; Filho, C.D.S.M.B.; Martinez-Gutierrez, M.; Sousa, D.P.D. Antiviral Role of Phenolic Compounds against Dengue Virus: A Review. Biomolecules 2020, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, A.C.; Mazzer, A.; Clarkson, G.J.J.; Taylor, G. Antioxidant Assays–Consistent Findings from FRAP and ORAC Reveal a Negative Impact of Organic Cultivation on Antioxidant Potential in Spinach but Not Watercress or Rocket Leaves. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 1, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.-N.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Xu, X.-R.; Chen, Y.-M.; Li, H.-B. Resources and Biological Activities of Natural Polyphenols. Nutrients 2014, 6, 6020–6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.-Y.; Liao, J.-H.; Hsu, A.-W.; Tsai, P.-W.; Hsueh, C.-C. Exploring Optimal Supplement Strategy of Medicinal Herbs and Tea Extracts for Bioelectricity Generation in Microbial Fuel Cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 256, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Lan, J.C.; Sun, Q.; Hsueh, C.; Chen, B.-Y. Deciphering Optimal Biostimulation Strategy of Supplementing Anthocyanin-Abundant Plant Extracts for Bioelectricity Extraction in Microbial Fuel Cells. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2019, 12, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Manefield, M.; Lee, M.; Kouzuma, A. Electron Shuttles in Biotechnology. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2009, 20, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Advances in Anti Hepatic Fibrotic Therapy with Traditional Chinese Medicine Herbal Formula. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 251, 112442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parameswaran, N.; Patial, S. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Signaling in Macrophages. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2010, 20, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayar, S.; Kürbüz, K.; Kahraman, R.; Öztürk, O.; Çalışkan, Z.; Doğanay, H.L.; Özdil, K. Risk of Hepatitis B Reactivation during Anti-TNF Therapy; Evaluation of Patients with Past Hepatitis B Infection. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 31, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).