Arsenic Removal from Drinking Water in Huanuara, Peru, Using Metalworking Residues: Characterization and Optimization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
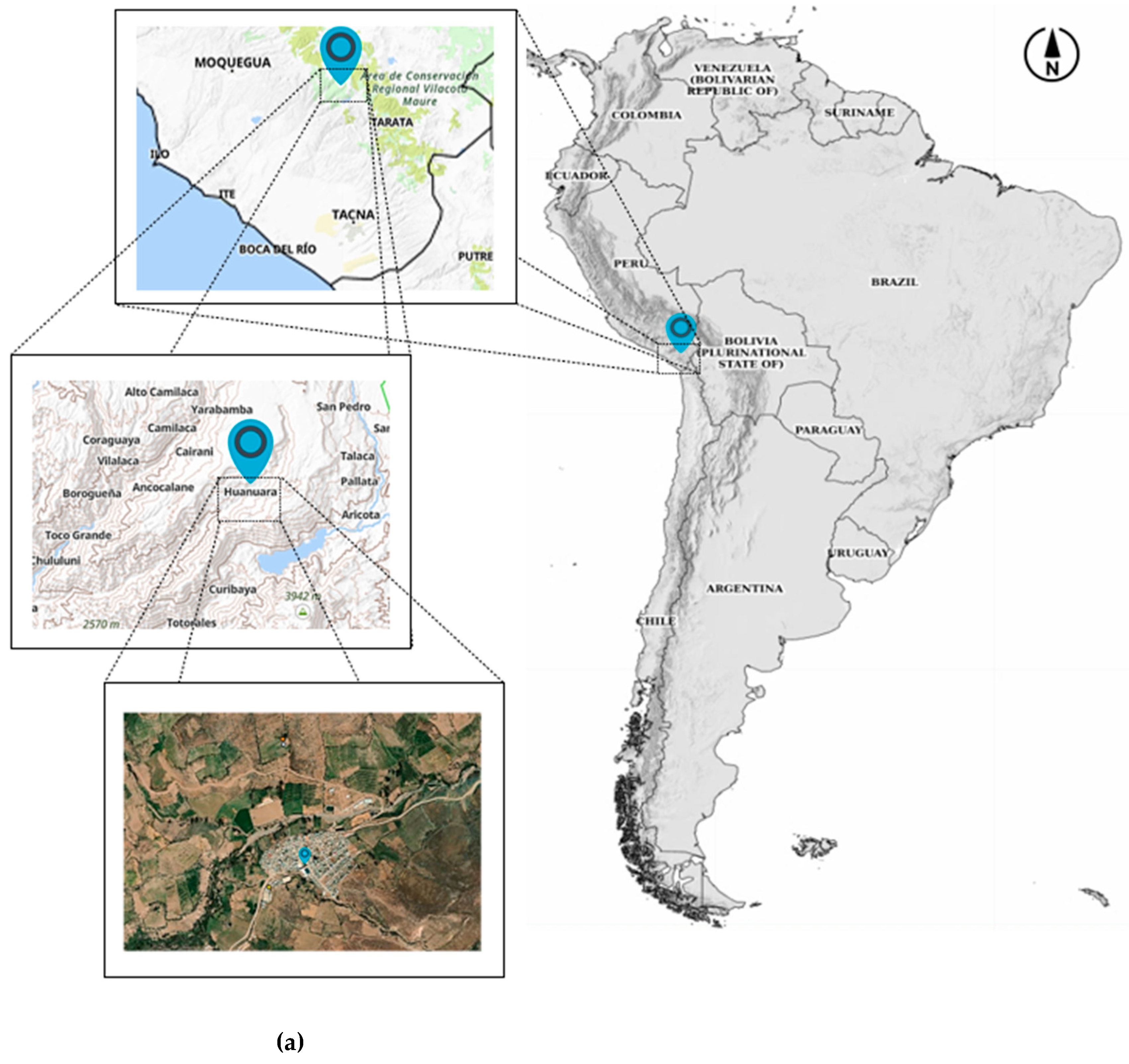
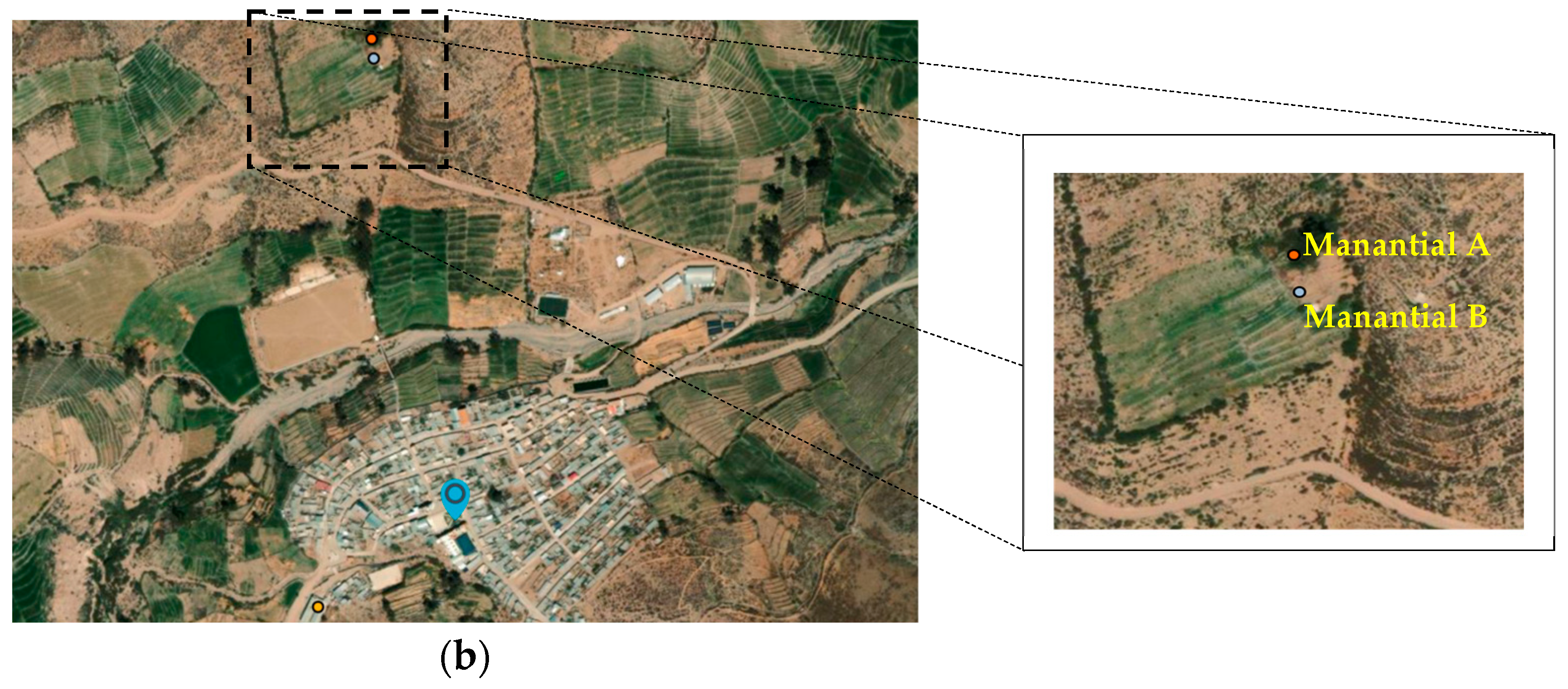
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
Water Sampling and Preservation
2.2. Adsorbent Material
Pretreatment Process of the Adsorbent
2.3. Adsorbent Characterization
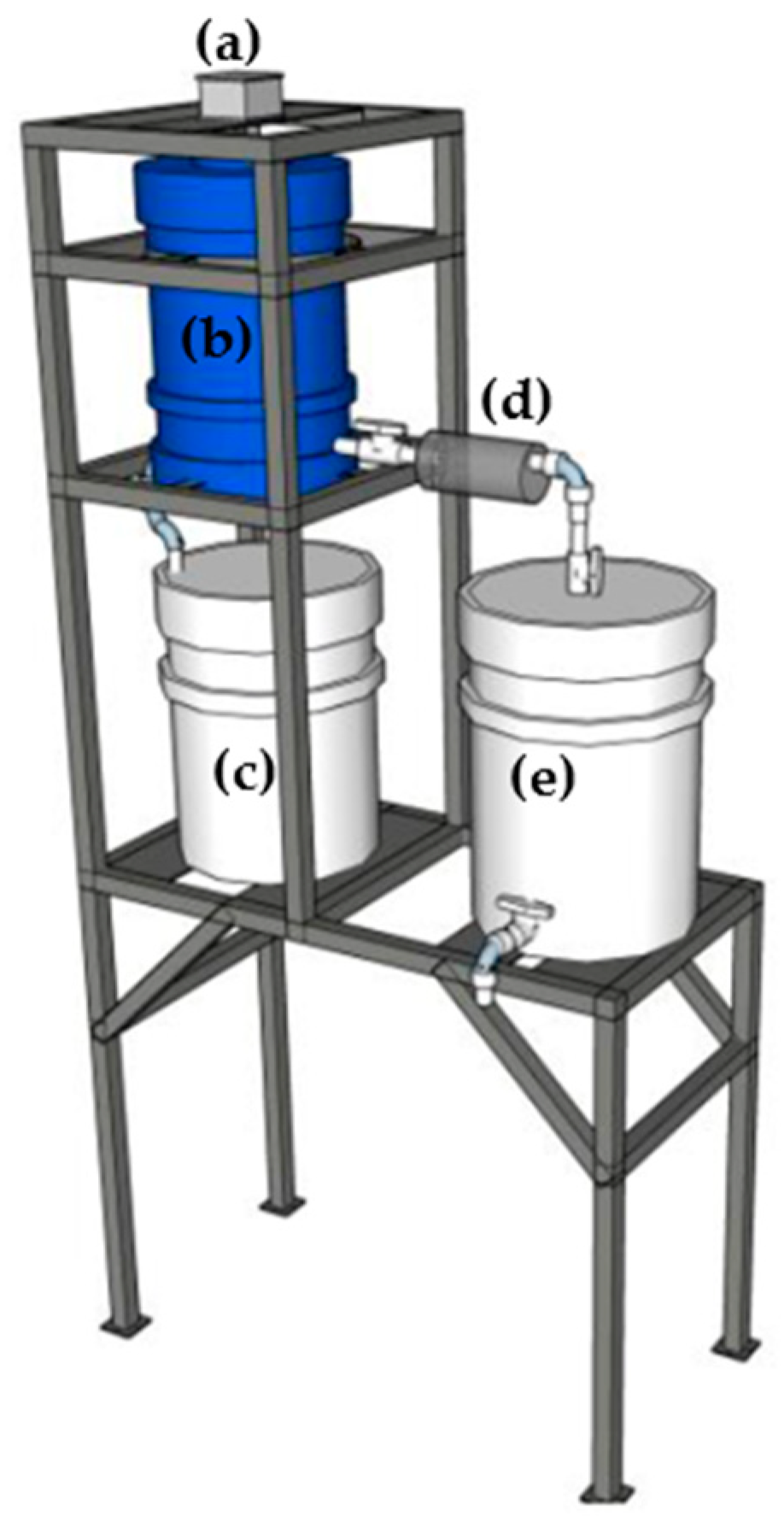
2.4. Batch Reactor System for Arsenic Removal
2.5. Experimental Design
2.6. Quantification of Arsenic, Iron, and Physicochemical Parameters
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Natural Water from Huanuara
3.1.1. Effect of pH and Physicochemical Parameters on Water Stability
3.1.2. Iron Leaching and Secondary Contamination
3.1.3. Interrelationship Between Arsenic Removal, pH, and Iron Concentration
3.2. Characterization of Processed Metalworking Residues
3.3. Optimization and Performance Analysis of Arsenic Removal Using Metalworking Residues
3.3.1. Statistical Validation and Model Significance
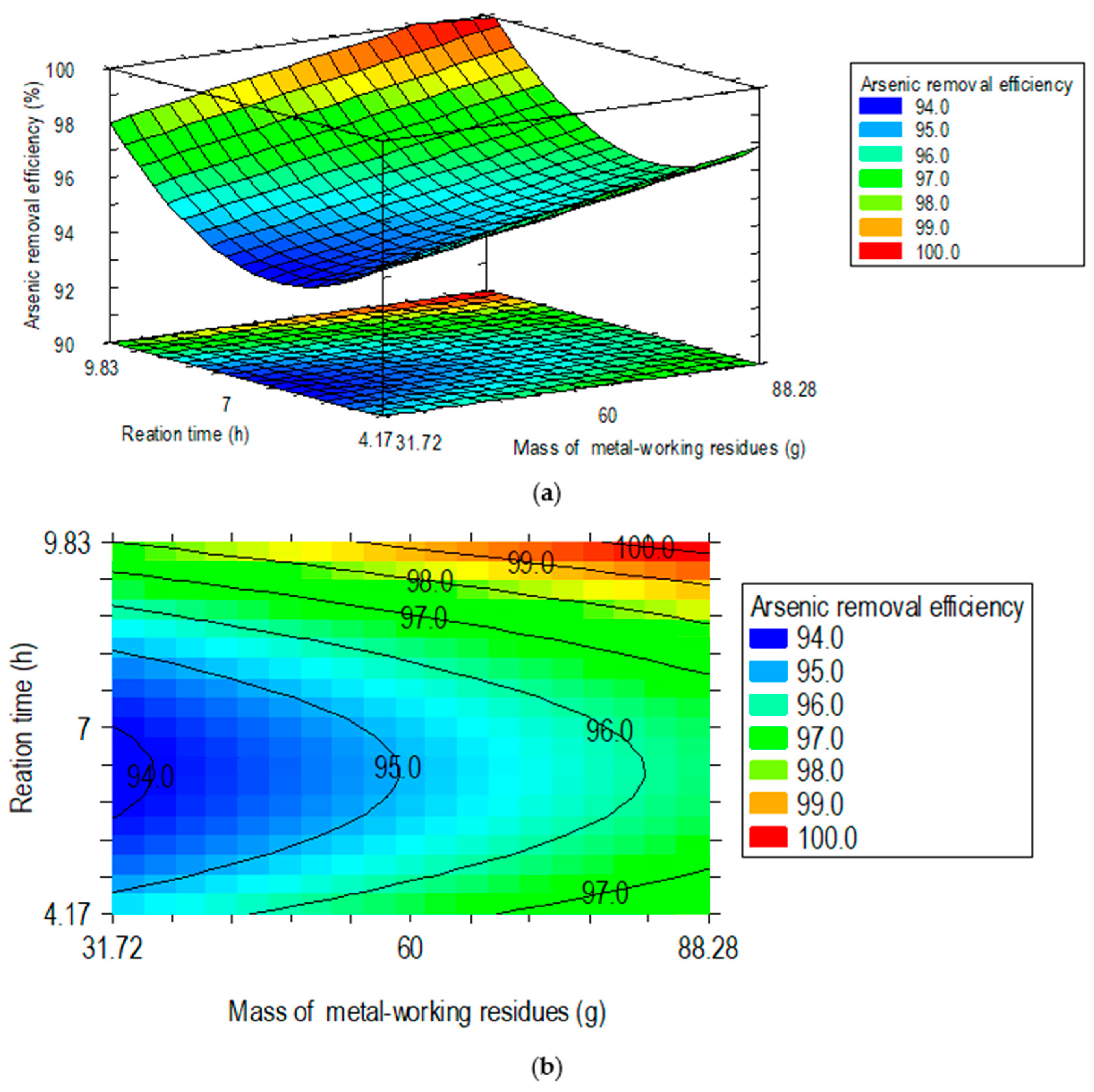
3.3.2. Effects of Adsorbent Mass and Contact Time on Arsenic Removal
3.3.3. Process Optimization and Practical Implications
3.4. Environmental and Practical Implications of Arsenic Removal Using Metalworking Residues
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| CCRD | Central Composite Rotatable Design |
| AAS | Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy |
| SEM-EDS | Scanning Electron Microscopy with Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy |
| XRD | X-ray Diffraction |
| BET | Brunauer–Emmett–Teller |
| ICP-MS | Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry |
| ORP | Oxidation-Reduction Potential |
| TDS | Total Dissolved Solids |
| EC | Electrical Conductivity |
| DO | Dissolved Oxygen |
| HDPE | High-Density Polyethylene |
| NSF/ANSI | National Sanitation Foundation/American National Standards Institute |
| UFPR | Federal University of Paraná |
| UNJBG | National University Jorge Basadre Grohmann |
References
- Niazi, N.K.; Bibi, I.; Aftab, T. (Eds.) Global Arsenic Hazard: Ecotoxicology and Remediation; Environmental Science and Engineering; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; ISBN 978-3-031-16359-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Patel, M.; Singh, P.; Bundschuh, J.; Pittman, C.U.; Trakal, L.; Mohan, D. Emerging Technologies for Arsenic Removal from Drinking Water in Rural and Peri-Urban Areas: Methods, Experience from, and Options for Latin America. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 694, 133427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating the First and Second Addenda; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; ISBN 978-92-4-004507-1.
- Repositorio Institucional INGEMMET: Hidrogeología de La Cuenca Del Río Locumba—[Boletín H 2]. Available online: https://repositorio.ingemmet.gob.pe/handle/20.500.12544/369?locale=es (accessed on 23 November 2024).
- Locumba, C.R. Estudio de los Recursos Hídricos Superficiales y Subterráneos e Infraestructura Hidráulica Para el Plan de Aprovechamiento en la Cuenca del río Locumba, en la Región de Tacna. 2017. Available online: https://repositorio.ana.gob.pe/handle/20.500.12543/3644 (accessed on 23 March 2025).
- Hao, L.; Liu, M.; Wang, N.; Li, G. A Critical Review on Arsenic Removal from Water Using Iron-Based Adsorbents. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 39545–39560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Day, P.A.; Vlassopoulos, D.; Meng, X.; Benning, L. Advances in Arsenic Research: Introductory Remarks. In Advances in Arsenic Research; ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; Volume 915, pp. 1–5. ISBN 978-0-8412-3913-5. [Google Scholar]
- Mahamallik, P.; Swain, R. A Mini-Review on Arsenic Remediation Techniques from Water and Future Trends. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 87, 3108–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spellman, F.R. Water Treatment Operations. In Handbook of Water and Wastewater Treatment Plant Operations; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2025; ISBN 978-1-003-58190-1. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, T.A. Adsorption Technology and Surface Science. In Interface Science and Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 34, pp. 39–64. ISBN 978-0-12-849876-7. [Google Scholar]
- Hezelova, M.; Pikna, E.; Dudova, M.; Fabian, V.; Pramuk, V.; Szilardiova, B. Arsenic Removal from Groundwater Using Iron Waste Materials. Desalination Water Treat. 2017, 68, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojiri, A.; Razmi, E.; KarimiDermani, B.; Rezania, S.; Kasmuri, N.; Vakili, M.; Farraji, H. Adsorption Methods for Arsenic Removal in Water Bodies: A Critical Evaluation of Effectiveness and Limitations. Front. Water 2024, 6, 1301648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohari, R.J.; Lau, W.J.; Halakoo, E.; Ismail, A.F.; Korminouri, F.; Matsuura, T.; Gohari, M.S.J.; Chowdhury, M.N.K. Arsenate Removal from Contaminated Water by a Highly Adsorptive Nanocomposite Ultrafiltration Membrane. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 8263–8272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neisan, R.S.; Saady, N.M.C.; Bazan, C.; Zendehboudi, S.; Al-nayili, A.; Abbassi, B.; Chatterjee, P. Arsenic Removal by Adsorbents from Water for Small Communities’ Decentralized Systems: Performance, Characterization, and Effective Parameters. Clean Technol. 2023, 5, 352–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Zhi, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, D.; Yu, L.; Gong, F.; Yin, Y.; Meng, F.; Li, C.; Chen, Z.; et al. Enhanced Arsenic Removal by Reusable Hexagonal CeO2/Fe2O3 Nanosheets with Exposed (0001) Facet. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edward, D.; Karungamye, P.; Nelson, G.; Selemani, J.; Njau, K.N. Removal of Arsenic in a Sand Filter Coupled with Zero Valent Iron. HydroResearch 2023, 6, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fano, D.; Vásquez-Velásquez, C.; Aguilar, J.; Gribble, M.O.; Wickliffe, J.K.; Lichtveld, M.Y.; Steenland, K.; Gonzales, G.F. Arsenic Concentrations in Household Drinking Water: A Cross-Sectional Survey of Pregnant Women in Tacna, Peru, 2019. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fano, D.; Vásquez-Velásquez, C.; Ramirez-Atencio, C.; Yucra, S.; Gonzales, G.F. Reproductive Outcomes in Pregnant Women and Its Association with Arsenic Contamination in Drinking Water, in a Region Characterized by High Birth Weight Rates in Peru. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2021, 34, 3997–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fano-Sizgorich, D.; Vásquez-Velásquez, C.; Yucra, S.; Vásquez, V.; Tokeshi, P.; Aguilar, J.; Ramírez-Atencio, C.; Barr, D.B.; Gonzales, G.F. Total Urinary Arsenic and Inorganic Arsenic Concentrations and Birth Outcomes in Pregnant Women of Tacna, Peru: A Cross-Sectional Study. Expo. Health 2021, 13, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ArcGIS Enterprise. Available online: https://geoportal.un.org/arcgis/home/index.html (accessed on 24 February 2025).
- SENAMHI-Mapa Climatico Del Peru. Available online: https://www.senamhi.gob.pe/?&p=mapa-climatico-del-peru (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Lopez, E.P.M.; Quispe, V.C. ANÁLISIS FISICOQUÍMICO Y BIOLÓGICO DEL AGUA PARA CONSUMO HUMANO EN EL DISTRITO DE HUANUARA. Cienc. Desarro. 2007, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estudio de Máximas Avenidas en las Cuencas de la Zona Centro de la Vertiente del Pacífico: Informe Final. 2010. Available online: https://repositorio.ana.gob.pe/handle/20.500.12543/796 (accessed on 23 March 2025).
- Informes y Publicaciones—Dirección Regional de Salud Tacna—Plataforma del Estado Peruano. Available online: https://www.gob.pe/institucion/regiontacna-diresa/informes-publicaciones?sheet=14 (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- ISO 5667-3: 2018; Water Quality—Sampling—Part 3: Preservation and Handling of Water Samples. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Metalworking. The Free Dictionary. Available online: https://www.thefreedictionary.com/metalworking (accessed on 23 March 2025).
- Moro, K.; Ello, A.S.; Koffi, K.R.; Eroi, N.S. Mixed Maghemite/Hematite Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Synthesis for Lead and Arsenic Removal from Aqueous Solution. J. Nanomater. 2023, 2023, 8216889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Singh, S.; Parihar, P.; Singh, V.P.; Prasad, S.M. Arsenic Contamination, Consequences and Remediation Techniques: A Review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 112, 247–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, J.I.; Newbury, D.E.; Michael, J.R.; Ritchie, N.W.M.; Scott, J.H.J.; Joy, D.C. Scanning Electron Microscopy and X-Ray Microanalysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-1-4939-6674-5. [Google Scholar]
- Schatten, H. (Ed.) Scanning Electron Microscopy for the Life Sciences; Advances in Microscopy and Microanalysis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012; ISBN 978-0-521-19599-7. [Google Scholar]
- Seeck, O.H.; Murphy, B. (Eds.) X-Ray Diffraction: Modern Experimental Techniques; Jenny Stanford Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-0-429-07189-8. [Google Scholar]
- Zolotoyabko, E. Basic Concepts of X-Ray Diffraction; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; ISBN 3-527-68118-3. [Google Scholar]
- Guinebretière, R. X-Ray Diffraction by Polycrystalline Materials; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; ISBN 1-118-61395-3. [Google Scholar]
- Marcil, C. (Ed.) Drinking Water: Quality Control, Distribution Systems and Treatment; Water resource planning, development and management; Nova Science Publishers, Inc: New York, NY, USA, 2020; ISBN 978-1-5361-8071-8. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.-L.; Bush, R. Highly Efficient and Rapid Removal of Arsenic(III) from Aqueous Solutions by Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron Supported on a Zirconium 1,4-Dicarboxybenzene Metal–Organic Framework (UiO-66 MOF). RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 39475–39487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, T.; Chopey, N. Handbook of Chemical Engineering Calculations; McGraw Hill Professional: New York, NY, USA, 2012; ISBN 0-07-176804-1. [Google Scholar]
- Scott Fogler, H. Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 2016; ISBN 0-13-388751-0. [Google Scholar]
- NSF/ANSI 61; Drinking Water System Components—Health Effects. American National Standards Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2024.
- 21 CFR Part 129—Processing and Bottling of Bottled Drinking Water. Available online: https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-21/part-129 (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Levenspiel, O. Chemical Reaction Engineering; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998; ISBN 0-471-25424-X. [Google Scholar]
- Ranade, V.V. Computational Flow Modeling for Chemical Reactor Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; ISBN 0-08-050229-6. [Google Scholar]
- Felder, R.M.; Rousseau, R.W.; Bullard, L.G. Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; ISBN 1-119-49863-5. [Google Scholar]
- SketchUp. Available online: https://app.sketchup.com/app (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Brezonik, P. Chemical Kinetics and Process Dynamics in Aquatic Systems; Routledge: London, UK, 2018; ISBN 1-315-13913-8. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, M.I.; Iemma, A.F. Experimental Design and Process Optimization; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; ISBN 1-4822-9955-0. [Google Scholar]
- Davim, J.P.; Machado, C. Management and Industrial Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Arsenic in Drinking-Water: Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/arsenic-in-drinking-water-background-document-for-development-of-who-guidelines-for-drinking-water-quality (accessed on 22 November 2024).
- Sista, K.S.; Kumar, D.; Sinha, G.R.; Moon, A.P.; Dwarapudi, S. Iron Powders as a Potential Material for Arsenic Removal in Aqueous Systems. ISIJ Int. 2021, 61, 2687–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, A.Q.; Ahmed, S.; Bhatti, Z.A.; Maitlo, G.; Shah, A.K.; Mazari, S.A.; Muhammad, A.; Jatoi, A.S.; Kandhro, G.A. Experimental Investigations of Arsenic Adsorption from Contaminated Water Using Chemically Activated Hematite (Fe2O3) Iron Ore. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 12898–12908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masscheleyn, P.H.; Delaune, R.D.; Patrick, W.H., Jr. Effect of Redox Potential and pH on Arsenic Speciation and Solubility in a Contaminated Soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1991, 25, 1414–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessen, S.; Larsen, F.; Koch, C.B.; Arvin, E. Sorption and Desorption of Arsenic to Ferrihydrite in a Sand Filter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 8045–8051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, C.-S.; Batjargal, T.; Seo, C.-I.; Yang, J.-S.; Baek, K. Removal of As(V) from Aqueous System Using Steel-Making by-Product. Desalination Water Treat. 2009, 7, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E. Water Quality: An Introduction; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; ISBN 978-3-030-23334-1. [Google Scholar]
- Martuza, M.A.; Shafiquzzaman, M.; Haider, H.; Ahsan, A.; Ahmed, A.T. Predicting Removal of Arsenic from Groundwater by Iron Based Filters Using Deep Neural Network Models. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 26428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahidul Hassan, H. A Review on Different Arsenic Removal Techniques Used for Decontamination of Drinking Water. Environ. Pollut. Bioavailab. 2023, 35, 2165964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Peng, B.; Min, X.; Liang, Y.; You, Y.; Chai, L. Modeling and Optimization of Lime-Based Stabilization in High Alkaline Arsenic-Bearing Sludges with a Central Composite Design. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2017, 52, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, C.; Rhee, S.; Oh, M.; Park, J. Removal Characteristics of As(III) and As(V) from Acidic Aqueous Solution by Steel Making Slag. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 213–214, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, M.M.; Sletten, R.S.; Bailey, R.P.; Bennett, T. Sorption and Filtration of Metals Using Iron-Oxide-Coated Sand. Water Res. 1996, 30, 2609–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deditius, A. Arsenic-Environmental Geochemistry, Mineralogy, and Microbiology. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, Volume 79 (RJ Bowell, CN Alpers, HE Jamieson, DK Nordstron, and J. Majzlan, Eds.); Society of Economic Geologists: Littleton, CO, USA, 2015; Volume 110, ISBN 0-939950-94-4. [Google Scholar]
- Fares, A.; Singh, S.K. Arsenic Water Resources Contamination; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pikaar, I.; Guest, J.; Ganigué, R.; Jensen, P.; Rabaey, K.; Seviour, T.; Trimmer, J.; van der Kolk, O.; Vaneeckhaute, C.; Verstraete, W. (Eds.) Resource Recovery from Water: Principles and Application; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2022; ISBN 978-1-78040-956-6. [Google Scholar]
- Cornell, R.M.; Schwertmann, U. The Iron Oxides: Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurrences, and Uses; Wiley-vch Weinheim: Weinheim, Germany, 2003; Volume 664. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, R. Recent Advances of Magnetite Nanomaterials to Remove Arsenic from Water. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 32197–32209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawardana, B.; Singhal, N.; Swedlund, P. Dechlorination of Pentachlorophenol by Zero Valent Iron and Bimetals: Effect of Surface Characteristics and Bimetal Preparation Procedure. 2012. Available online: https://scholarworks.umass.edu/entities/publication/2f323853-bacc-45f6-89e5-7a1f59019d92 (accessed on 23 March 2025).
- Sun, Y.-P.; Li, X.; Cao, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.P. Characterization of Zero-Valent Iron Nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 120, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, E.P.; Joyner, L.G.; Halenda, P.P. The Determination of Pore Volume and Area Distributions in Porous Substances. I. Computations from Nitrogen Isotherms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1951, 73, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angotzi, M.S.; Mameli, V.; Cara, C.; Borchert, K.B.L.; Steinbach, C.; Boldt, R.; Schwarz, D.; Cannas, C. Meso- and Macroporous Silica-Based Arsenic Adsorbents: Effect of Pore Size, Nature of the Active Phase, and Silicon Release. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 6100–6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luxton, T.P.; Eick, M.J.; Rimstidt, D.J. The Role of Silicate in the Adsorption/Desorption of Arsenite on Goethite. Chem. Geol. 2008, 252, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, P.; Balo Majumder, C.; Mohanty, B. Removal of Trivalent Arsenic (As(III)) from Contaminated Water by Calcium Chloride (CaCl2)-Impregnated Rice Husk Carbon. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 2550–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fan, H.; Yuan, J.; Tian, J.; Wang, Y.; Lu, C.; Han, H.; Sun, W. The Application and Mechanism of Iron Sulfides in Arsenic Removal from Water and Wastewater: A Critical Review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Yang, J.; Zhou, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, D. Fe-Containing Materials for Inorganic/Organic Arsenic Removal from Water: A Review of Current Status and Future Prospects. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 428, 139533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yean, S.; Cong, L.; Yavuz, C.T.; Mayo, J.T.; Yu, W.W.; Kan, A.T.; Colvin, V.L.; Tomson, M.B. Effect of Magnetite Particle Size on Adsorption and Desorption of Arsenite and Arsenate. J. Mater. Res. 2005, 20, 3255–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipley, H.J.; Yean, S.; Kan, A.T.; Tomson, M.B. A Sorption Kinetics Model for Arsenic Adsorption to Magnetite Nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2010, 17, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, J.W.; Fortner, J.; Work, S.; Avendano, C.; Gonzalez-Pech, N.I.; Zárate Araiza, R.; Li, Q.; Alvarez, P.J.; Colvin, V.; Kan, A. Arsenic Removal by Nanoscale Magnetite in Guanajuato, Mexico. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2014, 31, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.K.; Kim, Y.; Choi, Y.-G. Magnetite Synthesis Using Iron Oxide Waste and Its Application for Phosphate Adsorption with Column and Batch Reactors. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2019, 148, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, S.; Hering, J.G. Comparison of Arsenic(V) and Arsenic(III) Sorption onto Iron Oxide Minerals: Implications for Arsenic Mobility. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4182–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Ranjan, R.; Kushwaha, R.; Sonam; Markandeya; Shukla, S.P. Arsenic Removal Using Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Produced Employing a Green Synthesis Approach. Environ. Qual. Manag. 2024, 33, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phearom, S.; Shahid, M.K.; Choi, Y. Nature of Surface Interactions among Fe3O4 Particles and Arsenic Species during Static and Continuous Adsorption Processes. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 18, 100789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, T.B.; Milivojevich, A. Quality by Experimental Design, 4th ed.; Chapman and Hall/CRC: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-0-429-16137-7. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, A.; Sengupta, A.; Bhadu, M.K.; Pandey, A.; Mondal, A. Efficient Removal of Arsenic (V) from Water Using Steel-Making Slag. Water Environ. Res. 2014, 86, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Yu, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J.; Li, D. Arsenic(V) Removal by Granular Adsorbents Made from Water Treatment Residuals Materials and Chitosan. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 585, 124036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okanigbe, D.O. Resource Recovery and Recycling from Waste Metal Dust (I): Waste Iron Dust and Waste Aluminum Dust. In Resource Recovery and Recycling from Waste Metal Dust; Ogochukwu Okanigbe, D., Popoola, A.P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 3–14. ISBN 978-3-031-22492-8. [Google Scholar]
- Türk, T.; Alp, İ. Arsenic Removal from Aqueous Solutions with Fe-Hydrotalcite Supported Magnetite Nanoparticle. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, D.M.; Viraraghavan, T.; Jin, Y.-C. Iron Oxide Coated Sand for Arsenic Removal: Investigation of Coating Parameters Using Factorial Design Approach. Pract. Period. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste Manag. 2006, 10, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Miranda Avilés, R.; Serafin Muñoz, A.H.; Rocha Amador, D.O.; Perez Rodriguez, R.Y.; Hernández Anguiano, J.H.; Julia Navarro, C.; Zha, X.; Moncada, D.; de Jesús Puy Alquiza, M.; et al. Efficient Arsenic Removal from Water Using Iron-Impregnated Low-Temperature Biochar Derived from Henequen Fibers: Performance, Mechanism, and LCA Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Initial concentrations:
| ||||
| Assays | Metalworking Residues (Coded Value **) (g) | Contact Time (Coded Value) (h) | Residual Arsenic (µg·L−1) | Residual Iron * (µg·L−1) |
| 1 | −1 (40) | −1 (5) | 25.21 | 13.80 |
| 2 | +1 (80) | −1 (5) | 16.10 | 105.00 |
| 3 | −1 (40) | +1 (9) | 18.83 | 19.10 |
| 4 | +1 (80) | +1 (9) | 4.91 | 88.50 |
| 5 | −1.41 (31.72) | 0 (7) | 28.55 | 23.90 |
| 6 | +1.41 (88.28) | 0 (7) | 19.13 | 132.70 |
| 7 | 0 (60) | −1.41 (4.17) | 20.27 | 28.60 |
| 8 | 0 (60) | +1.41 (9.83) | 5.46 | 15.10 |
| 9 | 0 (60) | 0 (7) | 27.78 | 83.00 |
| 10 | 0 (60) | 0 (7) | 29.97 | 77.00 |
| 11 | 0 (60) | 0 (7) | 25.83 | 75.10 |
| Assays | pH | ORP (mV) | TDS (mg·L−1) | Resistivity (Ω·m) | EC (mS·m−1) | Salinity (g·kg−1) | Temperature (K) | DO (mg·L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Water Sample | 8.10 | 67.5 | 633 | 7.88 | 12.70 | 0.70 | 291.15 | 8.00 |
| 1 | 8.19 | 68.3 | 660 | 7.66 | 13.14 | 0.55 | 286.35 | 7.43 |
| 2 | 8.26 | 74.6 | 676 | 7.40 | 13.48 | 0.57 | 286.55 | 8.86 |
| 3 | 8.37 | 85.4 | 663 | 7.54 | 13.20 | 0.59 | 288.85 | 8.07 |
| 4 | 8.24 | 78.7 | 665 | 7.49 | 13.39 | 0.56 | 288.15 | 7.96 |
| 5 | 8.35 | 83.3 | 666 | 7.50 | 13.18 | 0.60 | 290.05 | 8.48 |
| 6 | 8.30 | 81.6 | 673 | 7.46 | 13.42 | 0.57 | 287.25 | 7.94 |
| 7 | 8.18 | 70.2 | 689 | 7.26 | 13.78 | 0.61 | 288.45 | 8.99 |
| 8 | 8.26 | 86.1 | 677 | 7.37 | 13.49 | 0.56 | 288.35 | 7.87 |
| 9 | 8.30 | 84.9 | 669 | 7.38 | 13.54 | 0.58 | 287.35 | 7.91 |
| 10 | 8.32 | 86.5 | 662 | 7.54 | 13.22 | 0.66 | 287.55 | 7.85 |
| 11 | 8.34 | 87.3 | 659 | 7.45 | 13.42 | 0.62 | 288.75 | 7.92 |
| Parameter | Unit | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Single-point surface area | m2·g−1 | 0.7056 |
| Specific surface area (BET) | m2·g−1 | 0.7469 |
| t-Plot micropore area | m2·g−1 | 0.1960 |
| t-Plot external surface area | m2·g−1 | 0.9276 |
| t-Plot micropore volume | m2·g−1 | 0.00006 |
| BJH adsorption average pore diameter | nm | 5.9732 |
| BJH desorption average pore diameter | nm | 6.2978 |
| Independent Variables Coded (Actual) | Arsenic Removal Efficiency (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assays | Mass of Metalworking Residues (g) | Contact Time (h) | Experimental | Predicted |
| 1 | −1 (40) | −1 (5) | 95.24 | 94.80 |
| 2 | +1 (80) | −1 (5) | 96.96 | 96.52 |
| 3 | −1 (40) | +1 (9) | 96.45 | 96.62 |
| 4 | +1 (80) | +1 (9) | 99.07 | 98.33 |
| 5 | −1.41 (31.72) | 0 (7) | 94.61 | 93.98 |
| 6 | +1.41 (88.28) | 0 (7) | 96.39 | 96.41 |
| 7 | 0 (60) | −1.41 (4.17) | 96.18 | 96.66 |
| 8 | 0 (60) | +1.41 (9.83) | 98.97 | 99.22 |
| 9 | 0 (60) | 0 (7) | 94.76 | 95.19 |
| 10 | 0 (60) | 0 (7) | 94.35 | 95.19 |
| 11 | 0 (60) | 0 (7) | 95.13 | 95.19 |
| The uncertainty associated with the values in the table can be shown as follows: Arsenic removal efficiency (Experimental)= ±2.07% | ||||
| Source of Variation | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean Square | F-Test | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regression | 24.12 | 3.00 | 8.04 | 22.02 | 0.0006 |
| Residual | 2.56 | 7.00 | 0.37 | ||
| Lack of fit | 2.25 | ||||
| Pure error | 0.30 | ||||
| Total | 26,68 | ||||
| R2 = 0.90; F3:7:0.05 = 4.35 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costa Gil, C.R.; Mamani López, E.P.; Avendaño Cáceres, E.O.; Vargas Conde, E.V.; Flores Cotrado, N.; Salazar Delgado, D.M.; Quispe Jiménez, O.A. Arsenic Removal from Drinking Water in Huanuara, Peru, Using Metalworking Residues: Characterization and Optimization. Processes 2025, 13, 1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041190
Costa Gil CR, Mamani López EP, Avendaño Cáceres EO, Vargas Conde EV, Flores Cotrado N, Salazar Delgado DM, Quispe Jiménez OA. Arsenic Removal from Drinking Water in Huanuara, Peru, Using Metalworking Residues: Characterization and Optimization. Processes. 2025; 13(4):1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041190
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosta Gil, Carlos R., Edilberto P. Mamani López, Edgardo O. Avendaño Cáceres, Erika V. Vargas Conde, Nancy Flores Cotrado, Diego M. Salazar Delgado, and Otto A. Quispe Jiménez. 2025. "Arsenic Removal from Drinking Water in Huanuara, Peru, Using Metalworking Residues: Characterization and Optimization" Processes 13, no. 4: 1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041190
APA StyleCosta Gil, C. R., Mamani López, E. P., Avendaño Cáceres, E. O., Vargas Conde, E. V., Flores Cotrado, N., Salazar Delgado, D. M., & Quispe Jiménez, O. A. (2025). Arsenic Removal from Drinking Water in Huanuara, Peru, Using Metalworking Residues: Characterization and Optimization. Processes, 13(4), 1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13041190









