Effect of CuO as Sintering Additive in Scandium Cerium and Gadolinium-Doped Zirconia-Based Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cell for Steam Electrolysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Cell Fabrication
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Electrochemical Performance Measurement
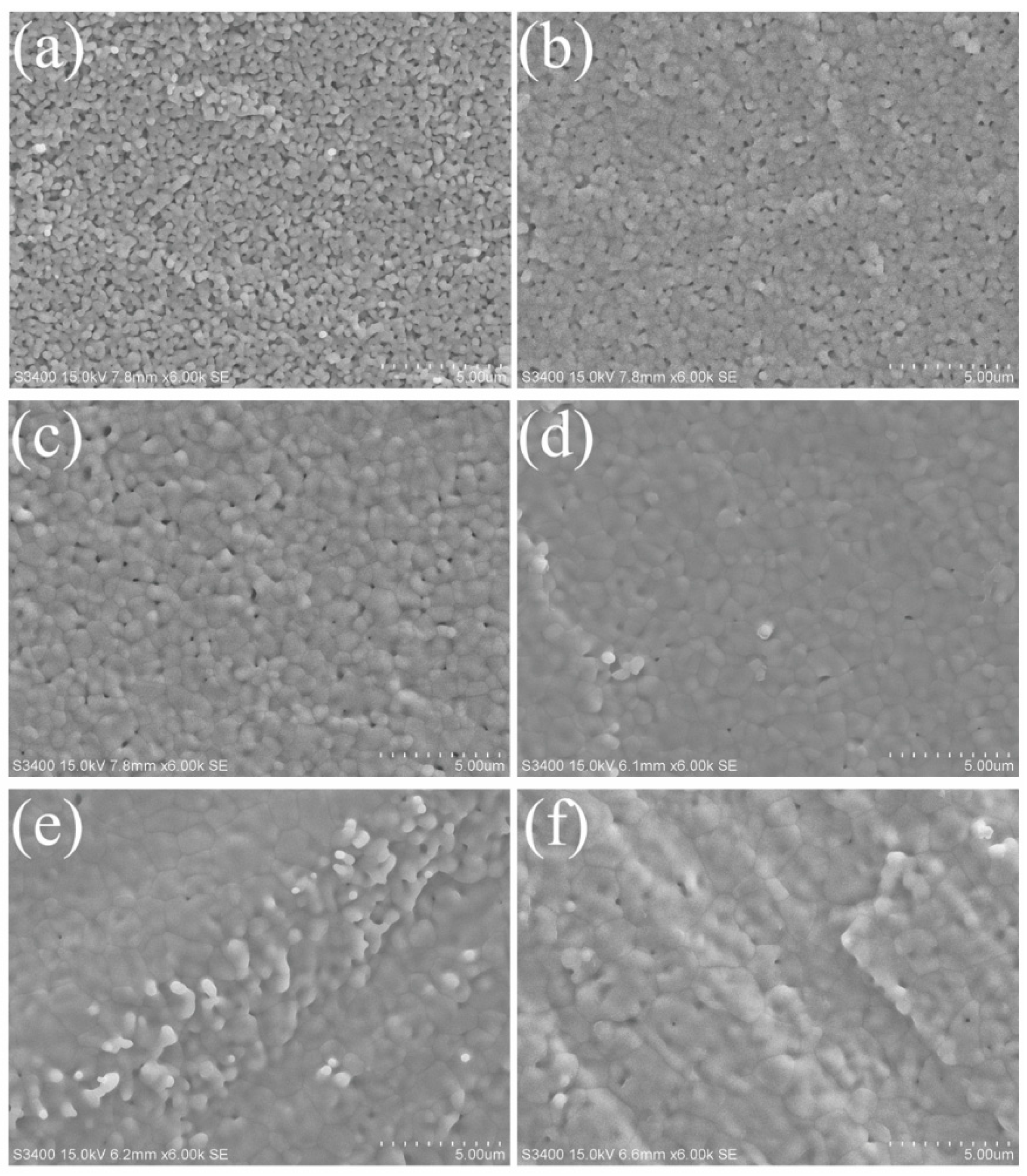
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Densification of the Fabricated Cell
3.2. Phase Identification
3.3. Activation Energy of Conduction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weng, G.-M.; Vanessa Li, C.-Y.; Chan, K.-Y. Hydrogen battery using neutralization energy. Nano Energy 2018, 53, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.-C.; Hsiao, Y.-S.; Yang, Y.-Z. The Optimization of Hybrid Power Systems with Renewable Energy and Hydrogen Generation. Energies 2018, 11, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, A.S.; McTernan, P.M.; Lian, H.; Kelly, R.M.; Adams, M.W.W. Biological conversion of carbon dioxide and hydrogen into liquid fuels and industrial chemicals. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiesberg, I.L.; de Medeiros, J.L.; Alves, R.M.B.; Coutinho, P.L.A.; Araújo, O.Q.F. Carbon dioxide management by chemical conversion to methanol: Hydrogenation and Bi-Reforming. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 125, 320–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likhittaphon, S.; Panyadee, R.; Fakyam, W.; Charojrochkul, S.; Sornchamni, T.; Laosiripojana, N.; Assabumrungrat, S.; Kim-Lohsoontorn, P. Effect of CuO/ZnO catalyst preparation condition on alcohol-assisted methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide and hydrogen. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 20782–20791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, H.; Sabato, A.G.; Herbrig, K.; Ferrero, D.; Walter, C.; Salvo, M.; Smeacetto, F. Design and characterization of novel glass-ceramic sealants for solid oxide electrolysis cell (SOEC) applications. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2018, 15, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim-Lohsoontorn, P.; Kim, Y.-M.; Laosiripojana, N.; Bae, J. Gadolinium doped ceria-impregnated nickel–yttria stabilised zirconia cathode for solid oxide electrolysis cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 9420–9427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, M.; Yuan, C.; Ye, X.; Zhan, Z.; Wang, S. High performance solid oxide electrolysis cell with impregnated electrodes. Electrochem. Commun. 2015, 54, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jun, A.; Gwon, O.; Yoo, S.; Liu, M.; Shin, J.; Lim, T.-H.; Kim, G. Hybrid-solid oxide electrolysis cell: A new strategy for efficient hydrogen production. Nano Energy 2018, 44, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-González, R.; Molina, T.; Savvin, S.; Moreno, R.; Makradi, A.; Núñez, P. Fabrication and electrical characterization of several YSZ tapes for SOFC applications. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 14253–14259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, T.; Sarrafi, M.H.; Haji, M.; Raissi, B.; Maghsoudipour, A. Investigation on microstructures of NiO–YSZ composite and Ni–YSZ cermet for SOFCs. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 9440–9447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fondard, J.; Bertrand, P.; Billard, A.; Fourcade, S.; Batocchi, P.; Mauvy, F.; Bertrand, G.; Briois, P. Manufacturing and testing of a metal supported Ni-YSZ/YSZ/La2NiO4 IT-SOFC synthesized by physical surface deposition processes. Solid State Ion. 2017, 310, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Yang, Z.; Han, M. Optimization of Ni-YSZ anodes for tubular SOFC by a novel and efficient phase inversion-impregnation approach. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 750, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.H.; Chiang, C.M.; Lo, W.C.; Chou, C.C. Co-doping effect of divalent (Mg2+, Ca2+, Sr) and trivalent (Y3+) cations with different ionic radii on ionic conductivity of zirconia electrolytes. J. Chin. Soc. Mech. Eng. Trans. Chin. Inst. Eng. Ser. C 2009, 30, 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Liu, J.; Chen, H.; Li, S.; He, T.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, J. The effect of Fe doping on the properties of SOFC electrolyte YSZ. Solid State Ion. 2008, 179, 1620–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubrin, R.; Blugan, G.; Kuebler, J. Influence of cerium doping on mechanical properties of tetragonal scandium-stabilized zirconia. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 37, 1651–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijaya Lakshmi, V.; Bauri, R. Phase formation and ionic conductivity studies on ytterbia co-doped scandia stabilized zirconia (0.9ZrO2–0.09Sc2O3–0.01Yb2O3) electrolyte for SOFCs. Solid State Sci. 2011, 13, 1520–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Gao, H.; Zhang, L.; Xuan, Y.; Ren, J.; Ni, M.; Lin, Z. Unlocking the nature of the co-doping effect on the ionic conductivity of CeO2-based electrolyte. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 3977–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.A.; Argirusis, C.; Kilo, M.; Wiemhöfer, H.-D.; Hammad, F.F.; Hanafi, Z.M. Preparation and conductivity of ternary scandia-stabilised zirconia. Solid State Ion. 2011, 184, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.C.; Yu, J.H.; Lim, K.T.; Lee, H.L.; Baik, K.H. Effects of Partial Substitution of CeO2 with M2O3 (M = Yb, Gd, Sm) on Electrical Degradation of Sc2O3 and CeO2 Co-doped ZrO2. J. Korean Ceram. Soc. 2016, 53, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, F.D.; Tan, C.Y.; Singh, R.; Muchtar, A.; Somalu, M.R.; Ng, C.K.; Yap, B.K.; Teh, Y.C.; Tan, Y.M. Effect of manganese oxide on the sinterability of 8mol% yttria-stabilized zirconia. Mater. Charact. 2016, 120, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.G.; Jeon, O.S.; Ryu, K.H.; Park, M.G.; Min, S.H.; Hyun, S.H.; Shul, Y.G. Effects of 8mol% yttria-stabilized zirconia with copper oxide on solid oxide fuel cell performance. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 7982–7988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satardekar, P.; Montinaro, D.; Sglavo, V.M. Fe-doped YSZ electrolyte for the fabrication of metal supported-SOFC by co-sintering. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 9806–9812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Honorato, E.; Dessoliers, M.; Shapiro, I.P.; Wang, X.; Xiao, P. Improvements to the sintering of yttria-stabilized zirconia by the addition of Ni. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 6777–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myung, J.-H.; Ko, H.J.; Park, H.-G.; Hwan, M.; Hyun, S.-H. Fabrication and characterization of planar-type SOFC unit cells using the tape-casting/lamination/co-firing method. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likhittaphon, S.; Pukkrueapun, T.; Seeharaj, P.; Wetwathana Hartley, U.; Laosiripojana, N.; Kim-Lohsoontorn, P. Effect of sintering additives on barium cerate based solid oxide electrolysis cell for syngas production from carbon dioxide and steam. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 173, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsoukov, E.; Mcdonald, J.R. Impedance Spectroscopy Theory, Experiment, and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Vu, H.; Nguyen, D.; Fisher, J.G.; Moon, W.-H.; Bae, S.; Park, H.-G.; Park, B.-G. CuO-based sintering aids for low temperature sintering of BaFe12O19 ceramics. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2013, 1, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, Y.-C.; Wu, C.-T.; Huang, Y.-L.; Chung, T.-C. Effect of CuO on CaTiO3 perovskite ceramics prepared using a direct sintering process. J. Nucl. Mater. 2009, 393, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsif, M.; Marrero-López, D.; Ruiz-Morales, J.C.; Savvin, S.N.; Núñez, P. Effect of sintering aids on the conductivity of BaCe0.9Ln0.1O3−δ. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 9154–9163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-S.; Li, H.; Xiao, W.-D. Sintering effect on crystallite size, hydrogen bond structure and morphology of the silane-derived silicon powders. Powder Technol. 2015, 273, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presto, S.; Viviani, M. Effect of CuO on microstructure and conductivity of Y-doped BaCeO3. Solid State Ion. 2016, 295, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, C. Effects of CuO on the microstructure and electrochemical properties of garnet-type Li6.3La3Zr1.65W0.35O12 solid electrolyte. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2019, 135, 109080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Sunarso, J.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, S. Enhanced oxygen permeability and electronic conductivity of Ce0.8Gd0.2O2−δ membrane via the addition of sintering aids. Solid State Ion. 2017, 310, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicollet, C.; Waxin, J.; Dupeyron, T.; Flura, A.; Heintz, J.-M.; Ouweltjes, J.P.; Piccardo, P.; Rougier, A.; Grenier, J.-C.; Bassat, J.-M. Gadolinium doped ceria interlayers for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells cathodes: Enhanced reactivity with sintering aids (Li, Cu, Zn), and improved densification by infiltration. J. Power Sources 2017, 372, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Decès-Petit, C.; Yick, S.; Robertson, M.; Kesler, O.; Maric, R.; Ghosh, D. A study on sintering aids for Sm0.2Ce0.8O1.9 electrolyte. J. Power Sources 2006, 162, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-J.; Na, Y.-H.; Kwak, M.; Kim, T.W.; Seo, D.-W.; Woo, S.-K.; Kim, S.-D. Development of solid oxide cells by co-sintering of GDC diffusion barriers with LSCF air electrode. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 13653–13660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sintering Temperature (K) | Average Grain Size (μm) | |
|---|---|---|
| SCGZ | SCGZ with 0.5 wt% CuO | |
| 1423 | - | 1.58 |
| 1473 | - | 2.66 |
| 1523 | 1.04 | 5.02 |
| 1573 | 1.20 | 5.11 |
| 1623 | 1.51 | 3.32 |
| 1673 | 2.28 | 3.77 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Visvanichkul, R.; Peng-Ont, S.; Ngampuengpis, W.; Sirimungkalakul, N.; Puengjinda, P.; Jiwanuruk, T.; Sornchamni, T.; Kim-Lohsoontorn, P. Effect of CuO as Sintering Additive in Scandium Cerium and Gadolinium-Doped Zirconia-Based Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cell for Steam Electrolysis. Processes 2019, 7, 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7120868
Visvanichkul R, Peng-Ont S, Ngampuengpis W, Sirimungkalakul N, Puengjinda P, Jiwanuruk T, Sornchamni T, Kim-Lohsoontorn P. Effect of CuO as Sintering Additive in Scandium Cerium and Gadolinium-Doped Zirconia-Based Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cell for Steam Electrolysis. Processes. 2019; 7(12):868. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7120868
Chicago/Turabian StyleVisvanichkul, R., S. Peng-Ont, W. Ngampuengpis, N. Sirimungkalakul, P. Puengjinda, T. Jiwanuruk, T. Sornchamni, and P. Kim-Lohsoontorn. 2019. "Effect of CuO as Sintering Additive in Scandium Cerium and Gadolinium-Doped Zirconia-Based Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cell for Steam Electrolysis" Processes 7, no. 12: 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7120868
APA StyleVisvanichkul, R., Peng-Ont, S., Ngampuengpis, W., Sirimungkalakul, N., Puengjinda, P., Jiwanuruk, T., Sornchamni, T., & Kim-Lohsoontorn, P. (2019). Effect of CuO as Sintering Additive in Scandium Cerium and Gadolinium-Doped Zirconia-Based Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cell for Steam Electrolysis. Processes, 7(12), 868. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7120868





