Abstract
As the lack of resources required to meet the demands of a growing population is increasingly evident, plant-based diets can be seen as part of the solution, also addressing ethical, environmental, and health concerns. The rise of vegetarian and vegan food regimes is a powerful catalyzer of a transition from animal-based diets to plant-based diets, which foments the need for innovation within the food industry. Vegetables and fruits are a rich source of protein, and bioactive compounds such as dietary fibres and polyphenols and can be used as technological ingredients (e.g., thickening agents, emulsifiers, or colouring agents), while providing health benefits. This review provides insight on the potential of plant-based ingredients as a source of alternative proteins, dietary fibres and antioxidant compounds, and their use for the development of food- and alternative plant-based products. The application of these ingredients on meat analogues and their impact on health, the environment and consumers’ acceptance are discussed. Given the current knowledge on meat analogue production, factors like cost, production and texturization techniques, upscaling conditions, sensory attributes and nutritional safety are factors that require further development to fully achieve the full potential of plant-based meat analogues.
1. Introduction
In a world where the population is expected to reach 9.7 billion by 2050 [], issues related to food availability as well as food security need to be addressed, while keeping agricultural practices within environmental limits at the same time, and delivering a significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. The current food systems are accountable for the cause and prevalence of factors like malnutrition and inadequate diets as the main concerns for a vast amount of the population []. Furthermore, current food industry production practices are failing to achieve a reduction in the environmental harm they cause []. The adoption of plant-based diets can help to improve one’s health through a variety of mechanisms [,]. Not only current food consumption trends point to an increase in vegetarian and vegan diets, there is also a growing consumer awareness for healthier diets, which reinforce the use of organic, plant-based and functional foods [,], all while shifting attention to the production of meat analogue products or enriched meat products with plant-based functional ingredients. Thus, meat analogue products emerge as one of the vegetarian/vegan alternatives that facilitate both meeting the demand for functional and complete foods, but also as products that, by being mimetic of meat both sensorially and nutritionally, make the transition from animal protein to a vegetarian diet easier.
Consequently, this review will focus on the potential of plant-based ingredients, mainly focusing on alternative proteins, dietary fibres, and bioactive compounds for food development, and how they could be used to produce alternative plant-based products, particularly meat analogues, beneficial both for the environment and for human health.
1.1. Trends in Animal-Based Food Consumption
Meat consumption can be traced back to the origins of humanity, having obtained a special place in the human diet throughout history. Despite what can be considered the common perception and tendency of meat consumption in Europe, the research and data show that there will be a worldwide increase in meat intake in the next few years, as a natural consequence of income and population growth [,]. As shown in the FAO Agricultural Outlook report, poultry, pig meat, beef, and sheep meat consumption are projected to grow 15%, 11%, 10%, and 15%, respectively, by 2032 [], with this increase being mainly caused by the consumption habits of low- and middle-income countries. This exhibits a good sign for the meat industry, as it can continue to expand. However, it is also important to diversify and explore other routes and their potential, as a slight decrease in meat demand in high income countries is also predicted, mainly due to the wide access to a plethora of food sources, leading to the population refraining the use of livestock meat as the preferential protein supply. Furthermore, the search for healthier eating habits results in more demanding standards when it comes to food choices. Hence, consumers’ awareness leads to the consumption of natural, clean label, sustainable and functional foods, as well as the adoption of some type of flexitarian, vegetarian, or vegan regime [,]. On the other hand, and despite being the optimal source to some essential amino acids like methionine, lysine, tryptophan [] or vitamins like vitamin B12 [], the putative negative health impact of meat and meat product consumption cannot be overlooked. For instance, red meat or processed meat may increase the incidence of cancer []. The aggravated risk of cancer can be further associated with the use of nitrites and nitrates in processed meat, as these compounds are used to improve sensorial aspects like flavour and colour or to act as antimicrobial agents. The major setback of these substances is that, during thermal processing, there is the risk of nitrosamine production, through the reaction with secondary amines present in the meat products [,]. In addition, the excessive consumption of red meat and processed products made with red meat has been linked to diseases like diabetes, gastrointestinal and colorectal cancer, cardiovascular diseases and all-cause mortality [,,], possibly due to the high levels of saturated fat, heme iron, and other additives present in red meats and processed derivatives []. These health-related implications are shown to modulate consumer behaviour towards red meat consumption [,].
Simultaneously, the environmental impact associated with meat production is extremely relevant, and the rising awareness and action against global climate change inevitably pressures the meat industry with regard to its production system. According to Arora and co-authors [], the production of animal-based food products consumes more resources and requires more land, but also produces about 250 times more greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions than plant-based food production. Additionally, there are factors other than climate change and GHG emissions that influence the negative impact of meat production. Life Cycle Assessments have been performed in different meat industries, with results pointing out the low energy efficiency of the production process and waste management procedures, as two of the main contributors to negative environmental impact []. Regarding the ethical reasoning behind the consumption/non-consumption of meat, animal welfare can be a modulating factor. As per Clonan et al. [], for meat consumers, a good animal welfare was perceived as an important parameter when buying meat, as it was an indicator of higher product quality, although it was not an impeachment on the consumption itself. On the other hand, a study conducted by Ploll and Stern [] revealed that animal welfare was the strongest motivational trigger amongst vegans and vegetarians to cease meat consumption. Lastly, religious beliefs also play a role regarding meat consumption. Muslims are proven to have a negative correlation with pork meat consumption, as well as Jews, although to a lesser extent. Also, cultures like Hinduism refrain from consuming beef, and certain Buddhist cultures vow against the ingestion of meat altogether [].
1.2. Uncovering Meat and Meat Analogues
Meat analogues, also known as meat replacers or mock meat, can be defined as mainly plant-based products that mimic the appearance, flavour, and the fibrous texture of animal meat []. In fact, the last few decades saw a significant rise of plant-based and/or meat-analogues available for consumers, with sales and consumption data forecasting a favourable future for the industry from a business perspective []. However, it is also important to understand the current tendencies and products available in the processed meat industry to make a plant-based oriented transition. According to the information present in the literature, three main categories of processed meat products can be distinguished: burgers, minced meat, and emulsion type products (e.g., ham, mortadella, sausages). Likewise, the trend for the meat analogue products currently being studied mimics the categories of the main processed meat products. Similarly, advances are also being made in partially replacing meat protein with plant-based protein. While more are reported, like whole beef mimetics or dried meat “jerky” analogues [], the previously mentioned ones are the most recurrent in the literature and the most updated ones. Though a mimetic product, meat analogues are expected to recreate the visual aspect and mouthfeel of processed meat. Furthermore, they face the complex task of not only reproducing the nutritional profile (amino acids, and vitamin content) but also a meat-like texture, odour, and flavour. It is also important to note that different products require different plant-based components. Since processed meat production has not been optimized to plant-based ingredients, the current solution is the mixture of two or more protein/ffibre/fat sources [].
Another focal point in meat analogue production is the increasing tendency to apply the concept of the circular economy to industrial systems. The circular economy can be holistically defined as an economic model that aims to optimize the use and reuse of resources while trying to minimize waste, although a consensual definition of this concept is still up for debate []. As an economic model that has been pioneered by some European high-income countries and progressively adopted worldwide, the reusing of the vegetable and fruit byproducts has acquired an increased interest in the meat industry, with potential applications as nutritional enrichment ingredients and additive replacers (e.g., as a natural colouring alternative to nitrites) in meat protein products or as plant-based protein sources for meat-analogues. Thus, this increasing demand for solutions and alternatives to the current resources available requires research and innovation in the food industry. For this reason, an analysis of the food industry and the potential of its byproducts is essential, since this sector is responsible for the production of several tonnes of byproducts each year. According to FAO [], and to the Food Waste Report by UNEP (United Nations Environment Programme) [], around 30% of the food produced/available goes to waste, with 13% occurring in the stages preceding retail sale. The main contributors to this waste are cereals and pulses, vegetables, fruit, and starchy roots. Although the data currently available may be inaccurate and certain estimates are unreliable, the fact remains that “the food industry waste and byproducts” contribute alarmingly to the degradation of the planet, contributing heavily to the world’s carbon footprint [,]. In a society where the concept of a circular economy is becoming an increasingly important parameter worldwide, monetary losses such as those reported by Parsafar and co-authors [] and Campos and co-authors [] are an alarming sign of how the food industry must change the way it deals with its waste, in order to not only generate economic but also technological wealth. Currently, food byproducts are mainly directed for animal feed or composting, thus neglecting the nutritional potential of these materials []. Taking into account both the initial matrix and the processing that led to this waste, their richness lies not only in their macronutritional content, such as proteins and dietary fibres, but also in their high content of bioactive compounds, such as polyphenols, carotenoids or vitamins [,].
2. Plant-Based Proteins in Food Formulations
According to the literature, most plant-based diets (if properly and correctly planned) result not only in a reduction in all-cause mortality, but also in a reduction in blood pressure, LDL cholesterol and total cholesterol levels, and in the incidence, prevalence, and mortality of diabetes. Furthermore, and despite the controversy it may address, it is possible to find literature wherein plant-based protein diets were found to be identical to animal protein diets when it comes to muscle and bone health [,,]. Finally, both the production and consumption of most plant-based protein is positively related to the reduction in environmental impact. According to Sabaté and co-authors [], 1 kg of bean protein requires 8~14 times less resources to produce than 1 kg of beef. Furthermore, the adoption of vegan or vegetarian regimes lead to an estimated reduction in greenhouse gas emissions of 50% and 35%, respectively [].
However, there is a need not to overlook the current limitations and setbacks related to this type of protein. Hence, these impairments can be divided into nutritional limitations and technological limitations. Paired with the poor availability of certain amino acids and a decreased digestibility, plant-based proteins, like soy or pea, often present some compounds that are considered anti-nutrients, such as phytates, oxalates and lectins [,]. On the other hand, there are the technological obstacles characteristic of the very nature of plant proteins, such as poor aqueous solubility, an increased sensitivity to pH, salt and temperature conditions, or even reduced bioavailability due to the polysaccharidic matrix that entrenches them. Moreover, the organoleptic profile of plant proteins needs to be addressed due to undesirable flavours and odours [].
Plant-based proteins can be sourced from multiple foods, like vegetables, cereals, and roots. Procedures to acquire plant-based proteins from pea pods, mung bean, potato fruit juice, peas and chickpeas, and wheat germ and bran [,,,,] are stated in the literature. According to Gençdağ and co-authors [], proteins have already been recovered from byproducts such as rice bran, oat bran, and rapeseed cake. Prandi B. and co-authors [] reported the successful extraction of protein from mushroom byproducts, while Privatti, R.T. [] described the technique to obtain a protein extract from soy okara, a byproduct of the soy-based beverage industry. Some progress has also been made in reusing surplus protein from soybeans or some starchy roots, such as potatoes []. The extraction techniques used can vary greatly, with the choice of the process being closely linked to the purpose of the protein/type of food in which it is to be incorporated. Common protein extraction techniques, such as alkaline extraction, are not entirely suitable for plant-based proteins, largely due to the characteristics described above. Thus, the industry has been focusing on emerging and innovative technologies that not only improve extraction yields but also technological and nutritional properties, mainly using biochemical (enzyme-assisted), physical (ultrasound, microwave, pulsed electric field, high-voltage electrical discharge) and solvent-based techniques (subcritical and supercritical extraction, and deep eutectic extraction) [,,,,,,]. As reported by Prandi and co-authors [], enzyme-assisted extraction can create a protein extract with a higher digestibility, whereas a direct aqueous extraction is preferred when the aim is to obtain a protein extract with a high degree of purity. Based on the demands of the end product, the ideal extraction technique will vary. Plant-based proteins are a viable alternative to both animal proteins and laboratory created meats, largely because they are cheaper and easier to obtain than animal proteins. In addition, they can also be used for their technofunctionalities. These include foaming capacity, emulsifying action, or viscosity forming properties []. It is also important to understand the nutritional value of these alternative proteins, identifying not only their strengths but also their main shortcomings. Firstly, most of commercially available plant-based proteins are known for having a deficiency in essential amino acids, such as leucine, lysine, or methionine [i.e., although they may have all the essential amino acids, their amounts are not enough to meet the parameters set by the World Health Organization (WHO)]. An in-depth analysis of the amino acid profile of ten proteins of plant origin was carried out by Gorissenand and co-authors []. For the recommended protein intake for adults of 0.66 g/kg body weight/day, it was reported that only potato protein met the essential amino acid requirements. Furthermore, despite containing all nine essential amino acids, neither soy, brown rice, lupin, oat, wheat, hemp, pea, or microalgae were found to contain enough lysine and/or methionine. Another study, assessing the protein quality regarding the Digestible Indispensable Amino Score (DIAAS) defined by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), presented some similar results. Starting from twelve plant-based proteins, it was stated that potato protein was the only vegetable protein in the “excellent quality” category. In addition, soy proteins were classified as “high quality”. In line with the previous study, proteins from lupin, canola, corn, hemp, oats, peas, broad beans, rapeseed, and rice showed very low levels of essential amino acids, acquiring a “no quality” classification []. Regarding all this, the aim is to increasingly enable the creation of differentiated products, facilitating the complete or partial replacement of animal proteins with plant-based proteins, without compromising the environment, nutritional efficiency, biological value, or production costs. However, and despite the technofunctionalities of plant-based proteins, a direct substitution of animal protein for vegetable protein is often not enough to obtain a satisfactory product. Thus, current solutions rely on the conjugation of two or more plant-based protein sources to complement existing alternatives.
Besides the protein content challenges, it is also necessary to look at other compounds of interest available in the byproducts of the food industry, such as fibres and polyphenols, which are upcoming solutions that, while not replacing proteins, can be used to further modulate both the nutritional and technological properties of plant-based products.
3. Dietary Fibres
3.1. Dietary Fibres in Food Formulation
The concept of dietary fibres encompasses a wide group of plant derived-carbohydrates, non-digestible/non-absorbable by humans, and a group of some non-carbohydrate plant cell wall compounds that present fibre-like effects []. Although generally categorized as soluble or insoluble dietary fibres in the majority of the literature, according to Ye, S. and co-authors [], a more adequate framing would be accomplished by dividing these dietary fibres into four smaller groups: non-starch polysaccharides (cellulose, hemicelluloses, pectin and other hydrocolloids, such as mucilages, gums, and β-glucans), resistant oligosaccharides (galacto-oligosaccharides, fructo-oligosaccharides), resistant starch and lignin.
There are numerous sources of dietary fibres depicted in the literature. Soluble fibres like pectin can be obtained from apple and cabbage, while gum can be obtained from oats and legumes, and mucilage from chia, aloe vera or aquatic plants. Insoluble fibres can be found in cereal bran, whole grains like rice and root vegetables (in the case of cellulose and hemicellulose) and in vegetables (lignin). Byproducts produced by the food industry are also rich in these types of compounds. Across the literature, examples can be found of dietary fibre extracted from grape pomace, peach byproducts and potato peels [,,], citric fruits like orange [], onion skin [], chickpeas [], carob [], pear pomace [], mango [] and date fruit byproducts [].
The great interest in dietary fibres arises both from the technofunctionalities that they are able to display and from the health benefits they provide. The physicochemical characteristics and composition of these fibres can vary, and so can their technofunctionality and biofunctionality. Hence, they can be used as thickener agents, binders, emulsifiers, jellifying agents, fat replacers, or to increase the water and fat holding capacity refer to [,] or [,,]. The increased viscosity and gel-forming capacities are great contributors for the low/no-caloric bulking profile of dietaryfibres []. Examples of some of these applications can be found in Table 1.

Table 1.
Examples of typical applications of dietary fibre.
3.2. Biofunctionality of Dietary Fibres
Dietary fibres can positively influence some health risk factors, like diabetes or obesity []. The physiological properties that characterize the soluble dietary fibres, like viscosity or gel-forming capacity, can also be a modulator of the satiety sensation, helping the treatment of obesity. Upon intake, and during digestion, the dietary fibres (mainly the soluble ones) form a gel-like matrix that constitutes a “physical barrier” in the intestine, which promotes a bigger digestion time, prolonging the presence of nutrients in the intestine and decreasing the glucose absorption [].
The gastrointestinal microbiota is of extreme relevance when considering a healthy individual, as a direct correlation has been proven between the equilibrium of the gastrointestinal bacteria ecosystem and metabolic pathways or health complications. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in portraying some dietary fibres as prebiotic agents. Cancer, cardiovascular diseases, depression or mental complications have been associated with a change in microbiota, making the importance of having a diet that can help maintain a healthy gastrointestinal tract obvious [,,].
Much of the benefits also occur from the short chain fatty acids (SCFAs) (compounds like acetate, propionate, and butyrate) that result of the fermentation of the dietary fibres by gut microbiota. After the production of these SCFAs, they take different metabolic pathways, thus having different functions and action mechanisms [,]. There are other examples through which dietary fibres exert their biofunctionalities. One of the mechanisms for diabetes treatment involves the ability of fibres to produce a hypoglycaemic effect by retaining the glucose absorption through a dietary fibre barrier, as well as enhancing insulin sensitivity. For this mechanism, Zheng, Y. and co-authors [] stated that soluble dietary fibres exhibited significantly higher glucose adsorbing capacity when compared with insoluble dietary fibres. Further pathways are proposed as routes for metabolic benefits with dietary fibres, like longer hepatic insulin extraction and bile acid binding.
However, it is important to note that the action mechanisms of fibres are complex and that their beneficial action is also greatly influenced by the interaction and properties of bioactive compounds, namely polyphenols, which are bound to their fibres matrix [].
4. Polyphenolic Compounds in Food Industry
4.1. Polyphenolic Compounds
Polyphenolic compounds are secondary plant metabolites, essential for multiple plant functions such as antioxidant protection, the response to environmental stress, and defence mechanisms []. More than 8000 different phenolic compounds have been identified in the plant kingdom, representing one of the largest and most diverse group of bioactive compounds []. In recent years, polyphenols have been under the spotlight in the food industry due to the nutraceutical benefits they provide, including antioxidant activity and their potential role in oxidative stress-related disease prevention. Moreover, some of the organoleptic properties of polyphenols can be of great use in innovative food development [].
From a chemical point of view, polyphenols comprise two main groups: the flavonoids and non-flavonoids [].
Phenolic acids are the main representatives of the non-flavonoid group. They can be subdivided into cinnamic acids derivatives, like caffeic or ferulic acid, or hydroxybenzoic acids derivatives, like gallic acid []. Flavonoids are the most abundant group of dietary polyphenols. These compounds branch out in anthocyanins, water-soluble compounds that are responsible for the colourful pigments of blue, red and violet, and other compounds like flavones, flavonols, isoflavones, flavan-3-ols, flavanones [,]. In Figure 1, a brief classification of the different polyphenol subclasses is presented.
As metabolites from plants, polyphenols are vastly distributed through vegetables, fruits, and seeds. The polyphenolic content of foods varies with several factors, such as genetic background, growing conditions, maturity stage, harvest date, and post-harvest handling techniques (storage temperature or radiation treatments) [,]. As reviewed by Abbas and co-authors [], flavonols are the most represented dietary flavonoids and can be found in onions, cabbage family vegetables or fruit peels [,,]. Moreover, legumes and soybean are the main carriers of isoflavones []. Phenolic acids can be found abundantly in cereal like barley or wheat [], in fruits such as red berries, pears and grapes [,], but also in starchy roots like potatoes [].
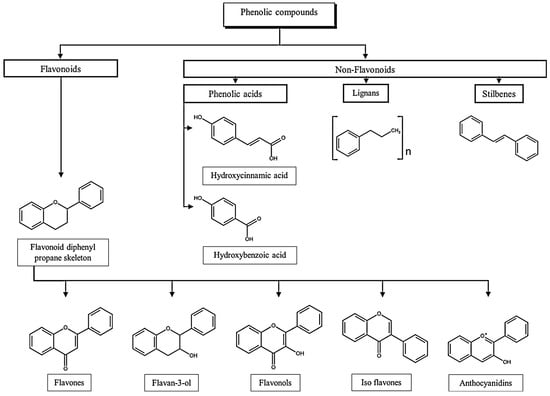
Figure 1.
Classification of phenolic compounds. Adapted from [,,,].
4.2. Technological Properties of Polyphenolic Compounds
The potential that the food industry sees in polyphenols relates to the ability to reassess and reuse their potential to create products that can enhance shelf life, reduce the usage of artificial/chemically synthesized food additives, and improve organoleptic properties, while maintaining the positive nutritional impact of these compounds. In this regard, polyphenols have been reported to be used as functional ingredients, texture enhancers, natural preservatives (antioxidants, antimicrobial), and colouring agents [,,]. From an industry perspective, synthetic preservatives, like nitrates for instance, despite their efficiency, are becoming an outdated and unappealing solution to food conservation due to their associated health risks and growing consumer awareness. Equally, a replacement for natural colourants is being pursued, creating the opportunity to use polyphenolic compounds like anthocyanins or flavonols to avail the red, blue, purple and yellow colours that are inherent to them []. Red berries are of particular interest, as the peels of these fruits, which are commonly discarded as a waste, are a great source of polyphenolic compounds, responsible for the characteristic pigmentation of the fruits. This conjures yet another clean path for the industry, not only creating new resources from previous byproducts but also healthier and additive free products. The potential of these polyphenolic applications has already been identified, as there are already some studies on the application of polyphenols in food products like bacterial biofilm inhibition, edible coatings, and smart packaging [,].
4.3. Biofunctionality of Polyphenolic Compounds
The interest in polyphenolic compounds is also sustained by the bioactivity they display (Figure 2). These properties are well characterized in the literature, encompassing antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, anticarcinogenic, and anti-neurodegenerative activities [].
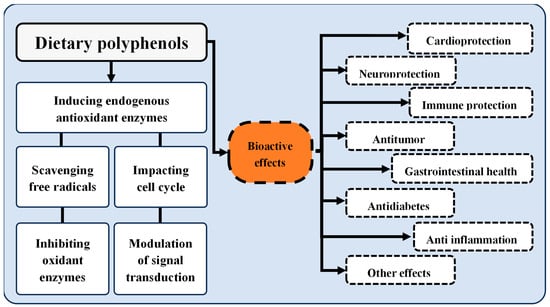
Figure 2.
Properties and bioactive effects of dietary polyphenols. Adapted from [].
Above all, polyphenols are acclaimed for their antioxidant and radical scavenging properties. Nonetheless, these activities may vary according to the polyphenolic compound in question, with the number and position of these hydroxyl groups greatly influencing the free radical scavenging ability. Polyphenols are not only able to halt free radical formation and stop lipid peroxidation reactions by displacing a radical scavenger role, but also exhibit metal chelating properties []. Polyphenols can be modulators of cell signalling and downregulate tumour progression by inducing proteins [,]. Moreover, a co-antioxidant function can be observed in these compounds, since they are involved in the regeneration of vitamin E []. The ability of polyphenols to modulate the expression of transcription factors that control inflammatory responses, such as NF-kβ factors, or pro-inflammatory mediators like Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) is of great value. Another use for the bioactive potential of polyphenols is in type 2 diabetes mellitus treatment. According to Malik and co-authors [], the major hypoglycaemic effect relates to the ability to reduce the intestinal absorption of carbohydrates. This modulation is also caused by α-glucosidase and α-amylase (as well as other enzymes responsible for glucose metabolism/transport) suppression, and by enhancing insulin production.
Besides these properties, polyphenols can be portrayed as antibacterial compounds, as the inhibition of L. monocytogenes and S. aureus has already been described in the literature []. Phenolic acids, like ferulic, ellagic and p-coumaric acid, were found to be able to inhibit harmful bacteria, like Gram-positive (Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes) and Gram-negative bacteria (Salmonella typhimurium, Escherichia coli) [].
However, and perhaps the most determinant factor for the in vivo action of polyphenols, is the bioaccessibility dilemma, since transformations in food processing, particle size, type of polyphenol, digestive interactions and food matrix interactions limit the effectiveness of polyphenol assimilation []. Adding to this is the bioavailability dilemma. Recognized as one of the main setbacks for the bio-efficiency of polyphenolic bioactivity in food products, the bioavailability factor cannot be overlooked. Due to their unstable nature, digestive modifications, and overall complexity, polyphenols tend to have a low absorption in the human body. Following this line of thought, in recent years it has been proposed that the nutraceutical effect of polyphenols arises from direct action with dietary fibres, since these compounds can be found chemically associated and entrapped within the plant fibre matrix. The concept of “antioxidant dietary fibre” derives from these polyphenol–fibre matrix associations, and is sustained by examples like the hydroxycinnamic acid links to fruit fibre or the fact that 95% of grain phenolic compounds are linked to dietary fibre polysaccharides []. This can be an interesting topic for the vegetable/fruit processed food industry, as it reveals the need to further comprehend how to correctly apply the polyphenol’s potential and how the polyphenol–dietary fibre matrix controls the polyphenols’ release rate and their behaviour during digestion. Above all, the formation of the polyphenolic–dietary fibre matrix will enhance the number of polyphenols delivered to the colon, to potentially interact with gut microbiota.
5. Polyphenols and Dietary Fibre Matrix Interactions
The non-extractable polyphenol classification encompasses a broad amount of polyphenols, ranging from low molecular weight ones like phenolic acids and flavan-3-ols to high molecular weight polyphenols like condensed and hydrolysable tannins []. Once synthesized, these polyphenols are transported to plant cell walls, where they will exert their functions. Therefore, polyphenols bond with a plethora of plant cell wall compounds like cellulose, hemicellulose, pectin, lignin or even proteins []. As previously revised, these cross-links are formed through covalent bonds that include ester bonds between the phenolic acid carboxyl group and the hydroxyl group of plan cell wall constituents [,,,]. Furthermore, a carbon atom or a hydroxyl group from both ends can bind through a C-C bond or an ether bond, respectively. However, non-covalent interactions, like electrostatic interactions, hydrophobic interactions, hydrogen bonds and ionic bonds, should not be ruled out, as they too contribute to the formation and stability of these complex matrixes [,]. All of this can serve a great purpose to the food industry, as it is possible to gather the practical examples of these polyphenol–fibre interactions that have already been reported in the literature and seize the potential of both compounds for product formulation. Table 2 shows some examples of dietary fibre and polyphenol content from various fruit and vegetable sources.

Table 2.
Examples of fruits and vegetables as sources of dietary fibre and polyphenols.
Polyphenol–Dietary Fibre Matrix—Technological Properties and Food Applications
Byproducts from the fruit and vegetable industries may be paired with the opportunity to harness the huge amount of dietary fibre and polyphenols that arise from these products. In line with what was previously mentioned, several studies point out the rich content in bioactive compounds like dietary fibresand polyphenols in food byproducts like apple, berry pomace, or potato, passion fruit, and orange peels (Table 2). Hence, the wastage problem requires new solutions from the industrial sector. The need for innovation, considering all the nutraceutical benefits of dietary fibres and polyphenols currently known, corroborates the increasing interest in the commercial application of bioactive compounds in the food industry, as a boost in functional food design can take place. Therefore, while being of relevance to evaluating and knowing the bioactivity of these compounds, it is important to access the technological properties of the different dietary fibres and polyphenols when applied in food products and, finally, study their digestibility, nutritional impact, and organoleptic profile.
Considering the recent research on polyphenols–dietary fibre interaction, Araújo and co-authors [] stated that the textural properties of starch can be altered by polyphenol usage. Compounds like phenolic acids, flavonoids and tannins are interlinked with the gelatinization, retrogradation, viscosity and digestibility properties of starch []. In Table 3, it is possible to see some other examples of the incorporation of polyphenol–dietary fibre matrixes and their impact on some food products.

Table 3.
Examples of the application of different sources of polyphenol–dietary fibre matrixes in food products.
As a shift towards greener and innovative solutions is taking place, both dietary fibres and polyphenols have great potential regarding the food industry. Considering the vast sources for these compounds and the low cost in pairing them, there is a lot to explore. Nonetheless, despite the antioxidant, antimicrobial and additive-like properties of these bioactive compounds, it is of extreme importance not to compromise food safety. Through the reviewed literature, the lack of studies on the microbial and overall food safety-related conditions of the newly formulated products was evident, with few articles reporting results regarding such parameters. A better understanding of the impact that byproducts and waste alternatives have on shelf life and product preservation is needed, as it would be of great interest for the consumers and the food industry.
6. Meat Analogues
6.1. The Creation of Meat Analogues
The creation of a vegan meat analogue requires a lot of understanding regarding the technofunctionalities of the ingredients. This applies not only to the protein source but also to fibres and other bioactive ingredients in the mixture. Although the synergic effect caused by the combination of different ingredients makes it difficult to give an accurate behaviour prediction, it is important to look out for some properties that are characteristic of specific components. In the case of proteins, good emulsion-forming capacity, water solubility and a good amino acid profile are valued. In the same sense, gelling and viscosity capacity, as well as good water and oil holding capacity, are decisive factors when choosing the fibres. Finally, regarding other components like polyphenols, it is important to look at their colour stability, bitterness, and additive substitute potential.
6.2. Alternative Protein Sources for Processed Meat and Meat Analogues
To begin, it is important to understand that the choice of protein source plays a major role in texture, colour, flavour and cooking loss []. As previously mentioned, there is a plethora of plant-based proteins described in the literature that can be sourced from food byproducts. Factors like the nutritional profile, environmental impact, and extraction yield modulate the main choices when it comes to defining the plant-based protein source. Thus, soy, wheat, pea and potato proteins are amongst the top choices [].
Soy protein has been one of the primal plant-based protein sources for meat alternatives, with its history dating back to ancient China. Recognized as a cheaper alternative, with good nutritional quality and good technological properties, soy derivatives like soy flour, soy protein concentrate, and soy protein isolates can be transformed in processed meat analogues. Soy industry byproducts, like soymeal, okara, soy-whey, and hull have been used to produce several meat analogues []. Despite its potential, soy protein has been progressively losing the spotlight in industry innovation. This can be due to the concerns raised about the consumption of genetically modified organisms, crop overexploitation or antinutritional factors []. In that sense, the addition of wheat gluten proteins to the formulation of meat analogues has been encouraged.
Wheat protein has unique characteristics, due to its gluten-rich nature. Although lacking in nutritional value (poor lysine content), wheat protein can function as an efficient stabilizer and texturizing agent, when used as a complement to another protein source. Across the literature, it is possible to find examples of the combined usage of wheat and soy proteins that resulted in acceptable meat analogues with high fibre texturization, and good protein value [,]. However, there is one big drawback: with a rise of gluten intolerance and the demand of gluten free products, wheat gluten protein inevitably becomes an unviable option as a standard in meat analogues.
Proteins from pulses, like chickpea or pea, due to their low risk of allergenicity, worldwide cultivation suitability, and due to not being genetically modified organisms [] are other alternatives to soy-based proteins. Like soy, pulse proteins are rooted in a lot of diets, and there are already some commercial pulse protein isolates available. Across the literature, it is possible to see that the extraction process of this protein greatly influences its functional properties. Hence, a wet pea protein isolate applied in a meat analogue had better emulsification and foaming properties, whereas dry pea protein isolates have higher solubility and water holding capacity []. Despite their potential, pulse proteins have major sensorial setbacks, like an intense off-flavour and odour, or poorer nutritional quality when compared with other alternatives. Thus, a deeper understanding of pea protein extraction, processing and application, as well as waste management, is needed in order to develop pea protein-based meat analogues [].
Potato starch is widely used in the food industry as a texture enhancer due to its unique gelling properties, and as a bulking agent []. Nonetheless, the spotlight is now pointed at potato protein, emerging as the most promising plant-based protein for meat analogue formulations. Potato protein displays a better amino acid profile than soy, the current standard in non-animal proteins []. With patatins and protease inhibitors as the two main proteins, potato protein preparations excel in some functional properties like solubility, as well as their foaming and emulsifying properties, performing like the commercial soy protein preparations. Also, potato protein has been successfully used to decrease cooking loss and inhibit the lipid oxidation of meat emulsions []. As an emerging solution, there are still some hindrances associated with potato proteins. Regarding sustainable processing, the isolation and purification of potato proteins from byproducts like potato juice or pulp has been attempted. However, the costs of the procedure and the bitter-tasting glycoalkaloids present in potato juice stand as the main obstacles for the larger industrialization of this method. Regardless, it is possible to find in the literature preparations of the main proteins of potato that have high nutritional value and valuable functional, antioxidant, and anti-obesity properties [,,].
As described earlier, the range of plant-based protein application has been further expanded with the evolution of production technologies. The textural and sensorial quality of meat analogues are the determinants of consumer acceptance []. Once again, the different classes of processed meat analogues will require specific textures, colours, and overall visual aspects. As a response to this need, and with the main goal of simulating the fibrous texture of meat, the industry developed different ways to extract plant-based proteins, such as thermos-extrusion, 3D printing, high temperature conical shear cell, electrospinning, and freeze structuring. Amongst them, extrusion methods are the most widely used in plant-based proteins for meat analogues, facilitating low moisture extrusion or high moisture extrusion. The techniques influence the functional properties of proteins, since low moisture extrusion is used for texturized plant-based protein production and high moisture extrusion is used for softer products [,]. Therefore, texturized proteins will perform better in products like burgers or minced meat analogues, while a higher temperature extrusion will benefit the production of ham and sausage analogues.
6.3. Plant-Based Fat Replacers for Processed Meat and Meat Analogues
In meat analogue formulation, there are several components that need to be accounted for to achieve a satisfactory product, such as vegetable fat, dietary fibres, and bioactive compounds. The vegetable fat present in plant-based meat analogues can be obtained from sources like rapeseed or sunflower oil, and is responsible for flavour enhancement, tenderness, and juiciness []. From a nutritional point of view, the fat content in meat analogues is reduced when compared to processed meat equivalents. Although healthier, vegetable meat often lacks the capacity for copying the sensory characteristics of meat []. Recent studies have reported that the next step in vegetable fat replacers are oleogels (structured oils prepared by the oleogelation of liquid oil using vegetable waxes, monoglycerides, alcohols or the esters of fatty acids, phospholipids and phytosterols) [] and emulsion gels, derived from vegetable oils, that have great potential to enhance the mimicking of the solid muscle-like texture of meat, while maintaining the nutritional benefits of vegetable fat [].
6.4. Polyphenols and Dietary Fibres Applications on Meat and Meat Analogue Products
As previously stated, dietary fibres and polyphenols have valuable nutraceutical properties and preventive activity for several non-communicable diseases, which represent great potential for their role as food-enriching products []. Nonetheless, the technological properties of these vegetable and fruit waste constituents have also been highlighted in the literature, like an increased bulking capacity and a natural colouring capacity.
From a technological point of view, dietary fibres are viewed as a great bulking agent, meat extender or fat replacer. Due to their nature, dietary fibres can increase the water holding capacity of products and their viscosity, promoting a bulk effect on the product and in some cases, acting as a meat extender [,]. Moreover, the incorporation of some dietary fibres in the food matrix can increase the oil and fat holding capacity, making these compounds potential texture modulators and fat mimetics. This translates to a higher cooking yield (and therefore a lower cooking loss), which allows for a reduction in fat content without jeopardizing the sensorial quality of the product [].
Polyphenols are of particular interest when it comes to processed meat products, as they can allow for the reduction in additives, like nitrates []. Nitrates are one of the most recurrent curing agents in processed meats, since they are capable of inhibiting Clostridium botulinum, reducing off flavours, contributing to texture improvement, and are responsible for the red/pink colour of such processed meats []. Some of these properties can be achieved using the dietary–polyphenol matrix of fruit and vegetable byproducts instead of chemical additives, assuring the quality of the product without the health concerns that nitrites are associated with. Efenberger-Szmechtyk and co-authors [] reported that although polyphenols had antimicrobial and antibacterial effects, the mechanisms and polyphenol–food matrix implications were still to be understood. While the food safety parameter might not be the ideal focus when considering nitrate replacement, the colouring agent and colour preservation of meat and meat analogues are things to be considered. Recent generations have been using natural solutions like beetroot juice to mimic meat properties, namely “bleeding” []. Whether incorporated in an intelligent package or as a natural food dye, the incorporation of extracts with high phenolic content has been proven to have a positive impact on the colour and colour conservation [,].
Despite this potential, the application of vegetable and fruit byproducts is still a challenging task to achieve. Due to the different nature of the matrix of processed meat and meat-analogue products, the obstacles and challenges differ between both, requiring different approaches. For instance, for research focused on polyphenols and dietary fibres as substitutes for additives, bulking agents, and nutritional enhancers, the processed meat matrix prevails over the plant-based. The fact that the base formulation for a well-established product is already known allows researchers to further explore the finer properties of plant-based byproducts in processed meats, i.e., their application as natural dyes, nutritional enhancers, or as extenders of the product shelf life. On the other hand, regarding plant-based meat analogues, the focus is primarily on the optimization of a formulation that can incorporate the plant-based protein without sacrificing the sensorial, technological and safety parameters of the meat equivalent. In Table 4, an extensive list of the applications of vegetable and fruit byproducts in processed meat and meat analogues is reported.

Table 4.
Vegetable and fruit applications in processed meat and meat analogues.
As said before, the aim of the application of plant-based ingredients in processed meat or processed meat analogues varies. As is possible to observe in Table 4, the results of recent studies show a clear tendency for harnessing vegetable and fruit byproducts to formulate hybrid or enriched products rather than completely substituting animal meat for a plant-based alternative. In addition to the protein, dietary fibres and polyphenol applications present in Table 4, there are also other components, like polysaccharides, vitamins and minerals that can be explored to further improve plant-based meat production. Nonetheless, different processed meat classes have their own focal points.
6.5. Meat Analogues Products
6.5.1. Burgers
Burgers (or patties) are a widespread food choice in global dietary habits, very much appreciated for their distinct mouthfeel, succulence, and flavour. They differ from minced meat due to their matrix composition. In the case of burgers, the product normally consists of ground meat mixed with spices, salt, binders (like breadcrumbs, starches, or fibres) and other additives. Burgers are a cohesive mass, usually cooked by shallow frying or baking/roasting []. In that sense, plant-based products that set out to mimic burgers rely on processing technologies like the protein texturization of soy and pea to obtain a fibrous meat-like structure. Furthermore, plant byproducts rich in dietary fibres have received great attention as potential fat replacers/reducers and cooking improving agents due to their water and oil holding capacity.
6.5.2. Minced Meat
Minced meat, also known as ground beef, is one of the most economic meat protein sources available to consumers. Just like burgers, it has a place in a lot of diets worldwide, due to its practicality and rich flavour. Once again, protein extrusion methods prevail to produce these analogues, although some innovative techniques like shear cell technology can be used to achieve the fibrous layered structure of meat. Despite being a processed meat product, minced meat has the closest similarities to whole-cut meat, as it does not require significant additions to the protein matrix. From the literature, it is possible to observe that, in most cases, more than one plant-based protein source is used []. Moreover, plant byproducts are mainly capitalized for their ability to enhance shelf life and prevent the product quality decay, primarily due to the antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of their bioactive compounds.
6.5.3. Emulsion Type Products (Ham, Mortadella, Sausages)
Emulsion-type meat foods comprise numerous products like ham, mortadella, and sausages. Their formulation incorporates finely chopped meat, water, fat, fibres, salt, and other additives. The emulsion is formed when the proteins bind to water and trap and hold fat, forming the characteristic texture of an emulsified product when cooked []. Like many other products, plant-based meat analogues tend to closely follow the formulations of their animal protein equivalents. Thus, to achieve good meat analogue, plant-based proteins must be able to display the emulsifying and jellifying nature and water holding capacity that animal proteins have. This type of product does not require a fibrous texture, allowing for a more diversified use of protein alternatives. Pea and soy proteins are once again the main choices for these types of products, although chickpea and mushrooms flour have also been reported as protein substitutes. Regarding this textural challenge, meat analogues can also rely on the incorporation of dietaryfibres. There have been reports wherein vegetables, fruits, and their byproducts, namely flours rich in dietary fibre or starches, have been used as a bulking agent/extender and as a nutritional and functional enhancer [,,]. These byproducts also contribute to a clean label formulation, serving as substitutes for additives or other ingredients that are not so well perceived by consumers []. Besides the structural concerns, it is also important to address the colour factor of these products. Vegetable proteins are not typically red/pink coloured, leading to a beige/grey emulsion if no colouring agent is added. Therefore, the use of fruit and vegetable byproducts to achieve a meat-like colour, like red berries or beetroot juice, has been reported in the literature []. In addition, the use of these polyphenol-rich ingredients extends their functionality to antioxidant and antimicrobial activity enhancers, allowing for a possible reduction in the additives added []. A major challenge in this field is to create a natural dye agent that can endure the high-temperature cooking process without losing their dying properties.
Overall, the emulsion-type meat products offer a larger range of choice when it comes to seizing plant-based alternatives, as it allows for the combination of the nutraceutical and functional properties of vegetables and fruits with plant-based proteins that meet the basic structural needs of these types of products. However, there is still a need to keep innovating, explore better-suited options, and reevaluate previous solutions. Factors like the environmental impact and extraction costs of byproduct processing, or the upscaling viability of current processing methods, need to be assessed to enable the food industry to fully transition to plant-based greener solutions.
7. Consumer Acceptance
In addition to the physicochemical, functional and nutraceutical properties that encompass the great potential of processed meat analogues, there is another pivotal point that weights on the long-term success of these products: consumer perception and acceptance of these types of analogues.
To begin understanding the different behaviours when it comes to food selection/experimentation, it is important to acknowledge the rich gastronomical patrimony that mankind has. Different geographic groups are conditioned by culture, traditions, and religion, which implies that even though food is essential to survival, different populations have different approaches to food and diets. For that same reason, it is possible to extrapolate that different populations will have different perceptions and receptivity to meat analogue consumption. As concluded by de Boer and Aiking [], studies performed in Europe showed that, although meat analogue consumption is growing, cultural, culinary and economic factors related to spatial variations can have complex impacts on the transition towards an alternative meat diet. Quite conversely, the study carried out by Tsvakirai and Zulu [] on the South Africa market revealed that meat analogues were perceived as a pricey symbol of class and status, remaining niche products in the studied area.
This socio-economical modulators of meat analogue consumption are followed by other factors, like the trend in vegetarian or vegan food regimes, animal welfare and other preconceptions that condition consumer behaviour towards meat analogue consumption [,,]. Within these, the driving reasons for a plant-based diet can be diverse and have different impacts [].
As previously mentioned, the current big obstacles in meat analogue acceptance are the texture, flavour profile and appearance of these products. As food is inevitably associated with the hedonistic act of eating, food choices will always tend towards products with better texture and flavour. Meat analogue consumption follows this logic, as it was possible to understand that similarity in taste has the largest impact on the willingness to eat a meat analogue. Likewise, another study by Kerslake and co-authors [] reported that parameters like texture, taste and appearance have a great impact on consumers’ choice in trying a meat substitute, and deciding if the meat substitute was enjoyable or not. However, while a meat-like texture and flavour can attract not only current meat analogue consumers but also consumers who are looking to transition to a more plant-based diet, it has been reported that closing the sensorial gap between meat and meat analogues can have a negative reception on some vegetarian consumers [].
This raises another difficult challenge to the meat analogue industry: How to target the population to attract new consumers and maintain them, while constantly adapting the industry products to better serve consumers’ interests? One of the answers might be related to marketing strategy. Banovic and Sveinsdóttir [] conducted a study on a female population from five different countries, concluding that the future success of meat analogues depends strongly on the successful marketing of meat analogues. They further suggested that raising the consumer awareness about the meat analogues’ health and environmental benefits could be a reasonable approach to this problem. However, according to Kerslake and co-authors [], a “one-size-fits-all” approach is not possible as a solution, as consumer habits differ between dietary groups. Additionally, it raises awareness in terms of labelling and transparency in communicating the product to consumers, as essential steps to increase meat analogue consumption.
Lastly, there is another factor that limits meat analogue ingestion: the risk factor. Neophobia has been proven to play a role in meat analogue consumption. Literature from Giampietri and co-authors [], and, in a more meat analogue-oriented perspective, from Begho and Zhu [], unveils that risk preference is an important determinant of food consumption for consumers. Furthermore, this last referenced study revealed that for Chinese consumers, the factors that condition the intention to try meat analogues for the first time are different from the factors that explain the intention to repeat the consumption of meat analogues. Thus, authors suggested that by addressing consumers’ concerns about risk, i.e., their risk perception, the acceptance of meat analogues could be increased, overcoming the initial barrier created by dietary concerns. Still regarding risk perception, this concept can be greatly influenced by misconceptions and/or misinformation. Studies have reported that US citizens have more negative mental associations with meat substitute products than positive mental associations. This can arise from concepts like the unhealthy–tasty intuition, where a health claim is perceived as negatively affecting taste [,]. Other assumptions, like an excessive use of additives, or association with a less natural/more processed product, are also important factors to consider.
Consumer preferences and behaviours are an important factor for meat analogue success, as this industry can only grow if the plant-based analogues fulfil their potential. Although globally there may be some variation in the main factors, the importance of taste, price, health concerns, and the environment and familiarity with the product in predicting consumer acceptance of plant-based meat alternatives has been argued in the literature. It is only by considering all these factors that the meat analogue industry can better understand consumer behaviour and work towards increasing the acceptance of its products.
8. Perspectives and Challenges
The meat sector has invested in the development of alternative solutions, both as animal protein substitutes/extenders and as clean label products that use natural additives of plant origin. Regarding protein substitution, according to the authors’ perception, the most recent developments fail to obtain a 100% plant-based processed meat analogue, and the available literature presents mainly plant-based proteins incorporated in hybrid products (meat extenders instead of meat replacers). Although the development of hybrid products is helpful as a starting point, research needs to further aim for vegan, 100% plant-based meat alternatives. In addition, the industry is continuously facing the challenge of allergenicity, antinutrients and the lower digestibility of plant proteins compared to animal proteins. Concerning this topic, progress has been made not only by focusing on emerging and innovative extraction technologies and by thoroughly studying its impact on plant-based protein nutritional value, but also on thermal processing/cooking techniques [,,]. Nonetheless, the current gap of knowledge in this field must be addressed to fully allow for a wider application of plant-based proteins.
9. Conclusions
Some of the products marketed as vegan or vegetarian that present themselves as meat analogues have already been studied in the literature. They usually consist of a mixture of vegetable proteins and binders, but they still use additives like flavour maskers, artificial colours, and preservatives. Regarding these products, the current panorama is that there is still no protein source that, alone, can mimic the desired characteristics of a meat analogue. Likewise, the excessive processing currently required in the production of meat analogues weakens the aspect of a functional, healthy, and environmentally friendly food, associated with plant-based products. Another aspect to mention is the lack of variety in the plant-based protein sources tested in these meat analogues. Even though there are examples in the literature that explore the use of proteins from pulses or mushrooms, there is a great inertia to diversify the protein sources used. It is important to use emerging methods to continue the study of meat analogues, exploring formulations that incorporate plant-based protein sources that are different from the products currently available on the market.
The valorisation of bioactive compounds such as dietary fibres and polyphenols, present in vegetables/fruits, can be carried out in several ways. From a nutritional point of view, its incorporation is achieved as a supplement of dietary fibre or antioxidant compounds. With the expansion of new plant-based protein alternatives, it is necessary to deepen the study of the impact of the same dietary fibre source with different protein sources. Polyphenols have been receiving an increased interest from the meat industry, as a shift to natural and clean label products is required. From acting as colourants, replacing synthetic additives in meat analogues as nutraceuticals and functional ingredients, or contributing to smart packaging, research around polyphenols still faces some challenges. Once again, the next steps for innovation in this industry revolve around better understanding the impact that different food matrixes can have on the colour stability and antioxidant properties of polyphenols. Given the current knowledge on plant-based meat analogue production, factors like cost, production and texturization techniques, upscaling conditions, sensory attributes, nutritional safety (regarding allergenicity and anti-nutritional factors), consumer acceptance, regulatory issues and health claims restrict the full development of these products. Thus, the need for a healthier and more sustainable lifestyle and a functional diet should be the catalyst for continuous research to act upon current limitations, allowing plant-based meat analogues to reach their full potential.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.F.; investigation, V.T.d.S.; writing—original draft preparation, V.T.d.S. and A.F.; writing—review and editing, N.M. and V.d.F.; visualization, A.F. and N.M.; supervision, V.d.F.; project administration, V.d.F.; funding acquisition, V.d.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work received financial support under the framework Projeto VIIAFOOD—Plataforma de Valorização, Industrialização e Inovação Comercial para o AgroAlimentar (C644929456-00000040), financed by financiado pelo PRR—Plano de Recuperação e Resiliência and by European funds NextGeneration EU.
Acknowledgments
This work received support and help from FCT/MCTES (LA/P/0008/2020 DOI 10.54499/LA/P/0008/2020, UIDP/50006/2020 DOI:10.54499/UIDP/50006/2020 and UIDB/50006/2020 DOI 10.54499/UIDB/50006/2020), through national funds. AF greatly acknowledges FCT through research contract (CEECIND/00029/2018/CP1545/CT0010).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors of this article declare that they have no conflicts of interest of any kind.
References
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. P.D. World Population Prospects 2022: Summary of Results, UN DESA/POP/2022/TR/NO. 3; United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- El Bilali, H.; Callenius, C.; Strassner, C.; Probst, L. Food and nutrition security and sustainability transitions in food systems. Food Energy Secur. 2019, 8, e00154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fresán, U.; Sabaté, J. Vegetarian Diets: Planetary Health and Its Alignment with Human Health. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, S380–S388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varela, P.; Arvisenet, G.; Gonera, A.; Myhrer, K.S.; Fifi, V.; Valentin, D. Meat replacer? No thanks! The clash between naturalness and processing: An explorative study of the perception of plant-based foods. Appetite 2022, 169, 105793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, C.J. Plant-based animal product alternatives are healthier and more environmentally sustainable than animal products. Future Foods 2022, 6, 100174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helkar, P.B.; Sahoo, A.K.; Patil, N. Review: Food industry by-products used as a functional food ingredients. Int. J. Waste Resour. 2016, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, Z.S.; Amir, S.; Sokač Cvetnić, T.; Jurinjak Tušek, A.; Benković, M.; Jurina, T.; Valinger, D.; Gajdoš Kljusurić, J. Sustainable Isolation of Bioactive Compounds and Proteins from Plant-Based Food (and Byproducts). Plants 2023, 12, 2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohlman, E.; Hansen, J.; Chambers, W. USDA Agricultural Projections to 2032; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2023; p. 119.
- Wang, H.H. The perspective of meat and meat-alternative consumption in China. Meat Sci. 2022, 194, 108982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development-Food Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2023–2032; Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development: Paris, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, I.; Hwang, Y.H.; Joo, S.T. Meat analog as future food: A review. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2020, 62, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Górska-Warsewicz, H.; Laskowski, W.; Kulykovets, O.; Kudlińska-Chylak, A.; Czeczotko, M.; Rejman, K. Food Products as Sources of Protein and Amino Acids—The Case of Poland. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, N.D. Vitamin B12 and Plant-Predominant Diets. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2022, 16, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. In Red Meat and Processed Meat; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Deveci, G.; Tek, N.A. N-Nitrosamines: A potential hazard in processed meat products. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 104, 2551–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Geng, Y.; Yao, J.; Ji, J.; Chen, F.; Xiao, J.; Hu, X.; Ma, L. N-nitrosamines in processed meats: Exposure, formation and mitigation strategies. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 13, 100645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Drouin-Chartier, J.P.; Sacks, F.M.; Hu, F.B.; Rosner, B.; Willett, W.C. Red meat intake and risk of type 2 diabetes in a prospective cohort study of United States females and males. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 118, 1153–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collatuzzo, G.; Etemadi, A.; Sotoudeh, M.; Nikmanesh, A.; Poustchi, H.; Khoshnia, M.; Pourshams, A.; Hashemian, M.; Roshandel, G.; Dawsey, S.M.; et al. Meat consumption and risk of esophageal and gastric cancer in the Golestan Cohort Study, Iran. Int. J. Cancer 2022, 151, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.D.; Li, Y.; Nguyen, X.M.; Ho, Y.L.; Hu, F.B.; Willett, W.C.; Wilson, P.W.; Cho, K.; Gaziano, J.M.; Djoussé, L. Red Meat Intake and the Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases: A Prospective Cohort Study in the Million Veteran Program. J. Nutr. 2024, 154, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etemadi, A.; Sinha, R.; Ward, M.H.; Graubard, B.I.; Inoue-Choi, M.; Dawsey, S.M.; Abnet, C.C. Mortality from different causes associated with meat, heme iron, nitrates, and nitrites in the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study: Population based cohort study. BMJ 2017, 357, j1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latvala, T.; Niva, M.; Mäkelä, J.; Pouta, E.; Heikkilä, J.; Kotro, J.; Forsman-Hugg, S. Diversifying meat consumption patterns: Consumers’ self-reported past behaviour and intentions for change. Meat Sci. 2012, 92, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheah, I.; Sadat Shimul, A.; Liang, J.; Phau, I. Drivers and barriers toward reducing meat consumption. Appetite 2020, 149, 104636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, S.; Kataria, P.; Nautiyal, M.; Tuteja, I.; Sharma, V.; Ahmad, F.; Haque, S.; Shahwan, M.; Capanoglu, E.; Vashishth, R.; et al. Comprehensive Review on the Role of Plant Protein as a Possible Meat Analogue: Framing the Future of Meat. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 23305–23319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo dos Santos, R.; Silva da Costa, J.; Maranduba, H.L.; Almeida Neto, J.A.d.; Rodrigues, L.B. Reducing the environmental impacts of Brazilian chicken meat production using different waste recovery strategies. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 341, 118021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clonan, A.; Wilson, P.; Swift, J.A.; Leibovici, D.G.; Holdsworth, M. Red and processed meat consumption and purchasing behaviours and attitudes: Impacts for human health, animal welfare and environmental sustainability. Public Health Nutr. 2015, 18, 2446–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ploll, U.; Stern, T. From diet to behaviour: Exploring environmental-and animal-conscious behaviour among Austrian vegetarians and vegans. Br. Food J. 2020, 122, 3249–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milford, A.B.; Le Mouël, C.; Bodirsky, B.L.; Rolinski, S. Drivers of meat consumption. Appetite 2019, 141, 104313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boukid, F. Plant-based meat analogues: From niche to mainstream. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2021, 247, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschemann-Witzel, J.; Gantriis, R.F.; Fraga, P.; Perez-Cueto, F.J.A. Plant-based food and protein trend from a business perspective: Markets, consumers, and the challenges and opportunities in the future. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 3119–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.-K.; Yong, H.I.; Cha, J.Y.; Park, S.-Y.; Jung, S.; Choi, Y.-S. Drying-induced restructured jerky analog developed using a combination of edible insect protein and textured vegetable protein. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizos, V.; Tuokko, K.; Behrens, A. The Circular Economy: A review of definitions, processes and impacts. In CEPS Papers; Centre for European Policy Studies: Burssels, Belgium, 2017; p. 12440. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Tracking Progress on Food and Agriculture-Related SDG Indicators 2022; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022; 179p. [Google Scholar]
- UNEP. Food Waste Index Report 2021; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Scialabba, N. Food Wastage Footprint & Climate Change; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015; 4p. [Google Scholar]
- Capanoglu, E.; Nemli, E.; Tomas-Barberan, F. Novel Approaches in the Valorization of Agricultural Wastes and Their Applications. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 6787–6804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsafar, B.; Ahmadi, M.; Jahed Khaniki, G.R.; Shariatifar, N.; Rahimi Foroushani, A. The impact of fruit and vegetable waste on economic loss estimation. Glob. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2023, 9, 871–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, D.A.; Gómez-García, R.; Vilas-Boas, A.A.; Madureira, A.R.; Pintado, M.M. Management of Fruit Industrial By-Products—A Case Study on Circular Economy Approach. Molecules 2020, 25, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pintado, M.E.; Teixeira, J.A. Valorização de subprodutos da indústria alimentar: Obtenção de ingredientes de valor acrescentado. Bol. Biotecnol. 2015, 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, L.; Panaite, S.A.; Bertazzo, A.; Visioli, F. Animal- and Plant-Based Protein Sources: A Scoping Review of Human Health Outcomes and Environmental Impact. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, C.A.; Kjeldsen, E.W.; Frikke-Schmidt, R. Vegetarian or vegan diets and blood lipids: A meta-analysis of randomized trials. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 2609–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlich, M.J.; Singh, P.N.; Sabaté, J.; Jaceldo-Siegl, K.; Fan, J.; Knutsen, S.; Beeson, W.L.; Fraser, G.E. Vegetarian dietary patterns and mortality in Adventist Health Study 2. JAMA Intern. Med. 2013, 173, 1230–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabaté, J.; Sranacharoenpong, K.; Harwatt, H.; Wien, M.; Soret, S. The environmental cost of protein food choices. Public Health Nutr. 2015, 18, 2067–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popova, A.; Mihaylova, D. Antinutrients in plant-based foods: A review. Open Biotechnol. J. 2019, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaghaghian, S.; McClements, D.J.; Khalesi, M.; Garcia-Vaquero, M.; Mirzapour-Kouhdasht, A. Digestibility and bioavailability of plant-based proteins intended for use in meat analogues: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 129, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikbakht Nasrabadi, M.; Sedaghat Doost, A.; Mezzenga, R. Modification approaches of plant-based proteins to improve their techno-functionality and use in food products. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 118, 106789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandolini, A.; Hidalgo, A. Wheat germ: Not only a by-product. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 63, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karabulut, G.; Yildiz, S.; Karaca, A.C.; Yemiş, O. Ultrasound and enzyme-pretreated extraction for the valorization of pea pod proteins. J. Food Process Eng. 2023, 46, e14452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prandi, B.; Zurlini, C.; Maria, C.I.; Cutroneo, S.; Di Massimo, M.; Bondi, M.; Brutti, A.; Sforza, S.; Tedeschi, T. Targeting the Nutritional Value of Proteins from Legumes By-Products Through Mild Extraction Technologies. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 695793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlangen, M.; Taghian Dinani, S.; Schutyser, M.A.I.; van der Goot, A.J. Dry fractionation to produce functional fractions from mung bean, yellow pea and cowpea flour. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 78, 103018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waglay, A.; Karboune, S.; Alli, I. Potato protein isolates: Recovery and characterization of their properties. Food Chem. 2014, 142, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gençdağ, E.; Görgüç, A.; Yılmaz, F.M. Recent Advances in the Recovery Techniques of Plant-Based Proteins from Agro-Industrial By-Products. Food Rev. Int. 2021, 37, 447–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prandi, B.; Cigognini, I.M.; Faccini, A.; Zurlini, C.; Rodríguez, Ó.; Tedeschi, T. Comparative Study of Different Protein Extraction Technologies Applied on Mushrooms By-products. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2023, 16, 1570–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privatti, R.T. Recuperação de Proteínas e Isoflavonas para Valorização do Okara, Coproduto da Agroindústria do Extrato Hidrossolúvel de Soja. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kleekayai, T.; Khalesi, M.; Amigo-Benavent, M.; Cermeño, M.; Harnedy-Rothwell, P.; FitzGerald, R.J. Enzyme-Assisted Extraction of Plant Proteins. In Green Protein Processing Technologies from Plants: Novel Extraction and Purification Methods for Product Development; Hernández-Álvarez, A.J., Mondor, M., Nosworthy, M.G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 131–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengar, A.S.; Thirunavookarasu, N.; Choudhary, P.; Naik, M.; Surekha, A.; Sunil, C.K.; Rawson, A. Application of power ultrasound for plant protein extraction, modification and allergen reduction—A review. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.-Y.; Shuang, F.-F.; Yang, J.-X.; Jv, Y.-X.; Hu, R.-Z.; Chen, T.; Yao, X.-H.; Zhao, W.-G.; Liu, L.; Zhang, D.-Y. A rapid and efficient method of microwave-assisted extraction and hydrolysis and automatic amino acid analyzer determination of 17 amino acids from mulberry leaves. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 186, 115271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswamy, R.; Krishnan, S.B.; Leong, S.S.J. Pulsed Electric Field Technology for Recovery of Proteins from Waste Plant Resources and Deformed Mushrooms: A Review. Processes 2024, 12, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, F.J.; Boussetta, N.; Vorobiev, E. Emerging technologies for the recovery of isothiocyanates, protein and phenolic compounds from rapeseed and rapeseed press-cake: Effect of high voltage electrical discharges. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2015, 31, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Domenico Ziero, H.; Buller, L.S.; Mudhoo, A.; Ampese, L.C.; Mussatto, S.I.; Carneiro, T.F. An overview of subcritical and supercritical water treatment of different biomasses for protein and amino acids production and recovery. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, H.; Durrani, R.; Delavault, A.; Durand, E.; Chenyu, J.; Yiyang, L.; Lili, S.; Jian, S.; Weiwei, H.; Fei, G. Application of deep eutectic solvents in protein extraction and purification. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 912411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Angelis, D.; Latrofa, V.; Caponio, F.; Pasqualone, A.; Summo, C. Techno-functional properties of dry-fractionated plant-based proteins and application in food product development: A review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 1884–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorissen, S.H.M.; Crombag, J.J.R.; Senden, J.M.G.; Waterval, W.A.H.; Bierau, J.; Verdijk, L.B.; van Loon, L.J.C. Protein content and amino acid composition of commercially available plant-based protein isolates. Amino Acids 2018, 50, 1685–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herreman, L.; Nommensen, P.; Pennings, B.; Laus, M.C. Comprehensive overview of the quality of plant- and animal-sourced proteins based on the digestible indispensable amino acid score. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 5379–5391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snauwaert, E.; Paglialonga, F.; Vande Walle, J.; Wan, M.; Desloovere, A.; Polderman, N.; Renken-Terhaerdt, J.; Shaw, V.; Shroff, R. The benefits of dietary fiber: The gastrointestinal tract and beyond. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2023, 38, 2929–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, S.; Shah, B.R.; Li, J.; Liang, H.; Zhan, F.; Geng, F.; Li, B. A critical review on interplay between dietary fibers and gut microbiota. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 124, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meral, H.; Savaş, İ.; Çiçek, Ş.K.; Demirdöven, A. Peach pomace: A potential probiotic carrier for fiber enrichment in milk. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2023, 18, 1933–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskaya-Sezer, D. The characteristics of microwave-treated insoluble and soluble dietary fibers from grape and their effects on bread quality. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 7877–7886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Jeddou, K.; Bouaziz, F.; Zouari-Ellouzi, S.; Chaari, F.; Ellouz-Chaabouni, S.; Ellouz-Ghorbel, R.; Nouri-Ellouz, O. Improvement of texture and sensory properties of cakes by addition of potato peel powder with high level of dietary fiber and protein. Food Chem. 2017, 217, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Moraes Crizel, T.; Jablonski, A.; de Oliveira Rios, A.; Rech, R.; Flôres, S.H. Dietary fiber from orange byproducts as a potential fat replacer. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 53, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.A.; Mansour, H.E.A.; Mosalam, E.M.; El-Shiekh, R.A.; Ezzat, S.M.; Zayed, A. Valorization of by-products Derived from Onions and Potato: Extraction Optimization, Metabolic Profile, Outstanding Bioactivities, and Industrial Applications. Waste Biomass Valorization 2023, 14, 1823–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niño-Medina, G.; Muy-Rangel, D.; de la Garza, A.L.; Rubio-Carrasco, W.; Pérez-Meza, B.; Araujo-Chapa, A.P.; Gutiérrez-Álvarez, K.A.; Urías-Orona, V. Dietary Fiber from Chickpea (Cicer arietinum) and Soybean (Glycine max) Husk Byproducts as Baking Additives: Functional and Nutritional Properties. Molecules 2019, 24, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanoğlu, A.; Karaoğlu, M.M.; Bedir, Y. The effect of carob, orange and carrot pulps on physical, chemical and microbiological properties of Turkish delight. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2023, 32, 100709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göksel Saraç, M.; Dogan, M. Incorporation of dietary fiber concentrates from fruit and vegetable wastes in butter: Effects on physicochemical, textural, and sensory properties. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2016, 242, 1331–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Sahar, A.; Usman, M.; Sameen, A.; Azhar, M.; Tahir, R.; Younas, R.; Khan, M.I. Extraction of dietary fiber and polyphenols from mango peel and its therapeutic potential to improve gut health. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haris, S.; Alam, M.; Galiwango, E.; Mohamed, M.M.; Kamal-Eldin, A.; Al-Marzouqi, A.H. Characterization analysis of date fruit pomace: An underutilized waste bioresource rich in dietary fiber and phenolic antioxidants. Waste Manag. 2023, 163, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Marcos, M.C.; Bailina, C.; Viuda-Martos, M.; Pérez-Alvarez, J.A.; Fernández-López, J. Properties of Dietary Fibers from Agroindustrial Coproducts as Source for Fiber-Enriched Foods. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2015, 8, 2400–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgil, D.; Barak, S. Chapter 2—Classification, Technological Properties, and Sustainable Sources. In Dietary Fiber: Properties, Recovery, and Applications; Galanakis, C.M., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 27–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Li, L.Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, J.Q.; Huang, X.J.; Hu, J.L.; Yin, J.Y.; Nie, S.P. Fractionation, physicochemical and structural characterization of polysaccharides from barley water-soluble fiber. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, S. Water-insoluble dietary-fibers from Flammulina velutiper used as edible stabilizers for oil-in-water Pickering emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgil, D.; Barak, S. Composition, properties and health benefits of indigestible carbohydrate polymers as dietary fiber: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 61, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Xue, P.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.; Peng, G.; Tian, S.; Chang, X.; Yu, Q. Effect of Soluble Dietary Fiber of Navel Orange Peel Prepared by Mixed Solid-State Fermentation on the Quality of Jelly. Foods 2023, 12, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakongpan, T.; Nitithamyong, A.; Luangpituksa, P. Extraction and Application of Dietary Fiber and Cellulose from Pineapple Cores. J. Food Sci. 2002, 67, 1308–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva Zamora, R.; Baldelli, A.; Pratap-Singh, A. Characterization of selected dietary fibers microparticles and application of the optimized formulation as a fat replacer in hazelnut spreads. Food Res. Int. 2023, 165, 112466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araujo-Chapa, A.P.; Urías-Orona, V.; Niño-Medina, G.; Muy-Rangel, D.; de la Garza, A.L.; Castro, H. Dietary Fiber from Soybean (Glycine max) Husk as Fat and Phosphate Replacer in Frankfurter Sausage: Effect on the Nutritional, Physicochemical and Nutraceutical Quality. Molecules 2023, 28, 4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, D.; Xu, Y.; Kong, B.; Cao, C.; Zhang, F.; Xia, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, J. Application of seaweed dietary fiber as a potential alternative to phosphates in frankfurters with healthier profiles. Meat Sci. 2023, 196, 109044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, A.; Zhao, Y. Wine grape pomace as antioxidant dietary fibre for enhancing nutritional value and improving storability of yogurt and salad dressing. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajila, C.M.; Aalami, M.; Leelavathi, K.; Rao, U.J.S.P. Mango peel powder: A potential source of antioxidant and dietary fiber in macaroni preparations. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2010, 11, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, H.; Sultan, Z.; Yousuf, O.; Malik, M.; Younis, K. A review of the health benefits, functional properties, and ultrasound-assisted dietary fiber extraction. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2023, 30, 100356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanders, A.J.; Jonathan, M.C.; van den Borne, J.J.G.C.; Mars, M.; Schols, H.A.; Feskens, E.J.M.; de Graaf, C. The effects of bulking, viscous and gel-forming dietary fibres on satiation. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 109, 1330–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahani-Sherafat, S.; Azimirad, M.; Raeisi, H.; Azizmohammad looha, M.; Tavakkoli, S.; Ahmadi Amoli, H.; Moghim, S.; Rostami-Nejad, M.; Yadegar, A.; Zali, M.R. Alterations in the gut microbiota and their metabolites in human intestinal epithelial cells of patients with colorectal cancer. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, J.R.; Borre, Y.; O’ Brien, C.; Patterson, E.; El Aidy, S.; Deane, J.; Kennedy, P.J.; Beers, S.; Scott, K.; Moloney, G.; et al. Transferring the blues: Depression-associated gut microbiota induces neurobehavioural changes in the rat. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2016, 82, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Chen, J.; Jiang, L.; Geng, T.; Tian, S.; Liao, Y.; Yang, K.; Zheng, Y.; He, M.; Tang, H.; et al. Gut microbiota-derived secondary bile acids, bile acids receptor polymorphisms, and risk of cardiovascular disease in individuals with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: A cohort study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 119, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verspreet, J.; Damen, B.; Broekaert, W.F.; Verbeke, K.; Delcour, J.A.; Courtin, C.M. A Critical Look at Prebiotics within the Dietary Fiber Concept. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 7, 167–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padayachee, A.; Day, L.; Howell, K.; Gidley, M.J. Complexity and health functionality of plant cell wall fibers from fruits and vegetables. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 59–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, Q.; Huang, J.; Fang, D.; Zhuang, W.; Luo, X.; Zou, X.; Zheng, B.; Cao, H. Hypoglycemic effect of dietary fibers from bamboo shoot shell: An in vitro and in vivo study. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 127, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobek, L.; Matić, P. Non-covalent dietary fiber-Polyphenol interactions and their influence on polyphenol bioaccessibility. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 83, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda-Chodak, A.; Tarko, T. Possible Side Effects of Polyphenols and Their Interactions with Medicines. Molecules 2023, 28, 2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Souto, E.B.; Cicala, C.; Caiazzo, E.; Izzo, A.A.; Novellino, E.; Santini, A. Polyphenols: A concise overview on the chemistry, occurrence, and human health. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 2221–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belščak-Cvitanović, A.; Durgo, K.; Huđek, A.; Bačun-Družina, V.; Komes, D. 1-Overview of polyphenols and their properties. In Polyphenols: Properties, Recovery, and Applications; Galanakis, C.M., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2018; pp. 3–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, R.K.; Dubey, A.K.; Garg, A.; Sharma, R.K.; Fiorino, M.; Ameen, S.M.; Haddad, M.A.; Al-Hiary, M. Natural Polyphenols: Chemical Classification, Definition of Classes, Subcategories, and Structures. J. AOAC Int. 2019, 102, 1397–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, S.; Kesavan, P.; Banerjee, A.; Banerjee, A.; Celep, G.S.; Bissi, L.; Marotta, F. Chapter 25—Metabolism of Dietary Polyphenols by Human Gut Microbiota and Their Health Benefits. In Polyphenols: Mechanisms of Action in Human Health and Disease, 2nd ed.; Watson, R.R., Preedy, V.R., Zibadi, S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, R. Chemistry and Biochemistry of Dietary Polyphenols. Nutrients 2010, 2, 1231–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Shen, T.; Lou, H. Dietary Polyphenols and Their Biological Significance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2007, 8, 950–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naoya Fukuda, M.E.; Yoshida, H.; Kusano, M. Effects of light quality, photoperiod, CO2 concentration, and air temperature on chlorogenic acid and rutin accumulation in young lettuce plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 186, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciocan, A.G.; Tecuceanu, V.; Enache-Preoteasa, C.; Mitoi, E.M.; Helepciuc, F.E.; Dimov, T.V.; Simon-Gruita, A.; Cogălniceanu, G.C. Phenological and Environmental Factors’ Impact on Secondary Metabolites in Medicinal Plant Cotinus coggygria Scop. Plants 2023, 12, 1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, M.; Saeed, F.; Anjum, F.M.; Afzaal, M.; Tufail, T.; Bashir, M.S.; Ishtiaq, A.; Hussain, S.; Suleria, H.A.R. Natural polyphenols: An overview. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, E.P.d.; Jansen, E.T.; Fonseca, L.M.; Hackbart, H.C.d.S.; Siebeneichler, T.J.; Pires, J.B.; Gandra, E.A.; Rombaldi, C.V.; Zavareze, E.d.R.; Dias, A.R.G. Red onion skin extract rich in flavonoids encapsulated in ultrafine fibers of sweet potato starch by electrospinning. Food Chem. 2023, 406, 134954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajkacz, S.; Ligor, M.; Baranowska, I.; Buszewski, B. Separation and determination of chemopreventive phytochemicals of flavonoids from brassicaceae plants. Molecules 2021, 26, 4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramli, A.N.M.; Manap, N.W.A.; Bhuyar, P.; Azelee, N.I.W. Passion fruit (Passiflora edulis) peel powder extract and its application towards antibacterial and antioxidant activity on the preserved meat products. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, Q.; Feng, Y.; Yang, S. Isoflavones from green vegetable soya beans and their antimicrobial and antioxidant activities. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 2043–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bey, D.; Mahfoudi, R.; Benalia, M.; Djeridane, A.; Ami, Y.; Yousfi, M. Inter- and intraspecific variability of phenolic content, antioxidant activities and α-amylase inhibitory potential of different bran and husk extracts from Algerian durum wheat (Triticum turgidum Desf.), barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) and their derived products (frik and mermez). J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 1158–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.; Simões, S.; Ferreira, I.M.P.L.V.O.; Alegria, M.J.; Mateus, N.; Raymundo, A.; de Freitas, V. Upcycling Rocha do Oeste Pear Pomace as a Sustainable Food Ingredient: Composition, Rheological Behavior and Microstructure Alone and Combined with Yeast Protein Extract. Molecules 2023, 28, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craciunescu, O.; Seciu-Grama, A.M.; Mihai, E.; Utoiu, E.; Negreanu-Pirjol, T.; Lupu, C.E.; Artem, V.; Ranca, A.; Negreanu-Pirjol, B.S. The Chemical Profile, Antioxidant, and Anti-Lipid Droplet Activity of Fluid Extracts from Romanian Cultivars of Haskap Berries, Bitter Cherries, and Red Grape Pomace for the Management of Liver Steatosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Soh, S.Y.; Bae, H.; Nam, S.-Y. Antioxidant and phenolic contents in potatoes (Solanum tuberosum L.) and micropropagated potatoes. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2019, 62, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.C.; Pinto, D.; Silva, A.M.S. Plant Flavonoids: Chemical Characteristics and Biological Activity. Molecules 2021, 26, 5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Goel, N. Phenolic acids: Natural versatile molecules with promising therapeutic applications. Biotechnol. Rep. 2019, 24, e00370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, A. Challenges and complexity of functionality evaluation of flavan-3-ol derivatives. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2017, 81, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Mena, A.; Ochoa-Martínez, L.A.; González-Herrera, S.M.; Rutiaga-Quiñones, O.M.; González-Laredo, R.F.; Olmedilla-Alonso, B.; Vega-Maturino, S. Coloring potential of anthocyanins from purple sweet potato paste: Ultrasound-assisted extraction, enzymatic activity, color and its application in ice pops. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 3, 100358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaalal, M.; Ydjedd, S.; Chemache, L.; López-Nicolás, R.; Sánchez-Moya, T.; Frontela-Saseta, C.; Ros-Berruezo, G.; Kati, D.E. Evaluation of the antimicrobial potential of digested and undigested carob phenolic extracts: Impact on selected gut microbiota. Acta Aliment. 2023, 52, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsebaie, E.M.; Essa, R.Y. Microencapsulation of red onion peel polyphenols fractions by freeze drying technicality and its application in cake. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, T.; Vilela, A. Healthy Drinks with Lovely Colors: Phenolic Compounds as Constituents of Functional Beverages. Beverages 2021, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pažarauskaitė, A.; Noriega Fernández, E.; Sone, I.; Sivertsvik, M.; Sharmin, N. Combined Effect of Citric Acid and Polyphenol-Rich Grape Seed Extract towards Bioactive Smart Food Packaging Systems. Polymers 2023, 15, 3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, V.; Bermúdez, R.; Mateus, N.; Guedes, A.; Lorenzo, J.M.; de Freitas, V.; Cruz, L. FoodSmarTag: An innovative dynamic labeling system based on pyranoflavylium- based colorimetric films for real-time monitoring of food freshness. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 143, 108914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coman, V.; Vodnar, D.C. Hydroxycinnamic acids and human health: Recent advances. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Qin, R.; Hou, M.; Xue, J.; Zhou, M.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Y. The interactions of polyphenols with Fe and their application in Fenton/Fenton-like reactions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 300, 121831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Zeng, H.L.; Shang, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, L.; Fang, M.; Zeng, F.; Yang, Q. Inhibitory effect of rosmarinic acid on IgE-trigged mast cell degranulation in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.Y.; Kim, J.; Hong, E.; Lee, K.; Na, Y.; Yeom, C.H.; Park, S. Curcumin inhibits human cancer cell growth and migration through downregulation of SVCT2. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2023, 41, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Wu, L.-M.; Yang, L.; Liu, Z.-L. Evidence for α-tocopherol regeneration reaction of green tea polyphenols in SDS micelles. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 38, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, F.; Iqbal, A.; Zia, S.; Ranjha, M.M.A.N.; Khalid, W.; Nadeem, M.; Selim, S.; Hadidi, M.; Moreno, A.; Manzoor, M.F.; et al. Role and mechanism of fruit waste polyphenols in diabetes management. Open Chem. 2023, 21, 20220272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouarab-Chibane, L.; Forquet, V.; Lantéri, P.; Clément, Y.; Léonard-Akkari, L.; Oulahal, N.; Degraeve, P.; Bordes, C. Antibacterial properties of polyphenols: Characterization and QSAR (Quantitative structure-activity relationship) models. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Camargo, A.C.; Regitano-d’Arce, M.A.B.; Rasera, G.B.; Canniatti-Brazaca, S.G.; do Prado-Silva, L.; Alvarenga, V.O.; Sant’Ana, A.S.; Shahidi, F. Phenolic acids and flavonoids of peanut by-products: Antioxidant capacity and antimicrobial effects. Food Chem. 2017, 237, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojtunik-Kulesza, K.; Oniszczuk, A.; Oniszczuk, T.; Combrzyński, M.; Nowakowska, D.; Matwijczuk, A. Influence of In Vitro Digestion on Composition, Bioaccessibility and Antioxidant Activity of Food Polyphenols—A Non-Systematic Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quirós-Sauceda, A.E.; Palafox-Carlos, H.; Sáyago-Ayerdi, S.G.; Ayala-Zavala, J.F.; Bello-Perez, L.A.; Álvarez-Parrilla, E.; de la Rosa, L.A.; González-Córdova, A.F.; González-Aguilar, G.A. Dietary fiber and phenolic compounds as functional ingredients: Interaction and possible effect after ingestion. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, T.; Chatterjee, N.; Capanoglu, E.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Das, A.K.; Dhar, P. The synergistic ramification of insoluble dietary fiber and associated non-extractable polyphenols on gut microbial population escorting alleviation of lifestyle diseases. Food Chem. X 2023, 18, 100697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahidi, F.; Yeo, J. Insoluble-Bound Phenolics in Food. Molecules 2016, 21, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLusky, S.R.; Bennett, M.H.; Beale, M.H.; Lewis, M.J.; Gaskin, P.; Mansfield, J.W. Cell wall alterations and localized accumulation of feruloyl-3′-methoxytyramine in onion epidermis at sites of attempted penetration by Botrytis allii are associated with actin polarisation, peroxidase activity and suppression of flavonoid biosynthesis. Plant J. 1999, 17, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Dixon, R.A. The ‘ins’ and ‘outs’ of flavonoid transport. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markham, K.R.; Ryan, K.G.; Gould, K.S.; Rickards, G.K. Cell wall sited flavonoids in lisianthus flower petals. Phytochemistry 2000, 54, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ying, D.; Sanguansri, L.; Cai, Y.; Le, X. Adsorption of catechin onto cellulose and its mechanism study: Kinetic models, characterization and molecular simulation. Food Res. Int. 2018, 112, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, A.; Oliveira, J.; Fonseca, F.; Ferreira-da-Silva, F.; Mateus, N.; Vincken, J.-P.; de Freitas, V. Molecular binding between anthocyanins and pectic polysaccharides–Unveiling the role of pectic polysaccharides structure. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 102, 105625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudha, M.; Baskaran, V.; Leelavathi, K. Apple pomace as a source of dietary fiber and polyphenols and its effect on the rheological characteristics and cake making. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasevičienė, Ž.; Čechovičienė, I.; Paulauskienė, A.; Gumbytė, M.; Blinstrubienė, A.; Burbulis, N. The Effect of Berry Pomace on Quality Changes of Beef Patties during Refrigerated Storage. Foods 2022, 11, 2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sozzi, A.; Zambon, M.; Mazza, G.; Salvatori, D. Fluidized bed drying of blackberry wastes: Drying kinetics, particle characterization and nutritional value of the obtained granular solids. Powder Technol. 2021, 385, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurevičiūtė, I.; Keršienė, M.; Bašinskienė, L.; Leskauskaitė, D.; Jasutienė, I. Characterization of Berry Pomace Powders as Dietary Fiber-Rich Food Ingredients with Functional Properties. Foods 2022, 11, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotchkiss, A.T.; Chau, H.K.; Strahan, G.D.; Nuñez, A.; Simon, S.; White, A.K.; Dieng, S.; Heuberger, E.R.; Yadav, M.P.; Hirsch, J. Structure and composition of blueberry fiber pectin and xyloglucan that bind anthocyanins during fruit puree processing. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 116, 106572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskin, R.T.; Xiong, J.; Lila, M.A. Comparison of berry juice concentrates and pomaces and alternative plant proteins to produce spray dried protein–polyphenol food ingredients. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 6286–6299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Q.; Penner, M.H.; Zhao, Y. Chemical composition of dietary fiber and polyphenols of five different varieties of wine grape pomace skins. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 2712–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soquetta, M.B.; Stefanello, F.S.; Huerta, K.d.M.; Monteiro, S.S.; da Rosa, C.S.; Terra, N.N. Characterization of physiochemical and microbiological properties, and bioactive compounds, of flour made from the skin and bagasse of kiwi fruit (Actinidia deliciosa). Food Chem. 2016, 199, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Xu, H.; Yuan, F.; Pan, Q.; Fan, R.; Gao, Y. Physicochemical characterization of five types of citrus dietary fibers. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2015, 4, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Z. The maturity degree, phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of Eureka lemon [Citrus limon (L.) Burm. f.]: A negative correlation between total phenolic content, antioxidant capacity and soluble solid content. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 243, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Camargo, A.d.P.; Gutiérrez, L.-F.; Vargas, S.M.; Martinez-Correa, H.A.; Parada-Alfonso, F.; Narváez-Cuenca, C.-E. Valorisation of mango peel: Proximate composition, supercritical fluid extraction of carotenoids, and application as an antioxidant additive for an edible oil. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2019, 152, 104574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrica, M.; Rebucci, R.; Giromini, C.; Tretola, M.; Cattaneo, D.; Baldi, A. Total phenolic content and antioxidant capacity of agri-food waste and by-products. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 18, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, T.; Huang, X.; Pan, S.; Wang, L. Physicochemical and functional properties of micronized jincheng orange by-products (Citrus sinensis Osbeck) dietary fiber and its application as a fat replacer in yogurt. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 65, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macagnan, F.T.; Santos, L.R.d.; Roberto, B.S.; de Moura, F.A.; Bizzani, M.; da Silva, L.P. Biological properties of apple pomace, orange bagasse and passion fruit peel as alternative sources of dietary fibre. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2015, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Reis, L.C.R.; Facco, E.M.P.; Salvador, M.; Flôres, S.H.; Rios, A.d.O. Characterization of Orange Passion Fruit Peel Flour and Its Use as an Ingredient in Bakery Products. J. Culin. Sci. Technol. 2020, 18, 214–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, A.M.P.; Toro, C.R.; Londoño, L.; Bolivar, G.; Ascacio, J.A.; Aguilar, C.N. Bioprocessing of pineapple waste biomass for sustainable production of bioactive compounds with high antioxidant activity. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2023, 17, 586–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, M.; Cheikhrouhou, S.; Renard, C.M.G.C.; Bureau, S.; Cuvelier, G.; Attia, H.; Ayadi, M.A. Characterization of pectins extracted from pomegranate peel and their gelling properties. Food Chem. 2017, 215, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walid, E.; Hedia, H.; Nizar, T.; Yassine, Y.; Nizar, N.; Ali, F. Total phenolic contents and antioxidant activities of pomegranate peel, seed, leaf and flower. J. Med. Plants Res. 2012, 6, 4724–4730. [Google Scholar]
- Górecka, D.; Pachołek, B.; Dziedzic, K.; Górecka, M. Raspberry pomace as a potential fiber source for cookies enrichment. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2010, 9, 451–461. [Google Scholar]
- Różyło, R.; Amarowicz, R.; Janiak, M.A.; Domin, M.; Gawłowski, S.; Kulig, R.; Łysiak, G.; Rząd, K.; Matwijczuk, A. Micronized Powder of Raspberry Pomace as a Source of Bioactive Compounds. Molecules 2023, 28, 4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-González, I.; García-Valverde, V.; García-Alonso, J.; Periago, M.J. Chemical profile, functional and antioxidant properties of tomato peel fiber. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1528–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šeremet, D.; Durgo, K.; Jokić, S.; Huđek, A.; Vojvodić Cebin, A.; Mandura, A.; Jurasović, J.; Komes, D. Valorization of Banana and Red Beetroot Peels: Determination of Basic Macrocomponent Composition, Application of Novel Extraction Methodology and Assessment of Biological Activity In Vitro. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Alcántara, A.M.; Totosaus, A.; Pérez-Chabela, M.L. Evaluation of Agro-Industrial Co-Products as Source of Bioactive Compounds: Fiber, Antioxidants and Prebiotic. Acta Univ. Cibiniensis. Ser. E Food Technol. 2016, 20, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaño, D.; Fernández-Pan, I.; Arozarena, Í.; Ibañez, F.C.; Vírseda, P.; Beriain, M.J. Revalorisation of broccoli crop surpluses and field residues: Novel ingredients for food industry uses. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2023, 249, 3227–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, D.K.; Das, A.K.; Banerjee, R.; Pateiro, M.; Nanda, P.K.; Gadekar, Y.P.; Biswas, S.; McClements, D.J.; Lorenzo, J.M. Application of Enoki Mushroom (Flammulina Velutipes) Stem Wastes as Functional Ingredients in Goat Meat Nuggets. Foods 2020, 9, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benítez, V.; Mollá, E.; Martín-Cabrejas, M.A.; Aguilera, Y.; López-Andréu, F.J.; Cools, K.; Terry, L.A.; Esteban, R.M. Characterization of Industrial Onion Wastes (Allium cepa L.): Dietary Fibre and Bioactive Compounds. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2011, 66, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, L.; Kaur, S.; Aggarwal, P.; Kaur, N. Characterisation of industrial potato waste for suitability in food applications. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 2686–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejri, F.; Ben Khoud, H.; Njim, L.; Baati, T.; Selmi, S.; Martins, A.; Serralheiro, M.L.M.; Rauter, A.P.; Hosni, K. In vitro and in vivo biological properties of pea pods (Pisum sativum L.). Food Biosci. 2019, 32, 100482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araújo, F.F.; de Paulo Farias, D.; Neri-Numa, I.A.; Pastore, G.M. Polyphenols and their applications: An approach in food chemistry and innovation potential. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 127535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Yao, F.; Zhang, M.; Khalifa, I.; Li, K.; Li, C. Effect of persimmon tannin on the physicochemical properties of maize starch with different amylose/amylopectin ratios. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 132, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupasinghe, H.P.V.; Wang, L.; Huber, G.M.; Pitts, N.L. Effect of baking on dietary fibre and phenolics of muffins incorporated with apple skin powder. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashanta Rupasinghe, H.P.; Wang, L.; Pitts, N.L.; Astatkie, T. Baking and Sensory Characteristics of Muffins Incorporated with Apple Skin Powder. J. Food Qual. 2009, 32, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, D.; Moreira, M.M.; Vieira, E.F.; Švarc-Gajić, J.; Vallverdú-Queralt, A.; Brezo-Borjan, T.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Rodrigues, F. Development and Characterization of Functional Cookies Enriched with Chestnut Shells Extract as Source of Bioactive Phenolic Compounds. Foods 2023, 12, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, D.; Moreira, M.M.; Švarc-Gajić, J.; Vallverdú-Queralt, A.; Brezo-Borjan, T.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Rodrigues, F. In-vitro gastrointestinal digestion of functional cookies enriched with chestnut shells extract: Effects on phenolic composition, bioaccessibility, bioactivity, and α-amylase inhibition. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viskelis, J.; Rubinskiene, M.; Bobinas, C.; Bobinaite, R. Enrichment of fruit leathers with berry press cake powder increase product functionality. In Proceedings of the 11th Baltic Conference on Food Science and Technology “Food Science and Technology in a Changing World”, Jelgava, Latvia, 27–28 April 2017; pp. 27–28. [Google Scholar]
- Amorim, F.L.; de Cerqueira Silva, M.B.; Cirqueira, M.G.; Oliveira, R.S.; Machado, B.A.S.; Gomes, R.G.; de Souza, C.O.; Druzian, J.I.; de Souza Ferreira, E.; Umsza-Guez, M.A. Grape peel (Syrah var.) jam as a polyphenol-enriched functional food ingredient. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 1584–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Mejía, E.; Sacristán, I.; Rosales-Conrado, N.; León-González, M.E.; Madrid, Y. Valorization of Citrus reticulata Blanco Peels to Produce Enriched Wheat Bread: Phenolic Bioaccessibility and Antioxidant Potential. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.-T.; Chang, Y.-H.; Shiau, S.-Y. Rheological, antioxidative and sensory properties of dough and Mantou (steamed bread) enriched with lemon fiber. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 61, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selani, M.M.; Shirado, G.A.N.; Margiotta, G.B.; Saldaña, E.; Spada, F.P.; Piedade, S.M.S.; Contreras-Castillo, C.J.; Canniatti-Brazaca, S.G. Effects of pineapple byproduct and canola oil as fat replacers on physicochemical and sensory qualities of low-fat beef burger. Meat Sci. 2016, 112, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, L.; Kaur, S.; Aggarwal, P. Techno and bio functional characterization of industrial potato waste for formulation of phytonutrients rich snack product. Food Biosci. 2022, 49, 101824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedrníček, J.; Jirotková, D.; Kadlec, J.; Laknerová, I.; Vrchotová, N.; Tříska, J.; Samková, E.; Smetana, P. Thermal stability and bioavailability of bioactive compounds after baking of bread enriched with different onion by-products. Food Chem. 2020, 319, 126562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, M.A.; Derbyshire, E.; Tiwari, B.K.; Brennan, C.S. Enrichment of Extruded Snack Products with Coproducts from Chestnut Mushroom (Agrocybe aegerita) Production: Interactions between Dietary Fiber, Physicochemical Characteristics, and Glycemic Load. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 4396–4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nour, V.; Ionica, M.E.; Trandafir, I. Bread enriched in lycopene and other bioactive compounds by addition of dry tomato waste. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 8260–8267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kołodziejczak, K.; Onopiuk, A.; Szpicer, A.; Poltorak, A. Meat Analogues in the Perspective of Recent Scientific Research: A Review. Foods 2022, 11, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriakopoulou, K.; Keppler, J.K.; van der Goot, A.J. Functionality of Ingredients and Additives in Plant-Based Meat Analogues. Foods 2021, 10, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Krishnaswamy, K. Sustainable zero-waste processing system for soybeans and soy by-product valorization. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 128, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, P.; Rawat, H.; Verma, N.; Mishra, S.; Nautiyal, A.; Anshul; Bhatt, S.; Bisht, N.; Aggarwal, K.; Bora, A.; et al. Analytical approach to assess anti-nutritional factors of grains and oilseeds: A comprehensive review. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 14, 100877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu Min, W.M.; Sun Yang, S.Y.; Bi ChongHao, B.C.; Ji Fang, J.F.; Li BoRui, L.B.; Xing JunJie, X.J. Effects of extrusion conditions on the physicochemical properties of soy protein/gluten composite. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2018, 11, 230–237. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, J.H.; Tay, W.; Ong, D.S.M.; Liebl, D.; Ng, C.P.; Henry, C.J. Physicochemical, textural and structural characteristics of wheat gluten-soy protein composited meat analogues prepared with the mechanical elongation method. Food Struct. 2021, 28, 100183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferawati, F.; Zahari, I.; Barman, M.; Hefni, M.; Ahlström, C.; Witthöft, C.; Östbring, K. High-Moisture Meat Analogues Produced from Yellow Pea and Faba Bean Protein Isolates/Concentrate: Effect of Raw Material Composition and Extrusion Parameters on Texture Properties. Foods 2021, 10, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.-G.; Tang, H.-Q.; Cheng, Y.-Q.; Li, Z.-G.; Tong, L.-T. Potential of preparing meat analogue by functional dry and wet pea (Pisum sativum) protein isolate. LWT 2021, 148, 111702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajpurohit, B.; Li, Y. Overview on pulse proteins for future foods: Ingredient development and novel applications. J. Future Foods 2023, 3, 340–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Maqtari, Q.A.; Li, B.; He, H.-J.; Mahdi, A.A.; Al-Ansi, W.; Saeed, A. An Overview of the Isolation, Modification, Physicochemical Properties, and Applications of Sweet Potato Starch. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2024, 17, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; He, Y.; Zhang, W.; He, J. Potato proteins for technical applications: Nutrition, isolation, modification and functional properties-A review. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2024, 91, 103533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Xiong, Y.L.; Chen, J. Antioxidant and emulsifying properties of potato protein hydrolysate in soybean oil-in-water emulsions. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pęksa, A.; Miedzianka, J. Potato Industry By-Products as a Source of Protein with Beneficial Nutritional, Functional, Health-Promoting and Antimicrobial Properties. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szenderák, J.; Fróna, D.; Rákos, M. Consumer Acceptance of Plant-Based Meat Substitutes: A Narrative Review. Foods 2022, 11, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, L.; Xiong, Y.L. Plant protein-based alternatives of reconstructed meat: Science, technology, and challenges. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 102, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, O.K.; Hamaker, B.R. Texturization of plant protein-based meat alternatives: Processing, base proteins, and other constructional ingredients. Future Foods 2023, 8, 100248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohrer, B.M. An investigation of the formulation and nutritional composition of modern meat analogue products. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2019, 8, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Monterroza, E.J.; Márquez-Cardozo, C.J.; Ciro-Velásquez, H.J. Rheological behavior of avocado (Persea americana Mill, cv. Hass) oleogels considering the combined effect of structuring agents. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 59, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Cui, L.; Meng, Z. Oleogels/emulsion gels as novel saturated fat replacers in meat products: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 137, 108313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.; Mateus, N.; de Freitas, V. Polyphenol-Dietary Fiber Conjugates from Fruits and Vegetables: Nature and Biological Fate in a Food and Nutrition Perspective. Foods 2023, 12, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-López, J.; Lucas-González, R.; Viuda-Martos, M.; Sayas-Barberá, E.; Ballester-Sánchez, J.; Haros, C.M.; Martínez-Mayoral, A.; Pérez-Álvarez, J.A. Chemical and technological properties of bologna-type sausages with added black quinoa wet-milling coproducts as binder replacer. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-López, J.; Lucas-González, R.; Viuda-Martos, M.; Sayas-Barberá, E.; Navarro, C.; Haros, C.M.; Pérez-Álvarez, J.A. Chia (Salvia hispanica L.) products as ingredients for reformulating frankfurters: Effects on quality properties and shelf-life. Meat Sci. 2019, 156, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marvizadeh, M.M.; Akbari, N. Development and Utilization of Rice Bran in Hamburger as a Fat Replacer. J. Chem. Health Risks 2019, 9, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nunzio, M.; Loffi, C.; Montalbano, S.; Chiarello, E.; Dellafiora, L.; Picone, G.; Antonelli, G.; Tedeschi, T.; Buschini, A.; Capozzi, F.; et al. Cleaning the Label of Cured Meat; Effect of the Replacement of Nitrates/Nitrites on Nutrients Bioaccessibility, Peptides Formation, and Cellular Toxicity of In Vitro Digested Salami. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakil, M.H.; Trisha, A.T.; Rahman, M.; Talukdar, S.; Kobun, R.; Huda, N.; Zzaman, W. Nitrites in Cured Meats, Health Risk Issues, Alternatives to Nitrites: A Review. Foods 2022, 11, 3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efenberger-Szmechtyk, M.; Nowak, A.; Czyzowska, A. Plant extracts rich in polyphenols: Antibacterial agents and natural preservatives for meat and meat products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 149–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camo, J.; Beltrán, J.A.; Roncalés, P. Extension of the display life of lamb with an antioxidant active packaging. Meat Sci. 2008, 80, 1086–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radha krishnan, K.; Babuskin, S.; Azhagu Saravana Babu, P.; Sasikala, M.; Sabina, K.; Archana, G.; Sivarajan, M.; Sukumar, M. Antimicrobial and antioxidant effects of spice extracts on the shelf life extension of raw chicken meat. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 171, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Mateos, M.J.; Delgado-Adámez, J.; Moreno-Cardona, D.; Valdés-Sánchez, M.E.; Ramírez-Bernabé, M.R. Application of White-Wine-Pomace-Derived Ingredients in Extending Storage Stability of Fresh Pork Burgers. Foods 2023, 12, 4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- França, F.; Harada-Padermo, S.d.S.; Frasceto, R.A.; Saldaña, E.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Vieira, T.M.F.d.S.; Selani, M.M. Umami ingredient from shiitake (Lentinula edodes) by-products as a flavor enhancer in low-salt beef burgers: Effects on physicochemical and technological properties. LWT 2022, 154, 112724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albergamo, A.; Vadalà, R.; Metro, D.; Nava, V.; Bartolomeo, G.; Rando, R.; Macrì, A.; Messina, L.; Gualtieri, R.; Colombo, N.; et al. Physicochemical, Nutritional, Microbiological, and Sensory Qualities of Chicken Burgers Reformulated with Mediterranean Plant Ingredients and Health-Promoting Compounds. Foods 2021, 10, 2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longato, E.; Lucas-González, R.; Peiretti, P.G.; Meineri, G.; Pérez-Alvarez, J.A.; Viuda-Martos, M.; Fernández-López, J. The Effect of Natural Ingredients (Amaranth and Pumpkin Seeds) on the Quality Properties of Chicken Burgers. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2017, 10, 2060–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarjuelo, L.; Rabadán, A.; Álvarez-Ortí, M.; Pardo-Giménez, A.; Pardo, I.; Pardo, J.E. Nutritional characteristics and consumer attitudes towards burgers produced by replacing animal fat with oils obtained from food by-products. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 104, 105500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besbes, S.; Attia, H.; Deroanne, C.; Makni, S.; Blecker, C. Partial Replacement of Meat by Pea Fiber and Wheat Fiber: Effect on the Chemical Composition, Cooking Characteristics and Sensory Properties of Beef Burgers. J. Food Qual. 2008, 31, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, N.P.d.; Vinhal Borges, Í.G.A.; de Castro, J.S.; Nascimento, C.P.d.; Bitu, L.A.; de Sousa, P.H.M.; da Silva, E.M.C. Enhancing the quality and antioxidant properties of beef burgers with dried Hibiscus sabdariffa L. leaves: Characterization and sensory evaluation. Food Biosci. 2024, 57, 103568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Marazeeq, K.; Al-Rousan, W.; Taha, S.; Osaili, T. The influence of cactus (Opuntia ficus-indica (L.) Mill) cladodes powder on improving the characteristics and shelf life of low-fat beef and chicken burgers. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 43, e124322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, A.S.; dos Santos, B.A.; Farias, C.A.A.; Correa, L.P.; Cordeiro, M.W.S.; Pinton, M.B.; Barcia, M.T.; Wagner, R.; Cichoski, A.J.; Barin, J.S.; et al. Raspberry Extract as a Strategy to Improve the Oxidative Stability of Pork Burgers Enriched with Omega-3 Fatty Acids. Foods 2023, 12, 1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedrníček, J.; Laknerová, I.; Linhartová, Z.; Kadlec, J.; Samková, E.; Bárta, J.; Bártová, V.; Mráz, J.; Pešek, M.; Winterová, R.; et al. Onion waste as a rich source of antioxidants for meat products. Czech J. Food Sci. 2019, 37, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Xiong, Y.L. Inhibition of Lipid Oxidation in Cooked Beef Patties by Hydrolyzed Potato Protein Is Related to Its Reducing and Radical Scavenging Ability. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 9186–9192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moll, P.; Salminen, H.; Schmitt, C.; Weiss, J. Pea protein–sugar beet pectin binders can provide cohesiveness in burger type meat analogues. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2023, 249, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpicer, A.; Onopiuk, A.; Barczak, M.; Kurek, M. The optimization of a gluten-free and soy-free plant-based meat analogue recipe enriched with anthocyanins microcapsules. LWT 2022, 168, 113849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, A.; Ahlborn, J.; Zajul, M.; Zorn, H. Edible mushroom mycelia of Pleurotus sapidus as novel protein sources in a vegan boiled sausage analog system: Functionality and sensory tests in comparison to commercial proteins and meat sausages. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2018, 244, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamani, M.H.; Meera, M.S.; Bhaskar, N.; Modi, V.K. Partial and total replacement of meat by plant-based proteins in chicken sausage: Evaluation of mechanical, physico-chemical and sensory characteristics. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 2660–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broucke, K.; Van Poucke, C.; Duquenne, B.; De Witte, B.; Baune, M.-C.; Lammers, V.; Terjung, N.; Ebert, S.; Gibis, M.; Weiss, J.; et al. Ability of (extruded) pea protein products to partially replace pork meat in emulsified cooked sausages. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 78, 102992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salejda, A.M.; Olender, K.; Zielińska-Dawidziak, M.; Mazur, M.; Szperlik, J.; Miedzianka, J.; Zawiślak, I.; Kolniak-Ostek, J.; Szmaja, A. Frankfurter-Type Sausage Enriched with Buckwheat By-Product as a Source of Bioactive Compounds. Foods 2022, 11, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocan, I.; Cadariu, A.-I.; Negrea, M.; Alexa, E.; Obistioiu, D.; Radulov, I.; Poiana, M.-A. Investigating the Antioxidant Potential of Bell Pepper Processing By-Products for the Development of Value-Added Sausage Formulations. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthana Priya, R.; Rawson, A.; Vidhyalakshmi, R.; Jagan Mohan, R. Development of vegan sausage using banana floret (Musa paradisiaca) and jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam.) as a meat substitute: Evaluation of textural, physico-chemical and sensory characteristics. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e16118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongkaew, M.; Sommano, S.R.; Tangpao, T.; Rachtanapun, P.; Jantanasakulwong, K. Mango Peel Pectin by Microwave-Assisted Extraction and Its Use as Fat Replacement in Dried Chinese Sausage. Foods 2020, 9, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.-M.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, H.-Y. Effects of Using Soybean Protein Emulsion as a Meat Substitute for Chicken Breast on Physicochemical Properties of Vienna Sausage. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2022, 42, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slozhenkina, M.I.; Gorlov, I.F.; Bozhkova, S.E.; Ermolova, K.A.; Serkova, A.E.; Khramova, V.N. Ham production using processed apple products. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 965, 012044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lise, C.C.; Marques, C.; da Cunha, M.A.A.; Mitterer-Daltoé, M.L. Alternative protein from Pereskia aculeata Miller leaf mucilage: Technological potential as an emulsifier and fat replacement in processed mortadella meat. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2021, 247, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auriema, B.E.; Correa, F.J.; Silva, R.; Soares, P.T.S.; Lima, A.L.; Vidal, V.A.S.; Raices, R.S.L.; Pollonio, M.A.R.; Luchese, R.H.; Esmerino, E.A.; et al. Fat replacement by green banana biomass: Impact on the technological, nutritional and dynamic sensory profiling of chicken mortadella. Food Res. Int. 2022, 152, 110890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biasi, V.; Huber, E.; de Melo, A.P.Z.; Hoff, R.B.; Verruck, S.; Barreto, P.L.M. Antioxidant effect of blueberry flour on the digestibility and storage of Bologna-type mortadella. Food Res. Int. 2023, 163, 112210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revilla, I.; Santos, S.; Hernández-Jiménez, M.; Vivar-Quintana, A.M. The Effects of the Progressive Replacement of Meat with Texturized Pea Protein in Low-Fat Frankfurters Made with Olive Oil. Foods 2022, 11, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belluco, C.Z.; Mendonça, F.J.; Zago, I.C.C.; Di Santis, G.W.; Marchi, D.F.; Soares, A.L. Application of orange albedo fat replacer in chicken mortadella. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 3659–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sośnicka, M.; Nowak, A.; Czyżowska, A.; Gałązka-Czarnecka, I.; Czerbniak, A. Polyphenolic Herbal Extract of Cistus incanus as Natural Preservatives for Sausages Enriched with Natural Colors. Processes 2021, 9, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasi, V.; Huber, E.; Goldoni, T.S.H.; de Melo, A.P.Z.; Hoff, R.B.; Verruck, S.; Barreto, P.L.M. Goldenberry flour as a natural antioxidant in Bologna-type mortadella during refrigerated storage and in vitro digestion. Meat Sci. 2023, 196, 109041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderón-Oliver, M.; Escalona-Buendía, H.B.; Ponce-Alquicira, E. Effect of the addition of microcapsules with avocado peel extract and nisin on the quality of ground beef. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 1325–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devatkal, S.K.; Naveena, B.M. Effect of salt, kinnow and pomegranate fruit by-product powders on color and oxidative stability of raw ground goat meat during refrigerated storage. Meat Sci. 2010, 85, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stobnicka, A.; Gniewosz, M. Antimicrobial protection of minced pork meat with the use of Swamp Cranberry (Vaccinium oxycoccos L.) fruit and pomace extracts. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazumder, M.A.R.; Sukchot, S.; Phonphimai, P.; Ketnawa, S.; Chaijan, M.; Grossmann, L.; Rawdkuen, S. Mushroom-Legume-Based Minced Meat: Physico-Chemical and Sensory Properties. Foods 2023, 12, 2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-López, J.; Ponce-Martínez, A.J.; Rodríguez-Párraga, J.; Solivella-Poveda, A.M.; Fernández-López, J.A.; Viuda-Martos, M.; Pérez-Alvarez, J.A. Beetroot juices as colorant in plant-based minced meat analogues: Color, betalain composition and antioxidant activity as affected by juice type. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleque, M.A.; Keya, C.A.; Hasan, K.N.; Hoque, M.M.; Inatsu, Y.; Bari, M.L. Use of cloves and cinnamon essential oil to inactivate Listeria monocytogenes in ground beef at freezing and refrigeration temperatures. LWT 2016, 74, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Diaz, J.M.; Kantanen, K.; Edelmann, J.M.; Jouppila, K.; Sontag-Strohm, T.; Piironen, V. Functionality of oat fiber concentrate and faba bean protein concentrate in plant-based substitutes for minced meat. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morshdy, A.E.; Gamal, S.; Saad, S.; Bkear, N.; Ali, E. Effect of Lemon Leaf Extracts on Bacterial Count and Keeping Quality of Minced Meat. Damanhour J. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S. Chapter 5—Meat-, fish-, and poultry-based snacks. In Snack Foods; Bhattacharya, S., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 117–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knipe, C.L. Sausages, types of: Emulsion. In Encyclopedia of Meat Sciences, 3rd ed.; Dikeman, M., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2024; pp. 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majzoobi, M.; Talebanfar, S.; Eskandari, M.H.; Farahnaky, A. Improving the quality of meat-free sausages using κ-carrageenan, konjac mannan and xanthan gum. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Hu, Y.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; McClements, D.J. Digestibility and gastrointestinal fate of meat versus plant-based meat analogs: An in vitro comparison. Food Chem. 2021, 364, 130439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.K.; Choi, J.S.; Moon, S.S.; Jeong, J.Y.; Kim, G.D. The Assessment of Red Beet as a Natural Colorant, and Evaluation of Quality Properties of Emulsified Pork Sausage Containing Red Beet Powder during Cold Storage. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2014, 34, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Boer, J.; Aiking, H. Prospects for pro-environmental protein consumption in Europe: Cultural, culinary, economic and psychological factors. Appetite 2018, 121, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsvakirai, C.Z.; Zulu, N.M. Investigating the motivations driving meat analogue purchase among middle-income consumers in Mbombela, South Africa. Agrekon 2022, 61, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussaoui, D.; Torres-Moreno, M.; Tárrega, A.; Martí, J.; López-Font, G.; Chaya, C. Evaluation of consumers’ response to plant-based burgers according to their attitude towards meat reduction. Food Qual. Prefer. 2023, 110, 104955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonheim, L.E.; Groufh-Jacobsen, S.; Stea, T.H.; Henjum, S. Consumption of meat and dairy substitute products amongst vegans, vegetarians and pescatarians. Food Nutr. Res. 2023, 67, 9081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, D.L. Why some choose the vegetarian option: Are all ethical motivations the same? Motiv. Emot. 2019, 43, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allès, B.; Baudry, J.; Méjean, C.; Touvier, M.; Péneau, S.; Hercberg, S.; Kesse-Guyot, E. Comparison of Sociodemographic and Nutritional Characteristics between Self-Reported Vegetarians, Vegans, and Meat-Eaters from the NutriNet-Santé Study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerslake, E.; Kemper, J.A.; Conroy, D. What’s your beef with meat substitutes? Exploring barriers and facilitators for meat substitutes in omnivores, vegetarians, and vegans. Appetite 2022, 170, 105864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIlveen, H.; Abraham, C.; Armstrong, G. Meat avoidance and the role of replacers. Nutr. Food Sci. 1999, 99, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banovic, M.; Sveinsdóttir, K. Importance of being analogue: Female attitudes towards meat analogue containing rapeseed protein. Food Control 2021, 123, 107833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giampietri, E.; Bugin, G.; Trestini, S. Exploring the Interplay of Risk Attitude and Organic Food Consumption. J. Food Syst. Dyn. 2020, 11, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begho, T.; Zhu, Y. Determinants of consumer acceptance of meat analogues: Exploring measures of risk preferences in predicting consumption. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 11, 100509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garaus, M.; Garaus, C. US consumers’ mental associations with meat substitute products. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1135476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garaus, M.; Lalicic, L. The unhealthy-tasty intuition for online recipes–when healthiness perceptions backfire. Appetite 2021, 159, 105066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadimu, G.J.; Olatunde, O.O.; Bandara, N.; Truong, T. Chapter 4—Reducing allergenicity in plant-based proteins. In Engineering Plant-Based Food Systems; Prakash, S., Bhandari, B.R., Gaiani, C., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, L.; Cakebread, J.A.; Loveday, S.M. Food proteins from animals and plants: Differences in the nutritional and functional properties. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 119, 428–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samtiya, M.; Aluko, R.E.; Dhewa, T. Plant food anti-nutritional factors and their reduction strategies: An overview. Food Prod. Process. Nutr. 2020, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).