Microbial Community Dynamics and Metabolite Changes during Wheat Starch Slurry Fermentation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
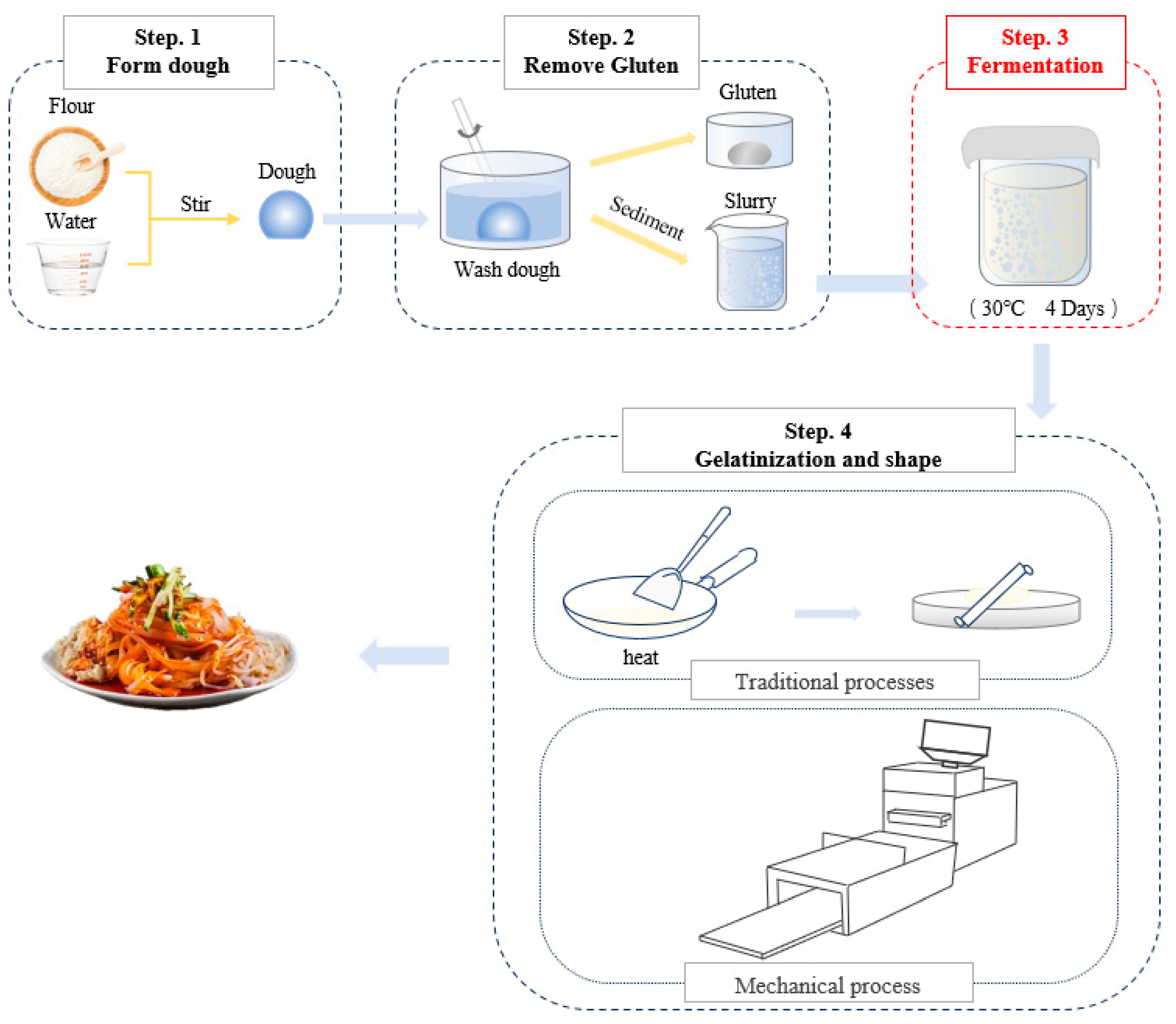
2.2. Preparation of Fermented Wheat Starch Slurry
2.3. Microbial Analysis of Fermented Starch Slurry
2.3.1. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification
2.3.2. Illumina MiSeq Sequencing and Processing of Sequencing Data
2.4. Analysis of Physicochemical Characteristics of Starch Slurry and Ganmianpi
2.5. Analysis of Volatile Flavor Compounds in Fermented Starch Slurry
2.6. Preparation of Ganmianpi
2.7. Texture Profile Analysis of Ganmianpi (TPA)
2.8. Sensory Evaluation Method of Ganmianpi
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in Microbial Communities
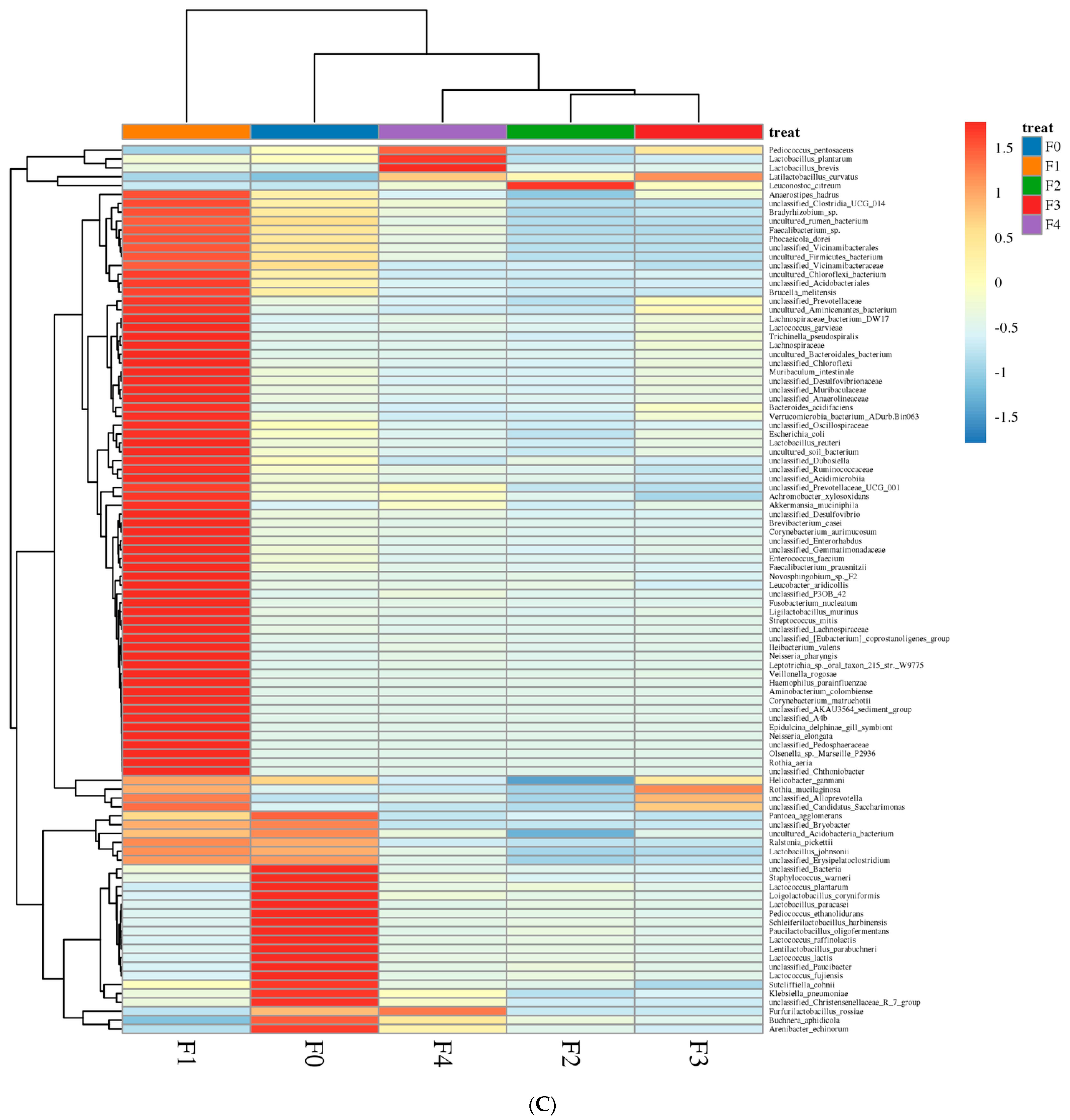
3.1.1. Analysis of Bacterial Community Dynamics during Fermentation
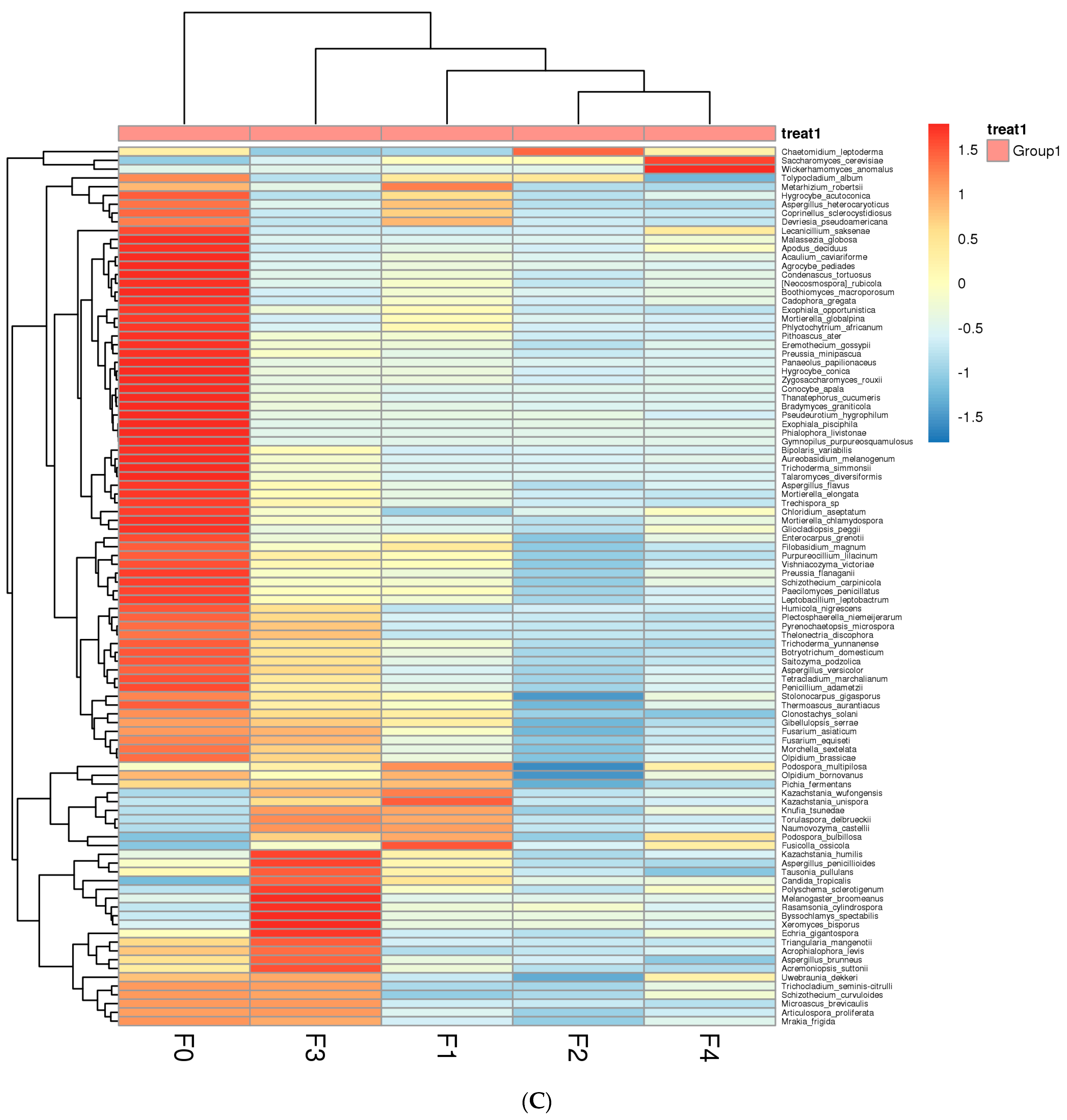
3.1.2. Analysis of Fungal Community Dynamics during Fermentation
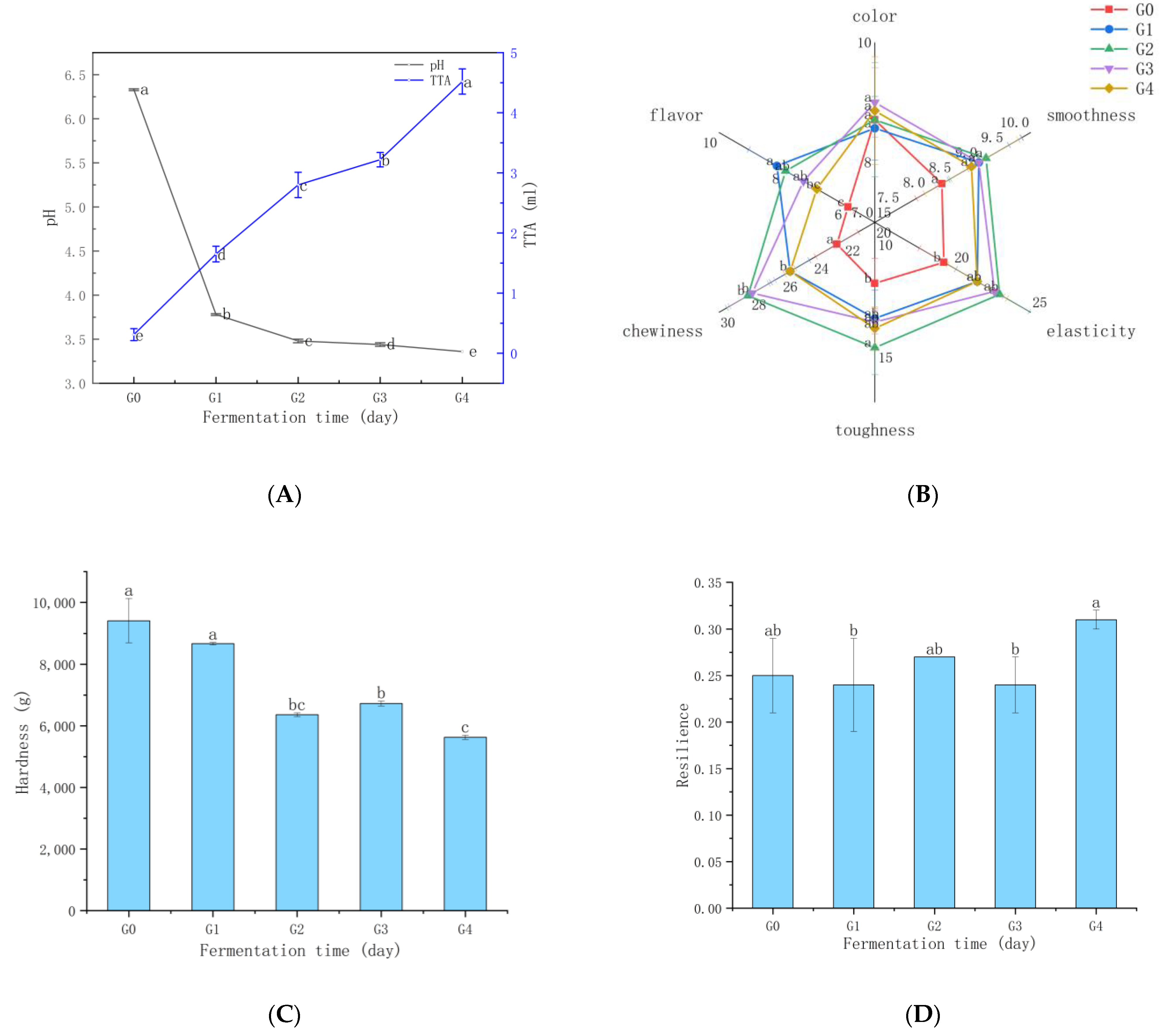
3.2. Changes in Organic Acids and Reducing Sugars
3.3. Analysis of Volatile Compounds during Fermentation
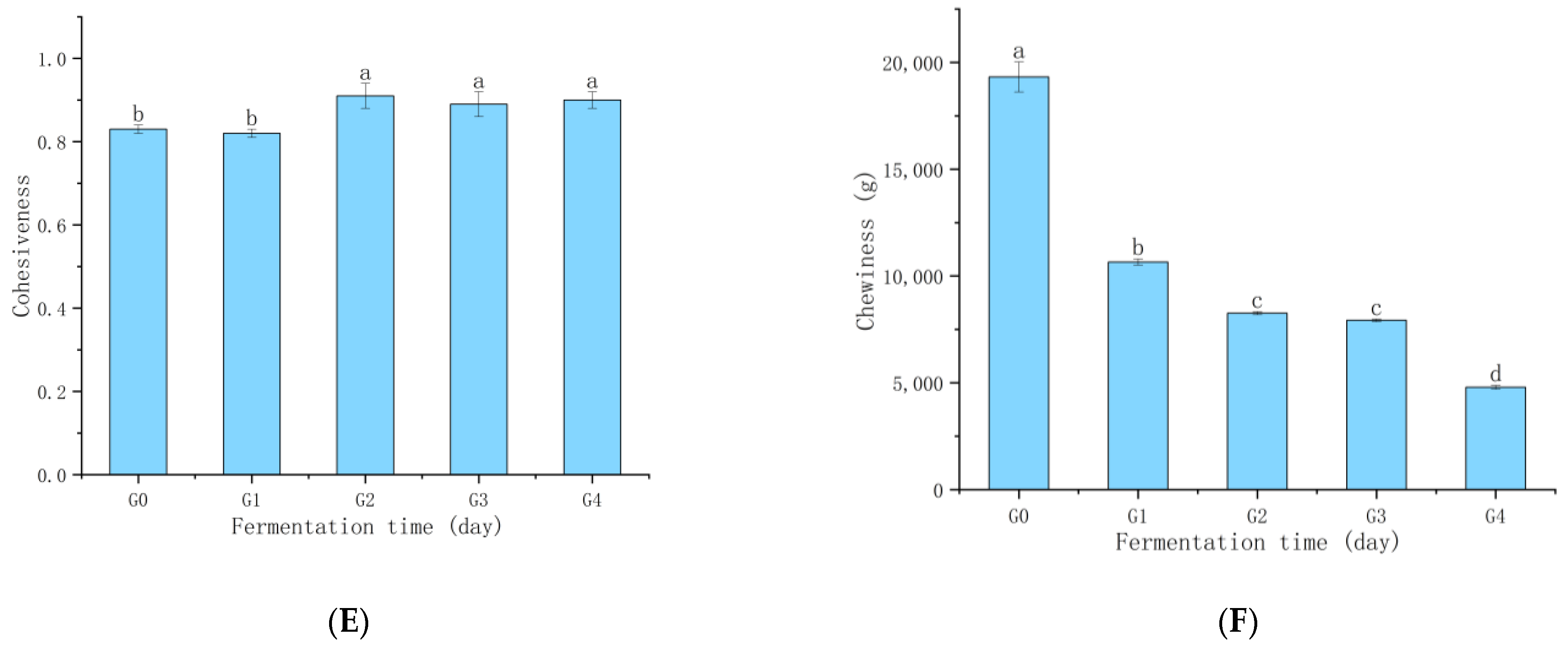
3.4. Ganmianpi Quality Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, S.; Xing, J.; Guo, X.; Zhu, K. Nonlinear rheological properties of Chinese cold skin noodle (liangpi) and wheat starch gels by large amplitude oscillatory shear (LAOS). Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 134, 108030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Pan, Z.; Huang, Z.; Ai, Z. A Comparative Study of Different Freezing Methods on Water Distribution, Retrogradation, and Digestion Properties of Liangpi (Starch Gel Food). Starch 2022, 74, 2100205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Chen, C.; Lei, Z. Meta-omics insights in the microbial community profiling and functional characterization of fermented foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 65, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Tsafrakidou, P.; Michaelidou, A.-M.; Biliaderis, C.G. Fermented Cereal-based Products: Nutritional Aspects, Possible Impact on Gut Microbiota and Health Implications. Foods 2020, 9, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Li, X.; Zhu, R.; Ma, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Hu, X. Effect of natural fermentation on the structure and physicochemical properties of wheat starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 218, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Li, X.; Ma, Z.; Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, D. Multiscale structural changes and retrogradation effects of addition of sodium alginate to fermented and native wheat starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 2286–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Qi, J.; Yang, H.; Lei, X.; Jiang, J.; Song, Y.; Qin, Y.; Liu, Y.-L. Fungal dynamic during apricot wine spontaneous fermentation and aromatic characteristics of Pichia kudriavzevii for potential as starter. Food. Chem. X 2023, 19, 100862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Jang, M.; Lee, M. Physicochemical changes in kimchi containing skate (Raja kenojei) pretreated with organic acids during fermentation. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 25, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Tang, F.; Guo, Z.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Ning, M.; Shan, C. Effects of pretreatment methods and leaching methods on jujube wine quality detected by electronic senses and HS-SPME–GC–MS. Food Chem. 2020, 330, 127330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.; Guan, Q.; Song, S.; Hao, M.; Xie, M. Dynamic changes of lactic acid bacteria flora during Chinese sauerkraut fermentation. Food Control 2012, 26, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, L.; Ma, F.; Zhou, J.-T.; Pi, W.-Q.; Gou, M. Optimization of metagenomic DNA extractionfrom activated sludge samples. Asia Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2009, 4, 509–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Mao, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Ji, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Ailati, A. Bacterial succession and the dynamics of volatile compounds during the fermentation of Chinese rice wine from Shaoxing region. World J. Microb. Biot. 2015, 31, 1907–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, G.; Qiu, H.; Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhen, B.; Li, H.; Niu, Q.; Qi, D.; Zhou, X. Little environmental adaptation and high stability of bacterial communities in rhizosphere rather than bulk soils in rice fields. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 169, 104183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wittouck, S.; Salvetti, E.; Franz, C.M.A.P.; Harris, H.M.B.; Mattarelli, P.; Toole, P.W.O.; Pot, B.; Vandamme, P.; Walter, J.; et al. A taxonomic note on the genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 novel genera, emended description of the genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Micr. 2020, 70, 2782–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yu, L.; Qiao, N.; Xiao, Y.; Tian, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Zhai, Q. Latilactobacillus curvatus: A Candidate Probiotic with Excellent Fermentation Properties and Health Benefits. Foods 2020, 9, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terán, L.C.; Coeuret, G.; Raya, R.; Zagorec, M.; Champomier-Vergès, M.-C.; Chaillou, S. Phylogenomic Analysis of Lactobacillus curvatus Reveals Two Lineages Distinguished by Genes for Fermenting Plant-Derived Carbohydrates. Genome Biol. Evol. 2018, 10, 1516–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkiene, E.; Bartkevics, V.; Pugajeva, I.; Krungleviciute, V.; Mayrhofer, S.; Domig, K. The contribution of P. acidilactici, L. plantarum, and L. curvatus starters and L-(+)-lactic acid to the acrylamide content and quality parameters of mixed rye-Wheat bread. LWT 2017, 80, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Michel, E.; Monfort, C.; Deffrasnes, M.; Guezenec, S.; Lhomme, E.; Barret, M.; Sicard, D.; Dousset, X.; Onno, B. Characterization of relative abundance of lactic acid bacteria species in French organic sourdough by cultural, qPCR and MiSeq high-throughput sequencing methods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 239, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roșca, M.-F.; Păucean, A.; Man, S.M.; Chiș, M.S.; Pop, C.R.; Pop, A.; Fărcaș, A.C. Leuconostoc citreum: A Promising Sourdough Fermenting Starter for Low-Sugar-Content Baked Goods. Foods 2024, 13, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zikmanis, P.; Brants, K.; Kolesovs, S.; Semjonovs, P. Extracellular polysaccharides produced by bacteria of the Leuconostoc genus. World J. Microb. Biot. 2020, 36, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axel, M.; Bernard, T.; Carine, N.; Elsa, G.; Denis, B.; Georges, D.; Etienne, T. High-throughput sequencing analysis reveals the genetic diversity of different regions of the murine norovirus genome during in vitro replication. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 1019–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Xie, S.; Xia, Z.; Wang, F.; Tong, L. Further Interpretation of the Volatile, Microbial Community and Edible Quality of Fresh Fermented Rice Noodles with Different Selected Strains. Foods 2023, 12, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoch, C.L.; Sung, G.-H.; López-Giráldez, F.; Townsend, J.P.; Miadlikowska, J.; Hofstetter, V.; Robbertse, B.; Matheny, P.B.; Kauff, F.; Wang, Z.; et al. The Ascomycota Tree of Life: A Phylum-wide Phylogeny Clarifies the Origin and Evolution of Fundamental Reproductive and Ecological Traits. Syst. Biol. 2009, 58, 224–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Kang, J.; Ma, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Hu, X. Microbial succession and metabolite changes during traditional serofluid dish fermentation. LWT 2017, 84, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, X.; Bi, Y.; Zhao, R.; Nie, Y.; Yuan, W. Dynamics of microbial community and changes of metabolites during production of type Ι sourdough steamed bread made by retarded sponge-dough method. Food Chem. 2020, 330, 127316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vuyst, L.; van Kerrebroeck, S.; Harth, H.; Huys, G.R.B.; Weckx, S. Microbial ecology of sourdough fermentations: Diverse or uniform? Food Microbiol. 2014, 37, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-khamaiseh, A.M.; Amr, A.S.; Al-Holy, M.A.; Al-Qadiri, H.M.; Shahein, M.H.; Albawarshi, Y. Physicochemical and microbiological properties of Arabic flatbread produced from wild natural sour starters. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammes, W.P.; Brandt, M.J.; Francis, K.L.; Rosenheim, J.; Seitter, M.F.H.; Vogelmann, S.A. Microbial ecology of cereal fermentations. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 16, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazo-Vélez, M.A.; Garzon, R.; Guardado-Félix, D.; Serna-Saldivar, S.O.; Rosell, C.M. Selenized chickpea sourdoughs for the enrichment of breads. LWT 2021, 150, 112082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, H.; Gu, Z.; Li, C.; Fang, Z.; Hu, B.; Wang, C.; Chen, S.; Tang, X.; Ren, Y.; Wu, W.; et al. Effect of fermentation time and addition amount of rice sourdoughs with different microbial compositions on the physicochemical properties of three gluten-free rice breads. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, V.; Stefova, M.; Vojnoski, B.; Stafilov, T.; Bíró, I.; Bufa, A.; Felinger, A.; Kilár, F. Volatile Composition of Macedonian and Hungarian Wines Assessed by GC/MS. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Fu, Z.; Sun, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xia, Y.; Huang, M.; Li, X. Roles of aging in the production of light-flavored Daqu. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2019, 127, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yuan, C.; Gao, X.; Kang, Y.; Huang, M.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y. Characterization of key aroma compounds in Huangjiu from northern China by sensory-directed flavor analysis. Food Res. Int. 2020, 134, 109238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz Carrascal, J.; García, C.M.; Muriel, E.; Andrés, A.I.; Ventanas, J. Influence of sensory characteristics on the acceptability of dry-cured ham. Meat Sci. 2002, 61, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, B.; Feng, S. Flavor characteristics of hulless barley wine fermented with mixed starters by molds and yeasts isolated from Jiuqu. Food Biosci. 2023, 52, 102349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, D.; Ren, L.; Song, S.; Ma, X.; Rong, Y. Effects of simultaneous and sequential cofermentation of Wickerhamomyces anomalus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae on physicochemical and flavor properties of rice wine. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemme, D.; Catherine, F.-S. Leuconostoc, characteristics, use in dairy technology and prospects in functional foods. Int. Dairy J. 2004, 14, 467–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Guo, X.; Zhu, K. Effect of Fermentation on the Quality of Dried Hollow Noodles and the Related Starch Properties. Foods 2022, 11, 3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, F.; Xiao, L.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, G. Spontaneous fermentation tunes the physicochemical properties of sweet potato starch by modifying the structure of starch molecules. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 213, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| No. | Compound | Species Number | Relative Content (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F0 | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | |||
| 1 | alcohols | 14 | 57.16 | 86.05 | 86.11 | 82.32 | 67.22 |
| 2 | esters | 15 | 24.59 | 4.3 | 2.71 | 4.32 | 4.24 |
| 3 | acids | 11 | 3.02 | 2.09 | 4.06 | 8.66 | 15.46 |
| 4 | others | 22 | 2.98 | 5.31 | 3.22 | 0.91 | 3.06 |
| 5 | total | 62 | 87.75 | 97.75 | 96.10 | 96.21 | 89.98 |
| Number | Compound | Relative Content (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F0 | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | ||
| 1 | Ethyl alcohol | 44.44 | 69.59 | 69.50 | 63.95 | 51.22 |
| 2 | 2-Octanol | 8.48 | 15.26 | 9.49 | 11.95 | 10.89 |
| 3 | Phenylethyl Alcohol | -- | -- | 6.95 | 5.59 | 4.42 |
| 4 | Octanoic acid, ethyl ester | -- | -- | 0.50 | 0.58 | 0.40 |
| 5 | Hexadecenoic acid, ethyl ester | 5.83 | 1.78 | 0.63 | 1.04 | 1.73 |
| 6 | Ethyl Oleate | 6.46 | 1.57 | -- | -- | -- |
| 7 | Acetic acid | -- | 0.67 | 1.55 | 6.12 | 10.52 |
| 8 | Octanoic Acid | 0.38 | 0.66 | 1.07 | 1.27 | 1.65 |
| 9 | n-Decanoic acid | -- | -- | 0.68 | 0.76 | 1.38 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Fan, X.; Hu, X. Microbial Community Dynamics and Metabolite Changes during Wheat Starch Slurry Fermentation. Foods 2024, 13, 2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13162586
Li X, Yang Y, Fan X, Hu X. Microbial Community Dynamics and Metabolite Changes during Wheat Starch Slurry Fermentation. Foods. 2024; 13(16):2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13162586
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiaoping, Yujin Yang, Xin Fan, and Xinzhong Hu. 2024. "Microbial Community Dynamics and Metabolite Changes during Wheat Starch Slurry Fermentation" Foods 13, no. 16: 2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13162586
APA StyleLi, X., Yang, Y., Fan, X., & Hu, X. (2024). Microbial Community Dynamics and Metabolite Changes during Wheat Starch Slurry Fermentation. Foods, 13(16), 2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13162586





