Combined Effects of Compound Low-Sodium Alternative Salts and Vacuum Tumbling on the Quality, Water Distribution, and Microstructure of Marinated Beef
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Marinated Beef Preparation
2.2. Product Yield and Cooking Loss
2.3. Texture Profile Analysis and Shear Force
2.4. Color
2.5. Water Activity and Water Content
2.6. Low Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LF-NMR) Analysis and Magnetic Relaxation Image (MRI) Measurements
2.7. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy
2.8. Histological Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
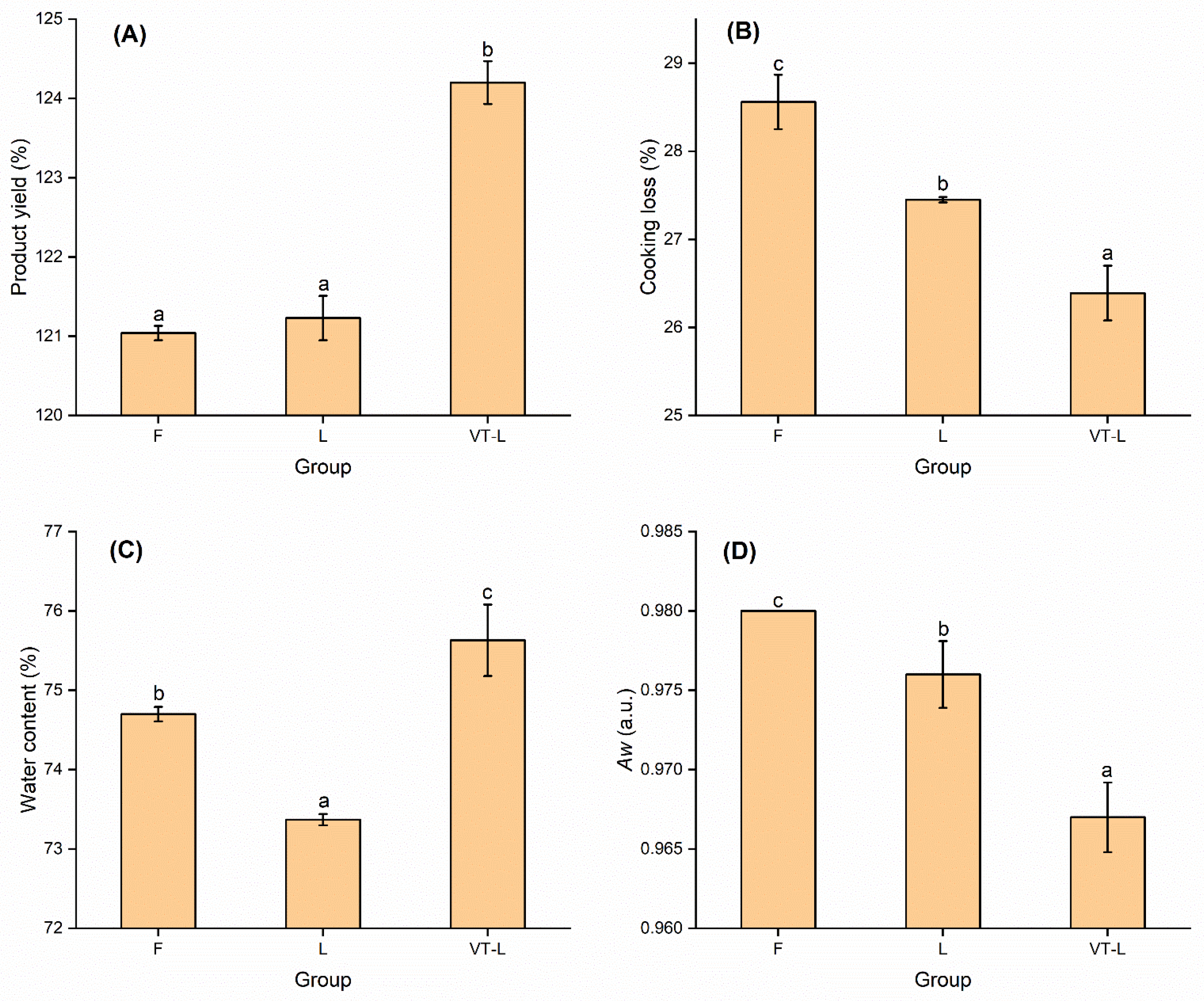
3.1. Product Yield and Cooking Loss
3.2. Water Content and Water Activity
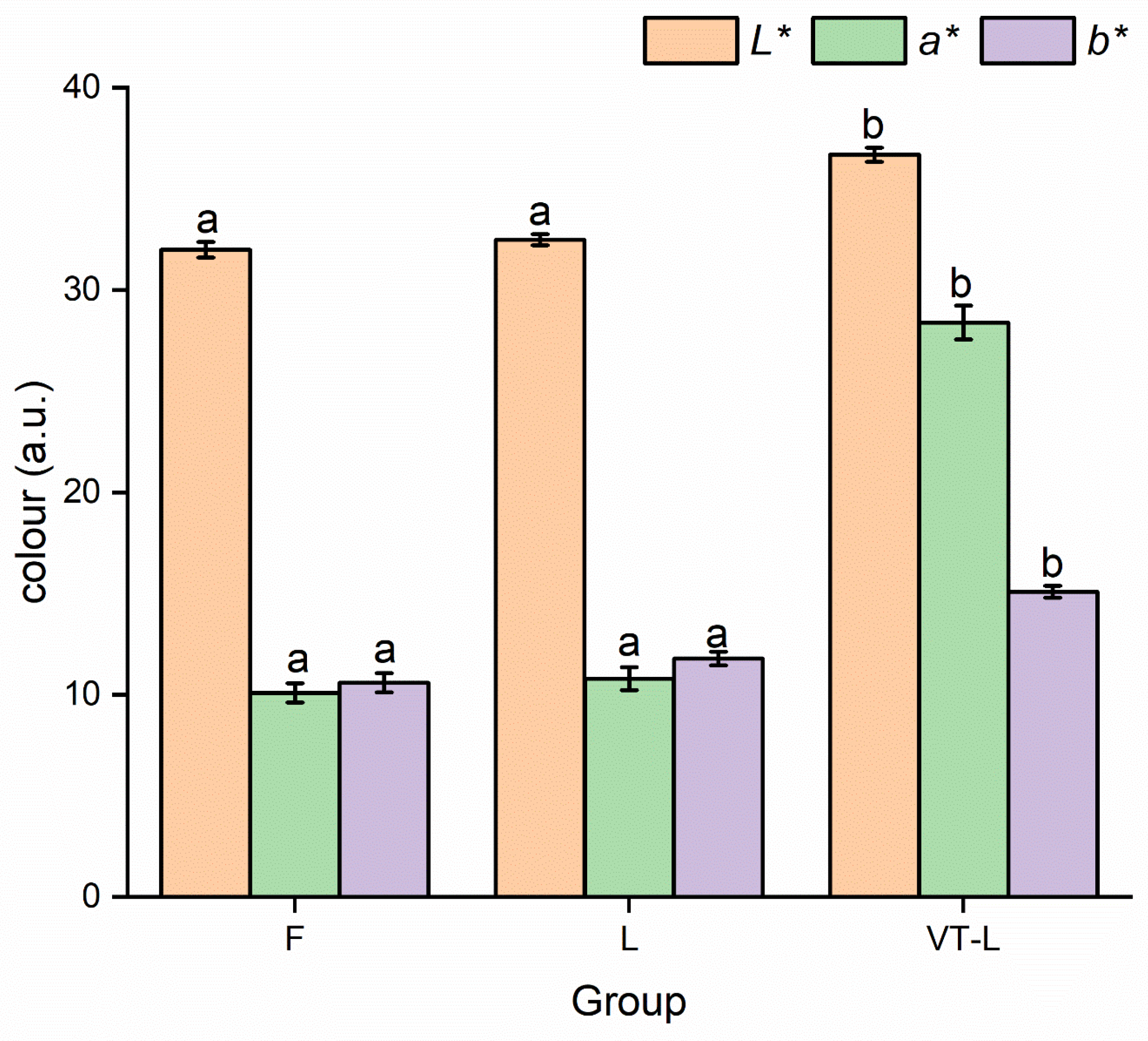
3.3. Color
3.4. Texture Profile Analysis and Shear Force
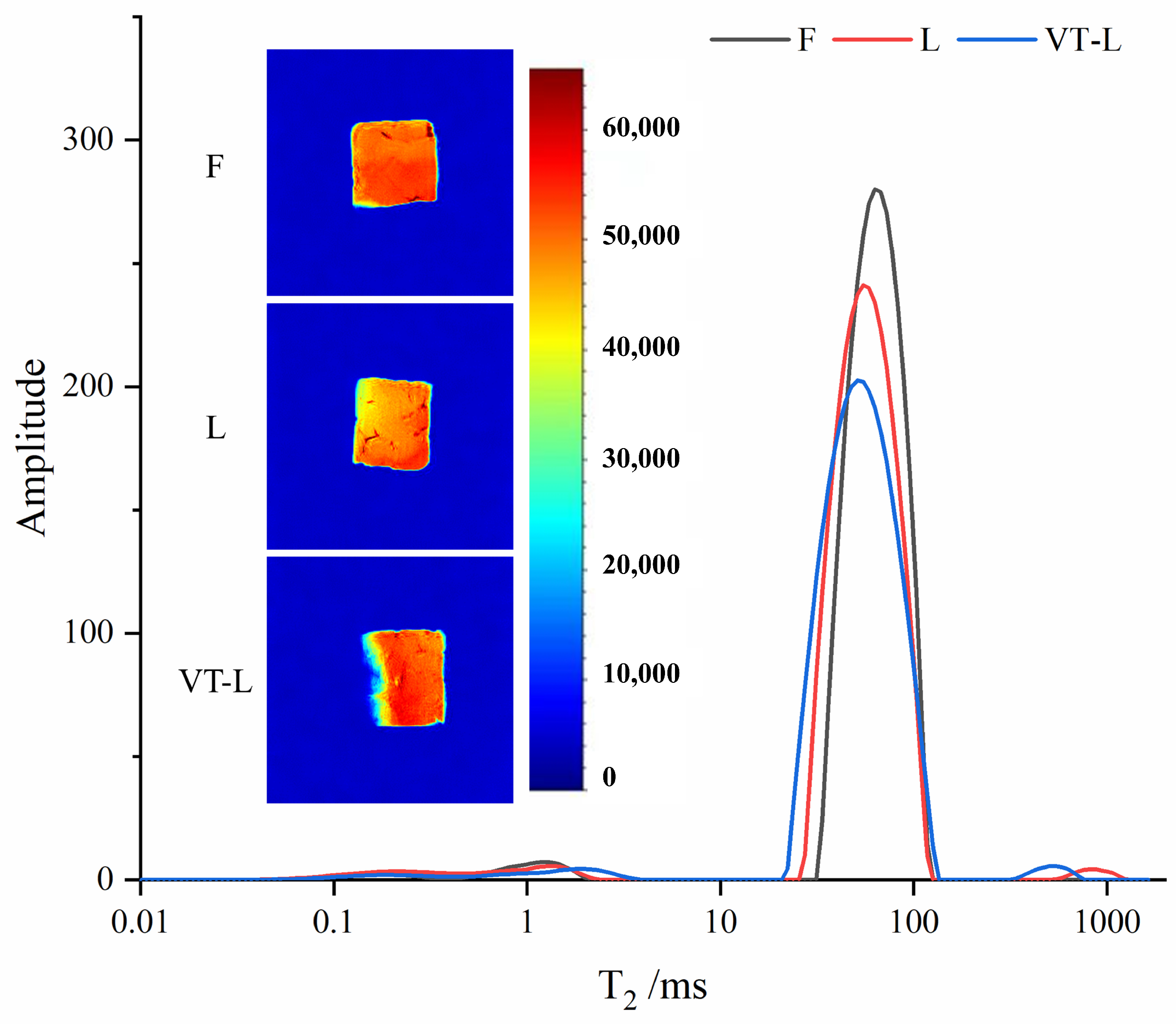
3.5. LF-NMR and MRI
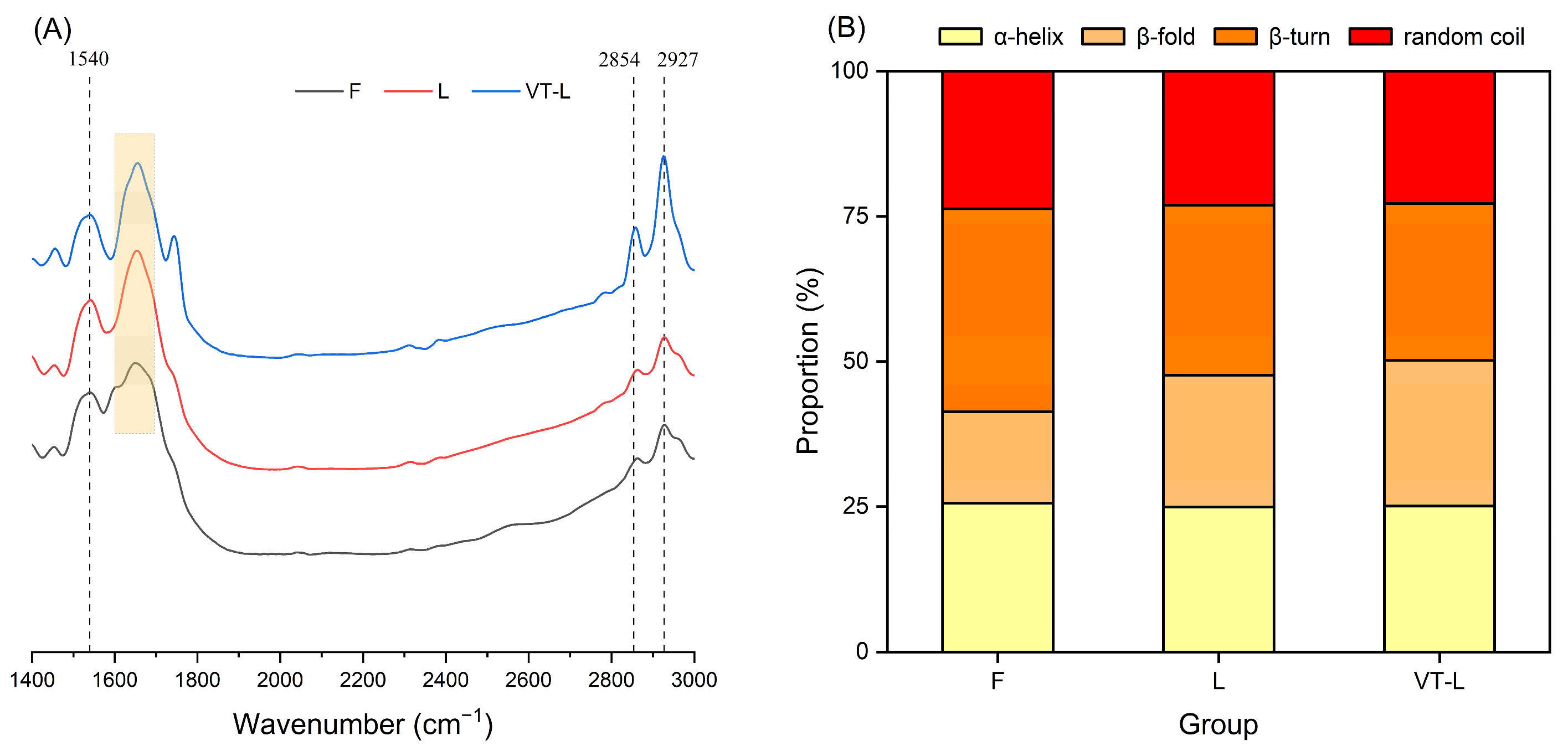
3.6. FT-IR
3.7. Histological Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Ju, R.; Mujumdar, A.S.; Wang, H. Advances in Prepared Dish Processing Using Efficient Physical Fields: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 4031–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peñaranda, I.; Egea, M.; Linares, M.B.; López, M.B.; Garrido, M.D. Marinade Injection of Pork as a Possible Technological Strategy to Reduce Boar Taint: Response and Attitude of the Consumer. Meat Sci. 2024, 212, 109462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusop, S.M.; O’Sullivan, M.G.; Kerry, J.F.; Kerry, J.P. Influence of Processing Method and Holding Time on the Physical and Sensory Qualities of Cooked Marinated Chicken Breast Fillets. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsanur Rahman, S.M.; Islam, S.; Pan, J.; Kong, D.; Xi, Q.; Du, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Oh, D.-H.; Han, R. Marination Ingredients on Meat Quality and Safety—A Review. Food Qual. Saf. 2023, 7, fyad027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serdaroglu, M.; Yüncü-Boyacı, Ö.; Karaman, M. Enhancing Meat Quality through Marination: Principle, Ingredients and Effects. Food Sci. Appl. Biotechnol. 2024, 7, 162–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinton, M.B.; dos Santos, B.A.; Correa, L.P.; Leães, Y.S.V.; Cichoski, A.J.; Lorenzo, J.M.; dos Santos, M.; Pollonio, M.A.R.; Campagnol, P.C.B. Ultrasound and Low-Levels of NaCl Replacers: A Successful Combination to Produce Low-Phosphate and Low-Sodium Meat Emulsions. Meat Sci. 2020, 170, 108244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vişan, V.-G.; Chiş, M.S.; Păucean, A.; Mureșan, V.; Pușcaș, A.; Stan, L.; Vodnar, D.C.; Dulf, F.V.; Țibulcă, D.; Vlaic, B.A.; et al. Influence of Marination with Aromatic Herbs and Cold Pressed Oils on Black Angus Beef Meat. Foods 2021, 10, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Bowker, B.; Yang, Y.; Pang, B.; Yu, X.; Tasoniero, G.; Zhuang, H. Water Properties and Marinade Uptake in Broiler Pectoralis Major with the Woody Breast Condition. Food Chem. 2022, 391, 133230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Wu, T.; Wu, J.; Chang, R.; Lan, X.; Wei, K.; Jia, X. Effects of Cations on the “Salt in” of Myofibrillar Proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 58, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudette, N.J.; Pickering, G.J. Modifying Bitterness in Functional Food Systems. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 464–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zheng, B.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H. Saltiness Perception Mechanism and Salt Reduction Strategies in Food. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 148, 104521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Zheng, M.; Zhou, F.; Hou, G.; Zou, Z.; Miao, S.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, B. SPI/SA Microgels Prepared by Phase Separation Improved the Water Retention and Sensory Perception of Low-Salt Pork Gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 156, 110370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Huang, X.; Chen, X.; Cai, X.; Huang, J.; Vincent, G.; Wang, S. Advances in Flavor Peptides with Sodium-Reducing Ability: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2023, 64, 9568–9584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, T.; Huang, S.; Yang, Y.; Hu, A.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, W. A Review of the World’s Salt Reduction Policies and Strategies—Preparing for the Upcoming Year 2025. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 2836–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, S.K.; Singh, K.; Sanghvi, S.; Loyo-Celis, V.; Varghese, L.; Singh, E.R.; Gururaja Rao, S.; Singh, H. Chloride Ions in Health and Disease. Biosci. Rep. 2024, 44, BSR20240029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Zheng, M.; Hou, G.; Zhou, F.; Deng, K.; Miao, S.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, B. Enhanced Gelation Properties and Saltiness Perception of Low-Salt Surimi Gel with Psyllium Husk Powder. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 28157–28166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, V.A.S.; Paglarini, C.S.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Pollonio, M.A.R. Salted Meat Products: Nutritional Characteristics, Processing and Strategies for Sodium Reduction. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 39, 2183–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, R.; Pateiro, M.; Pérez-Santaescolástica, C.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Lorenzo, J.M. Salt Reduction Strategies in Meat Products Made from Whole Pieces. In Strategies for Obtaining Healthier Foods; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 267–289. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Tang, X.; Chen, Y.; You, Y. Chemical Forces Study of Heat-Induced Myofibrillar Protein Gel as Affected by Partial Substitution of NaCl with KCl, MgCl2 and CaCl2. CyTA J. Food 2016, 14, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.M.; Jung, K.C.; Jo, H.M.; Nam, K.W.; Choe, J.H.; Rhee, M.S.; Kim, B.C. Combined Effects of Potassium Lactate and Calcium Ascorbate as Sodium Chloride Substitutes on the Physicochemical and Sensory Characteristics of Low-Sodium Frankfurter Sausage. Meat Sci. 2014, 96, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Shen, H.; Wang, D.; Liu, S.; Ding, Y.; Zhou, X. Novel NaCl Reduction Technologies for Dry-Cured Meat Products and Their Mechanisms: A Comprehensive Review. Food Chem. 2024, 431, 137142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wan, J.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, K.; Zhu, Q.; Tang, P.; Xu, S.; Song, L. Proteome Profile of Glycrol-Mediated Salt-Reduction Cured Meat Reveals the Formation Mechanism of Eating Quality. Food Chem. 2022, 382, 132395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Ma, X.; Huang, Y.; Lin, B.; Zhang, L.; Miao, S.; Zheng, B.; Deng, K. Comprehensive Effects of Potassium Lactate, Calcium Ascorbate and Magnesium Chloride as Alternative Salts on Physicochemical Properties, Sensory Characteristics and Volatile Compounds in Low-Sodium Marinated Beef. Foods 2024, 13, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, X.-H.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Li, S.; Dong, X.; Qin, L. Effect of Sodium Salt on Meat Products and Reduction Sodium Strategies—A Review. Meat Sci. 2023, 205, 109296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertram, H.C.; Wu, Z.; Straadt, I.K.; Aagaard, M.; Aaslyng, M.D. Effects of Pressurization on Structure, Water Distribution, and Sensory Attributes of Cured Ham: Can Pressurization Reduce the Crucial Sodium Content? J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 9912–9917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Luo, J.; Lou, A.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D.; Shen, Q.W. Duck Breast Muscle Proteins, Free Fatty Acids and Volatile Compounds as Affected by Curing Methods. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 128138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, L.S.; Sun, D.-W. Feasibility of Water Immersion Cooking of Beef Joints: Effect on Product Quality and Yield. J. Food Eng. 2006, 77, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffin, T.E.; Smith, M.A.; Bush, R.D.; Morris, S.; Hopkins, D.L. The Effect of Whole Carcase Medium Voltage Electrical Stimulation, Tenderstretching and Longissimus Infusion with Actinidin on Alpaca Meat Quality. Meat Sci. 2020, 164, 108107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U-Chupaj, J.; Malila, Y.; Gozzi, G.; Vannini, L.; Dellarosa, N.; Laghi, L.; Petracci, M.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W. Influence of Non-phosphate and Low-sodium Salt Marination in Combination with Tumbling Process on Properties of Chicken Breast Meat Affected by White Striping Abnormality. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, C.; Ramírez, C.; Núñez, H.; Jaques, A.; Simpson, R. Application of Vacuum Impregnation and CO2-Laser Microperforations in the Potential Acceleration of the Pork Marinating Process. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 66, 102500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, G.R.V.B.; Surasani, V.K.R.; Amaravathi, P.; Mandal, P.K.; Desai, A.S.; Sen, A.R. Influence of Whey Protein Concentrates as a Novel Binder on Physiochemical, Textural and Ultrastructural Properties of Restructured Buffalo Meat Slices. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 6362–6371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzudie, T.; Okubanjo, A. Effects of Rigor State and Tumbling Time on Quality of Goat Hams. J. Food Eng. 1999, 42, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toldrá, F. Lawrie’s Meat Science, 9th ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2022; ISBN 0-323-98453-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ruusunen, M.; Puolanne, E. Reducing Sodium Intake from Meat Products. Meat Sci. 2005, 70, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bower, C.G.; Stanley, R.E.; Fernando, S.C.; Sullivan, G.A. The Effect of Salt Reduction on the Microbial Community Structure and Quality Characteristics of Sliced Roast Beef and Turkey Breast. LWT 2018, 90, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horita, C.N.; Morgano, M.A.; Celeghini, R.M.S.; Pollonio, M.A.R. Physico-Chemical and Sensory Properties of Reduced-Fat Mortadella Prepared with Blends of Calcium, Magnesium and Potassium Chloride as Partial Substitutes for Sodium Chloride. Meat Sci. 2011, 89, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Shi, J.; Zhou, C.; Huang, X.; Zhai, X.; Yang, Z.; Li, Z.; Hu, X.; Li, Y.; Xiao, J.; et al. Effects of Sodium Chloride Substitutes on Physicochemical Properties of Salted Beef. Food Chem. X 2023, 20, 100885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Guo, X.; Fu, C.; Wang, J.; Meng, X.; Hui, T.; Peng, Z. Effect of Ultrasound-Assisted L-Lysine Treatment on Pork Meat Quality and Myofibrillar Protein Properties during Postmortem Aging. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 4162–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wachirasiri, K.; Wanlapa, S.; Uttapap, D.; Rungsardthong, V. Use of Amino Acids as a Phosphate Alternative and Their Effects on Quality of Frozen White Shrimps (Penaeus vanamei). LWT food Sci. Technol. 2016, 69, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Bai, X.; Wang, K.; Ru, A.; Xu, L.; Tian, W.; Hao, J.; Zhu, C.; Zhao, G. Mechanism of Tumbling-Curing to Improve Beef Quality: Insights from the Structural and Functional Properties of Myofibrillar Protein. LWT 2024, 207, 116692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N’Gatta, K.C.A.; Kondjoyan, A.; Favier, R.; Sicard, J.; Rouel, J.; Gruffat, D.; Mirade, P.-S. Impact of Combining Tumbling and Sous-Vide Cooking Processes on the Tenderness, Cooking Losses and Colour of Bovine Meat. Processes 2022, 10, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagnol, P.C.B.; dos Santos, B.A.; Morgano, M.A.; Terra, N.N.; Pollonio, M.A.R. Application of Lysine, Taurine, Disodium Inosinate and Disodium Guanylate in Fermented Cooked Sausages with 50% Replacement of NaCl by KCl. Meat Sci. 2011, 87, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, Y.-J.; Yan, X.-L.; Sun, D.-M.; Zhao, Y.-J.; Xu, W.; Zhao, J. Effect of Sorbitol on Water Holding Capacity and Texture of Fermented Sausages as Determined by NMR. Food Sci. 2013, 34, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Holman, B.W.B.; van de Ven, R.J.; Mao, Y.; Coombs, C.E.O.; Hopkins, D.L. Using Instrumental (CIE and Reflectance) Measures to Predict Consumers’ Acceptance of Beef Colour. Meat Sci. 2017, 127, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewthong, P.; Waiyagan, K.; Wattanachant, S. Imaging Analysis by Digital Camera for Separating Broiler Breast Meat with Low Water-Holding Capacity. J. Poult. Sci. 2017, 54, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uyarcan, M.; Kayaardi, S. Effects of High Pressure and Marination Treatment on Texture, Myofibrillar Protein Structure, Color and Sensory Properties of Beef Loin Steaks. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2019, 31, 573–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wu, W.; Ma, C.; Li, X.; Dai, R. Postmortem Changes in Sarcoplasmic Proteins Associated with Color Stability in Lamb Muscle Analyzed by Proteomics. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2016, 242, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zhou, G.-H.; Xu, X.-L.; Li, C.-B. Study on Kinetics of Mass Transfer in Water-Boiled Salted Duck during Wet-Curing. J. Food Eng. 2010, 100, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, R.O.; Ockerman, H.W.; Krol, B.; Van Roon, P.S.; Plimpton, R.F., Jr.; Cahill, V.R. Effect of Tumbling Method, Phosphate Level and Final Cook Temperature on Histological Characteristics of Tumbled Porcine Muscle Tissue. J. Food Sci. 1978, 43, 1514–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachowicz, K.; Sobczak, M.; Gajowiecki, L.; Zych, A. Effects of Massaging Time on Texture, Rheological Properties, and Structure of Three Pork Ham Muscles. Meat Sci. 2003, 63, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekhit, A.E.-D.A.; Carne, A.; Ha, M.; Franks, P. Physical Interventions to Manipulate Texture and Tenderness of Fresh Meat: A Review. Int. J. Food Prop. 2014, 17, 433–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktaş, N.; Kaya, M. Influence of Weak Organic Acids and Salts on the Denaturation Characteristics of Intramuscular Connective Tissue. A Differential Scanning Calorimetry Study. Meat Sci. 2001, 58, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Aung, S.H.; Abeyrathne, E.D.N.S.; Park, J.-Y.; Jung, J.H.; Jang, A.; Jeong, J.Y.; Nam, K.-C. Quality Enhancement of Frozen Chicken Meat Marinated with Phosphate Alternatives. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2023, 43, 245–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Huang, Y.; Chen, L.; Bao, P.; Fang, H.; Zhou, C. L-Arginine and L-Lysine Degrade Troponin-T, and L-Arginine Dissociates Actomyosin: Their Roles in Improving the Tenderness of Chicken Breast. Food Chem. 2020, 318, 126516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triyannanto, E.; Lee, K.T. Evaluation of Honey and Rice Syrup as Replacements for Sorbitol in the Production of Restructured Duck Jerky. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 29, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Wen, Q.-H.; Rahaman, A.; Zeng, X.-A. Effects of Pulsed Electric Field Pretreatment on Mass Transfer and Quality of Beef during Marination Process. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 80, 103061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, Z.; Lu, W.; Zhou, X.; Liu, S.; Zhu, S.; Ding, Y. Improving the Texture Attributes of Squid Meat (Sthenoteuthis oualaniensis) with Slight Oxidative and Phosphate Curing Treatments. Food Res. Int. 2024, 176, 113829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Yin, F.; Tian, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, G. Application of a Pressure-Transform Tumbling Assisted Curing Technique for Improving the Tenderness of Restructured Pork Chops. LWT 2019, 111, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Wu, J.; Shao, J.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G. Effect of Partially Substituting NaCl with KCl or MgCl2 on Emulsion Gel Properties of Pork Myofibrillar Protein. Food Sci. 2014, 35, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertram, H.C.; Karlsson, A.H.; Rasmussen, M.; Pedersen, O.D.; Dønstrup, S.; Andersen, H.J. Origin of Multiexponential T 2 Relaxation in Muscle Myowater. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 3092–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, R.H.; Andersen, H.J.; Bertram, H.C. Curing-Induced Water Mobility and Distribution within Intra- and Extra-Myofibrillar Spaces of Three Pork Qualities. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 42, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aursand, I.G.; Erikson, U.; Veliyulin, E. Water Properties and Salt Uptake in Atlantic Salmon Fillets as Affected by Ante-Mortem Stress, Rigor Mortis, and Brine Salting: A Low-Field 1H NMR and 1H/23Na MRI Study. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böcker, U.; Ofstad, R.; Wu, Z.; Bertram, H.C.; Sockalingum, G.D.; Manfait, M.; Egelandsdal, B.; Kohler, A. Revealing Covariance Structures in Fourier Transform Infrared and Raman Microspectroscopy Spectra: A Study on Pork Muscle Fiber Tissue Subjected to Different Processing Parameters. Appl. Spectrosc. 2007, 61, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Martínez, M.; Gallardo-Velázquez, T.; Osorio-Revilla, G.; Almaraz-Abarca, N.; Castañeda-Pérez, E. Application of MIR-FTIR Spectroscopy and Chemometrics to the Rapid Prediction of Fish Fillet Quality. CyTA J. Food 2014, 12, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.; Ji, Y.; Pan, H.; Sun, Z.; Li, Y.; Qin, G. Characterization of Thermal Denaturation Structure and Morphology of Soy Glycinin by FTIR and SEM. Int. J. Food Prop. 2015, 18, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellows, A.P.; Casford, M.T.L.; Davies, P.B. Spectral Analysis and Deconvolution of the Amide I Band of Proteins Presenting with High-Frequency Noise and Baseline Shifts. Appl. Spectrosc. 2020, 74, 597–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cando, D.; Herranz, B.; Borderías, A.J.; Moreno, H.M. Different Additives to Enhance the Gelation of Surimi Gel with Reduced Sodium Content. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- N’Gatta, K.C.A.; Kondjoyan, A.; Favier, R.; Rouel, J.; Vénien, A.; Astruc, T.; Gruffat, D.; Mirade, P.-S. Impact of Tumbling Process on the Toughness and Structure of Raw Beef Meat Pieces. Foods 2021, 10, 2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasulya, O.; Tsirulnichenko, L.; Potoroko, I.; Bogush, V.; Novikova, Z.; Sergeev, A.; Kuznetsova, T.; Anandan, S. The Study of Changes in Raw Meat Salting Using Acoustically Activated Brine. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 50, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahey, A.J.; Brameld, J.M.; Parr, T.; Buttery, P.J. The Effect of Maternal Undernutrition before Muscle Differentiation on the Muscle Fiber Development of the Newborn Lamb1,2. J. Anim. Sci. 2005, 83, 2564–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soji, Z. Effect of the Muscle Nanostructure Changes during Post-Mortem Aging on Tenderness of Different Beef Breeds. Anim. Biosci. 2021, 34, 1849–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Group | Solid–Liquid Ratio | Marinade Ingredients/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NaCl | K-Lactate | MgCl2 | Ca-Ascorbate | Lys | Sorbitol | ||
| F | 1:2 | 4 | - | - | - | - | - |
| L | 1:2 | 2.4 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 4 |
| VT-L | 10:3 | 2.4 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 4 |
| Groups | Hardness/N | Cohesiveness | Springiness/mm | Chewiness/mj | Shear Force/N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | 30.2 ± 0.04 c | 0.5 ± 0.00 a | 1.7± 0.03 a | 24.0± 0.36 c | 47.6 ± 0.46 a |
| L | 21.3 ± 0.72 b | 0.5 ± 0.02 a | 1.9 ± 0.09 a | 18.4 ± 0.55 b | 45.1 ± 0.46 a |
| VT-L | 17.9 ± 0.27 a | 0.4 ± 0.01 a | 1.8 ± 0.10 a | 14.3 ± 0.97 a | 39.7 ± 0.19 b |
| Groups | T2/ms | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T20 | T21 | T22 | T23 | |
| F | 0.68 ± 0.12 a | 1.17 ± 0.12 a | 58.87 ± 4.08 b | - |
| L | 0.19 ± 0.02 a | 1.34 ± 0.05 a | 54.79 ± 0.00 ab | 821.43 ± 0.00 b |
| VT-L | 0.43 ± 0.18 a | 1.73 ± 0.30 a | 51.11 ± 0.00 a | 554.57 ± 12.98 a |
| Groups | Absorbance/a.u. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1540 cm−1 | 2854 cm−1 | 2927 cm−1 | |
| F | 0.687 ± 0.004 b | 0.807 ±0.004 b | 0.749 ± 0.004 b |
| L | 0.663 ± 0.009 a | 0.789 ± 0.005 b | 0.722 ± 0.008 b |
| VT-L | 0.717 ± 0.005 c | 0.748 ± 0.007 a | 0.634 ± 0.006 a |
| Groups | Muscle Fiber Area/μm2 | Muscle Fiber Diameter/μm | Muscle Fiber Density/μm |
|---|---|---|---|
| F | 3695.94 ± 44.73 a | 7.98 ± 0.07 b | 110.00 ± 3.89 b |
| L | 2351.85 ± 33.58 b | 6.83 ± 0.08 a | 153.75 ± 2.10 c |
| VT-L | 3282.96 ± 63.08 a | 7.15 ± 0.15 a | 80.00 ± 1.15 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, L.; Miao, S.; Xu, Z.; Zheng, B.; Deng, K. Combined Effects of Compound Low-Sodium Alternative Salts and Vacuum Tumbling on the Quality, Water Distribution, and Microstructure of Marinated Beef. Foods 2025, 14, 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14040605
Huang Y, Yang S, Zhang L, Miao S, Xu Z, Zheng B, Deng K. Combined Effects of Compound Low-Sodium Alternative Salts and Vacuum Tumbling on the Quality, Water Distribution, and Microstructure of Marinated Beef. Foods. 2025; 14(4):605. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14040605
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yanfeng, Shujie Yang, Longtao Zhang, Song Miao, Zhiyong Xu, Baodong Zheng, and Kaibo Deng. 2025. "Combined Effects of Compound Low-Sodium Alternative Salts and Vacuum Tumbling on the Quality, Water Distribution, and Microstructure of Marinated Beef" Foods 14, no. 4: 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14040605
APA StyleHuang, Y., Yang, S., Zhang, L., Miao, S., Xu, Z., Zheng, B., & Deng, K. (2025). Combined Effects of Compound Low-Sodium Alternative Salts and Vacuum Tumbling on the Quality, Water Distribution, and Microstructure of Marinated Beef. Foods, 14(4), 605. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14040605








