Assessment of Radiation Exposure in a Nuclear Medicine Department during 99mTc-MDP Bone Scintigraphy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Methodology
2.2. The 99mTc Radionuclide Decay over Time
2.3. Statistical Analysis
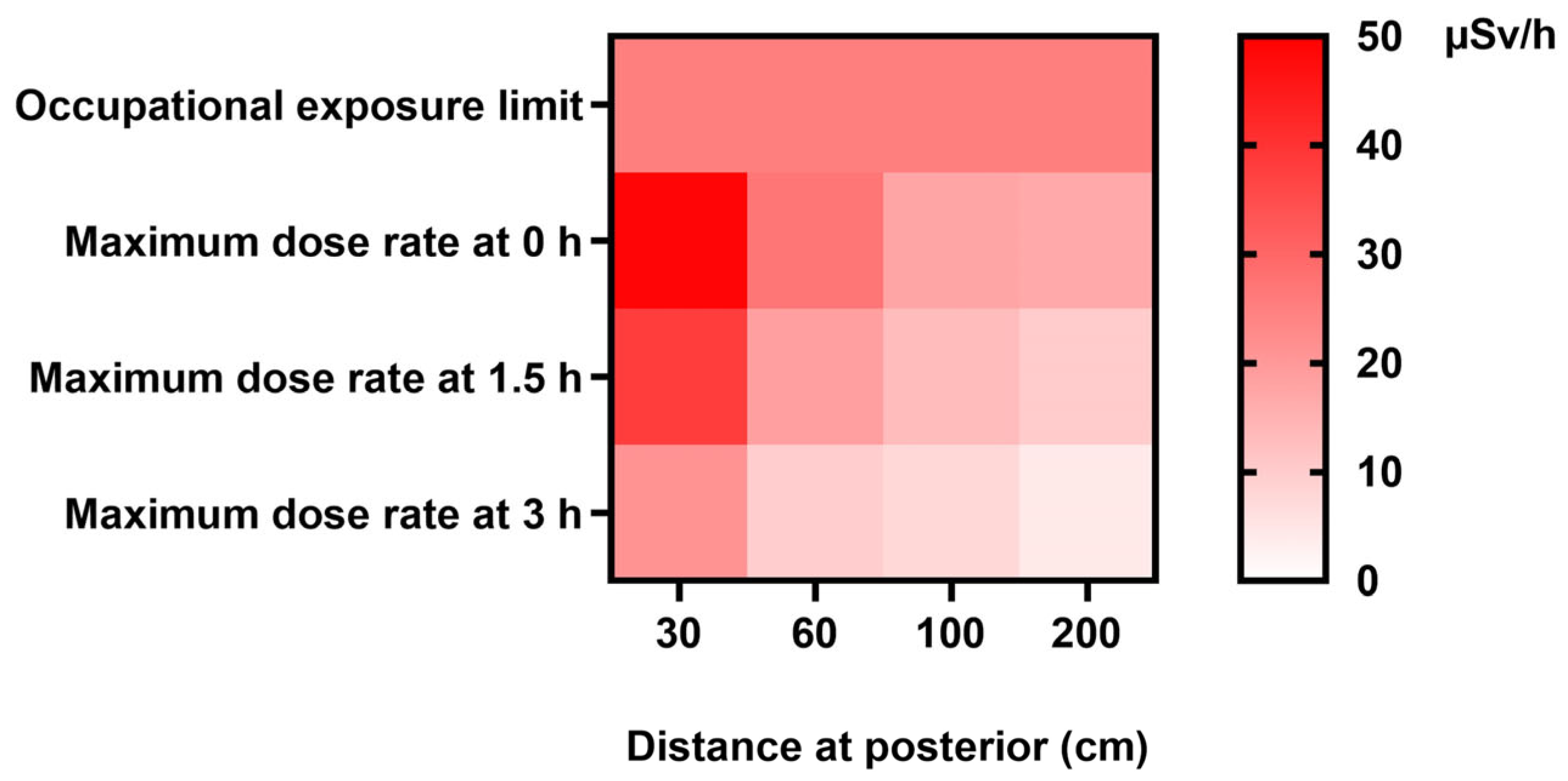
3. Results
3.1. Mean Radiation Doses at Different Times and Distances on the Left Lateral, Right Lateral, Anterior, and Posterior Positions
3.2. Occupational Radiation Risks from 99mTc-MDP
3.3. Forecasting Dose Rate based on Distance and Time after Injection: Exponential Regression Analysis
3.4. Patient Discharge Comparison with Public Exposure Limit from 99mTc-MDP
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brambilla, M.; Vassileva, J.; Kuchcinska, A.; Rehani, M.M. Multinational Data on Cumulative Radiation Exposure of Patients from Recurrent Radiological Procedures: Call for Action. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 2493–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassileva, J.; Holmberg, O. Radiation Protection Perspective to Recurrent Medical Imaging: What Is Known and What More Is Needed? Br. J. Radiol. 2021, 94, 20210477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehani, M.M.; Yang, K.; Melick, E.R.; Heil, J.; Šalát, D.; Sensakovic, W.F.; Liu, B. Patients Undergoing Recurrent CT Scans: Assessing the Magnitude. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 1828–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protection, R. ICRP Publication 103. Ann. ICRP 2007, 37, 2. [Google Scholar]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection. General Principles for the Radiation Protection of Workers: Adopted by the Commission in January 1997; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1997; ISBN 0-08-042741-3. [Google Scholar]
- Khamtuikrua, C.; Suksompong, S. Awareness about Radiation Hazards and Knowledge about Radiation Protection among Healthcare Personnel: A Quaternary Care Academic Center–Based Study. SAGE Open Med. 2020, 8, 2050312120901733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, C.; Din, A.S.; Tomas, M.B.; Kalapparambath, T.P.; Palestro, C.J. Radionuclide Bone Imaging: An Illustrative Review. Radiographics 2003, 23, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabakov, S.; Milano, F.; Stoeva, M.S.; Sprawls, P.; Tipnis, S.; Underwood, T. Encyclopaedia of Medical Physics: Two Volume Set; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; ISBN 0-429-95348-8. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, A.T. Radionuclides in Nephrourology, Part 1: Radiopharmaceuticals, Quality Control, and Quantitative Indices. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsini, F.; Puta, E.; Lorenzoni, A.; Erba, P.; Mariani, G. Single-Photon-Emitting Radiopharmaceuticals for Diagnostic Applications. In Nuclear Oncology: From Pathophysiology to Clinical Applications; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 67–84. ISBN 3-319-26234-3. [Google Scholar]
- Shulkin, B.L.; Mandell, G.A.; Cooper, J.A.; Leonard, J.C.; Majd, M.; Parisi, M.T.; Sfakianakis, G.N.; Balon, H.R.; Donohoe, K.J. Procedure Guideline for Diuretic Renography in Children 3.0. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2008, 36, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stagi, S.; Cavalli, L.; Iurato, C.; Seminara, S.; Brandi, M.L.; de Martino, M. Bone Metabolism in Children and Adolescents: Main Characteristics of the Determinants of Peak Bone Mass. Clin. Cases Miner. Bone Metab. 2013, 10, 172. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Wyngaert, T.; Strobel, K.; Kampen, W.; Kuwert, T.; Van der Bruggen, W.; Mohan, H.; Gnanasegaran, G.; Delgado-Bolton, R.; Weber, W.; Beheshti, M. The EANM Practice Guidelines for Bone Scintigraphy. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2016, 43, 1723–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattsson, S.; Johansson, L.; Leide Svegborn, S.; Liniecki, J.; Noßke, D.; Riklund, K.; Stabin, M.; Taylor, D.; Bolch, W.; Carlsson, S. ICRP Publication 128: Radiation Dose to Patients from Radiopharmaceuticals: A Compendium of Current Information Related to Frequently Used Substances. Ann. ICRP 2015, 44, 7–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattar, E.H. Assessment of Patient and Staff Annual Effective Doses at a Nuclear Medicine Department during Bone Scans. Open J. Radiol. 2022, 12, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, A.M.; Serulle, Y.; Wagner, S.; Noz, M.E.; Friedman, K. Quantifying the Increase in Radiation Exposure Associated with SPECT/CT Compared to SPECT Alone for Routine Nuclear Medicine Examinations. Int. J. Mol. Imaging 2011, 2011, 897202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mettler, F.A., Jr.; Huda, W.; Yoshizumi, T.T.; Mahesh, M. Effective Doses in Radiology and Diagnostic Nuclear Medicine: A Catalog. Radiology 2008, 248, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günay, O.; Sarihan, M.; Abamor, E.; Yarar, O. Environmental Radiation Doses from Patients Undergoing Tc-99m DMSA Cortical Renal Scintigraphy. Int. J. Comput. Exp. Sci. Eng. (IJCESEN) 2019, 5, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckerman, K.; Harrison, J.; Menzel, H.; Clement, C. ICRP Publication 119: Compendium of Dose Coefficients Based on ICRP Publication 60. Ann. ICRP 2012, 41, 1–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, M.; Fogelman, I. 99m Tc Diphosphonate Uptake Mechanism on Bone. In Bone Scanning in Clinical Practice; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1987; pp. 7–17. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, G.; Moore, A.; Park-Holohan, S.-J.; Fogelman, I. A Directin Vivomeasurement of 99mTc-Methylene Diphosphonate Protein Binding. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2003, 24, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, D.L.; Humm, J. Nuclear Medicine Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2014; ISBN 92-0-143810-9. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. International Basic Safety Standards for Protection against Ionizing Radiation and for the Safety of Radiation Sources; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Safety, IAEA Occupational Radiation Protection Program. Guide GSG-7; International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Guide, S.S. Radiation Protection and Safety in Medical Uses of Ionizing Radiation; IAEA Safety Standards Series No. SSG-46; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Moore Jr, R.M.; Kaczmarek, R.G. Occupational Hazards to Health Care Workers: Diverse, Ill-Defined, and Not Fully Appreciated. Am. J. Infect. Control 1990, 18, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asuero, A.G.; Sayago, A.; González, A. The Correlation Coefficient: An Overview. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2006, 36, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R. Interpretation of the Correlation Coefficient: A Basic Review. J. Diagn. Med. Sonogr. 1990, 6, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisstein, E.W. Correlation Coefficient. 2006. Available online: https://mathworld.wolfram.com/ (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Carey, J.E.; Kumpuris, T.M.; Wrobel, M.C. Release of Patients Containing Therapeutic Dosages of Iodine-131 from Hospitals. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 1995, 23, 144–149. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.Y. Radiation Protection and Regulations for the Nuclear Medicine Physician; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 44, pp. 215–228. [Google Scholar]
- Kocher, D. Environmental Radiation Standards; Oak Ridge National Lab.: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Soelberg, N.R.; Garn, T.G.; Greenhalgh, M.R.; Law, J.D.; Jubin, R.; Strachan, D.M.; Thallapally, P.K. Radioactive Iodine and Krypton Control for Nuclear Fuel Reprocessing Facilities. Sci. Technol. Nucl. Install. 2013, 2013, 702496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jubin, R.T.; Soelberg, N.R.; Strachan, D.M.; Ilas, G. Fuel Age Impacts on Gaseous Fission Product Capture during Separations; Pacific Northwest National Lab. (PNNL): Richland, WA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cool, D.; Peterson, H., Jr. Standards for Protection against Radiation, 10 CFR Part 20; US Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC): Washington, DC, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, C.G. The US Nuclear Regulatory Commission Radiation Protection Policy and Opportunities for the Future. J. Radiol. Prot. 2019, 39, R51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klemic, G. Environmental Radiation Monitoring in the Context of Regulations on Dose Limits to the Public; US Department of Energy Environmental Measurements Lab.: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, F.D.; Fahey, F.H.; Packard, A.B.; Davis, R.T.; Alavi, A.; Treves, S.T. Skeletal PET with 18F-Fluoride: Applying New Technology to an Old Tracer. J. Nucl. Med. 2008, 49, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Chen, W.; Sun, T.; Duan, S.; Jia, B.; Zhang, H. Estimated Cosmic Radiation Doses for Flight Personnel. Hang Tian Yi Xue Yu Yi Xue Gong Cheng = Space Med. Med. Eng. 2002, 15, 265–269. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, J.; Balonov, M.; Bochud, F.; Martin, C.; Menzel, H.; Ortiz-Lopez, P.; Smith-Bindman, R.; Simmonds, J.; Wakeford, R. ICRP Publication 147: Use of Dose Quantities in Radiological Protection. Ann. ICRP 2021, 50, 9–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauptmann, M.; Byrnes, G.; Cardis, E.; Bernier, M.-O.; Blettner, M.; Dabin, J.; Engels, H.; Istad, T.S.; Johansen, C.; Kaijser, M. Brain Cancer after Radiation Exposure from CT Examinations of Children and Young Adults: Results from the EPI-CT Cohort Study. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.J.; Choi, Y.; Ko, S.; Cha, E.S.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.M.; Kong, K.A.; Seo, S.; Bang, Y.J.; Ha, Y.W. Projected Lifetime Cancer Risks from Occupational Radiation Exposure among Diagnostic Medical Radiation Workers in South Korea. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkey, A.R.; Gambhir, P.; Saraskani, S.; Walker, R.; Hajilou, A.; Bassett, P.; Sandhu, N.; Croasdale, P.; Honey, I.; Diamantopoulos, A. Occupational Radiation Exposure in Doctors: An Analysis of Exposure Rates over 25 Years. Br. J. Radiol. 2021, 94, 20210602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, D.Z.; Lacasse, M.C.; Khan, R.; Murphy, K.J. Radiation Cataractogenesis: The Progression of Our Understanding and Its Clinical Consequences. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2017, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, S.G.; Hamada, N. Individual Response of the Ocular Lens to Ionizing Radiation. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2022, 99, 138–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathy, M.; Khalil, M.M.; Elshemey, W.M.; Mohamed, H.S. Occupational Radiation Dose to Nuclear Medicine Staff Due to Tc99m, F18-FDG PET and Therapeutic I-131 Based Examinations. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2019, 186, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Esaei, A.M.; Khalil, M.M.; El Shazly, R.M.; Kany, A.M.; Saleh, E.E.; Elmaghraby, S. Assessment of Radiation Exposure Dose for Nuclear Medicine Workers from 18F-FDG, 99mTc MDP, and 99mTc. Curr. Radiopharm. 2022, 15, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zuckier, L.S.; Martineau, P. Altered Biodistribution of Radiopharmaceuticals Used in Bone Scintigraphy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 45, pp. 81–96. [Google Scholar]
- Peller, P.; Ho, V.B.; Kransdorf, M. Extraosseous Tc-99m MDP Uptake: A Pathophysiologic Approach. Radiographics 1993, 13, 715–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolus, N.E. Review of Common Occupational Hazards and Safety Concerns for Nuclear Medicine Technologists. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2008, 36, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aro, I. IAEA Safety Fundamentals: The Safety of Nuclear Installations and the Defence in Depth Concept; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, A.; Memmott, M. UK Audit of Variation in Nuclear Medicine Occupational Exposure Calculations in 2021. J. Radiol. Prot. 2023, 43, 013501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, M.P.; Azizova, T.V.; Richardson, D.B.; Tapio, S.; Bernier, M.-O.; Kreuzer, M.; Cucinotta, F.A.; Bazyka, D.; Chumak, V.; Ivanov, V.K. Ionising Radiation and Cardiovascular Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMJ 2023, 380, e072924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.S.; Husson, O.; Drey, N.; Murray, I.; May, K.; Thurston, J.; Oyen, W.J. Radiation Exposure Awareness from Patients Undergoing Nuclear Medicine Diagnostic 99mTc-MDP Bone Scans and 2-Deoxy-2-(18F) Fluoro-D-Glucose PET/Computed Tomography Scans. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2020, 41, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faggioni, L.; Paolicchi, F.; Bastiani, L.; Guido, D.; Caramella, D. Awareness of radiation protection and dose levels of imaging procedures among medical students, radiography students, and radiology residents at an academic hospital: Results of a comprehensive survey. Eur. J. Radiol. 2017, 86, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Patient Position | Distance from Patient (cm) | Time after the Injection (h) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.5 | 3 | ||
| Mean Dose Rate ± SD (Range) µSv/h | Mean Dose Rate ± SD (Range) µSv/h | Mean Dose Rate ± SD (Range) µSv/h | ||
| Left lateral | 30 | 15.43 ± 5.41 (8.00–44.00) | 9.53 ± 4.87 (3.80–38.00) | 5.09 ± 2.64 (1.99–21.00) |
| 60 | 8.65 ± 3.44 (3.40–18.60) | 4.90 ± 2.14 (2.10–11.90) | 3.06 ± 1.32 (0.99–8.20) | |
| 100 | 5.09 ± 2.81 (1.32–17.00) | 3.13 ± 1.61 (1.34–9.90) | 1.91 ± 0.89 (0.57–4.60) | |
| 200 | 3.12 ± 2.30 (1.04–15.00) | 1.85 ± 1.12 (0.62–7.40) | 1.13 ± 0.64 (0.30–4.00) | |
| Right lateral | 30 | 15.07 ± 3.43 (8.20–27.00) | 8.69 ± 2.99 (4.10–19.60) | 4.82 ± 2.08 (1.90–11.00) |
| 60 | 8.60 ± 2.96 (4.20–18.80) | 4.84 ± 2.03 (2.30–11.60) | 3.02 ± 1.38 (0.93–9.20) | |
| 100 | 4.94 ± 2.58 (2.60–16.50) | 3.00 ± 1.43 (1.42–9.90) | 1.79 ± 0.79 (0.72–3.90) | |
| 200 | 2.92 ± 2.02 (1.25–15.10) | 1.77 ± 1.09 (0.68–7.50) | 1.04 ± 0.53 (0.34–3.00) | |
| Anterior | 30 | 23.35 ± 5.49 (9.90–38.00) | 14.36 ± 4.55 (4.60–32.00) | 7.56 ± 3.23 (2.20–18.70) |
| 60 | 12.44 ± 3.04 (4.60–20.00) | 7.39 ± 2.46 (3.30–18.60) | 4.34 ± 1.51 (1.45–9.80) | |
| 100 | 7.18 ± 3.02 (2.40–17.20) | 4.20 ± 1.87 (1.31–12.40) | 2.62 ± 1.25 (0.89–7.60) | |
| 200 | 3.72 ± 2.60 (1.43–16.50) | 2.28 ± 1.28 (0.78–8.00) | 1.39 ± 0.79 (0.42–4.20) | |
| Posterior | 30 | 24.57 ± 5.03 (6.30–49.00) | 15.47 ± 4.49 (8.00–36.00) | 8.45 ± 3.68 (2.30–20.00) |
| 60 | 13.37 ± 3.73 (4.50–26.80) | 7.71 ± 2.49 (3.00–16.10) | 4.54 ± 1.48 (1.28–9.00) | |
| 100 | 7.50 ± 3.31 (3.30–17.60) | 4.47 ± 1.90 (2.40–13.10) | 2.71 ± 1.04 (0.98–5.70) | |
| 200 | 3.85 ± 2.74 (1.70–16.60) | 2.43 ± 1.47 (0.82–9.90) | 1.46 ± 0.77 (0.41–4.00) | |
| Patient Position | Distance (cm) | Time (h) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.5 | 3 | |||||
| (Exponential Regression) Dose * (μSv/h) | Fold Change from 0 h at 30 cm | (Exponential Regression) Dose * (μSv/h) | Fold Change from 1.5 h at 30 cm | (Exponential Regression) Dose * (μSv/h) | Fold Change from 3 h at 30 cm | ||
| Left lateral | 30 | 12.27 | 7.37 | 4.23 | |||
| 60 | 9.41 | −0.23 | 5.66 | −0.23 | 3.30 | −0.22 | |
| 100 | 6.61 | −0.46 | 3.97 | −0.46 | 2.36 | −0.44 | |
| 200 | 2.73 | −0.78 | 1.64 | −0.78 | 1.03 | −0.76 | |
| Right lateral | 30 | 12.14 | 6.97 | 4.08 | |||
| 60 | 9.23 | −0.24 | 5.36 | −0.23 | 3.15 | −0.23 | |
| 100 | 6.40 | −0.47 | 3.78 | −0.46 | 2.23 | −0.45 | |
| 200 | 2.57 | −0.79 | 1.58 | −0.77 | 0.94 | −0.77 | |
| Anterior | 30 | 18.67 | 11.17 | 6.25 | |||
| 60 | 13.77 | −0.26 | 8.24 | −0.26 | 4.71 | −0.25 | |
| 100 | 9.17 | −0.51 | 5.49 | −0.51 | 3.23 | −0.48 | |
| 200 | 3.32 | −0.82 | 1.99 | −0.82 | 1.25 | −0.80 | |
| Posterior | 30 | 19.80 | 11.87 | 6.75 | |||
| 60 | 14.51 | −0.27 | 8.75 | −0.26 | 5.06 | −0.25 | |
| 100 | 9.59 | −0.52 | 5.83 | −0.51 | 3.44 | −0.49 | |
| 200 | 3.41 | −0.83 | 2.11 | −0.82 | 1.31 | −0.81 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marshall, S.K.; Prom-on, P.; Sangkue, S.; Thiangsook, W. Assessment of Radiation Exposure in a Nuclear Medicine Department during 99mTc-MDP Bone Scintigraphy. Toxics 2023, 11, 814. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11100814
Marshall SK, Prom-on P, Sangkue S, Thiangsook W. Assessment of Radiation Exposure in a Nuclear Medicine Department during 99mTc-MDP Bone Scintigraphy. Toxics. 2023; 11(10):814. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11100814
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarshall, Suphalak Khamruang, Piyatida Prom-on, Siriluck Sangkue, and Wasinee Thiangsook. 2023. "Assessment of Radiation Exposure in a Nuclear Medicine Department during 99mTc-MDP Bone Scintigraphy" Toxics 11, no. 10: 814. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11100814
APA StyleMarshall, S. K., Prom-on, P., Sangkue, S., & Thiangsook, W. (2023). Assessment of Radiation Exposure in a Nuclear Medicine Department during 99mTc-MDP Bone Scintigraphy. Toxics, 11(10), 814. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11100814







