Toxicity of Difenoconazole and Atrazine and Their Photodegradation Products on Aquatic Biota: Environmental Implications in Countries Lacking Good Agricultural Practices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Difenoconazole and Atrazine Photodegradation
2.2. Toxicity Tests with Lemna Minor
2.3. Toxicity Tests with Daphnia Magna
2.4. Data Analysis
| Name | Structure | Formula | m/z | RT | Family | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Difenoconazole |  | C19H17Cl2N3O3 | 405.9 | 6.9 | Triazole | Inhibitor of the biosynthesis of ergosterol in the cellular membrane of fungi [4]. |
| A-Difenoconazole |  | C19H19N3O4 | 354.9 | 2.9 | Triazole | Affects the normal development of aquatic vegetation and reduces chlorophyll production. Affects the mortality of invertebrates (in this study). |
| B-Difenoconazole |  | C19H18ClN3O3 | 370.0 | 5.2 | Triazole | Affects the normal development of aquatic vegetation and reduces chlorophyll production. Affects the mortality of invertebrates (in this study). |
| Atrazine |  | C8H14ClN5 | 215.7 | 19.0 | Triazine | Inhibitors of photosynthetic electron transport [26]. |
| A-Atrazine | 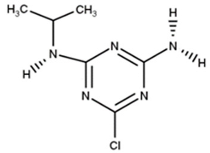 | C6H10ClN5 | 187.0 | 5.5 | Triazine | Affects the normal development of aquatic vegetation and reduces chlorophyll production (in this study). |
3. Results
3.1. Photodegradation of Difenoconazole and Atrazine
3.2. Toxicity Tests with L. minor
3.3. Toxicity Tests with D. magna
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferhi, S.; Vieillard, J.; Garau, C.; Poultier, O.; Demey, L.; Beaulieu, R.; Penalva, P.; Gobert, V.; Portet-Koltalo, F. Pilot-scale direct UV-C photodegradation of pesticides in groundwater and recycled wastewater for agricultural use. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severo, E.S.; Marins, A.T.; Cerezer, C.; Costa, D.; Nunes, M.; Prestes, O.D.; Zanella, R.; Loro, V.L. Ecological risk of pesticide contamination in a Brazilian river located near a rural area: A study of biomarkers using zebrafish embryos. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klementová, Š.; Hornychová, L.; Šorf, M.; Zemanová, J.; Kahoun, D. Toxicity of atrazine and the products of its homogeneous photocatalytic degradation on the aquatic organisms Lemna minor and Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Pollut Res. 2019, 26, 27259–27267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, R.; De Araujo, G.; Rego, A.; Daam, M.; Rocha, O.; Soares, A.; Loureiro, S. Effects of abamectin-based and difenoconazole-based formulations and their mixtures in Daphnia magna: A multiple endpoint approach. Ecotoxicology 2020, 29, 1486–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inticher, J.J.; Cabrera, L.C.; Guimarães, R.E.; Zorzo, C.F.; Pellenz, L.; Seibert, D.; Borba, F.H. Advanced treatment of water contaminated with atrazine, difenoconazole and fipronil mixture, its by-products and bio-toxicity levels. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SGA. Sistema Globalmente Armonizado de Clasificación y Etiquetado de Productos Químicos. 2019. Available online: https://www.un-ilibrary.org/content/books/9789210040853 (accessed on 9 January 2023).
- Tiwari, M.K.; Guha, S. Kinetics of biotransformation of chlorpyrifos in aqueous and soil slurry environments. Water Res. 2014, 51, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OMS. Clasificación Recomendada por la OMS de los Plaguicidas por el Peligro que Presentan; 2019; ISBN 9789240016057. Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/chemical-safety/pesticides/9789240016057-corrigenda-sp.pdf?sfvrsn=539aab18_17 (accessed on 9 January 2023).
- Man, Y.; Stenrød, M.; Wu, C.; Almvik, M.; Holten, R.; Clarke, J.L.; Yuan, S.; Wu, X.; Xu, J.; Dong, F.; et al. Degradation of difenoconazole in water and soil: Kinetics, degradation pathways, transformation products identification and ecotoxicity assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evgenidou, E.; Fytianos, K. Photodegradation of triazine herbicides in aqueous solutions and natural waters. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 6423–6427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, R.; Bridgewater, L. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, WA, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-087553-287-5. [Google Scholar]
- González, C.; Vallarino, A. Bioindicadores: Guardianes de Nuestro Futuro Ambiental; González, C., Vallarino, A., Perez, J., Low Pfeng, A., Eds.; 2014; ISBN 9786078429059. Available online: https://agua.org.mx/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/Bioindicadores-Guardianes-de-nuestro-futuro-ambiental.pdf (accessed on 9 January 2023).
- Sikorski, Ł.; Baciak, M.; Bęś, A.; Adomas, B. The effects of glyphosate-based herbicide formulations on Lemna minor, a non-target species. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 209, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modlitbová, P.; Novotný, K.; Pořízka, P.; Klus, J.; Lubal, P.; Zlámalová-Gargošová, H.; Kaiser, J. Comparative investigation of toxicity and bioaccumulation of Cd-based quantum dots and Cd salt in freshwater plant Lemna minor L. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, M.; Hurtado, J. Bioensayos de toxicidad aguda utilizando Daphnia magna Straus (Cladocera, Daphniidae) desarrollada en medio de cultivo modificado. Rev. Peru Biol. 2005, 12, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, F.; Noldin, J.A.; Resgalla, C. Toxicidade aguda e análise de risco de herbicidas e inseticidas utilizados na lavoura do arroz irrigado sobre o cladócero Daphnia magna. Capa 2006, 16, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- INEC. Módulo de Información Ambiental y Tecnificación Agropecuaria. Available online: https://www.ecuadorencifras.gob.ec/documentos/web-inec/Encuestas_Ambientales/Modulo_Ambiental_ESPAC_2020/PRINC_RESUL_MOD_AGROTEC_2020_08_4.pdf (accessed on 9 January 2023).
- FAO. FAOSTAT: Pesticides Indicators. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/EP/visualize (accessed on 9 January 2023).
- Naranjo, A. La Otra Guerra: La Situación de los Plaguicidas en el Ecuador; Maldonado, A., Chérrez, C., Bravo, E., Eds.; 2017; Available online: https://www.accionecologica.org/la-otra-guerra-situacion-de-los-plaguicidas-en-ecuador/ (accessed on 9 January 2023).
- Ochoa-Cueva, P.A.; Arteaga, J.; Arévalo, A.P.; Kolok, A.S. A potential pesticides exposure index (PPEI) for developing countries: Applied in a transboundary basin. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2021, 2021, 235267474. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/A-potential-pesticides-exposure-index- (accessed on 9 January 2023).
- Arnon, D.I. Copper Enzymes in Isolated Chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta Vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 1949, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marr, I.L.; Suryana, N.; Lukulay, P.; Marr, M.I. Determination of chlorophyll a and b by simultaneous multi-component spectrophotometry. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1995, 352, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Foundation for Statistical Computing. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, V.L.; Buerkner, P.; Giné-Vázquez, I.; Herve, M.; Jung, M.; Love, J.; Miguez, F.; Riebl, H.; Singmann, H. emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, aka Least-Squares Means. R package version 1.8.4-1 2023. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web//packages/emmeans/emmeans.pdf (accessed on 9 January 2023).
- Ritz, C.; Strebig, J.C. Drc: Analysis of Dose-Response Curves. 2016. Available online: https://mran.microsoft.com/snapshot/2023-01-28/web/packages/drc/drc.pdf (accessed on 9 January 2023).
- Tagun, R.; Boxall, A.B.A. The Response of Lemna minor to Mixtures of Pesticides That Are Commonly Used in Thailand. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 100, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, P.; Palma, V.L.; Fernandes, R.M.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Barbosa, I.R. Acute toxicity of atrazine, endosulfan sulphate and chlorpyrifos to Vibrio fischeri, Thamnocephalus platyurus and Daphnia magna, relative to their concentrations in surface waters from the Alentejo region of Portugal. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 81, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, M.R.; Cohen, R.A. The Effects of an Herbicide and Antibiotic Mixture on Aquatic Primary Producers and Grazers. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 101, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamkhanter, H.; Frindy, S.; Park, Y.; Sillanpää, M.; Mountacer, H. Photocatalytic degradation of fungicide difenoconazole via photo-Fento process using α-Fe2O3. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 267, 124713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafula, Y.A.; Thoré, E.S.J.; Philippe, C.; Munishi, L.K.; Moyo, F.; Vanschoenwinkel, B.; Brendonck, L. Environmental risks of a commonly used pyrethroid: Insights from temporary pond species of the Lake Manyara Basin, Tanzania. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 868, 161698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoré, E.S.J.; Philippe, C.; Brendonck, L.; Pinceel, T. Towards improved fish tests in ecotoxicology—Efficient chronic and multi-generational testing with the killifish Nothobranchius furzeri. Chemosphere 2021, 273, 129697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, G.; Julcour, C.; Jáuregui-Haza, U. El Estado actual y perspectivas de la degradación de pesticidas por procesos avanzados de oxidación. Rev. Cubana De Química 2017, 29, 492–516. Available online: scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S2224-54212017000300013 (accessed on 9 January 2023).
- Aguilar, S.D.; Ramos, D.R.; Santaballa, J.A.; Canle, M. Preparation, characterization and testing of a bulky non-supported photocatalyst for water pollution abatement. Catal. Today 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, R.A.; Lemmens, P.; Cours, M.; Denys, L.; Adriaens, D.; Packet, J.; Venderickx, J.; Vercauteren, T.; Parmentier, K.; Knockaert, M.; et al. A moderate differential effect of organic and conventional agriculture across taxonomic groups inhabiting farmland ponds. Freshw. Biol. 2023, 2023, 1–14. Available online: https://pureportal.inbo.be/en/publications/a-moderate-differential-effect-of-organic-and-conventional-agricu (accessed on 9 January 2023). [CrossRef]
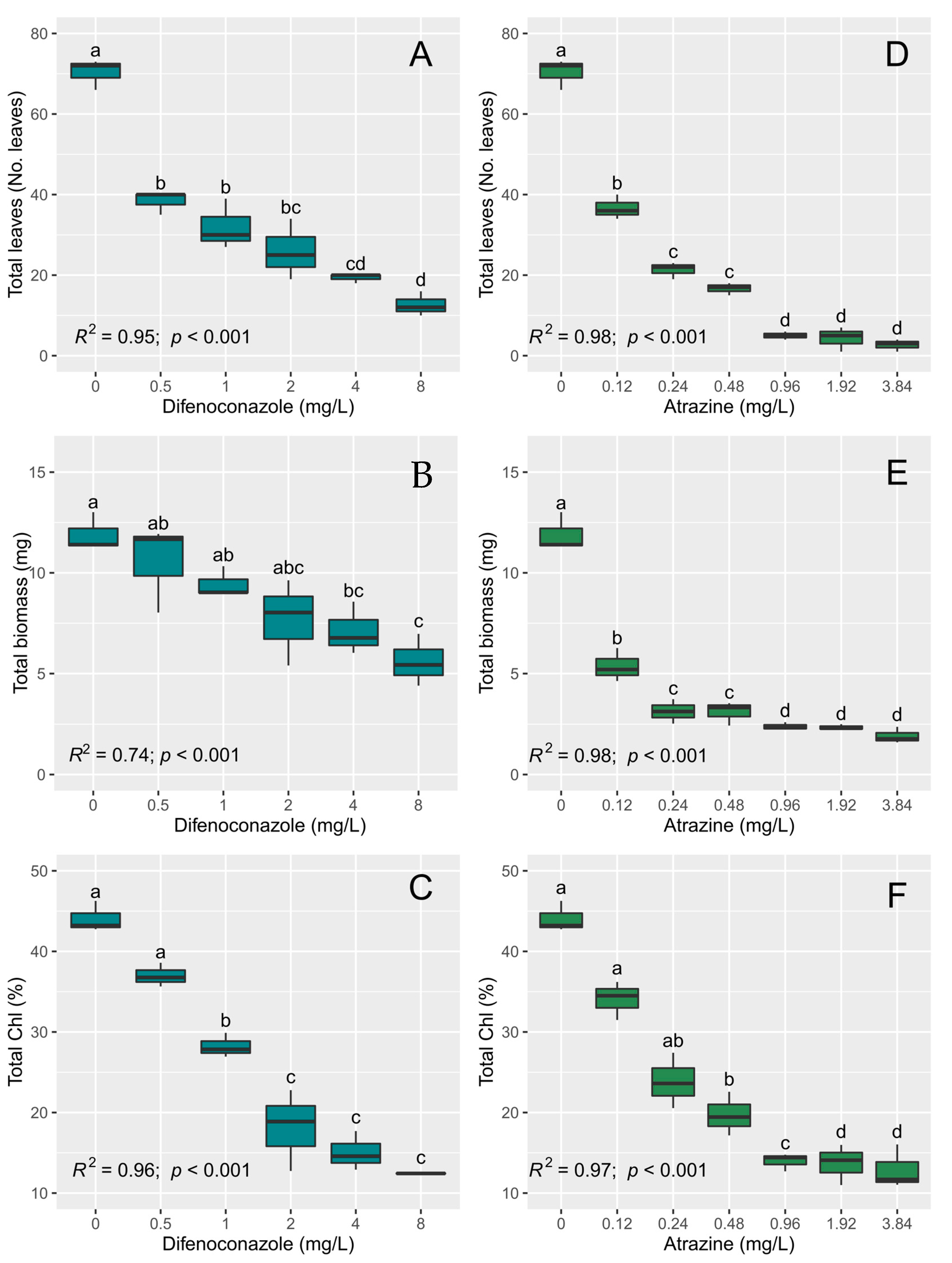
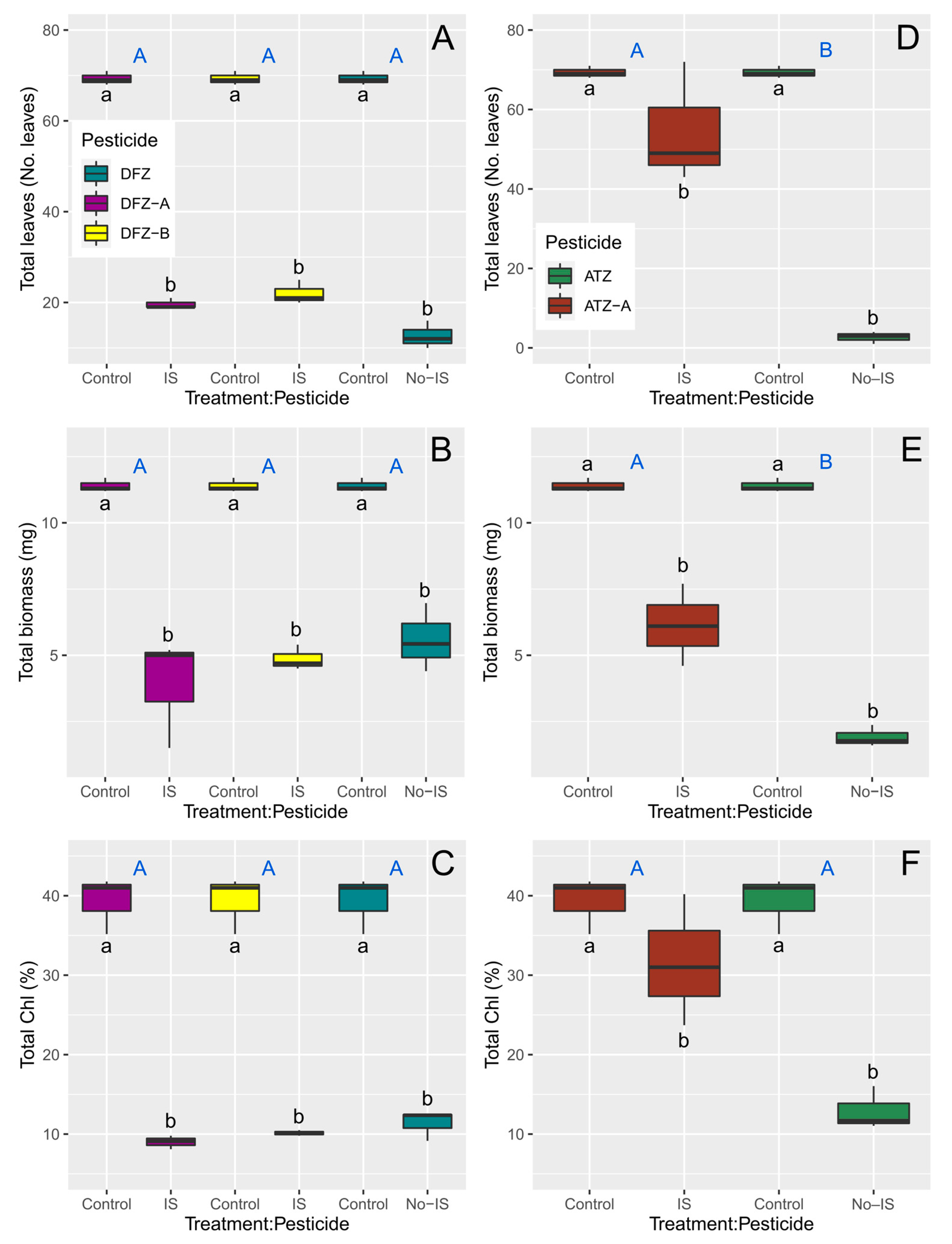
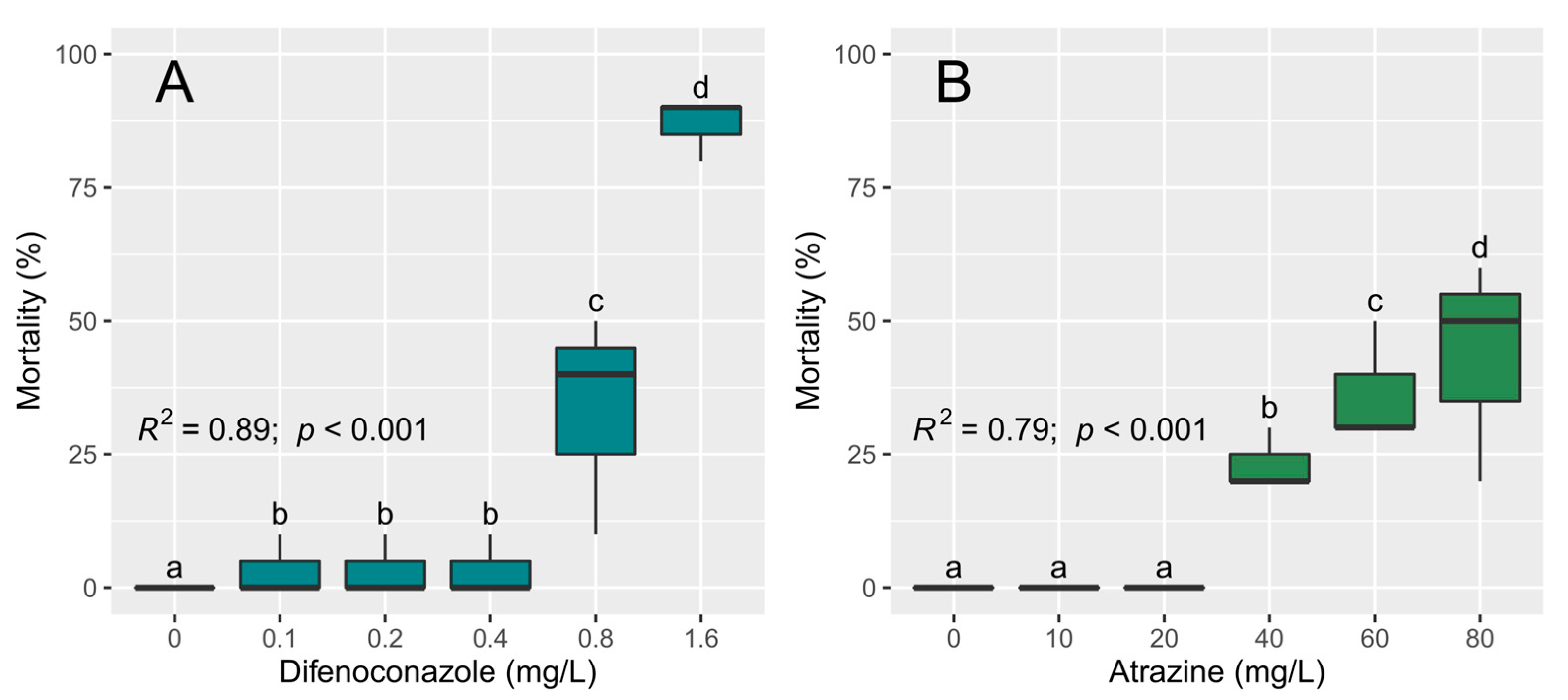

| Species | Pesticide | Variable | Source of Variation | Df | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lemna minor | Difenoconazole | No. of leaves | Treatments | 12 | 34.38 | <0.001 |
| Biomass | Treatments | 12 | 6.95 | 0.003 | ||
| Total chlorophyll | Treatments | 12 | 70.64 | <0.001 | ||
| Atrazine | No. of leaves | Treatments | 12 | 67.94 | <0.001 | |
| Biomass | Treatments | 12 | 103.83 | <0.001 | ||
| Total chlorophyll | Treatments | 12 | 72.20 | <0.001 | ||
| Daphnia magna | Difenoconazole | Mortality | Treatments | 12 | 37.09 | 0.001 |
| Atrazine | Mortality | Treatments | 12 | 11.92 | <0.001 |
| Species | Pesticide | Variable | Source of Variation | Df | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L. minor | Difenoconazole | No. of leaves | Treatments | 16 | 288.10 | <0.001 |
| Pesticides | 14 | 0.82 | 0.443 | |||
| Biomass | Treatments | 16 | 25.02 | <0.001 | ||
| Pesticides | 14 | 0.13 | 0.874 | |||
| Total chlorophyll | Treatments | 16 | 165.13 | <0.001 | ||
| Pesticides | 14 | 0.08 | 0.920 | |||
| Atrazine | No. of leaves | Treatments | 10 | 104.38 | <0.001 | |
| Pesticides | 9 | 41.89 | <0.001 | |||
| Biomass | Treatments | 10 | 78.27 | <0.001 | ||
| Pesticides | 9 | 6.40 | 0.032 | |||
| Total chlorophyll | Treatments | 10 | 16.80 | 0.003 | ||
| Pesticides | 9 | 5.07 | 0.051 | |||
| D. magna | Difenoconazole | Mortality | Treatments | 10 | 9.24 | 0.009 |
| Pesticides | 9 | 6.60 | 0.010 | |||
| Atrazine | Mortality | Treatments | 10 | 8.69 | 0.016 | |
| Pesticides | 9 | 4.67 | 0.060 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mendieta Herrera, J.; Iñiguez Armijos, C.; Rosado Alcarria, D.; Aguilar Ramírez, S. Toxicity of Difenoconazole and Atrazine and Their Photodegradation Products on Aquatic Biota: Environmental Implications in Countries Lacking Good Agricultural Practices. Toxics 2023, 11, 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11030213
Mendieta Herrera J, Iñiguez Armijos C, Rosado Alcarria D, Aguilar Ramírez S. Toxicity of Difenoconazole and Atrazine and Their Photodegradation Products on Aquatic Biota: Environmental Implications in Countries Lacking Good Agricultural Practices. Toxics. 2023; 11(3):213. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11030213
Chicago/Turabian StyleMendieta Herrera, Julia, Carlos Iñiguez Armijos, Daniel Rosado Alcarria, and Silvio Aguilar Ramírez. 2023. "Toxicity of Difenoconazole and Atrazine and Their Photodegradation Products on Aquatic Biota: Environmental Implications in Countries Lacking Good Agricultural Practices" Toxics 11, no. 3: 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11030213
APA StyleMendieta Herrera, J., Iñiguez Armijos, C., Rosado Alcarria, D., & Aguilar Ramírez, S. (2023). Toxicity of Difenoconazole and Atrazine and Their Photodegradation Products on Aquatic Biota: Environmental Implications in Countries Lacking Good Agricultural Practices. Toxics, 11(3), 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11030213









