Effect of pH, Temperature, and Salinity Levels on Heavy Metal Fraction in Lake Sediments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Sampling Sites and Dates
2.3. Laboratory Methods
- (a)
- Experimental setup
- (1)
- Maintain the salinity and pH value of the water, and change the water temperature. The temperature levels of the water in the controlled group were 5 °C, 15 °C, 25 °C, and 35 °C. The pH value of the water was 7, and the salinity was 1.5 g/L.
- (2)
- Maintain the temperature and salinity of the water, and change the pH value of the water. The levels of pH in the water were 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9. The temperature of the water was 25 °C, and the salinity was 1.5 g/L.
- (3)
- Maintain the temperature and pH value of the water, and change the salinity of the water. The levels of salinity in the controlled group were 0.5 g/L, 1.5 g/L, 2.5 g/L, 3.5 g/L, 4.5 g/L, and 5.0 g/L. The pH value of the water was 7, and the temperature was 25 °C.
- (b)
- Analysis of Samples
- (b-1)
- Physical characterization
- (b-2)
- The total Cu and Zn
- (b-3)
- Cu and Zn fraction
2.4. Quality Assurance and Quality Control
2.5. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sediment Properties
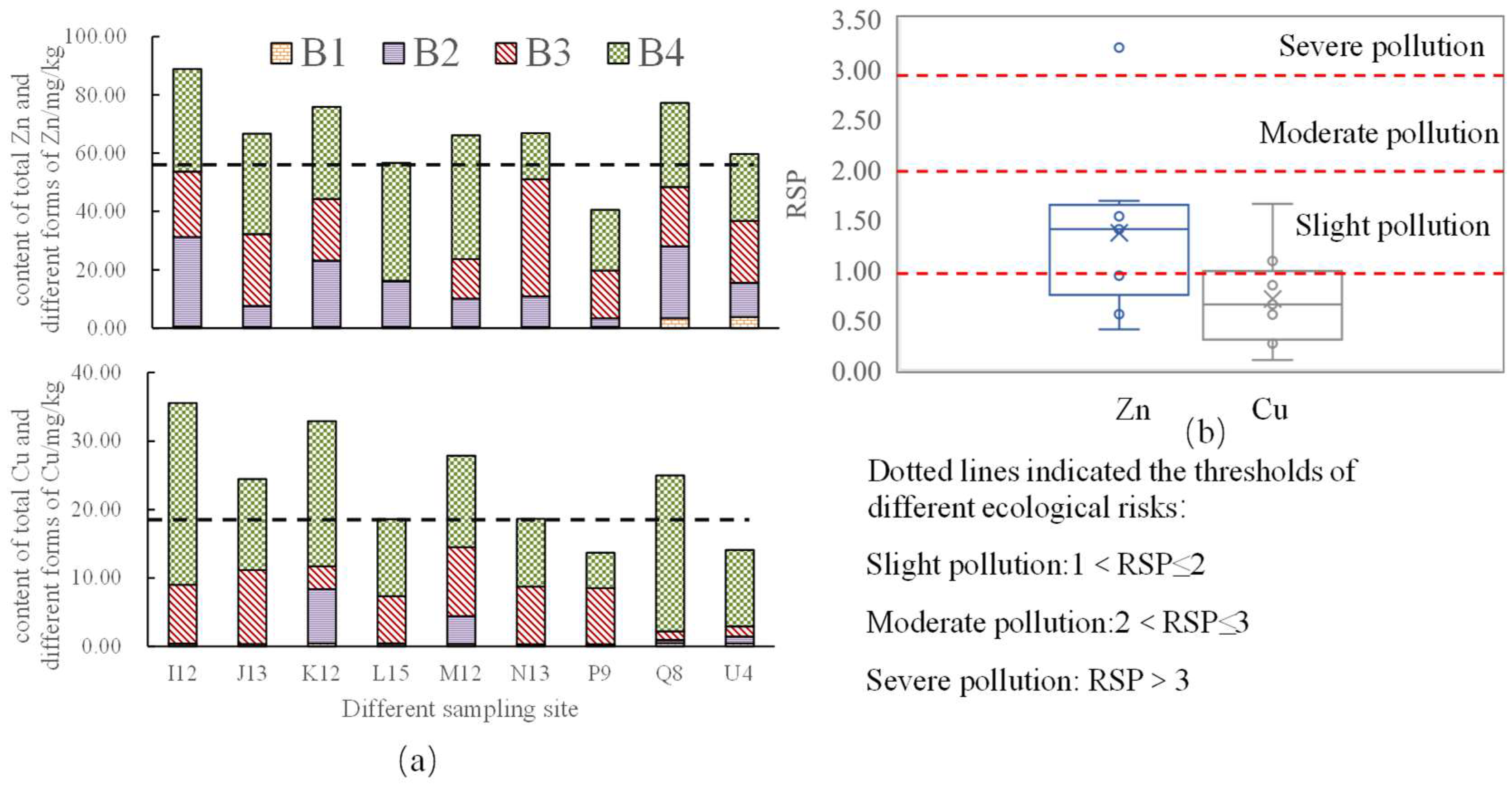
3.2. Total Amount and Fraction of HMs in Sediments
3.3. Metal Release and Fraction Changes in Sediments Caused by pH, Temperature, and Salinity Changes
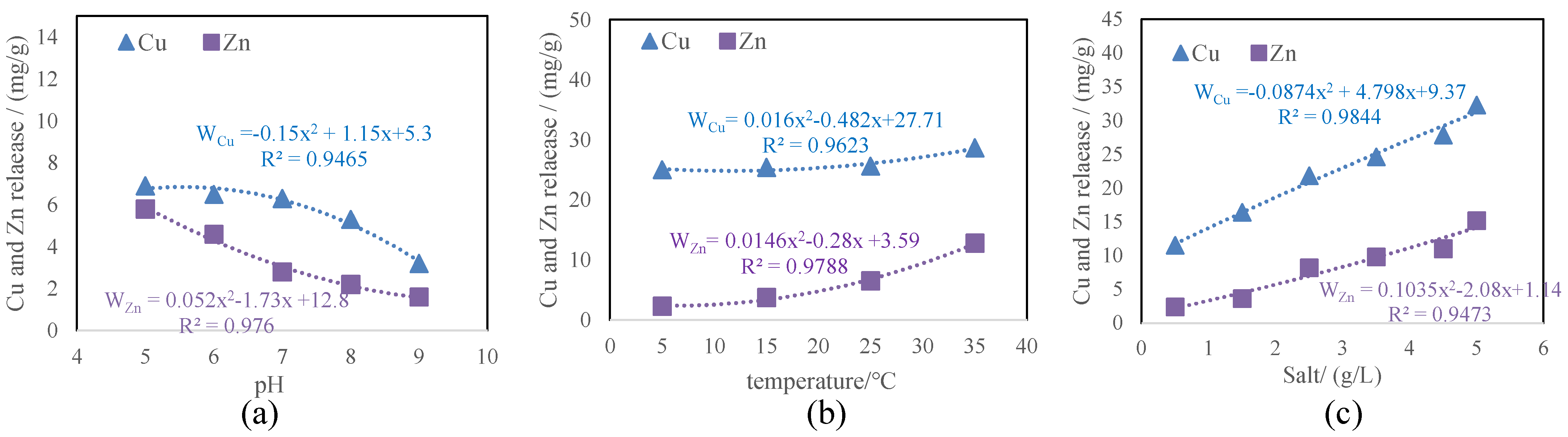
3.3.1. Metal Release and Fraction Changes in Sediments Caused by pH
3.3.2. Metal Release and Fraction Changes in Sediments Caused by Temperature
3.3.3. Metal Release and fraction Changes in Sediments Caused by Salinity Changes
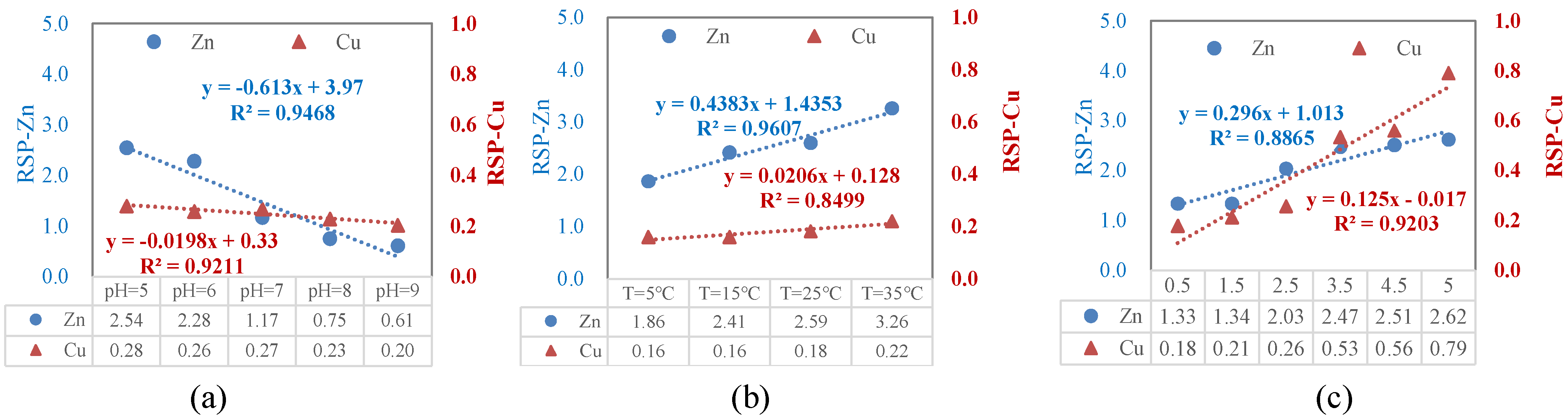
3.3.4. Relationships of Cu and Zn Fraction in Sediments with the Released Amounts
3.4. Implication of pH, Salinity, and Temperature Changes for HM Ecological Risk
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Che, F.; Chen, J.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, X.; Wang, S. Distribution, risk and bioavailability of metals in sediments of Lake Yamdrok Basin on the Tibetan Plateau, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 97, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Yan, C.; Yan, Y.; Chi, Q. Assessment of metal contamination in coastal sediments of the Maluan Bay (China) using geochemical indices and multivariate statistical approaches. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 99, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Ali, A.D.; Laune, R.D. Physico-chemical forms of copper in water and sediments of Lake Pontchartrain basin, USA. Chemosphere 2018, 195, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campana, O.; Spadaro, D.A.; Blasco, J.; Simpson, S.L. Sublethal effects of copper to benthic invertebrates explained by changes in sediment properties and dietary exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6835–6842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jancula, D.; Marsalek, B. Critical review of actually available chemical compounds for prevention and management of cyanobacterial blooms. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, R.J.; Benoit, D.A.; Mattson, V.R. The effect of water chemistry on the toxicity of copper to fathead minnows. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1996, 15, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Holbach, A.; Wilhelms, A.; Krieg, J.; Qin, Y.; Zheng, B.; Zou, H.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Wu, T.; et al. Identifying spatio-temporal dynamics of trace metals in shallow eutrophic lakes on the basis of a case study in Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 1148–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, S.; Shi, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Wu, S. Heavy metals in food crops, soil, and water in the Lihe River watershed of the Taihu Region and their potential health risks when ingested. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnitskiy, S. Nickel: The last of the essential micronutrients. Agron. Colomb. 2011, 29, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Luo, J.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Shaoqi Zhou Geochemical fractionation, bioavailability, and potential risk of heavy metals in sediments of the largest influent river into Chaohu Lake, China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Woodhouse, J.N.; Te, S.H.; Gin, K.Y.H.; He, Y.; Xu, C.; Chen, L. Seasonal variation in the bacterial community composition of a large estuarine reservoir and response to cyanobacterial proliferation. Chemosphere 2018, 202, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Teng, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, J. Source apportionment of trace metals in river sediments: A comparison of three methods. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 211, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch, A.C.; O’Neill, B.; Sigge, G.O.; Kerwath, S.E.; Hoffman, L.C. Heavy metals in marine fish meat and consumer health: A review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, F.; Qu, L.; Wang, T.; Luo, L.; Chen, H.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Zhang, M.; Mei, K.; Huang, H. Distribution and source analysis of heavy metal pollutants in sediments of a rapid developing urban river system. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, X.; Gui, S.; Huang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Guo, W. Ecological risk assessment and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediment from the Liaohe River protected area, China. Chemosphere 2017, 175, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Mathew, G.W.; Li, J.; Joelle, Y. Mixing, stratification, and plankton under lake-ice during winter in a large lake: Implications for spring dissolved oxygen levels. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2020, 65, 2713–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Hua, X.; Jiang, X.; Dong, D.; Liang, D.; Guo, Z.; Zheng, N.; Huang, X. Effects of tubificid bioturbation on bioaccumulation of Cu and Zn released from sediment by aquatic organisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Huang, Y.; Yan, X.; Jiang, L.; Wu, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X. Effect of overlying water pH, temperature, and hydraulic disturbance on heavy metal and nutrient release from drinking water reservoir sediments. Water Environ. Res. 2021, 93, 2135–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Shi, A.; Li, M.; Zhang, X. Effect of pH, temperature, dissolved oxygen, and flow rate of overlying water on heavy metals release from storm sewer sediments. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 434012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Gao, L.; Peng, W.; Gao, B.; Xu, D.; Sun, K. Assessment of labile Zn in reservoir riparian soils using DGT, DIFS, and sequential extraction. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 160, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Bission, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of paniculate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.W.C.; Selvam, A. Speciation of heavy metals during co-composting of sewage sludge with lime. Chemosphere 2006, 63, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, S.K.; Banerjee, D.K. Operationally determined speciation of copper and zinc in sewage sludge. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 1998, 10, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, Z.; Zeng, G.; Jiang, M.; Yang, Z.; Cui, F.; Zhu, M.; Shen, L.; Hu, L. Effects of sediment geochemical properties on heavy metal bioavailability. Environ. Int. 2014, 73, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Mamas, Z.; Ye, Q. Sources identification and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Bortala River, Northwest China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2016, 126, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.; Tian, Y.; Peng, S.; Wang, M. Effect of dissolved oxygen and nutrient levels on heavy metal contents and fractions in river surface sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Esteban, J.; Escolástico, C.; Masaguer, A.; Vargas, C.; Moliner, A. Soluble organic carbon and pH of organic amendments affect metal mobility and chemical speciation in mine soils. Chemosphere 2014, 103, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Fan, W.; Xin, X.; Pan, X.; Zhang, L.; Sun, D. Stepwise Synthesis of Diverse Isomer MOFs via Metal-Ion Metathesis in a Controlled Single-Crystal-to-Single-Crystal Transformation. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 4084–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Wu, M.; Yang, J. Mobilities and leachabilities of heavy metals in sludge with humus soil. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Q.; He, J.; Lü, C.W.; Fan, M.D.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.Q.; Xie, Z.; Wang, J.H.; Yu, B.; En, H.; et al. Effects of Fulvic Acid on Absorption and Form Distribution of Heavy Metals on Sediments. Environ. Sci. 2016, 37, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar]
- Sapna, S.; Kevin, B.; Alessandro, F.; Arshad, M. Forecasting the Permanent Loss of Lake Ice in the Northern Hemisphere within the 21st Century. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, 1245–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.; Li, C.; Shi, X.; Zhao, S.; Tian, W.; Li, Z.; Bai, Y.; Cao, X.; Wang, Q.; Huotari, J.; et al. Under-ice metabolism in a shallow lake in a cold and arid climate. Freshw. Biol. 2019, 48, 256–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.N.; McMahon, T.E.; Cutting, K.A.; Jaeger, M.E. Environmental and climatic factors affecting winter hypoxia in a freshwater lake: Evidence for a hypoxia refuge and for re-oxygenation prior to spring ice loss. Hydrobiologia 2020, 81, 3983–3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baehr, M.M.; DeGrandpre, M.D. In situ pCO2 and DO dynamics during turnover and stratification in Lake Placid, Montana, USA, and observed light driven mixing and net metabolism under ice before ice break-up. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2004, 49, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puklakov, V.V.; Edel’Shtein, K.K.; Kremenetskaya, E.R. Water Self-Purification in the Mozhaisk Reservoir in Winter. Water Resour. 2002, 29, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, D.J.; Gates, T.E.; Davies, R.W. Oxygen conditions on two pothole lakes during winter ice cover. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1987, 44, 1092–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzhevik, A.; Golosov, S.; Palshin, N.; Mitrokhov, A.; Zdorovennov, R.; Zdorovennova, G.; Kirillin, G.; Shipunova, E.; Zverev, I. Some features of the thermal and dissolved oxygen structure in boreal, shallow ice-covered Lake Vendyurskoe, Russia. Aquat. Ecol. 2009, 43, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, A.; Trenholm, N.; Loose, B.; Glastra, L.; Strock, J.; Kim, J. Microplastics Distribution within Western Arctic Seawater and Sea Ice. Toxics 2023, 11, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolsenga, S.J.; Vanderploeg, H.A. Estimating photosynthetically available radiation into open and ice-covered freshwater lakes from surface characteristics; A high transmittance case study. Hydrobiologia 1992, 243, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cota, G.F. Photoadaptation of high Arctic ice algae. Nature 1985, 315, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertilsson, S.; Burgin, A.; Carey, C.C.; Fey, S.B.; Smyth, R. The under-ice microbiome of seasonally frozen lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2013, 58, 1998–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.H.; Yu, H.F.; Zhao, S.N.; Sun, B.; Liu, Y.; Huo, H.B.; Wang, S.H.; Wang, J.L.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Impacts of environmental factors on Chlorophyll-a in lakes in cold and arid regions: A 10-year study of Wuliangsuhai Lake, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; Zuo, Q.T.; Feng, F.; Jia, H.T. Occurrence and Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals from Wuliangsuhai Lake, Yellow River Basin, China. Water 2022, 14, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.F.; Shi, X.H.; Wang, S.H.; Zhao, S.N.; Sun, B.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.X. Trophic status of a shallow lake in Inner Mongolia: Long-term, seasonal, and spatial variation. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 111167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati, K.; Bakar, N.K.A.; Abas, M.R.; Sobhanzadeh, E. Speciation of heavy metals by modified BCR sequential extraction procedure in different depths of sediments from Sungai Buloh, Selangor, Malaysia. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wu, E.; Zhang, B.; Bai, X.; Lei, P.; Qiao, X.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Wu, G.; Gao, Y. Pollution characteristics and ecological risks associated with heavy metals in the Fuyang river system in North China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 281, 116994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.X.; Wang, X.K.; Zhang, Q.; Li, S.B. Characteristics of Soil Background Value in Hetao Area, Inner Mongolia. Geol. Resour. 2007, 16, 209–2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Peng, B.; Yang, Z.X.; Xie, W.C.; Fang, X.H.; Zeng, D.Z. Speciation of heavy metals in riverbed sediments of heavy pollution section of the lowermost of the Xiangjiang River. Environ. Chem. 2017, 36, 1977–1986. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Song, Y.H.; Zhang, G.C.; Yan, Z.C.; Jin, F.Y.; Yu, H.B. Application of solid surface EEM fluorescence spectroscopy for analyzing orgnaic matter structral composition of lake sediment. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2020, 40, 483–488. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.H.; Lamb, D.; Paneerselvam, P.; Choppala, G.; Bolan, N.; Chung, J.W. Role of organic amendments on enhanced bioremediation of heavy metal(loid) contaminated soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 549–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappuyns, V.; Swennen, R.; Verhulst, J. 2004. Assessment of acid neutralizing capacity and potential mobilization of trace metals from land-disposed dredged sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 333, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borma, L.D.; Ehrlich, M.; Barbosa, M.C. Acidification and release of heavy metals in dredged sediments. Can. Geotech. J. 2003, 40, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lores, E.M.; Pennock, J.R. The effect of salinity on binding of Cd, Cr, Cu and Zn to dissolved organic matter. Chemosphere 1998, 37, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Step | Soil Phases | Extractant | Shaking Time and Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | Acid-extractable | 20 mL 0.11 mol/L CH3COOH | shaken at 25 °C for 30 r/min for 16 h and then centrifuged at 4000 r/min for 20 min |
| B2 | Fe-Mn oxide-combined | 20 mL 0.1 mol/L NH2OH·HCI (pH = 2) | shaken at 25 °C for 30 r/min for 16 h and centrifuged at 4000 r/min for 20 min |
| B3 | Organic matter and sulfide-combined | 5 mL 8.8 mol/L H2O2 (pH = 2) then 5 mL 8.8 mol/L H2O2, add 25 mL 1mol/L NH4OAc (pH = 2) | water bath at 25 °C for 1 h then 85 °C for 1 h shaken at 25 °C for 30 r/min for 16 h and centrifuged at 4000 r/min for 20 min |
| B4 | Residual | 10 mL (HClO4:HNO3 = 1:4) | heated on hot plate to dryness |
| pH | T | Salinity | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | Total | B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | Total | B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | Total | |
| R-Cu | 0.913 * | 0.87 * | 0.622 | −0.925 ** | −0.369 | 0.52 | 0.497 | 0.941 * | −0.987 ** | −0.764 | 0.892 * | 0.715 | 0.948 ** | −0.951 ** | −0.396 |
| R-Zn | 0.723 | 0.873 * | 0.98 * | −0.98 ** | 0.478 | 0.073 | 0.884 * | 0.778 | −0.956 ** | 0.485 | −0.5 | 0.167 | 0.823 ** | −0.95 ** | −0.414 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, S.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J. Effect of pH, Temperature, and Salinity Levels on Heavy Metal Fraction in Lake Sediments. Toxics 2024, 12, 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12070494
Zhao S, Zhao Y, Cui Z, Zhang H, Zhang J. Effect of pH, Temperature, and Salinity Levels on Heavy Metal Fraction in Lake Sediments. Toxics. 2024; 12(7):494. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12070494
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Shengnan, Yunxi Zhao, Zhimou Cui, Hui Zhang, and Jinda Zhang. 2024. "Effect of pH, Temperature, and Salinity Levels on Heavy Metal Fraction in Lake Sediments" Toxics 12, no. 7: 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12070494
APA StyleZhao, S., Zhao, Y., Cui, Z., Zhang, H., & Zhang, J. (2024). Effect of pH, Temperature, and Salinity Levels on Heavy Metal Fraction in Lake Sediments. Toxics, 12(7), 494. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12070494





