Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils Based on Multi-Receptor Modeling Combined with Monte Carlo Simulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
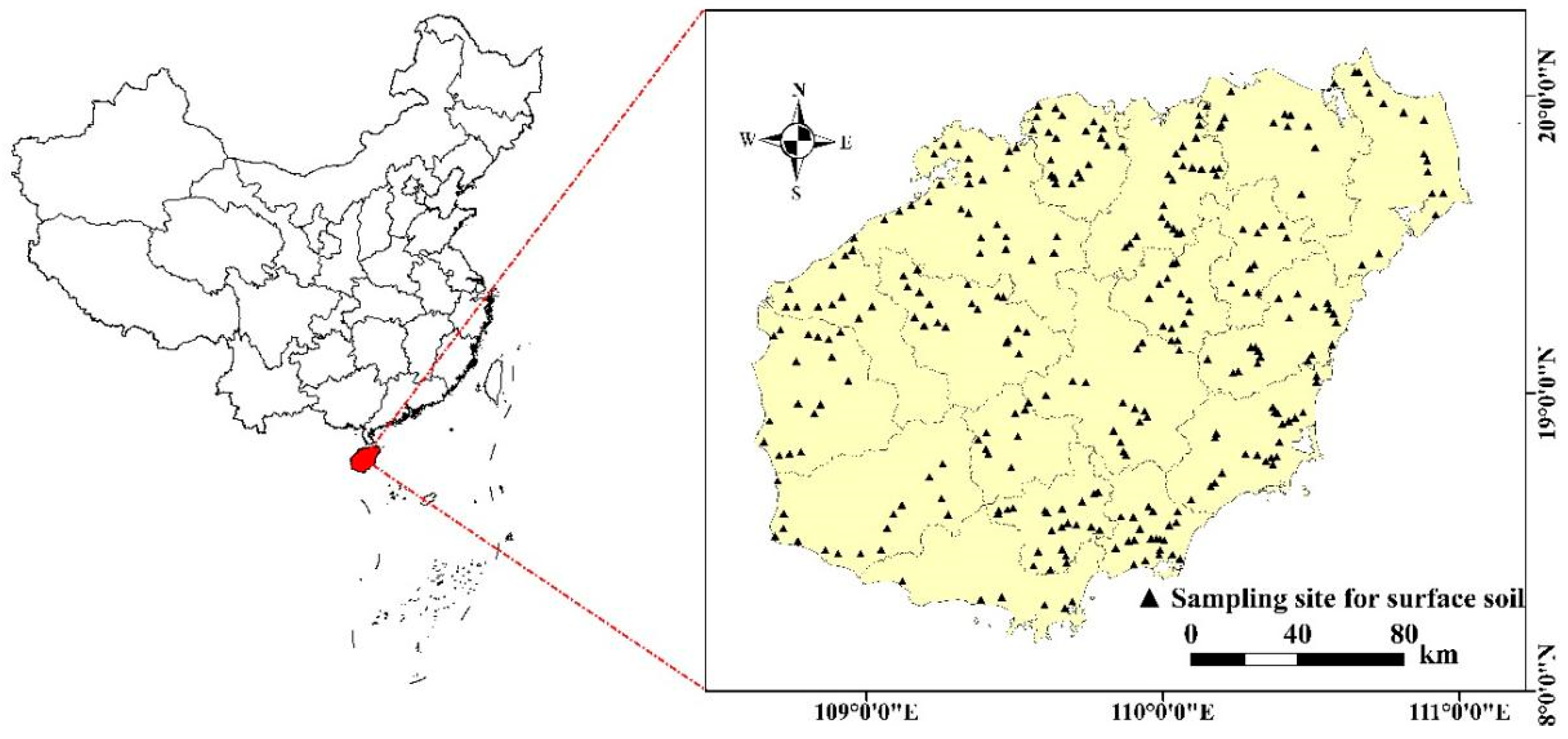
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. Methods for Evaluating Heavy Metal Pollution of Soils
2.3.1. Pollution Index and Nemerow Composite Pollution Index
2.3.2. Index of Geo-Accumulation
2.3.3. Ecological Risk Assessment Methods for Heavy Metals in Soils
2.4. Source Analysis of Soil Heavy Metals
2.4.1. Absolute Factor Score Multiple Linear Regression (APCS-MLR) Model
2.4.2. Positive Definite Matrix Factorization Model (PMF)
2.5. Human Health Risk Assessment Model (HHR)
2.6. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Soil pH and Total Heavy Metal Content
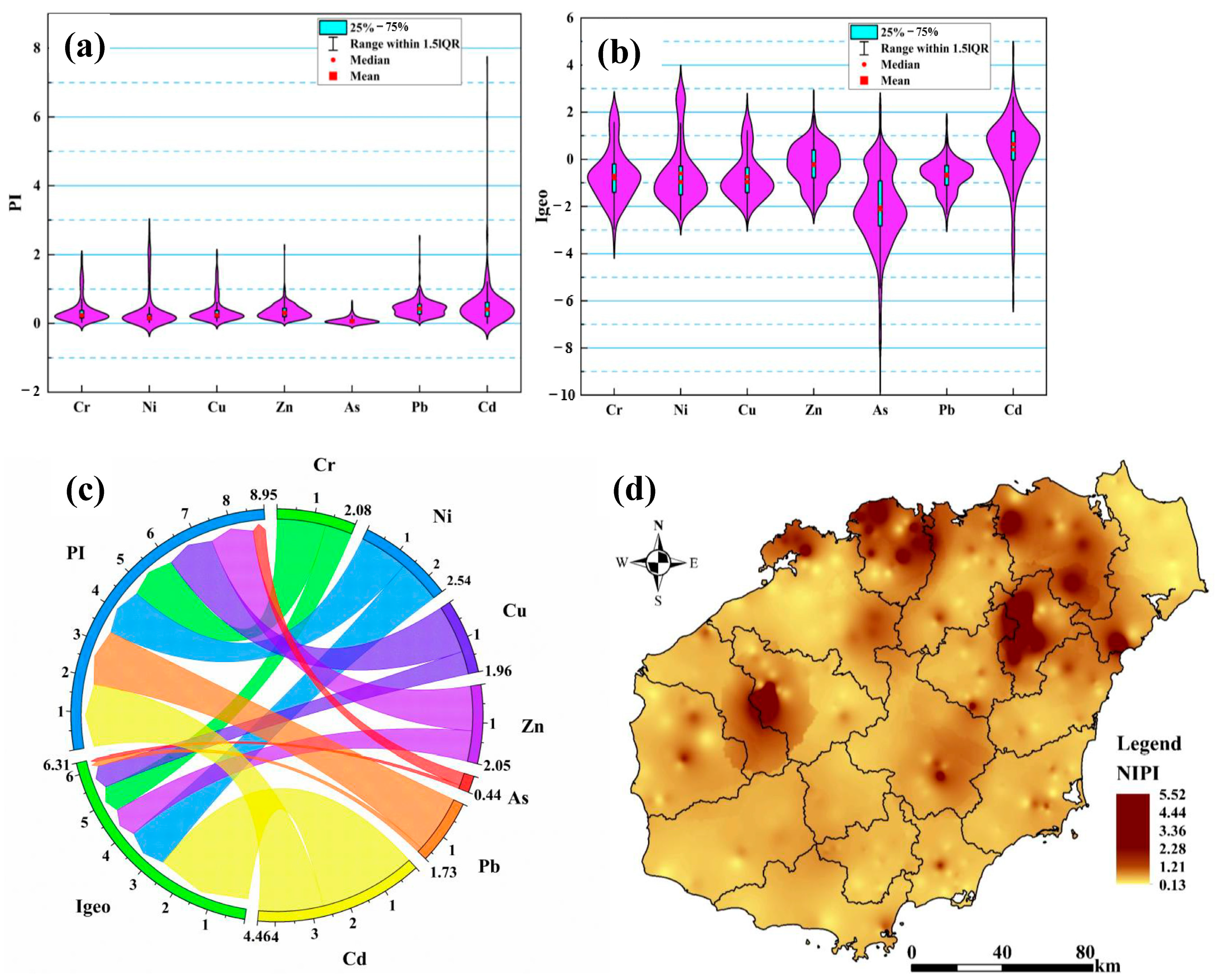
3.2. Distribution Characteristics of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution
3.2.1. Levels of Soil Heavy Metal Contamination
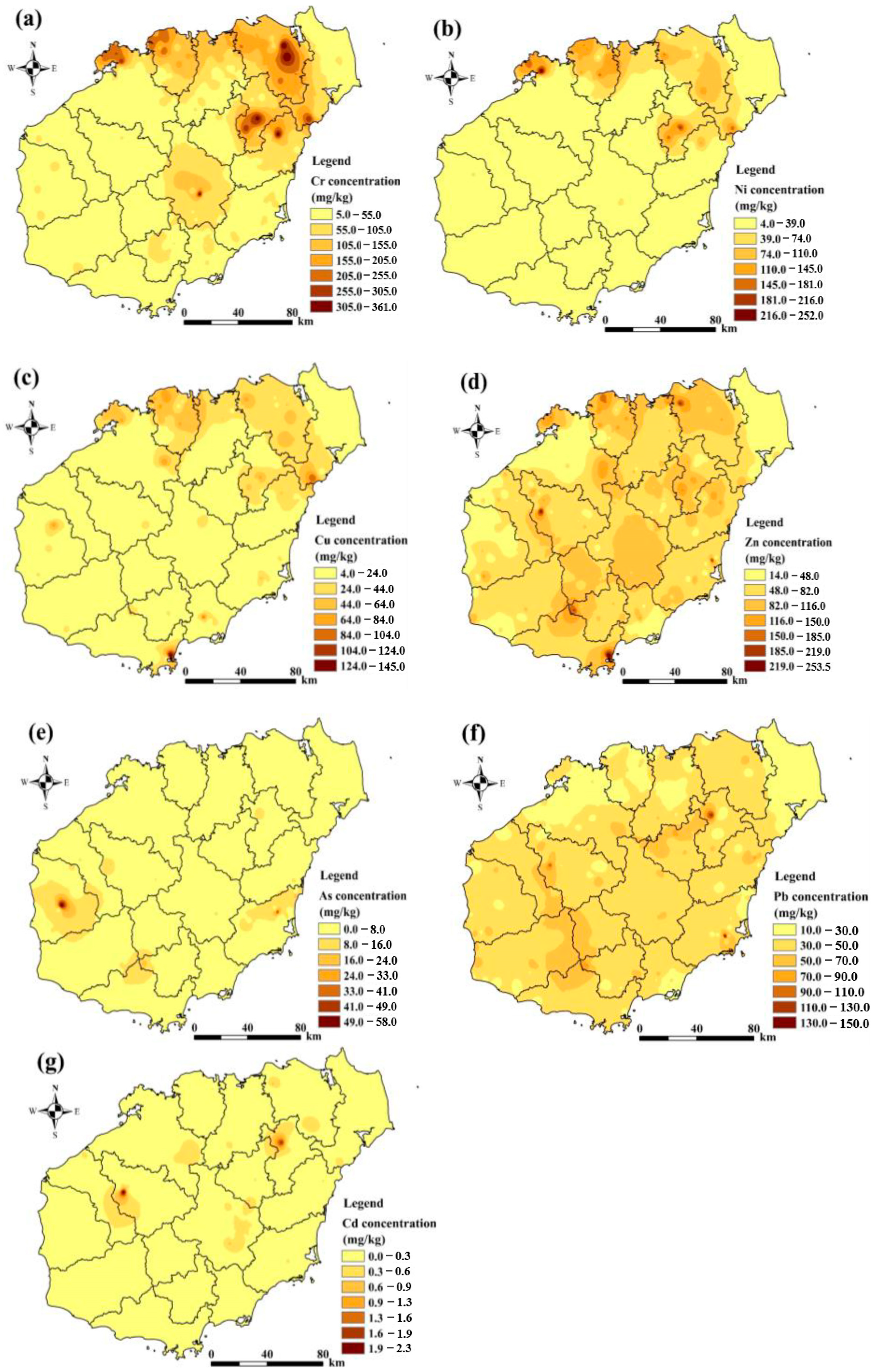
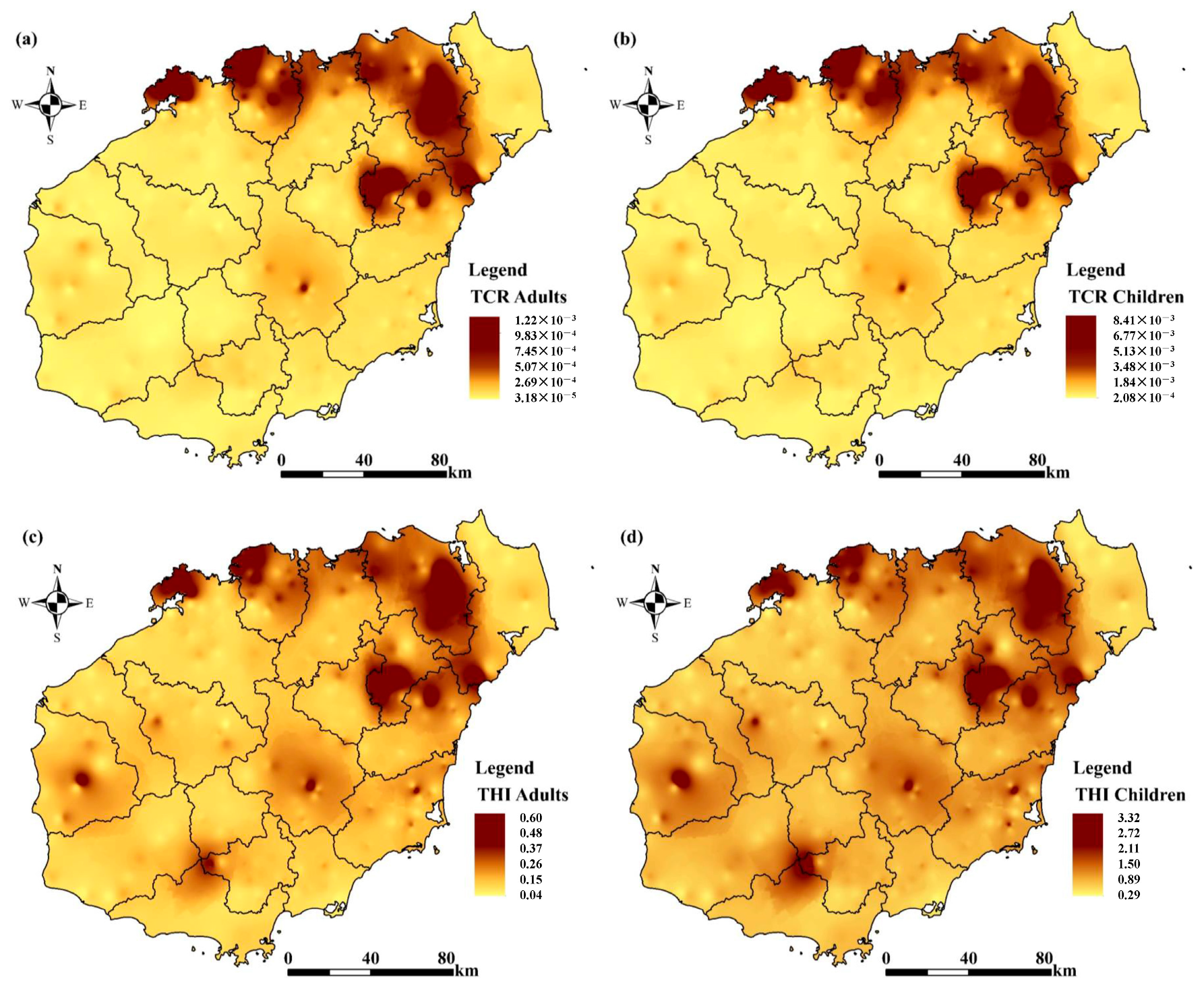
3.2.2. Characteristics of the Spatial Distribution of Soil Heavy Metals
3.2.3. Assessment of Potential Ecological Risk of Soil
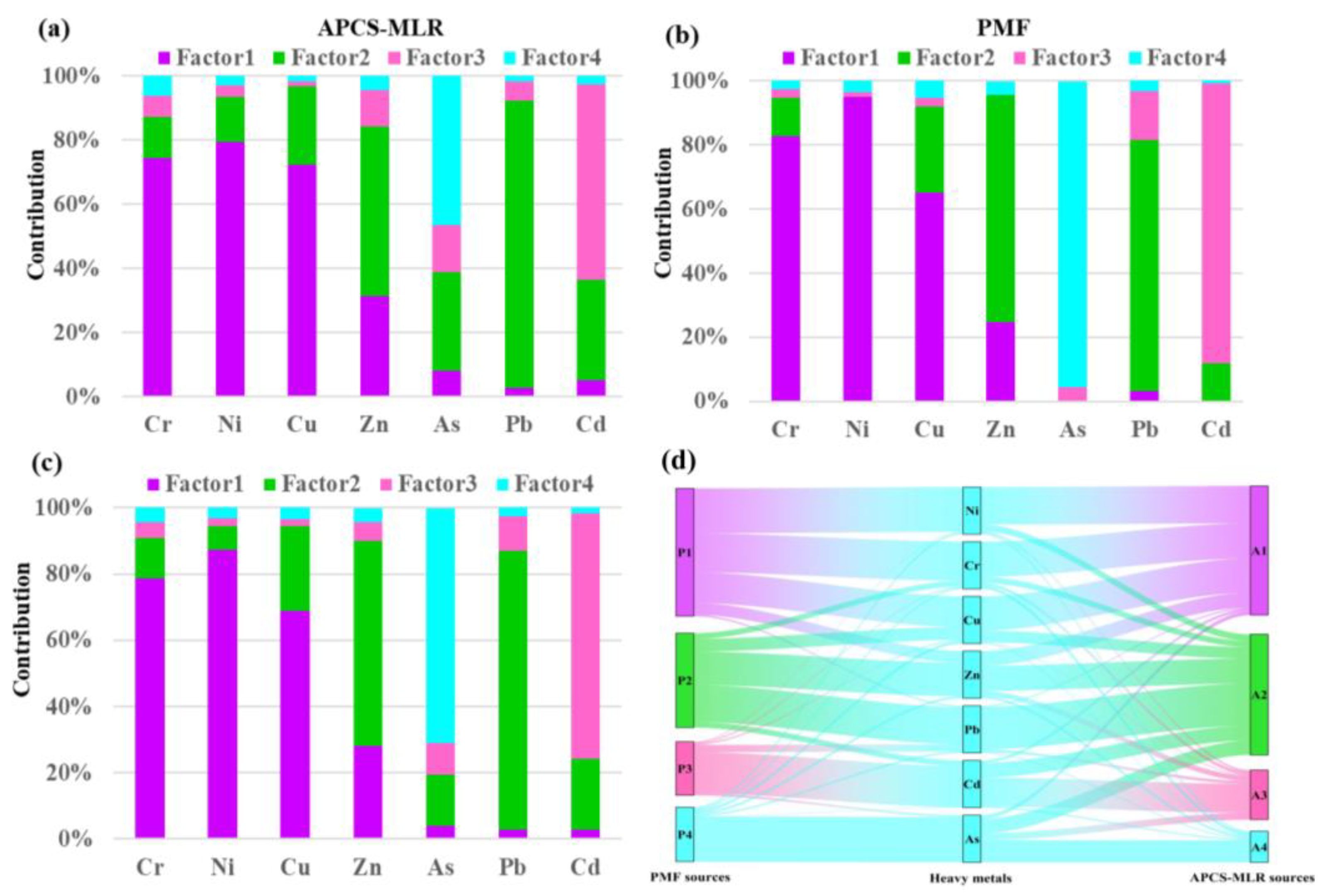
3.3. Soil Heavy Metal Source Analysis
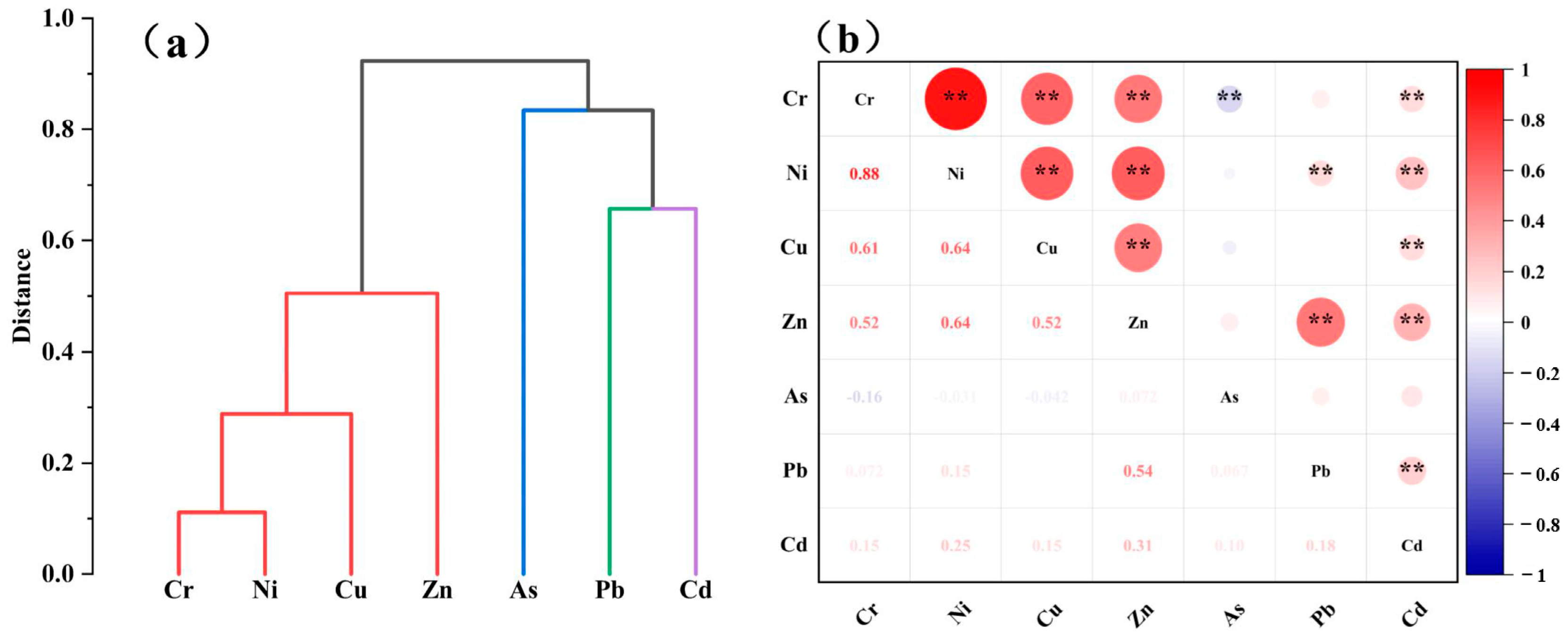
3.3.1. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
3.3.2. Comparison of Different Receptor Models
3.3.3. Explanation of the Origin of Each Factor
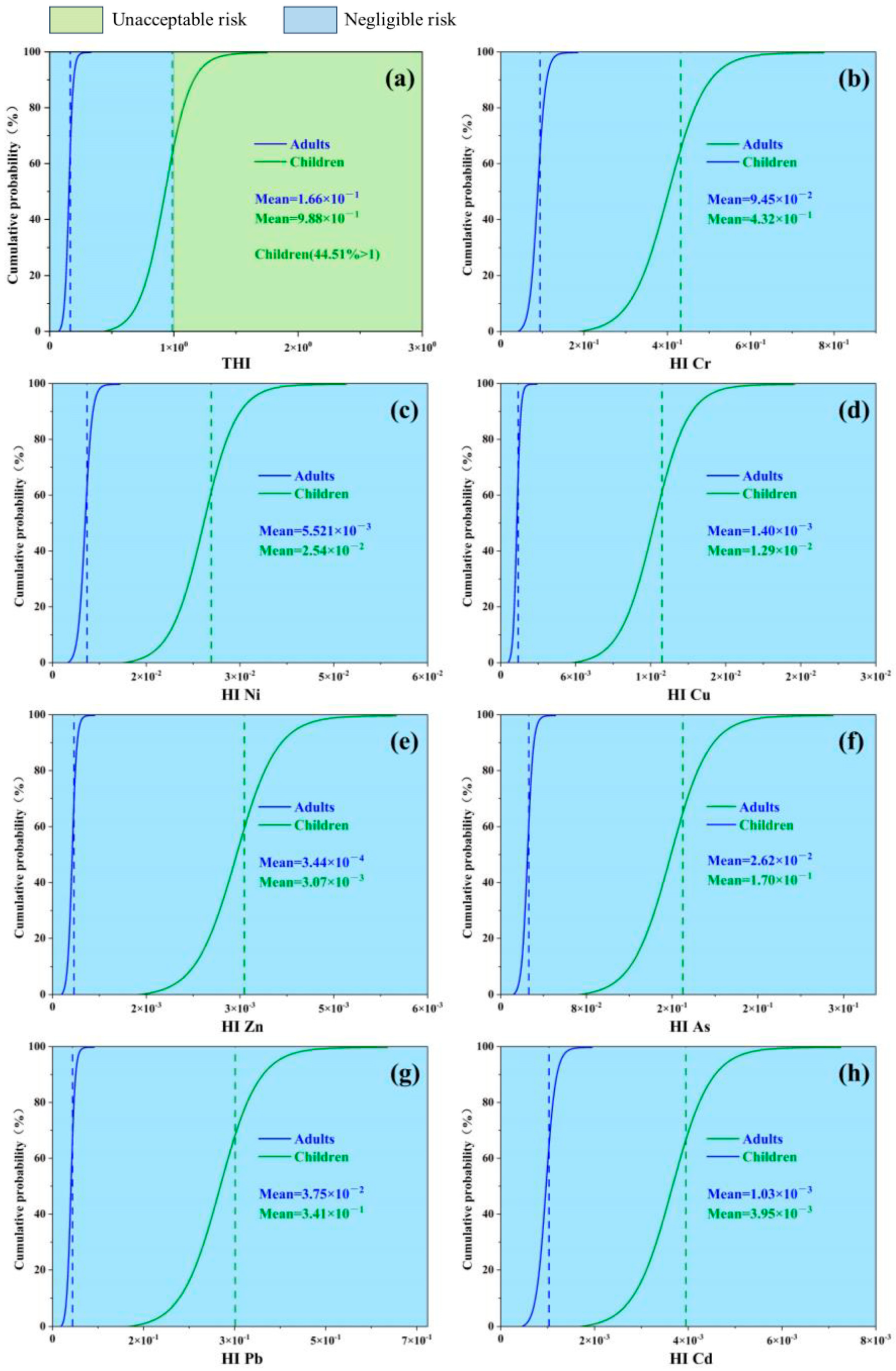
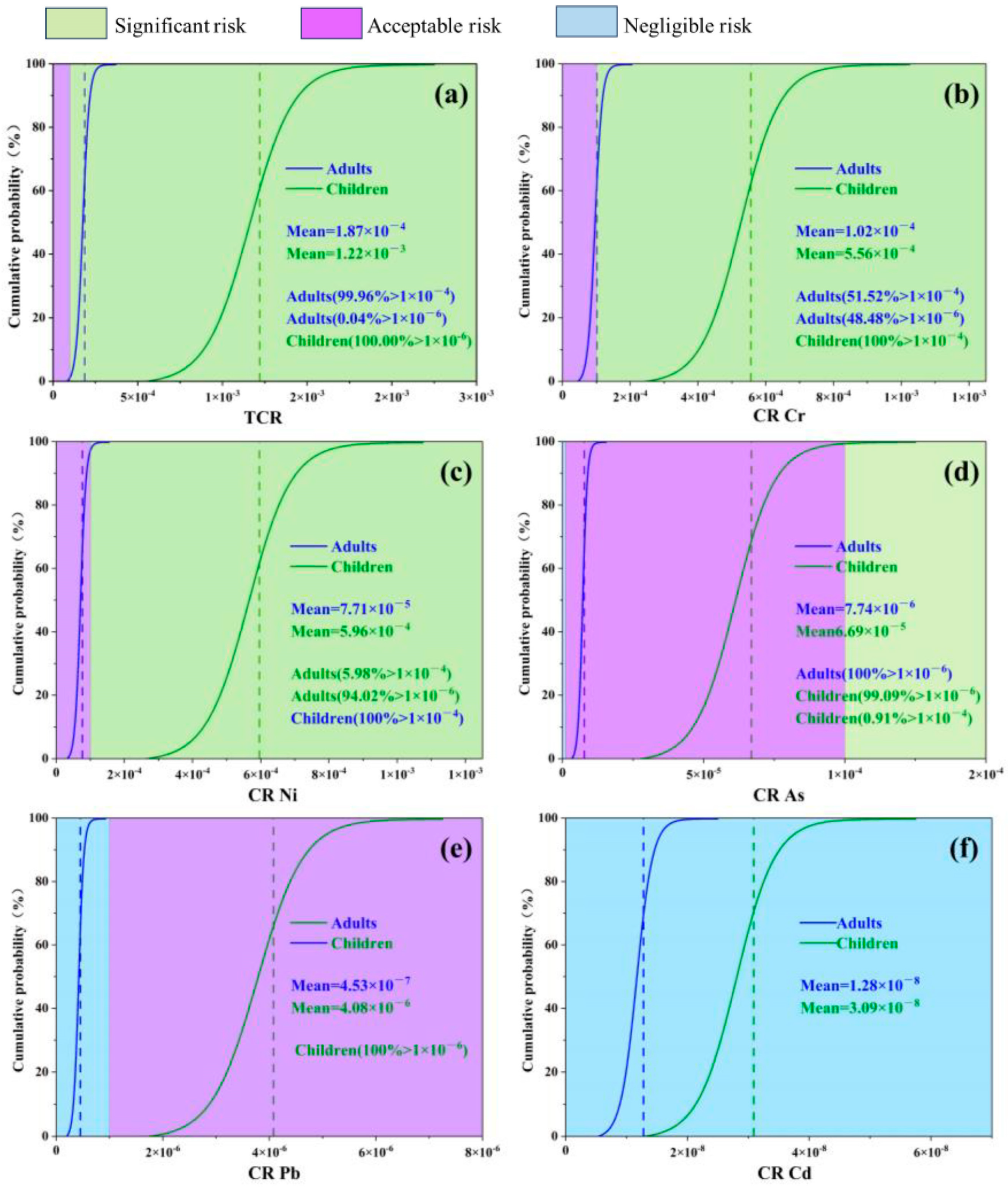
3.4. Human Health Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Q.; Hu, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, P.; Wang, X.; Huang, B. Spatial distribution, ecological risk and sources of heavy metals in soils from a typical economic development area, Southeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Yu, M.; Yuan, Q.; Meng, Y.; Qie, Y.; Shang, Z.; Luan, F.; Zhang, D. Spatial distribution, pollution assessment, and source identification of heavy metals in the Yellow River. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayeri, S.; Dehghanian, Z.; Asgari Lajayer, B.; Thomson, A.; Astatkie, T.; Price, G.W. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated genetically edited ornamental and aromatic plants: A promising technology in phytoremediation of heavy metals. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 428, 139512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Cheng, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhuang, D. Effects of natural factors on the spatial distribution of heavy metals in soils surrounding mining regions. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 578, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tepanosyan, G.; Sahakyan, L.; Belyaeva, O.; Asmaryan, S.; Saghatelyan, A. Continuous impact of mining activities on soil heavy metals levels and human health. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Martín, J.D. Bioavailability and health risk of toxic heavy metals (As, Hg, Pb and Cd) in urban soils: A Monte Carlo simulation approach. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Han, Q.; Gui, C.; Cao, J.; Liu, Y.; He, X.; He, Y. Differences in the risk assessment of soil heavy metals between newly built and original parks in Jiaozuo, Henan Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 676, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, X.; Christakos, G.; Xiao, R.; Ren, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lv, X. Improved heavy metal mapping and pollution source apportionment in Shanghai City soils using auxiliary information. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 661, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yang, Y.; Christakos, G.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X. Assessment of soil heavy metal pollution using stochastic site indicators. Geoderma 2019, 337, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, B.; Teng, Y. Soil environmental quality in greenhouse vegetable production systems in eastern China: Current status and management strategies. Chemosphere 2017, 170, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Wang, M.; Xu, X.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, S.; Wang, M. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in road dust from the fourth-tier industrial city in central China based on Monte Carlo simulation and bioaccessibility. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 252, 114627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liu, Q.; Ma, J.; Wu, H.; Qu, Y.; Gong, Y.; Yang, S.; An, Y.; Zhou, Y. Heavy metal(loid)s in the topsoil of urban parks in Beijing, China: Concentrations, potential sources, and risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Zhao, R.; Pan, N.; Wang, F.; Yang, Y.; Luo, H. Source apportionment of heavy metals in farmland soil of Wuwei, China: Comparison of three receptor models. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Shi, Y.; Li, D.; Holm, P.E.; Ou, Q.; Hu, W. Quantitative source apportionment, risk assessment and distribution of heavy metals in agricultural soils from southern Shandong Peninsula of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 144879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Chao, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, A.; Cao, H. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil for a township in Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1658–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Cai, L.-M.; Wen, H.-H.; Luo, J.; Wang, Q.-S.; Liu, X. Spatial distribution and source apportionment of heavy metals in soil from a typical county-level city of Guangdong Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paatero, P. Least squares formulation of robust non-negative factor analysis. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1997, 37, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Fang, W.; Shafi, M.; Wu, D.; Li, Y.; Zhong, B.; Ma, J.; Liu, D. Source apportionment of heavy metals in farmland soil with application of APCS-MLR model: A pilot study for restoration of farmland in Shaoxing City Zhejiang, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 184, 109495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Li, K.; Guo, G.; Ju, T. Source-specific health risks apportionment of soil potential toxicity elements combining multiple receptor models with Monte Carlo simulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 152899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Liu, Z.; Shao, W.; Tian, J.; Luo, H.; Ni, F.; Shan, Y. Probabilistic risk assessment of heavy metals in urban farmland soils of a typical oasis city in northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhao, B.; Jin, M.; Hu, L.; Zhong, H.; He, Z. A comprehensive survey on the horizontal and vertical distribution of heavy metals and microorganisms in soils of a Pb/Zn smelter. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Yang, Q.; Ma, H.; Liang, J.; Niu, C.; Martin, J.D. Health risk assessment of phreatic water based on triangular fuzzy theory in Yinchuan plain. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 164, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Wu, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Geng, X.; Zhao, M.; Sun, T.; Fan, Z. Health risk assessment of heavy metal(loid)s in park soils of the largest megacity in China by using Monte Carlo simulation coupled with Positive matrix factorization model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Du, Q.; Guan, Q.; Luo, H.; Shan, Y.; Shao, W. A Monte Carlo simulation-based health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils of an oasis agricultural region in northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guleria, A.; Singh, R.; Chakma, S.; Birke, V. Ecological and human health risk assessment of chromite ore processing residue (COPR) dumpsites in Northern India: A multi–pathways based probabilistic risk approach. Process. Saf. Environ. 2022, 163, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Gu, Q.; Martín, J.D. Speciation, in vitro bioaccessibility and health risk of antimony in soils near an old industrial area. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; An, M.; Song, Y.; Fu, G.; Ruan, W.; Wu, D.; Li, X.; Yuan, K.; Wan, X.; Chen, Z.; et al. Soil heavy metals in tropical coastal interface of eastern Hainan Island in China: Distribution, sources and ecological risks. Ecol. Ind. 2023, 154, 110659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gong, J.; Gao, J.; Tang, S.; Ma, S.; Duan, Z. Heavy metal pollution in agricultural soils of a typical volcanic area: Risk assessment and source appointment. Chemosphere 2022, 304, 135340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal in Soils in the North of Hainan Province with High Background Value. Master’s Thesis, Hainan University in South China, Haikou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, W.; Zou, W.; Xu, S.; Li, J. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in soil of Hainan agricultural land. J. Trop. Biol. 2023, 14, 668–674. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, C.; Ma, L.; Cheng, H.; Liu, Y.; Xu, D.; Li, B.; Liu, F.; Ren, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, C. Characterization of the particle size fraction associated heavy metals in tropical arable soils from Hainan Island, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 139, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yu, T.; Li, M.; Xi, X.; Yun, W.; Ye, J.; Liu, R.; Cheng, H.; Zhou, G.; Cao, S.; et al. Specification for Geochemical Evaluation of Land Quality; Ministry of Land and Resources: Beijing, China, 2016; DZ/T 0295-2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Zhang, L.; Dong, J.; Wu, J.; Ye, Z.; Zhao, W.; Ding, L.; Fu, W. Risk assessment, spatial patterns and source apportionment of soil heavy metals in a typical Chinese hickory plantation region of southeastern China. Geoderma 2020, 360, 114011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, J.; Dai, L.; Jiang, H.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, F. Pollution characteristics and sources of heavy metals in paddy soils in a county of Hunan Province, China. J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2019, 38, 573–582. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.; Tai, L.; Qiao, Z.; Zhong, L.; Wang, Z.; Fu, K.; Chen, G. Contamination source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil around municipal solid waste incinerator: A case study in North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Yang, Y.; He, Y. Hainan Island 1:250,000 Multi-Target Regional Geochemical Survey Report. Natl. Geol. Libr. 2008, 10, 35080. [Google Scholar]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control.a sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Gong, J.; Song, D.; Li, Q.; Su, D. Evaluation of soil heavy metal pollution in Jinchuan mining area. Non-Ferr. Met. (Mine) 2018, 70, 88–93. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, S.; Liu, K.; Wang, G.; Wang, J. Application of APCA-MLR receptor model for source apportionment of char and soot in sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 746, 141165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. EPA Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) 5.0 Fundamentals and User Guide; U.S. Environment Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2014.
- Guan, Q.; Wang, F.; Xu, C.; Pan, N.; Lin, J.; Zhao, R.; Yang, Y.; Luo, H. Source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soil based on PMF: A case study in Hexi Corridor, northwest China. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepanosyan, G.; Sahakyan, L.; Belyaeva, O.; Saghatelyan, A. Origin identification and potential ecological risk assessment of potentially toxic inorganic elements in the topsoil of the city of Yerevan, Armenia. J. Geochem. Explor. 2016, 167, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Office of Health and Environmental Assessment, US Environmental Protection Agency. Exposure Factors Handbook; Office of Health and Environmental Assessment, US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1989.
- MEPPRC. Technical Guidelines for Risk Assessment of Contaminated Sites, HJ 25.3-2014; Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2014. (In Chinese)
- US EPA. Exposure Factors Handbook, 2011st ed.; EPA/600/R-09/052F; National Center for Environmental Assessment Office of Research and Development, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2011.
- US EPA. Soil Screening Guidance: Technical Background Document, Superfund US EPA; U.S. Environment Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1996.
- Men, C.; Liu, R.; Xu, F.; Wang, Q.; Guo, L.; Shen, Z. Pollution characteristics, risk assessment, and source apportionment of heavy metals in road dust in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Wang, Q.; Guan, Q.; Ma, Y.; Ni, F.; Yang, E.; Zhang, J. Heavy metal pollution levels, source apportionment and risk assessment in dust storms in key cities in Northwest China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 422, 126878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US EPA. Region IX, Regional Screening Levels (Formerly PRGs); US EPA: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2013.
- Zhao, R.; Guan, Q.; Luo, H.; Lin, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, F.; Yang, Y. Fuzzy synthetic evaluation and health risk assessment quantification of heavy metals in Zhangye agricultural soil from the perspective of sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 134126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Zhu, W.; Hao, S.; Hua, M.; Liao, Q.; Jing, Y.; Liu, L.; Gu, X. Prediction heavy metals accumulation risk in rice using machine learning and mapping pollution risk. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 448, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, R.; Tang, R.; Kong, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, G.; Yuan, J. Effects of phosphate-containing additives and zeolite on maturity and heavy metal passivation during pig manure composting. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MEE. Ministry of Ecology and Environment, PRC. Soil Environmental Quality-Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land. GB15618—2018 (In Chinese). 2018. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/trhj/201807/t20180703_446029.shtml (accessed on 20 August 2024).
- Wang, A.-T.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Yuan, G.-L.; Albanese, S.; Petrik, A. Geo-statistical and multivariate analyses of potentially toxic elements’ distribution in the soil of Hainan Island (China): A comparison between the topsoil and subsoil at a regional scale. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 197, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chi, H.; Tan, Z.; Yang, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, Z.; Hu, K.; Hao, F.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; et al. Heavy metals distribution characteristics, source analysis, and risk evaluation of soils around mines, quarries, and other special areas in a region of northwestern Yunnan, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 458, 132050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Cheng, Z.; Su, L. Pollution characteristics, spatial distributions, and source apportionment of heavy metals in cultivated soil in Lanzhou, China. Ecol. Ind. 2021, 125, 107507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Wang, H.; Dong, L.; Huang, B.; Borggaard, O.K.; Bruun Hansen, H.C.; He, Y.; Holm, P.E. Source identification of heavy metals in peri-urban agricultural soils of southeast China: An integrated approach. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.-l.; Zhi, Y.-y.; Yang, L.-p.; Shi, J.-c.; Zeng, L.-z.; Wu, L.-s. Positive matrix factorization as source apportionment of soil lead and cadmium around a battery plant (Changxing County, China). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 7698–7707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.A.R.; Arias, M.L.; Corbí, J.M.G. Heavy metals contents in agricultural topsoils in the Ebrobasin (Spain). application of the multivariate geostatistical methods to study spatial variations. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 144, 1001–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanesch, M.; Scholger, R.; Dekkers, M.J. The application of fuzzy C-means cluster analysis and non-linear mapping to a soil data set for the detection of polluted sites. Phys. Chem. Earth 2001, 26, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Hedding, D.W.; Nel, W.; Ji, J.; Chen, J. Geochemical behavior and potential health risk of heavy metals in basalt-derived agricultural soil and crops: A case study from Xuyi County, eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 139058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, R.; Li, Y.C.; Peng, Y.; Ni, X.J.E.; Safety, E. Distribution, accumulation, and potential risks of heavy metals in soil and tea leaves from geologically different plantations. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 195, 110475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Guan, Q.; Tian, J.; Lin, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L.; Pan, N. Contamination characteristics, source apportionment, and health risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soil in the hexi corridor. Catena 2020, 191, 104573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lu, X. Contamination characteristics and source apportionment of heavy metals in topsoil from an area in Xi’an city, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 151, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Kang, H.; Tao, W.; Li, H.; He, D.; Ma, L.; Tang, H.; Wu, S.; Yang, K.; Li, X. A spatial distribution—Principal component analysis (SD-PCA) model to assess pollution of heavy metals in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, M.; Peng, C. Regional accumulation characteristics of cadmium in vegetables: Influencing factors, transfer model and indication of soil threshold content. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nziguheba, G.; Smolders, E. Inputs of trace elements in agricultural soils viaphosphate fertilizers in European countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 390, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Qiu, S.; He, P. Changes of heavy metals in soil and wheat grain under longterm environmental impact and fertilization practices in North China. J. Plant Nutr. 2018, 41, 1970–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Wen, J.; Mu, L.; Gao, Z.; Weng, J.; Li, X.; Hu, X. Regulation of arsenite toxicity in lettuce by pyrite and glutamic acid and the related mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, H.; Guo, Z.; Yi, L.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y. Pollution characteristics and source identification of soil metal(loid)s at an abandoned arsenic-containing mine, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timofeev, I.; Kosheleva, N.; Kasimov, N. Health risk assessment based on the contents of potentially toxic elements in urban soils of Darkhan, Mongolia. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 242, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Classification Level | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Individual pollution index () | ||
| Class 1 | Non-pollution | < 1 |
| Class 2 | Moderate pollution | 1 ≤ < 2 |
| Class 3 | Strong pollution | 2 ≤ < 3 |
| Class 4 | Extremely strong pollution | ≥ 3 |
| Composite pollution index (INPI) | ||
| Class 1 | safety | INPI ≤ 0.7 |
| Class 2 | Alert Limit | 0.7 < INPI ≤ 1.0 |
| Class 3 | Lightly contaminated | 1 < INPI ≤ 2 |
| Class 4 | Medium Pollution | 2 < INPI ≤ 3 |
| Class 5 | Heavily polluted | 3 < INPI |
| Land Cumulative Pollution Index () | ||
|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | Not to weakly contaminated | ≤ 0 |
| Class 2 | Weakly to moderately contaminated | 0 < ≤ 1 |
| Class 3 | Moderately contaminated | 1 < ≤ 2 |
| Class 4 | Moderately to strongly contaminated | 2 < ≤ 3 |
| Class 5 | Strongly contaminated | 3 < ≤ 4 |
| Class 6 | Strongly to extremely contaminated | 4 < ≤ 5 |
| Class 7 | Extremely contaminated | 5 < |
| Classification Level | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Index of single-factor ecological risk () | ||
| Class 1 | Low risk | < 40 |
| Class 2 | Moderate risk | 40 ≤ < 80 |
| Class 3 | Considerable risk | 80 ≤ < 160 |
| Class 4 | High risk | 160 ≤ < 320 |
| Class 5 | Extremely high risk | ≥ 320 |
| Index of comprehensive ecological risk () | ||
| Class 1 | Low risk | RI < 150 |
| Class 2 | Moderate risk | 150 ≤ RI < 300 |
| Class 3 | Considerable risk | 300 ≤ RI < 600 |
| Class 4 | High risk | 600 ≤ RI < 1200 |
| Class 5 | Extremely high risk | RI ≥ 1200 |
| Indicator | Meaning | Unit | Adult | Child |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| lngR | Soil intake rate | mg·d−1 | 100 | 200 |
| EF | Frequency of exposure | d·year | 350 | 350 |
| ED | Years of exposure | year | 24 | 6 |
| BW | Average body weight | kg | 56.8 | 15.9 |
| AT | Average exposure time | d | 24 × 365 | 6 × 365 |
| SA | Exposed skin surface area | cm2 | 5938 | 2493 |
| AF | Skin Adhesion Factor | mg·(cm2·d)−1 | 0.07 | 0.2 |
| ABS | Skin absorption factor | - | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| APM | Particulate Volume per Unit Volume | mg·m−3 | 0.0651 | 0.0651 |
| lnhR | Daily air intake | m3·d−1 | 14.5 | 7.5 |
| Heavy Metal | RfD (mg/kg/day) | SF (per mg/kg/day) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ingest | Dermal | Inhalation | Ingest | Dermal | Inhalation | |
| Cr | 3.0 × 10−3 | 3.0 × 10−5 | 2.86 × 10−5 | 5.01 × 10−1 | 2.0 × 101 | 4.2 × 101 |
| Ni | 2.0 × 10−2 | 5.4 × 10−3 | 9.0 × 10−5 | 1.7 | 4.25 × 101 | 8.4 × 10−1 |
| Cu | 4.0 × 10−2 | 1.2 × 10−2 | - | - | - | - |
| Zn | 3.0 × 10−1 | 6.0 × 10−2 | - | - | - | - |
| As | 3.0 × 10−4 | 1.23 × 10−4 | 4.29 × 10−6 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.51 × 101 |
| Pb | 1.4 × 10−3 | 5.24 × 10−4 | - | 8.5 × 10−3 | - | 4.2 × 10−2 |
| Cd | 1.0 × 10−3 | 2.5 × 10−5 | 2.86 × 10−6 | - | - | 6.3 |
| Elemental | pH | Cr | Ni | Cu | Zn | As | Pb | Cd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | 3.88 | 5.22 | 3.65 | 3.92 | 13.84 | 0 | 7.57 | 0 |
| Max | 7.65 | 363.45 | 253.87 | 146.64 | 446.75 | 58.66 | 173.82 | 2.30 |
| Mean | 5.62 | 65.51 | 25.42 | 19.93 | 70.57 | 3.37 | 36.81 | 0.156 |
| Standard deviation | 0.71 | 62.27 | 38.77 | 18.85 | 44.04 | 5.67 | 18.36 | 0.186 |
| Coefficient of variation | 1.02 | 1.49 | 0.93 | 0.63 | 1.66 | 0.50 | 1.18 | |
| Hainan soil background | 27.50 | 7.24 | 6.10 | 44.4 | 1.34 | 24.4 | 0.04 | |
| Soil background in China | 61.00 | 27.00 | 23.00 | 74.00 | 11.00 | 26.00 | 0.097 |
| APCS-MLR | PMF | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | ||
| APCS-MLR | F1 | 1 | |||||||
| F2 | −0.116 * | 1 | |||||||
| F3 | 0.139 ** | 0.071 | 1 | ||||||
| F4 | −0.301 ** | −0.039 | −0.026 | 1 | |||||
| PMF | F1 | 0.848 ** | −0.054 | 0.311 ** | −0.266 ** | 1 | |||
| F2 | 0.048 | 0.818 ** | −0.166 ** | −0.053 | −0.012 | 1 | |||
| F3 | −0.150 ** | −0.146 ** | 0.793 ** | 0.109 * | −0.045 | −0.330 ** | 1 | ||
| F4 | 0.153 ** | −0.035 | 0.018 | 0.680 ** | 0.033 | 0.058 | 0 | 1 | |
| Risk | Soil PTEs | 5% | Mean | Median | 95% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HI | Cr | Adults | 7.97 × 10−2 | 9.36 × 10−2 | 6.22 × 10−2 | 1.04 × 10−1 |
| Children | 3.65 × 10−1 | 4.29 × 10−1 | 2.85 × 10−1 | 4.75 × 10−1 | ||
| Ni | Adults | 4.13 × 10−3 | 5.47 × 10−3 | 2.37 × 10−3 | 6.33 × 10−3 | |
| Children | 1.90 × 10−2 | 2.52 × 10−2 | 1.09 × 10−2 | 2.92 × 10−2 | ||
| Cu | Adults | 6.15 × 10−4 | 7.09 × 10−4 | 4.67 × 10−4 | 7.78 × 10−4 | |
| Children | 5.58 × 10−3 | 6.43 × 10−3 | 4.24 × 10−3 | 7.06 × 10−3 | ||
| Zn | Adults | 3.22 × 10−4 | 3.41 × 10−4 | 2.98 × 10−4 | 3.63 × 10−4 | |
| Children | 2.89 × 10−3 | 3.05 × 10−3 | 2.67 × 10−3 | 3.25 × 10−3 | ||
| As | Adults | 1.98 × 10−2 | 2.60 × 10−2 | 1.71 × 10−2 | 3.05 × 10−2 | |
| Children | 1.29 × 10−1 | 1.69 × 10−1 | 1.11 × 10−1 | 1.99 × 10−1 | ||
| Pb | Adults | 3.56 × 10−2 | 3.71 × 10−2 | 3.47 × 10−2 | 3.90 × 10−2 | |
| Children | 3.25 × 10−1 | 3.39 × 10−1 | 3.17 × 10−1 | 3.56 × 10−1 | ||
| Cd | Adults | 8.82 × 10−4 | 1.02 × 10−3 | 8.61 × 10−4 | 1.14 × 10−3 | |
| Children | 3.40 × 10−3 | 3.93 × 10−3 | 3.32 × 10−3 | 4.42 × 10−3 | ||
| THI | Total | Adults | 1.41 × 10−1 | 1.64 × 10−1 | 1.18 × 10−1 | 1.82 × 10−1 |
| Children | 8.50 × 10−1 | 9.76 × 10−1 | 7.34 × 10−1 | 1.07 × 100 | ||
| CR | Cr | Adults | 8.60 × 10−5 | 1.01 × 10−4 | 6.71 × 10−5 | 1.12 × 10−4 |
| Children | 4.70 × 10−4 | 5.52 × 10−4 | 3.67 × 10−4 | 6.11 × 10−4 | ||
| Ni | Adults | 5.76 × 10−5 | 7.63 × 10−5 | 3.31 × 10−5 | 8.84 × 10−5 | |
| Children | 4.47 × 10−4 | 5.92 × 10−4 | 2.57 × 10−4 | 6.85 × 10−4 | ||
| As | Adults | 5.84 × 10−6 | 7.66 × 10−6 | 5.05 × 10−6 | 9.00 × 10−6 | |
| Children | 5.06 × 10−5 | 6.64 × 10−5 | 4.37 × 10−5 | 7.80 × 10−5 | ||
| Pb | Adults | 4.30 × 10−7 | 4.49 × 10−7 | 4.19 × 10−7 | 4.72 × 10−7 | |
| Children | 3.88 × 10−6 | 4.05 × 10−6 | 3.79 × 10−6 | 4.26 × 10−6 | ||
| Cd | Adults | 1.10 × 10−8 | 1.27 × 10−8 | 1.08 × 10−8 | 1.43 × 10−8 | |
| Children | 2.66 × 10−8 | 3.07 × 10−8 | 2.60 × 10−8 | 3.45 × 10−8 | ||
| TCR | Total | Adults | 1.50 × 10−4 | 1.85 × 10−4 | 1.06 × 10−4 | 2.10 × 10−4 |
| Children | 9.72 × 10−4 | 1.21 × 10−3 | 6.72 × 10−4 | 1.38 × 10−3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Mu, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, Q.; Su, T.; Yang, Q.; Milinga, A.; Zhang, Y. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils Based on Multi-Receptor Modeling Combined with Monte Carlo Simulation. Toxics 2024, 12, 643. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12090643
Wu Y, Xia Y, Mu L, Liu W, Wang Q, Su T, Yang Q, Milinga A, Zhang Y. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils Based on Multi-Receptor Modeling Combined with Monte Carlo Simulation. Toxics. 2024; 12(9):643. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12090643
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yundong, Yan Xia, Li Mu, Wenjie Liu, Qiuying Wang, Tianyan Su, Qiu Yang, Amani Milinga, and Yanwei Zhang. 2024. "Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils Based on Multi-Receptor Modeling Combined with Monte Carlo Simulation" Toxics 12, no. 9: 643. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12090643
APA StyleWu, Y., Xia, Y., Mu, L., Liu, W., Wang, Q., Su, T., Yang, Q., Milinga, A., & Zhang, Y. (2024). Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils Based on Multi-Receptor Modeling Combined with Monte Carlo Simulation. Toxics, 12(9), 643. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12090643









