Surgical Management of a Salter-Harris Type I Distal Physeal Fracture of the Tibia in a Calf: A Case Report
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
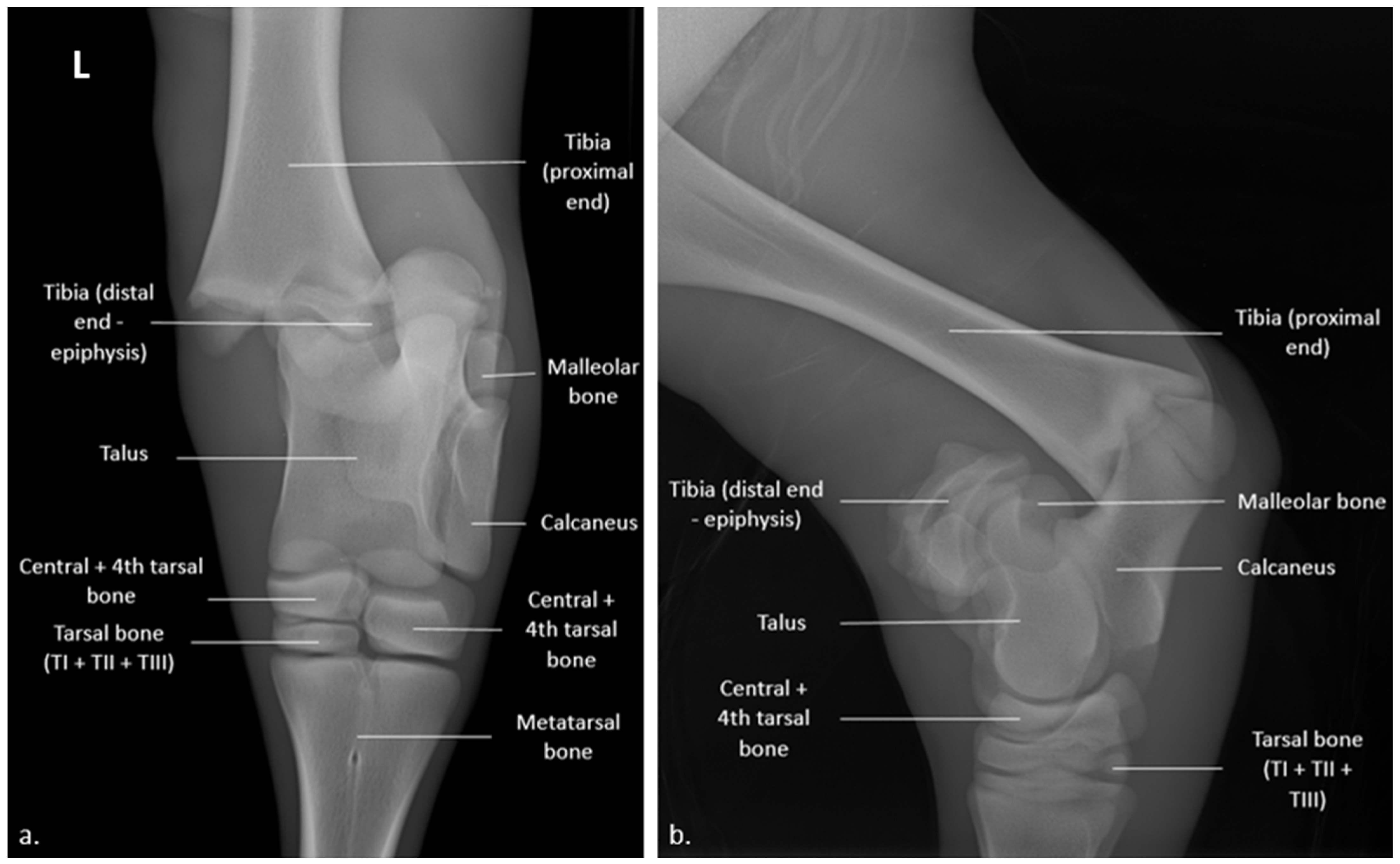
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Sahar, M.W.; Beaver, A.; Daros, R.R.; Von Keyserlingk, M.A.G.; Weary, D.M. Measuring lameness prevalence: Effects of case definition and assessment frequency. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 7728–7737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis-Unger, J.; Schwartzkopf-Genswein, K.S.G.; Pajor, E.A.; Hendrick, S.; Marti, S.; Dorin, C.; Orsel, K. Prevalence and lameness-associated risk factors in Alberta feedlot cattle. Transl. Anim. Sci. 2019, 3, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francoz, D.; Nichols, S.; Schelcher, F. Guide Pratique des Maladies du Veau; Med’com: Paris, France, 2017; p. 335. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, J.G.; Dehghani, S.; Petrali, E.H. Fractures of the femur in newborn calves. Can. Vet. J. 1990, 31, 289–291. [Google Scholar]
- Ivany Ewoldt, J.M.; Hull, B.L.; Ayars, W.H. Repair of femoral capital physeal fractures in 12 cattle. Vet. Surg. 2003, 32, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loyd, A.F.; Tatarniuk, D.M.; Naiman, J.H.; Merkatoris, P.T.; Troy, J.R. Case report: Fluoroscopic-assisted closed reduction and minimally invasive femoral capital physeal fracture repair in four calves. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 970220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.-Y.; Kim, E.-J.; Kim, M.-S.; Lee, K.; Kim, N.-S.; Lee, H.B. Use of Cross Pins and Temporal External Skeletal Fixator for Stabilization of a Tibial Physeal Fracture in a Korean Native Calf. J. Vet. Clin. 2012, 29, 198–201. [Google Scholar]
- Seddighi, R.; Doherty, T.J. Field Sedation and Anesthesia of Ruminants. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2016, 32, 553–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latte, Y.; Meynard, J.-A. Manuel de Fixation Externe: Applications au Chien et au Chat; Pratique Médicale et Chirurgicale de l’Animal de Compagnie: Paris, France, 1997; pp. 237–242. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, R.H. External Fixators and Minimally Invasive Osteosynthesis in Small Animal Veterinary Medicine. Vet. Clin. Small Anim. 2012, 42, 913–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roush, J.K. Fractures of the Tibia. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 1992, 22, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, G.F.; Turner, A.S.; Ferguson, J.G.; Pharr, J.W. Slipped capital femoral epiphysis in calves. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1978, 172, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar]
- Hindson, J.C. Quantification of obstetrical traction. Vet. Rec. 1978, 102, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersjes, A.W.; Nemeth, F.; Rutgers, L.J.E. Atlas of Large Animal Surgery; Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1985; pp. 118–119. [Google Scholar]
- Embertson, R.M.; Bramlage, L.R.; Gabel, A.A. Physeal fractures in the horse I. Classification and incidence. Vet. Surg. 1986, 15, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazaheri-Khameneh, R.; Azizi, S.; Davoodi, F.; Gooran, M.M. Surgical management of a Salter-Harris type I proximal physeal fracture of the tibia in a foal: A case report. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.E.; Jean, G.S. Management of fractures in field settings. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2008, 24, 567–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, D.G.; Aitken, M.R. Physeal Fractures in Foals. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2017, 33, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, W.G.; Aron, D.N.; Rowland, G.N.; Odend’hal, S.; Brown, J. The effect of trans-stifle external skeletal fixation and hyaluronic acid therapy on articular cartilage in the dog. Vet. Surg. 1994, 23, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elisé, S.; Maynou, C.; Mestdagh, H.; Forgeois, P.; Labourdette, P. Simple tibiotalar luxation. Apropos of 16 cases. Acta Orthop. Belg. 1998, 64, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Vasseur, P.B.; Levy, J.; Dowd, E.; Eliot, J. Surgical wound infection rates in dogs and cats. Data from a teaching hospital. Vet. Surg. 1988, 17, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselin, R.A.; Roberts, I.; Gillespie, W.J. Antibiotics for preventing infection in open limb fractures. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2004, CD003764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupp, M.; Popp, D.; Alt, V. Prevention of infection in open fractures: Where are the pendulums now? Injury 2020, 51, S57–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittem, T.L.; Johnson, A.L.; Smith, C.W.; Schaeffer, D.J.; Coolman, B.R.; Averill, S.M.; Cooper, T.K.; Merkin, G.R. Effect of perioperative prophylactic antimicrobial treatment in dogs undergoing elective orthopedic surgery. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1999, 215, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wiggins, C.E.; Nelson, C.L.; Clarke, R.; Thompson, C.H. Concentration of antibiotics in normal bone after intravenous injection. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1978, 60, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkington, M.S.; Davison, M.J.; Wheelwright, E.F.; Jenkins, P.J.; Anthony, I.; Lovering, A.M.; Blyth, M.; Jones, B. Bone penetration of intravenous flucloxacillin and gentamicin as antibiotic prophylaxis during total hip and knee arthroplasty. Bone Jt. J. 2017, 99-B, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, L.M.; Boothe, H.W., Jr. Antimicrobial use in the surgical patient. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2006, 36, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Therapeutic Guidelines on Antimicrobial Prophylaxis in Surgery. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 1999, 56, 1839–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network. Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Surgery, a National Clinical Guideline; SIGN: Edinburgh, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, S.J.; Chow, M. Gentamicin nephrotoxicity. Nephron 1978, 22, 596–597. [Google Scholar]




| Distances between the Pins | Values (cm) |
|---|---|
| a | 5 |
| b | 3 |
| c | 2 |
| d | 4 |
| e | 2 |
| f | 3 |
| g | 2 |
| h | 1.5 |
| i | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lemaitre, V.; Cote, E.; Bellon, C.; Cassard, H.; Schelcher, F.; Maillard, R.; Robcis, R. Surgical Management of a Salter-Harris Type I Distal Physeal Fracture of the Tibia in a Calf: A Case Report. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 463. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10070463
Lemaitre V, Cote E, Bellon C, Cassard H, Schelcher F, Maillard R, Robcis R. Surgical Management of a Salter-Harris Type I Distal Physeal Fracture of the Tibia in a Calf: A Case Report. Veterinary Sciences. 2023; 10(7):463. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10070463
Chicago/Turabian StyleLemaitre, Victor, Emeline Cote, Christophe Bellon, Hervé Cassard, François Schelcher, Renaud Maillard, and Rodolphe Robcis. 2023. "Surgical Management of a Salter-Harris Type I Distal Physeal Fracture of the Tibia in a Calf: A Case Report" Veterinary Sciences 10, no. 7: 463. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10070463
APA StyleLemaitre, V., Cote, E., Bellon, C., Cassard, H., Schelcher, F., Maillard, R., & Robcis, R. (2023). Surgical Management of a Salter-Harris Type I Distal Physeal Fracture of the Tibia in a Calf: A Case Report. Veterinary Sciences, 10(7), 463. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10070463





