Microbiota in Mild Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Can Be Modulated by Beta-Glucans and Mannanoligosaccharides: A Randomized, Double-Blinded Study in Dogs
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Microbiota Analysis
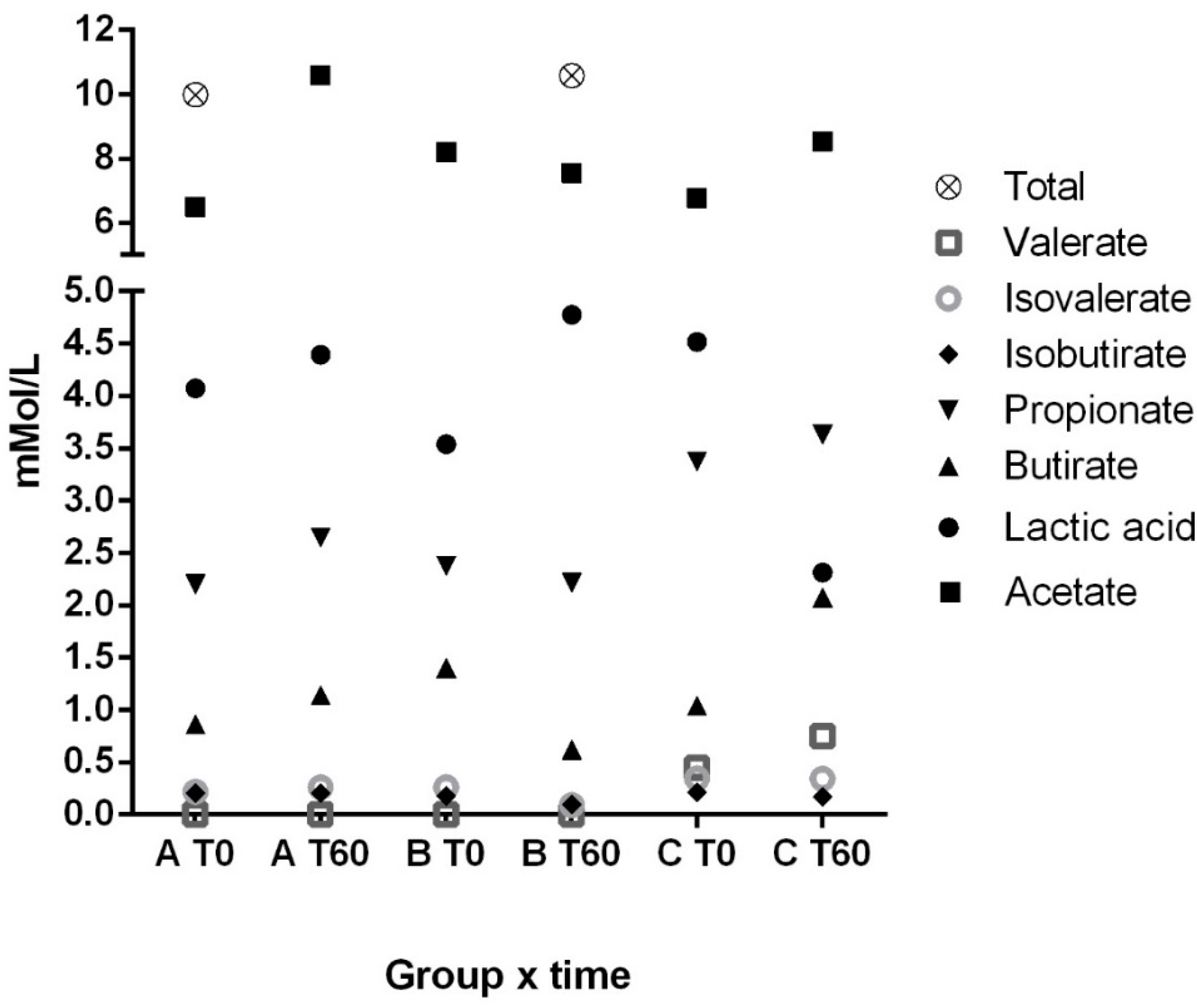
2.3. Short and Branched-Chain Fatty Acid Concentrations
2.4. Prebiotic Composition
2.5. Statistics
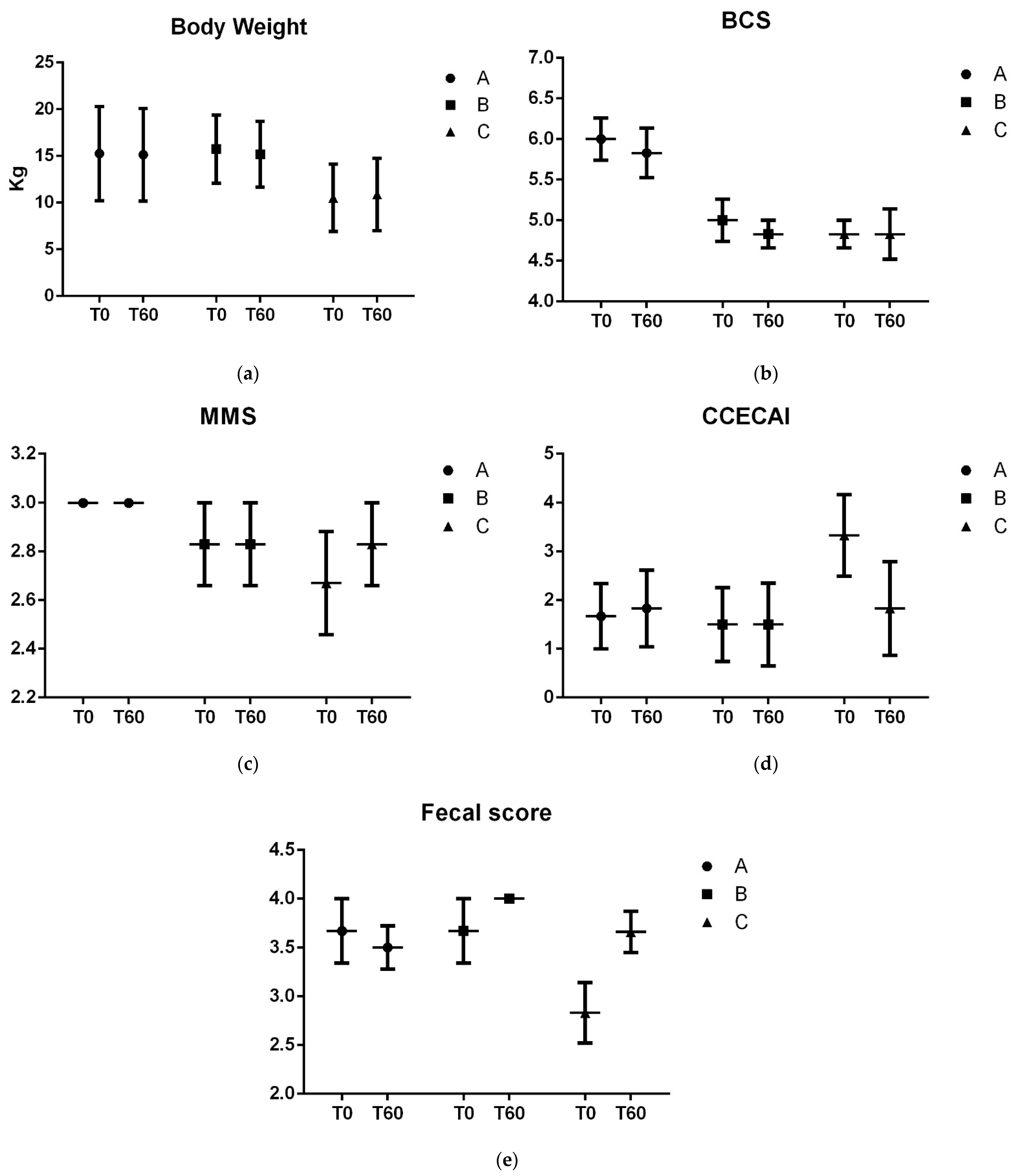
3. Results
3.1. Fecal Lactic Acid, Short and Branched-Chain Fatty Acids
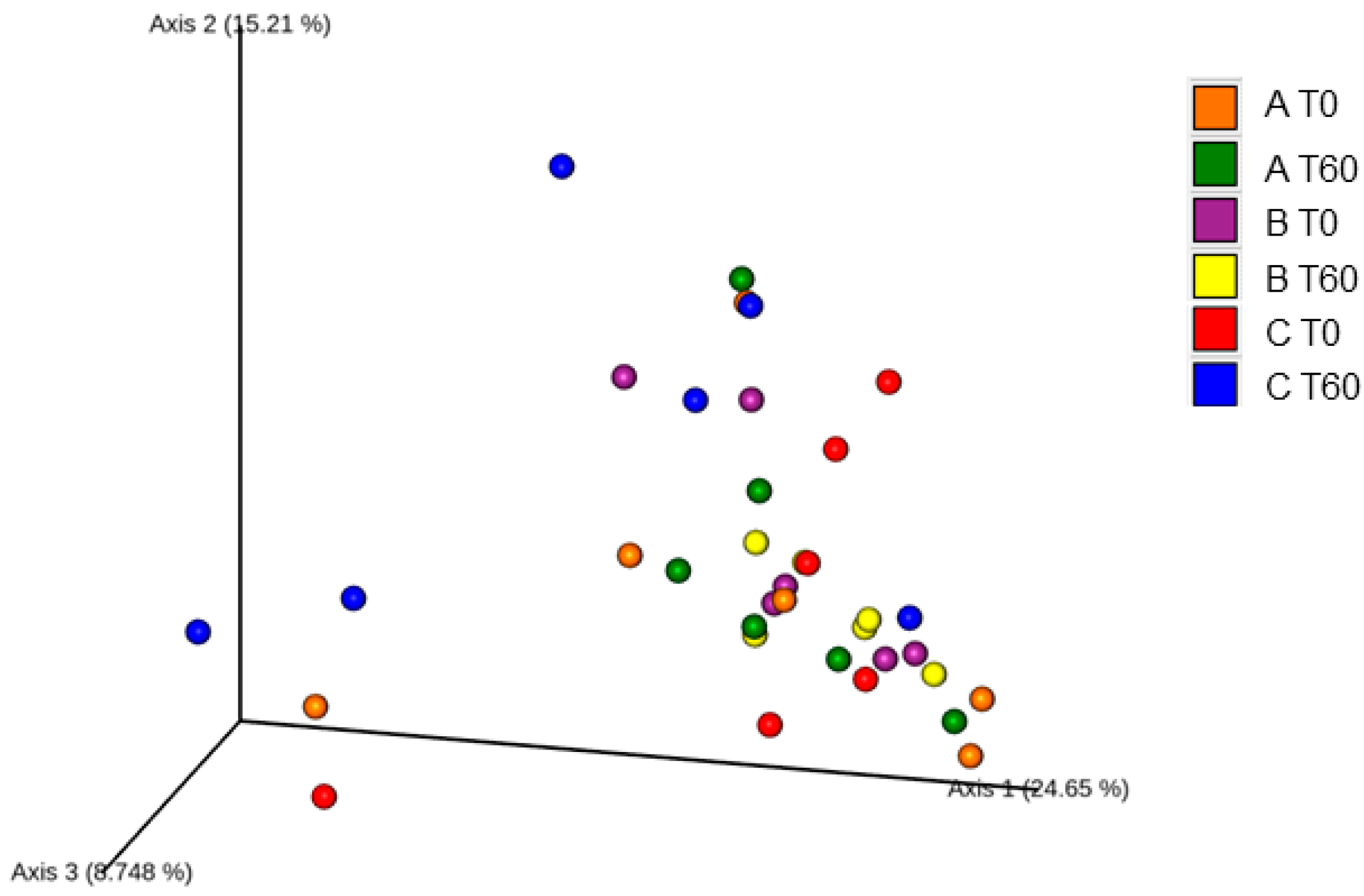
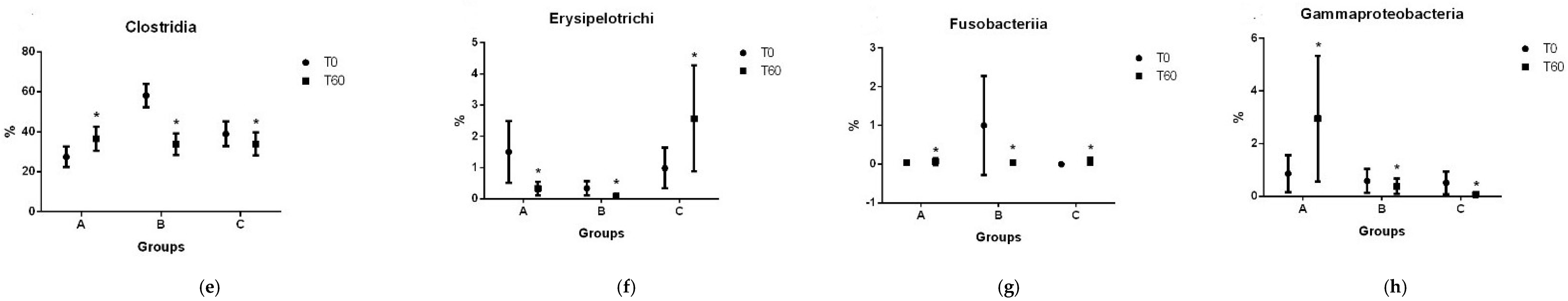
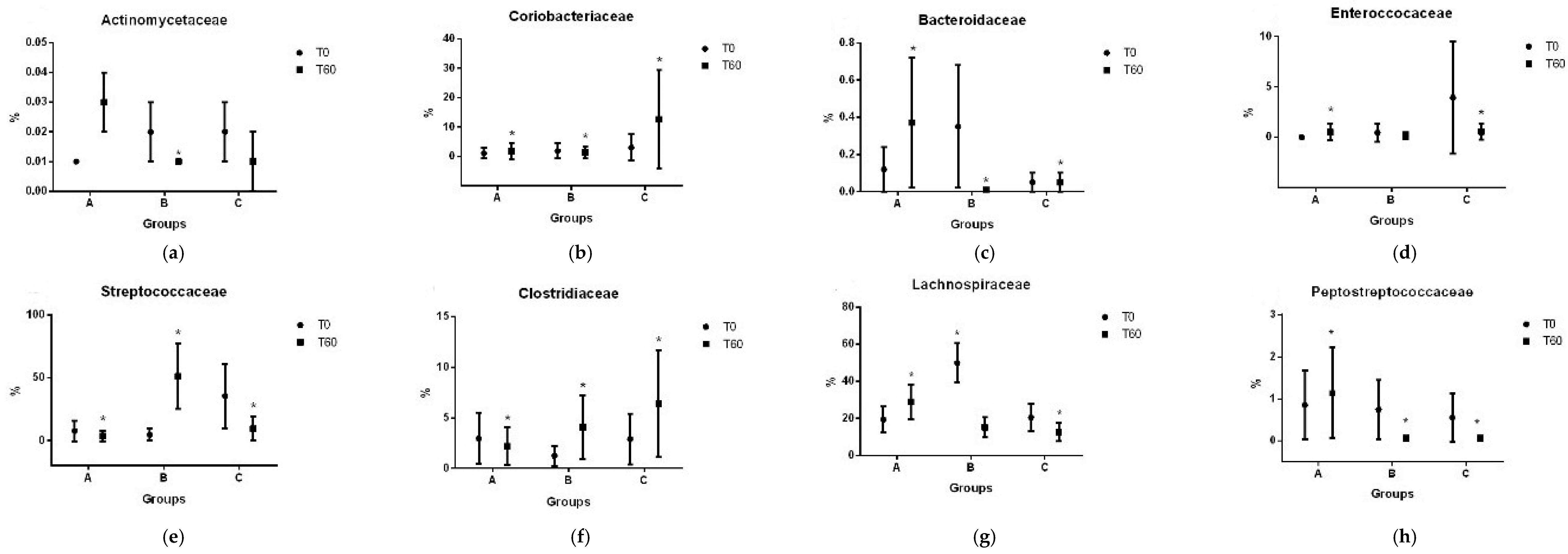
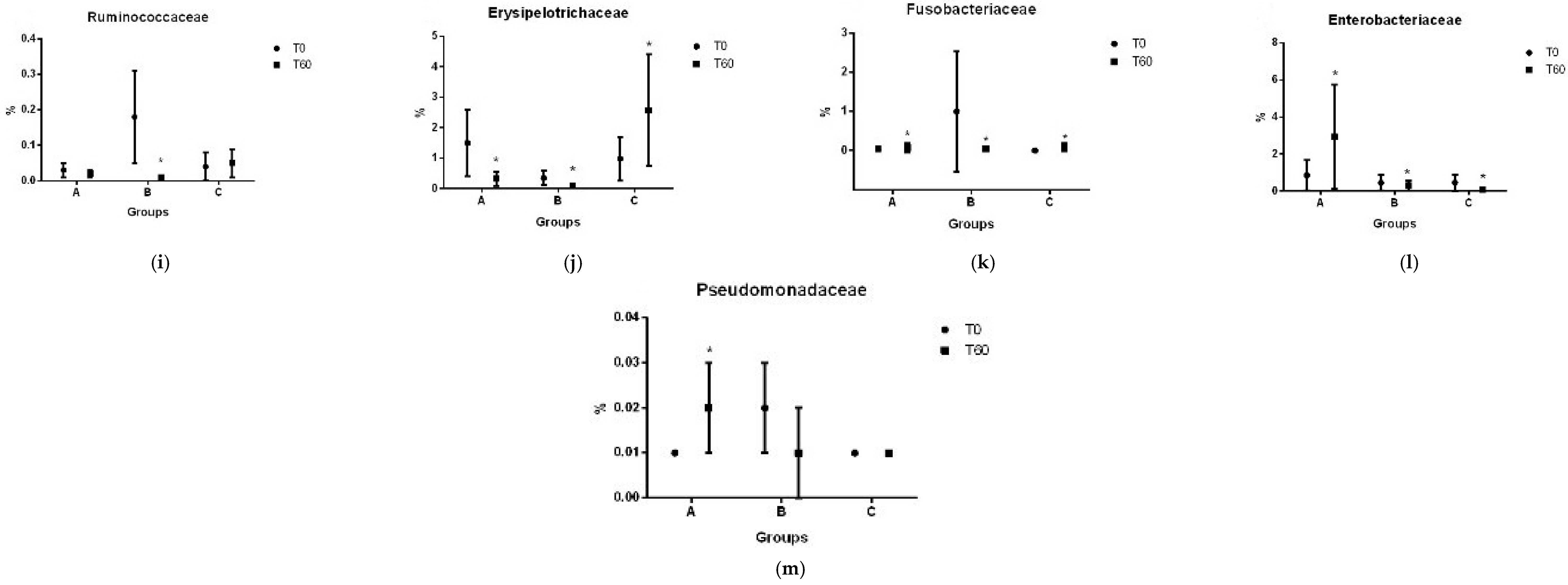
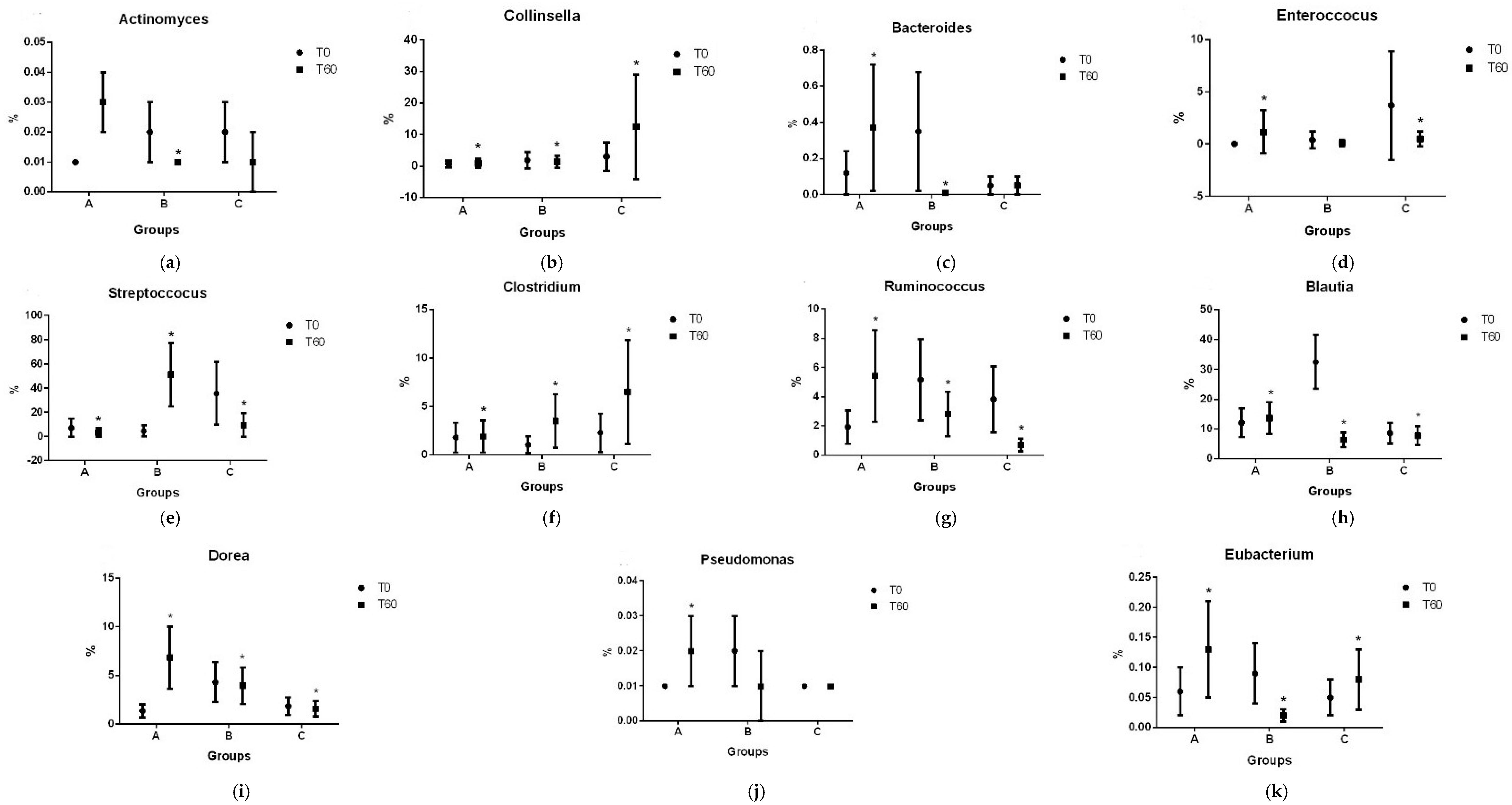
3.2. Gut Microbiota
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Minamoto, Y.; Otoni, C.C.; Steelman, S.M.; Büyükleblebici, O.; Steiner, J.M.; Jergens, A.E.; Suchodolski, J.S. Alteration of the Fecal Microbiota and Serum Metabolite Profiles in Dogs with Idiopathic Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gut Microbes 2015, 6, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cave, N. Nutritional Management of Gastrointestinal Diseases. In Applied Veterinary Clinical Nutrition; Fascetti, A.J., Delaney, S.J., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 175–219. ISBN 9781118785669. [Google Scholar]
- Davenport, D.J.; Jergens, A.E.; Remmilard, R. Inflammatory Bowel Disease. In Small Animal Clinical Nutritional; Hand, M.S., Thatcher, C.D., Remillard, R.L., Roudebush, P., Novotny, B.J., Eds.; Mark Morris Institute: Topeka, KS, USA, 2010; pp. 1065–1076. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka, K.; Kanai, T. The Gut Microbiota and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Semin. Immunopathol. 2015, 37, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blake, A.B.; Suchodolski, J.S. Importance of Gut Microbiota for the Health and Disease of Dogs and Cats. Anim. Front. 2016, 6, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlShawaqfeh, M.K.; Wajid, B.; Minamoto, Y.; Markel, M.; Lidbury, J.A.; Steiner, J.M.; Serpedin, E.; Suchodolski, J.S. A Dysbiosis Index to Assess Microbial Changes in Fecal Samples of Dogs with Chronic Inflammatory Enteropathy. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, fix136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Pan, Z.; Yang, R.; Bi, Y.; Xiong, X. The Canine Gastrointestinal Microbiota: Early Studies and Research Frontiers. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 635–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suchodolski, J.S.; Markel, M.E.; Garcia-Mazcorro, J.F.; Unterer, S.; Heilmann, R.M.; Dowd, S.E.; Kachroo, P.; Ivanov, I.; Minamoto, Y.; Dillman, E.M.; et al. The Fecal Microbiome in Dogs with Acute Diarrhea and Idiopathic Inflammatory Bowel Disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suchodolski, J.S. Analysis of the Gut Microbiome in Dogs and Cats. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2022, 50, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penner, R.; Fedorak, R.N.; Madsen, K.L. Probiotics and Nutraceuticals: Non-Medicinal Treatments of Gastrointestinal Diseases. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2005, 5, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilla, R.; Suchodolski, J.S. The Gut Microbiome of Dogs and Cats, and the Influence of Diet. Vet. Clin. North. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2021, 51, 605–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topping, D.L. Short-Chain Fatty Acids Produced by Intestinal Bacteria. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 5, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Chaitman, J.; Gaschen, F. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Dogs. Vet. Clin. North. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2021, 51, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rychlik, A.; Nieradka, R.; Kander, M.; Nowicki, M.; Wdowiak, M.; Kołodziejska-Sawerska, A. The Effectiveness of Natural and Synthetic Immunomodulators in the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Dogs. Acta Vet. Hung. 2013, 61, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orel, R.; Trop, T.K. Intestinal Microbiota, Probiotics and Prebiotics in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 11505–11524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malewska, K.; Rychlik, A.; Nieradka, R.; Kander, M. Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) in Dogs and Cats. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2011, 14, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segarra, S.; Martínez-Subiela, S.; Cerdà-Cuéllar, M.; Martínez-Puig, D.; Muñoz-Prieto, A.; Rodríguez-Franco, F.; Rodríguez-Bertos, A.; Allenspach, K.; Velasco, A.; Cerón, J. Oral Chondroitin Sulfate and Prebiotics for the Treatment of Canine Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Randomized, Controlled Clinical Trial. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyła, E.; Dziendzikowska, K.; Gajewska, M.; Wilczak, J.; Harasym, J.; Gromadzka-Ostrowska, J. Beneficial Effects of Oat Beta-Glucan Dietary Supplementation in Colitis Depend on Its Molecular Weight. Molecules 2019, 24, 3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, A.R.; Risolia, L.W.; Rentas, M.F.; Marchi, P.H.; Balieiro, J.C.C.; Vendramini, T.H.; Brunetto, M.A. Translating Human and Animal Model Studies to Dogs’ and Cats’ Veterinary Care: Beta-Glucans Application for Skin Disease, Osteoarthritis, and Inflammatory Bowel Disease Management. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washabau, R.J.; Day, M.J.; Willard, M.D.D.; Hall, E.J.; Jergens, A.E.; Mansell, J.; Minami, T.; Bilzer, T.W. Endoscopic, Biopsy, and Histopathologic Guidelines for the Evaluation of Gastrointestinal Inflammation in Companion Animals. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2010, 24, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allenspach, K.A.; Mochel, J.P.; Du, Y.; Priestnall, S.L.; Moore, F.; Slayter, M.; Rodrigues, A.; Ackermann, M.; Krockenberger, M.; Mansell, J.; et al. Correlating Gastrointestinal Histopathologic Changes to Clinical Disease Activity in Dogs With Idiopathic Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Vet. Pathol. 2019, 56, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carciofi, A.C.; Takakura, F.S.; De-Oliveira, L.D.; Teshima, E.; Jeremias, J.T.; Brunetto, M.A.; Prada, F. Effects of Six Carbohydrate Sources on Dog Diet Digestibility and Post-Prandial Glucose and Insulin Response. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2008, 92, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laflamme, D.P. Development and Validation of a Body Condition Score System for Dogs. Canine Pract. 1997, 22, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, K.E.; Anderson, W.; Cupp, C.; Laflamme, D.P. Correlation of a Feline Muscle Mass Score with Body Composition Determined by Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 106, S57–S59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- NRC Nutrient Requirements of Dogs and Cats. In Nutrient Requirements of Dogs and Cats; National Academy Press, Ed.; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; p. 33. ISBN 0309086280.
- Pryce, J.D. A Modification of the Barker-Summerson Method for the Determination of Lactic Acid. Analyst 1969, 26, 1151–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erwin, E.S.; Marco, G.J.; Emery, E.M. Volatile Fatty Acid Analyses of Blood and Rumen Fluid by Gas Chromatography. J. Dairy. Sci. 1961, 44, 1768–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehain, S.O.; Haines, J.M.; Lee, P.M. Platelet Indices as Biomarkers for Characterization and Determination of Severity in Canine Chronic Enteropathy. Vet. J. 2019, 248, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridgway, J.; Jergens, A.E.; Niyo, Y. Possible Causal Association of Idiopathic Inflammatory Bowel Disease with Thrombocytopenia in the Dog. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2001, 37, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agouridis, A.; Moses, E.; Milionis, H.J. An Overview of Lipid Abnormalities in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2011, 24, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sappati Biyyani, R.S.R.; Putka, B.S.; Mullen, K.D. Dyslipidemia and Lipoprotein Profiles in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2010, 4, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeire, S.; Van Assche, G.; Rutgeerts, P. Laboratory Markers in IBD: Useful, Magic, or Unnecessary Toys? Gut 2006, 55, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, Y.; Ohta, H.; Kagawa, Y.; Osuga, T.; Morishita, K.; Sasaki, N.; Takiguchi, M. Plasma Amino Acid Profiles in Dogs with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 1602–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celikbilek, M.; Dogan, S.; Ozbakir, O.; Zararsiz, G.; Kücük, H.; Gürsoy, S.; Yurci, A.; Güven, K.; Yücesoy, M. Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Predictor of Disease Severity in Ulcerative Colitis. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2013, 27, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherfane, C.E.; Gessel, L.; Cirillo, D.; Zimmerman, M.B.; Polyak, S. Monocytosis and a Low Lymphocyte to Monocyte Ratio Are Effective Biomarkers of Ulcerative Colitis Disease Activity. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 1769–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchesi, M.C.; Maggi, G.; Cremonini, V.; Miglio, A.; Contiero, B.; Guglielmini, C.; Antognoni, M.T. Monocytes Count, NLR, MLR and PLR in Canine Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Animals 2024, 14, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, D.N.; St. Amand, A.L.; Feldman, R.A.; Boedeker, E.C.; Harpaz, N.; Pace, N.R. Molecular-Phylogenetic Characterization of Microbial Community Imbalances in Human Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13780–13785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhya, I.; Hansen, R.; El-Omar, E.M.; Hold, G.L. IBD-What Role Do Proteobacteria Play? Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blake, A.B.; Guard, B.C.; Honneffer, J.B.; Lidbury, J.A.; Steiner, J.M.; Suchodolski, J.S. Altered Microbiota, Fecal Lactate, and Fecal Bile Acids in Dogs with Gastrointestinal Disease. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, K.S.; Grieshop, C.M.; Flickinger, E.A.; Bauer, L.L.; Healy, H.P.; Dawson, K.A.; Merchen, N.R.; Fahey, G.C. Supplemental Fructooligosaccharides and Mannanoligosaccharides Influence Immune Function, Ileal and Total Tract Nutrient Digestibilities, Microbial Populations and Concentrations of Protein Catabolites in the Large Bowel of Dogs. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fries, W.; Comunale, S. Ulcerative Colitis: Pathogenesis. Curr. Drug Targets 2011, 12, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, I.; Kim, M. Comparison of Gut Microbiota of 96 Healthy Dogs by Individual Traits: Breed, Age, and Body Condition Score. Animals 2021, 11, 2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handl, S.; German, A.J.; Holden, S.L.; Dowd, S.E.; Steiner, J.M.; Heilmann, R.M.; Grant, R.W.; Swanson, K.S.; Suchodolski, J.S. Faecal Microbiota in Lean and Obese Dogs. Fed. Eur. Microbiol. Soc. Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 84, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handl, S.; Dowd, S.E.; Garcia-Mazcorro, J.F.; Steiner, J.M.; Suchodolski, J.S. Massive Parallel 16S RRNA Gene Pyrosequencing Reveals Highly Diverse Fecal Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Healthy Dogs and Cats. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 76, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omori, M.; Maeda, S.; Igarashi, H.; Ohno, K.; Sakai, K.; Yonezawa, T.; Horigome, A.; Odamaki, T.; Matsuki, N. Fecal Microbiome in Dogs with Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Intestinal Lymphoma. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2017, 79, 1840–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Bassler, B.L. Bacterial Quorum Sensing in Complex and Dynamically Changing Environments. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abisado, R.G.; Benomar, S.; Klaus, J.R.; Dandekar, A.A.; Chandler, J.R. Bacterial Quorum Sensing and Microbial Community Interactions. MBio 2018, 9, e02331-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perini, M.P.; Rentas, M.F.; Pedreira, R.; Amaral, A.R.; Zafalon, R.V.A.; Rodrigues, R.B.A.; Henríquez, L.B.F.; Zanini, L.; Vendramini, T.H.A.; Balieiro, J.C.C.; et al. Duration of Prebiotic Intake Is a Key-Factor for Diet-Induced Modulation of Immunity and Fecal Fermentation Products in Dogs. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, C.; Round, J.L. Defining Dysbiosis and Its Influence on Host Immunity and Disease. Cell Microbiol. 2014, 16, 1024–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.I.; Jewell, D.E. Docosahexaenoate-Enriched Fish Oil and Medium Chain Triglycerides Shape the Feline Plasma Lipidome and Synergistically Decrease Circulating Gut Microbiome-Derived Putrefactive Postbiotics. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Macrogard® * | |
| Beta-glucan (g/100 g) | 60.0 |
| Fat (g/100 g) | 18.0 |
| Protein (N × 6.25) (g/100 g) | 8.0 |
| Ash | 10.0 |
| Solubility in water | 7.9 |
| Prebiotic blend | |
| Beta-glucan (g/100 g) | 25.0 |
| MOS (g/100 g) | 20.0 |
| MOS solubility in water | 100.0 |
| Groups | p-Value | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | SEM | Ref 1 | Treatment | Time | Treatment × Time | |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.92 | 4.12 | 3.56 | 0.176 | 2.3–3.8 | 0.1015 | 0.1082 | 0.8482 |
| Total protein (g/dL) | 6.87 | 6.98 | 6.34 | 0.289 | 5.3–7.6 | 0.2744 | 0.4543 | 0.6651 |
| ALT (U/L) | 37.55 | 21.65 | 24.00 | 5.856 | 10–88 | 0.1513 | 0.1418 | 0.1880 |
| Alkaline phosphatase (U/L) | 250.50 | 68.83 | 48.30 | 85.104 | 20–150 | 0.2143 | 0.6185 | 0.5766 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 32.60 | 29.40 | 39.27 | 4.835 | 20–40 | 0.3635 | 0.0265 | 0.1308 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.92 | 1.01 | 0.83 | 0.072 | 0.7–1.4 | 0.2695 | 0.9872 | 0.8450 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 275.03 | 96.43 | 100.95 | 69.994 | 40–169 | 0.1381 | 0.9931 | 0.9888 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 278.90 A | 164.69 B | 207.09 AB | 26.852 | 125–270 | 0.0273 | 0.9801 | 0.9469 |
| Cobalamin (ng/L) | 700.17 | 511.67 | 428.58 | 79.859 | 252–836 2 | 0.0781 | 0.7180 | 0.9386 |
| Folate (nmol/L) | 45.58 | 35.50 | 35.00 | 5.559 | 7–39 2 | 0.3420 | 0.1976 | 0.4427 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 63.61 | 9.37 | 33.93 | 32.406 | 0–10 | 0.5108 | 0.1646 | 0.4455 |
| Spec (ng/mL) | 166.83 | 98.33 | 55.51 | 37.412 | <200 | 0.1395 | 0.0494 | 0.1266 |
| TLI (mcg/L) | 30.66 | 24.25 | 21.41 | 4.918 | 9–50 | 0.4167 | 0.8689 | 0.0887 |
| Total leucocyte (/μL) | 8482.50 | 10,203.00 | 9175.00 | 851.060 | 6.000–15.000 | 0.3679 | 0.4915 | 0.2606 |
| Lymphocytes (/μL) | 1789.50 | 1679.42 | 2169.83 | 359.310 | 1.500–5.000 | 0.6064 | 0.9219 | 0.3593 |
| Monocytes (/μL) | 672.33 | 396.17 | 468.37 | 63.758 | 0–800 | 0.0129 | 0.6250 | 0.0226 |
| Eosinophil (/μL) | 347.50 | 592.00 | 543.00 | 164.290 | 0–1.300 | 0.5512 | 0.5671 | 0.2877 |
| Basophil (/μL) | 69.16 | 39.16 | 47.50 | 27.937 | 0–140 | 0.7394 | 0.5324 | 0.5025 |
| Platlets (103/μL) | 473.08 A | 289.67 B | 407.33 AB | 41.422 | 200–600 | 0.0014 | 0.4776 | 0.5747 |
| Time | |||||
| Groups | T0 | T60 | |||
| Average | SEM | Average | SEM | ||
| Shannon | A | 2.34 Ab | 0.28 | 2.87 Aa | 0.28 |
| B | 2.64 Aa | 0.28 | 2.29 Aa | 0.28 | |
| C | 2.48 Aa | 0.28 | 2.72 Aa | 0.28 | |
| OTUS | A | 52.96 Aa | 3.87 | 57.61 Aa | 3.87 |
| B | 54.08 Aa | 3.87 | 48.20 Aa | 3.87 | |
| C | 44.71 Aa | 3.87 | 61.95 Aa | 3.87 | |
| Simpson | A | 3.33 Aa | 0.80 | 4.88 Aa | 1.05 |
| B | 6.00 Aa | 2.06 | 2.73 Aa | 0.32 | |
| C | 4.11 Aa | 0.73 | 4.17 Aa | 0.81 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amaral, A.R.; Rentas, M.F.; Rosa, T.C.T.; Pereira, T.A.E.; Marchi, P.H.; Teixeira, F.A.; Filho, F.d.O.R.; Putarov, T.C.; Cogliati, B.; Vendramini, T.H.A.; et al. Microbiota in Mild Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Can Be Modulated by Beta-Glucans and Mannanoligosaccharides: A Randomized, Double-Blinded Study in Dogs. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11080349
Amaral AR, Rentas MF, Rosa TCT, Pereira TAE, Marchi PH, Teixeira FA, Filho FdOR, Putarov TC, Cogliati B, Vendramini THA, et al. Microbiota in Mild Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Can Be Modulated by Beta-Glucans and Mannanoligosaccharides: A Randomized, Double-Blinded Study in Dogs. Veterinary Sciences. 2024; 11(8):349. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11080349
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmaral, Andressa Rodrigues, Mariana Fragoso Rentas, Thais Caroline Taveira Rosa, Thais Araújo Esteves Pereira, Pedro Henrique Marchi, Fabio Alves Teixeira, Fernando de Oliveira Roberti Filho, Thaila Cristina Putarov, Bruno Cogliati, Thiago Henrique Annibale Vendramini, and et al. 2024. "Microbiota in Mild Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Can Be Modulated by Beta-Glucans and Mannanoligosaccharides: A Randomized, Double-Blinded Study in Dogs" Veterinary Sciences 11, no. 8: 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11080349
APA StyleAmaral, A. R., Rentas, M. F., Rosa, T. C. T., Pereira, T. A. E., Marchi, P. H., Teixeira, F. A., Filho, F. d. O. R., Putarov, T. C., Cogliati, B., Vendramini, T. H. A., Balieiro, J. C. d. C., & Brunetto, M. A. (2024). Microbiota in Mild Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Can Be Modulated by Beta-Glucans and Mannanoligosaccharides: A Randomized, Double-Blinded Study in Dogs. Veterinary Sciences, 11(8), 349. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11080349







