Non-Melibiose Fermentation and Tellurite Resistance by Shigatoxigenic and Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli O80:H2 from Diseased Calves: Comparison with Human Shigatoxigenic E. coli O80:H2
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Escherichia coli O80 Strains
2.2. Genetic Studies
2.2.1. MF-Encoding mel Operon and the 70mel DNA Sequence
2.2.2. Tellurite Resistance-Encoding ter Operon
2.3. Phenotypic Assays
2.3.1. Melibiose Fermentation
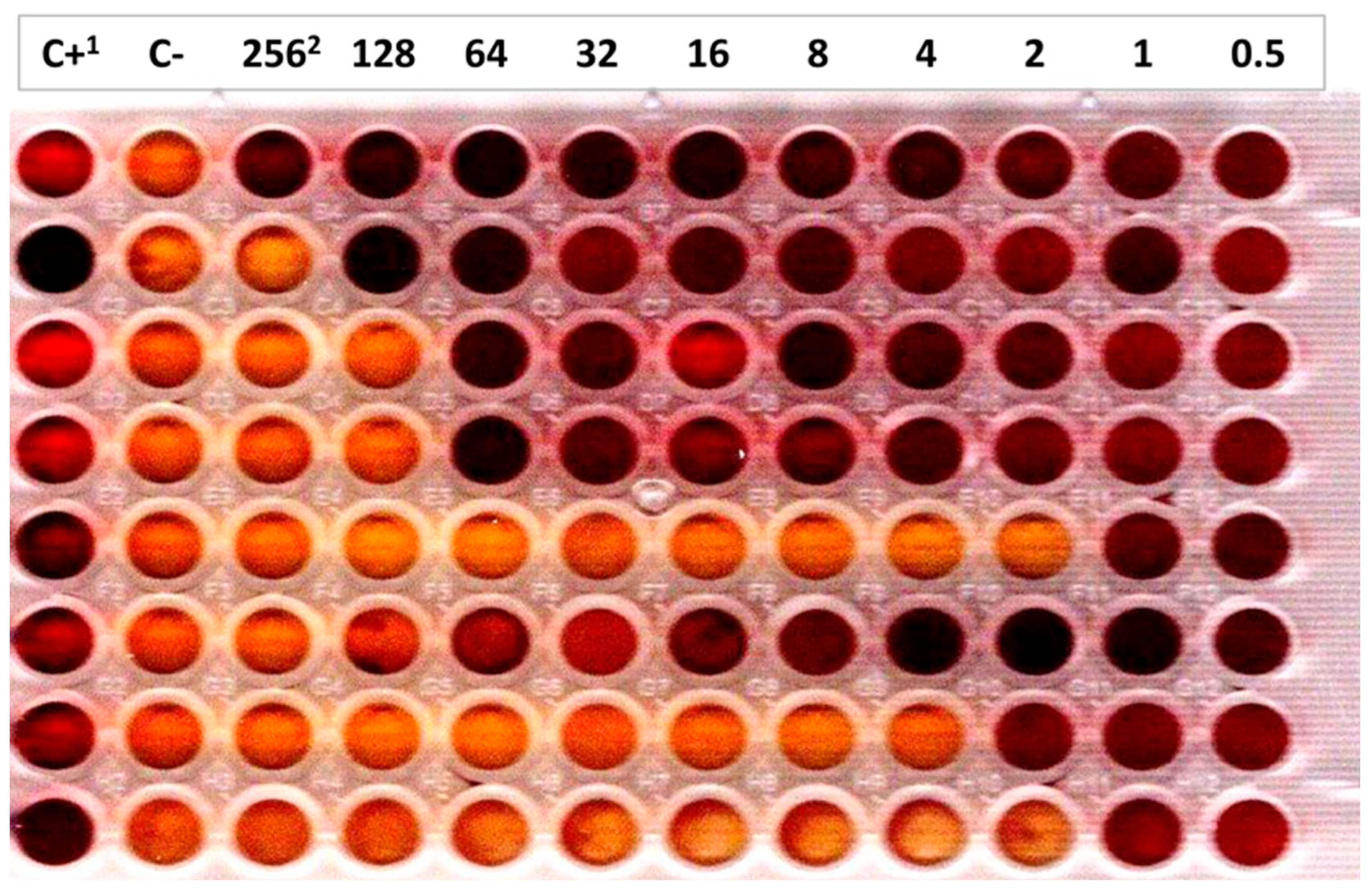
2.3.2. Potassium Tellurite Minimal Inhibitory Concentrations
2.4. Detection Limit of E. coli O80:H2 in Fecal Material in Presence of Potassium Tellurite
2.5. Attempts to Isolate of AE-STEC and EPEC O80:H2 from Bovine Fecal Samples
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Analysis
3.2. Phenotypic Assays
3.3. Detection Limit of E. coli O80:H2 in Bovine Fecal Material
3.4. Attempts to Isolate AE-STEC and EPEC O80:H2 from Bovine Fecal Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tozzoli, R.; Scheutz, F. Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli infections in humans. In Pathogenic Escherichia coli: Molecular and Cellular Microbiology; Morabito, S., Ed.; Caister Academic Press: Norfolk, UK, 2014; pp. 1–18. ISBN 978-1-908230-37-9. [Google Scholar]
- Mainil, J.G.; Fairbrother, M.J. Pathogenic Escherichia coli in domestic mammals and birds. In Pathogenic Escherichia coli: Molecular and Cellular Microbiology; Morabito, S., Ed.; Caister Academic Press: Norfolk, UK, 2014; pp. 19–43. ISBN 978-1-908230-37-9. [Google Scholar]
- Piérard, D.; De Greve, H.; Haesebrouck, F.; Mainil, J. O157:H7 and O104:H4 Vero/Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli outbreaks: Respective role of cattle and humans. Vet. Res. 2012, 43, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karmali, M.A.; Mascarenhas, M.; Shen, S.; Ziebell, K.; Johnson, S.; Reid-Smith, R.; Isaac-Renton, J.; Clark, C.; Rahn, K.; Kaper, J.B. Association of genomic O island 122 of Escherichia coli EDL 933 with Verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli seropathotypes that are linked to epidemic and/or serious disease. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 4930–4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakih, I.; Thiry, D.; Duprez, J.-N.; Saulmont, M.; Iguchi, A.; Piérard, D.; Jouant, L.; Daube, G.; Ogura, Y.; Hayashi, T.; et al. Identification of Shiga toxin-producing (STEC) and enteropathogenic (EPEC) Escherichia coli in diarrhoeic calves and comparative genomics of O5 bovine and human STEC. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 202, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Garcia, F. Escherichia coli O104:H4 pathogenesis: An enteroaggregative E. coli /Shiga toxin-producing E. coli explosive cocktail of high virulence. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014, 2, EHEC-0008-2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruyand, M.; Mariani-Kurkdjian, P.; Le Hello, S.; King, L.-A.; Van Cauteren, D.; Lefevre, S.; Gouali, M.; Jourdan-da Silva, N.; Mailles, A.; Donguy, M.-P.; et al. Paediatric haemolytic uraemic syndrome related to Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli, an overview of 10 years of surveillance in France, 2007 to 2016. Euro. Surveill. 2019, 24, 1800068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soysal, N.; Mariani-Kurkdjian, P.; Smail, Y.; Liguori, S.; Gouali, M.; Loukiadis, E.; Fach, P.; Bruyand, M.; Blanco, J.; Bidet, P.; et al. Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli hybrid pathotype O80:H2 as a new therapeutic challenge. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1604–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cointe, A.; Birgy, A.; Mariani-Kurkdjian, P.; Liguori, S.; Courroux, C.; Blanco, J.; Delannoy, S.; Fach, P.; Loukiadis, E.; Bidet, P.; et al. Emerging multidrug-resistant hybrid pathotype Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O80 and related strains of Clonal Complex 165, Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 2262–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSES (Agence nationale de sécurité sanitaire de l’alimentation, de l’environnement et du travail), Avis relatif à la définition des souches pathogènes d’Escherichia coli productrices de Shiga-toxines, Saisine n° 2020-SA-0095, n°2016-SA-0121, 2010-SA-0031. 2023. Available online: https://www.anses.fr/fr/system/files/BIORISK2020SA0095.pdf (accessed on 3 June 2024).
- EFSA-ECDC (European Food Safety Authority—European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control). The European Union one health 2022 zoonoses report. EFSA J. 2023, 21, e8442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiry, D.; Saulmont, M.; Takaki, S.; De Rauw, K.; Duprez, J.-N.; Iguchi, A.; Piérard, D.; Mainil, J.G. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli O80:H2 in young calves with diarrhea, Belgium. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 2093–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habets, A.; Crombé, F.; Nakamura, K.; Guérin, V.; De Rauw, K.; Piérard, D.; Saulmont, M.; Hayashi, T.; Mainil, J.G.; Thiry, D. Genetic characterization of Shigatoxigenic and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli O80:H2 from diarrhoeic and septicaemic calves and relatedness to human Shigatoxigenic E. coli O80:H2. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 130, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleau, N.; Ganet, S.; Werlen, S.; Collignon, L.; Cointe, A.; Bonacorsi, S.; Sergentet, D. First Isolation of the heteropathotype Shiga toxin-producing and extra-intestinal pathogenic (STEC-ExPEC) E. coli O80:H2 in French healthy cattle: Genomic characterization and phylogenetic position. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizot, E.; Cointe, A.; Smadja, N.; Sergentet, D.; Lefèvre, S.; Weill, F.-X.; Levy, C.; Cohen, R.; Mariani-Kurkdjian, P.; Bonacorsi, S. Improved molecular diagnosis and culture of the emerging heteropathotype enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O80:H2 using its non-melibiose-fermenting and antibiotic-resistance properties. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2022, 60, e0153021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerangart, S.; Douëllou, T.; Delannoy, S.; Fach, P.; Beutin, L.; Sergentet-Thévenot, D.; Cournoyer, B.; Loukiadis, E. Variable tellurite resistance profiles of clinically-relevant Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) influence their recovery from foodstuffs. Food Microbiol. 2016, 59, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, G.L.; Jorgensen, Q.R.; Loy, J.D.; Moxley, R.A. Tellurite resistance in Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. Curr. Microbiol. 2018, 75, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, R.; Bai, X.; Fu, S.; Xu, Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Xiong, Y. Tellurite resistance profiles and performance of different chromogenic agars for detection of non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli. Int. J. Food. Microbiol. 2018, 266, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Makino, K.; Ohnishi, M.; Kurokawa, K.; Ishii, K.; Yokoyama, K.; Han, C.G.; Ohtsubo, E.; Nakayama, K.; Murata, T.; et al. Complete genome sequence of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 and genomic comparison with a laboratory strain K-12. DNA Res. 2001, 8, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rauw, K.; Thiry, D.; Caljon, B.; Saulmont, M.; Mainil, J.; Piérard, D. Characteristics of Shiga toxin-producing and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli of the emerging serotype O80:H2 isolated from humans and diarrheic calves in Belgium. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 111.e5–111.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, R.; Nakamura, K.; Saulmont, M.; Habets, A.; Duprez, J.-N.; Korsak, N.; Hayashi, T.; Thiry, D.; Mainil, J.G. Escherichia coli O80 in healthy cattle: Absence of Shigatoxigenic and enteropathogenic E. coli O80:H2 and (phylo)genomics of non-clonal complex 165 E. coli O80. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.H.; Kikuchi, T.; Tokunaga, T.; SIyoda, S.; Iguchi, A. Diversity of the tellurite resistance gene operon in Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 681175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.E.; Rooker, M.; Keelan, M.; Ng, L.-K.; Martin, I.; Perna, N.T.; Burland, N.T.V.; Blattner, F.R. Genomic variability of O islands encoding tellurite resistance in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 isolates. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 4690–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, R.; Laforêt, F.; Antoine, C.; Adachi, M.; Nakamura, K.; Habets, A.; Kler, C.; De Rauw, K.; Hayashi, T.; Mainil, J.M.; et al. Virulence of Shigatoxigenic and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli O80:H2 in Galleria mellonella larvae: Comparison of the roles of the pS88 plasmids and STX2d phage. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menge, C. The role of Escherichia coli Shiga toxins in STEC colonization of cattle. Toxins 2020, 12, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, M.; Blanco, J.E.; Mora, A.; Dahbi, G.; Alonso, M.P.; González, E.A.; Bernárdez, M.I.; Blanco, J. Serotypes, virulence genes, and intimin types of Shiga toxin (verotoxin)-producing Escherichia coli isolates from cattle in Spain and identification of a new intimin variant gene (eae-xi). J. Clin. Microbiol 2004, 42, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiry, D.; De Rauw, K.; Takaki, S.; Duprez, J.-N.; Iguchi, A.; Piérard, D.; Korsak, N.; Mainil, J.G. Low prevalence of the “gang of seven” and absence of the O80:H2 serotypes among Shigatoxigenic and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (STEC and EPEC) in intestinal contents of healthy cattle at two slaughterhouses in Belgium in 2014. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habets, A.; Engelen, F.; Duprez, J.-N.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Heyndrickx, M.; De Zutter, L.; Thiry, D.; Cox, E.; Mainil, J. Identification of Shigatoxigenic and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli serotypes in healthy young dairy calves in Belgium by recto-anal mucosal swabbing. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Diemen, P.M.; Dziva, F.; Stevens, M.P.; Wallis, T.S. Identification of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O26:H- genes required for intestinal colonization in calves. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, F.; Dziva, F.; van Diemen, P.; Phillips, A.D.; Stevens, M.P.; Frankel, G. Adherence of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157, O26, and O111 strains to bovine intestinal explants ex vivo. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 3084–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, R.; Singh, P. Prevalence and implications of Shiga toxin-producing E. coli in farm and wild ruminants. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarr, P.I.; Bilge, S.S.; Vary, J.C.; Jelacic, S.; Habeeb, R.L.; Ward, T.R.; Baylor, M.R.; Besser, T.E. Iha: A novel Escherichia coli O157:H7 adherence-conferring molecule encoded on a recently acquired chromosomal island of conserved structure. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 1400–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWilliams, B.D.; Torres, A.G. Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli adhesins. Microbiol. Spectrum 2014, 2, EHEC-0003-2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, M.; Terajima, J.; Kurokawa, K.; Nakayama, K.; Murata, T.; Tamura, K.; Ogura, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Hayashi, T. Genomic diversity of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157 revealed by whole genome PCR scanning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 17043–17048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogura, Y.; Ooka, T.; Asadulghani, M.; Terajima, J.; Nougayrède, J.-P.; Kurokawa, K.; Tashiro, K.; Tobe, T.; Nakayama, K.; Kuhara, S.; et al. Extensive genomic diversity and selective conservation of virulence-determinants in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli strains of O157 and non-O157 serotypes. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielaszewska, M.; Middendorf, B.; Tarr, P.I.; Zhang, W.; Prager, R.; Aldick, T.; Dobrindt, U.; Karch, H.; Mellmann, A. Chromosomal instability in enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7: Impact on adherence, tellurite resistance and colony phenotype. Mol. Microbiol. 2011, 79, 1024–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, S.C.; Gonzalez-Escalona, N.; Kotewicz, M.L.; Fischer, M.; Kase, J.A. Genome sequencing and comparative genomics of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O145:H25 and O145:H28 reveal distinct evolutionary paths and marked variations in traits associated with virulence & colonization. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.; Beutin, L. Characteristics of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli from meat and milk products of different origins and association with food producing animals as main contamination sources. Int. J. Food. Microbiol. 2011, 146, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Sánchez, S.; Sánchez, S.; Sánchez, M.; Herrera-León, S.; Hanning, I.; Vidal, D. Detection and characterization of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in game meat and ready-to-eat meat products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 160, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Serotype 1 | Source 1 (No. Strains) | Virulotype 1 | Melibiose Fermentation | Tellurite Resistance | (Sub-)Lineage (L/SL) 1 | No. Strains | iha Gene (WGS) 1,2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mel Operon (WGS) 2 | 70mel DNA Sequence (WGS) 2 | Melibiose McConkey 3 | ter Type Operon (WGS) 2,4 | Te++ MIC (ug/mL) 5 | ||||||
| O80:H2 | Calves (21) | eaeξ | - | + | - | + (t1) | >256 | L1/SL1.1 | 1 | + |
| 256 | 4 | |||||||||
| 128 | 2 | |||||||||
| 8 | 1 | |||||||||
| - | 2 | L1/SL1.2 | 3 | - | ||||||
| eaeξ stx1a | - | + | - | + (t1) | >256 | L1/SL1.1 | 1 | + | ||
| L2 6 | 2 | |||||||||
| eaeξ stx2d | - | + | - | - | 2 | L1/SL1.2 | 5 | - | ||
| L1/SL1.4 | 2 | + | ||||||||
| Humans (19) | eaeξ stx1a | - | + | ND | + (t1) | ND | L1/SL1.1 | 3 | + | |
| eaeξ stx2a | - | + | ND | + (t1) | ND | L1/SL1.1 | 1 | + | ||
| L1/SL1.3 | 1 | |||||||||
| eaeξ stx2d | - | + | ND | + (t3) | ND | L1/SL1.2 | 3 | - | ||
| - | 11 | - | ||||||||
| O80:non-H2 | Bovines | - | + | - | + | - | 2–4 | - | 4 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ikeda, R.; Nakamura, K.; Korsak, N.; Duprez, J.-N.; Hayashi, T.; Thiry, D.; Mainil, J.G. Non-Melibiose Fermentation and Tellurite Resistance by Shigatoxigenic and Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli O80:H2 from Diseased Calves: Comparison with Human Shigatoxigenic E. coli O80:H2. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030274
Ikeda R, Nakamura K, Korsak N, Duprez J-N, Hayashi T, Thiry D, Mainil JG. Non-Melibiose Fermentation and Tellurite Resistance by Shigatoxigenic and Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli O80:H2 from Diseased Calves: Comparison with Human Shigatoxigenic E. coli O80:H2. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(3):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030274
Chicago/Turabian StyleIkeda, Rie, Keiji Nakamura, Nicolas Korsak, Jean-Noël Duprez, Tetsuya Hayashi, Damien Thiry, and Jacques G. Mainil. 2025. "Non-Melibiose Fermentation and Tellurite Resistance by Shigatoxigenic and Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli O80:H2 from Diseased Calves: Comparison with Human Shigatoxigenic E. coli O80:H2" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 3: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030274
APA StyleIkeda, R., Nakamura, K., Korsak, N., Duprez, J.-N., Hayashi, T., Thiry, D., & Mainil, J. G. (2025). Non-Melibiose Fermentation and Tellurite Resistance by Shigatoxigenic and Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli O80:H2 from Diseased Calves: Comparison with Human Shigatoxigenic E. coli O80:H2. Veterinary Sciences, 12(3), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12030274






