Scalable Production of Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus Vectors Expressing Soluble Viral Receptors for Broad-Spectrum Inhibition of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Type 2
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells
2.2. Virus
2.3. Optimization of the Conditions for rAAV Production
2.4. Preparation of Baculovirus-Infected Insect Cells (BIICs)
2.5. Large-Scale rAAV Production
2.6. Purification of Recombinant Adeno-Associated Viruses
2.7. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.8. Immunofluorescence
2.9. Western Blotting
2.10. Viral Infection Blocking Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
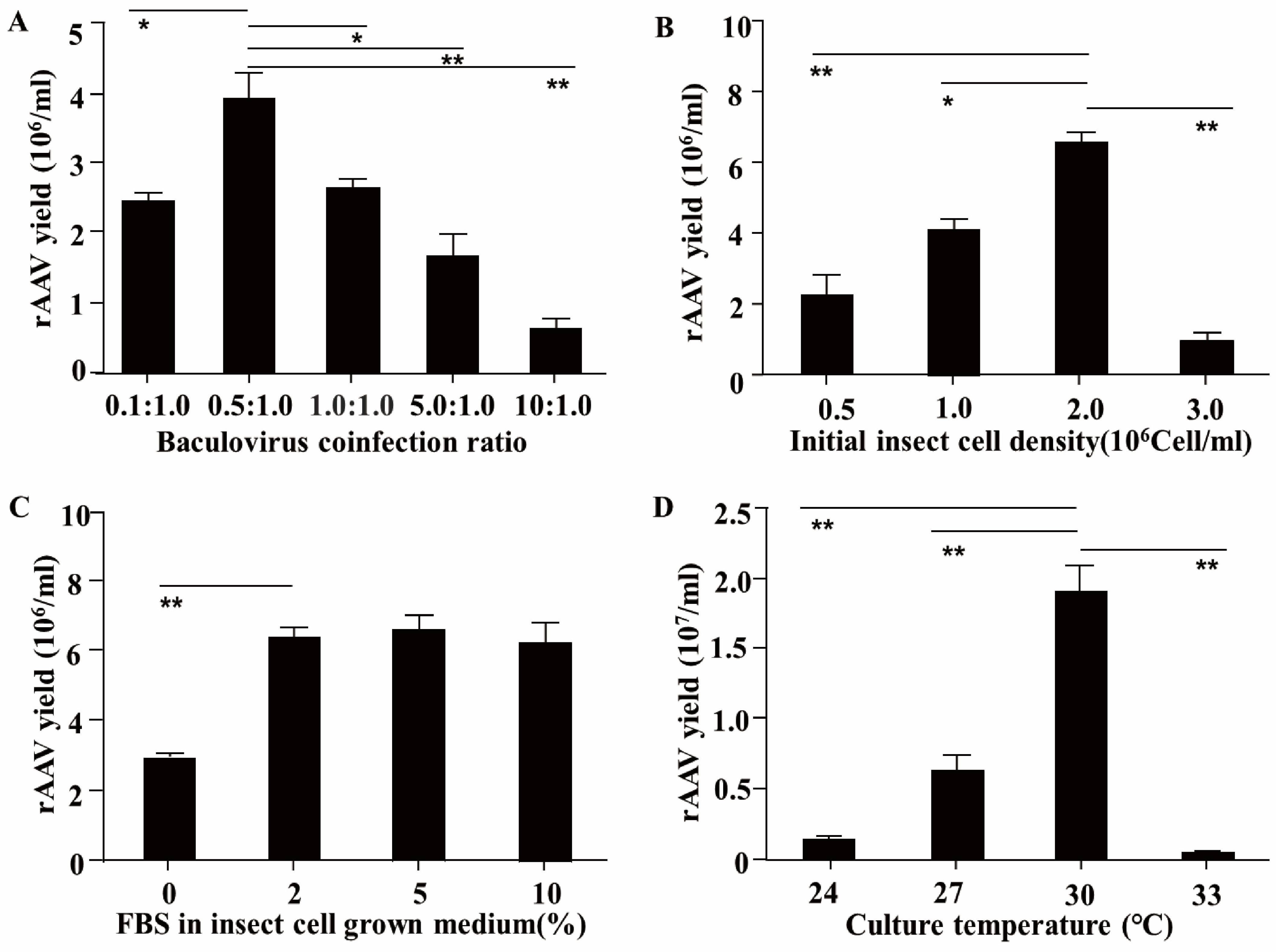
3.1. Determination of the Optimal Packaging Conditions for rAAV
3.2. Baculovirus-Infected Insect Cells (BIICs) Production
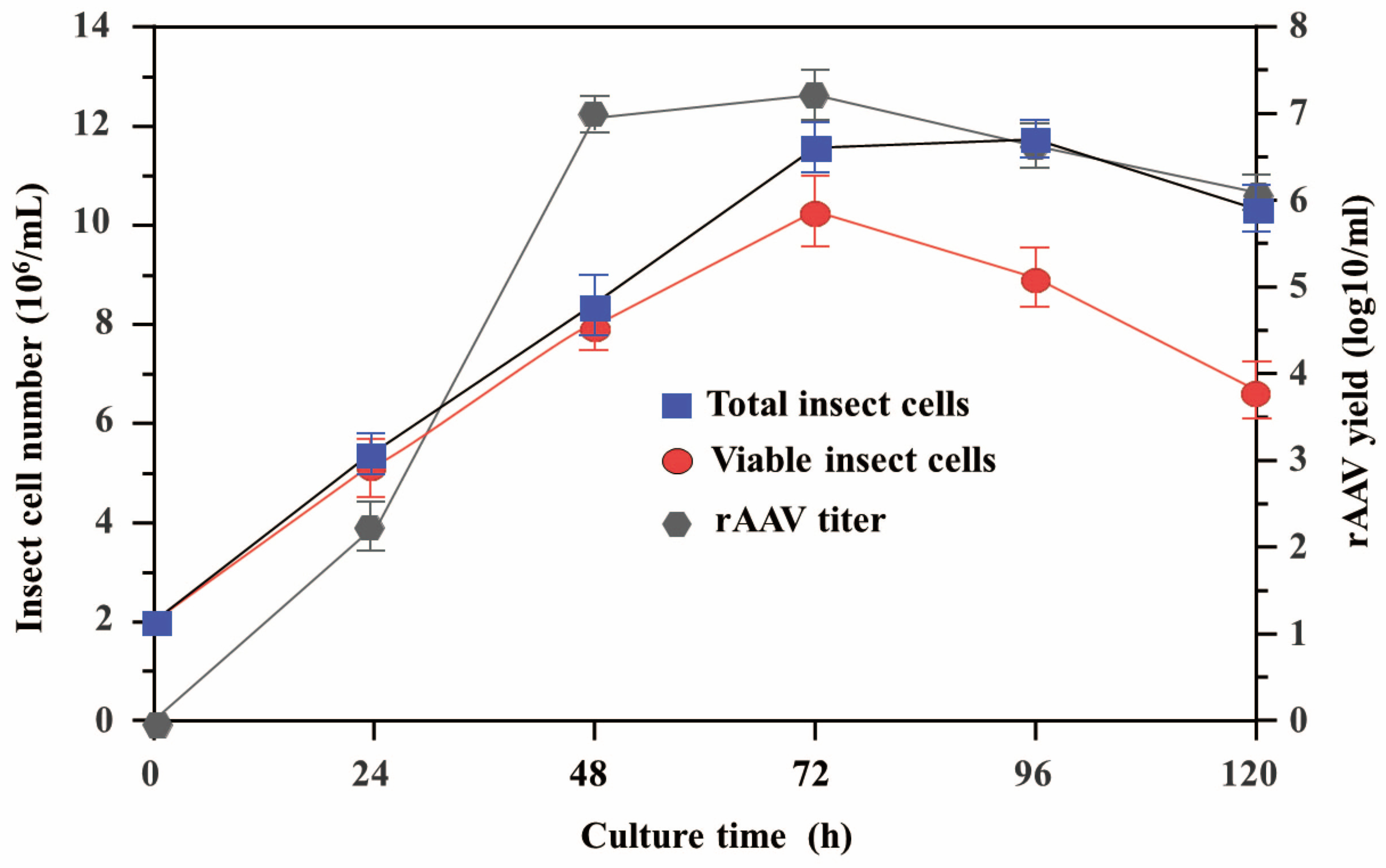
3.3. High Yields of Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus Packaging
3.4. Identification of rAAV Produced and SVR Expressed In Vitro
3.5. Anti-PRRSV Activities of SVR Fusions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neumann, E.J.; Kliebenstein, J.B.; Johnson, C.D.; Mabry, J.W.; Bush, E.J.; Seitzinger, A.H.; Green, A.L.; Zimmerman, J.J. Assessment of the economic impact of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome on swine production in the United States. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2005, 227, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terpstra, C.; Wensvoort, G.; Pol, J.M. Experimental reproduction of porcine epidemic abortion and respiratory syndrome (mystery swine disease) by infection with Lelystad virus: Koch’s postulates fulfilled. Vet. Q. 1991, 13, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunney, J.K.; Benfield, D.A.; Rowland, R.R. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus: An update on an emerging and re-emerging viral disease of swine. Virus Res. 2010, 154, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pejsak, Z.; Stadejek, T.; Markowska-Daniel, I. Clinical signs and economic losses caused by porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in a large breeding farm. Vet. Microbiol. 1997, 55, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.E.; Lager, K.M.; Golde, W.; Faaberg, K.S.; Sinkora, M.; Loving, C.; Zhang, Y.I. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS): An immune dysregulatory pandemic. Immunol. Res. 2014, 59, 81–108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Charemtantanakul, W. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus vaccines: Immunogenicity, efficacy and safety aspects. World J. Virol. 2012, 1, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimman, T.G.; Cornelissen, L.A.; Moormann, R.J.; Rebel, J.M.; Stockhofe-Zurwieden, N. Challenges for porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) vaccinology. Vaccine 2009, 27, 3704–3718. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kappes, M.A.; Faaberg, K.S. PRRSV structure, replication and recombination: Origin of phenotype and genotype diversity. Virology 2015, 479–480, 475–486. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, M.; Lam, T.T.; Hon, C.C.; Hui, R.K.; Faaberg, K.S.; Wennblom, T.; Murtaugh, M.P.; Stadejek, T.; Leung, F.C. Molecular epidemiology of PRRSV: A phylogenetic perspective. Virus Res. 2010, 154, 7–17. [Google Scholar]
- Van Breedam, W.; Delputte, P.L.; Van Gorp, H.; Misinzo, G.; Vanderheijden, N.; Duan, X.; Nauwynck, H.J. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus entry into the porcine macrophage. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 1659–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gorp, H.; Van Breedam, W.; Van Doorsselaere, J.; Delputte, P.L.; Nauwynck, H.J. Identification of the CD163 protein domains involved in infection of the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 3101–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Breedam, W.; Van Gorp, H.; Zhang, J.Q.; Crocker, P.R.; Delputte, P.L.; Nauwynck, H.J. The M/GP5 glycoprotein complex of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus binds the sialoadhesin receptor in a sialic acid-dependent manner. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Guo, R.; He, S.; Zhang, X.; Xia, X.; Sun, H. Additive inhibition of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection with the soluble sialoadhesin and CD163 receptors. Virus Res. 2014, 179, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Wu, Z.; Guo, C.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, X.; Xia, X.; Sun, H. Recombinant adenovirus-delivered soluble CD163 and sialoadhesin receptors protected pigs from porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 219, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xia, W.; Zhang, X.; Xia, X.; Sun, H. Fusion expression of the two soluble viral receptors of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus with a single adeno-associated virus vector. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 135, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daya, S.; Berns, K.I. Gene therapy using adeno-associated virus vectors. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 21, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, A.M.; Nicolson, S.C.; Warischalk, J.K.; Samulski, R.J. AAV’s anatomy: Roadmap for optimizing vectors for translational success. Curr. Gene Ther. 2010, 10, 319–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bish, L.T.; Morine, K.; Sleeper, M.M.; Sanmiguel, J.; Wu, D.; Gao, G.; Wilson, J.M.; Sweeney, H.L. Adeno-associated virus (AAV) serotype 9 provides global cardiac gene transfer superior to AAV1, AAV6, AAV7, and AAV8 in the mouse and rat. Hum. Gene Ther. 2008, 19, 1359–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.F.; Li, Q.H.; Shenoy, V.; Zingler, M.; Jun, J.Y.; Verma, A.; Katovich, M.J.; Raizada, M.K. Comparison of the transduction efficiency of tyrosine-mutant adeno-associated virus serotype vectors in kidney. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2013, 40, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urabe, M.; Ding, C.; Kotin, R.M. Insect cells as a factory to produce adeno-associated virus type 2 vectors. Hum. Gene Ther. 2002, 13, 1935–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mietzsch, M.; Casteleyn, V.; Weger, S.; Zolotukhin, S.; Heilbronn, R. OneBac 2.0: Sf9 Cell Lines for Production of AAV5 Vectors with Enhanced Infectivity and Minimal Encapsidation of Foreign DNA. Hum. Gene Ther. 2015, 26, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wensvoort, G.; Terpstra, C.; Pol, J.M.; ter Laak, E.A.; Bloemraad, M.; de Kluyver, E.P.; Kragten, C.; van Buiten, L.; den Besten, A.; Wagenaar, F. Mystery swine disease in The Netherlands: The isolation of Lelystad virus. Vet. Q. 1991, 13, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, K.; Yu, X.; Zhao, T.; Feng, Y.; Cao, Z.; Wang, C.; Hu, Y.; Chen, X.; Hu, D.; Tian, X.; et al. Emergence of fatal PRRSV variants: Unparalleled outbreaks of atypical PRRS in China and molecular dissection of the unique hallmark. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhe, M.; Xin, H.; Lei, C.; Fan, H. Construction and immunogenicity of a recombinant swinepox virus expressing a multi-epitope peptide for porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43990. [Google Scholar]
- Cecchini, S.; Virag, T.; Kotin, R.M. Reproducible high yields of recombinant adeno-associated virus produced using invertebrate cells in 0.02-to 200-liter cultures. Hum. Gene Ther. 2011, 22, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwae, S.; Ohda, T.; Tamashima, H.; Miki, H.; Kobayashi, K. Development of a fed-batch culture process for enhanced production of recombinant human antithrombin by Chinese hamster ovary cells. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2005, 100, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, T.; Elliger, S.; Elliger, C.; Podsakoff, G.; Villarreal, L.; Kurtzman, G.J.; Iwaki, Y.; Colosi, P. Adeno-associated virus vectors can be efficiently produced without helper virus. Gene Ther. 1998, 5, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Park, C.K.; Nam, E.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, O.S.; Lee, D.S.; Lee, C. Generation of a porcine alveolar macrophage cell line for the growth of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. J. Virol. Methods 2010, 163, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, A.C.; Hermann, J.R.; Munoz-Zanzi, C.; Prickett, J.R.; Roof, M.B.; Yoon, K.J. Stability of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus at ambient temperatures. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig 2010, 22, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meghrous, J.; Aucoin, M.G.; Jacob, D.; Chahal, P.S.; Arcand, N.; Kamen, A.A. Production of recombinant adeno–associated viral vectors using a baculovirus/insect cell suspension culture system: From shake flasks to a 20-L bioreactor. Biotechnol. Prog. 2005, 21, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carinhas, N.; Bernal, V.; Yokomizo, A.Y.; Carrondo, M.J.; Oliveira, R.; Alves, P.M. Baculovirus production for gene therapy: The role of cell density, multiplicity of infection and medium exchange. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 81, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aucoin, M.G.; Perrier, M.; Kamen, A.A. Improving AAV vector yields in insect cells by modulating the temperature after infection. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2007, 97, 1501–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, D.; Kleinschmidt, J.A. Progress in adeno- associated virus type 2 vector production: Promises and prospects for clinical use. Hum. Gene Ther. 1999, 10, 2445–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lock, M.; McGorray, S.; Auricchio, A.; Ayuso, E.; Beecham, E.J.; Blouin-Tavel, V.; Bosch, F.; Bose, M.; Byrne, B.J.; Caton, T.; et al. Characterization of a recombinant adeno-associated virus type 2 Reference Standard Material. Hum. Gene Ther. 2010, 21, 1273–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.K.; Yang, C.J.; Liu, C.L.; Shen, C.R.; Shiau, L.D. Using a fed-batch culture strategy to enhance rAAV production in the baculovirus/insect cell system. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2010, 110, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, G.J.; Nielsen, J.; Madsen, J.S. Soluble receptors as antiviral agents. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2000, 11, 448–453. [Google Scholar]
- Fechner, H.; Pinkert, S.; Geisler, A.; Poller, W.; Kurreck, J. Pharmacological and biological antiviral therapeutics for cardiac coxsackievirus infections. Molecules 2011, 16, 8475–8503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Primer Pair | Sequence (5′→3′) | Amplicon (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AAV-Rep (of rBac-RC) | Sense | TGGTGGACGAGTGCTACA | 113 | [15] |
| Antisense | CTCCGTGAGATTCAAACAGG | |||
| PCMV (of Bac-SRCR59-Fc/Sn4D-Fc) | Sense | ATGGTGATGCGGTTTTGGC | 123 | [15] |
| Antisense | AGTCCCGTTGATTTTGGTG |
| Packaging Strategy | Yield (IVPs/mL) | Yield (IVPs/Cell) | Recovery (%) | Purity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell flask (72 h) | 1.9 ± 0.3 × 107 | 1~10 | 75.3 ± 3.1 | 89.7 ± 1.7 |
| Cell bioreactor (144 h) | 5.4 ± 0.9 × 109 | 200~600 | 80.4 ± 2.9 | 83.1 ± 5.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Xu, N.; Song, X.; Zhuang, L.; Shen, Q.; Sun, H. Scalable Production of Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus Vectors Expressing Soluble Viral Receptors for Broad-Spectrum Inhibition of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Type 2. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 366. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040366
Liu X, Xu N, Song X, Zhuang L, Shen Q, Sun H. Scalable Production of Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus Vectors Expressing Soluble Viral Receptors for Broad-Spectrum Inhibition of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Type 2. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(4):366. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040366
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaoming, Nuo Xu, Xiaoli Song, Linlin Zhuang, Qiuping Shen, and Huaichang Sun. 2025. "Scalable Production of Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus Vectors Expressing Soluble Viral Receptors for Broad-Spectrum Inhibition of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Type 2" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 4: 366. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040366
APA StyleLiu, X., Xu, N., Song, X., Zhuang, L., Shen, Q., & Sun, H. (2025). Scalable Production of Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus Vectors Expressing Soluble Viral Receptors for Broad-Spectrum Inhibition of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Type 2. Veterinary Sciences, 12(4), 366. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040366







