Multiple Meningioma Resection by Bilateral Extended Rostrotentorial Craniotomy with a 3D-Print Guide in a Cat
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Case Presentation
2.1. Case
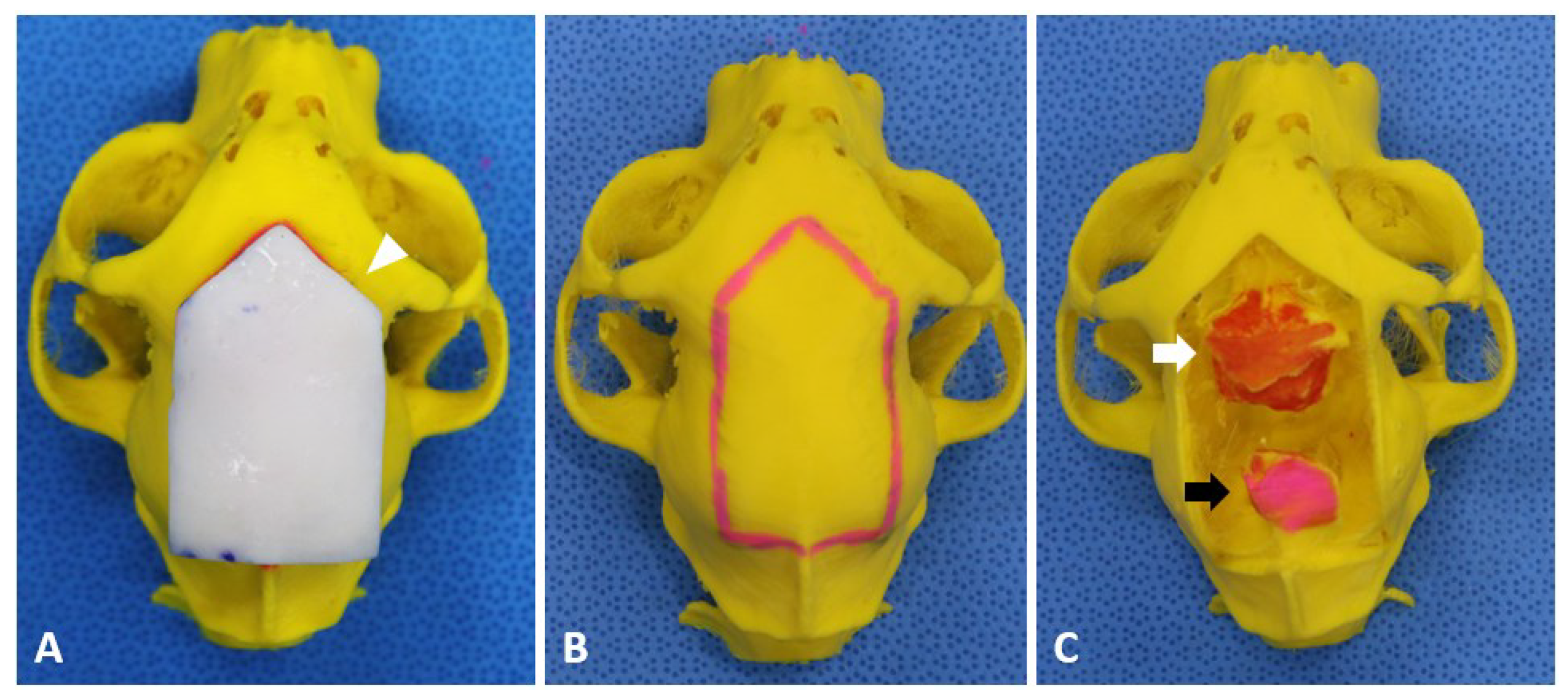
2.2. Preoperative Planning and Rehearsal Surgery
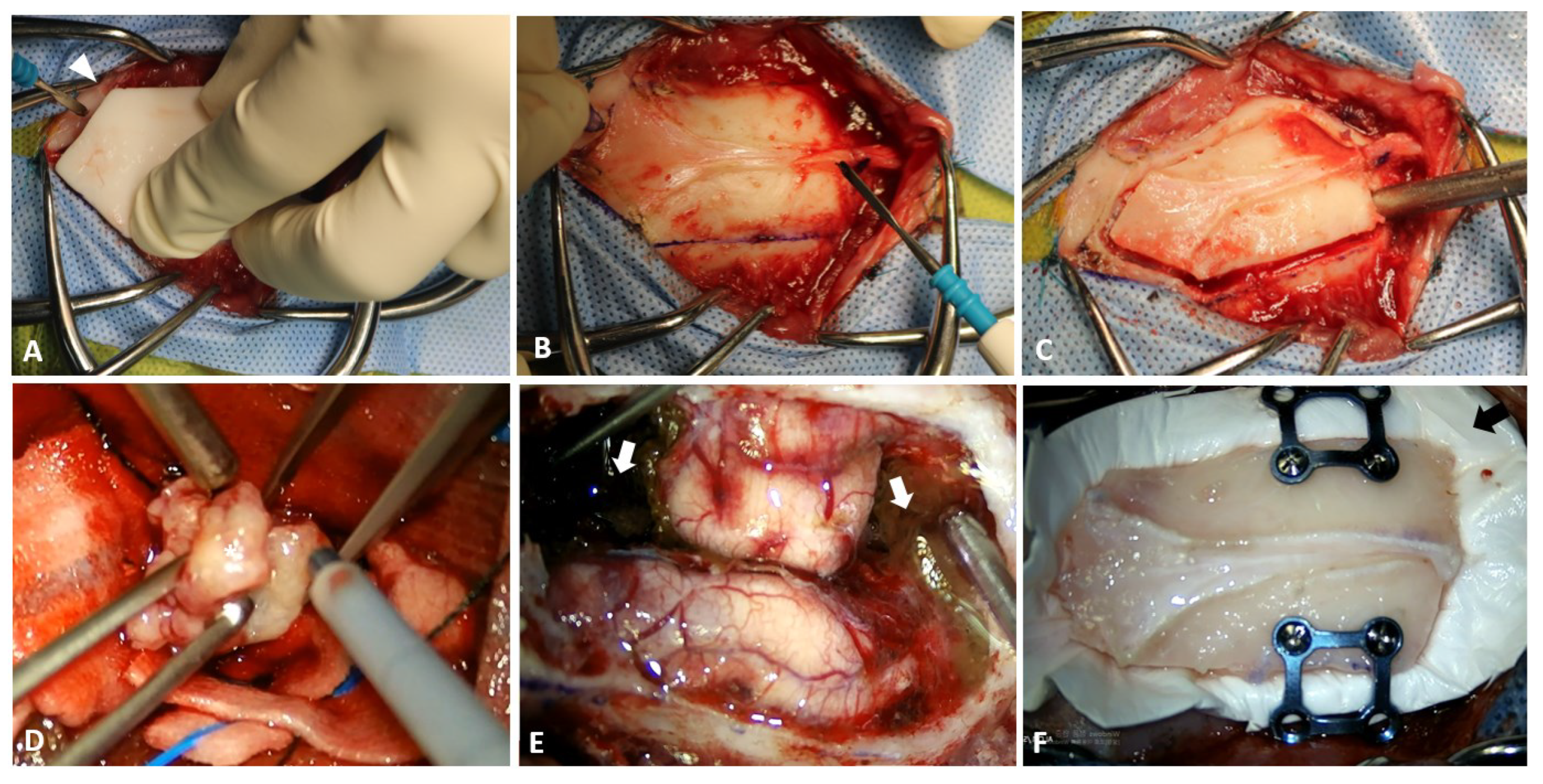
2.3. Surgical Techniques
2.4. Postoperative Care, Outcomes, and Pathological Examination
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Troxel, M.T.; Vite, C.H.; Van Winkle, T.J.; Newton, A.L.; Tiches, D.; Dayrell-Hart, B.; Kapatkin, A.S.; Shofer, F.S.; Steinberg, S.A. Feline intracranial neoplasia: Retrospective review of 160 cases (1985–2001). J. Vet. Intern Med. 2003, 17, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motta, L.; Mandara, M.T.; Skerritt, G.C. Canine and feline intracranial meningiomas: An updated review. Vet. J. 2012, 192, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forterre, F.; Tomek, A.; Konar, M.; Vandevelde, M.; Howard, J.; Jaggy, A. Multiple meningiomas: Clinical, radiological, surgical, and pathological findings with outcome in four cats. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2007, 9, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winn, H. Youmans and Winn Neurological Surgery; Elsevier: Philadelpia, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Adamo, P.F.; Forrest, L.; Dubielzig, R. Canine and feline meningiomas: Diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. Compendium 2004, 26, 951–966. [Google Scholar]
- Salvati, M.; Caroli, E.; Ferrante, L.; Rocchi, G.; D’Andrea, G.; Piccirilli, M.; Delfini, R. Spontaneous, multiple meningiomas. Zentralbl. Neurochir. 2004, 65, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domenicucci, M.; Santoro, A.; D’Osvaldo, D.H.; Delfini, R.; Cantore, G.P.; Guidetti, B. Multiple intracranial meningiomas. J. Neurosurg. 1989, 70, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, L.E.; Thacher, C.; Matthiesen, D.T.; Joseph, R.J. Results of craniotomy for the treatment of cerebral meningioma in 42 cats. Vet. Surg. 1994, 23, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, S.; Rishniw, M.; Miller, A.D.; Sturges, B.; Dewey, C.W. Characteristics and survival of 121 cats undergoing excision of intracranial meningiomas (1994–2011). Vet. Surg. 2015, 44, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Yang, R.; Hang, F.; Zhuang, J.; Lin, Q.; Wang, Z.; Lao, Y. Neurosurgical craniotomy localization using interactive 3D lesion mapping for image-guided neurosurgery. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 10606–10616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orringer, D.A.; Golby, A.; Jolesz, F. Neuronavigation in the surgical management of brain tumors: Current and future trends. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2012, 9, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mert, A.; Buehler, K.; Sutherland, G.R.; Tomanek, B.; Widhalm, G.; Kasprian, G.; Knosp, E.; Wolfsberger, S. Brain tumor surgery with 3-dimensional surface navigation. Neurosurgery 2012, 71, ons286–ons294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omay, S.B.; Barnett, G.H. Surgical navigation for meningioma surgery. J. Neurooncol. 2010, 99, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wininger, F. Neuronavigation in small animals: Development, techniques, and applications. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2014, 44, 1235–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, A.J.; Shetty, V.; Bhagavan, K.R.; Ragothaman, A.; Shetty, V.; Koneru, G.; Agarwala, M. Improved Surgery Planning Using 3-D Printing: A Case Study. Indian J. Surg. 2016, 78, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hespel, A.M. Three-dimensional printing role in neurologic disease. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2018, 48, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, M.; Olby, N.; Early, P.; Mariani, C.; Muñana, K.; Seiler, G.; Griffith, E. Clinical and diagnostic imaging features of brain herniation in dogs and cats. J. Vet. Intern Med. 2016, 30, 1672–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rho, Y.H.; Cho, C.W.; Ryu, C.H.; Lee, J.H.; Jeong, S.M.; Lee, H.B. Comparison between novice and experienced surgeons performing corrective osteotomy with patient-specific guides in dogs based on resulting position accuracy. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quentin, C.; Charbonneau, S.; Moumdjian, R.; Lallo, A.; Bouthilier, A.; Fournier-Gosselin, M.P.; Bojanowski, M.; Ruel, M.; Sylvestre, M.-P.; Girard, F. A comparison of two doses of mannitol on brain relaxation during supratentorial brain tumor craniotomy: A randomized trial. Anesth. Analg. 2013, 116, 862–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gelb, A.; Flexman, A.; Ji, F.; Meng, L. Definition, evaluation, and management of brain relaxation during craniotomy. Br J. Anaesth. 2016, 116, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forterre, F.; Fritsch, G.; Kaiser, S.; Matiasek, K.; Brunnberg, L. Surgical approach for tentorial meningiomas in cats: A review of six cases. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2006, 8, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, A.; Muhonen, M.; Loudon, W. FloSeal hemostatic matrix use for intraventricular hemorrhage during a neuroendoscopic procedure. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2011, 54, 132–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duke-Novakovski, T.; Vries, M.D.; Seymour, C. BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Anaesthesia and Analgesia; British Small Animal Veterinary Association: Aberystwyth, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Meuten, D.J. Tumors in Domestic Animals; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Nanda, A.; Bir, S.C.; Maiti, T.K.; Konar, S.K.; Missios, S.; Guthikonda, B. Relevance of Simpson grading system and recurrence-free survival after surgery for World Health Organization Grade I meningioma. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 126, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirimanoff, R.O.; Dosoretz, D.E.; Linggood, R.M.; Ojemann, R.G.; Martuza, R.L. Meningioma: Analysis of recurrence and progression following neurosurgical resection. J. Neurosurg. 1985, 62, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagley, R. Intracranial surgery. In Textbook of Small Animal Surgery; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2002; pp. 1261–1277. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, R.J.; Bringas, J.R. A review of brain retraction and recommendations for minimizing intraoperative brain injury. Neurosurgery 1993, 33, 1052–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckstein, O.; Stemmer-Rachamimov, A.; Nunes, F.; Hoch, D.; Ojemann, R.; MacCollin, M. Multiple meningiomas in brain and lung due to acquired mutation of the NF2 gene. Neurology 2004, 62, 1904–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthigeyan, M.; Rajasekhar, R.; Salunke, P.; Singh, A. Modified unilateral approach for mid-third giant bifalcine meningiomas: Resection using an oblique surgical trajectory and falx window. Acta Neurochir. 2019, 161, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spottiswoode, B.; Van den Heever, D.; Chang, Y.; Engelhardt, S.; Du Plessis, S.; Nicolls, F.; Hartzenberg, H.; Gretschel, A. Preoperative three-dimensional model creation of magnetic resonance brain images as a tool to assist neurosurgical planning. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2013, 91, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canzi, P.; Avato, I.; Marconi, S.; Del Maestro, M.; Lucifero, A.G.; Magnetto, M.; Carlotto, E.; Auricchio, F.; Luzzi, S.; Benazzo, M. A 3D printed custom-made mask model for frameless neuronavigation during retrosigmoid craniotomy. Ann. Ital. Chir. 2020, 91, 526–533. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, I.; Squelch, A.; Wan, Y.; Wong, A.; Ducke, W.; Sun, Z. Patient-specific 3D printed model in delineating brain glioma and surrounding structures in a pediatric patient. Digit. Med. 2017, 3, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limbu, P.; Dhimal, K.; Biswakarma, P. Incidence of dural Injury during craniotomy—A single center study. East. Green Neurosurg. 2020, 2, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhardt, M.; Uhlenbruch, S.; Christmann, A.; Miede, C.; Eufinger, H.; Scholz, M.; Harders, A.; Schmieder, K. Accidential dural tears occurring during supratentorial craniotomy—A prospective analysis of predisposing factors in 100 Patients. Zentralb. Neurochir. 2005, 66, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlato, C.; Granata, R.; Moraci, A.; Accardo, M. Dural reconstruction in meningioma surgery. In Monleon D. Meningiomas-Management and Surgery; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 103–124. [Google Scholar]
- Leng, L.Z.; Brown, S.; Anand, V.K.; Schwartz, T.H. “Gasket-seal” watertight closure in minimal-access endoscopic cranial base surgery. Neurosurgert 2008, 62, ONS342–ONS343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gousias, K.; Schramm, J.; Simon, M. The Simpson grading revisited: Aggressive surgery and its place in modern meningioma management. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 125, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violaris, K.; Katsarides, V.; Sakellariou, P. The recurrence rate in meningiomas: Analysis of tumor location, histological grading, and extent of resection. Open J. Mod. Neurosurg. 2011, 2012, 17024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, D. The recurrence of intracranial meningiomas after surgical treatment. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1957, 20, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, N.; Kakkar, A.; Sarkar, C.; Agrawal, D. Does bony hyperostosis in intracranial meningioma signify tumor invasion? A radio-pathologic study. Neurol. India 2012, 60, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Quintana, R.; Gunn-Moore, D.A.; Lamm, C.G.; Penderis, J. Feline intracranial meningioma with skull erosion and tumour extension into an area of skull hyperostosis. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2011, 13, 266–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, T.H.; McDermott, M.W. The Simpson grade: Abandon the scale but preserve the message. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 135, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehresman, J.S.; Garzon-Muvdi, T.; Rogers, D.; Lim, M.; Gallia, G.L.; Weingart, J.; Brem, H.; Bettegowda, C.; Chaichana, K.L. The relevance of Simpson grade resections in modern neurosurgical treatment of World Health Organization grade I, II, and III meningiomas. World Neurosurg. 2018, 109, e588–e593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, B.L.; Othman, M.I.C.; Fathil, M.F.M.; San Liew, D.N.; San Lim, S.; Bujang, M.A.; Wong, A.S.H. Does putting back hyperostotic bone flap in meningioma surgery cause tumor recurrence? An observational prospective study. World Neurosurg. 2019, 127, e497–e502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, K.; Lee, H.; Jeong, J.; Roh, Y. Multiple Meningioma Resection by Bilateral Extended Rostrotentorial Craniotomy with a 3D-Print Guide in a Cat. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9100512
Song K, Lee H, Jeong J, Roh Y. Multiple Meningioma Resection by Bilateral Extended Rostrotentorial Craniotomy with a 3D-Print Guide in a Cat. Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(10):512. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9100512
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Kyohyuk, Haebeom Lee, Jaemin Jeong, and Yoonho Roh. 2022. "Multiple Meningioma Resection by Bilateral Extended Rostrotentorial Craniotomy with a 3D-Print Guide in a Cat" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 10: 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9100512
APA StyleSong, K., Lee, H., Jeong, J., & Roh, Y. (2022). Multiple Meningioma Resection by Bilateral Extended Rostrotentorial Craniotomy with a 3D-Print Guide in a Cat. Veterinary Sciences, 9(10), 512. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9100512





