Abstract
Xylariomycetidae comprises extremely diverse taxa that are widespread on decaying wood worldwide. An investigation of the diversity of microfungi on oil tree plantations in Sichuan Province was conducted during 2020–2021. Twelve saprobic taxa representing five species were identified as members of Amphisphaeriales and Xylariales through morphological comparisons. Phylogenetic analyses of combined ITS, LSU, rpb2, tub2 and tef1 sequence data indicated a distinct clade formed by three strains within Xylariomycetidae, unrelated to any currently recognized families. Thus, a novel anthostomella-like genus, Bicellulospora, is proposed and treated as Xylariales genera incertae sedis. Bicellulospora is characterized by dark brown to black, immersed, subglobose ascomata with a clypeus, cylindrical asci, and hyaline to yellowish brown, inequilaterally ellipsoidal ascospores with a large upper cell and a dwarf lower cell. Two new species of Amphisphaeria, namely A. oleae and A. verniciae, are introduced based on multi-gene phylogenetic analyses (ITS, LSU, rpb2 and tub2) coupled with morphological characteristics. Amphisphaeria micheliae and Endocalyx ptychospermatis are reported as new host records.
1. Introduction
Xylariomycetidae is a phylogenetically and morphologically diverse fungal assemblage containing three orders, viz., Amphisphaeriales, Delonicicolales and Xylariales [,]. Many genera in the subclass are polyphyletic and paraphyletic, e.g., Anthostomella, Biscogniauxia, Eutypa, Sporidesmium and Xylaria [,,,,,]. Their morphologies have undergone convergent/divergent evolution but lack phylogenetic informativeness []. Anthostomella is a typical polyphyletic genus in Xylariales with highly variable morphological characteristics []. Species of Anthostomella are characterized by immersed ascomata, with or without a clypeus, amyloid or sometimes non-amyloid ascus apices, and brown ascospores bearing a gelatinous sheath or a hyaline dwarf cell []. Samarakoon et al. [] divided Anthostomella into two clades, viz., clade “A. formosa” and clade “A. helicofissa”, based on multi-gene phylogenetic analyses and morphological features. Most species in the clade “A. formosa” have inequilaterally oblong–ellipsoidal ascospores with a hyaline dwarf cell, while species in the clade “A. helicofissa” have equilaterally ellipsoidal, dark brown, unicellular ascospores, with or without a mucilaginous sheath. Anthostomella-like species with a dwarf cell are accepted in different families as a polyphyletic character, e.g., Entosordaria (Barrmaeliaceae), Occultitheca (Xylariaceae), Pyriformiascoma (Xylariaceae) and Vamsapriya (Vamsapriyaceae) [,].
Cainiaceae was introduced by Krug [] and was recently subsumed to Xylariales [,]. Based on the molecular data, Endocalyx was transferred from Apiosporaceae to Cainiaceae [,]. Endocalyx is a well-resolved genus in Cainiaceae, in which five species are accepted [,]. Endocalyx has a strong host specificity to palm but also occurs on dead vines, lilies or twigs of woody trees [,,].
Amphisphaeriales was introduced by Eriksson and Hawksworth [] and is phylogenetically a sister to Xylariales within Xylariomycetidae []. The family Amphisphaeriaceae was first introduced as “Amphisphaerieae” and was formally established as “Amphisphaeriaceae” by Winter []. Wijayawardene et al. [] accepted Amphisphaeria, Griphosphaerioma and Lepteutypa in Amphisphaeriaceae, whereas Lepteutypa was synonymized to Amphisphaeria by Samarakoon et al. []. As a result of these studies, only Amphisphaeria and Griphosphaerioma are retained within Amphisphaeriaceae []. The sexual morph of Amphisphaeria has immersed, erumpent or rarely superficial, globose, subglobose or ellipsoidal ascomata; a two-layered peridium; cylindrical asci with a J+ or J− apical ring; and uniseriate, ellipsoidal to fusiform, 1–3-septate, hyaline or brown ascospores. The asexual morph is characterized by solitary or aggregated, globose, dark brown conidiomata; branched conidiophores; and hyaline, elongate–fusiform, one-celled conidia []. Members of Amphisphaeria are mostly discovered on dead plant materials in terrestrial and marine habitats [,,,,].
During an investigation of fungal diversity on oil tree plantations in Sichuan Province from 2020 to 2021, a new anthostomella-like genus, Bicellulospora, was established and classified in Xylariales as genera incertae sedis, with B. elaeidis as the type species. Two new species of Amphisphaeria, namely A. oleae and A. verniciae, are introduced and justified by their morphological characteristics coupled with phylogenetic analyses. Two new host records, Amphisphaeria micheliae and Endocalyx ptychospermatis, are presented with detailed descriptions and illustrations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection, Isolation and Morphology
Specimens were collected from decayed stems or twigs and were placed in paper bags or envelopes when taken to the laboratory. Macro–micro morphological observations were carried out, as mentioned in Samarakoon et al. []. Single-spore isolation was performed as described in Senanayake et al. []. Germinated spores were individually transferred to potato dextrose agar (PDA) plates and grown at 25 °C in the dark. Measurements were made with the Tarosoft (R) Image Framework program v. 0.9.7, following the procedures outlined by Liu et al. []. Photo plates representing fungal structures were processed in Adobe Photoshop CS6 software (Adobe Systems Inc., San Jose, CA, USA).
Herbarium specimens were deposited in the herbarium of Cryptogams, Kunming Institute of Botany Academia Sinica (HKAS), Kunming, China, and the herbarium of the University of Electronic Science and Technology (HUEST), Chengdu, China. The isolates obtained in this study were deposited in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), Beijing, China, and the University of Electronic Science and Technology Culture Collection (UESTCC), Chengdu, China. MycoBank numbers were registered as outlined in MycoBank (http://www.MycoBank.org, accessed on 21 April 2023).
2.2. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification and Sequencing
Fresh mycelia scraped from 7-day-old isolates on PDA were used to extract genomic DNA using the EZ geneTM fungal gDNA kit (GD2416), according to the manufacturer’s instructions and protocols. The following loci were amplified and sequenced: the partial 28S large subunit rDNA (LSU), partial RNA polymerase II second largest subunit (rpb2), β-tubulin (tub2), translation elongation factor 1-alpha (tef1) and internal transcribed spacer (ITS). The forward and reverse primer pairs LR0R/LR5 [], fRPB2-5F/fRPB2-7cR [], T1/T22 [], EF1-983F/EF1-2218R [] and ITS5/ITS4 [] were used to amplify the PCR fragments of these genes, respectively. The PCR amplification conditions followed those by Samarakoon et al. []. Sequencing of PCR products was performed by Beijing Tsingke Biological Engineering Technology and Sangon Biotech (Shanghai) Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China.
2.3. Phylogenetic Analyses
The related sequences for phylogenetic analyses were downloaded from GenBank (Table S1). Single-gene sequences were aligned using the MAFFT v.7.429 online service (https://mafft.cbrc.jp/alignment/server/, accessed on 15 October 2022) [], and the ambiguous sites were trimmed by TrimAI v1.2 []. The best-fitting evolutionary models for Bayesian analysis (BI) and maximum likelihood (ML) were determined independently for each gene by MrModeltest v. 2.3 []. Each sequence matrix was concatenated by the software SequenceMatrix v1.7.6 for multiple-gene phylogenetic analyses [].
ML and BI were performed on the CIPRES Science Gateway platform []. ML analyses were made with RAxML-HPC2 on XSEDE v 8.2.8 with default parameters and bootstrapping with 1000 replicates []. MrBayes analyses were conducted in CIPRES with MrBayes on XSEDE 3.2.7a. Four simultaneous Markov chains were run for 20,000,000 generations, and trees were sampled every 1000th generation. The first 20% of the trees of the generations were discarded as burn-in, and the posterior probabilities (PP) were calculated from the remaining 80% of the trees []. BI posterior probabilities and maximum likelihood bootstrap values equal to or greater than 0.95/75% are indicated near each node of the phylogenetic tree.
Phylograms were visualized on FigTree v.1.4.0 [], and the layouts of the trees were drawn in the Adobe Illustrator CS6 software (Adobe Systems, USA). All newly generated sequences in the study were deposited in GenBank, and relevant sequences for phylogenetic analyses are included in the Table S1.
3. Results
3.1. Phylogenetic Analyses
Two phylogenetic analyses were conducted to resolve the relationships among taxa in Amphisphaeria (Amphisphaeriaceae) and Xylariomycetidae.
The first phylogenetic tree represents the genus Amphisphaeria (Figure 1). Seven strains obtained in this study were analyzed with other taxa of Amphisphaeria based on the concatenated dataset of ITS, LSU, rpb2 and tub2. The data matrix comprised 43 taxa, with Anungitea eucalyptorum (CBS 137967), Bartalinia pini (CBS 143891) and B. pondoensis (CBS 125525) as the outgroup taxa. The dataset consists of 3333 total characters (ITS: 1–648 bp, LSU: 649–1483 bp, rpb2: 1484–2462 bp, tub2: 2463–3333 bp, including gaps). These seven strains clustered within Amphisphaeria, representing two new and one known species. Two strains of A. verniciae (CGMCC 3.24960 and UESTCC 23.0122) formed a distinct clade as a sister to A. curvaticonidia, while two strains of A. oleae (CGMCC 3.24959 and UESTCC 23.0120) were sisters to A. uniseptata (CBS 114967) with 100% ML statistical support. The remaining three strains (UESTCC 23.0123, UESTCC 23.0124 and UESTCC 23.0125) grouped with A. micheliae, forming a well-supported clade (100% ML/1.00 PP).
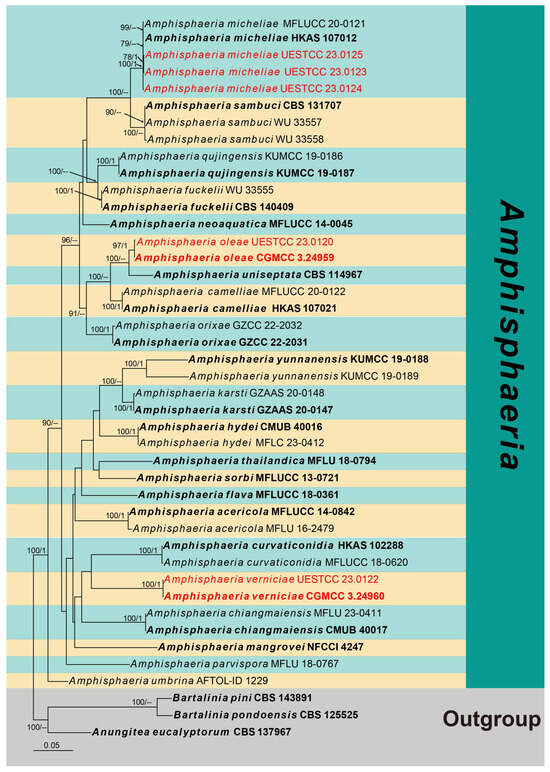
Figure 1.
Phylogram generated from RAxML analysis based on the combined ITS, LSU, rpb2 and tub2 sequence data of Amphisphaeria isolates. Bootstrap values for maximum likelihood of ≥75% and Bayesian posterior probabilities of ≥0.95 are given near the nodes as ML/PP. Isolates from this study are marked in red, and ex-type strains are in bold.
The second phylogeny represents the subclass Xylariomycetidae (Figure 2). Five strains obtained in this study were analyzed with other taxa of Xylariomycetidae based on the concatenated dataset of ITS, LSU, rpb2, tub2 and tef1. The data matrix comprised 135 taxa, with Achaetomium macrosporum (CBS 532.94), Chaetomium elatum (CBS 374.66) and Sordaria fimicola (CBS 723.96) as the outgroup taxa. The dataset consists of 4849 total characters (ITS: 1–478 bp, LSU 479–1827 bp, rpb2 1828–3021 bp, tub2 3022–4141 bp, tef1: 4142–4849 bp, including gaps). Three strains (CGMCC 3.24962, UESTCC 23.0127 and UESTCC 23.0128) formed a separate clade in Xylariales close to Barrmaeliaceae and Castellaniomyces rosae (MFLUCC 15-0536), with poor statistical support. The other two strains (UESTCC 23.0129 and UESTCC 23.0130) clustered with Endocalyx ptychospermatis (ZHKUCC 21-0008), with absolute bootstrap support (100% ML/1.00 PP).

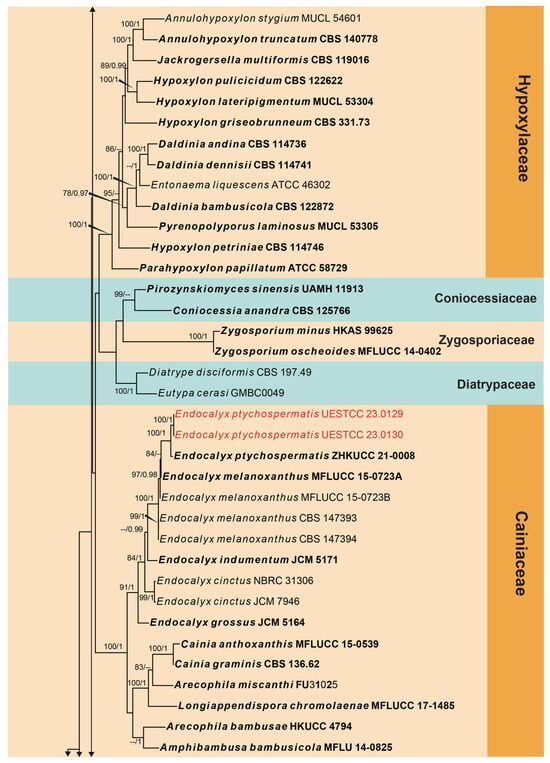
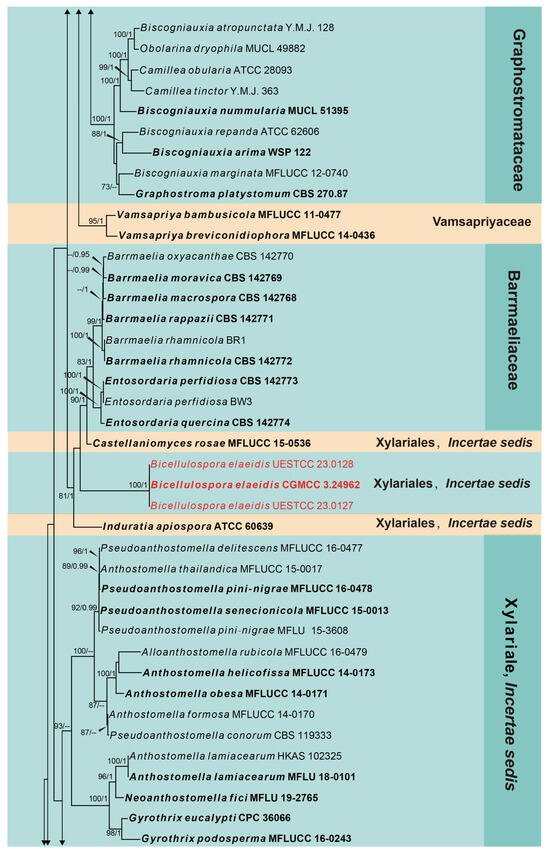
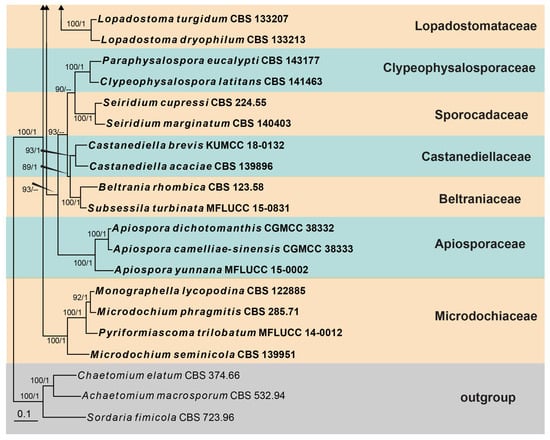
Figure 2.
Phylogram generated from RAxML analysis based on the combined ITS, LSU, rpb2, tub2 and tef1 sequence matrix of Xylariomycetidae. Bootstrap values for maximum likelihood of ≥75% and Bayesian posterior probabilities of ≥0.95 are given near the nodes as ML/PP. Isolates obtained from this study are in red, and ex-type strains are in bold.
3.2. Taxonomy
Amphisphaeria micheliae Samarak., Jian K. Liu & K.D. Hyde, Journal of Fungi 6(3): 16 (2020) (Figure 3).
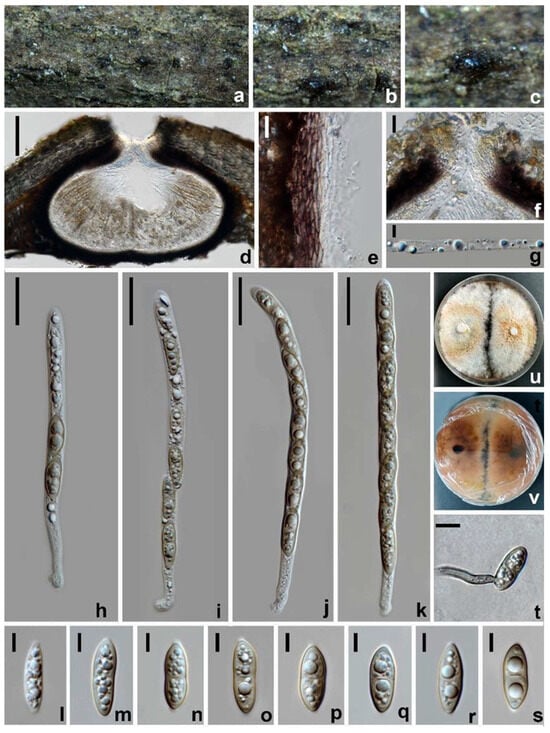
Figure 3.
Amphisphaeria micheliae (HUEST 23.0123, new host record). (a–c) The appearance of ascomata on substrate. (d) Vertical section of an ascoma. (e) Peridium. (f) Ostiole. (g) Paraphyses. (h–k) Asci. (l–s) Ascospores. (t) Germinated ascospore. (u) Colonies on PDA from above. (v) Colonies on PDA from below. Scale bars: (d) 100 µm; (e,g,t) 10 µm; (f) 40 µm; (h–k) 20 µm; (l–s) 5 µm.
MycoBank number: MB 836112.
Saprobic on dead branches of Acer truncatum. Sexual morph: Ascomata 200–270 × 380–505 µm ( = 240 × 470 µm, n = 10), dark brown to black, immersed, solitary, scattered, subglobose or oblate. Ostiole 56–67 µm wide, centric. Peridium 20–40 µm wide, leathery, two-layered; outer layer consisting of reddish brown, polygonal to elongated, thick-walled cells of textura angularis; inner layer with hyaline, flattened, thin-walled cells of textura angularis. Paraphyses 3–5.5 µm wide, hyaline, cellular, septate, guttulate. Asci 96–147 × 6.5–9.5 µm ( = 118 × 8.5 µm, n = 30), eight-spored, cylindrical, with an elongated pedicel and a discoid apical ring. Ascospores 17–22 × 6.5–7.5 µm ( = 19 × 7 µm, n = 30), uniseriate, partially overlapping, narrowly ellipsoidal to fusiform, one-septate, becoming slightly narrower towards both ends, initially hyaline, pale yellow to yellowish brown when aged, guttulate. Asexual morph: Undetermined.
Culture characteristics: Colonies on PDA reaching 13–17 mm diam. after one week at 25 °C in the dark, colonies circular, flattened, dense, with a rough surface, concentrically zonate, milky white to pale reddish brown, mycelium velvety; from below: reddish brown to dark brown at the center, pale brown at the margin, producing yellow pigments in PDA.
Materials examined: China, Sichuan Province, Chengdu city, Pidu district, 30°49′26.76″ N, 103°47′41.24″ E, elevation 442 m, on branches of Acer truncatum, 19 March 2021, W.L. Li, 095 (HUEST 23.0123), living culture UESTCC 23.0123; ibid., Leshan city, Jingyan county, 29°30′23.23″ N, 103°57′30.52″ E, elevation 410 m, on branches of Idesia polycarpa, 23 July 2021, W.L. Li, 319 (HUEST 23.0124), living culture UESTCC 23.0124; ibid., Mianyang city, Youxian district, 31°22′28.88″ N, 104°50′42.00″ E, elevation 398 m, on branches of Olea europaea, 10 June 2021, W.L. Li, 277 (HUEST 23.0125), living culture UESTCC 23.0125.
Notes: The multi-gene phylogenetic analyses showed our isolates (UESTCC 23.0123, UESTCC 23.0124 and UESTCC 23.0125) to be clustered with Amphisphaeria micheliae, with 100% ML/1.00 PP statistical support (Figure 1). Morphologically, the new collections share similar characteristics with A. micheliae (MFLUCC 20-0120 and HKAS 107012). However, the colony of the strain UESTCC 23.0123 produces yellowish brown pigments on PDA, while pigmentation is not observed in the ex-type strain MFLUCC 20-0121 in the same medium []. Considering that light, temperature, humidity and the incubation time can affect the colony morphology, the new collections are identified as A. micheliae.
Amphisphaeria oleae W.L. Li, R.R. Liang & Jian K. Liu, sp. nov. (Figure 4).
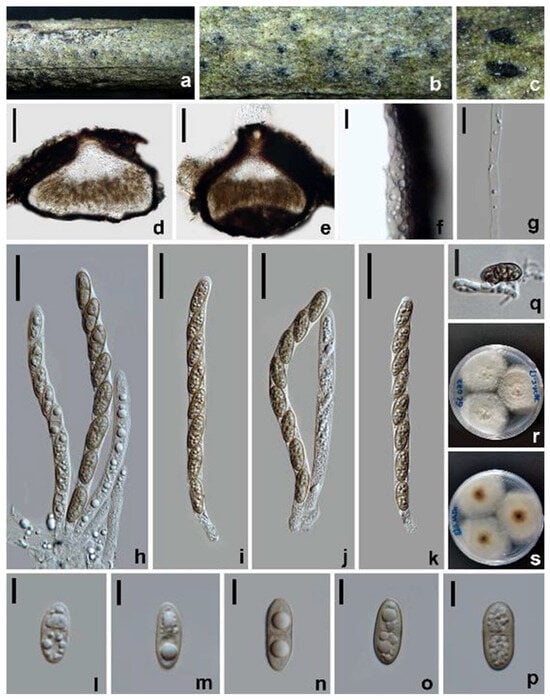

Figure 4.
Amphisphaeria oleae (HKAS 128843, holotype). (a–c) The appearance of ascomata on substrate. (d,e) Vertical section of ascomata. (f) Peridium. (g) Paraphyses. (h–k) Asci. (l–p) Ascospores. (q) Germinated ascospore. (r) Colonies on PDA from above. (s) Colonies on PDA from below. Scale bars: (d,e) 100 µm; (f,g,q) 10 µm; (h–k) 20 µm; (l–p) 5 µm.
MycoBank number: 849633.
Etymology: The epithet ‘oleae’ refers to the host genus Olea, on which the fungus was collected.
Holotype: HKAS 128843.
Saprobic on decaying branches of Olea europaea. Sexual morph: Ascomata 210–240 × 290–375 µm ( = 230 × 320 µm, n = 10), immersed, visible as black spots, surrounded by a pale gray halo on the surface, solitary, aggregated, globose to subglobose, ostiolate, papillate. Ostiole 55–87 µm diam., periphysate, conical or circular. Peridium 23.5−32.5 µm thick, consisting of multi-layered cells of textura angularis; inner layers with hyaline to pale gray, thin-walled cells; outer layers with dark brown to black, thick-walled cells. Paraphyses 3.5−5 µm wide, hyaline, filamentous, septate, guttulate. Asci 91–115 × 7–8.5 µm ( = 101 × 7.5 µm, n = 30), eight-spored, unitunicate, cylindrical, with a cylindrical pedicel and an apical ring. Ascospores 13–15 × 4.5–7 µm ( = 14 × 6 µm, n = 30), L/W 2.2, uniseriate, ellipsoidal, hyaline when young, becoming yellowish brown at maturity, with a median septum, smooth- and thick-walled, guttulate. Asexual morph: Undetermined.
Culture characteristics: Ascospores germinating on PDA within 12 h at 25 °C. Colonies growing on PDA reaching 3.2–3.4 cm diam. after one week at 25 °C in the dark, white to pale yellow, circular, flat, center denser than the edge; in reverse, white becoming yellowish brown to brown from the center with age.
Materials examined: China, Sichuan Province, Guangyuan city, Chaotian district, 30°19′57.04″ N, 103°59′46.66″ E, elevation 432 m, on branches of Olea europaea, 30 January 2021, W.L. Li, 32a (HKAS 128843, holotype), ex-type living culture CGMCC 3.24959; 32b (HUEST 23.0120, isotype), ex-isotype living culture UESTCC 23.0120.
Notes: The multi-gene phylogeny indicated that Amphisphaeria oleae (CGMCC 3.24959) is nested within Amphisphaeria and clustered with A. uniseptata (CBS 114967) in a sister clade with 100% ML statistical support (Figure 1). The BLASTn search of the tub2 sequence of A. oleae (CGMCC 3.24959) showed 92.61% (351/379 bp, eight gaps) similarity with A. camelliae (MFLU 20-0181). Comparisons of the tub2 sequence of A. oleae (CGMCC 3.24959) and A. uniseptata (CBS 114967) showed 85% sequence identity (257/301 base pairs (bp), 12 gaps). Morphologically, A. oleae resembles A. uniseptata in having cylindrical asci and uniseriate, ellipsoidal, hyaline to brown ascospores with a median septum, but differs from the latter by having a two-layered ascomatal wall (Figure 4e) (vs. three-layered) and smaller ascospores (L/W 2.4 vs. L/W 2.7) []. Thus, A. oleae is hereby introduced as a novel species in Amphisphaeria.
Amphisphaeria verniciae W.L. Li, R.R. Liang & Jian K. Liu, sp. nov. (Figure 5).
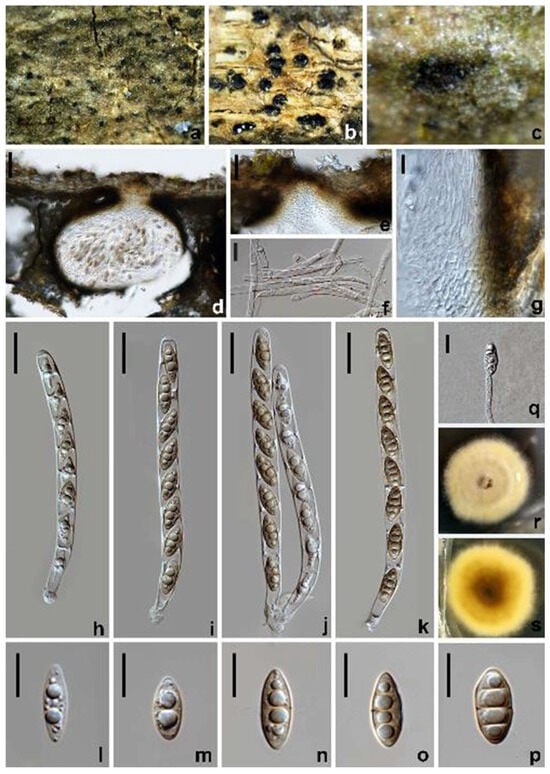
Figure 5.
Amphisphaeria verniciae (HKAS 128844, holotype). (a–c) The appearance of ascomata on substrate. (d) Vertical section of an ascoma. (e) Ostiole. (f) Paraphyses. (g) Peridium. (h–k) Asci. (l–p) Ascospores. (q) Germinated ascospore. (r) Colony on PDA from above. (s) Colony on PDA from below. Scale bars: (d) 50 µm; (e) 40 µm; (f,g,l–q) 10 µm; (h–k) 20 µm.
MycoBank number: 849634.
Etymology: The epithet ‘verniciae’ refers to the host genus Vernicia, on which the holotype was collected.
Holotype: HKAS 128844.
Saprobic on decaying branches of Vernicia fordii. Sexual morph: Ascomata 110–200 × 130–240 µm ( = 150 × 170 µm, n = 10), immersed, visible as black spots, globose to subglobose, solitary, scattered, ostiolate, papillate. Ostiole 37–53 µm diam., periphysate, conical or circular. Peridium 23−30.5 µm thick, consisting of multi-layered cells of textura angularis; inner layers with hyaline, polyhedral to elongated cells; outer layers with dark brown to brown cells. Paraphyses 2.5−5 µm wide, hyaline, filamentous, septate. Asci 111–143 × 9–13.5 µm ( = 130 × 11 µm, n = 30), eight-spored, unitunicate, cylindrical, with a short pedicel and a minute thin apical ring. Ascospores 16–19 × 6–7.5 µm ( = 17 × 6.5 µm, n = 30), L/W 2.4, uniseriate, narrowly fusiform to ellipsoidal, hyaline, bi-guttulate when immature, becoming pale brown, multi-guttulate when aged, 0–3-septate. Asexual morph: Undetermined.
Culture characteristics: Ascospores germinating on PDA within 12 h at 25 °C. Colonies growing on PDA reaching 2–2.3 cm diam. after one week at 25 °C in the dark, white to pale yellow, circular, flat, with a smooth surface and entire margin; in reverse, yellowish brown at the center, paler towards the margin.
Materials examined: China, Sichuan Province, Guangyuan city, Chaotian district, 32°41′05.48″ N, 106°01′22.40″ E, elevation 628 m, on dead branches of Vernicia fordii, 19 April 2021, W.L. Li, 217a (HKAS 128844, holotype), ex-type living culture CGMCC 3.24960; 217b (HUEST 23.0121, isotype), ex-isotype living culture UESTCC 23.0121.
Notes: The BLASTn searches of the LSU sequence of Amphisphaeria verniciae (CGMCC 3.24960) resulted in 97.62% (861/882 bp, 1 gap) and 97.38% (854/877 bp, 1 gap) matches with A. fuckelii (LEF1) and A. camelliae (HKAS 107021). The rpb2 and tub2 BLASTn results showed 82.65% (872/1055 bp, two gaps) and 90.34% (870/963 bp, nine gaps) matches with A. fuckelii (LEF1), respectively. The multi-gene phylogeny (Figure 1) showed that A. verniciae (CGMCC 3.24960 and UESTCC 23.0122) is closely related to A. curvaticonidia. Morphologically, A. verniciae is comparable to A. camelliae, A. curvaticonidia and A. fuckelii. However, A. curvaticonidia and A. fuckelii can be distinguished from A. verniciae by their cylindrical ascospores with rounded ends []. Ascospores of A. verniciae are mostly three-septate, while in A. camelliae, they are often one-septate [,]. In addition, they are different in terms of the L/W of ascospores (A. camelliae L/W 3.1 vs. A. curvaticonidia L/W 2.7, A. fuckelii L/W 2.9 vs. A. verniciae L/W 2.4) [,]. Therefore, we introduce A. verniciae as a new species in Amphisphaeria.
Bicellulospora W. L. Li, R. R. Liang & Jian K. Liu, gen. nov.
MycoBank number: 849635.
Etymology: ‘Bicellulospora’ refers to the two-celled ascospores.
Saprobic on wood or bark. Sexual morph: Ascomata immersed to semi-immersed, black, globose to subglobose, solitary or in small groups, ostiolate. Ostiole pore rounded, centric. Peridium multi-layered, comprising pale brown to dark brown cells of textura angularis. Paraphyses numerous, filamentous, hyaline, septate, unbranched, guttulate, smooth. Asci eight-spored, unitunicate, cylindrical, with a short stipe, apically rounded, with a discoid apical ring. Ascospores uniseriate or partially overlapping, inequilaterally oblong–ellipsoidal, with a lower deeply constricted septum, hyaline when young, becoming olivaceous brown at maturity, smooth-walled, lacking a germ slit and a sheath. Asexual morph: Undetermined.
Type species—Bicellulospora elaeidis.
Notes: The phylogenetic analyses revealed that three new collections (CGMCC 3.24962, UESTCC 23.0127 and UESTCC 23.0128) formed a distinct lineage in Xylariales. They clustered with Barrmaeliaceae (Barrmaelia and Entosordaria) and Castellaniomyces rosae (MFLUCC 15-0536), with poor statistical support. Species of Barrmaelia can be separated from Bicellulospora by their one-celled ascospores without a dwarf cell. Entosordaria possesses ellipsoid to allantoid, two-celled ascospores consisting of a dark brown larger cell and a small, hyaline dwarf cell []. Castellaniomyces rosae differs from Bicellulospora in having elongated fusiform, brown to dark brown, and equally two-celled ascospores surrounded by a thick mucilaginous sheath [].
Bicellulospora is similar to Anthostomella, Apiospora, Occultitheca, Pyriformiascoma and Vamsapriya in having inequilaterally ellipsoidal ascospores consisting of a larger cell and a dwarf cell [,,,,,,]. However, Occultitheca (O. rosae) can be easily distinguished from Bicellulospora by a basal hyaline dwarf cell and a well-visible germ slit on the ascospores []. Apiospora (A. guiyangensis) and Vamsapriya (V. mucosa) differ from Bicellulospora in having ellipsoid to reniform, hyaline ascospores []. Pyriformiascoma (P. trilobatum) differs from Bicellulospora in possessing two-celled ascospores with a brown or olivaceous green larger cell and a hyaline dwarf cell. Additionally, its asci with cytoplasm form a fork-like invagination below the indistinct apical apparatus []. Although several Anthostomella species (e.g., A. castnopsis, A. clypeata, A. cynaroides, A. formosa, A. proteae and A. tomicoides) have similar ascus and ascospore shapes to Bicellulospora elaeidis, they can be distinguished through detailed comparisons (Table 1). Based on the phylogenetic analyses and morphological characteristics, the new genus Bicellulospora is established in Xylariales as genera incertae sedis, with B. elaeidis designed as the type species.

Table 1.
Comparison of Bicellulospora and Anthostomella species.
Bicellulospora elaeidis W.L. Li, R.R. Liang and Jian K. Liu, sp. nov. (Figure 6).
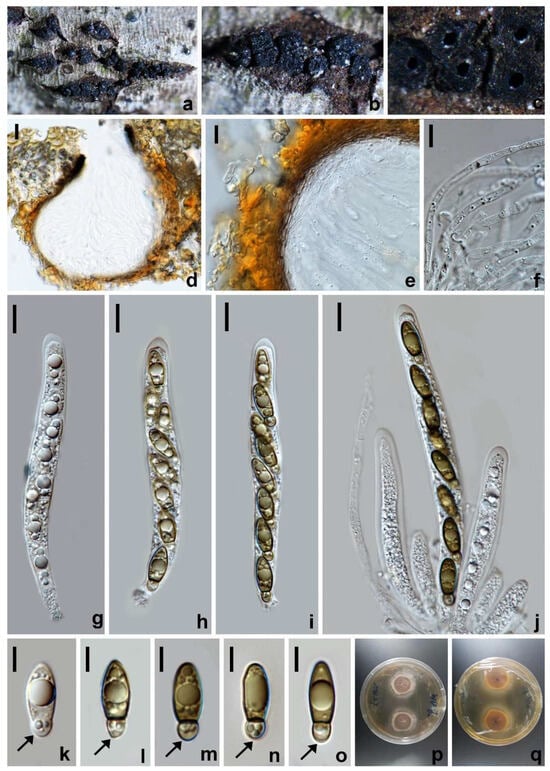
Figure 6.
Bicellulospora elaeidis (HKAS 128845, holotype). (a–c) The appearance of ascomata on substrate. (d) Vertical section of an ascoma. (e) Peridium. (f) Paraphyses. (g–j) Asci. (k–o) Ascospores; the structures indicated by the arrows are dwarf cells. (p) Colonies on PDA from above. (q) Colonies on PDA from below. Scale bars: (d) 20 µm; (e,f,g–j) 10 µm; (k–o) 5 µm.
MycoBank number: 849636.
Etymology: The epithet ‘elaeidis’ refers to the host genus Elaeis, on which the holotype was collected.
Holotype: HKAS 128845.
Saprobic on decaying branches of Elaeis guineensis. Sexual morph: Ascomata 140–170 × 120–140 µm ( = 160 × 130 µm, n = 10), semi-immersed, scattered or gregarious, globose to subglobose, uniloculate, black, papillate, with a central ostiole. Ostiole 55–87 µm diam., central. Peridium 14−24 µm thick, coriaceous, thin-walled, inner layer of hyaline cells of textura angularis, outer layer of pale brown to dark brown cells of textura angularis. Paraphyses 3−4.5 µm wide, hyaline, septate, guttulate. Asci 85.5–100 × 7.5–10 µm ( = 94 × 9 µm, n = 30), eight-spored, unitunicate, cylindrical, with a short stipe, apically rounded, with a flattened apical ring. Ascospores 14.5–17.5 × 5.5–6.5 µm ( = 16 × 6 µm, n = 30), uniseriate or partially overlapping, inequilaterally oblong–ellipsoidal, hyaline when young, becoming olivaceous brown when mature, smooth-walled, with a lower constricted septum at about one-quarter of the length to the base; larger cells bullet-shaped, containing a big guttule and several small guttules; lacking a germ slit and a sheath, dwarf cells subglobose, containing 2–3 small guttules, sometimes slightly paler than the larger cells. Asexual morph: Undetermined.
Culture characteristics: Ascospores germinating on PDA within 48 h at 25 °C. Colonies growing on PDA reaching 1.9−2.2 cm diam. after two weeks at 25 °C in the dark, circular, velvety, pinkish brown in the middle, white at the outer rings, with dense mycelia in the inner rings, sparse at the entire margin; in reverse, brown in the center, pale yellow at the middle ring and white at the margin.
Materials examined: China, Sichuan Province, Chengdu city, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China (UESTC), 30°45′24.71″ N, 103°55′21.07″ E, elevation 465 m, on dead branches of Elaeis guineensis, 30 November 2020, W.L. Li, W62a (HKAS 128845, holotype), ex-type living culture CGMCC 3.24962; W62b (HUEST 23.0127, isotype), ex-isotype living culture UESTCC 23.0127; W62c (HUEST 23.0128, isotype), isotype living culture UESTCC 23.0128.
Notes: Bicellulospora elaeidis was identified as a new species isolated from the dead branches of Elaeis guineensis. The BLASTn search of the LSU sequence of Bi. elaeidis (CGMCC 3.24962) showed 97.07% (893/920 bp, 8 gaps) and 94.94% (939/989 bp, 24 gaps) similarity with Entosordaria perfidiosa (BW3) and Barrmaelia rhamnicola (BR), respectively. The BLASTn search of the tef1 sequences resulted in 87.81% (850/968 bp, seven gaps) and 87.51% (848/969 bp, nine gaps) similarity with E. perfidiosa (EPE) and Ba. rappazii (Cr2), respectively. The ITS sequence of Bi. elaeidis (CGMCC 3.24962) presented only 86.07% (488/567 bp, 25 gaps) and 85.69% (491/573 bp, 26 gaps) similarity with Ba. oxyacanthae (BO) and E. quercina (CBS 142774), respectively. The multi-gene analyses indicated that Bi. elaeidis (CGMCC 3.24962, UESTCC 23.0127 and UESTCC 23.0128) formed a distinct clade that is a sister to the clade containing Barrmaelia, Castellaniomyces and Entosordaria (Figure 2). However, they have significant differences in morphology.
Endocalyx ptychospermatis Y.R. Xiong, Manawas & K.D. Hyde, Fungal Diversity 114: 327–386 (2022) (Figure 7).
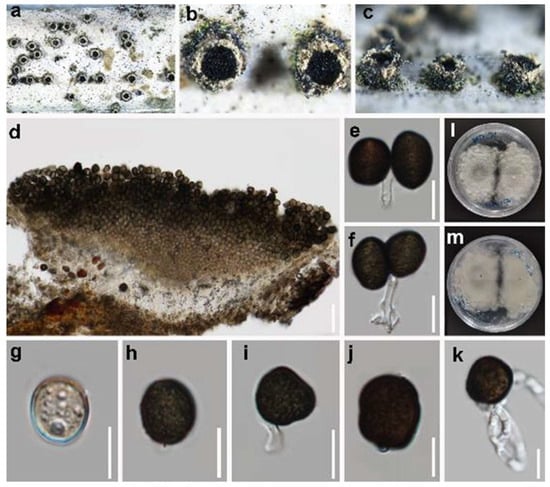

Figure 7.
Endocalyx ptychospermatis (HUEST 23.0129). (a–c) The appearance of conidiomata on the substrate. (d) Vertical section of a conidioma. (e,f) Conidiphore and conidia. (g–j) Conidia. (k) Germinated conidium. (l) Colonies on PDA from above. (m) Colonies on PDA from below. Scale bars: (d) 100 µm; (e–k) 10 µm.
Saprobic on decaying branches of Trachycarpus fortunei (Palmae). Sexual morph: Undetermined. Asexual morph: Conidiomata 600–640 × 300–379 µm ( = 625 × 350 µm, n = 10), raised, cup-shaped or cylindrical, scattered or aggregated, pale yellow to pale green, surrounded by numerous yellow hyphal rings. Conidiophores 2–2.5 µm ( = 2.4 µm, n = 10) wide, filiform, hyaline, septate. Conidiogenous cells hyaline, integrated, globose or cylindrical. Conidia 11.5–16 × 10.5–13.5 µm ( = 14 × 12 µm, n = 30), unicellular, elliptical to irregular polygonal, pale brown when immature, dark brown to blackish brown when aged, some with a longitudinal germ slit, rough-walled.
Culture characteristics: Conidia germinating on PDA within 12 h at 25 °C. Colonies growing on PDA reaching 1.2–1.4 cm diam. after one week at 25 °C in the dark; white, undulate at the edge, rough from above; dull white from below.
Material examined: China, Sichuan Province, Chengdu city, Pidu district, 30°45′25.01″ N, 103°55′21.97″ E, elevation 466 m, on dead branches of Trachycarpus fortunei (Palmae), 30 November 2020, W.L. Li, W71a (HUSET 23.0129), living culture UESTCC 23.0129; W71b (HUEST 23.0130), living culture UESTCC 23.0130.
Notes: Our collection is similar to Endocalyx ptychospermatis in terms of the shape and size of conidiomata and conidia. They were collected from different species of palm (Trachycarpus fortune vs. Ptychosperma macarthurii) []. The phylogenetic analyses indicated that the new collection clustered with the type of E. ptychosepermatis (ZHKUCC 21-0008) with 100% ML/1.00 PP statistical support (Figure 2).
4. Discussion
Xylariomycetidae is a taxonomically complex fungal group, and most of its taxa were classified based on their morphological characteristics before the wide application of molecular data [,,]. However, phylogenetic studies have indicated that fungi with similar spore-bearing structures have not evolved from the same ancestral lineages [].
Stromatic characteristics, such as the length of the ascus stipe [], amyloid reactions [], and the shape and size of the ascus apical ring [], are used to delimit xylarialean taxa. The number of ascospores per ascus [], color [], septation [], appendage [,] and character of the germ slit [,] also play a vital role in the identification of xylarialean taxa. Though morphological characteristics are used for traditional generic circumscriptions (such as stromal morphology), they do not commonly reflect phylogenetic relationships. Several anthostomella-like genera (e.g., Anthostomella, Apiospora, Entosordaria, Occultitheca, Pyriformiascoma and Vamsapriya), with dwarf cells of ascospores, were shown to be morphologically comparable but are phylogenetically distinct throughout Xylariomycetidae []. Therefore, the morphology of dwarf cells does not reflect phylogenetic relationships at the familial level but could be informative at the generic level. The new genus Bicellulospora has inequilateral ascospores with an olivaceous brown dwarf cell, distinguishing it from other similar genera such as Entosordaria and Castellaniomyces rosae (Xylariales genera incertae sedis), as they differ in morphology. Based on the molecular data and morphological comparison, a new monotypic genus, Bicellulospora, with type species B. elaeidis, is hereby established and placed in Xylariales as genera incertae sedis.
Samarakoon et al. [] considered that the number of septa cannot be used as a basis for classification at the genus level. Consequently, Lepteutypa was synonymized to Amphisphaeria based on its holomorphic morphology and multi-gene phylogeny. In our study, two new species (A. oleae and A. verniciae) and A. micheliae were isolated from woody oil plants in Sichuan Province, China. Amphisphaeria oleae and A. micheliae share one-septate ascospores, while A. camelliae and A. verniciae clustered close to A. curvaticonidia, as they all have three-septate ascospores. Though the number of septa has less taxonomic significance for generic delimitation, it can properly reflect interspecific relationships.
Endocalyx was introduced by Berkeley and Broome [] and is characterized by sporodochial or synnematous, cylindrical to cup-shaped conidiomata enclosed by yellow or brown sterile peridial hyphae; hyaline to subhyaline, basauxic conidiophores bearing unicellular, elliptical and brown conidia, with a smooth or echinulate surface; and a hyaline germ slit. Delgado et al. [] conducted a comprehensive assessment of Endocalyx based on the molecular data from specimens and strains collected in Japan, Hawaii and the continental U.S.A. Four species were eventually accepted in Endocalyx (E. cinctus, E. indumentum, E. grossus and E. melanoxanthus). Recently, a fifth species, E. ptychospermatis, was reported after its identification in a dead petiole of Ptychosperma macarthurii (palm) in China []. Here, we provide another collection of E. ptychospermatis from Trachycarpus fortunei (Palmae) as a new host record.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jof10030189/s1, Table S1: Taxa used in this study and their GenBank accession numbers.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.-L.L. and J.-K.L.; methodology, W.-L.L. and R.-R.L.; software, W.-L.L. and R.-R.L.; validation, W.-L.L. and J.-K.L.; formal analysis, W.-L.L. and R.-R.L.; investigation, W.-L.L.; resources, W.-L.L.; data curation, W.-L.L.; writing—original draft preparation, R.-R.L. and W.-L.L.; writing—review and editing, W.-L.L., R.-R.L., J.Y. and J.-K.L.; supervision, J.-K.L.; project administration, J.-K.L.; funding acquisition, J.-K.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research (STEP) Program (2019QZKK0503) and the Joint Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Karst Science Research Center of Guizhou province (Grant No. U1812401).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All sequence data are available in NCBI GenBank following the accession numbers in the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
Wen-Li Li thanks Sajeewa S. N. Maharachchikumbura for his valuable suggestions and comments on the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Samarakoon, M.C.; Hyde, K.D.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Stadler, M.; Gareth Jones, E.B.; Promputtha, I.; Suwannarach, N.; Camporesi, E.; Bulgakov, T.S.; Liu, J.K. Taxonomy, phylogeny, molecular dating and ancestral state reconstruction of Xylariomycetidae (Sordariomycetes). Fungal Divers. 2022, 112, 1–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Su, P.W.; Hyde, K.D.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N. Phylogenomics and diversification of Sordariomycetes. Mycosphere 2023, 14, 414–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daranagama, D.A.; Hyde, K.D.; Sir, E.B.; Thambugala, K.M.; Tian, Q.; Samarakoon, M.C.; McKenzie, E.H.C.; Jayasiri, S.C.; Tibpromma, S.; Bhat, J.D.; et al. Towards a natural classification and backbone tree for Graphostromataceae, Hypoxylaceae, Lopadostomataceae and Xylariaceae. Fungal Divers. 2017, 88, 1–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendt, L.; Sir, E.B.; Kuhnert, E.; Heitkämper, S.; Lambert, C.; Hladki, A.I.; Romero, A.I.; Luangsa-ard, J.J.; Srikitikulchai, P.; Peršoh, D.; et al. Resurrection and emendation of the Hypoxylaceae, recognised from a multigene phylogeny of the Xylariales. Mycol. Prog. 2017, 17, 115–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Chen, Y.P.; Ariyawansa, H.A.; Hyde, K.D.; Haelewaters, D.; Perera, R.H.; Samarakoon, M.C.; Wanasinghe, D.N.; Bustamante, D.E.; Liu, J.K.; et al. Integrative approaches for species delimitation in Ascomycota. Fungal Divers. 2021, 109, 155–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, B.D.; Jeewon, R.; Wu, W.P.; Bhat, D.J.; Hyde, K.D. Ribosomal and RPB2 DNA sequence analyses suggest that Sporidesmium and morphologically similar genera are polyphyletic. Mycol. Res. 2006, 110, 916–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayawardene, N.N.; Hyde, K.D.; Al-Ani, L.K.T.; Tedersoo, L.; Haelewaters, D.; Rajeshkumar, K.C.; Zhao, R.L.; Aptroot, A.; Leontyev, D.V.; Saxena, R.K.; et al. Outline of Fungi and fungus-like taxa. Mycosphere 2020, 11, 1060–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.K.; Chomnunti, P.; Cai, L.; Phookamsak, R. Phylogeny and morphology of Neodeightonia palmicola sp. nov. from palms. Sydowia 2010, 62, 261–276. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, B.S. A World Monograph of Anthostomella. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Hong Kong, Pok Fu Lam, Hong Kong, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Voglmayr, H.; Friebes, G.; Gardiennet, A.; Jaklitsch, W.M. Barrmaelia and Entosordaria in Barrmaeliaceae (fam. nov., Xylariales) and critical notes on Anthostomella-like genera based on multigene phylogenies. Mycol. Prog. 2018, 17, 155–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, J. The genus Cainia and a new family, Cainiaceae. Sydowia 1978, 30, 122–133. [Google Scholar]
- Hyde, K.D.; Norphanphoun, C.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Bhat, D.J.; Jones, E.B.G.; Bundhun, D.; Chen, Y.J.; Bao, D.F.; Boonmee, S.; Calabon, M.S.; et al. Refined families of Sordariomycetes. Mycosphere 2020, 11, 305–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konta, S.; Hyde, K.D.; Eungwanichayapant, P.D.; Karunarathna, S.C.; Samarakoon, M.C.; Xu, J.; Dauner, L.A.; Aluthwattha, S.T.; Lumyong, S.; Tibpromma, S. Multigene phylogeny reveals Haploanthostomella elaeidis gen. et sp. nov. and familial replacement of Endocalyx (Xylariales, Sordariomycetes, Ascomycota). Life 2021, 11, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, G.; Miller, A.N.; Hashimoto, A.; Iida, T.; Ohkuma, M.; Okada, G. A phylogenetic assessment of Endocalyx (Cainiaceae, Xylariales) with E. grossus comb. et stat. nov. Mycol. Prog. 2022, 21, 221–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phukhamsakda, C.; Nilsson, R.H.; Bhunjun, C.S.; de Farias, A.R.G.; Sun, Y.R.; Wijesinghe, S.N.; Raza, M.; Bao, D.F.; Lu, L.; Tibpromma, S.; et al. The numbers of fungi: Contributions from traditional taxonomic studies and challenges of metabarcoding. Fungal Divers. 2022, 114, 327–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, S.J. Fungi from the Gold Coast II. Mycol. Pap. 1953, 50, 1–104. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, S.J. New Zealand fungi 25. Miscellaneous species. N. Z. J. Bot. 1978, 16, 311–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, G.; Tubaki, K.J.M. A new species and a new variety of Endocalyx (Deuteromycotina) from Japan. Mycologia 1984, 76, 300–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, O.; Hawksworth, D.L. Notes on ascomycete systematics, Nos. 1-224. Syst. Ascomycetum 1986, 5, 113–174. [Google Scholar]
- Senanayake, I.C.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Hyde, K.D.; Bhat, J.D.; Jones, E.B.G.; McKenzie, E.H.C.; Dai, D.Q.; Daranagama, D.A.; Dayarathne, M.C.; Goonasekara, I.D.; et al. Towards unraveling relationships in Xylariomycetidae (Sordariomycetes). Fungal Divers. 2015, 73, 73–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilze, W.H., II. Abtheilung. Ascomyceten: Gymnoasceen und Pyrenomyceten. In Rabenhorst’s Kryptogamen-Flora von Deutschland, Oesterreich und der Schweiz, 2nd ed.; Rabenhorst, G.L., Ed.; Kummer: Leipzig, Germany, 1885; Volume 21, pp. 203–238. [Google Scholar]
- Wijayawardene, N.N.; Hyde, K.D.; Lumbsch, H.T.; Liu, J.K.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Ekanayaka, A.H.; Tian, Q.; Phookamsak, R. Outline of ascomycota: 2017. Fungal Divers. 2018, 88, 167–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarakoon, M.C.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Liu, J.K.; Hyde, K.D.; Promputtha, I.; Stadler, M. Molecular Phylogeny and Morphology of Amphisphaeria (= Lepteutypa) (Amphisphaeriaceae). J. Fungi 2020, 6, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanayake, I.C.; Lian, T.T.; Mai, X.M.; Camporesi, E.; Zeng, Y.J.; Tian, S.L.; Xie, N. Taxonomy and phylogeny of Amphisphaeria acericola sp. nov. from Italy. Phytotaxa 2019, 403, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Aptroot, A.; Hyde, K.D. Revision of the genus Amphisphaeria. Hong Kong SAR, China. Fungal Divers. Res. Ser. 2004, 13, 1–168. [Google Scholar]
- Phookamsak, R.; Lu, Y.Z.; Hyde, K.D.; Jeewon, R.; Li, J.F.; Doilom, M.; Boonmee, S.; Promputtha, I. Phylogenetic characterization of two novel Kamalomyces species in Tubeufiaceae (Tubeufiales). Mycol. Prog. 2018, 17, 647–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarakoon, M.C.; Liu, J.K.; Hyde, K.D.; Promputtha, I. Two new species of Amphisphaeria (Amphisphaeriaceae) from northern Thailand. Phytotaxa 2019, 391, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanayake, I.C.; Rathnayaka, A.R.; Marasinghe, D.S.; Calabon, M.S.; Gentekaki, E.; Lee, H.B.; Hurdeal, V.G.; Pem, D.; Dissanayake, L.S.; Wijesinghe, S.N.; et al. Morphological approaches in studying fungi: Collection, examination, isolation, sporulation and preservation. Mycosphere 2020, 11, 2678–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilgalys, R.; Hester, M. Rapid Genetic Identification and Mapping of Enzymatically Amplified Ribosomal DNA from Several Cryptococcus Species. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 4238–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Whelen, S.; Hall, B.D. Phylogenetic relationships among ascomycetes: Evidence from an RNA polymerse II subunit. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 1799–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, K.; Cigelnik, E. Two divergent intragenomic rDNA ITS2 types within a monophyletic lineage of the fungusfusariumare nonorthologous. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1997, 7, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehner, S.A.; Samuels, G.J. Taxonomy and phylogeny of Gliocladium analysed from nuclear large subunit ribosomal DNA sequences. Mycol. Res. 1994, 98, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J.W. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., White, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1990; Volume 18, pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S.; Silla-Martínez, J.M.; Gabaldón, T. trimAl: A tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nylander, J. MrModeltest v25; Evolutionary Biology Centre, Uppsala University: Uppsala, Sweden, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Vaidya, G.; Lohman, D.J.; Meier, R. SequenceMatrix: Concatenation software for the fast assembly of multi-gene datasets with character set and codon information. Cladistics 2011, 27, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Pfeiffer, W.; Schwartz, T. Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. In Proceedings of the 2010 Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE), New Orleans, LA, USA, 14 November 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rannala, B.; Yang, Z. Probability distribution of molecular evolutionary trees: A new method of phylogenetic inference. J. Mol. Evol. 1996, 43, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A. FigTree, a Graphical Viewer of Phylogenetic Trees; Institute of Evolutionary Biology University of Edinburgh: Edinburgh, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tsui, C.K.M.; Hyde, K.D.; Hodgkiss, I.J. Paraniesslia tuberculata gen. et sp. nov., and new records or species of Clypeosphaeria, Leptosphaeria and Astrosphaeriella in Hong Kong freshwater habitats. Mycologia 2001, 93, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaklitsch, W.M.; Gardiennet, A.; Voglmayr, H. Resolution of morphology-based taxonomic delusions: Acrocordiella, Basiseptospora, Blogiascospora, Clypeosphaeria, Hymenopleella, Lepteutypa, Pseudapiospora, Requienella, Seiridium and Strickeria. Persoonia 2016, 37, 82–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, K.D.; Norphanphoun, C.; Abreu, V.P.; Bazzicalupo, A.; Thilini Chethana, K.W.; Clericuzio, M.; Dayarathne, M.C.; Dissanayake, A.J.; Ekanayaka, A.H.; He, M.Q.; et al. Fungal diversity notes 603–708: Taxonomic and phylogenetic notes on genera and species. Fungal Divers. 2017, 87, 1–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daranagama, D.A.; Camporesi, E.; Tian, Q.; Liu, X.; Chamyuang, S.; Stadler, M.; Hyde, K.D. Anthostomella is polyphyletic comprising several genera in Xylariaceae. Fungal Divers. 2015, 73, 203–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minter, D.W.; Cannon, P.F. Anthostomella tomicoides. In Descriptions of Fungi and Bacteria; Sheet 1990; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Seonju, L.; Crous, P.W. New species of Anthostomella on fynbos, with a key to the genus in South Africa. Mycol. Res. 2003, 107, 360–370. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, J.B.; Everhart, B.M. New West American Fungi; University of California: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1893. [Google Scholar]
- Jepson, W.L. Erythea: A Journal of Botany, West American and General; University of California: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1893; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Barr, M.E. Prodromus to Class Loculoascomycetes; Hamilton I. Newell, Inc.: Amherst, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, H.M.; Lin, C.R.; Fang, M.J.; Rogers, J.D.; Fournier, J.; Lechat, C.; Ju, Y.M. Phylogenetic status of Xylaria subgenus Pseudoxylaria among taxa of the subfamily Xylarioideae (Xylariaceae) and phylogeny of the taxa involved in the subfamily. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2010, 54, 957–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaklitsch, W.M.; Fournier, J.; Rogers, J.D.; Voglmayr, H. Phylogenetic and taxonomic revision of Lopadostoma. Persoonia 2014, 32, 52–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willis, K.J. State of the World’s Fungi 2018. Report; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2018; pp. 1–92. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, J.D. The Xylariaceae: Systematic, biological and evolutionary aspects. Mycologia 1979, 71, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwannasai, N.; Whalley, M.A.; Whalley, A.J.; Thienhirun, S.; Sihanonth, P. Ascus apical apparatus and ascospore characters in Xylariaceae. IMA Fungus 2012, 3, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, M.E. Prodromus to nonlichenized, pyrenomycetous members of class Hymenoascomycetes. Mycotax 1990, 39, 43–184. [Google Scholar]
- Maharachchikumbura, S.S.M.; Hyde, K.D.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Xu, J.; Crous, P.W. Pestalotiopsis revisited. Stud. Mycol. 2014, 79, 121–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.; Moss, S. Ascospore appendages of marine ascomycetes: An evaluation of appendages as taxonomic criteria. Mar. Biol. 1978, 49, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkeley, M.J.; Broome, C.E. Supplement to the enumeration of fungi of Ceylon. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 1876, 15, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).