Abstract
In addition to the production of albumin cheese, biogas and whey powder, whey has also been used as a raw material for the production of alcoholic beverages. The aim of this research was to investigate the potential of using Istrian albumin cheese whey in the production of whey distillate. Three batches of Istrian albumin cheese were produced in a small-scale cheese plant. The remaining whey after the production of albumin cheese was fermented using Kluyveromyces marxianus subsp. marxianus for 5 days and then distilled. In the whey samples before and after fermentation, the content of total solids, protein, milk fat and lactose was determined. The ethanol content and the composition of volatile compounds in the distillate was determined. The content of all components of the chemical composition of whey, except for the content of fat, decreased during fermentation. In the whey distillate with an alcohol content of 35%, the following compounds were determined: acetaldehyde, methanol, n-propanol, i-butanol, n-butanol, 3-methyl-1-ol, 2-methylbutan-1-ol and ethyl-lactate. The distillate obtained confirmed the potential of using whey for the production of spirits. However, further research is needed due to the potential presence of the harmful effects of certain volatile compounds on human health.
1. Introduction
Due to its chemical composition, i.e., because it contains 70% lactose in dry matter, minerals, vitamins and bioactive substances, in recent years, much attention has been paid to the possibilities of whey biotechnological use for the production of various products such as whey powders, whey protein concentrates and isolates, whey-based beverages, albumin cheeses, functional foods and beverages, edible films and coatings, bioplastics, biofuels and bio-alcohol [1,2]. In general, the composition of whey depends on the type of cheese produced, i.e., the technological process, the microbial cultures and the rennet used [3], so we distinguish sweet and sour whey. Sweet whey is produced during the production of soft, hard and semi-hard cheeses using rennet, while sour whey is a by-product of the acidification of milk during the production of, for example, fresh (quark-like) cheese [4]. The largest amount of whey is produced in the manufacture of hard cheese but also in the manufacture of some other dairy products such as Greek yogurt or concentrated yogurt. According to the 2016 European Dairy Association [5] report, the annual production of whey in the world was about 190 million tons, of which about 6 million tons of whey was produced in Europe and only 197 thousand tons in Croatia. In the last 10 years, there has been a trend of increasing cheese production, so the amount of whey produced in the world increases by 1–2% every year [6]. In the past, whey was exclusively a feed for farm animals, but due to its extremely high biological and nutritional value, it has recently become increasingly present in human diets. Unfortunately, only half of the whey produced (54%) is reused in food production, while the rest mostly ends up as untreated waste in nature, posing a major threat to the environment [7]. Whey, nowadays, represents a serious environmental problem as evidenced by the high levels of COD (chemical oxygen demand) and BOD (biological oxygen demand) [8,9]. Indeed, the dairy industry faces the problem that waste must be adequately processed before being discharged to natural waters or the ground, which implies additional costs for the dairy industry, especially for dairies with a lower production capacity. Moreover, the processing of such by-products in the production of whey products is quite expensive, which is reflected in the cost price of the final product and thus can have a significant impact on the price of the product itself [10]. For this very reason, efforts have recently been made to find effective and permanent solutions for the disposal of whey, i.e., to develop technological and biotechnological processes for its use in order to preserve the natural habitats of many plant and animal species, especially in microenvironments where milk is processed into cheese [10,11]. One of the possible solutions is the production of an alcoholic beverage because after fermentation, its BOD can be reduced by 75%. Thus, in the last decade, whey has become a raw material for the production of various alcoholic beverages, such as vodka [12]. Scientific research is aimed at improving the whey fermentation technology (temperature, mixing speed, initial concentration of the inoculum and the substrate itself and the amount of dissolved oxygen due to optimal yeast fermentation under aerobic conditions), as the composition of whey can greatly affect the composition of the distillate and the final quality of the product. This is extremely important for the popularization of such beverages on the market. Previous research focused on the use of deproteinized whey obtained by membrane filtration of whey. A similar effect is obtained by the production of albumin cheese, i.e., whey is deproteinized by the coagulation of whey proteins due to the effect of elevated temperatures and a decrease in pH. Whey separated after albumin cheese production is a cheap raw material available in large quantities and can be a good substitute for raw materials such as sugar cane or sugar beet, as well as various agricultural crops from which bio-alcohol has been obtained so far [1]. By improving whey fermentation technology, production costs can be optimized, making it more acceptable to producers [13]. The yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus is most commonly used for the conversion of lactose to ethanol, i.e., for the production of bio-alcohol and alcoholic beverages from whey or whey permeate [14]. Kluyveromyces marxianus is tolerant to temperatures of 45–50 °C [15], which makes it ideal for use in fermentations that occur at higher temperatures, but its optimal temperature for ethanol production is 40 °C [16]. Kluyveromyces marxianus has the ability to grow on lactose, galactose, glucose, fructose, xylose and inulin in culture media where these sugars are the only carbon source [17]. For this reason, lactose from whey is a very favorable and effective medium for its growth [18]. The tolerance of Kluyveromyces marxianus to ethanol is lower than that of yeast S. cerevisiae, so it may limit ethanol production [19]. Other microorganisms such as Kluyveromyces lactis and S. cerevisiae are used in the production of food and beverages, but research on their potential to convert lactose into alcohol distillate has only been conducted under experimental conditions with genetically modified organisms. The idea for this work came from the fact that whey is a valuable raw material but also from the major problem of environmental pollution due to its uncontrolled release into the environment. Therefore, the aim of this research was to investigate the potential of using Istrian albumin cheese whey in the production of whey distillate.
2. Materials and Methods
The research was conducted in 2021 on a family farm in peninsula Istria (Croatia), which breeds cattle for milk production and has its own milk processing plant. Three batches of semi-hard Istrian cheese were produced from cows’ milk. After separating the curd and forming the cheese, the whey was used to produce 3 batches of Istrian albumin cheese. Istrian albumin cheese is produced according to the technology described in the paper [20], with modifications due to the different type of milk and the production technology commonly used in Istria. At a temperature of 63 °C, raw milk (3%), and sea salt (2%) were added to the whey. At a temperature of 83 °C, citric acid (0.2%) was added. Finally, whey was cooked to >96 °C to separate Istrian albumin cheese. After albumin cheese production, 100 liters of whey were separated and fermented in a duplicator with the addition of the previously prepared yeast culture Kluyveromyces marxianus subsp. marxianus at a temperature of 35 °C for 5 days. Before adding the yeast culture, the whey was filtered to remove curd residues. The fermented whey was then distilled using a simple pot still (alembic). The distillation process was carried out in one step. The fermented whey was heated in pot still until it evaporated, the vapor condensed, and the condensed distillates were collected. The distillation process was carried out until the alcohol content in the outgoing distillates was below 5% vol. Before and after fermentation, a whey sample was taken for analysis.
2.1. Whey Analysis before and during Fermentation
Analysis of whey before and during fermentation was performed in the Reference Laboratory for Milk and Dairy Products at the Department of Dairy Science, University of Zagreb Faculty of Agriculture. The physico-chemical analysis of whey included the determination of the amount of fat, protein, lactose, dry matter and fat-free dry matter using the method of infrared (mid IR) spectrometry [21] with the instrument Milkoscan FT 120 (Foss, Hillerød, Denmark), pH using the potentiometric method with SevenMulti pH meter (Mettler Toledo, Zürich, Switzerland) and titration acidity by measuring °SH [22].
2.2. Analysis of Whey Distillates
After the distillation of whey, the obtained distillates were analyzed for its alcohol content, and an analysis of the volatile components present in the distillates was performed. The alcohol content of the obtained distillate was determined using the densitometric method with densitometer (Anton Paar SNAP 41) at the Department of Viticulture and Winemaking, University of Zagreb Faculty of Agriculture. The content of volatile components of distillates was determined using gas chromatography according to the modified method by Madrera and Suárez Valles [23] on a gas chromatograph with a FID detector (SRI 8610C) at the Department of Chemistry University of Zagreb, Faculty of Agriculture. The chromatographic analysis was performed on a 30 m MXT WAX capillary column with a diameter of 0.53 mm and a stationary phase length of 0.25 μm. A flame ionization (FID) detector was used for detection, the temperature of which was 250 °C, while the temperature of the injector was 230 °C. Injected volume of the sample was 2 μL. Identification of individual chemical compounds of the distillate was based on their retention time. After determining the peak areas, the concentration of the corresponding compounds was calculated, and the obtained results were converted into mg/L a.a. (absolute alcohol) considering the alcohol content (%) of each sample.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Whey Composition before and during Fermentation
The average chemical composition of whey before fermentation is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Chemical composition of Istrian albumin cheese whey before fermentation.
According to the average composition, whey contained 93.84 g/100 g of water, while the content of dry matter was about 6 g/100 g. Therefore, whey possesses about 50% of the dry matter of milk, and many of the nutrients of milk remain in the whey [10]. The largest part of whey solids is lactose (4.86 g/100 g), while the content of protein is 0.5 g/100 g (Table 1). Tratnik [24] and Blažić et al. [2] report similar values. In general, the composition of whey is highly variable and depends largely on the way it is obtained, so it is divided into sweet and acid whey. Sweet whey, which is produced by processing milk into various soft, semi-hard and hard cheeses, contains a small amount of lactic acid because rennet is used to coagulate casein, while sour whey is separated during lactic acid fermentation in fresh cheese production and contains correspondingly larger amounts of lactic acid [25].
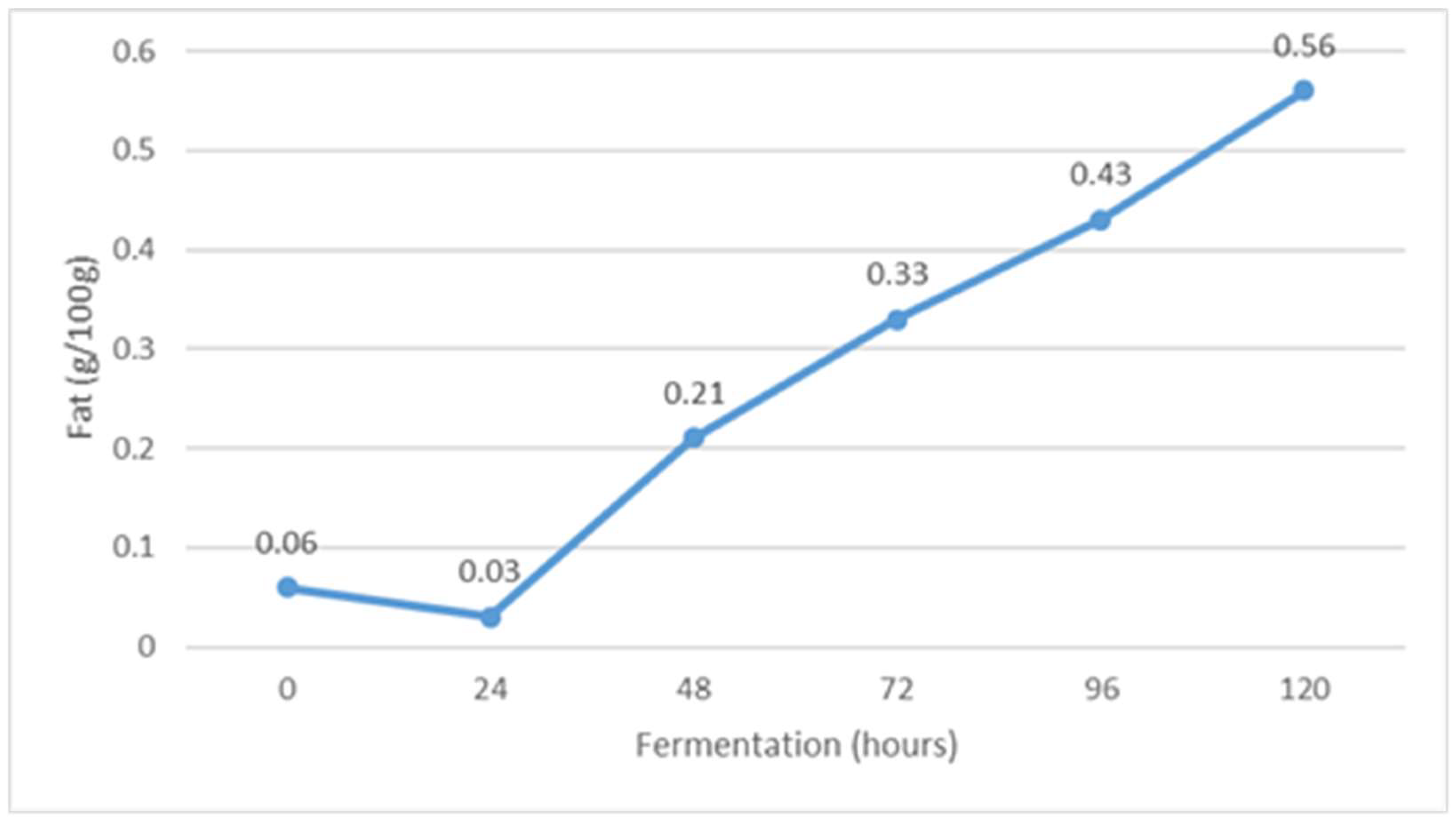
The average physico-chemical properties of whey during fermentation is shown in Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7. The fat content changed during fermentation from 0.06 g/100 g at the beginning of fermentation to 0.56 g/100 g after 120 h of fermentation. It is assumed that the relative fat content increased during fermentation due to the conversion of other organic components of whey into lipid compounds through the action of the yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus subsp. marxianus. In fact, the influence of fermentation on the content of milk fat in fermented whey has not been the subject of scientific investigations so far, considering the results of similar studies.
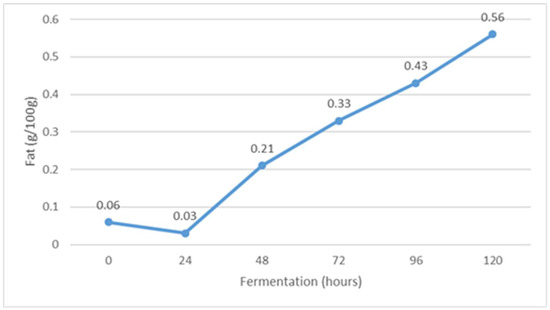
Figure 1.
The content of fat during Istrian albumin cheese whey fermentation using yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus subsp. marxianus.
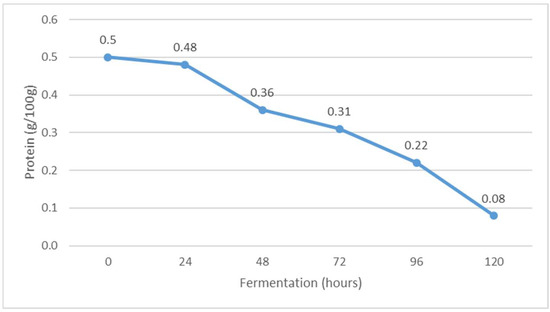
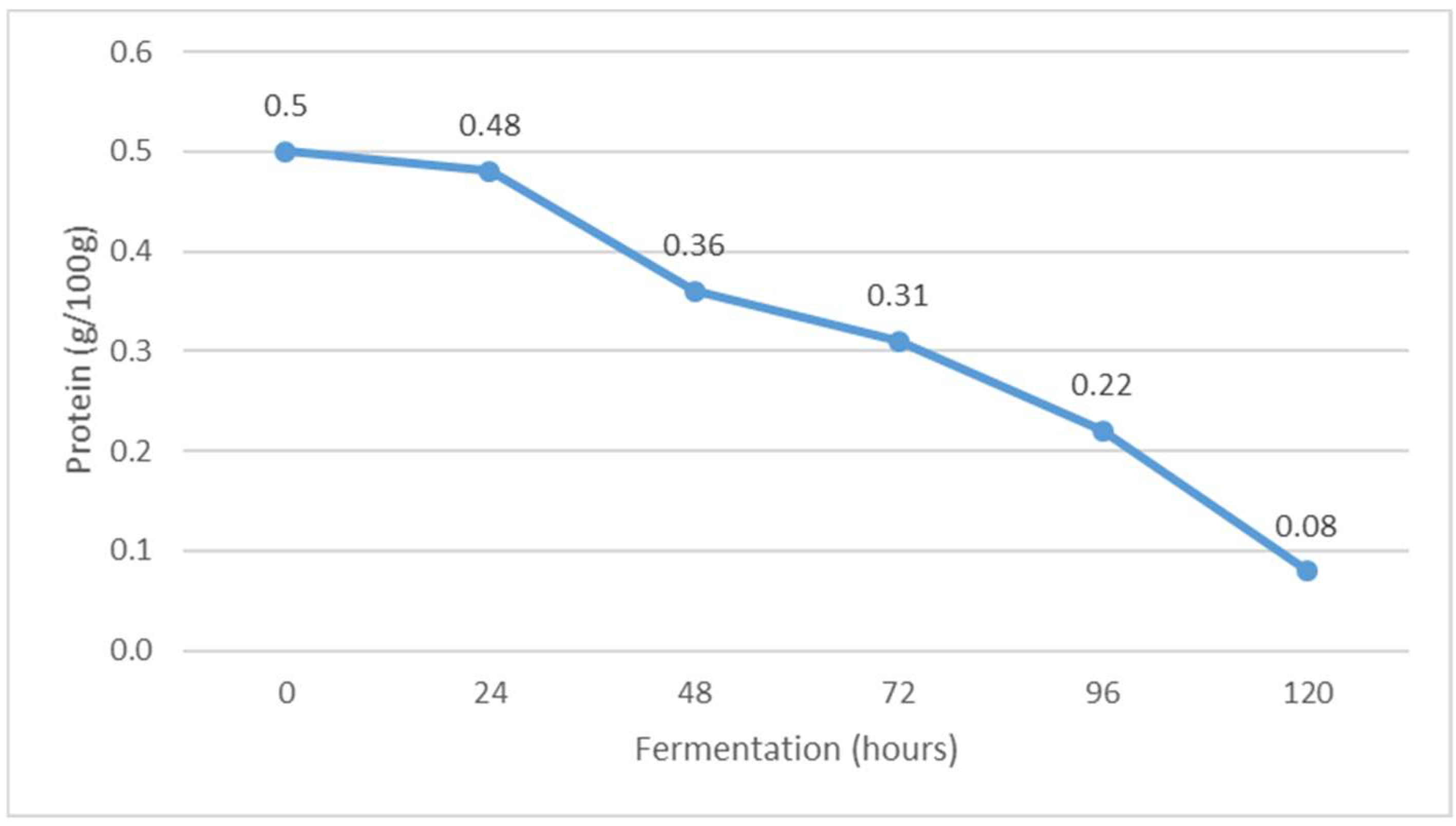
Figure 2.
The content of protein during Istrian albumin cheese whey fermentation using yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus subsp. marxianus.
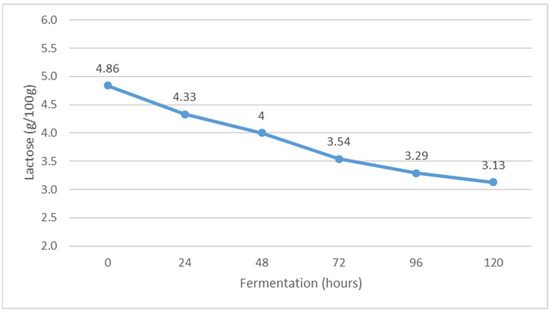
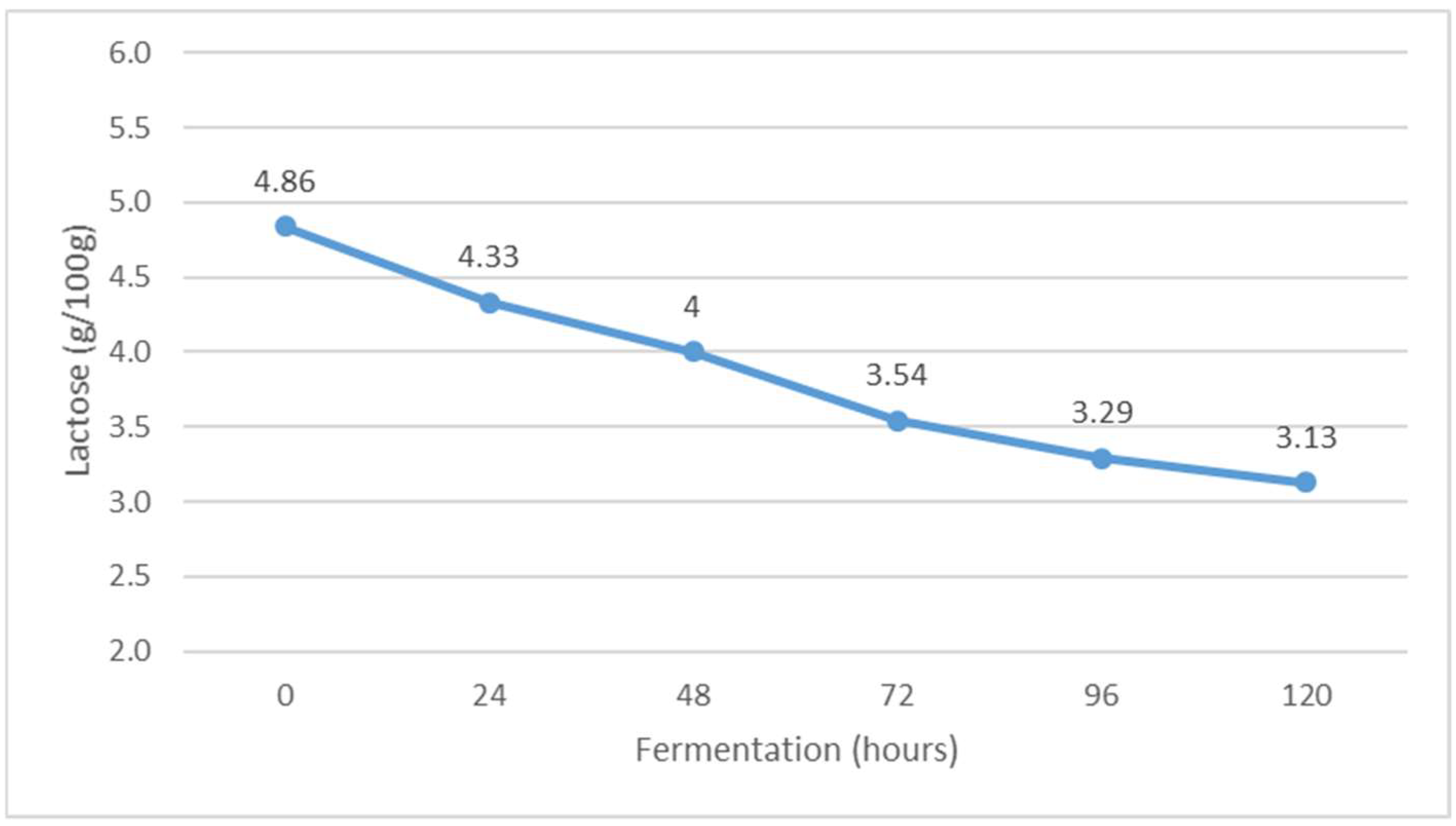
Figure 3.
The content of lactose during Istrian albumin cheese whey fermentation using yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus subsp. marxianus.
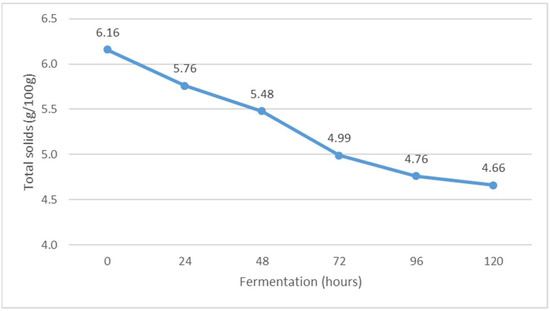
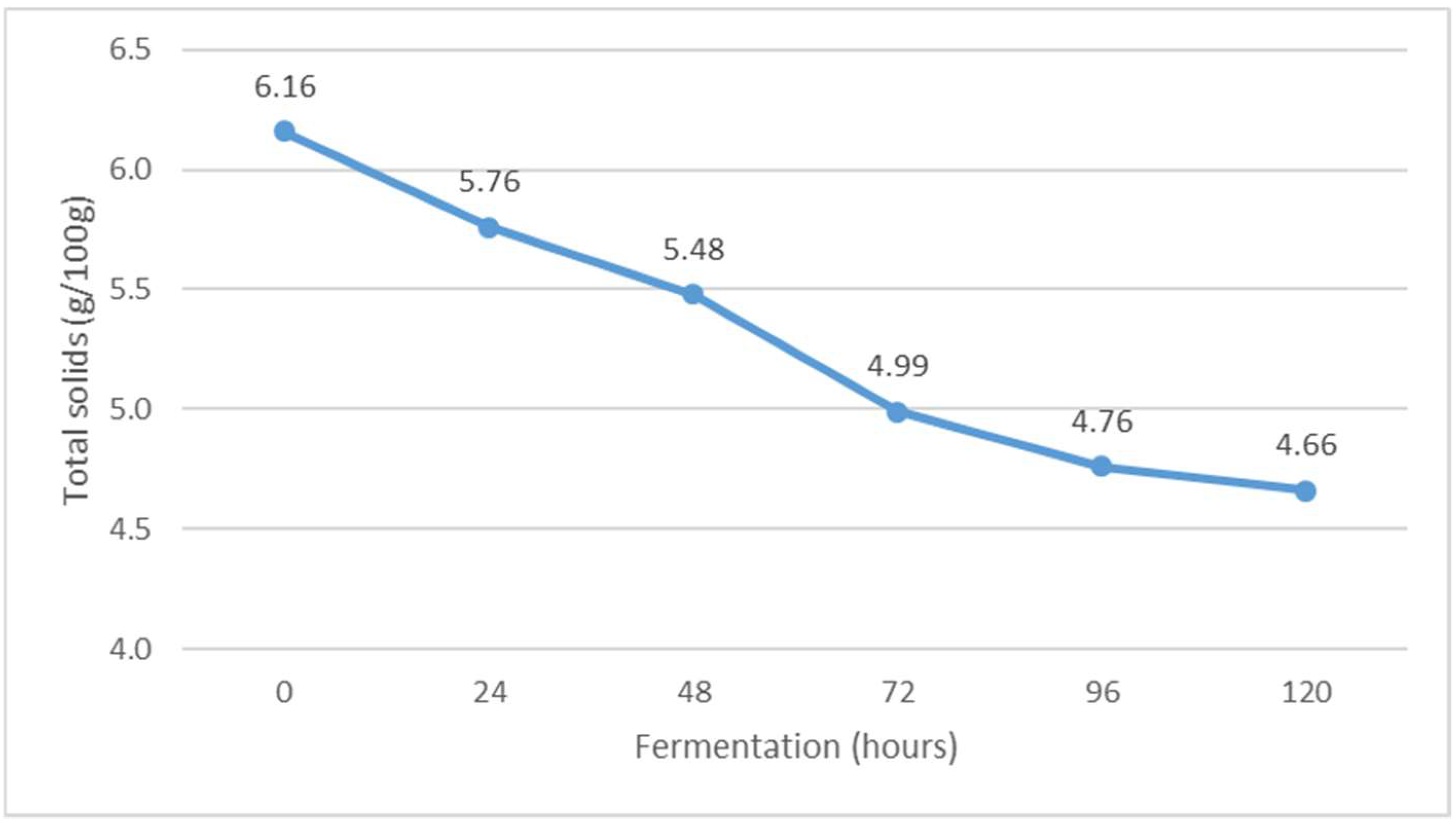
Figure 4.
The content of total solids during Istrian albumin cheese whey fermentation using yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus subsp. marxianus.
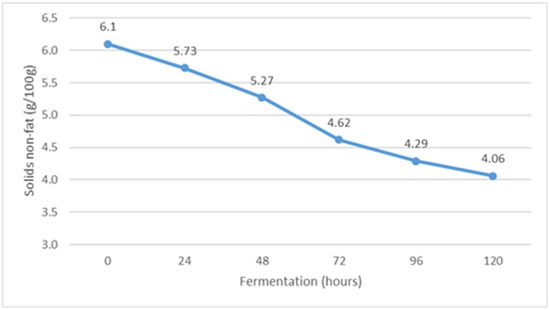
Figure 5.
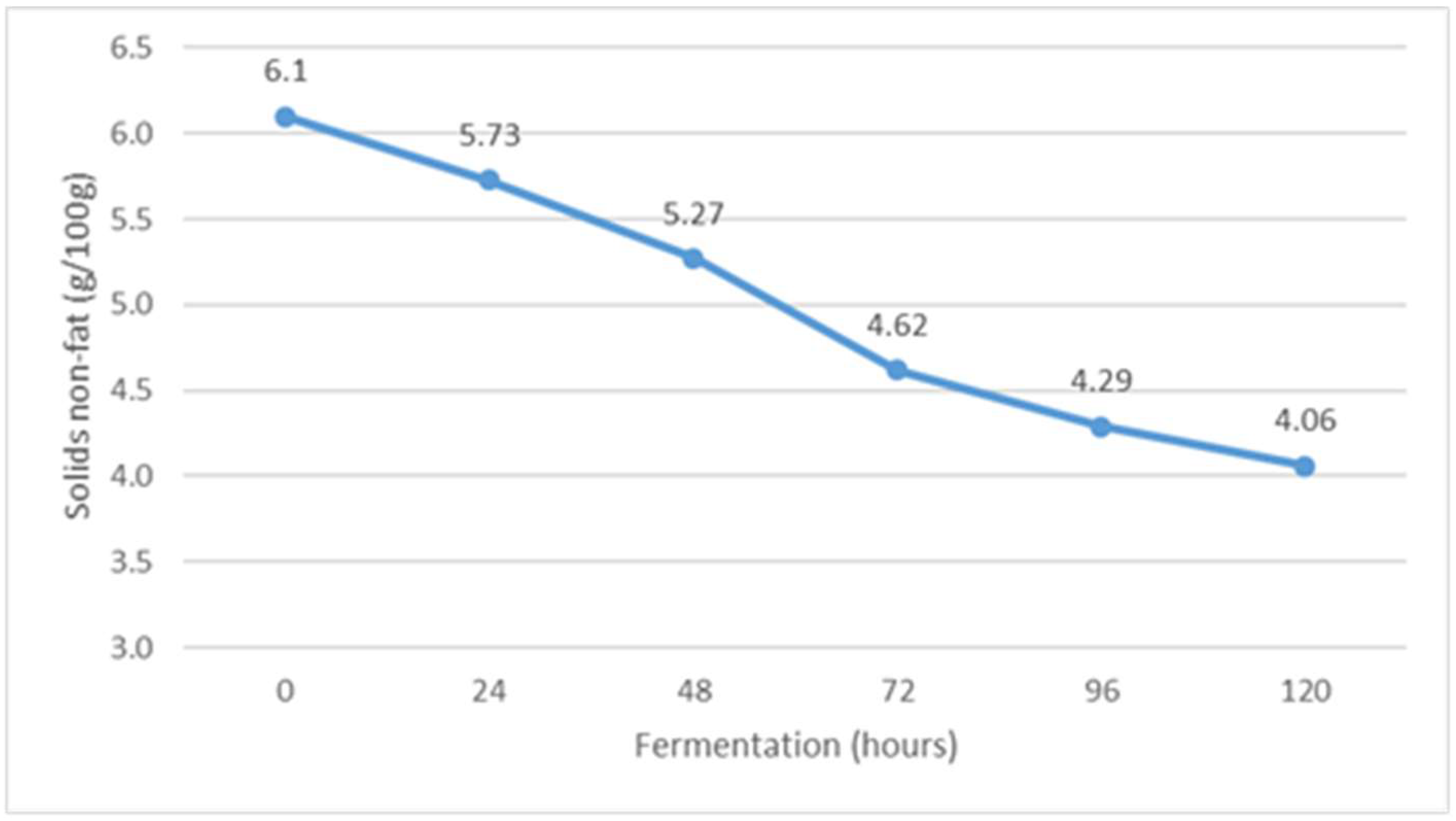
The content of non-fat solids during Istrian albumin cheese whey fermentation using yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus subsp. marxianus.
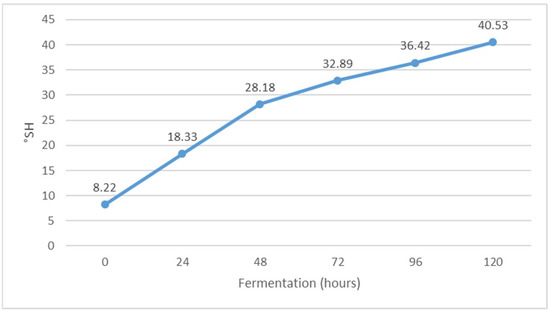
Figure 6.
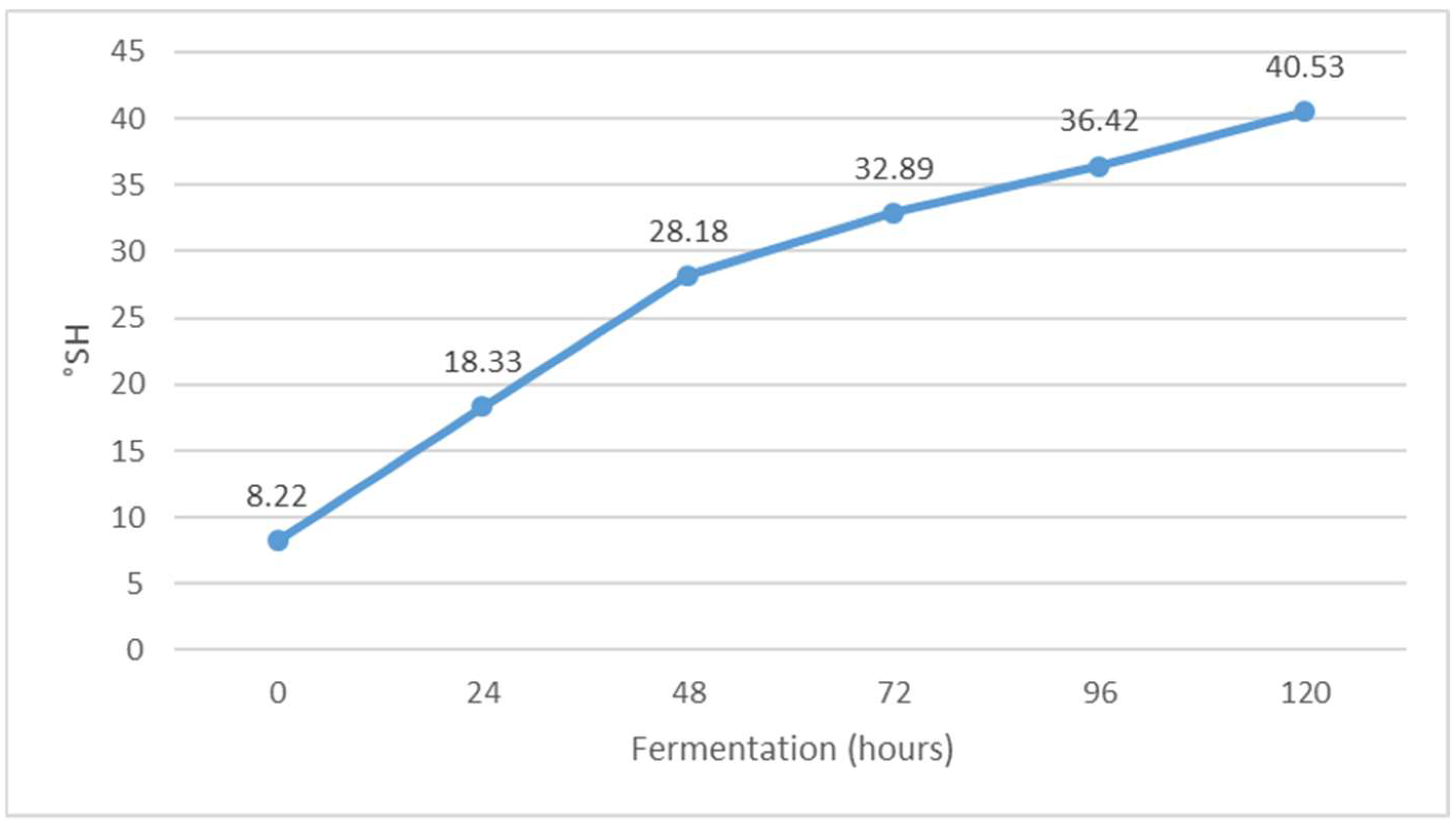
Change in titratable acidity (°SH) value during Istrian albumin cheese whey fermentation using yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus subsp. marxianus.
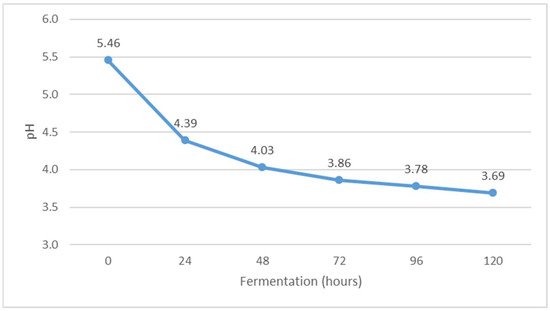
Figure 7.
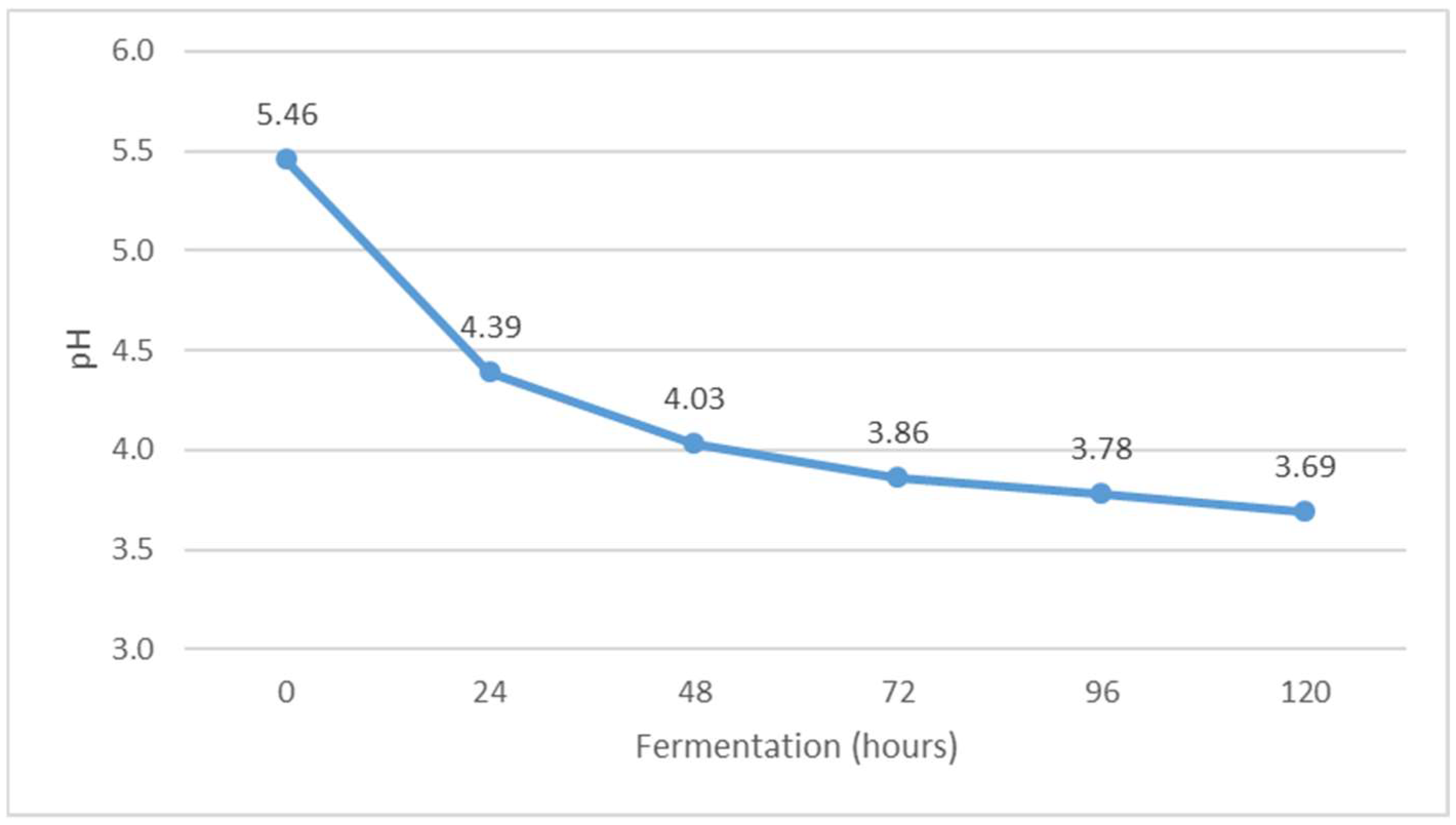
Change in pH value during Istrian albumin cheese whey fermentation using yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus subsp. marxianus.
In contrast to the fat content, the whey protein content decreased during fermentation from 0.50 g/100 g before fermentation to 0.08 g/100 g at the end of fermentation (Figure 2). It is suggested that the decrease in protein content was due to the precipitation (settlement) of denatured whey proteins as a result of a decrease in pH, i.e., reaching the isoelectric point of whey proteins and an increase in alcohol concentration. It is concluded that alcohols act mainly as hydrogen bond donors whose binding to the polypeptide chain is stabilized by hydrophobic interactions. The electronegativity of the oxygen atom may also play a role in stabilizing contacts with the protein [26]. The other possible reason for decreasing the protein content could be due to the proteolysis of K. marxianus, as it was reported that this yeast shows moderate proteolytic activity in milk [27]. In reviewing the available results of previous research, none of the authors have yet investigated the effect of fermentation on the amount of protein in fermented whey.
The lactose content decreased from the beginning of fermentation to the end by 1.71 g/100 g (Figure 3). The decrease in lactose content is consistent with the results of previous studies [28]. It can be assumed that the microbial culture of Kluyveromyces marxianus subsp. marxianus used the lactose from the substrate for growth and multiplication, so the lactose content decreased during fermentation. The obtained results are also in agreement with the research results of Dragone et al. [29], who found a decrease in lactose content in whey due to the effect of Kluyveromyces marxianus subsp. marxianus.
Fermentation of whey obtained after the production of Istrian albumin cheese resulted in a decrease in total solids (Figure 4), and at the same time, the conversion of lactose into fermentation products resulted in a decrease in the content of non-fat solids (Figure 5). Thus, the yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus subsp. marxianus contributes to the reduction of total solids and total non-fat solids in fermented whey by utilizing lactose and other whey compounds during fermentation. Moreover, the content of non-fat solids decreases as a result of the precipitation of denatured whey proteins (Figure 5).
The pH value decreased during fermentation (Figure 7), while the value of °SH increased (Figure 6). The pH of whey before fermentation was 5.46, while the value of °SH was 8.20. The results obtained are in agreement with the results of previous studies [30]. The decrease in pH is probably due to the formation of organic acids during alcoholic fermentation. Indeed, Kluyveromyces marxianus subsp. marxianus has been shown to form acetic, propionic, succinic, malic and citric acids during fermentation [31]. When the pH approaches 4.5, i.e., the isoelectric point of whey protein, additional buffering occurs, which reduces the further effects of the increase in the concentration of organic acids on further lowering the pH of whey [32]. The pH indicates the concentration of free hydrogen ions in the solution, which come mainly from lactic acid but also from other acidic components of whey [28]. In addition, the same authors note that Kluyveromyces marxianus subsp. marxianus is very adaptable to different pH values in the environment in which it occurs and tolerates low pH values, which can be very effective in the fermentation of lactose to bio-alcohol [33].
3.2. Composition of Whey Distillate
The alcohol content of the obtained alcoholic distillate was 35% vol., which confirms the possibility of obtaining alcohol from Istrian albumin cheese whey using Kluyveromyces marxianus subsp. marxianus. The obtained value agrees with the results of Dragone et al. [29], who obtained a distillate of 35.4% vol. from fermented whey. Table 2 shows the composition of the whey distillate. During the distillation process, alcohol and aroma compounds, which are produced during the alcoholic fermentation of sugars, are extracted. In addition to alcohol and water, other volatile components occur, such as aldehydes, ketones and esters. The aim of distillation is to extract ethanol in a favorable ratio to other volatile components so that the distillate has the best possible sensory properties. After the sugars from the whey, mainly lactose and other monosaccharides, have been converted to ethanol, the alcohol must be concentrated to an alcohol content suitable for alcoholic beverages. In the literature, the ethanol yield during whey fermentation is given as 2 to 5% vol. [13]. More complex equipment during distillation implies the production of a cleaner distillate, which is obviously desirable. In order to purify the distillate and remove undesirable substances, redistillation is carried out. Whey fermented using yeast is actually a dilute solution of ethanol in water, and this ethanol must be concentrated to form the basis for the actual alcoholic beverage. However, other volatile components, either derived from the whey or produced during fermentation as secondary metabolites, may contribute to the flavor of the distilled alcoholic beverage, even if they are present in relatively low concentrations.

Table 2.
Volatile compounds in the whey distillate of fermented Istrian albumin cheese whey by the activity of Kluyveromyces marxianus subsp. marxianus.
The following volatile components were found in the fermented whey distillate: acetaldehyde, methanol, n-propanol, i-butanol, n-butanol, 3-methyl-1-ol, 2-methylbutan-1-ol and ethyl-lactate, while diethyl-succinate was not determined. The obtained results are consistent with the results of previous studies, which state that the concentration of these compounds depends on the type and quality of the raw material, as well as on the conditions of the fermentation process itself [34].
Acetaldehyde is commonly found in alcoholic beverages as a by-product of yeast fermentation and as a result of alcohol oxidation at various stages of beverage production. However, Wardencki [35] state that the presence of low molecular weight compounds, such as aldehydes and ketones, is not desirable because some of them are responsible for unpleasant sensory properties of alcoholic beverages. In this study, acetaldehyde was the only such chemical compound identified among the main volatile components of the distillate. The concentration of acetaldehyde was 87.34 to 88.91 mg/L a.a. (absolute alcohol). Methanol was also found in the samples at an average concentration of 126.55 mg/L a.a. In some studies, the concentration of methanol during distillation was found to vary, depending on the technique used to perform the distillation. However, due to its toxic effect, it is extremely important to control the concentration of methanol in the distillate or alcoholic beverage [36]. According to the Croatian Ordinance on spirits [37], the maximum permissible concentration of methanol in fruit spirits is 1000 g/hL, converted to 100% alcohol by volume. In contrast, the permissible amount for alcoholic beverages produced by distillation from fermented whey is not specified. At higher than permissible concentrations, methanol causes disorientation and vomiting and at much higher concentrations, blindness and death. This is due to the oxidation of methanol to toxic formaldehyde and methane (formic acid). The problem of the presence of methanol could be avoided by modifying the distillation conditions, which could be the aim of the continuation of this research.
In addition to the main product, ethanol, alcoholic fermentation produces a number of other compounds, including carbonyl compounds, other alcohols, esters, acids and acetates, which significantly affect the quality of the final product [38]. The composition and concentration of these compounds can vary, thus affecting the organoleptic properties of the distillate [29]. The hydrolysis of lactose to simple sugars can introduce glucose into the fermentation process, leading to the accumulation of higher alcohols in the alcoholic distillate. Higher alcohols are quantitatively the most represented group of aromatic compounds in distillates and contribute to the aroma and essential character of distillates [39]. Among the higher alcohols, the following were found in the samples studied: i-butanol and n-butanol. The amyl alcohol 2-methylbutan-1-ol is formed during fermentation in deamination and decarboxylation reactions from isoleucine and leucine [40], and its concentration in the samples, together with the alcohol 3-methyl-1-ol, averages 380.55 mg/L a.a. The proportion of higher alcohols must be controlled so that their excessive amounts do not adversely affect the sensory properties of the fermented whey distillate. For example, 3-methyl-1-ol and 2-methylbutan-1-ol are compounds that account for about 40 to 70% of all higher alcohols present in fruit spirits. They are grouped under the term i-amyl alcohols. In concentrations of less than 500 g/hL a.a., they impart positive properties to distillates and contribute to a desirable taste, while higher concentrations have a negative effect on the sensory properties of alcoholic beverages (strong and unpleasant smell and taste). For example, at higher concentrations, the taste of distilled spirits is described as sweet and alcoholic, which is an undesirable sensory characteristic of strong alcoholic beverages [29].
Ethyl lactate ester was also found in the fermented whey distillate sample, while diethyl succinate ester was not. Esters have a low boiling point, so they evaporate first during distillation. For this reason, it is necessary to control at what point the distillation is stopped in order to keep the esters at the desired concentrations [36]. According to Mingorance-Cazorla et al. [41], the yeast used in the fermentation process has a major influence on the formation of esters. Ethyl esters are generally compounds associated with pleasant fruity and floral aromas and are also present in other alcoholic beverages, such as tequila, mezcal, moura, wine, beer and others [42]. Ethyl lactate ester can stabilize the flavor of distillates and mitigate sharp and pungent flavor characteristics when present in low concentrations [43]. During alcoholic fermentation, esters are synthesized during the esterification of higher acids and ethanol or higher alcohols. The concentration of esters increases as the duration of fermentation increases. The formation of esters can be attributed to the fatty acid metabolism of Kluyveromyces marxianus [44] and other microbial metabolic processes. According to some authors [42,43], ethyl esters, alcohols with three or more carbon atoms and acetaldehyde are the main compounds responsible for the flavor of alcoholic beverages, and their quantity determines the quality of the distillate itself. Finally, the taste of spirits depends on the concentration and nature of the volatile components present.
4. Conclusions
Recently, efforts have been made to develop technological and biotechnological processes for the utilization of whey, which should provide new value-added products from whey and contribute to the protection of the environment. As whey has started to be used as a raw material for the production of alcoholic beverages in the last decade, this research aimed to show that it is possible to produce alcohol from whey obtained after the production of Istrian albumin cheese. Alcoholic fermentation of Istrian albumin cheese significantly changes its composition, increasing the amount of fat in the whey and its acidity, while decreasing the amount of protein, lactose, non-fat solids and total solids, so it may have less impact on the environment as waste. The resulting distillates contain a number of volatile aromatic compounds, some of which may have a positive effect on the potential sensory properties of an alcoholic beverage at lower concentrations, while others may be harmful at higher concentrations, so this research should further focus on finding optimal conditions to obtain distillates with a composition favorable for human consumption.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.B.L., S.K., J.K. and M.T.K.; methodology, S.K. and M.T.K.; software, I.D.Š.; formal analysis, M.M.Ž. and L.M.B.; investigation, J.K.; resources, D.B.L. and J.K.; writing—original draft preparation, D.B.L.; writing—review and editing, S.K., J.K., I.D.Š., M.M.Ž. and L.M.B.; visualization, M.T.K.; supervision, M.T.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Božanić, R.; Barukčić, I.; Jakopović, K.L.; Tratnik, L. Possibilities of Whey Utilisation. Austin J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2014, 2, 1036. [Google Scholar]
- Blažić, M.; Zavladav, S.; Kralj, E.; Šarić, G. Production of whey protein as nutritional valuable foods. Croat. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 10, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsermoula, P.; Khakimov, B.; Nielsen, H.J.; Engelsen, B.S. Whey—The waste-stream that became more valuable than the food product. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 118, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havranek, J.; Kalit, S.; Antunac, N.; Samaržija, D. Sirarstvo; Hrvatska Mljekarska Udruga: Zagreb, Croatia, 2014; pp. 63–106. [Google Scholar]
- European Dairy Association, Economic Report 2016/17. Available online: http://eda.euromilk.org/fileadmin/user_upload/Public_Documents/Facts_and_Figures/EDA_EWPA_Economic_Report_2016.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2023).
- Çelik, K.; Yuksel, Z. Whey Every Aspect. Sonçağ Matbaacılık. 2016. Istanbul Cadedesi, Istanbul. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Zerrin-Yuksel/publication/320979714_Whey_Every_Aspect/links/5a40b4a2458515f6b0498e10/Whey-Every-Aspect.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2022).
- Tratnik, L.J. Uloga sirutke u Proizvodnji Funkcionalne Mliječne Hrane. Mljekarstvo 2003, 53, 325–352. [Google Scholar]
- Cristiani-Urbina, E.; Netzahuatl-Munoz, A.R.; Manriquez-Rojas, F.J.; Juarez-Ramirez, C.; Ruiz-Ordaz, N.; Galindez-Mayer, J. Batch and fed-batch cultures for the treatment of whey with mixed cultures. Process Biochem. 2000, 35, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappa, I.K.; Papadaki, A.; Kachrimanidou, V.; Terpou, A.; Koulougliotis, D.; Eriotou, E.; Kopsahelis, N. Cheese Whey Processing: Integrated Biorefinery Concepts and Emerging Food Applications. Foods 2019, 8, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matijević, B. Mogućnosti Iskorištavanja i Upotrebe Sirutke. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference “The Holistic Approach to Environment”, Sisak, Croatia, 13–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, K.C. Whey to Ethanol: A Biofuel Role for Dairy Cooperatives? Research Report; Rural Business and Cooperative Programs: Washington, DC, USA, 2008; p. 214. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, R.; Wansbrough, H. The Manufacture of Ethanol from Whey, New Zealand Institute of Chemistry. 2017. Available online: https://www.bioenergy.org.nz/documents/resource/Reports/Manufacture-of-Ethanol-from-Whey-3H.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2022).
- Sansonetti, S.; Curcio, S.; Calabrò, V.; Iorio, G. Bio-ethanol production by fermentation of ricotta cheese whey as an effective alternative non-vegetable source. Biomass Bioenergy 2009, 33, 1687–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvnjak, Z. Sirutka i njeno korištenje u prehrambenoj i fermentacijskoj industriji. Mljekarstvo 1983, 33, 45–60. [Google Scholar]
- Marcišauskas, S.; Bojang, J.; Nielsen, J. Reconstruction and analysis of a Kluyveromyces marxianus genome-scale metabolic model. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanase, S. Ethanol production from cellulosic materials using cellulase-expressing yeast. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 5, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentjuss, A.; Stalidzans, E.; Liepins, J. Model-based biotechnological potential analysis of Kluyveromyces marxianus central metabolism. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 44, 1177–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, S.; Owais, M. Ethanol production from crude whey by Kluyveromyces marxianus. Biochem. Eng. J. 2006, 27, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoppellari, F.; Bardi, L. Production of bioethanol from effluents of the dairy industry by Kluyveromyces marxianus. New Biotechnol. 2013, 30, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunac, N.; Hudik, S.; Mikulec, N.; Horvat, I.; Radeljević, B.; Havranek, J. Proizvodnja i kemijski sastav Istarske i Paške skute. Mljekarstvo 2011, 61, 326–335. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 9622; Milk and Liquid Milk Products—Guidelines for the Application of Mid-Infrared Spectrometry. International Organization for Standards: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- ISO/TS 11869 IDF/RM 150; Fermented Milks—Determination of Titratable Acidity—Potentiometric Method. International Organization for Standards: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- Madrera, R.R.; Valles, B.S. Determination of volatile compounds in cider spirits by gas chromatography with direct injection. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2007, 45, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tratnik, L.J. Mlijeko—Tehnologija, Biokemija i Mikrobiologija; Hrvatska Mljekarska Udruga: Zagreb, Croatia, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Risner, D.; Tomasino, E.; Hughes, P.; Meunier-Goddik, L. Volatile aroma composition of distillates produced from fermented sweet and acid whey. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, D.S.; Bradley, R.J. Chemical properties of alcohols and their protein binding sites. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2020, 57, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloch, C.; Querol, A.; Barrio, E. Yeasts and molds. Kluyveromyces spp. In Encyclopedia of Dairy Sciences, 2nd ed.; Roginski, H., Fuquay, J.W., Fox, P.F., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2011; Volume 4, pp. 754–764. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, A.D.; Kádár, Z.; Oleskowicz-Popiel, P.; Thomsen, M.H. Production of bioethanol from organic whey using Kluyveromyces marxianus. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 38, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragone, G.; Mussatto, S.I.; Oliveira, J.M.; Teixeira, J.A. Characterisation of volatile compounds in an alcoholic beverage produced by whey fermentation. Food Chem. 2009, 112, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coote, N.; Kirsop, B.H. Factors responsible for the decrease in pH during beer fermentations. J. Inst. Brew. 1976, 82, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkowska, A.; Kregiel, D.; Guneser, O.; Karagul Yuceer, Y. Growth and by-product profiles of Kluyveromyces marxianus cells immobilized in foamed alginate. Yeast 2015, 32, 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Morand, M.; Dekkari, A.; Guyomarc’h, F.; Famelart, M. Increasing the hydrophobicity of the heat-induced whey protein complexes improves the acid gelation of skim milk. Int. Dairy J. 2012, 25, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardani, A.K.; Egawa, S.; Nagahisa, K.; Shimizu, H.; Shioya, S. Robustness of cascade pH and dissolved oxygen control in symbiotic nisin production process system of Lactococcus lactis and Kluyveromyces marxianus. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2006, 101, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plutowska, B.; Wardencki, W. Application of gas chromatography-olfactometry (GC-O) in analysis and quality assessment of alcoholic beverages—A review. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardencki, W.; Sowinski, P.; Curylo, J. Evaluation of headspace solid-phase microextraction for the analysis of volatile carbonyl compounds in spirits and alcoholic beverages. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 984, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikićević, N.; Tešević, V. Proizvodnja Voćnih Rakija Vrhunskog Kvaliteta; NIKPRESS: Belgrade, Serbia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ordinance on Strong Alcoholic Beverages; Official Gazette; Ministry of Agriculture: Zagreb, Croatia, 2009; Volume 61, pp. 1–21.
- Christoph, N.; Bauer-Christoph, C. Flavour of spirit drinks: Raw materials, fermentation, distillation, and ageing. In Flavours and Fragrances; Berger, R.G., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 219–239. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, V.; Hernandez-Orte, P.; Escudero, A.; Lopez, R.; Cacho, J. Semipreparative reversed-phase liquid chromatographic fractionation of aroma extracts from wine and other alcoholic beverages. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 864, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulton, R.B.; Singleton, V.L.; Bisson, L.F.; Kunkee, R.E. Principles and Practices of Winemaking; Chapman & Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Mingorance-Cazorla, L.; Clemente-Jiménez, J.; Martínez-Rodríguez, S.; Las Heras Vázquez, F.; Rodriguez-Vico, F. Contribution of different natural yeasts to the aroma of two alcoholic beverages. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 19, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-Rodríguez, A.; González-Hernández, L.; Barba de la Rosa, A.P.; Escalante-Minakata, P.; López, M.G. Characterization of volatile compounds of Mezcal, an ethnic alcoholic beverage obtained from Agave salmiana. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 1337–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolopoulou, A.A.; Flouros, A.I.; Demertzis, P.G.; Akrida-Demertzi, K. Differences in concentration of principal volatile constituents in traditional Greek distillates. Food Control 2005, 16, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, H.S.; Proctor, A. Kinetics and mechanism of free fatty acid formation on the surface of milled rice. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 7161–7163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).