Antibacterial Activity of Bacillus Strains against Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease-Causing Vibrio campbellii in Pacific White Leg Shrimp
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacillus and Vibrio Candidate Isolation and Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
| Target | Primers | Sequence (5′–3′) | Amplicon Size (bp) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacillus | BacF | GCTGGTTAGAGCGCACGCCTGATA | 263 | [31] |
| BacR | CATCCACCGTGCGCCCTTTCTAAC | |||
| AHPND toxin | VpPirA-284F | TGACTATTCTCACGATTGGACTG | 284 | [35] |
| VpPirA-284R | CACGACTAGCGCCATTGTTA | |||
| VpPirA-392F | TGATGAAGTGATGGGTGCTC | 392 | ||
| VpPirA-392R | TGTAAGCGCCGTTTAACTCA | |||
| V. parahaemolyticus | Tox R-F | GTCTTCTGACGCAATCGTTG | 368 | [33] |
| Tox R-R | ATACGAGTGGTTGCTGTCATG | |||
| V. campbellii | Vc.fts.z-F | AAGACAGAGATAGACTTAAAGAT | 294 | [34] |
| Vc.fts.z-R | CTTCTAGCAGCGTTACAC | |||
| V. harveyi | Vh.topA-F | TGGCGCAGCGTCTATACG | 121 | |
| Vh.topA-R | TATTTGTCACCGAACTCAGAACC |
2.2. Antimicrobial Activity Test (In Vitro)
2.3. Antimicrobial Activity Test (Challenge Test)
2.4. Genome Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis of the Selected Bacillus Strains
2.5. Accession Numbers of Nucleotide Sequences and Strain Deposition
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Bacillus and Vibrio Strains
3.2. Antimicrobial Activity Test (In Vitro)
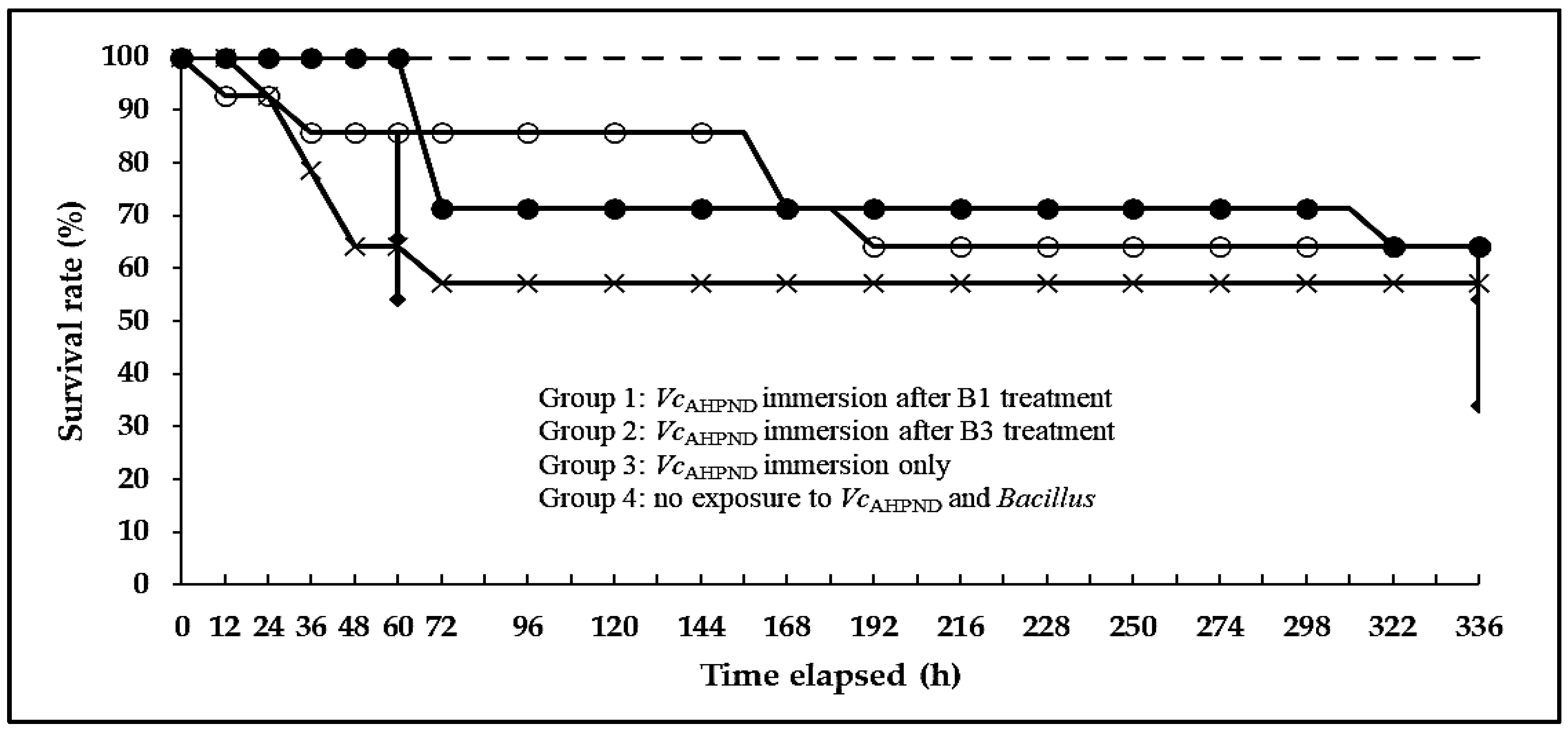
3.3. Antimicrobial Activity Test (Challenge Test)
3.4. Genome Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis of the Selected Bacillus Strains
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tran, L.; Nunan, L.; Redman, R.M.; Mohney, L.L.; Pantoja, C.R.; Fitzsimmons, K.; Lightner, D.V. Determination of the infectious nature of the agent of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis syndrome affecting penaeid shrimp. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2013, 105, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, H.; Van, P.T.; Dang, L.T.; Hirono, I. Draft genome sequence of non-Vibrio parahaemolyticus acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease strain KC13. 17.5, isolated from diseased shrimp in Vietnam. Genome Announc. 2015, 3, e00978-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Wang, H.; Zou, P.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, J. Complete genome sequence of Vibrio campbellii strain 20130629003S01 isolated from shrimp with acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease. Gut Pathog. 2017, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Li, S.; Yu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Yu, K.; Li, F. Pathogenicity of a Vibrio owensii strain isolated from Fenneropenaeus chinensis carrying pirAB genes and causing AHPND. Aquaculture 2021, 530, 735747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kua, B.C.; Iar, A.; Siti Zahrah, A.; Irene, J.; Norazila, J.; Nik Haiha, N.Y.; Fadzilah, Y.; Mohammed, M.; Siti Rokhaiya, B.; Omar, M.; et al. Current status of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) of farmed shrimp in Malaysia. In Proceedings of the Addressing Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease (AHPND) and Other Transboundary Diseases for Improved Aquatic Animal Health in Southeast Asia, Makati City, Philippines, 22–24 February 2016; pp. 55–59. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, J.; Srisala, J.; Truong, V.H.; Chen, I.T.; Nuangsaeng, B.; Suthienkul, O.; Lo, C.F.; Flegel, T.W.; Sritunyalucksana, K.; Thitamadee, S. Variation in Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolates from a single Thai shrimp farm experiencing an outbreak of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND). Aquaculture 2014, 428, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunan, L.; Lightner, D.; Pantoja, C.; Gomez-Jimenez, S. Detection of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) in Mexico. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2014, 111, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leobert, D.; Cabillon, N.A.R.; Catedral, D.D.; Amar, E.C.; Usero, R.C.; Monotilla, W.D.; Calpe, A.T.; Fernandez, D.D.G.; Saloma, C.P. Acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) outbreaks in Penaeus vannamei and P. monodon cultured in the Philippines. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2015, 116, 251–254. [Google Scholar]
- Dhar, A.K.; Piamsomboon, P.; Caro, L.F.A.; Kanrar, S.; Adami, R., Jr.; Juan, Y.S. First report of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) occurring in the USA. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2019, 132, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.E.; Choi, S.K.; Han, S.H.; Lee, S.C.; Jeon, H.J.; Lee, C.; Kim, K.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Park, S.C.; Rhee, G.; et al. Genomic and histopathological characteristics of Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from an acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease outbreak in Pacific white shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) cultured in Korea. Aquaculture 2020, 524, 735284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.T.; Chen, I.T.; Yang, Y.T.; Ko, T.P.; Huang, Y.T.; Huang, J.Y.; Huang, M.F.; Lin, S.J.; Chen, C.Y.; Lin, S.S.; et al. The opportunistic marine pathogen Vibrio parahaemolyticus becomes virulent by acquiring a plasmid that expresses a deadly toxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 10798–10803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.; Koshio, S.; Esteban, M.Á. Beneficial roles of feed additives as immunostimulants in aquaculture: A review. Rev. Aquac. 2018, 10, 950–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekiel, A.; Wiecek, J.; Bielecki, W.; Gajewska, J.; Cichowicz, M.; Kulisiewicz, J.; Batorska, M.; Roszkowski, T.; Beyga, K. Effect of addition of feed antibiotic flavomycin or prebiotic BIO-MOS on production results of fatteners, blood biochemical parameters, morphometric indices of intestine and composition of microflora. Archi. Tierz. Dummerstorf 2007, 50, 172–180. [Google Scholar]
- Defoirdt, T.; Sorgeloos, P.; Bossier, P. Alternatives to antibiotics for the control of bacterial disease in aquaculture. COMICR 2011, 14, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capita, R.; Alonso-Calleja, C. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria: A challenge for the food industry. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 11–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, N.V. The use of probiotics in aquaculture. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 917–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lulijwa, R.; Rupia, E.J.; Alfaro, A.C. Antibiotic use in aquaculture, policies and regulation, health and environmental risks: A review of the top 15 major producers. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 640–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F. A review on the application of herbal medicines in the disease control of aquatic animals. Aquaculture 2020, 526, 735422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogeley, J.L.; Interaminense, J.A.; Buarque, D.S.; da Silva, S.M.B.C.; Coimbra, M.R.M.; Peixoto, S.M.; Soares, R.B. Growth and immune gene expression of Litopenaeus vannamei fed Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus circulans supplemented diets and challenged with Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Aquac. Int 2019, 27, 1451–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoah, K.; Dong, X.H.; Tan, B.P.; Zhang, S.; Chi, S.Y.; Yang, Q.H.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.T. Administration of probiotic Bacillus licheniformis induces growth, immune and antioxidant enzyme activities, gut microbiota assembly and resistance to Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquac. Nutr. 2020, 26, 1604–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.; Singh, R. Probiotics in aquaculture: A promising emerging alternative approach. Symbiosis 2019, 77, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khademzade, O.; Zakeri, M.; Haghi, M.; Mousavi, S.M. The effects of water additive Bacillus cereus and Pediococcus acidilactici on water quality, growth performances, economic benefits, immunohematology, and bacterial flora of whiteleg shrimp (Penaeus vannamei Boone, 1931) reared in earthen ponds. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 1759–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithya, V.; Halami, P.M. Evaluation of the probiotic characteristics of Bacillus species isolated from different food sources. Ann. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flegel, T.W.; Lightner, D.V.; Lo, C.F.; Owens, L. Shrimp Disease Control: Past, Present, and Future; Bondad-Reantaso, M.G., Mohan, C.V., Crumlish, M., Subasinghe, R.P., Eds.; Diseases in Asian Aquaculture VI. Fish Health Section; Asian Fisheries Society: Manila, Philippines, 2008; Volume 505, pp. 355–378. [Google Scholar]
- Kewcharoen, W.; Srisapoome, P. Probiotic effects of Bacillus spp. from Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) on water quality and shrimp growth, immune responses, and resistance to Vibrio parahaemolyticus (AHPND strains). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 94, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galaviz-Silva, L.; Cázares-Jaramillo, G.E.; Ibarra-Gámez, J.C.; Molina-Garza, V.M.; Sánchez-Díaz, R.; Molina-Garza, Z.J. Assessment of probiotic bacteria from marine coasts against Vibrio parahaemolyticus (AHPND strains) in Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 6396–6409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paopradit, P.; Aksonkird, T.; Mittraparp-arthorn, P. Indole inhibits quorum sensing-dependent phenotypes and virulence of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease-causing Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 3586–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, J.W.; Han, J.E.; Tang, K.F.; Lightner, D.V.; Kim, J.; Seo, S.W.; Park, S.C. Potential application of bacteriophage pVp-1: Agent combating Vibrio parahaemolyticus strains associated with acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) in shrimp. Aquaculture 2016, 457, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, J.W.; Han, J.E.; Giri, S.S.; Tang, K.F.; Zhou, X.; Aranguren, L.F.; Kim, H.J.; Yun, S.; Chi, C.; Kim, S.G.; et al. Phage application for the protection from acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) in Penaeus vannamei. Indian J. Microbiol. 2018, 58, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.D.; Pande, G.S.J.; Kashem, M.A.; Baruah, K.; Bossier, P. Acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) toxin degradation by Bacillus subtilis DSM33018. Aquaculture 2021, 540, 736634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solichová, K.; Němečková, I.; Šviráková, E.; Horáčková, Š. Novel identification methods including a species-specific PCR for hazardous Bacillus species. Acta Aliment. 2019, 48, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashti, A.A.; Jadaon, M.M.; Abdulsamad, A.M.; Dashti, H.M. Heat treatment of bacteria: A simple method of DNA extraction for molecular techniques. Kuwait Med. J. 2009, 41, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.B.; Okuda, J.U.N.; Matsumoto, C.; Takahashi, N.; Hashimoto, S.; Nishibuchi, M. Identification of Vibrio parahaemolyticus strains at the species level by PCR targeted to the toxR gene. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 1173–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano-Gomez, A.; Høj, L.; Owens, L.; Baillie, B.K.; Andreakis, N. A multiplex PCR-based protocol for identification and quantification of Vibrio harveyi-related species. Aquaculture 2015, 437, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.E.; Tang, K.F.; Tran, L.H.; Lightner, D.V. Photorhabdus insect-related (Pir) toxin-like genes in a plasmid of Vibrio parahaemolyticus, the causative agent of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) of shrimp. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2015, 113, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spelhaug, S.R.; Harlander, S.K. Inhibition of foodborne bacterial pathogens by bacteriocins from Lactococcus lactis and Pediococcus pentosaceous. J. Food Prot. 1989, 52, 856–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.E.; Tang, K.F.; Pantoja, C.R.; White, B.L.; Lightner, D.V. qPCR assay for detecting and quantifying a virulence plasmid in acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) due to pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Aquaculture 2015, 442, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.D.J.; Ferreira, L.C.; Campos, V.P.; Cruz-Magalhães, V.; Barros, A.F.; Andrade, J.P.; Roberts, D.P.; de Souza, J.T. Complete genome sequence of the biocontrol agent Bacillus velezensis UFLA258 and its comparison with related species: Diversity within the commons. GBE 2019, 11, 2818–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, K.; Shaw, S.; Kloosterman, A.M.; Charlop-Powers, Z.; Van Wezel, G.P.; Medema, M.H.; Weber, T. antiSMASH 6.0: Improving cluster detection and comparison capabilities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W29–W35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.; Biosciences, I.; Carlsbad, C. BioEdit: An important software for molecular biology. GERF Bull. Biosci. 2011, 2, 60–61. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Bio. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefort, V.; Desper, R.; Gascuel, O.F. 2.0: A comprehensive, accurate, and fast 684 distance-based phylogeny inference program. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 685, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, B.; Blom, J.; Klenk, H.P.; Borriss, R. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, Bacillus velezensis, and Bacillus siamensis form an “operational group B. amyloliquefaciens” within the B. subtilis species complex. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.; Rakhisi, Z.; Ahmady, A.Z. Isolation and identification of Bacillus species from soil and evaluation of their antibacterial properties. AJCMI 2015, 2, 23233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.L.; Yang, S.J.; Son, S.H.; Kim, W.S.; Lee, N.K.; Paik, H.D. Evaluation of probiotic Bacillus subtilis P229 isolated from cheonggukjang and its application in soybean fermentation. LWT 2018, 97, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.A.; Farag, A.G.; Youssef, S.A. Phosphate solubilization by Bacillus subtilis and Serratia marcescens isolated from tomato plant rhizosphere. J. Environ. Prot. Sci. 2018, 9, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.E.; Tang, K.F.J.; Aranguren, L.F.; Piamsomboon, P. Characterization and pathogenicity of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease natural mutants, pirABvp (−) V. parahaemolyticus, and pirABvp (+) V. campbellii strains. Aquaculture 2017, 470, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauyod, K.; Rattanavarin, S.; Sarapukdee, P.; Porntheeraphat, S.; Sritunyalucksana, K.; Khemthongcharoen, N. Bacillus velezensis suppression on the growth of Vibrio parahaemolyticus causing acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease in marine shrimp. J. Appl. Aquac. 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, Z.B.; Zhang, Z.; Zha, J.W.; Qu, S.Y.; Qi, X.Z.; Wang, G.X.; Ling, F. Effects of potential probiotic Bacillus velezensis K2 on growth, immunity and resistance to Vibrio harveyi infection of hybrid grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus♂× E. fuscoguttatus♀). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2019, 93, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, X.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, H.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, X. Characterization of a Bacillus velezensis with antibacterial activity and inhibitory effect on common aquatic pathogens. Aquaculture 2020, 523, 735165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monzón-Atienza, L.; Bravo, J.; Torrecillas, S.; Montero, D.; Canales, A.F.G.D.; de la Banda, I.; Galindo-Villegas, J.; Ramos-Vivas, J.; Acosta, F. Isolation and Characterization of a Bacillus velezensis D-18 Strain, as a Potential Probiotic in European Seabass Aquaculture. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 13, 1404–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumi, C.D.; Yang, B.W.; Yeo, I.C.; Hahm, Y.T. Antimicrobial peptides of the genus Bacillus: A new era for antibiotics. Can. J. Microbiol. 2015, 61, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.M.; Rong, Y.J.; Zhao, M.X.; Song, B.; Chi, Z.M. Antibacterial activity of the lipopetides produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens M1 against multidrug-resistant Vibrio spp. isolated from diseased marine animals. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.; Kiesewalter, H.T.; Kovács, R.; Frisvad, J.C.; Weber, T.; Larsen, T.O.; Kovacs, A.T.; Ding, L. Depiction of secondary metabolites and antifungal activity of Bacillus velezensis DTU001. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2019, 4, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Strain | Origin | Source | Isolation Year | PCR Identification | Accession No a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacillus strains | |||||
| B1 | South Korea | Seawater | 2019 | Bacillus spp. | OP364972 |
| B3 | South Korea | Seawater | 2019 | Bacillus spp. | OP364977 |
| B5 | South Korea | Seawater | 2019 | Bacillus spp. | - |
| B7 | South Korea | Seawater | 2019 | Bacillus spp. | - |
| B8 | South Korea | Seawater | 2019 | Bacillus spp. | - |
| Vibrio strains | |||||
| 16-904/1 | Mexico | Shrimp | 2016 | AHPND Vibrio campbellii | - |
| 13-028/A3 | Vietnam | Shrimp | 2015 | AHPND V. parahaemolyticus | KM067908 |
| 15-250/20 | Latin America | Shrimp | 2015 | AHPND V. parahaemolyticus | - |
| CH49 | Thailand | Seawater | 2019 | AHPND V. parahaemolyticus | - |
| CH50 | Thailand | Seawater | 2019 | AHPND V. parahaemolyticus | - |
| CH51 | Thailand | Seawater | 2019 | AHPND V. parahaemolyticus | - |
| CH52 | Thailand | Seawater | 2019 | AHPND V. parahaemolyticus | - |
| CH53 | Thailand | Seawater | 2019 | AHPND V. parahaemolyticus | - |
| 19-021D1 | South Korea | Seawater | 2019 | AHPND V. parahaemolyticus | MN631018, MN631020 |
| 19-022A1 | South Korea | Seawater | 2019 | AHPND V. parahaemolyticus | MN631019, MN631021 |
| NSU116 | Latin America | Shrimp | 2016 | Non-AHPND V. parahaemolyticus | - |
| LB4 | USA | Seawater | 2017 | Non-AHPND V. harveyi | - |
| Vibrio Strains | Bacillus Strains | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type Strain a (B. velezensis) | B1 | B3 | B5 | B7 | B8 | |
| 16-904/1 | + | ++ | ++ | − | + | + |
| 13-028/A3 | ++ | − | + | − | − | − |
| 15-250/20 | + | − | + | + | − | + |
| CH49 | + | + | + | − | − | − |
| CH50 | + | − | + | − | − | + |
| CH51 | − | − | + | ++ | − | − |
| CH52 | + | − | + | − | − | − |
| CH53 | − | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | + |
| 19-021D1 | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | + |
| 19-022A1 | + | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | + |
| NSU116 | + | ++ | ++ | + | + | + |
| LB4 | − | + | + | + | − | − |
| Survival (%) | Treatments | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | Group 4 | |
| 60 h | 100 ± 0.0 a | 85.7 ± 20.2 ab | 64.3 ± 10.1 b | 100 ± 0.0 a |
| 336 h | 64.3 ± 10.1 | 64.3 ± 30.3 | 57.1 ± 0.0 | 100 ± 0.0 |
| Features | Strains | |
|---|---|---|
| B1 | B3 | |
| Size (bp) | 3,929,791 | 3,929,788 |
| G+C content (%) | 46.50 | 46.50 |
| Contigs | 1 | 1 |
| Chromosomes | 1 | 1 |
| Plasmids | 0 | 0 |
| tRNAs | 86 | 86 |
| rRNAs | 27 | 27 |
| Protein-coding genes | 3750 | 3750 |
| GenBank accession number | CP100040 | CP100041 |
| Region | Position | Biosynthetic Gene Clusters | Substance | Similarity (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| From | To | ||||
| 1 | 127,555 | 178,059 | NRP 1 | Bacillibactin | 100 |
| RiPP:head-to-tail cyclized peptide 2 | Amylocyclicin | 100 | |||
| NRP | Paenibactin | 100 | |||
| NRP:NRP siderophore | Bacillibactin | 100 | |||
| 2 | 804,233 | 896,592 | Polyketide + NRP | Difficidin | 100 |
| 5 | 1,180,156 | 1,314,466 | NRP | Fengycin | 100 |
| NRP | Plipastatin | 100 | |||
| Polyketide + NRP:lipopeptide | Bacillomycin D | 100 | |||
| Polyketide + NRP | Mycosubtilin | 100 | |||
| Polyketide + NRP | Iturin | 88 | |||
| NRP | Paenilarvins | 100 | |||
| 6 | 1,388,208 | 1,488,773 | Polyketide + NRP | Bacillaene | 100 |
| 7 | 1,707,961 | 1,796,194 | Polyketide | Macrolactin H | 100 |
| Polyketide | Macrolactin H/ macrolactin B/macrolactin 1c/macrolactin E | 100 | |||
| 11 | 2,792,616 | 2,858,023 | NRP:lipopeptide | Surfactin | 82 |
| 12 | 3,479,618 | 3,521,036 | Other | Bacilysin | 100 |
| Other | Bacilysin | 100 | |||
| Region | Position | Biosynthetic Gene Clusters | Substance | Similarity (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| from | to | ||||
| 2 | 117,650 | 251,960 | NRP 1 | Fengycin | 100 |
| NRP | Plipastatin | 100 | |||
| Polyketide + NRP:lipopeptide | Bacillomycin D | 100 | |||
| Polyketide + NRP | Mycosubtilin | 100 | |||
| Polyketide + NRP | Iturin | 88 | |||
| NRP | Paenilarvins | 100 | |||
| 3 | 325,702 | 426,267 | Polyketide + NRP | Bacillaene | 100 |
| 4 | 645,796 | 733,631 | Polyketide | Macrolactin H | 100 |
| Polyketide | Macrolactin H/ | 100 | |||
| macrolactin B/ | |||||
| macrolactin 1c/ | |||||
| macrolactin E | |||||
| 8 | 1,730,328 | 1,794,305 | NRP:Lipopeptide | Surfactin | 82 |
| 9 | 2,417,108 | 2,458,526 | Other | Bacilysin | 100 |
| Other | Bacilysin | 100 | |||
| 10 | 2,994,836 | 3,046,627 | NRP | Bacillibactin | 100 |
| RiPP:head-to-tail cyclized peptide 2 | Amylocyclicin | 100 | |||
| NRP | Paenibactin | 100 | |||
| NRP:NRP siderophore | Bacillibactin | 100 | |||
| 11 | 3,671,331 | 3,765,123 | Polyketide + NRP | Difficidin | 100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeon, H.J.; Song, J.W.; Lee, C.; Kim, B.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Han, J.E.; Park, J.H. Antibacterial Activity of Bacillus Strains against Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease-Causing Vibrio campbellii in Pacific White Leg Shrimp. Fishes 2022, 7, 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050287
Jeon HJ, Song JW, Lee C, Kim B, Park SY, Kim JH, Han JE, Park JH. Antibacterial Activity of Bacillus Strains against Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease-Causing Vibrio campbellii in Pacific White Leg Shrimp. Fishes. 2022; 7(5):287. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050287
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeon, Hye Jin, Jae Won Song, Chorong Lee, Bumkeun Kim, Seon Young Park, Ji Hyung Kim, Jee Eun Han, and Jae Hak Park. 2022. "Antibacterial Activity of Bacillus Strains against Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease-Causing Vibrio campbellii in Pacific White Leg Shrimp" Fishes 7, no. 5: 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050287
APA StyleJeon, H. J., Song, J. W., Lee, C., Kim, B., Park, S. Y., Kim, J. H., Han, J. E., & Park, J. H. (2022). Antibacterial Activity of Bacillus Strains against Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease-Causing Vibrio campbellii in Pacific White Leg Shrimp. Fishes, 7(5), 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes7050287







