Indoor PM2.5 and Heavy Metal Composition in Blacksmithing Factories: A Pilot Study in Bandung Regency, Indonesia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
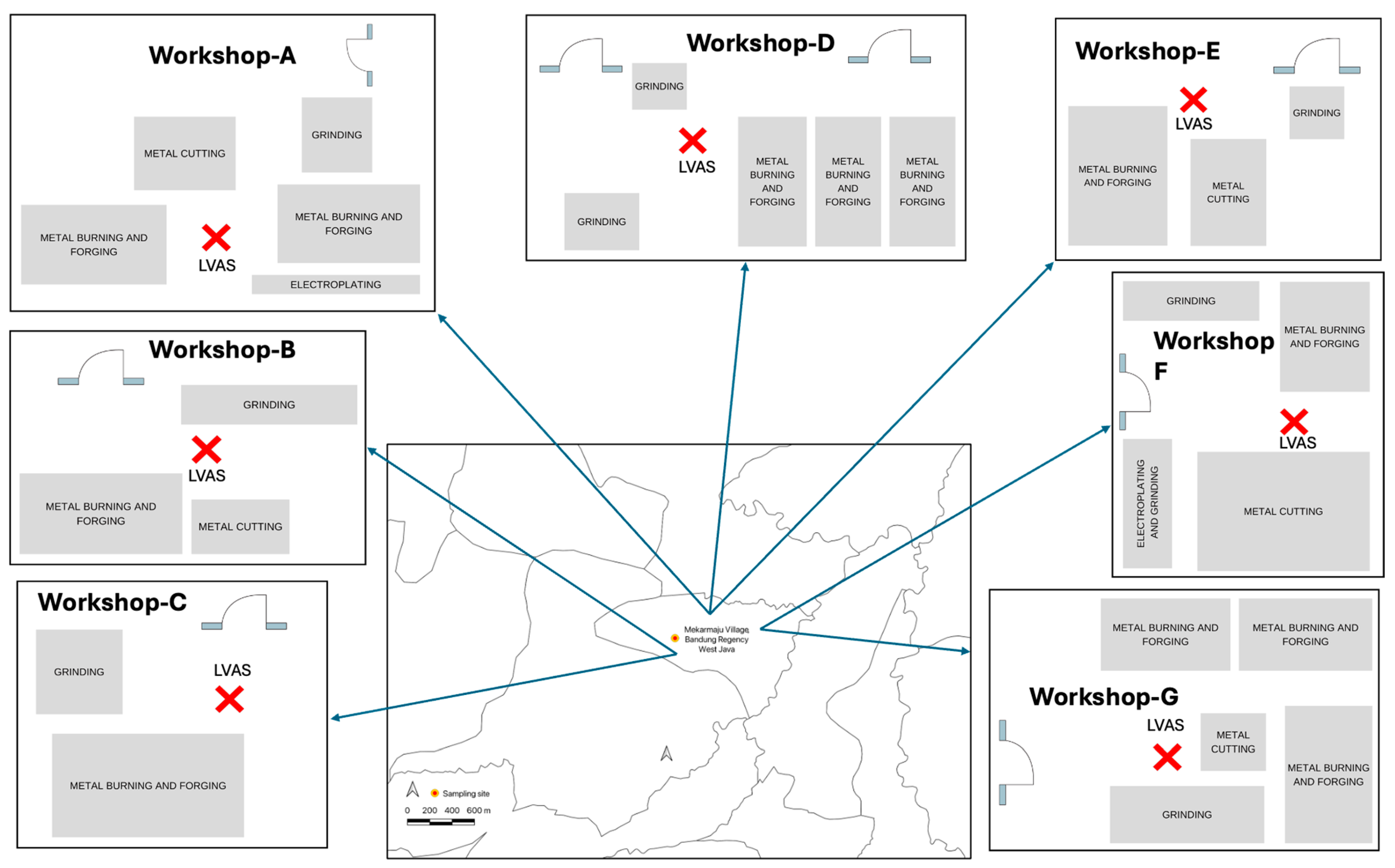
2.1. Study Area and Site Selection
2.2. Indoor PM2.5 Sampling
2.3. Chemical Analysis of Heavy Metals
3. Results and Discussion
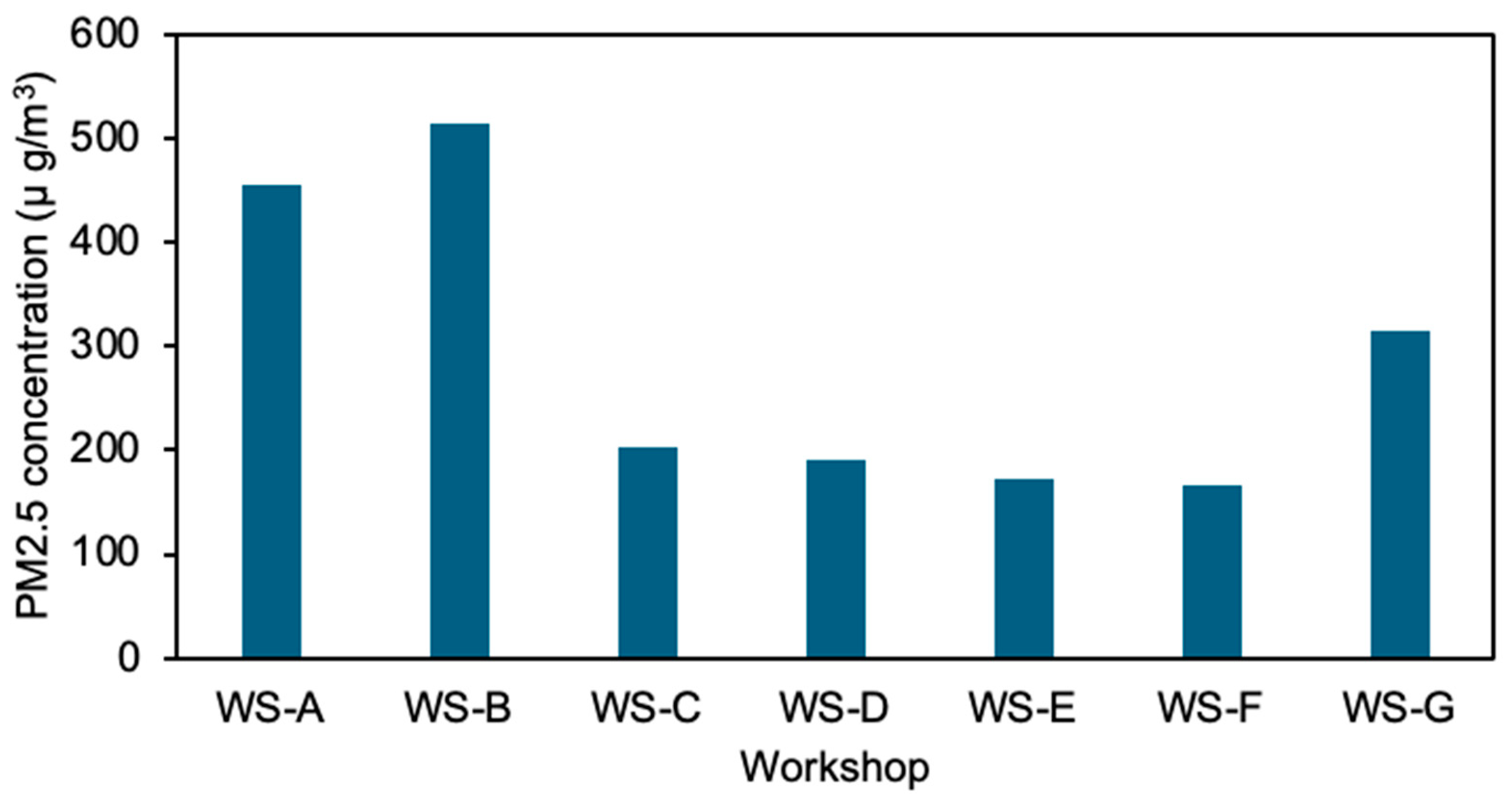
3.1. Variation in Indoor PM2.5
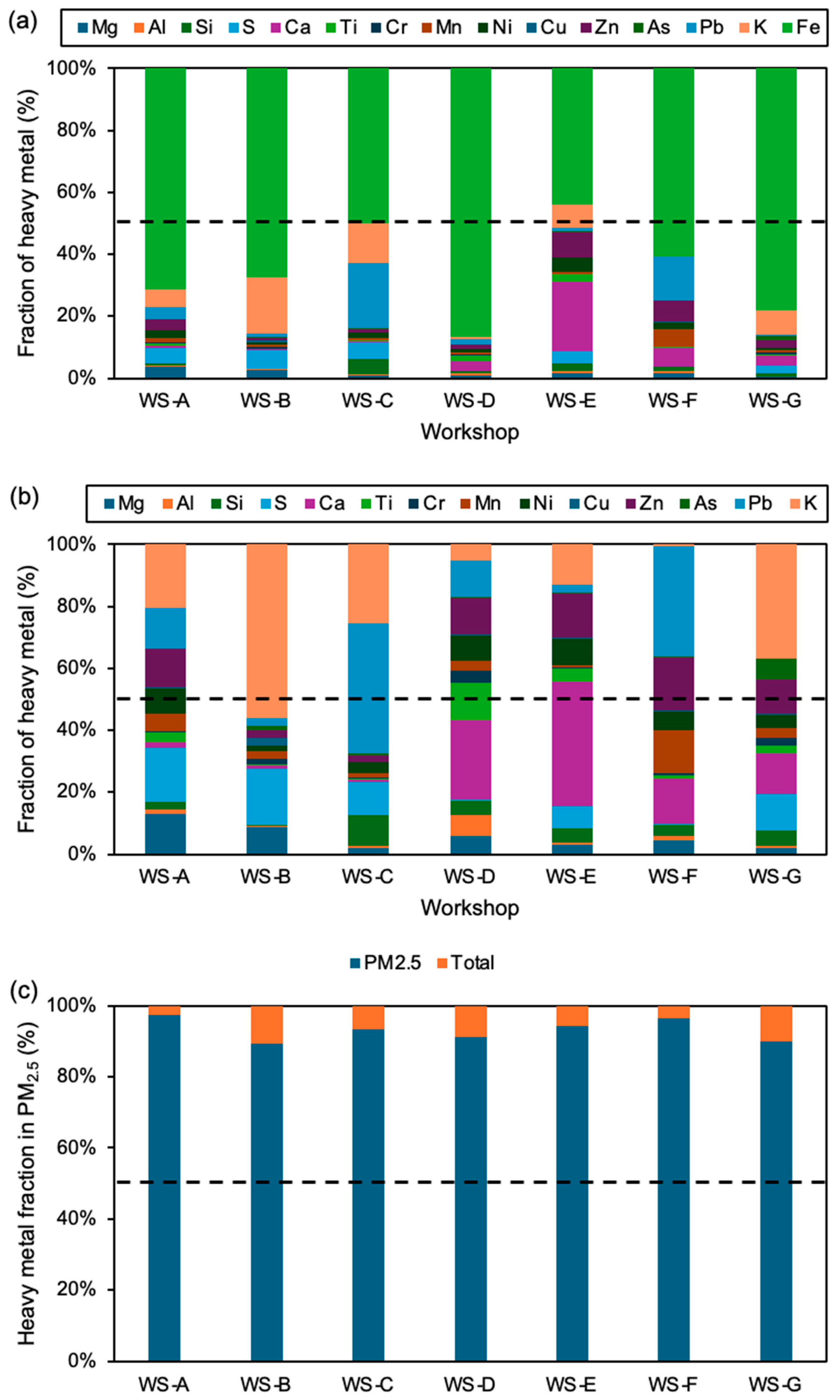
3.2. Composition of Heavy Metal in PM2.5
3.3. Correlation of PM2.5, Its Chemical Composition, and the Health Implication
3.4. Limitations and Future Research
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Landrigan, P.J. Air pollution and health. Lancet Public Health 2017, 2, e4–e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.D. Air pollution: A global problem needs local fixes. Nature 2019, 570, 437–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.U.; Liu, G.; Yousaf, B.; Ullah, H.; Abbas, Q.; Munir, M.A.M. A Systematic Review on Global Pollution Status of Particulate Matter-Associated Potential Toxic Elements and Health Perspectives in Urban Environment. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 1131–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Lim, C.C.; Gurmu, B.L.; Kim, M.; Lee, S.; Park, J.; Kim, S. Comparison of Personal or Indoor PM2.5 Exposure Level to That of Outdoor: Over Four Seasons in Selected Urban, Industrial, and Rural Areas of South Korea: (K-IOP Study). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milner, J.; Armstrong, B.G.; Davies, M.; Ridley, I.A.; Chalabi, Z.; Shrubsole, C.; Vardoulakis, S.; Wilkinson, P. An Exposure-Mortality Relationship for Residential Indoor PM2.5 Exposure from Outdoor Sources. Climate 2017, 5, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepadi, M.M.; Nkosi, V. Personal PM2.5 Exposure Monitoring of Informal Cooking Vendors at Indoor and Outdoor Markets in Johannesburg, South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajizadeh, Y.; Jafari, N.; Mohammadi, A.; Momtaz, S.M.; Fanaei, F.; Abdolahnejad, A. Concentrations and mortality due to short-and long-term exposure to PM2.5 in a megacity of Iran (2014–2019). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 38004–38014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masri, S.; Rea, J.; Wu, J. Use of Low-Cost Sensors to Characterize Occupational Exposure to PM2.5 Concentrations Inside an Industrial Facility in Santa Ana, CA: Results from a Worker- and Community-Led Pilot Study. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kero, I.T.; Blom, A.; Jørgensen, R.B. Particle Size Distributions of Airborne Particulate Matter in a Ferrosilicon Smelter. In Proceedings of the 16th International Ferro-Alloys Congress (INFACON XVI); SINTEF/NTNU/FFF: Trondheim, Norway, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmadini, A.F.; Andarini, D.; Camelia, A.; Ermi, N.; Lestari, M. Occupational Health and Safety Risk Assessment on Informal Workers in Ogan Ilir, South Sumatra. Indones. J. Occup. Saf. Health 2021, 10, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafez, K. Occupational Ergonomic and Safety Assessments Survey at Various Blacksmith Shops in Jeddah City. Ergon. Int. J. 2024, 8, 328. [Google Scholar]
- Narwal, K.; Sharma, P.; Joshi, P. Risk Assessment of Forging Workers in Unorganized Sector of Uttrakhand, India. In Advances in Social and Organizational Factors AHFE International Conference; Vinkeds, P., Ed.; AHFE International: San Diego, CA, USA, 2020; Volume 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zendrato, R.R.P.; Sunardi, S. Penerapan prinsif kesehatan dan keselamatan kerja di ukm pande besi tradisional. Adi Widya J. Pengabdi. Masy. 2020, 4. (In Bahasa) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buljat, A.; Čargonja, M.; Mekterović, D. Source Apportionment of Particulate Matter in a Metal Workshop. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2024, 21, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Insley, A.L.; Maskrey, J.R.; Hallett, L.; Reid, R.C.; Hynds, E.S.; Winter, C.; Panko, J.M. Occupational survey of airborne metal exposures to welders, metalworkers, and bystanders in small fabrication shops. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2019, 16, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maung, T.Z.; Bishop, J.E.; Holt, E.; Turner, A.M.; Pfrang, C. Indoor Air Pollution and the Health of Vulnerable Groups: A Systematic Review Focused on Particulate Matter (PM), Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) and Their Effects on Children and People with Pre-Existing Lung Disease. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Donaire-Gonzalez, D.; Helbich, M.; van Nunen, E.; Hoek, G.; Vermeulen, R.C. Validity of Mobility-Based Exposure Assessment of Air Pollution: A Comparative Analysis with Home-Based Exposure Assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 10685–10695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verniers, K.; Losfeld, F.; Pollet, I.V.; Laverge, J. Impact of ventilation type on indoor generated PM and VOC levels for different indoor activities. Int. J. Vent. 2023, 22, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shezi, B.; Jafta, N.; Naidoo, R.N. Potential Health Risks of Indoor Particulate Matter Heavy Metals in Resource-Constrained Settings of South Africa. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husaini, H. Correlation of Metal Fume and Vapor with Total Ige Serum of The Blacksmith. Al-Ulum 2014, 62, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Jayasinghe, K. Monitoring of Total Suspended Particles & Toxic Gasses in Stationary Combustion Systems. Eng. J. Inst. Eng. 2011, 44, 37. [Google Scholar]
- Sturm, R. Modelling the deposition of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in the human respiratory tract. AME Med. J. 2020, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayu, R.; Anggraeni, Y.; Lestari, K.S. The impact of PM2.5 air pollutant exposure on human respiratory health: A literature review. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2023, 19, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilera, R.; Gershunov, A.; Ilango, S.D.; Guzman-Morales, J.; Benmarhnia, T. Santa Ana Winds of Southern California Impact PM2.5 With and Without Smoke From Wildfires. Geo. Health 2020, 4, e2019GH000225. [Google Scholar]
- Pino-Vallejo, M.; Tierra, A.; Haro, A.; Perugachi, N. Prediction of concentrations of PM2.5 in downtown Quito using the chaos theory. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 2003, 020013. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, W.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, L.; Ye, L. Adverse effects of PM2.5 on cardiovascular diseases. Rev. Environ. Health 2021, 37, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmanuel, C.I.; Faith, O.O.; Benedicta, A.O.; Aminat, A.A. Source Identification and Heavy Metal Analysis of Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) in an Industrialized Urban Area of Lagos State, Nigeria. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 321, 120344. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Lin, X.; Yao, J.; Tian, T.; Li, Z.; Chen, S.; Hu, W.; Jiang, J.; Tang, H.; Cai, H.; et al. Potential causal links of long-term exposure to PM2.5 and its chemical components with the risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma recurrence: A 10-year cohort study in South China. Int. J. Cancer 2024, 155, 1558–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez, C.; Amador, D.O.R.; Gutiérrez, J.M.L.; Mosqueda, E.R.; Barcia, G.E.C.; Patlán, F.D.R.; Salazar, R.C. Chemical Characterization and Assessment of Public Health Risk due to Inhalation of PM2.5 in the City of Salamanca, Guanajuato. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2024, 113, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Kaur, M.; Li, T.; Pan, F. Effect of Different Pollution Parameters and Chemical Components of PM2.5 on Health of Residents of Xinxiang City, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmalkar, J.; Lee, K.; Ahn, J.; Lee, J.; Song, M. Comparisons of Spatial and Temporal Variations in PM2.5-Bound Trace Elements in Urban and Rural Areas of South Korea, and Associated Potential Health Risks. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, Y. Association Between Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) and the Reproductive System: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Nurs. Res. 2022, 6, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatelopoulou, A.; Dasopoulou, M.; Bairachtari, K.A.; Karavoltsos, S.; Sakellari, K.; Maggos, T. Contamination and Potential Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) and Heavy Metals in House Settled Dust Collected from Residences of Young Children. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bur’yanov, I.; Logachev, K.; Uvarov, V.A. Determination Of The Main Properties Of Dust Particles In The Grinding Area. Bull. Belgorod State Technol. Univ. Named VG Shukhov 2020, 5, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, M.; Thakur, L.S. Heavy Metal Cu, Ni And Zn. Toxicity, Health Hazards and Their Removaltechniques By Low Cost Adsorbents: A Short Overview. Int. J. Plant Anim. Environ. Sci. 2013, 3, 143–157. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.; Lai, C.; Hsieh, T.; Tsai, C. Source apportionment and health effects of particle-bound metals in PM2.5 near a precision metal machining factory. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2022, 15, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullu Arslan, N.; Uzun, Z.; Adıgüzel, M.; Bakırtaş, M. Heavy metal worker’s pneumonoconiosis with lung parenchymal damage and Peripheral neuropathy: Case report. Arch. Environ. Occup. Health 2023, 78, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, B.; Padhy, P.K.; Niyogi, S.; Patra, P.K.; Hecker, M. A Comparative Study of Heavy Metal Pollution in Ambient Air and the Health Risks Assessment in Industrial, Urban and Semi-Urban Areas of West Bengal, India: An Evaluation of Carcinogenic, Non-Carcinogenic, and Additional Lifetime Cancer Cases. Environments 2023, 10, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.; Prajati, G.; Humairoh, G.P.; Putri, R.M.; Phairuang, W.; Hata, M.; Furuuchi, M. Characterization of size-fractionated carbonaceous particles in the small to nano-size range in Batam city, Indonesia. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anggraini, F.J.; Shalsabila, A.; Rodhiyah, Z. Sebaran Particulate Matter (PM10, PM2.5, PM1, PM0.1) di SMP Negeri 1 Kota Jambi Menggunakan Model CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics). J. Sains Dan Teknol. 2023, 2, 690–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Chao, Y.C.; Wu, C.H.; Tsai, C.J.; Uang, S.N.; Shih, T.S. Measurements of ultrafine particle concentrations and size distribution in an iron foundry. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 158, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elihn, K.; Berg, P.; Lidén, G. Correlation between airborne particle concentrations in seven industrial plants and estimated respiratory tract deposition by number, mass and elemental composition. J. Aerosol Sci. 2011, 42, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.E.; Heitbrink, W.A.; Slavin, T.J.; Peters, T.M. Ultrafine and respirable particles in an automotive grey iron foundry. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2008, 52, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Bhanarkar, A.D.; Tamhane, S.M.; Dhopte, S.M. Assessment of in-plant Particulate Matter and its toxic metals contents of sponge iron industry in Goa, India. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 85, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alnagran, H.; Mansour, H.; Alashrah, S.; Suardi, N.; Rahman, A.A. Evaluation of Toxic Heavy Metals and Health Risk in Airborne Particulate Matter at Qassim Region, Saudi Arabia. Trends Sci. 2023, 20, 6978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ao, R.; Chen, H.; Li, J.; Wei, L.; Wang, Z. Characteristics of PM2.5 and CO2 Concentrations in Typical Functional Areas of a University Campus in Beijing Based on Low-Cost Sensor Monitoring. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobba, N.A.E.K.; Hussein Ali, A.; El Sharawy, D.E.; Hussein, M.A. The potential hazardous effect of exposure to iron dust in Egyptian smoking and nonsmoking welders. Arch. Environ. Occup. Health 2018, 73, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullahi, I.L.; Sani, A.; Jibril, B.A. Occupational exposure to metals among blacksmiths in Kano metropolis, Nigeria. Environ. Health Eng. Manag. 2020, 7, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, A. The Health Effects of Anthropogenic PM2.5 Emissions. Thesis, Honors Theses and Capstones. 660. University of New Hampshire, Durham, NH, USA, 2022. Available online: https://scholars.unh.edu/honors/660 (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Sciannameo, V.; Ricceri, F.; Soldati, S.; Scarnato, C.; Gerosa, A.; Giacomozzi, G.; d’Errico, A. Cancer mortality and exposure to nickel and chromium compounds in a cohort of Italian electroplaters. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2019, 62, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prueitt, R.L.; Li, W.; Chang, Y.; Boffetta, P.; Goodman, J.E. Systematic review of the potential respiratory carcinogenicity of metallic nickel in humans. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2020, 50, 60–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, B.S.; D’Souza, G.; Padukudru Anand, M. Effect of Indoor Air Pollution on Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Deaths in Southern Asia—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Toxics 2021, 9, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Iron Load Toxicity in Medicine: From Molecular and Cellular Aspects to Clinical Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, N.; Hurrell, R.F.; Kelishadi, R. Review on iron and its importance for human health. J. Res. Med. Sci. Off. J. Isfahan Univ. Med. Sci. 2014, 19, 164–174. [Google Scholar]
- Abidin, A.U.; Henita, N.; Rahmawati, S.; Maziya, F.B. Analisis Risiko Kesehatan Paparan Debu Terhadap Fungsi Paru Pada Pekerja Di Home Industry C-Max. J. Sains Dan Teknol. Lingkung. 2014, 13, 34–39. (In Bahasa) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazaya, M.R. Analisis Risiko Kesehatan Lingkungan Pajanan Particulate Matter 2,5 Terhadap Pekerja Packing Plant Pt. Semen Padang. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitas Andalas, Padang, Indonesian, 2024. (In Bahasa). [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Standard Operating Procedure for Particulate Matter (PM) Gravimetric Analysis; Environmental and Industrial Science Division: Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Vargas, F.A.; Rojas, N.Y.; Pachon, J.E.; Russell, A.G. PM10 characterization and source apportionment at two residential areas in Bogota. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2012, 3, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, A.; Alexanda, S.; Larry, A. Approaching a universal sample Preparation method for XRF analysis of powder materials. Adv. X-Ray Anal. 2001, 44, 368–370. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, D.G. Pharmaceutical Analysis: A Textbook for Pharmaceutical Chemists; Churchill Livingstone: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bryan, L.; Landrigan, P.J. PM2.5 pollution in Texas: A geospatial analysis of health impact functions. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1286755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, T.B.; Vo, L.T.; Van, D.; Nguyen, T.T.; Dao, D.N.; Nghiem, T.; Nguyen, Q.D. Occurrence of PM0.1 and PM2.5 at High Polluting Event Days In Hanoi And Health Implication. Vietnam. J. Sci. Technol. 2024, 61, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D. All About Steel as a Manufacturing Material. 2023. Available online: https://www.xometry.com/resources/materials/steel/ (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Zhang, J.; Billiet, J.; Nagels, M.; Dams, R. Survey of total and respirable suspended particulate matter in an iron foundry. Comparison of stationary sampling and personal monitoring. Sci. Total Environ. 1983, 30, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Mizumura, K.; Gon, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Kozu, Y.; Shikano, S.; Iida, Y.; Hikichi, M.; Okamoto, S.; Tsuya, K.; et al. Iron-Dependent Mitochondrial Dysfunction Contributes to the Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 643980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarjanli, Z.; Ghaedi, K.; Esmaeili, A.; Rahgozar, S.; Zarrabi, A. Iron oxide nanoparticles may damage to the neural tissue through iron accumulation, oxidative stress, and protein aggregation. BMC Neurosci. 2017, 18, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Weichenthal, S.; Kwong, J.C.; Burnett, R.T.; Hatzopoulou, M.; Jerrett, M.; van Donkelaar, A.; Bai, L.; Martin, R.V.; Copes, R.; et al. Long-term exposure to iron and copper in fine particulate air pollution and their combined impact on reactive oxygen species concentration in lung fluid: A population-based cohort study of cardiovascular disease incidence and mortality in Toronto, Canada. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 50, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Ardehali, H.; Min, J.; Wang, F. The molecular and metabolic landscape of iron and ferroptosis in cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2023, 20, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, Z.; Singh, V.P. The relative impact of toxic heavy metals (THMs) (arsenic (As), cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr)(VI), mercury (Hg), and lead (Pb)) on the total environment: An overview. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yatera, K.; Morimoto, Y.; Ueno, S.; Noguchi, S.; Kawaguchi, T.; Tanaka, F.; Suzuki, H.; Higashi, T. Cancer Risks of Hexavalent Chromium in the Respiratory Tract. J. UOEH 2018, 40, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, A.W.; Erikson, K.M.; Aschner, M. Manganese neurotoxicity. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1012, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizvi, I.; Garg, R.K.; Malhotra, H.S.; Kumar, N.; Uniyal, R. Manganese, manganism and other neurodegenerative diseases: Is it a cause of concern? Neurol. India 2017, 65, 1248–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proudfoot, O. Manganese in manganism, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and Batten disease: A narrative review. Neurol. India 2017, 65, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, G.; Niculita-Hirzel, H.; Correia, D.; Pralong, J.A.; Vernez, D. A proposed synergetic mechanism for metal fume fever involving ZnO and Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisgen, M.; Thomas, K.; Beilmann, V.; Markert, A.; Gerhards, B.; Krichel, T.; Schmidt, K.; Kraus, T.; Martin, C.; Brand, P.; et al. The role of cell-derived inflammation in metal fume fever–blood count changes after exposure with zinc- and copper-containing welding fumes. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 648. [Google Scholar]
- Brenner, B.E.; Keyes, D. Metal Fume Fever. 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK583199 (accessed on 1 November 2024).
- Mueller, E.J.; Seger, D.L. Metal fume fever—A review. J. Emerg. Med. 1985, 2, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhao, Q.; Chai, X.; Song, Y.; Li, X.; Lu, X.; Li, S.; Chen, X.; Yuan, Y.; Cai, Z.; et al. Contribution and Effects of PM2.5-Bound Lead to the Cardiovascular Risk of Workers in a Non-Ferrous Metal Smelting Area Considering Chemical Speciation and Bioavailability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 1743–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshney, P.; Bansal, R.; Tiwari, R.; Halve, A.K.; Taneja, A. Atmospheric Concentration of Trace Metals in PM2.5 and Their Bioavailability in Different Areas of Gwalior Region. Int. J. Appl. Chem. 2019, 6, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, B.; Shi, T.; Yang, Q. Association between PM2.5-bound metals and pediatric respiratory health in Guangzhou: An ecological study investigating source, health risk, and effect. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1137933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N. Cutting-Edge Strategies for Reducing Industrial SO2 Emissions. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2023, 12, 1897–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Workshop | PM2.5 (µg/m3) | Mg (µg/m3) | Al (µg/m3) | Si (µg/m3) | S (µg/m3) | Ca (µg/m3) | Ti (µg/m3) | Cr (µg/m3) | Mn (µg/m3) | Ni (µg/m3) | Cu (µg/m3) | Zn (µg/m3) | As (µg/m3) | Pb (µg/m3) | K (µg/m3) | Fe (µg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WS-A | 455.18 | 0.47 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 0.63 | 0.06 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.20 | 0.30 | 0.01 | 0.45 | 0.01 | 0.47 | 0.74 | 8.98 |
| WS-B | 513.80 | 1.77 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 3.68 | 0.22 | 0.03 | 0.38 | 0.52 | 0.36 | 0.45 | 0.51 | 0.26 | 0.52 | 11.31 | 41.63 |
| WS-C | 203.47 | 0.16 | 0.04 | 0.74 | 0.77 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.12 | 0.24 | 0.01 | 0.16 | 0.03 | 3.11 | 1.87 | 7.39 |
| WS-D | 190.86 | 0.14 | 0.17 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.63 | 0.31 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.20 | 0.02 | 0.29 | 0.01 | 0.30 | 0.13 | 16.28 |
| WS-E | 172.05 | 0.17 | 0.05 | 0.26 | 0.41 | 2.32 | 0.25 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.48 | 0.02 | 0.84 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.76 | 4.54 |
| WS-F | 166.88 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.35 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.33 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 0.41 | 0.00 | 0.86 | 0.01 | 3.67 |
| WS-G | 315.20 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0.40 | 0.89 | 1.01 | 0.18 | 0.20 | 0.24 | 0.34 | 0.02 | 0.86 | 0.50 | 0.02 | 2.82 | 27.14 |
| average | 288.21 | 0.43 | 0.06 | 0.25 | 0.92 | 0.66 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.22 | 0.29 | 0.08 | 0.50 | 0.12 | 0.77 | 2.52 | 15.66 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oginawati, K.; Faiqah, N.S.A.; Suharyanto; Regia, R.A.; Amin, M. Indoor PM2.5 and Heavy Metal Composition in Blacksmithing Factories: A Pilot Study in Bandung Regency, Indonesia. Urban Sci. 2024, 8, 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci8040230
Oginawati K, Faiqah NSA, Suharyanto, Regia RA, Amin M. Indoor PM2.5 and Heavy Metal Composition in Blacksmithing Factories: A Pilot Study in Bandung Regency, Indonesia. Urban Science. 2024; 8(4):230. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci8040230
Chicago/Turabian StyleOginawati, Katharina, Naja Safira Al Faiqah, Suharyanto, Rinda Andhita Regia, and Muhammad Amin. 2024. "Indoor PM2.5 and Heavy Metal Composition in Blacksmithing Factories: A Pilot Study in Bandung Regency, Indonesia" Urban Science 8, no. 4: 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci8040230
APA StyleOginawati, K., Faiqah, N. S. A., Suharyanto, Regia, R. A., & Amin, M. (2024). Indoor PM2.5 and Heavy Metal Composition in Blacksmithing Factories: A Pilot Study in Bandung Regency, Indonesia. Urban Science, 8(4), 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci8040230








