An Advanced Compression Molding Simulation and Validation of a Thick-Walled Carbon Fiber Sheet Molding Compound Brake Caliper
Abstract
1. Introduction
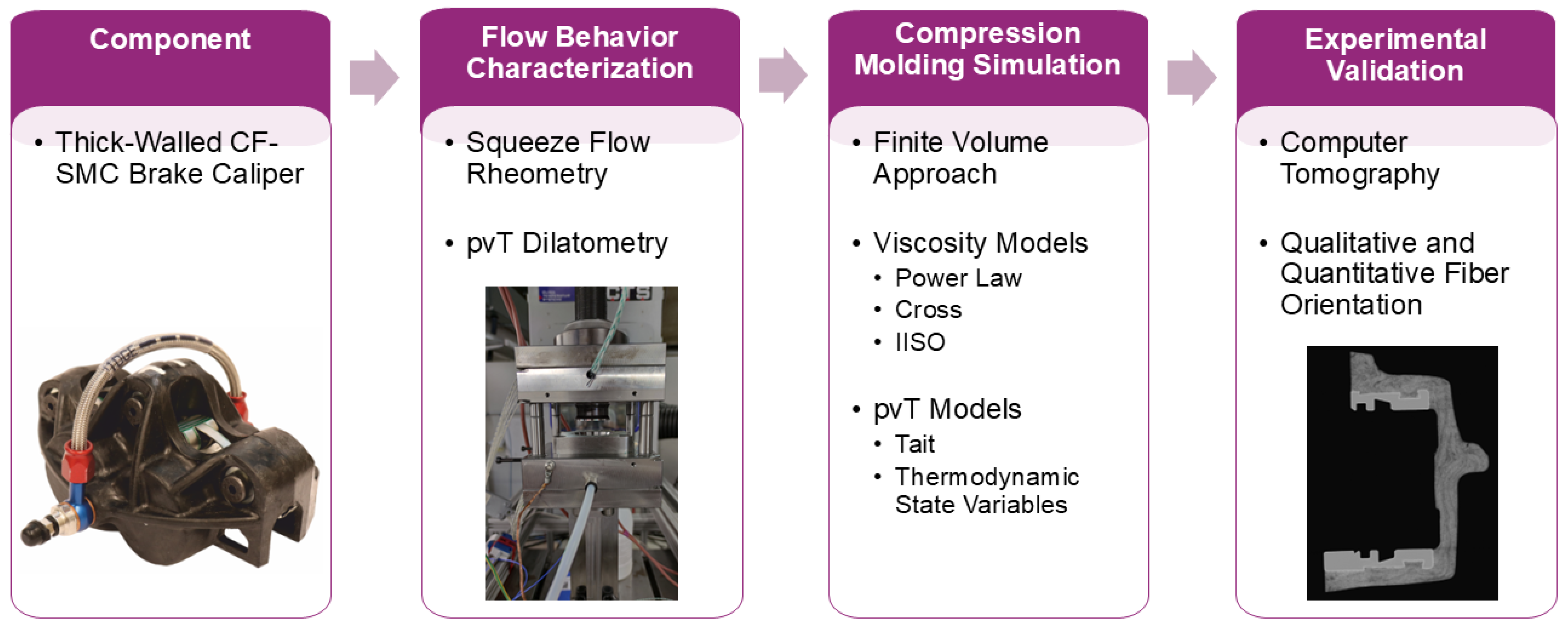
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Sheet Molding Compound
2.2. Experimental Methodology and Data Generation
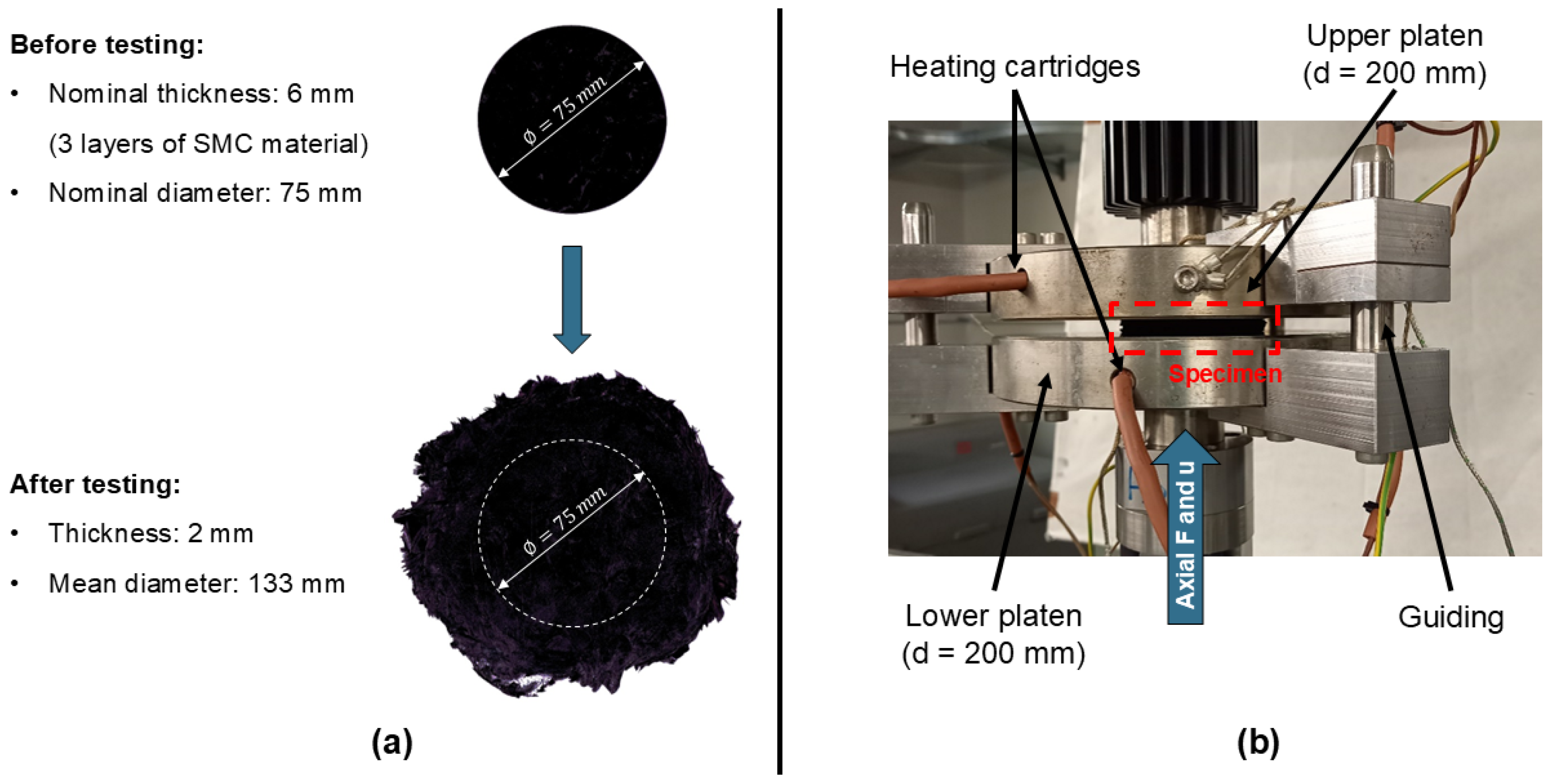
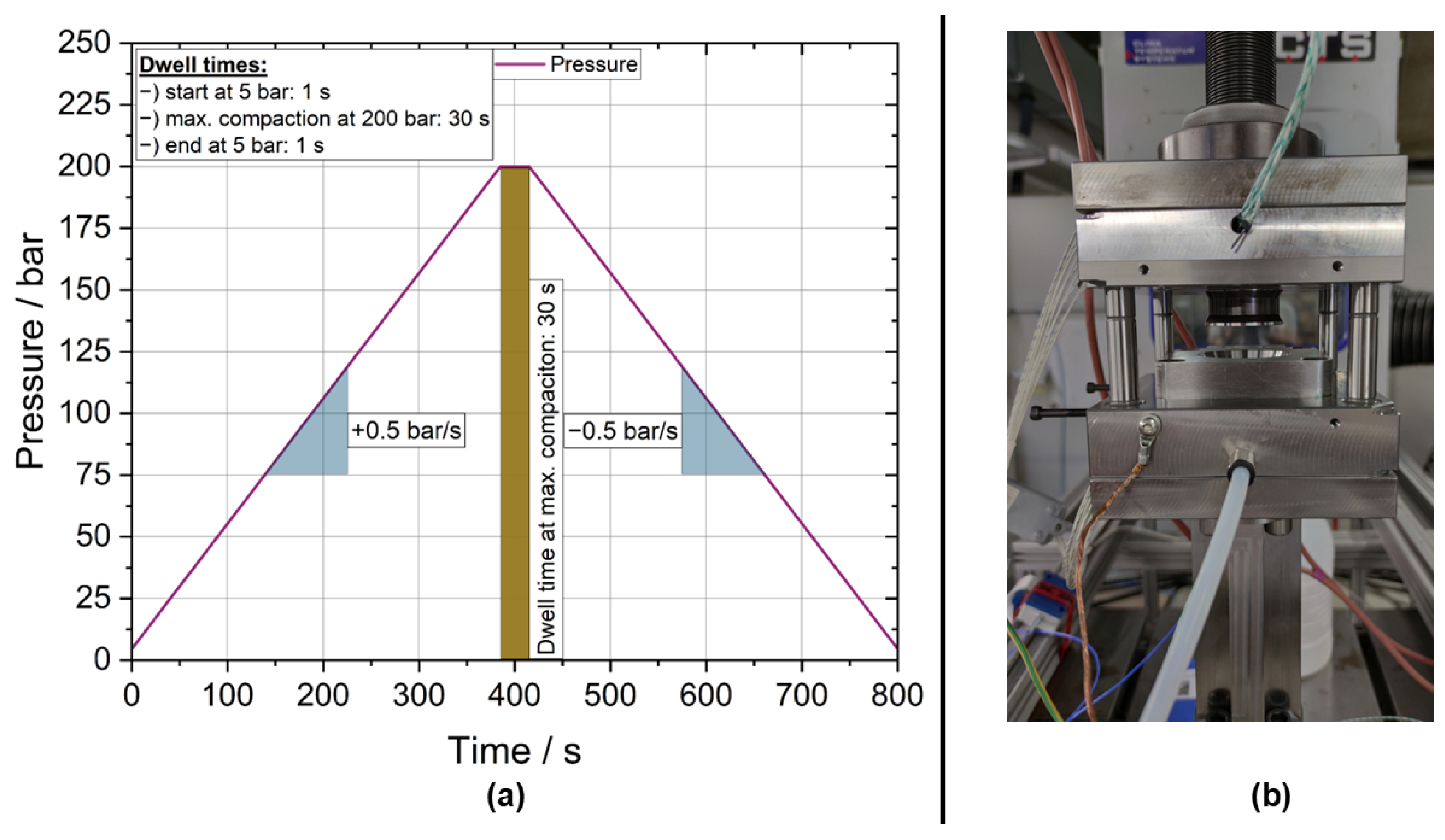
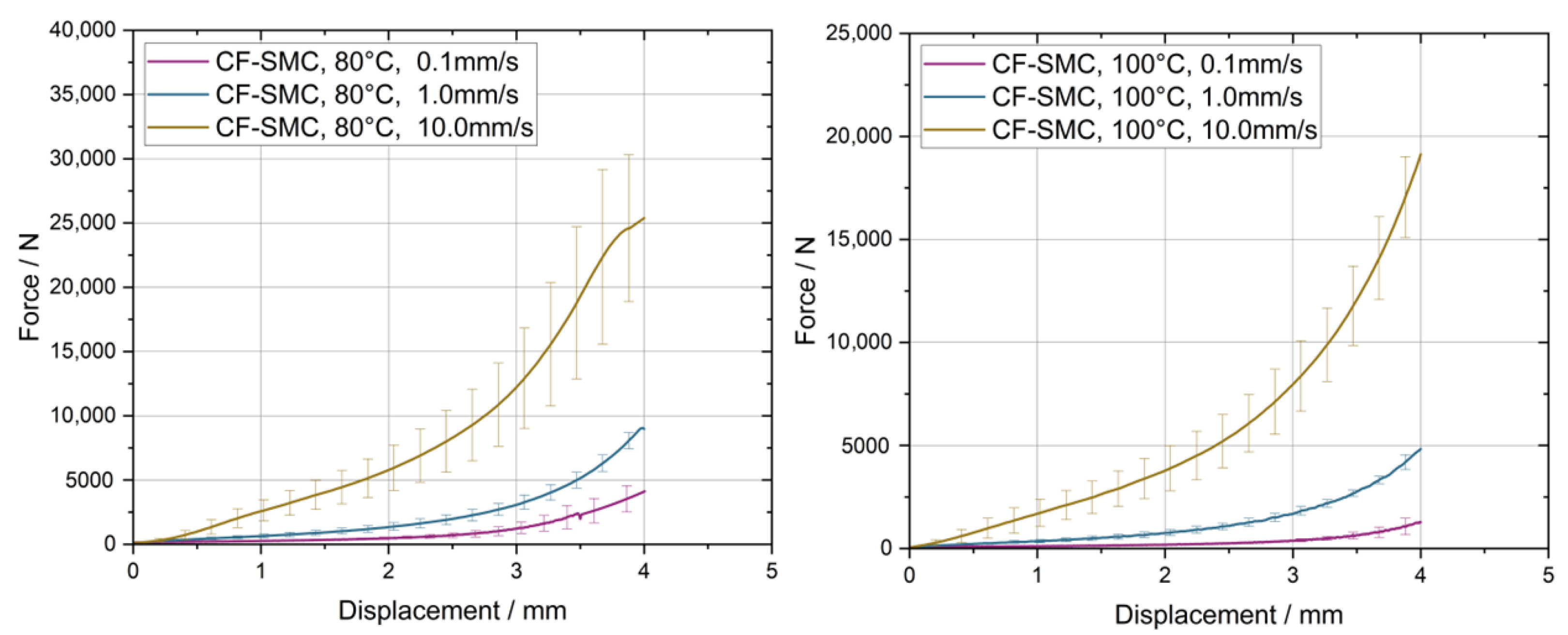
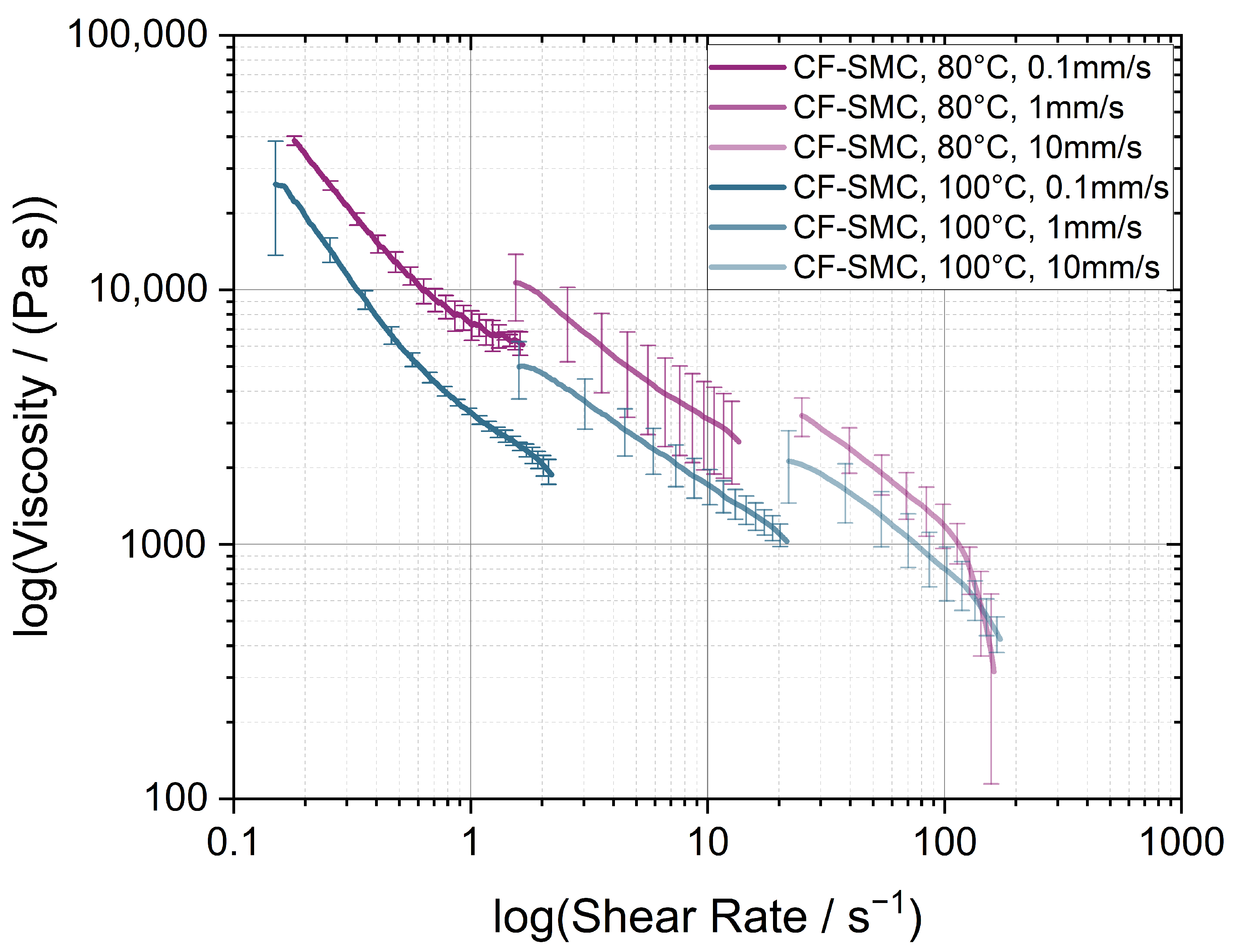
2.2.1. Squeeze Flow Rheometry
2.2.2. Pressure–Volume–Temperature Dilatometry
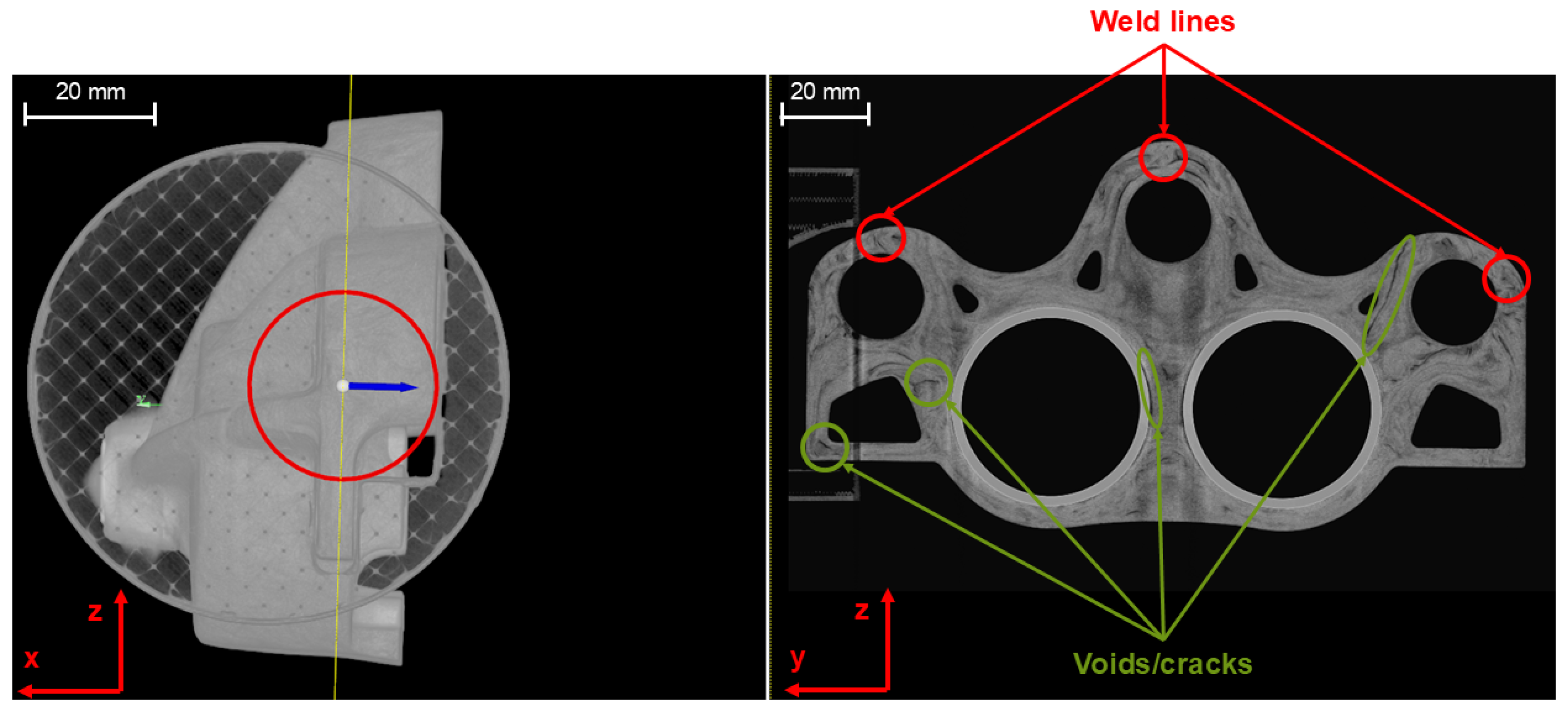
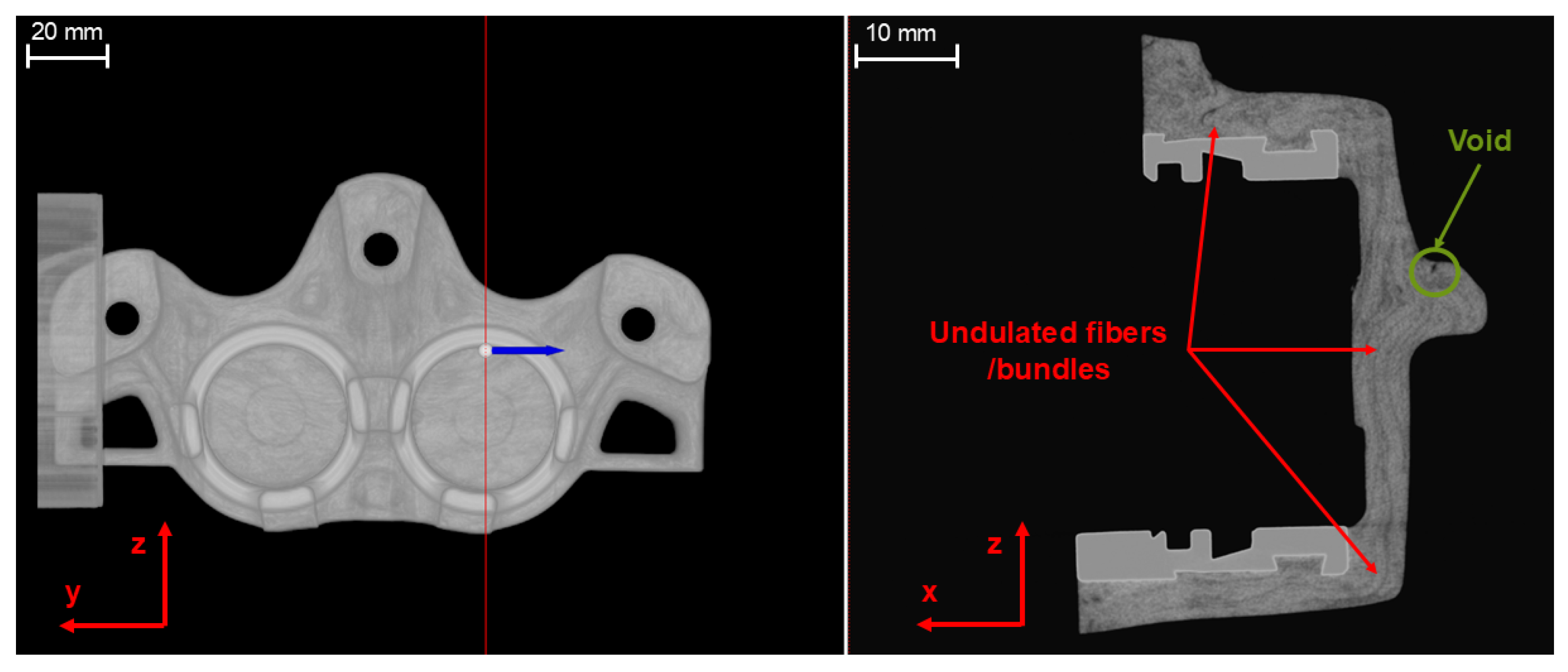
2.2.3. X-Ray Computer Tomography
3. Results
3.1. Squeeze Flow Rheometry—Viscosity Model
3.2. pvT Dilatometry—Temperature-Dependent Compaction Behavior
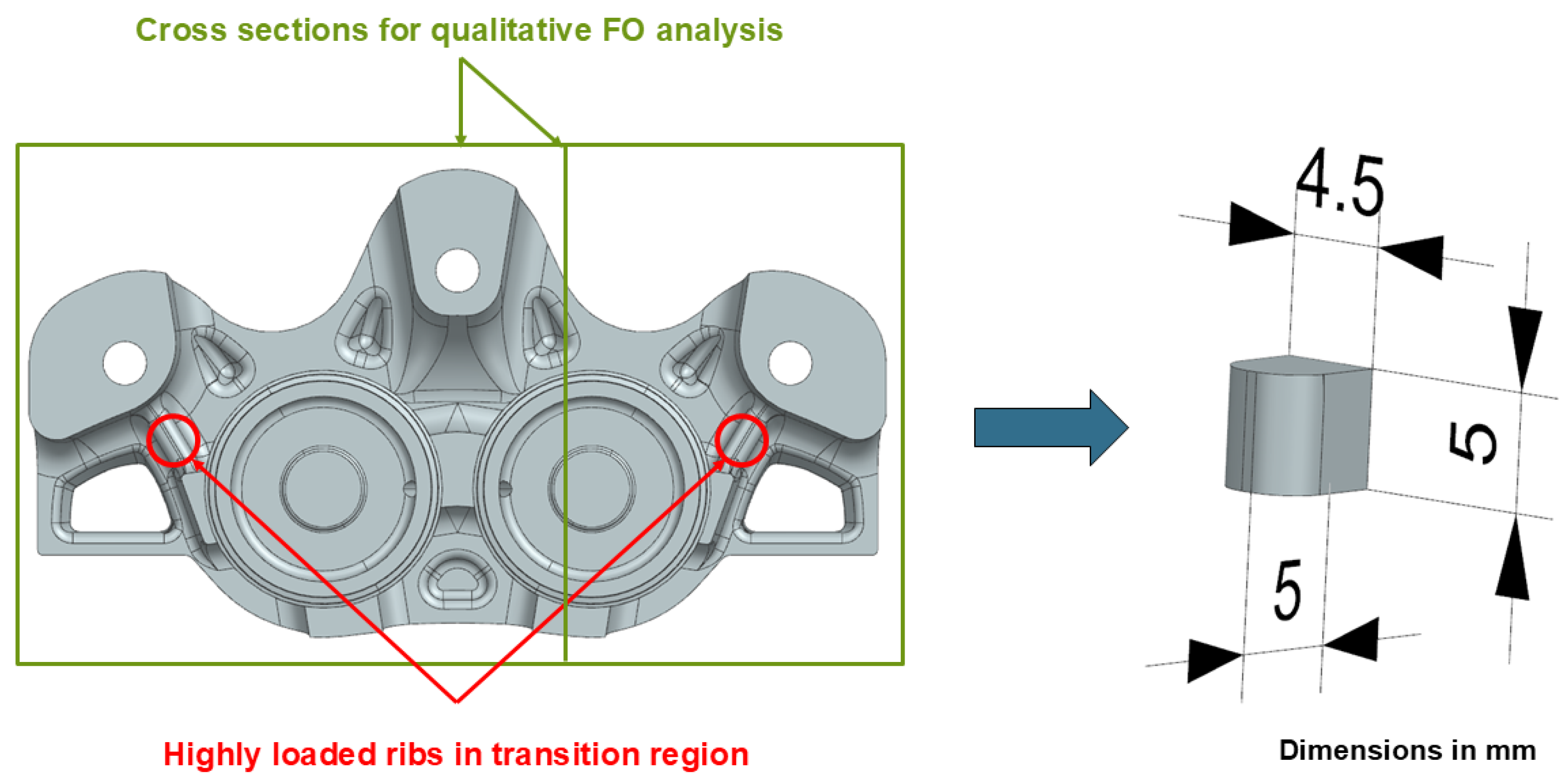
3.3. Qualitative and Quantitative Fiber Orientation Analysis of Brake Caliper
4. Numerical Implementation
4.1. Flow Model Validation
4.2. Compression Molding Simulation of Brake Caliper
4.3. Fiber Orientation Validation
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- SMC materials require specialized equipment for characterization (e.g., squeeze flow rheometers and pvT dilatometers).
- Standard Tait models fail to capture the temperature-dependent porosity at low pressures, while a model based on thermodynamic state variables (TSVs) can provide this capability.
- The informed isotropic (IISO) viscosity model led to numerical divergence when combined with the Cross model. Consequently, it is suggested that a simpler but stable power law (PL) description be applied as the basis for the IISO model, which still provides accurate results in the required shear rate range.
- The best results were obtained using the PL-IISO and TSV model.
- The prediction capabilities for fiber orientations were not satisfactory for either qualitative or quantitative analysis due to the simplification of fibers to non-deformable, rigid rods.
- Finite volume modeling approaches for the compression molding of CF-SMC materials are mainly limited to compressive force considerations and the determination of the weld line positions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alnersson, G.; Tahir, M.W.; Ljung, A.L.; Lundström, T.S. Review of the Numerical Modeling of Compression Molding of Sheet Molding Compound. Processes 2020, 8, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaloro, A.J.; Sommer, D.E.; Denos, B.R.; Pipes, R.B. Simulation of prepreg platelet compression molding: Method and orientation validation. J. Rheol. 2018, 62, 1443–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohberg, M.; Kärger, L.; Henning, F.; Hrymak, A. Rheological measurements and rheological shell model Considering the compressible behavior of long fiber reinforced sheet molding compound (SMC). Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 95, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görthofer, J.; Meyer, N.; Pallicity, T.D.; Schöttl, L.; Trauth, A.; Schemmann, M.; Hohberg, M.; Pinter, P.; Elsner, P.; Henning, F.; et al. Virtual process chain of sheet molding compound: Development, validation and perspectives. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 169, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, N.; Ilinzeer, S.; Hrymak, A.N.; Henning, F.; Kärger, L. Non-isothermal direct bundle simulation of SMC compression molding with a non-Newtonian compressible matrix. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2022, 310, 104940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.C.; Yuan, H.; Jesri, M.; Khan, M.; Kendall, K.N. Flow Behaviour of Carbon Fibre Sheet Moulding Compound. Key Eng. Mater. 2022, 926, 1350–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanenko, V.; Duhovic, M.; Schommer, D.; Hausmann, J.; Eschl, J. Advanced process simulation of compression molded carbon fiber sheet molding compound (C-SMC) parts in automotive series applications. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 157, 106924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothenhäusler, F.; Meyer, N.; Wehler, S.; Hohberg, M.; Gude, M.; Henning, F.; Kärger, L. Experimental and Numerical Analysis of SMC Compression Molding in Confined Regions—A Comparison of Simulation Approaches. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousins, D.S.; Suzuki, Y.; Murray, R.E.; Samaniuk, J.R.; Stebner, A.P. Recycling glass fiber thermoplastic composites from wind turbine blades. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 1252–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauklis, A.E.; Karl, C.W.; Gagani, A.I.; Jørgensen, J.K. Composite Material Recycling Technology—State-of-the-Art and Sustainable Development for the 2020s. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stieven Montagna, L.; Ferreira de Melo Morgado, G.; Lemes, A.P.; Roberto Passador, F.; Cerqueira Rezende, M. Recycling of carbon fiber-reinforced thermoplastic and thermoset composites: A review. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2023, 36, 3455–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savandaiah, C.; Kapshammer, A.; Plank, B.; Stolcer, V.; Marschik, C.; Major, Z. Thermo-mechanical characterisation of polycarbonate-based sheet moulded composites fabricated from off-cut waste unidirectional tapes. Express Polym. Lett. 2024, 18, 883–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emminger, C.; Kapshammer, A.; Birtha, J.; Cakmak, U.; Fischer, J.; Major, Z. Improving Damping Performance of Thermoplastic Composite Materials Through SMC—TPU Hybridization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2025, e56938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martulli, L.M.; Kerschbaum, M.; Lomov, S.V.; Swolfs, Y. Weld lines in tow-based sheet moulding compounds tensile properties: Morphological detrimental factors. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 139, 106109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martulli, L.M.; Muyshondt, L.; Kerschbaum, M.; Pimenta, S.; Lomov, S.V.; Swolfs, Y. Morphology-induced fatigue crack arresting in carbon fibre sheet moulding compounds. Int. J. Fatigue 2020, 134, 105510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravchenko, S.G.; Sommer, D.E.; Denos, B.R.; Favaloro, A.J.; Tow, C.M.; Avery, W.B.; Pipes, R.B. Tensile properties of a stochastic prepreg platelet molded composite. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 124, 105507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.; Martulli, L.M.; Kerschbaum, M.; Swolfs, Y.; Lomov, S.V.; Pimenta, S. A 3D finite element stochastic framework for the failure of tow-based discontinuous composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2023, 232, 109846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, D.E.; Kravchenko, S.G.; Pipes, R.B. A numerical study of the meso-structure variability in the compaction process of prepreg platelet molded composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 138, 106010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arquier, R.; Miquelard-Garnier, G.; Iliopoulos, I.; Régnier, G. Assessing the shear viscous behavior of continuous carbon fiber reinforced PEKK composites with squeeze flow measurements. Polym. Test. 2023, 123, 108060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldex3D 2023 Help. Available online: https://university.moldex3d.cloud/#/help?url=2023%2Fen%2F4-1-1_analysislog.html (accessed on 13 April 2025).
- Rienesl, K.; Stelzer, P.S.; Major, Z. Squeeze flow rheometry and data analysis of carbon fiber sheet molding compounds. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 62, 2433–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaloro, A.J.; Tseng, H.C.; Pipes, R.B. A new anisotropic viscous constitutive model for composites molding simulation. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 115, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaloro, A.J.; Sommer, D.E. On the use of orientation tensors to represent prepreg platelet orientation state and variability. J. Rheol. 2020, 64, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, H.C.; Chang, R.Y.; Hsu, C.H. Phenomenological improvements to predictive models of fiber orientation in concentrated suspensions. J. Rheol. 2013, 57, 1597–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, H.C.; Chang, R.Y.; Hsu, C.H. An Integration of Microstructure Predictions and Structural Analysis in Long-Fiber-Reinforced Composite with Experimental Validation. Int. Polym. Process. 2017, 32, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, H.C.; Chang, R.Y.; Hsu, C.H. Improved fiber orientation predictions for injection molded fiber composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 99, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teuwsen, J.; Hohn, S.K.; Osswald, T.A. Direct Fiber Simulation of a Compression Molded Ribbed Structure Made of a Sheet Molding Compound with Randomly Oriented Carbon/Epoxy Prepreg Strands—A Comparison of Predicted Fiber Orientations with Computed Tomography Analyses. J. Compos. Sci. 2020, 4, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Shin, D.; Kim, G.; Ji, W. Numerical model for compression molding process of hybridly laminated thermoplastic composites based on anisotropic rheology. Compos. Part C Open Access 2022, 7, 100215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörr, D.; Ivanov, S.; Gergely, R.; Meyer, N.; Henning, F.; Straatman, A.G.; Hrymak, A. A Sequential Approach for Simulation of Thermoforming and Squeeze Flow of Glass Mat Thermoplastics. In Proceedings of the ESAFORM 2021: 24th International Conference on Material Forming, Liege, Belgium, 14–16 April 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doppelbauer, L.K.; Rienesl, K.; Stelzer, P.S.; Zulueta, K.; Chang, L.Y.; Major, Z. A macroscopic model of the compaction process during compression molding of carbon fiber sheet molding compounds. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2023, 169, 107535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidler, A.; Zulueta, K.; Kapshammer, A.; Altemirov, A.; Stiefmann, M.; Huemer-Kals, S.; Fischer, P.; Bruyneel, M. (Eds.) Carbon-fibre reinforced sheet moulding compound in brakes: Design and simulation of a lightweight motorcycle brake calliper. In Proceedings of the Eurobrake 2023: Europe’s Braking Technology Conference & Exhibition, Barcelona, Spain, 12–14 September 2023; FISITA: Bishops Stortford, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidler, A.; Huemer-Kals, S.; Kapshammer, A.; Mersch, C.; Dos Santos, M.; Belategi, U.A.; Fischer, P. (Eds.) Carbon fibre reinforced sheet moulding compound in brakes: Manufacturing and testing of a lightweight motorcycle brake calliper. In Proceedings of the EuroBrake 2024: Europe’s Braking Technology Conference & Exhibition, Mainz, Germany, 17–19 June 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martulli, L.M.; Creemers, T.; Schöberl, E.; Hale, N.; Kerschbaum, M.; Lomov, S.V.; Swolfs, Y. A thick-walled sheet moulding compound automotive component: Manufacturing and performance. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 128, 105688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Technical Data Sheet Forged Molding Compound STR120N131. Available online: https://www.m-chemical.co.jp/carbon-fiber/en/product/fmc/ (accessed on 13 April 2025).
- Carbon Fiber Tow (Continuous Fiber) Properties. Available online: https://www.m-chemical.co.jp/carbon-fiber/pdf/tow/Carbon%20Fiber%20Tow%20(Continuous%20Fiber)%2020240930.pdf (accessed on 13 April 2025).
- Engmann, J.; Servais, C.; Burbidge, A.S. Squeeze flow theory and applications to rheometry: A review. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2005, 132, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferré-Sentis, D.; Dumont, P.; Orgéas, L.; Martoïa, F.; Sager, M. Rheological response of compressible SMCs under various deformation kinematics: Experimental aspects and simple modelling approach. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 154, 106774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiraud, O.; Dumont, P.; Orgéas, L.; Favier, D. Rheometry of compression moulded fibre-reinforced polymer composites: Rheology, compressibility, and friction forces with mould surfaces. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2012, 43, 2107–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, J. Versuche über die scheinbare Adhäsion. In Sitzungsberichte der Mathematisch-Naturwissenschaftlichen Classe. Abteilung II; Kaiserl. Akademie der Wissenschaften in Wien: Wien, Austria, 1874; Volume 69, pp. 713–735. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Khan, M.; Peijs, T.; Qian, C. Experimental process characterisation for high-volume compression moulding of hybrid-architecture composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2024, 181, 108137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, H.C.; Chang, R.Y.; Hsu, C.H. Numerical prediction of fiber orientation and mechanical performance for short/long glass and carbon fiber-reinforced composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 144, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, H.C.; Favaloro, A.J. The use of informed isotropic constitutive equation to simulate anisotropic rheological behaviors in fiber suspensions. J. Rheol. 2019, 63, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.T.; Lai, C.H. Investigation on the Coupling Effects between Flow and Fibers on Fiber-Reinforced Plastic (FRP) Injection Parts. Polymers 2020, 12, 2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, D.E.; Favaloro, A.J.; Pipes, R.B. Coupling anisotropic viscosity and fiber orientation in applications to squeeze flow. J. Rheol. 2018, 62, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaloro, A.J.; Tucker, C.L. Analysis of anisotropic rotary diffusion models for fiber orientation. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 126, 105605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



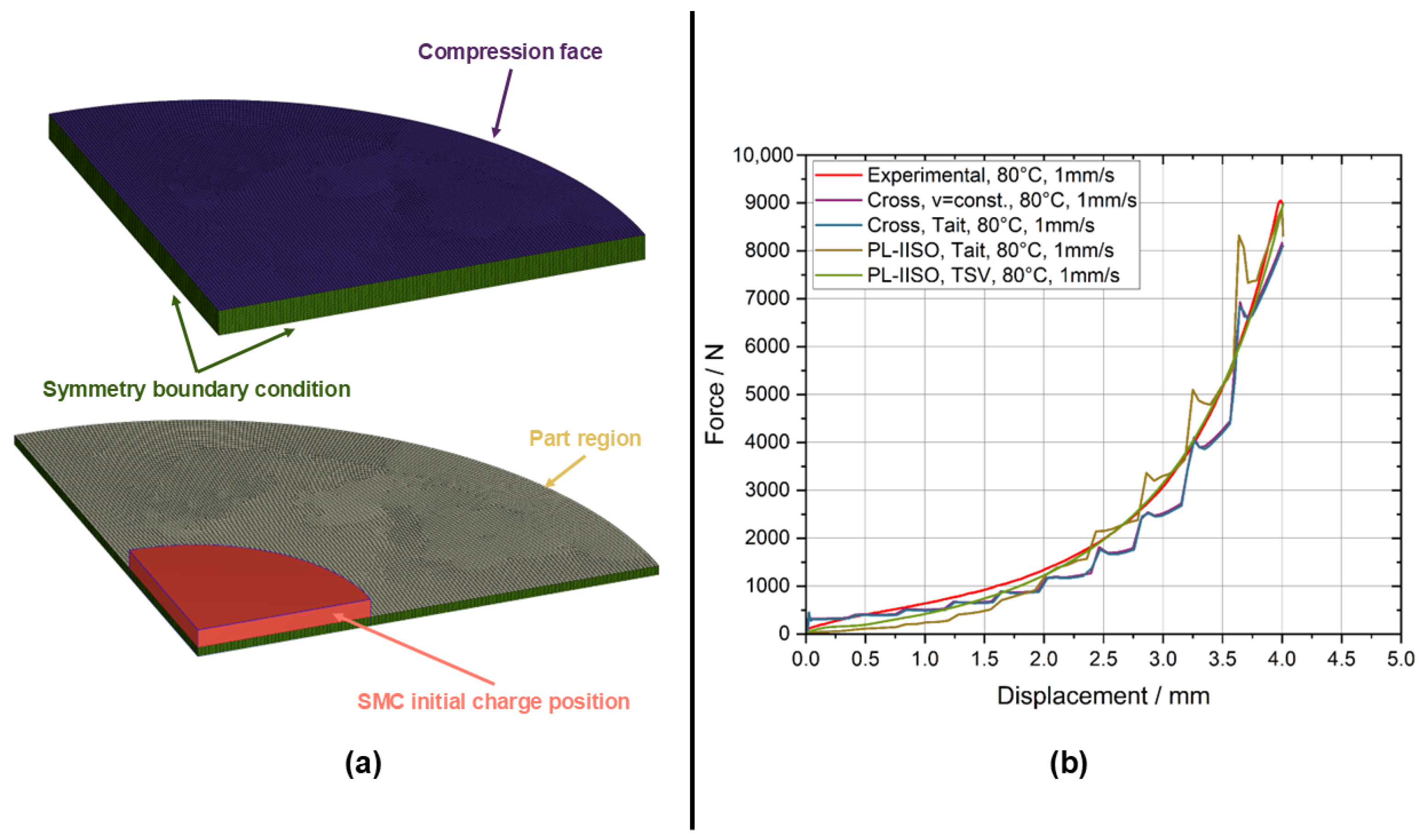
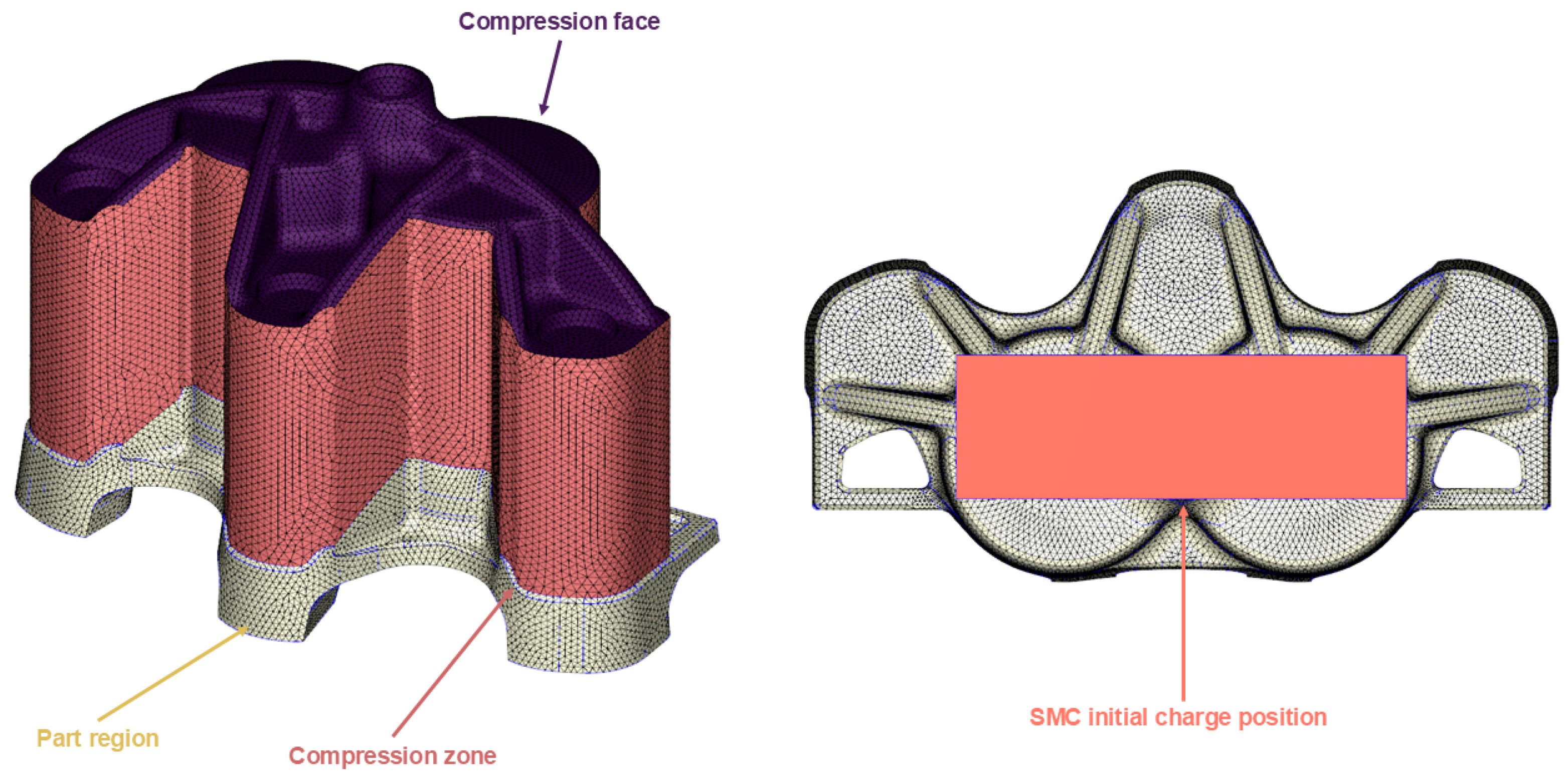
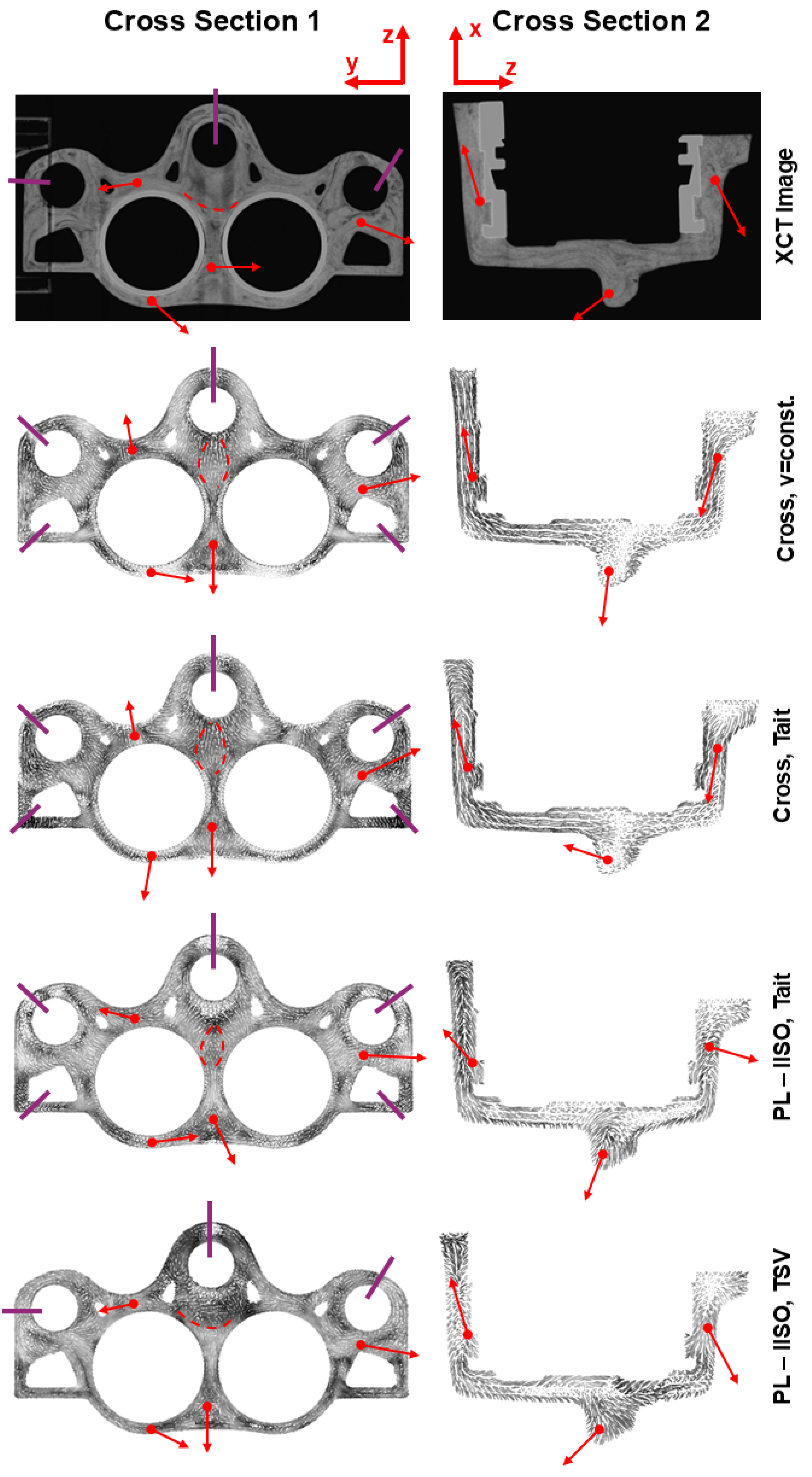
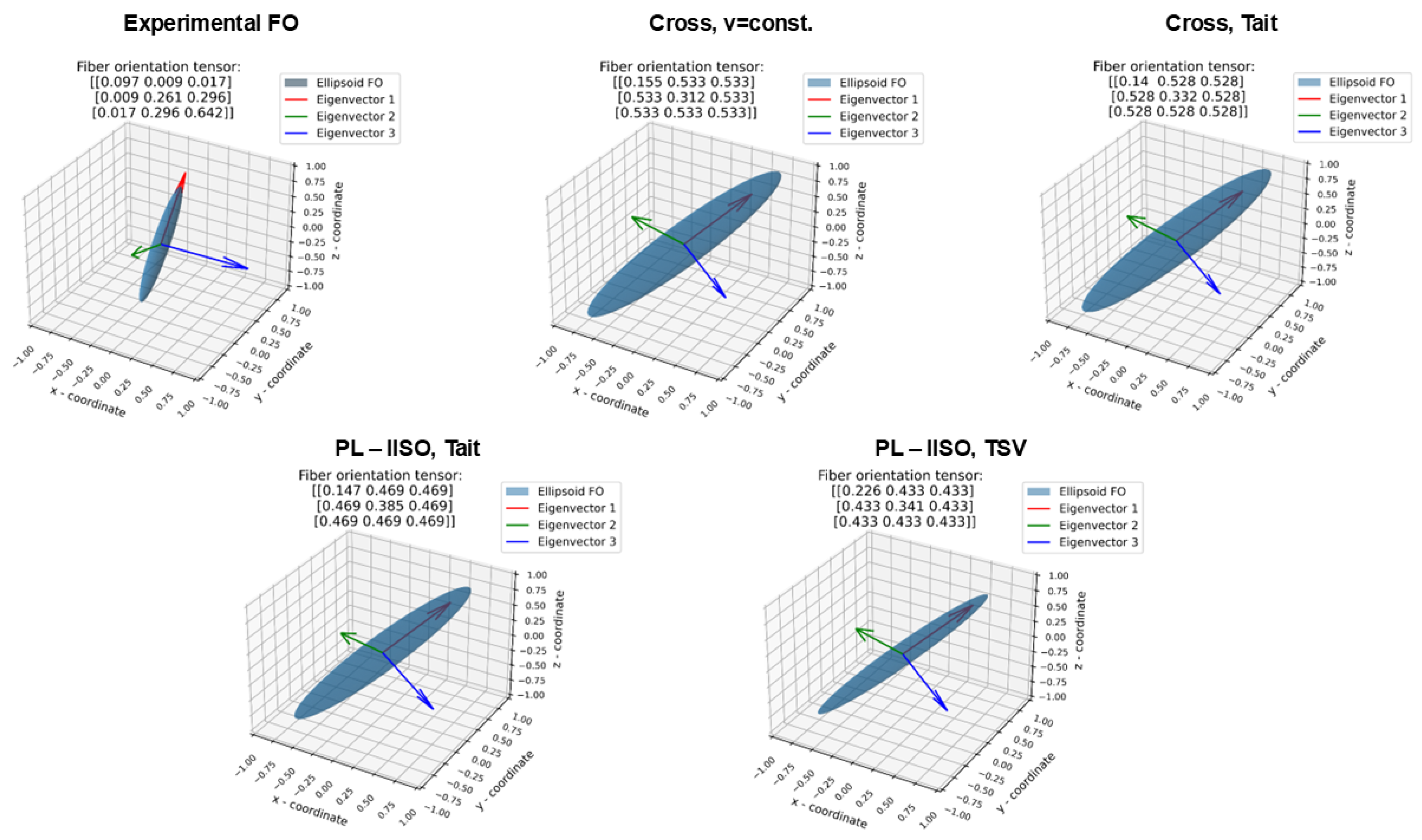
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| A | Pa s | |
| 29,610.55 | K | |
| 2000 | Pa | |
| n | 0.233 | - |
| Isotropic PL Model | IISO PL Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Value | Unit | Parameter | Value | Unit |
| A | 0.18742 | Pa s | A | Pa s | |
| 4055.19 | K | 4055.19 | K | ||
| n | 0.2 | - | n | 0.2 | - |
| Tait Model Parameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Value | Unit | |
| m3/kg | |||
| m3/(kg K) | |||
| Pa | |||
| 0.01029 | 1/K | ||
| C | 0.0894 | - | |
| TSV Model Parameters | |||
| Parameter | Value at 80 °C | Value at 100 °C | Unit |
| m3/kg | |||
| m3/kg | |||
| m3/kg | |||
| 0.025 | 0.02 | - | |
| 0.35 | 1.04 | - | |
| 2.64 | bar | ||
| 5.38 | 2.75 | bar | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kapshammer, A.; Huemer-Kals, S.; Zulueta, K.; Fischer, P.; Major, Z. An Advanced Compression Molding Simulation and Validation of a Thick-Walled Carbon Fiber Sheet Molding Compound Brake Caliper. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2025, 9, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9040137
Kapshammer A, Huemer-Kals S, Zulueta K, Fischer P, Major Z. An Advanced Compression Molding Simulation and Validation of a Thick-Walled Carbon Fiber Sheet Molding Compound Brake Caliper. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2025; 9(4):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9040137
Chicago/Turabian StyleKapshammer, Andreas, Severin Huemer-Kals, Kepa Zulueta, Peter Fischer, and Zoltan Major. 2025. "An Advanced Compression Molding Simulation and Validation of a Thick-Walled Carbon Fiber Sheet Molding Compound Brake Caliper" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 9, no. 4: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9040137
APA StyleKapshammer, A., Huemer-Kals, S., Zulueta, K., Fischer, P., & Major, Z. (2025). An Advanced Compression Molding Simulation and Validation of a Thick-Walled Carbon Fiber Sheet Molding Compound Brake Caliper. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 9(4), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9040137





