Abstract
Pyrolysis oil derived from waste tires consists of sulfur content in the range of 7000 to 9000 ppm. For use in diesel engines, its sulfur content must be lowered to 10 to 15 ppm. Though conventional hydrodesulfurization is suitable for the removal of sulfur from tire pyrolysis oil, its high cost provides an avenue for alternative desulfurization technologies to be explored. In this study, oxidative desulfurization (ODS), a low-cost technology, was explored for the desulfurization of tire pyrolysis oil. Two categories of titanium-incorporated mesoporous supports with 20 wt% loaded heteropoly molybdic acid catalyst (HPMo/Ti-Al2O3 and HPMo/Ti-TUD-1) were developed and tested for ODS of tire pyrolysis oil at mild process conditions. Catalysts were characterized by X-ray diffraction, BET-N2 physisorption, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The incorporation of Ti into Al2O3 and TUD-1 frameworks was confirmed by XPS. The surface acidity of catalysts was studied by the temperature-programmed desorption of NH3 and pyridine FTIR analyses. HPMo/Ti-Al2O3 and HPMo/Ti-TUD-1 catalysts contained both Lewis and Brønsted acid sites. The presence of titanium in catalysts was found to promote the ODS activity of phosphomolybdic acid. The Ti-TUD-1-supported catalysts performed better than the Ti-Al2O3-supported catalysts for the ODS of tire pyrolysis oil. Hydrogen peroxide and cumene peroxide were found to be better oxidants than tert-butyl hydroperoxide for oxidizing sulfur compounds of tire pyrolysis oil. Process parameter optimization by the design of experiments was conducted with an optimal catalyst along with the catalyst regeneration study. An ANOVA statistical analysis demonstrated that the oxidant/sulfur and catalyst/oil ratios were more significant than the reaction temperature for the ODS of tire pyrolysis oil. It followed the pseudo-first-order kinetics over HPMo/Ti-TUD-1.
1. Introduction
The conversion of wastes to energy plays a pertinent role in the generation of alternative resources to supplement dwindling conventional resources. Typically, at the end of their lives, waste tires are discarded into landfills where they pose health and fire hazards due to their non-biodegradable nature. In addition, the disposal of scrap tires takes enormous dumping space and hosts potential disease-bearing vectors [1]. That notwithstanding, waste or scrap tires can be utilized as excellent feedstocks for fuel production as their calorific value is comparable to that of coal and crude oil [2]. The heating value of an average size passenger tire is between 13,000 and 15,000 Btu/lb [3]. In this regard, waste tires can be converted into pyrolysis oil, heating gases (CO, H2, CO2, etc.), and carbon black via pyrolysis [4,5]. Figure 1 shows the schematic of the pyrolysis of scrap tires.
Figure 1.
Schematic of scrap tire pyrolysis process.
The pyrolysis of waste tires is an emerging field of research. Tire pyrolysis oil (TPO) comprises C6–C24 hydrocarbons with a calorific value of around 42 MJ/kg, which is comparable to that of crude oil (42–47 MJ/kg) [4,6]. It can be used as fuel in cement kilns, thermal power plants, industrial boilers, and vehicles [7,8,9]. However, the presence of nitrogen and sulfur compounds limits its direct use. Pyrolysis oil needs to be desulfurized for its commercial use as fuel [10]. Hydrodesulfurization is the current commercial desulfurization process, which is typically used in petroleum refineries around the world. It can be used to remove sulfur compounds from pyrolysis oil, but it is a hydrogen-demanding process. In this study, oxidative desulfurization (ODS) is explored for the removal of sulfur species from tire pyrolysis oil under mild process conditions. It is one of the low-cost alternative desulfurization methods and does not require hydrogen. ODS is a two-stage process, where the sulfur in the aromatic ring is oxidized into sulfone and sulfoxide in the presence of a catalyst and an oxidizing agent during the first stage. In the second stage, the highly polar sulfoxide and sulfone are separated from the oil phase by solvent extraction or adsorption [10].
As given in Table 1, homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts were applied for oxidative desulfurization at atmospheric pressure. Desulfurization through ODS was proven with model and simulated petroleum feedstocks using oxidants such as hydrogen peroxide, tert-butyl hydroperoxide, and cumene peroxide [11]. The model compounds used in ODS are mostly dibenzothiophene (DBT) and 4,6-dimethyl dibenzothiophene (4,6-DMDBT). Doustkhah et al. [12] synthesized a new type of catalyst by merging periodic mesoporous organosilica with aluminosilica and investigated its catalytic performance for the oxidation of DBT. This bifunctional catalyst is easily recoverable and reusable for several consecutive cycles. Recently, Fan et al. [13] reported oxidative desulfurization of DBT under ultrasound irradiation over Ti-TUD-1-supported Keggin-type molybdenum heteropolyacid catalysts.

Table 1.
Oxidative desulfurization of petroleum fuels and model sulfur compounds.
Upgrading of tire pyrolysis oil into heating oil through ODS was carried out by Ahamad et al. [5]. They reported the best desulfurization activity with hydrogen peroxide–acetic acid mixture. A mixture of hydrogen peroxide and formic acid was also found to be effective for ODS of tire pyrolysis oil [20]. Al-Lal et al. [21] desulfurized tire pyrolysis oil with 8700 ppm of sulfur under ultrasound using a formic acid and hydrogen peroxide combination at 70 °C for 30 min. They succeeded in removing 53% of the sulfur from the tire pyrolysis oil. A mixture of pyrolysis char, formic acid, and hydrogen peroxide was used for the ODS of the naphtha fraction of tire pyrolysis oil by Bunthid et al. [6]. The char was found to be effective for desulfurization through adsorption and oxidation.
Mesoporous materials such as MCM-41 and SBA-15 are often used as catalyst supports as they have a high specific surface area (up to 1000 m2/g) and wide pores (∼4 nm) for the adsorption of bulky molecules. Polikarpova et al. [22] studied the ODS of model and real fuels over molybdenum, tungsten, and vanadium oxides supported on mesoporous silica MCM-41. A study by Sikarwar et al. [23] proved that Mo/MCM-41 can be a potential catalyst for the ODS of DBT from liquid fuels. Similarly, SBA-15 loaded with molybdenum oxide was found to be an effective catalyst for oxidative desulfurization [24].
Mesoporous alumina as a catalyst support was prioritized over other supports due to its stable pore structures, easy preparation, and low cost [25,26]. Similarly, mesoporous TUD-1 support has been considered a valuable catalyst carrier due to its tunable textural properties, high stability, and the possibility of the substitution of several metals in its framework [27]. It has been found that the incorporation of titanium in microporous and mesoporous silica supports can promote oxidation due to its Lewis acid character [28,29]. Oxidative desulfurization of petroleum crudes was studied over supported and unsupported heteropoly acid catalysts [30,31]. However, research on ODS of tire pyrolysis oil over heteropolyacid catalysts is limited in the literature. Moreover, catalysts supported on mesoporous Ti-Al2O3 and Ti-TUD-1 have not been studied for the oxidative desulfurization of tire pyrolysis oil. In this study, two different series of heteropoly molybdic acid-loaded catalysts were prepared based on Ti-Al2O3 and Ti-TUD-1 supports. The impact of titanium substitution in both supports on ODS was investigated. Efficiencies of various oxidants such as H2O2, cumene hydroperoxide, and tert-butyl hydroperoxide were studied for ODS tire pyrolysis oil. An ANOVA statistical analysis was carried out with optimal catalysts and oxidants to investigate the significance of process parameters.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Ti-Al2O3 Supports and HPMo Supported Catalysts
Titania-incorporated mesoporous Al2O3 supports were prepared by following the synthesis method mentioned in the literature with few modifications [32]. The chemicals used were Pluronic F127, ethanol (EtOH), isopropanol (iPrOH), aluminum tert-butoxide (C12H27AlO3), titanium isopropoxide (C12H28O4Ti), and water (H2O). These chemicals were combined as discussed below following a molar ratio of 1 C12H27AlO3:1 F127:8 EtOh:6 iPrOH:2 H2O in addition to titanium isopropoxide based on the required Ti/Al molar ratio. Typically, an appropriate amount of Pluronic F127 was dissolved in a mixture of ethanol and isopropanol under continuous stirring at 50 °C, which was followed by the addition of aluminum tert-butoxide. The resulting solution was then stirred for about 30 min, and then the required amount of titanium isopropoxide was added dropwise and stirred for 30 min. Finally, the calculated quantity of water was added dropwise and stirred for another 15 min. The resultant gel was kept overnight at room temperature. The gel was transferred into an autoclave and heated at 80 °C for 48 h. After hydrothermal treatment, the resulted material was filtered and then calcined in a muffle furnace at 550 °C for 6 h to remove the F127 surfactant. A series of titania-incorporated mesoporous Al2O3 supports with Ti/Al of 0, 0.0125, 0.025, and 0.05 was prepared by this one-pot synthesis approach. Heteropolymolybdic acid (HPMo)-loaded Ti-Al2O3 catalysts were prepared by an incipient wet impregnation technique. The prepared supports were loaded with 20 wt% of HPMo using methanol solution of phosphomolybdic acid. The loaded support was dried for 6 h at 100 °C and calcined at 400 °C for 2 h with a ramp rate of 1 °C/min. The final catalysts are labeled as HPMo/Ti-Al2O3(X), where X represents the molar ratio of Ti/Al.
2.2. Synthesis of Ti-TUD-1 Supports and HPMo Supported Catalysts
Titania-incorporated TUD-1 supports were synthesized by the sol-gel method mentioned in the literature with minor changes [33]. Typically, 20 g of tetraethyl orthosilicate was added to the required amount of titanium butoxide and stirred for 15 min. To this mixture, 14.3 g of triethanolamine was added and vigorously stirred for 1 h, and then 5 g of deionized water was added dropwise under stirring for another 30 min. Finally, 13 g of tetraethylammonium hydroxide solution (35 wt% in H2O) was added and stirred for another 2 h. A gel was formed which was aged at 30 °C for 24 h. The resultant mixture was dried at 100 °C for 24 h. After drying, the material was subjected to hydrothermal treatment in an autoclave at 200 °C for 6 h and calcined at 600 °C for 6 h with a ramp rate of 1 °C/min. Based on this procedure, four different TUD-1 supports with Ti/Si of 0, 0.0125, 0.025, and 0.05 were prepared. For the preparation of Ti-TUD-1 catalysts, the prepared supports were loaded with 20 wt% of HPMo using phosphomolybdic acid. Typically, a required amount of methanol solution of phosphomolybdic acid hydrate was added to TUD-1 support. The mixture was dried at 100 °C for 4 h and then calcined in a muffle furnace at 400 °C for 2 h with a ramp rate of 1 °C/min. The catalysts prepared based on TUD-1 are denoted as HPMo/Ti-TUD-1(X), where X is the Ti/Si molar ratio.
2.3. Supports and Catalysts Characterization
The textural properties such as surface area, pore volume, and pore diameter of the Ti-Al2O3 and Ti-TUD-1 supports and their corresponding HPMo-loaded catalysts were measured using a Micromeritics ASAP 2020 instrument (Micromeritics Instrument Corporation, Norcross, GA, USA). Before analysis, all the samples were degassed at 200 °C. The surface area was calculated from adsorption-desorption of nitrogen at −196 °C by the multipoint Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) method. The pore volume was calculated by the amount of N2 adsorbed at the condition P/Po = 0.95. The pore diameter and pore size distribution were determined using the Barret–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) method [34].
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy with pyridine (Pyridine FTIR) as a probe molecule was used for differentiating Lewis and Brønsted acid sites of catalysts. The catalyst sample was exposed to pyridine vapors and then degassed at 70 °C to remove residual pyridine and then the spectroscopic study was done in a Bruker Vertex 70 FTIR spectrometer (Bruker Corporation, Billerica, MA, USA). NH3-temperature-programmed desorption (NH3-TPD) study was carried out in a ChemBET-3000TPR/TPD analyzer (Quantachrome, Boynton Beach, FL, USA). In a quartz U tube, 40 mg of the sample was degassed 300 °C under the flow of helium for 30 min. The degassed sample was purged with 15% NH3 in He at 100 °C. TPD profile was obtained by heating the sample at a ramp rate of 10 °C/min from 100 to 650 °C.
XRD analysis was performed in the wide-angle range (2θ = 10 to 90°) with a Bruker AXS D8 diffractometer (Bruker Corporation, Billerica, MA, USA) using a high-intensity radiation source of Cu Kα generated at 40 kV and 40 mA with λ = 0.15406. The scanning of every sample was performed at a rate of 3° per min. The X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) data were obtained using a AXIS Supra system (Kratos Analytical, Manchester, UK) equipped with a 500-mm Rowland circle monochromated Al K-α (1486.6 eV) source. The high-resolution scans of several regions were obtained using 0.05 eV steps and a pass energy of 20 eV. The data was processed with Casa XPS software.
2.4. Catalytic Oxidative Desulfurization
Preliminary catalyst screening tests were conducted using light gas oil (LGO) due to the limited availability of tire pyrolysis oil. LGO had a sulfur content of 0.6 wt%, which is similar to the sulfur content of tire pyrolysis oil. The catalyst screening experiments were performed in a 250-mL Parr batch reactor. The most active catalyst in each series was applied for ODS of tire pyrolysis oil with a sulfur content of 0.72 wt%. The efficiency of different oxidants, namely, hydrogen peroxide, cumene hydroperoxide, and tert-butyl hydroperoxide, was evaluated over the best catalyst. In a typical catalytic ODS run, after completion, the reactor was cooled down to room temperature, and all the gases were vented out. The biphasic reaction mixture was filtered to remove the catalyst, and then aqueous and oil phases were separated using a separating funnel. The oxidized sulfur compounds from the oil phase were removed by solvent extraction using methanol. The ODS product sample was analyzed for sulfur using the Antek 9000 N/S analyzer as per the ASTM 5453 method. The aqueous phase was analyzed for molybdenum by Thermo Scientific iCAP 7000 series ICP-OES spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.5. Process Parameter Optimization
The impacts of process conditions on ODS of tire pyrolysis oil were investigated over an optimal catalyst. The process conditions were optimized using the central composite design (CCD) in Design Expert® software (version 6.0.11, State-Ease Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA). As given in Table 2, the run temperature, amount of catalyst, and oxidant/sulfur (O/S) molar ratio were varied in the range: 35–70 °C, 5–13 wt%, and 3–10, respectively, in a set of 20 experiments. The feed amount and reaction time were kept constant at 40 g and 2 h, respectively.

Table 2.
Design of experiment for process optimization.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Catalyst Characterization
The wide-angle XRD spectra depicted in Figure 2 show the fingerprint of Keggin-type phosphomolybdic acid in the HPMo/Ti-TUD-1 type catalysts [35]. These Keggin ion peaks are absent in the HPMo/Ti-Al2O3 catalysts. The basic OH groups of Al2O3 in the Ti-Al2O3 support are known to interact with phosphomolybdic acid and depolymerize the polyoxometallate (Keggin) anion [36]. Due to depolymerization, the Keggin structure of phosphomolybdic acid is not preserved on the Ti-Al2O3 support, unlike Ti-TUD-1. The XRD pattern of the catalysts does not show characteristic peaks of bulk TiO2. The absence of titania peaks in XRD indicates the non-existence of bulk TiO2 species (anatase, rutile) on the supports.
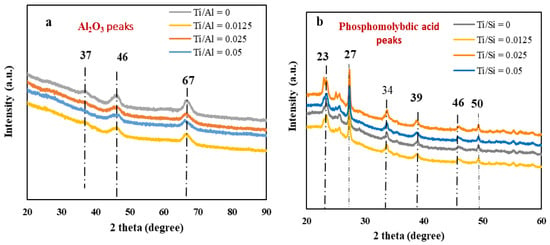
Figure 2.
XRD spectra of (a) HPMo/Ti-Al2O3 and (b) HPMo/Ti-TUD-1 catalysts.
The nitrogen adsorption-desorption isotherms of HPMo/Ti-Al2O3 and HPMo/ Ti-TUD-1 catalysts are shown in Figure 3. Both types of catalysts show the Type IV isotherm with an H1 hysteresis loop that is characteristic of mesoporous materials. Textural properties such as the BET surface area, pore volume, and BJH pore diameter of the supports and their respective catalysts as determined by N2 physisorption are given in Table 3. The loading of the phosphomolybdic acid reduces the surface area and pore volume of supports significantly due to the filling of mesopores by the Keggin anion (large cluster of twelve MO6 octahedra), which has a kinetic diameter of around 1.2 nm [37].
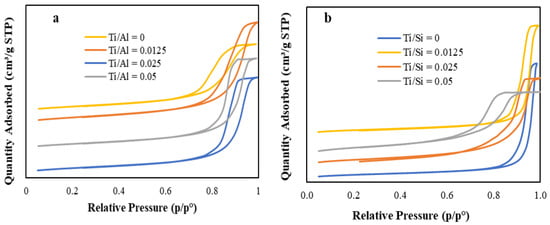
Figure 3.
N2 isotherm of (a) HPMo/Ti-Al2O3 and (b) HPMo/Ti-TUD-1 catalysts.

Table 3.
Textural properties of supports and catalysts.
The NH3 temperature-programmed desorption study was carried out to quantify the total acidity of HPMo/Ti-TUD-1 and HPMo/Ti-Al2O3 catalysts. The total acidity of each catalyst is given in Table 3. In each series, the amount of acid sites is gradually increasing with an increase in the Ti content of catalysts. Lewis and Brønsted acidic sites of catalysts were determined by pyridine FTIR analysis and spectra are shown in Figure 4. Pyridine adsorption on HPMo/Ti-Al2O3 and HPMo/Ti-TUD-1 series results in bands at 1448, 1539, 1488 cm−1, which are characteristic of Lewis acid (LA), Brønsted acid (BA), and overlap of Brønsted and Lewis acid sites, respectively [34]. The pyridine FTIR study confirms that HPMo/Ti-Al2O3 and HPMo/Ti-TUD-1 catalysts contain both Brønsted and Lewis acid sites.
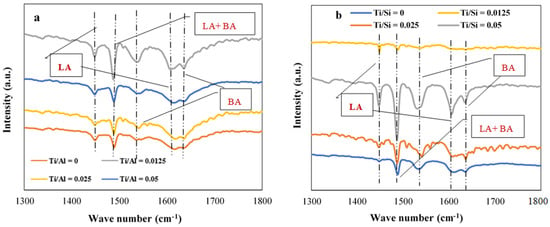
Figure 4.
Pyridine-FTIR spectra of (a) HPMo/Ti-Al2O3 and (b) HPMo/Ti-TUD-1 catalysts.
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy was performed to study the coordination environment and oxidation states of Ti in HPMo/Ti-Al2O3 and HPMo/Ti-TUD-1 catalysts. The Ti 2p core-level spectra of HPMo/Ti-TUD-1and HPMo/Ti-Al2O3 catalysts are shown in Figure 5. Generally, the framework and non-framework Ti species exist in the tetrahedral and octahedral coordination, respectively. The binding energies at 458.4 and 464 eV are associated with 2p3/2 and 2p1/2 orbital spin electrons of tetrahedral coordinated Ti (IV) species [37]. The intensities of these peaks are increasing with the Ti loading and appear predominant for the Ti/Si(Al) ratio of 0.05. The XPS result confirms the successful substitution of Ti in the Al2O3 and TUD-1 frameworks.
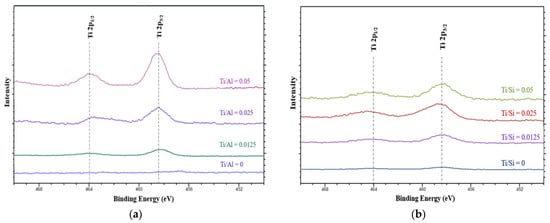
Figure 5.
Ti 2p XPS of (a) HPMo/Ti-Al2O3 and (b) HPMo/Ti-TUD-1 catalysts.
3.2. Catalyst Screening for Oxidative Desulfurization
The catalyst screening experiments were performed using light gas oil and hydrogen peroxide oxidant and the sulfur removal activities of both series are shown in Figure 6. The desulfurization trend confirms that the Lewis acidity associated with Ti influences the removal of sulfur by promoting the oxidation activity of HPMo. In both series, the promotion effect of Ti reaches its optimum when the Ti/Si(Al) ratio is 0.025. A similar promotional effect of Ti on the ODS activity of HPMo with heavy gas oil was observed in our earlier study [37]. The optimum catalysts of both series, which were identified in ODS of LGO were tested for ODS of tire pyrolysis oil. As shown in Figure 7, HPMo/Ti-TUD-1(0.025) shows better ODS activity than HPMo/Ti-Al2O3 (0.025) with the highest sulfur removal efficiency of 45.2% in tire pyrolysis oil. The loading of HPMo on Ti-Al2O3 support does not promote the ODS activity. As evidenced by XRD, the interaction of Al2O3 with HPMo depolymerizes polyoxometallate anion, as a result, the Keggin structure of phosphomolybdic acid is not preserved on the Ti-Al2O3 support, unlike Ti-TUD-1, and thus, the loading of HPMo on the Ti-Al2O3 support does not promote ODS activity.
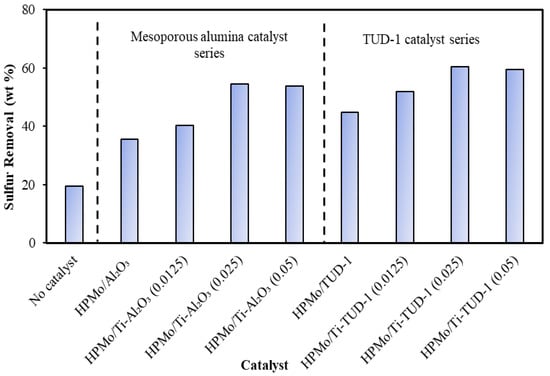
Figure 6.
ODS of light gas oil over HPMo/Ti-Al2O3 and HPMo/Ti-TUD-1 catalysts: catalyst/feed = 0.05; T = 70 °C; oxidant = 30% H2O2; H2O2/S = 10; t = 2 h; and stirring rate = 550 rpm.
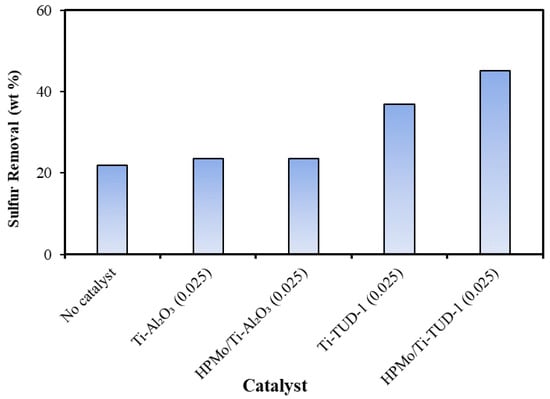
Figure 7.
ODS of tire pyrolysis oil over HPMo/Ti-Al2O3 (0.025) and HPMo/Ti-TUD-1(0.025) catalyst/feed = 0.05; T = 70 °C; oxidant = 30% H2O2; H2O2/S = 10; t = 2 h; and stirring rate = 550 rpm.
The ODS activity of HPMo/TUD-1 catalyst dropped significantly when the feedstock was switched from light gas oil to tire pyrolysis oil. This is due to the differences in the composition of sulfur compounds among these feedstocks. The ODS reactivity order is as follows: dibenzothiophene > benzothiophene > thiophene [38]. The hydrodesulfurization reactivity is in the reverse order of ODS. The light gas oil used in this study was hydrodesulfurized and thus contains mostly dibenzothiophene-type sulfur compounds, which are refractory to hydrodesulfurization but highly reactive for ODS. On the other hand, the tire pyrolysis oil (not treated for hydrodesulfurization) contains all types of sulfur compounds (both ODS reactive and ODS unreactive sulfur compounds).
Among the prepared catalysts, HPMo/Ti-TUD-1(0.025), which had maximum desulfurization activity with tire pyrolysis oil, was used to investigate the efficiency of various oxidants at an oxidant to sulfur molar ratio of 10. During the ODS process, the oxidant provides oxygen to sulfur to form sulfone and sulfoxide. Oxidants such as hydrogen peroxide, cumene hydroperoxide, and tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP) were screened for the ODS of tire pyrolysis oil. A blank experiment was also conducted without an oxidant. As shown in Figure 8, hydrogen peroxide and cumene peroxide were found to be better oxidants than tert-butyl hydroperoxide for the ODS of tire pyrolysis oil. Generally, TBHP is a stronger oxidant than H2O2. However, the efficiency of an oxidant in an ODS reaction over a mesoporous catalyst depends on its diffusion rate through mesopores and its ability to interact with the Mo = O of heteropoly acid to form hydroperoxymolybdate [37]. Since TBHP is bulkier than H2O2, its diffusion ability through its mesoporous structure and its rate of hydroperoxymolybdate formation are expected to be slower than H2O2. Among cumene peroxide and hydrogen peroxide, the latter is less expensive and is used for further studies.
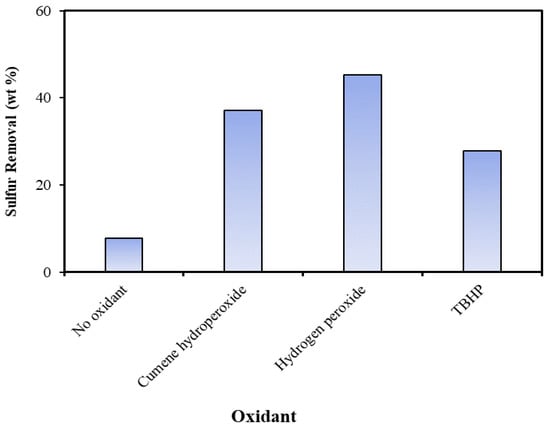
Figure 8.
Effects of oxidants on ODS of tire pyrolysis oil over HPMo/TiTUD-1 (0.025) catalyst: catalyst/feed ratio = 0.05; T = 70 °C; oxidant/S = 0; t = 2 h; and stirring = 550 rpm.
3.3. Optimization of ODS Parameters
HPMo/Ti-TUD-1(0.025) catalyst and hydrogen peroxide were used for the parameter optimization study. Three-dimensional graphs were plotted to determine the effects of interactions between two parameters while keeping the third parameter constant at its mid-value. The effects of temperature, the amount of catalyst in oil, and the oxidant/sulfur (O/S) molar ratio are shown in Figure 9. Figure 9a shows a significant increase in desulfurization when the amount of catalyst and the O/S ratio are increased to their mid-values. Figure 9b displays that temperature and catalyst amount moderately influence desulfurization. In Figure 9a,c significant enhancement in desulfurization is noticed when the O/S ratio is increased from three to six. The central point coordinates in the 3D plots represent the corresponding optimum parameter values. In this study, the HPMo/TiTUD-1 (0.025) catalyst showed its highest desulfurization of 44.3% when the temperature, catalyst amount, and O/S ratio were kept at 50 °C, 8 wt%, and 6, respectively. Typically, ODS requires two moles of oxidant for one mole of sulfur. In this study, the optimum oxidant to sulfur ratio was found to be six. This suggests that the oxidation of unsaturates also occurred under the reaction conditions. To confirm this, the olefin hydrogen content of feedstock and the ODS product oil was determined by 1H-NMR. The olefin hydrogen content of the ODS product oil was significantly lower than that of the feedstock, evidencing the consumption of hydrogen peroxide by olefins. As given in Table 4, the ODS activity of HPMo/Ti-TUD-1 is comparable with other reported catalysts for the desulfurization of tire pyrolysis oil.
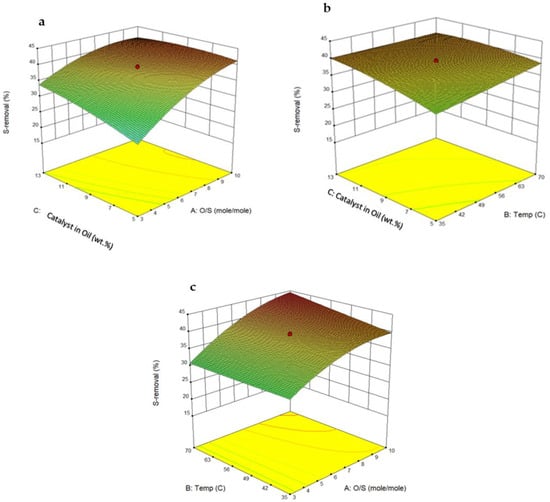
Figure 9.
Three-dimensional response plots: (a) effects of catalyst amount (wt%) and O/S (molar ratio) on sulfur removal, (b) effects of catalyst amount (wt%) and temperature (°C) on sulfur removal, and (c) effects of temperature (°C) and O/S (molar ratio) on sulfur removal.

Table 4.
Comparison of HPMo/Ti-TUD-1 catalyst for ODS of tire pyrolysis oil with other reported catalysts.
An analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted to evaluate the impacts of process parameters such as temperature, the O/S molar ratio, and the catalyst amount on sulfur removal. The ANOVA results are given in Table 5. The statistical significance of the model was established by the F-test and p-test. The model has F and p values of 9.12 and 0.0009, respectively. These values mean that the model has a high level of fit to experimental data. The p-values of <0.05 and F-values of >1.0 indicate that independent variables A and C and quadratic parameter A2 are significant. F-values of individual variables show that the reaction temperature is a statistically less significant factor for the removal of sulfur during the ODS of tire pyrolysis oil.

Table 5.
ANOVA for ODS of tire pyrolysis oil over HPMo/Ti-TUD-1(0.025) catalyst.
A regression analysis of the experimental results showed the best fit to the second-order polynomial shown in Equation (1) for predicting the sulfur removal performance of the HPMo/Ti-TUD-1(0.025) catalyst:
Sulfur removal (%) = 39.08 + 5.56A + 1.16B+ 1.87C + 1.24AB − 1.84AC − 1.10BC − 2.56A2 + 0.06B2 − 0.84C2
3.4. Kinetics of the ODS of Tire Pyrolysis Oil
The ODS of tire pyrolysis oil is classified as a three-phase heterogeneous reaction as it includes the oil phase (tire pyrolysis oil), the aqueous phase (aqueous hydrogen peroxide), and the solid phase (catalyst) [41]. The external mass transfer effects are assumed to be negligible in this study due to a high rate of stirring. The ODS reaction is shown in Figure 10, where the transfer of oxygen from hydrogen peroxide to sulfur compounds is facilitated by a catalyst to form sulfone and sulfoxide. The reaction mechanism of ODS over HPMo/Ti-TUD-1 was discussed in detail in our previous publication [37].
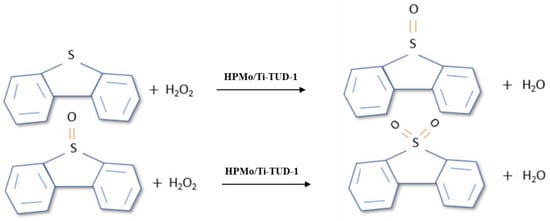
Figure 10.
Oxidation reaction pathway of sulfur compounds.
Since hydrogen peroxide is used in excess for ODS, the reaction kinetic is assumed as the zero-order to an oxidant [41,42]. The kinetics of oxidative desulfurization reaction over mesoporous catalysts were studied by Chamack et al. [43]. The oxidation of sulfur into sulfone was found to be a rate-controlling step. The heat transfer and mass transfer limitations were assumed to be negligible. The surface reactions are shown in Equations (2) and (3):
where C = the sulfur compound in tire pyrolysis oil, * refers to an activated surface site that adsorbs C and produces C*, and k1, kdes, and kads correspond to the rate constants for surface reaction, desorption, and adsorption, respectively. As shown in Equation (3), C* is converted to CO, which is the rate-limiting step. The rate of reaction (r) could be expressed by considering the Langmuir–Hinshelwood mechanism as:
r = k1 [C*]
With the steady-state approximation, the concentration of activated intermediate is in accordance with the Equation (5) as follows:
[C*] = kads [C] [*]/(kdes + k1)
If the rate constant is defined as shown in Equation (6):
then the rate equation is equal to the following Equation (7):
[k] = k1 kads [*]/(kdes + k1)
r = k [C]
So, it can be seen that the ODS reaction is pseudo-first-order to [C]. If [C]0: concentration of C at t = 0 and [C]t: concentration of C at t = t, the reaction rate constant (k) can be expressed by Equation (8):
ln ([C]0/[C]t) = kt
The plot of ln ([C]0/[C]t) versus the reaction time provides the rate constant. In this study, the kinetic of the ODS of tire pyrolysis oil was explored over HPMo/TiTUD-1 (0.025) catalyst at different run times: 15, 30, 60, and 120 min. The plot of ln ([C]0/[C]t) versus the run time is shown in Figure 11. The kinetic data fit well to the pseudo-first-order kinetic rate. The previous studies on the catalytic oxidation of sulfur compounds of fuel oils have reported that ODS typically follows the pseudo-first-order reaction [37,44].
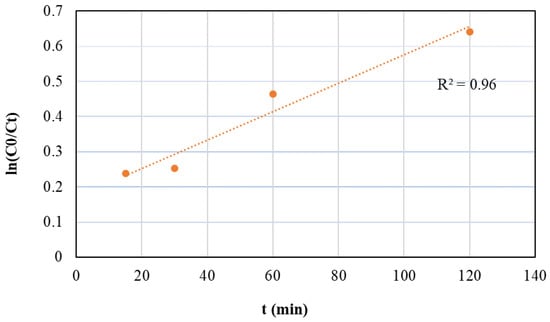
Figure 11.
Pseudo-first-order kinetics of ODS runs with HPMo/Ti-TUD-1(0.025) catalyst; catalyst/feed ratio = 0.05; T = 70 °C; oxidant, 30% H2O2; H2O2/S = 10; and stirring = 550 rpm.
3.5. Catalyst Reusability
The reusability study was conducted to foresee the economic feasibility of the ODS of tire pyrolysis oil with HPMo/TiTUD-1 (0.025) catalyst. The spent catalyst was washed with toluene, dried in the oven at 100 °C for 1 h, and then calcined at 500 °C. The catalyst was regenerated after each run. The reusability was tested three times at the optimized condition. The fresh, first-time recycled, second-time recycled, and third-time recycled catalysts showed desulfurization of 45.2, 43, 41 and 38 wt%, respectively. The sulfur removal efficiency of the HPMo/TiTUD-1 (0.025) catalyst gradually dropped by 4–6 wt% after each use. This is due to the leaching of molybdenum Keggin ions from the surface of TUD-1 by aqueous hydrogen peroxide. The leaching of Keggin ions is verified by comparing the XRD patterns of the spent catalyst after first and third regenerations with the fresh catalyst. As it can be seen from Figure 12, all the characteristic peaks of molybdenum Keggin ions gradually decrease after each regeneration, evidencing the leaching of HPMo. To confirm HPMO leaching, ICP analysis of the aqueous phase of each reusability run was carried out. The presence of 2000–2500 ppm of Mo in the aqueous phase of all three recycle runs evidences the gradual leaching of HPMo by 30% aq H2O2.
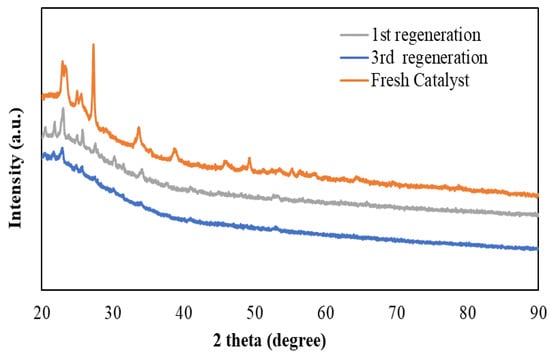
Figure 12.
XRD of spent catalyst HPMo/Ti-TUD-1(Ti/Si = 0.025) after regeneration.
4. Conclusions
Phosphomolybdic acid-loaded titania-incorporated mesoporous Al2O3 and TUD-1 catalysts were successfully prepared and evaluated for the catalytic oxidation desulfurization of tire pyrolysis oil at mild process conditions. The XRD results substantiate that HPMo retained its Keggin structure in the TUD-1-supported catalysts, whereas it suffered decomposition in the Al2O3-supported catalysts. The XPS characterization results evidenced the successful incorporation of Ti into the Al2O3 and TUD-1 frameworks. The Pyridine FTIR results authenticated the presence of both Brønsted and Lewis acid sites in HPMo/Ti-Al2O3 and HPMo/Ti-TUD-1 catalysts. Titanium evidenced a promotional effect on the ODS activity of phosphomolybdic acid. Between the two series of catalysts, HPMo/Ti-TUD-1(0.025) was found to be the most active catalyst for the ODS of tire pyrolysis oil. As per the ANOVA statistical study, the reaction temperature was found to be a less significant factor than the concentrations of oxidant and catalyst for promoting the ODS of tire pyrolysis oil. The sulfur oxidation on HPMo/Ti-TUD-1(0.025) followed the pseudo-first-order kinetics. The results of the catalyst regeneration study show that the catalyst can be reused at least three times with a marginal loss in sulfur removal efficiency.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology—J.K., S.V. and P.B.; validation and investigation—J.K.; writing—original draft preparation—J.K. and S.V.; writing review and editing—S.V. and A.K.D.; supervision and funding acquisition—A.K.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank AirScience Technologies and MITACS for funding this project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bockstal, L.; Berchem, T.; Schmetz, Q.; Richel, A. Devulcanisation and reclaiming of tires and rubber by physical and chemical processes: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnecko, H. Rubber recycling. Macromol. Symp. 1998, 135, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazyari, A.; Khodadadi, A.A.; Mamaghani, A.H.; Beheshtian, J.; Thompson, L.T.; Mortazavi, Y. Microporous titania–silica nanocomposite catalyst-adsorbent for ultra-deep oxidative desulfurization. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 180, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quek, A.; Balasubramanian, R. Liquefaction of waste tires by pyrolysis for oil and chemicals—A review. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2013, 101, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Ahmad, M.I.; Naeem, K.; Humayun, M.; Sebt-E-Zaeem, S.; Faheem, F. Oxidative desulfurization of tire pyrolysis oil. Chem. Ind. Chem. Eng. Q. 2016, 22, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bunthid, D.; Prasassarakich, P.; Hinchiranan, N. Oxidative desulfurization of tire pyrolysis naphtha in formic acid/H2O2/pyrolysis char system. Fuel 2010, 89, 2617–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Huang, C.; Li, D.; Huo, P.; Wang, M.; Han, L.; Chen, G.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Derived oil production by catalytic pyrolysis of scrap tires. Chin. J. Catal. 2016, 37, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, D.T.; Agboola, O.; Ayeni, A.O. Pyrolysis of waste tyre for high-quality fuel products: A review. AIMS Energy 2020, 8, 869–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, H.; Teoh, Y.; Sher, F.; Jamil, M.; Murtaza, D.; Al Qubeissi, M.; Hassan, M.U.; Mujtaba, M. Current Status and Potential of Tire Pyrolysis Oil Production as an Alternative Fuel in Developing Countries. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.N.; Park, H.C.; Choi, H.S. A Comprehensive Review on Catalytic Oxidative Desulfurization of Liquid Fuel Oil. Catalysts 2019, 9, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Estephane, G.; Lancelot, C.; Blanchard, P.; Toufaily, J.; Hamiye, T.; Lamonier, C. Sulfur compounds reactivity in the ODS of model and real feeds on W–SBA based catalysts. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 13714–13721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doustkhah, E.; Mohtasham, H.; Hasani, M.; Ide, Y.; Rostamnia, S.; Tsunoji, N.; Assadi, M.H.N. Merging periodic mesoporous organosilica (PMO) with mesoporous aluminosilica (Al/Si-PMO): A catalyst for green oxidation. Mol. Catal. 2020, 482, 110676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Chen, A.; Saxena, S.; Vedachalam, S.; Dalai, A.K.; Zhang, W.; Emwas, A.H.; Roberts, W.L. Ultrasound-assisted oxidative desulfurization of Arabian extra light oil (AXL) with molecular characterization of the sulfur compounds. Fuel 2021, 305, 121612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhu, W.; Li, H.; Chao, Y.; Xun, S.; Chang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Z. Mechanism and optimization for oxidative desulfurization of fuels catalyzed by Fenton-like catalysts in hydrophobic ionic liquid. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2014, 382, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Zhu, W.; Xun, S.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, W.; Qin, Y.; Li, H. Deep oxidative desulfurization of dibenzothiophene using low-temperature-mediated titanium dioxide catalyst in ionic liquids. Fuel 2015, 159, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzalinia, A.; Mirzaie, A.; Nikseresht, A.; Musabeygi, T. Ultrasound-assisted oxidative desulfurization process of liquid fuel by phosphotungstic acid encapsulated in a interpenetrating amine-functionalized Zn(II)-based MOF as catalyst. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 34, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.-S.; Yang, G.-Y. Recent Advances in Polyoxometalate-Catalyzed Reactions. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 4893–4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Lin, S.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, S.; Xiong, J.-R. Ultrasound-assisted oxidative desulfurization of bunker-C oil using tert-butyl hydroperoxide. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2013, 20, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, D.M.; Isah, A.G.; Musa, U.; Shehu, A.; Abdullahi, Y.N. Comparative study on sulphur reduction from heavy petroleum—Solvent extraction and microwave irradiation approach. Int. J. Energy Environ. 2012, 3, 949–960. [Google Scholar]
- Dogan, O.; Çelik, M.B.; Ozdalyan, B. The effect of tire derived fuel/diesel fuel blends utilization on diesel engine performance and emissions. Fuel 2012, 95, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Lal, A.-M.; Bolonio, D.; Llamas, A.; Lapuerta, M.; Canoira, L. Desulfurization of pyrolysis fuels obtained from waste: Lube oils, tires and plastics. Fuel 2015, 150, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polikarpova, P.; Akopyan, A.; Shigapova, A.; Glotov, A.; Anisimov, A.; Karakhanov, E. Oxidative Desulfurization of Fuels Using Heterogeneous Catalysts Based on MCM-41. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 10898–10903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikarwar, P.; Kumar, U.A.; Gosu, V.; Subbaramaiah, V. Catalytic oxidative desulfurization of DBT using green catalyst (Mo/MCM-41) derived from coal fly ash. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 1736–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akopyan, A.; Polikarpova, P.; Gul, O.; Anisimov, A.; Karakhanov, E. Catalysts Based on Acidic SBA-15 for Deep Oxidative Desulfurization of Model Fuels. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 14611–14619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Tian, Y.; Wang, G.; Zeng, D.; Xu, Q.; Cui, J. Ultra-deep oxidative desulfurization of fuel with H2O2catalyzed by molybdenum oxide supported on alumina modified by Ca2+. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 48208–48213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Čejka, J. Organized mesoporous alumina: Synthesis, structure and potential in catalysis. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2003, 254, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telalović, S.; Ramanathan, A.; Mul, G.; Hanefeld, U. TUD-1: Synthesis and application of a versatile catalyst, carrier, material…. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 642–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, C.; Wang, Y.J.; Xu, J.H.; Luo, G.S. Oxidative desulfurization of DBT with H2O2catalysed by TiO2/porous glass. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraile, J.M.; Gil, C.; Mayoral, J.A.; Muel, B.; Roldán, L.; Vispe, E.; Calderón, S.; Puente, F. Heterogeneous titanium catalysts for oxidation of dibenzothiophene in hydrocarbon solutions with hydrogen peroxide: On the road to oxidative desulfurization. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 180, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, H. Polyoxometalate as effective catalyst for the deep desulfurization of diesel oil. Catal. Today 2010, 149, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Li, S.; Jin, Q.; Zhao, J. Review on oxidative desulfurization of fuel by supported heteropolyacid catalysts. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 82, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesaint, C.; Glomm, W.R.; Borg, Ø.; Eri, S.; Rytter, E.; Øye, G. Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous alumina with large pore size and their performance in Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2008, 351, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Z.; Gianotti, E.; Jansen, J.C.; Peters, J.A.; Marchese, L.; Maschmeyer, T. One-step synthesis of a highly active, mesoporous, titanium-containing silica by using bifunctional templating. Chem.—A Eur. J. 2001, 7, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badoga, S.; Sharma, R.V.; Dalai, A.K.; Adjaye, J. Hydrotreating of Heavy Gas Oil on Mesoporous Mixed Metal Oxides (M–Al2O3, M = TiO2, ZrO2, SnO2) Supported NiMo Catalysts: Influence of Surface Acidity. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 18729–18739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marosi, L.; Platero, E.E.; Cifre, J.; Areán, C.O. Thermal dehydration of H3 + xPVxM12 − xO40·yH2O Keggin type heteropolyacids; formation, thermal stability and structure of the anhydrous acids H3PM12O40, of the corresponding anhydrides PM12O38.5 and of a novel trihydrate H3PW12O40·3H2O. J. Mater. Chem. 2000, 10, 1949–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Veen, J.A.R.; Hendriks, P.A.J.M.; Andrea, R.R.; Romers, E.J.G.M.; Wilson, A.E. Chemistry of phosphomolybdate adsorption on alumina surfaces. 2. The molybdate/phosphated alumina and phosphomolybdate/alumina systems. J. Phys. Chem. 1990, 94, 5282–5285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedachalam, S.; Boahene, P.E.; Dalai, A.K. Oxidative Desulfurization of Heavy Gas Oil over a Ti–TUD-1-Supported Keggin-Type Molybdenum Heteropolyacid. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 15299–15312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.; Vedachalam, S.; Dalai, A.K. Review on recent advances in adsorptive desulfurization. Fuel Process. Technol. 2021, 214, 106685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhu, M.; Jones, I.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D. Desulfurization of Spent Tire Pyrolysis Oil and Its Distillate via Combined Catalytic Oxidation using H2O2 with Formic Acid and Selective Adsorption over Al2O3. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 6209–6219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.N.; Choi, M.K.; Park, H.C.; Choi, H.S. Purifying of Waste Tire Pyrolysis Oil Using an S-ZrO2/SBA-15-H2O2 Catalytic Oxidation Method. Catalysts 2020, 10, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sengupta, A.; Kamble, P.D.; Basu, J.K.; Sengupta, S. Kinetic Study and Optimization of Oxidative Desulfurization of Benzothiophene Using Mesoporous Titanium Silicate-1 Catalyst. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Li, G.; Wang, X. Kinetics and Mechanism of Liquid-Phase Oxidation of Thiophene over TS-1 Using H2O2Under Mild Conditions. Catal. Lett. 2004, 92, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamack, M.; Mahjoub, A.; Aghayan, H. Cesium salts of tungsten-substituted molybdophosphoric acid immobilized onto platelet mesoporous silica: Efficient catalysts for oxidative desulfurization of dibenzothiophene. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 255, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houda, S.; Lancelot, C.; Blanchard, P.; Poinel, L.; Lamonier, C. Oxidative Desulfurization of Heavy Oils with High Sulfur Content: A Review. Catalysts 2018, 8, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).