Fetal Hypoxia Detection Using Machine Learning: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
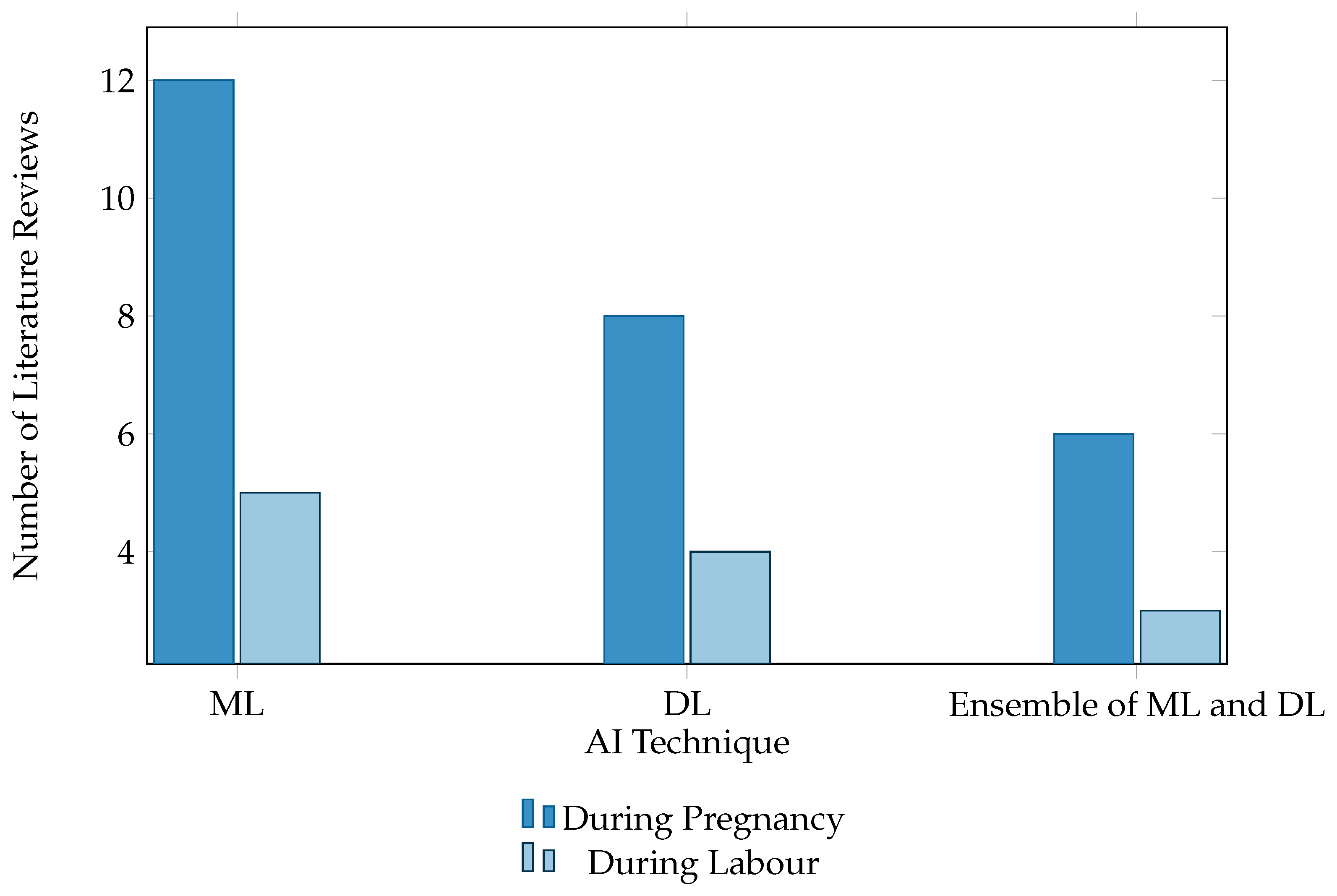
2. Review of the Literature
2.1. Fetal Hypoxia during Pregnancy Using ML
2.2. Fetal Hypoxia during Labor Using ML
2.3. Fetal Hypoxia during Pregnancy Using DL
2.4. Fetal Hypoxia during Labor Using DL
2.5. Fetal Hypoxia during Pregnancy Using Ensemble
2.6. Fetal Hypoxia during Labor Using Ensemble
3. Gap Analysis
4. Summary Tables of Earlier Utilized Algorithm
5. Discussion
6. Future Work
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AdaBoost | Adaptive Boosting |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| AUC | Area Under the ROC Curve |
| BT | Bagging Tree |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| CTG | Cardiotocograph |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| DT | Decision Tree |
| EFM | electronic fetal monitoring |
| FHR | Fetal Heart Rate |
| FIGO | International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics |
| GB | Gradient Boosting |
| GBM | Gradient Boosting Machine |
| GBT | Gradient Boosted Tree |
| KNN | K-Nearest Neighbors |
| LARA | Long-term Antepartum Risk Analysis system |
| LightGBM | Light Gradient Boosting Machine |
| LM | Levenberg-Marquardt |
| LR | Logistic Regression |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| MLP | Multilayer Perceptron |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| MSE | Mean Squared Error |
| NB | Naïve Bayes |
| NN | Neural Network |
| PNN | Probabilities Neural Network |
| ResNet | Residual Network |
| RF | Random Forest |
| RP | Recurrence Plot |
| SMOTE | Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| UC | Uterine Contraction |
| XGBoost | eXtreme Gradient Boosting |
References
- Li, X.; Zheng, D.; Zhou, S.; Tang, D.; Wang, C.; Wu, G. Approximate entropy of fetal heart rate variability as a predictor of fetal distress in women at term pregnancy. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2005, 84, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, K.A.; Brandon, D.H. Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy: Pathophysiology and experimental treatments. Newborn Infant Nurs. Rev. 2011, 11, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mejhim, F.M.; Al-Najashi, S.S. Trends in perinatal mortality at King Fahd Hospital of the University, Al-Khobar, Saudi Arabia: A ten years study. J. Fam. Community Med. 1998, 5, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Mendis, L.; Palaniswami, M.; Brownfoot, F.; Keenan, E. Computerised Cardiotocography Analysis for the Automated Detection of Fetal Compromise during Labour: A Review. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santo, S.; Ayres-de Campos, D.; Costa-Santos, C.; Schnettler, W.; Ugwumadu, A.; Da Graça, L.M.; Collaboration, F.C. Agreement and accuracy using the FIGO, ACOG and NICE cardiotocography interpretation guidelines. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2017, 96, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayres-de Campos, D.; Spong, C.Y.; Chandraharan, E. FIGO consensus guidelines on intrapartum fetal monitoring: Cardiotocography. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2015, 131, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, D.; Harrison, A.; Zhang, L.; Yan, K.; Wang, Y.; Cai, J.; Miao, S.; Lu, L. Artificial Intelligence in Radiology. In Artificial Intelligence in Medicine; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 265–289. [Google Scholar]
- Ben M’Barek, I.; Jauvion, G.; Vitrou, J.; Holmström, E.; Koskas, M.; Ceccaldi, P.F. DeepCTG® 1.0: An interpretable model to detect fetal hypoxia from cardiotocography data during labor and delivery. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1190441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karabulut, E.M.; Ibrikci, T. Analysis of cardiotocogram data for fetal distress determination by decision tree based adaptive boosting approach. J. Comput. Commun. 2014, 2, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, R.; Hussain, A.; Al-Jumeily, D.; Baker, T.; Khattak, A. Classification of foetal distress and hypoxia using machine learning approaches. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Computing Methodologies: 14th International Conference, ICIC 2018, Wuhan, China, 15–18 August 2018; Part III 14. pp. 767–776. [Google Scholar]
- Improta, G.; Ricciardi, C.; Amato, F.; D’Addio, G.; Cesarelli, M.; Romano, M. Efficacy of machine learning in predicting the kind of delivery by cardiotocography. In Proceedings of the XV Mediterranean Conference on Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing–MEDICON 2019: Proceedings of MEDICON 2019, Coimbra, Portugal, 26–28 September 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 793–799. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Comert, Z.; Deng, Y. Computer-aided diagnosis system of fetal hypoxia incorporating recurrence plot with convolutional neural network. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cömert, Z.; Şengür, A.; Budak, Ü.; Kocamaz, A.F. Prediction of intrapartum fetal hypoxia considering feature selection algorithms and machine learning models. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2019, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.Z.; Ahmed, R.; Sadia, U.H.; Tultul, M.S.I.; Chakma, R. Decision tree method using for fetal state classification from cardiotography data. J. Adv. Eng. Comput. 2020, 4, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaggaf, W.; Cömert, Z.; Nour, M.; Polat, K.; Brdesee, H.; Toğaçar, M. Predicting fetal hypoxia using common spatial pattern and machine learning from cardiotocography signals. Appl. Acoust. 2020, 167, 107429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxi, S. Machine learning based clinical decision support system to predict fetal hypoxia in women during antenatal check-up. Paripex Indian J. Res. 2021, 10, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pini, N.; Lucchini, M.; Esposito, G.; Tagliaferri, S.; Campanile, M.; Magenes, G.; Signorini, M.G. A machine learning approach to monitor the emergence of late intrauterine growth restriction. Front. Artif. Intell. 2021, 4, 622616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gude, V.; Corns, S. Integrated Deep Learning and Supervised Machine Learning Model for Predictive Fetal Monitoring. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedia, A.; Sanjitha, N.; Agarwal, R.V.; Manasa, T.P.; Naheed, Y. Fetal Health Classification based on CTG using Machine Learning. Int. J. Adv. Res. Innov. Ideas Educ. 2023, 9, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Davis Jones, G.; Cooke, W.; Vatish, M. Identifying high-risk pre-term pregnancies using the fetal heart rate and machine learning. medRxiv 2024, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Mooney, C.; O’Boyle, D.; Finder, M.; Hallberg, B.; Walsh, B.H.; Henshall, D.C.; Boylan, G.B.; Murray, D.M. Predictive modelling of hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy risk following perinatal asphyxia. Heliyon 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, M.; Yi, H.; Lai, F.; Liu, M.; Zeng, R.; Kang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Rong, J.; Wang, H.; Bai, J.; et al. CTGNet: Automatic analysis of fetal heart rate from cardiotocograph using artificial intelligence. Matern.-Fetal Med. 2022, 4, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Mukherjee, H.; Roy, K.; Saha, C. Fetal Health Classification from Cardiotocograph for Both Stages of Labor—A Soft-Computing-Based Approach. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben M’Barek, I.; Jauvion, G.; Ceccaldi, P.F. Computerized cardiotocography analysis during labor–A state-of-the-art review. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2023, 102, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mennickent, D.; Rodríguez, A.; Opazo, M.C.; Riedel, C.A.; Castro, E.; Eriz-Salinas, A.; Appel-Rubio, J.; Aguayo, C.; Damiano, A.E.; Guzmán-Gutiérrez, E.; et al. Machine learning applied in maternal and fetal health: A narrative review focused on pregnancy diseases and complications. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1130139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundar, C.; Chitradevi, M.; Geetharamani, G. Classification of cardiotocogram data using neural network based machine learning technique. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2012, 47, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Yılmaz, E. Fetal state assessment from cardiotocogram data using artificial neural networks. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2016, 36, 820–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cömert, Z.; Kocamaz, A. A study of artificial neural network training algorithms for classification of cardiotocography signals. Bitlis Eren Univ. J. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Khullar, V.; Singh, H.P.; Bala, M. Perinatal hypoxia diagnostic system by using scalable machine learning algorithms. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. 2019, 8, 1954–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma’sum, M.; Intan, P.; Jatmiko, W.; Krisnadhi, A.; Setiawan, N.; Suarjaya, I. Improving deep learning classifier for fetus hypoxia detection in cardiotocography signal. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Workshop on Big Data and Information Security (IWBIS), Bali, Indonesia, 11 October 2019; pp. 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Aswathi Mohan, P.P.; Uma, V. Fetal Hypoxia Detection using CTG Signals and CNN Models. Int. Res. J. Adv. Sci. Hub 2023, 5, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaidullah, S.M.; Das, S.; Mahmud, M.; Kaiser, M.S.; Roy, K.; Saha, C.K.; Goswami, K. A machine learning pipeline to classify foetal heart rate deceleration with optimal feature set. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, N.; Li, R.; Liu, Q.; Ma, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Hong, S. Deep Learning with Information Fusion and Model Interpretation for Health Monitoring of Fetus based on Long-term Prenatal Electronic Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring Data. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.15337. [Google Scholar]
- Fergus, P.; Hussain, A.; Al-Jumeily, D.; Huang, D.S.; Bouguila, N. Classification of caesarean section and normal vaginal deliveries using foetal heart rate signals and advanced machine learning algorithms. Biomed. Eng. Online 2017, 16, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrozziello, A.; Jordanov, I.; Papageorghiou, T.; Redman, W.; Georgieva, A. Deep learning for continuous electronic fetal monitoring in labor. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 5866–5869. [Google Scholar]
- Alkanan, M. A Study on Classifying Fetal Distress from Large-Scale Cardiotocographic (CTG) Data Using Different Machine Learning Approaches. Ph.D. Thesis, Tokyo University of Technology, Hachioji, Japan, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, F.; Wu, H.; Luz, S.; Townsend, R.; Stock, S. Detecting Intrapartum Fetal Hypoxia from Cardiotocography Using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 Computing in Cardiology (CinC), Tampere, Finland, 4–7 September 2022; Volume 498, pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, K.M. Application of Machine Learning Techniques to Classify Fetal Hypoxia. Ph.D. Thesis, National College of Ireland, Dublin, Ireland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fergus, P.; Selvaraj, M.; Chalmers, C. Machine learning ensemble modelling to classify caesarean section and vaginal delivery types using Cardiotocography traces. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 93, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riskyana, P.; Ma’sum, M.; Alfiany, N.; Jatmiko, W.; Kekalih, A.; Bustamam, A. Ensemble learning versus deep learning for Hypoxia detection in CTG signal. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Workshop on Big Data and Information Security (IWBIS), Bali, Indonesia, 11 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hoodbhoy, Z.; Noman, M.; Shafique, A.; Nasim, A.; Chowdhury, D.; Hasan, B. Use of machine learning algorithms for prediction of fetal risk using cardiotocographic data. Int. J. Appl. Basic Med. Res. 2019, 9, 226. [Google Scholar]
- Dixit, R.R. Predicting Fetal Health using Cardiotocograms: A Machine Learning Approach. J. Adv. Anal. Healthc. Manag. 2022, 6, 43–57. [Google Scholar]
- Chidambaram, M.; Joy, J. Comparative Analysis of Ensemble Learning Methods for Enhancing Fetal Health Prediction using Cardiotocography. Int. J. Sci. Res. Comput. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2022, 8, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, A.M.; O’Toole, J.M.; Proietti, J.; Livingstone, V.; Mitra, S.; Marnane, W.P.; Finder, M.; Dempsey, E.M.; Murray, D.M.; Boylan, G.B.; et al. Machine learning for the early prediction of infants with electrographic seizures in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Epilepsia 2023, 64, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Duhayyim, M.; Abbas, S.; Al Hejaili, A.; Kryvinska, N.; Almadhor, A.; Mughal, H. Ensemble Learning for Fetal Health Classification. Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 2023, 47, 823–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asfaw, D.; Jordanov, I.; Impey, L.; Namburete, A.; Lee, R.; Georgieva, A. Multimodal Deep Learning for Predicting Adverse Birth Outcomes Based on Early Labour Data. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


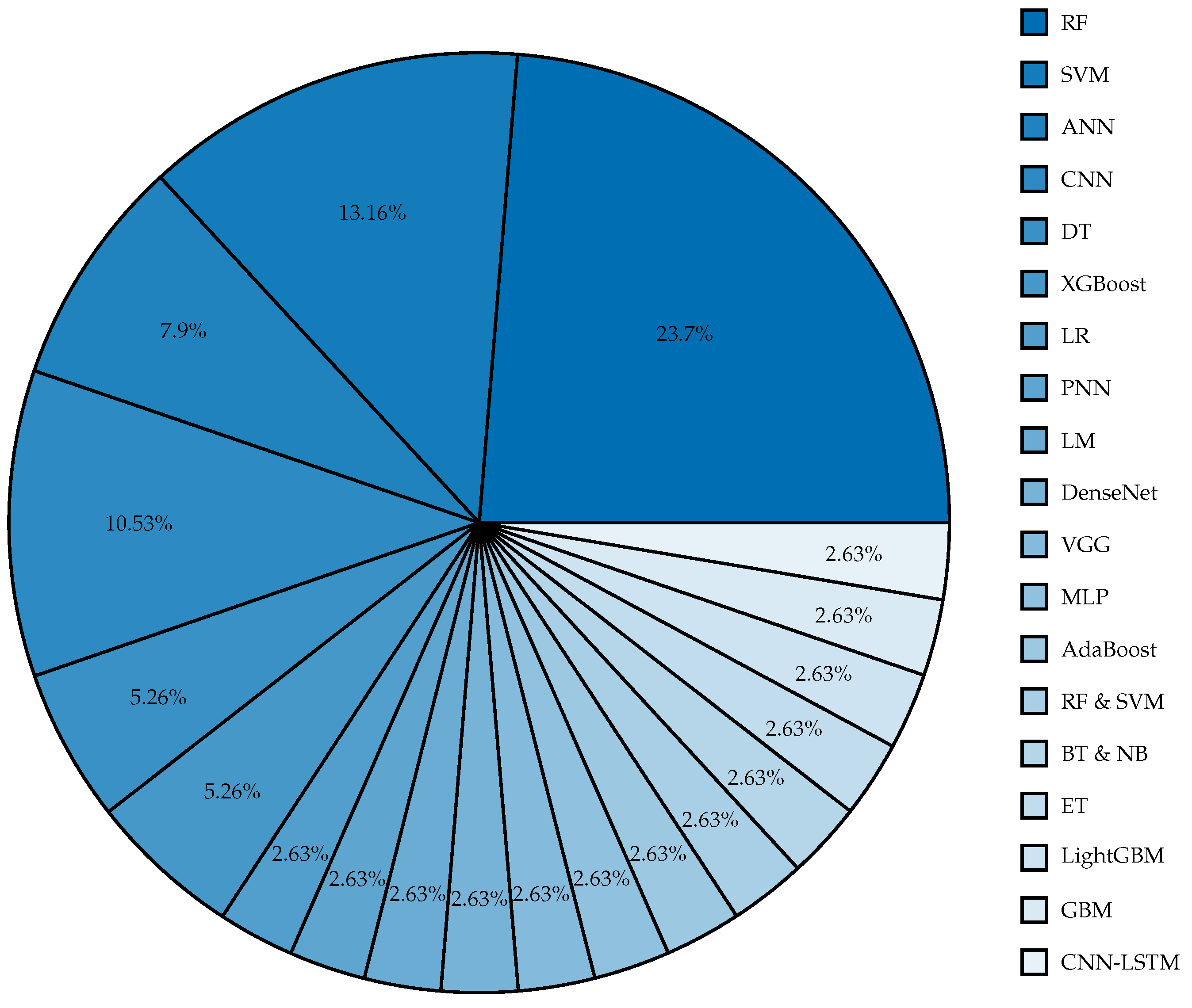
| Ref. | Yr | Dataset | Best Technique | Accuracy | AUC | Sensitivity | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| During Pregnancy | |||||||
| [9] | ’14 | CTG-UCI ML | DT | 95.01% | - | - | - |
| [10] | ’18 | CTU-CHB | RF | 95% | - | - | - |
| [11] | ’19 | Private Dataset | RF | 87.6% | - | - | - |
| [12] | ’19 | CTG-UCI ML | RF | 97% | 0.97 | 99% | 98% |
| [13] | ’19 | CTG-UHB | SVM | 88.85% | - | 77.4% | - |
| [14] | ’20 | CTG-UCI ML | DT | 98.7% | - | - | - |
| [15] | ’20 | Private Dataset | SVM | 94.75% | - | - | - |
| [16] | ’21 | CTG-UCI ML | RF | 94.71% | - | - | - |
| [17] | ’21 | Private Dataset | SVM | 93% | - | 93% | - |
| [18] | ’22 | Private Dataset | SVM | 72.22% | - | 66.66% | - |
| [19] | ’23 | CTG-UCI ML | RF | 96% | - | - | - |
| [20] | ’24 | Private Dataset | RF | - | - | 76.2% | 81.7% |
| During Labor | |||||||
| [21] | ’21 | CTG-UHB | RF | 94% | - | - | - |
| [22] | ’22 | Private Dataset | SVM | - | - | - | 86.85% |
| [23] | ’23 | Private Dataset | RF | - | - | 96.4% | - |
| [24] | ’23 | CTG-UHB | LR | - | 0.756 | - | - |
| [25] | ’23 | Review Paper | RF | - | 0.92 | - | - |
| Ref. | Yr | Dataset | Best Technique | Accuracy | AUC | Sensitivity | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| During Pregnancy | |||||||
| [26] | ’12 | CTG-UCI ML | ANN | - | - | - | 97.84% |
| [27] | ’16 | CTG-UCI ML | PNN | 92.15% | - | - | 85.16% |
| [28] | ’17 | CTG-UCI ML | LM | 91.27% | 0.9877 | 82.36% | - |
| [29] | ’20 | CTG-UCI ML | CNN | 98.69% | 98.70% | 99.29% | - |
| [30] | ’20 | CTU-CHB | DenseNet | - | - | - | 81% |
| [31] | ’23 | CTU-CHB | VGG16 | - | - | - | 81% |
| [32] | ’23 | CTG-UHB | MLP | 97.94% | - | 97.94% | 97.94% |
| [33] | ’24 | Peking University | CNN | 81.6% | 0.872 | - | 0.415 |
| During Labor | |||||||
| [34] | ’17 | CTG-UHB | ANN | - | 99% | 94% | 100% |
| [35] | ’22 | Oxford EFM | CNN | - | - | TPR 44% at FPR 15% | - |
| [36] | ’22 | Multiple Hospitals | CNN | - | 95.8% | - | - |
| [37] | ’23 | CTG-UHB | ANN | - | - | 100% | 97% |
| Ref. | Yr | Dataset | Best Technique | Accuracy | AUC | Sensitivity | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| During Pregnancy | |||||||
| [38] | ’16 | CTG-UCI ML | AdaBoost | 98.70% | - | - | - |
| [39] | ’18 | CTG-UCI ML | RF and SVM | - | 96% | 87% | - |
| [40] | ’19 | Private Dataset | BT and NB | - | - | - | 0.45 |
| [41] | ’19 | CTG-UCI ML | XGBoost | - | - | 92% | - |
| [42] | ’21 | CTG-UCI ML | ET | 93.66% | - | 93.66% | - |
| [43] | ’22 | CTG-UCI ML | LightGBM | 95.9% | - | - | - |
| During Labor | |||||||
| [44] | ’22 | Private Dataset | GB | - | 0.746 | - | - |
| [45] | ’23 | CTG-UCI ML | XGBoost | 99% | - | - | - |
| [46] | ’23 | Private Dataset | CNN-LSTM | - | 0.85 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alharbi, N.; Youldash, M.; Alotaibi, D.; Aldossary, H.; Albrahim, R.; Alzahrani, R.; Saleh, W.A.; Olatunji, S.O.; Aldossary, M.I. Fetal Hypoxia Detection Using Machine Learning: A Narrative Review. AI 2024, 5, 516-532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai5020026
Alharbi N, Youldash M, Alotaibi D, Aldossary H, Albrahim R, Alzahrani R, Saleh WA, Olatunji SO, Aldossary MI. Fetal Hypoxia Detection Using Machine Learning: A Narrative Review. AI. 2024; 5(2):516-532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai5020026
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlharbi, Nawaf, Mustafa Youldash, Duha Alotaibi, Haya Aldossary, Reema Albrahim, Reham Alzahrani, Wahbia Ahmed Saleh, Sunday O. Olatunji, and May Issa Aldossary. 2024. "Fetal Hypoxia Detection Using Machine Learning: A Narrative Review" AI 5, no. 2: 516-532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai5020026
APA StyleAlharbi, N., Youldash, M., Alotaibi, D., Aldossary, H., Albrahim, R., Alzahrani, R., Saleh, W. A., Olatunji, S. O., & Aldossary, M. I. (2024). Fetal Hypoxia Detection Using Machine Learning: A Narrative Review. AI, 5(2), 516-532. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai5020026







