Abstract
In dry flue gas treatment systems, gas–solid interactions are modulated by the reagent molecular composition and physical attributes. In the present investigation, sodium- and calcium-based sorbents were screened for structural and compositional variations for their subsequent application in sulphur dioxide capture. Mined sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) in its unprocessed form and commercial-grade hydrated lime (Ca(OH)2) were subjected to morphological analyses, employing scanning electron microscopy (SEM), particle size distribution (PSD), Brunauer–Emmett–Teller surface area evaluation, and Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) pore structure classification. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) was leveraged for a surface elemental chemical assessment. Pursuant to the BET report, Ca(OH)2 presented a larger specific surface area (4.2360 m2/g) as opposed to NaHCO3 (0.2303 m2/g), which was supported by the weighted mean value (D43) from the PSD analysis. Although Ca(OH)2 had a higher pore volume (0.089822 cm3/g), the totality of the NaHCO3 pore size (117.312 Å) was classified as mesoporous. The SEM assessment suggested that the lower NaHCO3 surface area stemmed from larger particle sizes. The FTIR spectrum indicated a greater carbonate concentration in the NaHCO3 sorbent material, which also structures the pore morphology of the reagent. These findings offer critical information pertinent to the intricate dry flue gas desulphurisation process. The data generated will help us to design fixed bed experiments in a subsequent study.
1. Introduction
The availability of highly reactive and cost-effective sorbents for dry flue gas desulphurisation (DFGD) creates a conundrum for process designers. Unlike wet and semi-dry systems that use slurry reagents, the sulphation activity in the DFGD occurs between a powdered sorbent and the target sulphur dioxide (SO2) gas [1]. In hindsight, maximal SO2 capture profits from an ideal gas–solid interaction, which is influenced by the sorbent reaction area and pore morphology. Hydrated lime (Ca(OH)2) is primarily preferred in dry systems due to its high reactivity and finer particle sizes that induce a higher surface area compared to limestone (CaCO3) and lime (CaO) [2]. Unrefined sodium-based sorbents can serve as standard reagent compounds with a higher reactivity than Ca2+, Equation (1), as suggested by the increased reactivity of Na+, Equation (2), in the reactivity series.
The sulphation process benefits from the interaction with a strong basic Ca(OH)2 salt (pH ≈ 12.4) as the reaction kinetics with an acidic gas are faster. This chemistry enables the maintenance of pH levels during the neutralisation process, thereby enhancing reaction performance. Sodium bicarbonate (pH ≈ 8.3) displays amphoteric properties and can be applied as an alkali reagent in sulphation reactions. Despite being a weak base, several investigators have indicated high SO2 removal efficiencies with sodium-based sorbents [2,3,4].
Gas–solid intimate contact in DFGD is directed by the ability of the flue gas to effectively diffuse into desulphuriser particles, initiate a surface chemical reaction, and diffuse through the product layer to the unreacted surface. As a result, particle size affects the surface area and the availability of active sites after product layer formation. Generally, the molar volume of the product (sulphite–SO32− and sulphate–SO42−) formed after SO2 capture is larger than the unreacted particle, which reduces the accessible reaction area [5].
In this paper, Ca(OH)2 and NaHCO3 will be subject to scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET), Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH), particle size distribution (PSD), and ex situ Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) analysis to study the surface properties and functional groups concerning SO2 adsorption. Emphasis will be based on particle size, pore distribution, and pore density. Ca(OH)2 can be generated through a reaction of lime (CaO) and water in a hydration procedure, which further upsurges operational costs, particularly in retrofit applications. In contrast, nahcolite is a naturally occurring mineral salt consisting of NaHCO3 that necessitates no formulation processes for desulphurisation. Therefore, it is vital to simultaneously analyse the structural and chemical characteristics of these two sorbents, offering significant insights into the elements influencing their reactivity during SO2 extraction and establishing the basis for enhancing DFGD procedures.
2. Materials and Methods
Sodium bicarbonate in its natural form (nahcolite) was sourced from Botswana Ash (Pty) Ltd. (Botash), Alrode, South Africa. From the energy dispersive systems (EDSs) analysis, NaHCO3 was found to have a mineralogical composition of 98.47% Na2O, 1.38% P2O5, 0.01% CaO, 0.06% TiO2, and 0.07% MnO. Hydrated lime was of commercial grade (86.9 wt. %) from Kayla Africa, Wadeville, South Africa. It had a mineral species of 90.18% CaO, 0.23% Na2O, 1.12% MgO, 0.79% Al2O3, 7.43% SiO2, 0.13% SO3, 0.05% K2O, 0.06% TiO2, 0.12% MnO4, 0.19% SrO, and 0.02% ZrO2.
Nitrogen adsorption–desorption appraised the specific surface area (SSA), pore volume, and pore size using the BET and BJH procedures in a micromeritics analyser. SEM assessments employed a Philips XL-30S machine, while the Malvern Mastersizer 2000 conducted sorbent PSD measurements within the 0.01–2000 μm limit. The PerkinElmer Spectrum Two FTIR device characterised the surface functional groups of the sorbents in the 4500 to 500 cm−1 wavenumber range.
3. Results and Discussion
Subject to N2 adsorption–desorption (77 K), Table 1 revealed that Ca(OH)2 had a higher reaction surface (4.2360 m2/g) for SO2 scrubbing compared to NaHCO3 (0.2303 m2/g). Ideally, a sorbent with a larger exposed surface promotes optimum gas–solid interaction, which is required for a successful sulphation reaction in a dry FGD system [6]. Ca(OH)2 had a pore size of 601.753 Å (60.1753 nm), classified in the macro pore size range (>50 nm) and a volume of 0.089822 cm3/g. NaHCO3 displayed mesopore (2–50 nm) pore sizes of 117.312 Å (11.7312 nm), falling within the ideal region of SO2 capture. In comparison to Ca(OH)2, the NaHCO3 pore volume was lower, at 0.000639 cm3/g [7,8].

Table 1.
Physical properties of Ca(OH)2 and NaHCO3 from BET and BJH analysis.
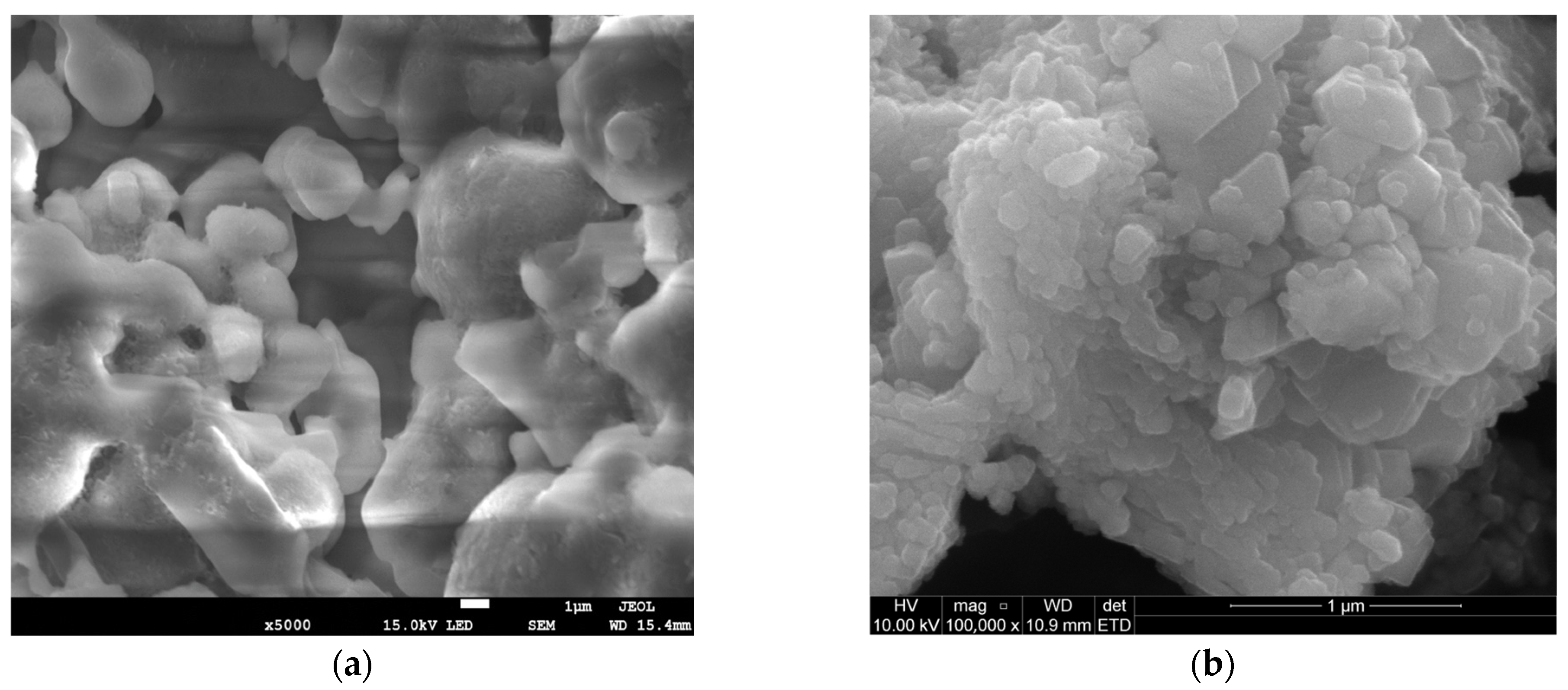
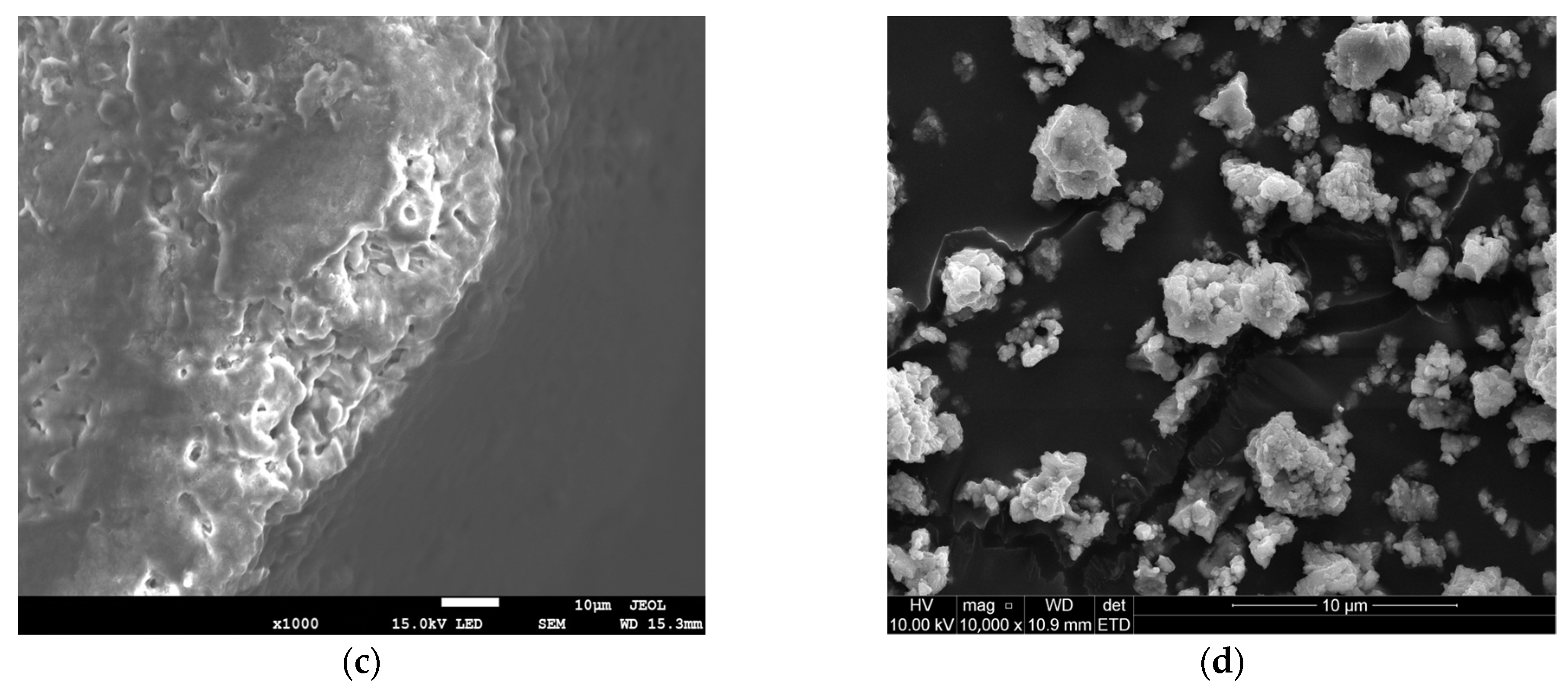
The SEM observations complemented the BET results by revealing a larger NaHCO3 particle size (Figure 1c) as opposed to Ca(OH)2 (Figure 1d), viewed at the same scale of 1 μm. The orientation of the NaHCO3 directly impacted the available reaction area for efficient sulphation reaction. Conventionally, larger particle sizes exhibit lower SA, as seen in Table 1. From Figure 1a, NaHCO3 is characterised by intraparticle pores, which are beneficial for SO2 diffusion and likely stem from the cohesion of irregularly shaped particles (lumps) during material conception [9]. This supplements the pore morphology on the NaHCO3 particle surface, evident in Figure 1c. The Ca(OH)2 structure appears to have a spherical shape and is also formed from the aggregation of smaller independent particles (Figure 1b,d). The uneven clumping of individual particles during hydration results in a void formation [10], although not as pronounced as in NaHCO3. The resulting higher HK maximum pore volume of 0.003861 cm3/g for Ca(OH)2 suggests a microporous pore diameter. Generally, SO2 capture is promoted by a reagent having mesoporous properties as it limits diffusion resistances, compared to the smaller micropores. From this, even though Ca(OH)2 exhibits a higher surface area, raw NaHCO3 can be considered a similarly competitive adsorbent from the dense surface and intraparticle pore existence.
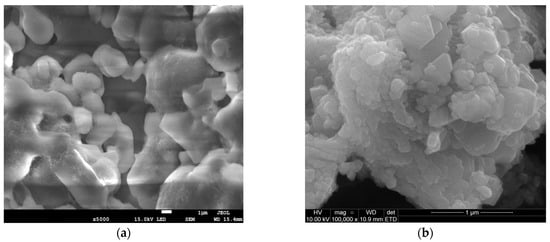
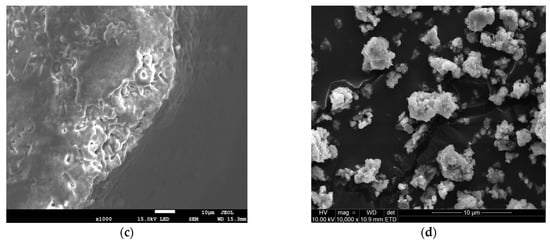
Figure 1.
SEM images of NaHCO3 sorbent—(a,c) and Ca(OH)2 sorbent—(b,d).
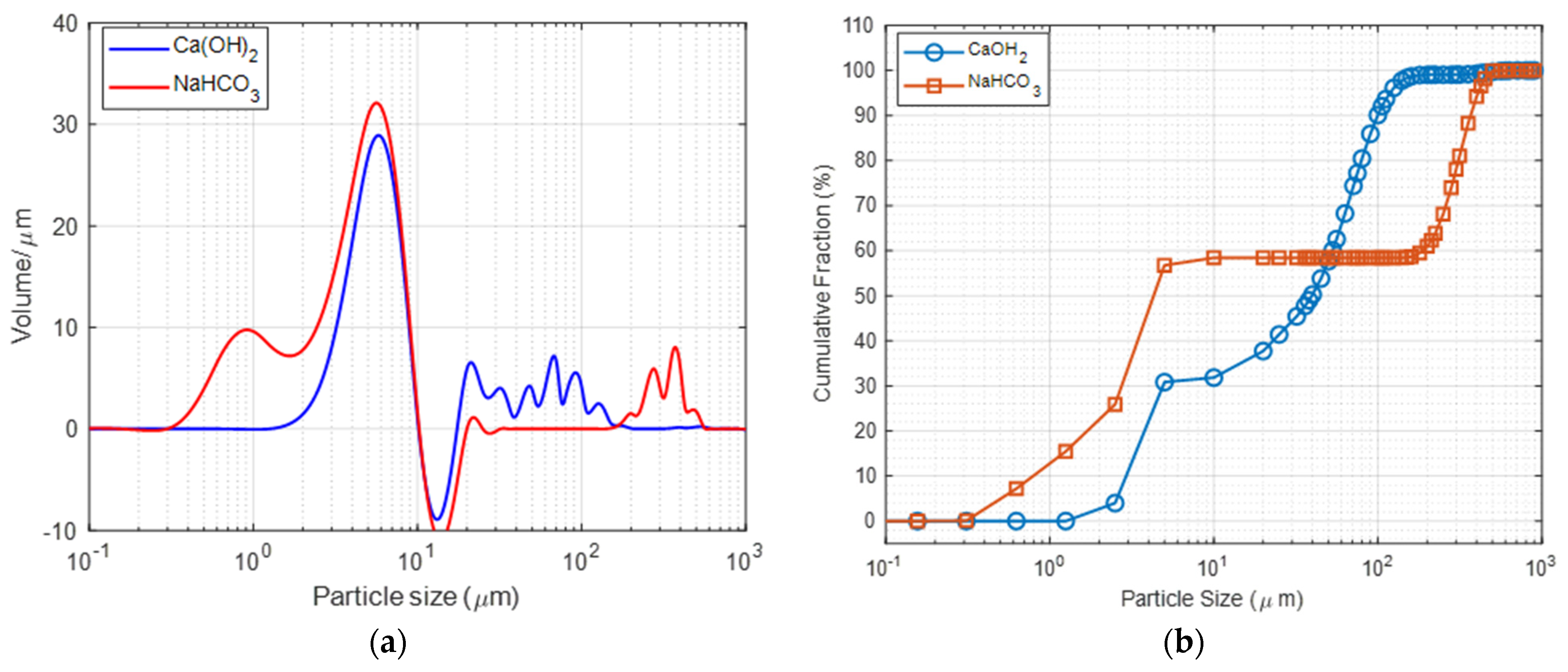
Particle size determines the exposure of active sites to the target acidic gas. Desirable sorbent particles should be small and refined to attain a greater surface area. Figure 2a provides the PSD data for both reagents, indicating a multimodal distribution with various particle size ranges. The mean volume diameter of the smallest particle range is nearly identical, with Ca(OH)2 at 5.77 μm and NaHCO3 at 5.67 μm. However, the nahcolite salt (NaHCO3) includes coarse particles ranging from 100 to 1000 μm. The coarse particle fraction of calcium hydroxide ranges from 10 to 100 m. Ca(OH)2 exhibits a considerably lower weighted mean value (D43) of 47.58 μm as opposed to nahcolite, which has a D43 of 130.833 μm, confirming finer particle orientation. The cumulative distribution plot in Figure 2b illustrates this finding.
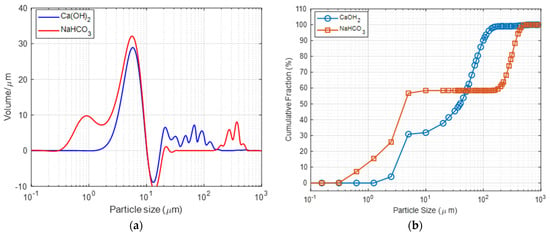
Figure 2.
(a) Particle size distribution and (b) reagent cumulative distribution of the Ca(OH)2 and NaHCO3.
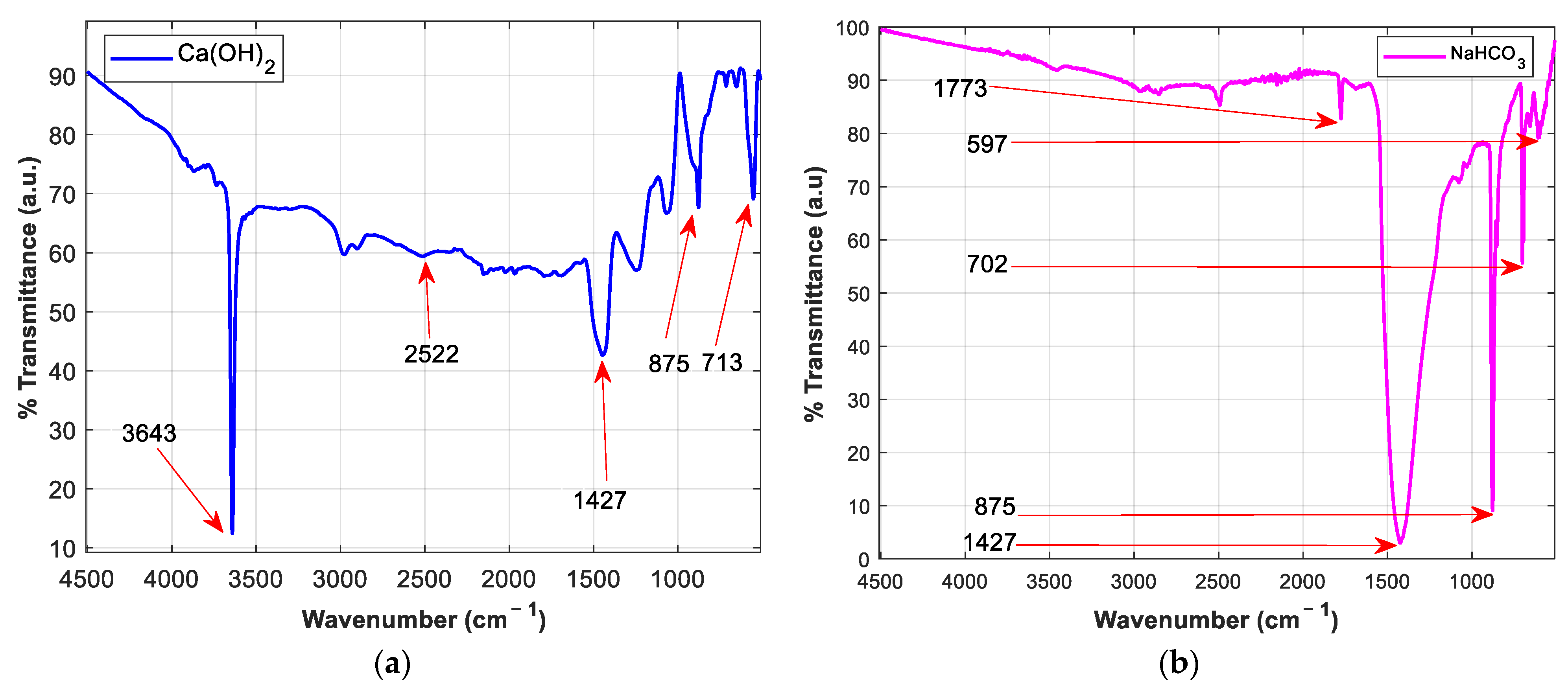
Understanding the chemical bonds necessary for sorbent activity is useful in examining the molecular structural differences between Ca(OH)2 and NaHCO3. The reaction temperature in the DFGD units surpasses 120 °C, ensuring the breakdown of NaHCO3 to Na2CO3 (Equations (3) and (4)) as the active species (popcorn effect), contrary to Ca(OH)2 (Equation (5)) which reacts in its native form [11]. The sulphation byproduct generated mainly comprises a dry sulphite salt. The ex situ FTIR spectrum from Figure 3a displays the sharp hydroxyl stretching band (O–H) at 3643 cm–1 responsible for the strong alkaline property (pH ≈ 12.4), suggesting a hexagonal h-CaO phase. Calcite (CaCO3) formation at 2522 cm–1 corresponds to a reaction with free CO2 whose eventuality reduces the active Ca(OH)2 sites, considering the poor CaCO3 activity in dry FGD. The broad peak at 1427 cm–1 depicts the irregular stretching of CO32−. The O–C–O in-plane bending peak vibrations are marked at 713 cm–1, while the out-of-plane bending is centered at 875 cm–1 [12]. The nahcolite structure in Figure 3b illustrates a higher carbonate concentration at 1427 cm–1 (CO32– group), 875 cm−1 (CO2 out-of-plane bending), and 702 cm–1 (O–C–O bending vibrations). The peaks at 1773 cm–1 and 597 cm–1 relate to HCO3– and OC–(OH), respectively. The formation of the weak carbonic acid (H2CO3) and its interaction with the hydroxyl group (OH) results in the reduced alkalinity of the NaHCO3 sorbent [13]. This feature influences the reactivity of the acid–base sulphation process. As a strong base, Ca(OH)2 has a higher ability to accept protons in a reaction with a strong acid, ensuring that the reaction process is completed and a stable product is formed. NaHCO3, however, falls second in the reactivity series and hence possesses a greater tendency to engage in a reaction. The contrast presented by the physiochemical properties of these reagents is the motivation to pursue a direct sorbent injection process simulating dry FGD. Both sorbents will be tested for dry SO2 removal, where additional data concerning the reaction mechanisms, spontaneity, and molecular interactions between the gas and the adsorbent will be studied and compared.
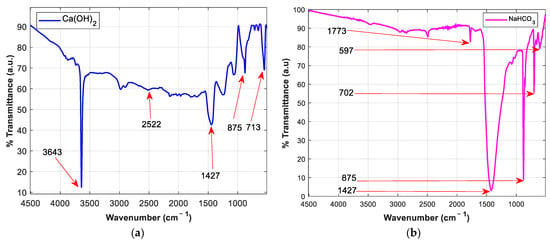
Figure 3.
FTIR spectrum of (a) Ca(OH)2 and (b) NaHCO3 (nahcolite).
4. Conclusions
The screening assessments within this paper were aimed at evaluating the chemical and physical attributes of the Ca(OH)2 and NaHCO3 reagents relevant to dry desulphurisation. It should be noted that NaHCO3 was considered in its raw form (nahcolite) as an alternative, given the higher cost price associated with Ca(OH)2 synthesis techniques. Both sorbents have alkaline properties and can attract acidic SO2 gas in flue gas. Available reaction sites processed by BET and BJH report show Ca(OH)2 would promote more gas–solid contact given the superior SSA of 4.2360 m2/g and pore volume (BJH) of 0.089822 m2/g. Ca(OH)2 had smaller and finer particles as per the SEM micrographs and PSD calculations, attaining a volume mean diameter (D43) of 47.58 µm. Upon chemical reaction, this sorbent possesses performance advantages. Nonetheless, SO2 diffusion through the NaHCO3 particles was stimulated by its mesoporous property of 11.7312 nm, aside from the larger and coarser particles indicated by a D43 of 130.83 µm. Additionally, the internal pores observed in the SEM analysis validated NaHCO3 integration in the sulphation process. Molecular characterisation from the FTIR outcome indicated that the combination of CO32− and HCO3− formed a more significant proportion of the surface chemical groups, from which the hydrogen potential of NaHCO3 was 8.3. Additionally, this involved an interaction with the OH group in the NaHCO3 structure, reducing the basicity. The more significant proportion of the hydroxyl band (OH) in the Ca(OH)2 sorbent outweighed the contaminant CO32– groups; hence, the basic reactivity was scarcely affected. While Ca(OH)2 has beneficial properties based on the characterisation reports, raw NaHCO3 cannot be disregarded as a prospective substitute for DFGD as well as an alternative to what is obtained from the Solvay process.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, R.M. and L.K.; methodology, R.M., L.K., H.R., A.A. and S.K.; formal analysis, R.M., L.K, H.R., A.A. and N.K.; investigation, R.M. and L.K.; resources, L.K., H.R., A.A. and N.K.; data curation, R.M. and L.K.; writing—original draft preparation, R.M.; writing—review and editing, R.M., L.K., H.R., A.A. and S.K.; visualisation, R.M. and L.K.; supervision, L.K., H.R. and A.A.; project administration, L.K., H.R. and A.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Ngeleshi Kibambe for invaluable assistance with the scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis, which greatly contributed to the quality of this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Deng, Y.; Ansart, R.; Baeyens, J.; Zhang, H. Flue Gas Desulphurization in Circulating Fluidised Beds. Energies 2019, 12, 3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, A.M. Low Water FGD Technologies; IEA Clean Coal Centre: London, UK, 2012; Vol December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Walawska, B.; Szymanek, A.; Pajdak, A.; Nowak, M. Flue Gas Desulfurization by Mechanically and Thermally Activated Sodium Bicarbonate. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2014, 16, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidi Bibalani, I.; Ale Ebrahim, H. Kinetic Study of Low-Temperature Sulfur Dioxide Removal Reaction by Sodium Carbonate Using Random Pore Model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 6334–6346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makomere, R.S.; Rutto, H.L.; Koech, L. The Use of Cellulose Nanocrystals to Support Ca(OH)2 Nanoparticles with Diatomite Incorporation in Sulphur Capture at Low Temperatures: Optimisation and Modelling. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2023, 48, 8871–8885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maina, P.; Mbarawa, M. Enhancement of Lime Reactivity by Addition of Diatomite. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 1910–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.-Q.; Gao, X.-M.; Lin, B.; Hua, D.-X.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Xiao, W.-D. An Efficient Calcium-Based Sorbent for Flue Gas Dry-Desulfurization: Promotion Roles of Nitrogen Oxide and Oxygen. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koech, L.; Everson, R.; Neomagus, H.; Rutto, H. Dissolution Kinetics of South African Coal Fly Ash and the Development of a Semi-Empirical Model to Predict Dissolution. Chem. Ind. Chem. Eng. Q. 2015, 21, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudibyo, S.; Suharto, S.; Rarasati, S.A.A.; Wulandari, Y.R.; Shintawati, S.; Rohman, F.S. Optimization of Sodium Bicarbonate Production from Ammonium Hydroxide Using a Froth Flotation Column. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2022, 45, 1952–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xie, C. Effect of Reaction Conditions on Agglomeration of Aluminum Hydroxide in the Recovery of Waste Aluminum-Catalyst. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 248, 116978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mchabe, D.; Hattingh, B.B.; Koech, L.; Rutto, H.; Neomagus, H.W.J.P. Sodium-Based Flue Gas Desulphurisation for the South African Coal-Fired Power Industry a Review. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2024, 48, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, A.; Chanda, D.K.; Das, P.S.; Ghosh, J.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Dey, A. Synthesis of Nano Calcium Hydroxide in Aqueous Medium. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 99, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelking, L.R. Chapter 93—Alkalinizing and Acidifying Solutions. In Textbook of Veterinary Physiological Chemistry, 3rd ed.; Engelking, L.R., Ed.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 606–611. ISBN 978-0-12-391909-0. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).