Bio-inspired Computation and Applications
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Prof. Dr. Abdelhamid Mellouk
Prof. Dr. Abdelhamid Mellouk
 Prof. Dr. Abdelhamid Mellouk
Prof. Dr. Abdelhamid Mellouk
E-Mail
Website
Guest Editor
Networks & Telecommunications (N&T) Department and Tinc-NET/LiSSi Laboratory, University of Paris-Est (UPEC), Paris, France
Interests: signal, image and video processing; artificial neural networks; wireless sensor network
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Traditional computing technologies have problems with handling the complex cases like pattern recognition, robotic sensors, etc. A new way of using biological concepts in traditional computing technology has been developed, namely bio-inspired computing. Bio-inspired computing (BIC) is focused on the design and development of computer algorithms and models based on living phenomena, biological mechanisms and creature motivations. It could definitely improve understandability
Computing over the years has evolved from a simply mathematical processing machine to a problem-solving entity around reasoning and intelligence. Many scientists and engineers have closely observed some of the biological processes, achieving certain things in a more efficient and simple fashion than traditional computational mechanisms. This has led to the development of various techniques and algorithms that test these biological processes.
Prof. Dr. Abdelhamid Mellouk
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Applied Sciences is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Bio-inspired computing
- BIC
- neural networks
- Algorithms
- Bio-inspired applications
Published Papers (13 papers)
Open AccessArticle
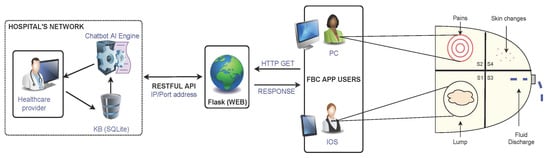
Online Textual Symptomatic Assessment Chatbot Based on Q&A Weighted Scoring for Female Breast Cancer Prescreening
by
Jen-Hui Chen, Obinna Agbodike, Wen-Ling Kuo, Lei Wang, Chiao-Hua Huang, Yu-Shian Shen and Bing-Hong Chen
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 4634
Abstract
The increasing number of female breast cancer (FBC) incidences in the East predominated by Chinese language speakers has generated concerns over women’s medicare. To minimize the mortality rate associated with FBC in the region, governments and health experts are jointly encouraging women to
[...] Read more.
The increasing number of female breast cancer (FBC) incidences in the East predominated by Chinese language speakers has generated concerns over women’s medicare. To minimize the mortality rate associated with FBC in the region, governments and health experts are jointly encouraging women to undergo mammography screening at the earliest suspicion of FBC symptoms. However, studies show that a huge number of women affected by FBC tend to delay medical consultation at its early stage as a result of factors such as complacency due to unawareness of FBC symptoms, procrastination due to lifestyle, and the feeling of embarrassment in discussing private matters especially with medical personnel of the opposite gender. To address these issues, we propose a symptomatic assessment chatbot (SAC) based on artificial intelligence (AI) designed to prescreen women for FBC symptoms via a textual question-and-answer (Q&A) approach. The purpose of our chatbot is to assist women in engaging in communication regarding FBC symptoms, so as to subsequently initiate formal medical consultations for early FBC diagnosis and treatment. We implemented the SAC systematically with some of the latest natural language processing (NLP) techniques suitable for Chinese word segmentation (CWS) and trained the model with real-world FBC Q&A data obtained from a major hospital in Taiwan. The results from our experiments showed that the SAC achieved very high accuracy in FBC assessment scoring in comparison to FBC patients’ screening benchmark scores obtained from doctors.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
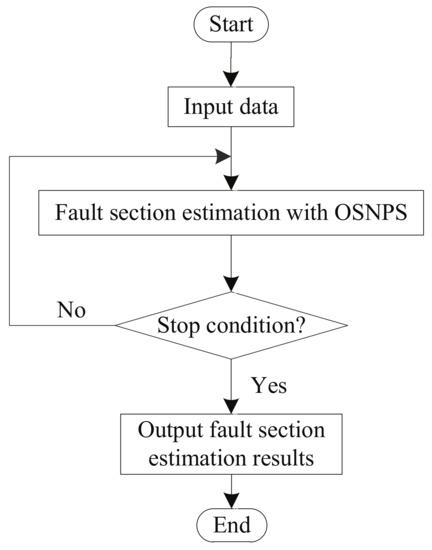
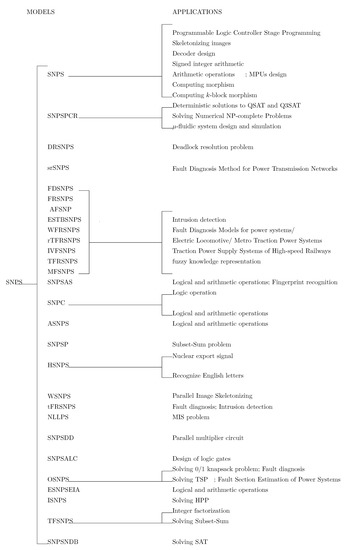
A Review of Power System Fault Diagnosis with Spiking Neural P Systems
by
Yicen Liu, Ying Chen, Prithwineel Paul, Songhai Fan, Xiaomin Ma and Gexiang Zhang
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 3159
Abstract
With the advancement of technologies it is becoming imperative to have a stable, secure and uninterrupted supply of power to electronic systems as well as to ensure the identification of faults occurring in these systems quickly and efficiently in case of any accident.
[...] Read more.
With the advancement of technologies it is becoming imperative to have a stable, secure and uninterrupted supply of power to electronic systems as well as to ensure the identification of faults occurring in these systems quickly and efficiently in case of any accident. Spiking neural P system (SNPS) is a popular parallel distributed computing model. It is inspired by the structure and functioning of spiking neurons. It belongs to the category of neural-like P systems and is well-known as a branch of the third generation neural networks. SNPS and its variants can perform the task of fault diagnosis in power systems efficiently. In this paper, we provide a comprehensive survey of these models, which can perform the task of fault diagnosis in transformers, power transmission networks, traction power supply systems, metro traction power supply systems, and electric locomotive systems. Furthermore, we discuss the use of these models in fault section estimation of power systems, fault location identification in distribution network, and fault line detection. We also discuss a software tool which can perform the task of fault diagnosis automatically. Finally, we discuss future research lines related to this topic.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
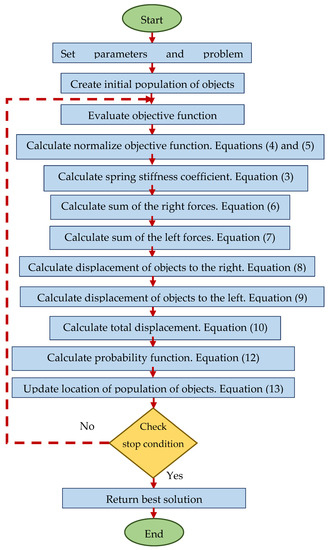
Binary Spring Search Algorithm for Solving Various Optimization Problems
by
Mohammad Dehghani, Zeinab Montazeri, Ali Dehghani, Om P. Malik, Ruben Morales-Menendez, Gaurav Dhiman, Nima Nouri, Ali Ehsanifar, Josep M. Guerrero and Ricardo A. Ramirez-Mendoza
Cited by 38 | Viewed by 3920
Abstract
One of the most powerful tools for solving optimization problems is optimization algorithms (inspired by nature) based on populations. These algorithms provide a solution to a problem by randomly searching in the search space. The design’s central idea is derived from various natural
[...] Read more.
One of the most powerful tools for solving optimization problems is optimization algorithms (inspired by nature) based on populations. These algorithms provide a solution to a problem by randomly searching in the search space. The design’s central idea is derived from various natural phenomena, the behavior and living conditions of living organisms, laws of physics, etc. A new population-based optimization algorithm called the Binary Spring Search Algorithm (
BSSA) is introduced to solve optimization problems.
BSSA is an algorithm based on a simulation of the famous Hooke’s law (physics) for the traditional weights and springs system. In this proposal, the population comprises weights that are connected by unique springs. The mathematical modeling of the proposed algorithm is presented to be used to achieve solutions to optimization problems. The results were thoroughly validated in different unimodal and multimodal functions; additionally, the
BSSA was compared with high-performance algorithms: binary grasshopper optimization algorithm, binary dragonfly algorithm, binary bat algorithm, binary gravitational search algorithm, binary particle swarm optimization, and binary genetic algorithm. The results show the superiority of the
BSSA. The results of the Friedman test corroborate that the
BSSA is more competitive.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
A Bio-Inspired Model of Picture Array Generating P System with Restricted Insertion Rules
by
Gexiang Zhang, G. Samdanielthompson, N. Gnanamalar David, Atulya K. Nagar and K.G. Subramanian
Viewed by 2286
Abstract
In the bio-inspired area of membrane computing, a novel computing model with a generic name of
P system was introduced around the year 2000. Among its several variants, string or array language generating
P systems involving rewriting rules have been considered. A new
[...] Read more.
In the bio-inspired area of membrane computing, a novel computing model with a generic name of
P system was introduced around the year 2000. Among its several variants, string or array language generating
P systems involving rewriting rules have been considered. A new picture array model of array generating
P system with a restricted type of picture insertion rules and picture array objects in its regions, is introduced here. The generative power of such a system is investigated by comparing with the generative power of certain related picture array grammar models introduced and studied in two-dimensional picture language theory. It is shown that this new model of array
P system can generate picture array languages which cannot be generated by many other array grammar models. The theoretical model developed is for handling the application problem of generation of patterns encoded as picture arrays over a finite set of symbols. As an application, certain floor-design patterns are generated using such an array
P system.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Object Detector for Real-Time Waste Identification
by
Daniel Octavian Melinte, Ana-Maria Travediu and Dan N. Dumitriu
Cited by 74 | Viewed by 8857
Abstract
This paper presents an extensive research carried out for enhancing the performances of convolutional neural network (CNN) object detectors applied to municipal waste identification. In order to obtain an accurate and fast CNN architecture, several types of Single Shot Detectors (SSD) and Regional
[...] Read more.
This paper presents an extensive research carried out for enhancing the performances of convolutional neural network (CNN) object detectors applied to municipal waste identification. In order to obtain an accurate and fast CNN architecture, several types of Single Shot Detectors (SSD) and Regional Proposal Networks (RPN) have been fine-tuned on the TrashNet database. The network with the best performances is executed on one autonomous robot system, which is able to collect detected waste from the ground based on the CNN feedback. For this type of application, a precise identification of municipal waste objects is very important. In order to develop a straightforward pipeline for waste detection, the paper focuses on boosting the performance of pre-trained CNN Object Detectors, in terms of precision, generalization, and detection speed, using different loss optimization methods, database augmentation, and asynchronous threading at inference time. The pipeline consists of data augmentation at the training time followed by CNN feature extraction and box predictor modules for localization and classification at different feature map sizes. The trained model is generated for inference afterwards. The experiments revealed better performances than all other Object Detectors trained on TrashNet or other garbage datasets with a precision of 97.63% accuracy for SSD and 95.76% accuracy for Faster R-CNN, respectively. In order to find the optimal higher and lower bounds of our learning rate where the network is actually learning, we trained our model for several epochs, updating the learning rate after each epoch, starting from 1 × 10
−10 and decreasing it until reaching 1 × 10
−1.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
On Applications of Spiking Neural P Systems
by
Songhai Fan, Prithwineel Paul, Tianbao Wu, Haina Rong and Gexiang Zhang
Cited by 24 | Viewed by 3751
Abstract
Over the years, spiking neural P systems (SNPS) have grown into a popular model in membrane computing because of their diverse range of applications. In this paper, we give a comprehensive summary of applications of SNPS and its variants, especially highlighting power systems
[...] Read more.
Over the years, spiking neural P systems (SNPS) have grown into a popular model in membrane computing because of their diverse range of applications. In this paper, we give a comprehensive summary of applications of SNPS and its variants, especially highlighting power systems fault diagnoses with fuzzy reasoning SNPS. We also study the structure and workings of these models, their comparisons along with their advantages and disadvantages. We also study the implementation of these models in hardware. Finally, we discuss some new ideas which can further expand the scope of applications of SNPS models as well as their implementations.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
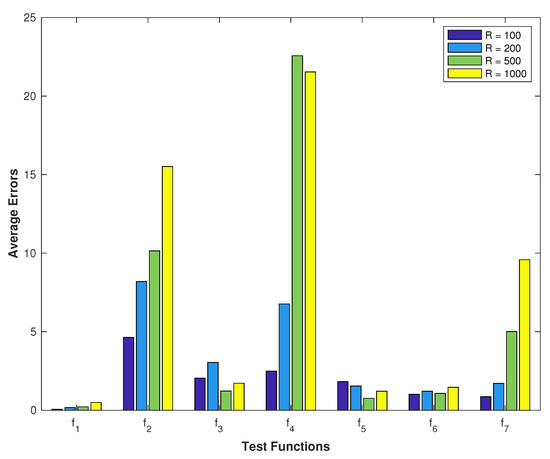
Estimation of Distribution Algorithms with Fuzzy Sampling for Stochastic Programming Problems
by
Abdel-Rahman Hedar, Amira A. Allam and Alaa Fahim
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2714
Abstract
Generating practical methods for simulation-based optimization has attracted a great deal of attention recently. In this paper, the estimation of distribution algorithms are used to solve nonlinear continuous optimization problems that contain noise. One common approach to dealing with these problems is to
[...] Read more.
Generating practical methods for simulation-based optimization has attracted a great deal of attention recently. In this paper, the estimation of distribution algorithms are used to solve nonlinear continuous optimization problems that contain noise. One common approach to dealing with these problems is to combine sampling methods with optimal search methods. Sampling techniques have a serious problem when the sample size is small, so estimating the objective function values with noise is not accurate in this case. In this research, a new sampling technique is proposed based on fuzzy logic to deal with small sample sizes. Then, simulation-based optimization methods are designed by combining the estimation of distribution algorithms with the proposed sampling technique and other sampling techniques to solve the stochastic programming problems. Moreover, additive versions of the proposed methods are developed to optimize functions without noise in order to evaluate different efficiency levels of the proposed methods. In order to test the performance of the proposed methods, different numerical experiments were carried out using several benchmark test functions. Finally, three real-world applications are considered to assess the performance of the proposed methods.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
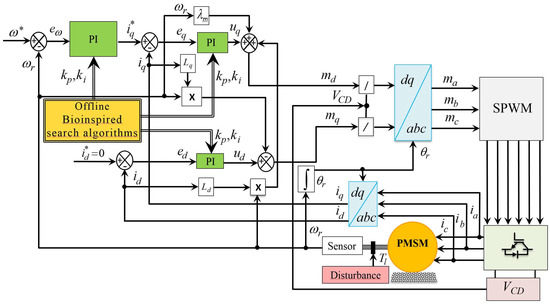
Comparison and Ranking of Metaheuristic Techniques for Optimization of PI Controllers in a Machine Drive System
by
Omar Aguilar-Mejía, Hertwin Minor-Popocatl and Ruben Tapia-Olvera
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 3530
Abstract
Proportional integral (PI) control is still the most widely deployed controller in the industrial drives due to its simplicity and the fact that it is easy to understand and implement. Nevertheless, they are successes applied to systems with a complex behavior with a
[...] Read more.
Proportional integral (PI) control is still the most widely deployed controller in the industrial drives due to its simplicity and the fact that it is easy to understand and implement. Nevertheless, they are successes applied to systems with a complex behavior with a nonlinear representation, but a disadvantage is the procedure to find the optimal PI controller gains. The optimal values of PI parameters must be computed during the tuning process. However, traditional tuning techniques are based on model and do not provide optimal adjustment parameters for the PI controllers because the transient response could produce oscillations and a large overshoot. In this paper, six swarm intelligence-based algorithms (whale, moth-flame, flower pollination, dragonfly, cuckoo search, and modified flower pollination), are correctly conditioned and delimited to tune the PI controllers, the results are probed in a typical industry actuator. Also, a rigorous study is developed to evaluate the quality and reliability of these algorithms by a statistical analysis based on non-parametric test and post-hoc test. Finally, with the obtained results, some time simulations are carried out to corroborate that the nonlinear system performance is improved for high precision industrial applications subjected to endogenous and exogenous uncertainties in a wide range of operating conditions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
BSM-Data Reuse Model Based on In-Vehicular Computing
by
Khireddine Benaissa, Salim Bitam and Abdelhamid Mellouk
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 4803
Abstract
Basic Safety Messages that are frequently generated from multiple connected vehicles can play a primordial role in providing transport data see credible and reliable information they contain. Otherwise, when considering the way Basic Safety Messages (BSMs) are treated, multiple deficiencies prevent the latter
[...] Read more.
Basic Safety Messages that are frequently generated from multiple connected vehicles can play a primordial role in providing transport data see credible and reliable information they contain. Otherwise, when considering the way Basic Safety Messages (BSMs) are treated, multiple deficiencies prevent the latter to be capable of constituting a precious data source. As we know, data become more useful the more widely are used, which is the exact opposite of what happens with the BSMs that exist only temporarily, used locally, considered disposable, and are never stored. In this paper, we introduce a data reuse model that retains collected BSMs, stores, and processes them inside the vehicle constituting a continuous data source holding retained snapshots along the roadway. Our model provided a primary data source available on a large scale, considered to be a worthy dataset for machine learning tasks, capable of visualizing different traffic-related indicators to enhance analytics and support decisions-making. In the study case, we set up an in-vehicle data platform, where we achieved an 80% of BSMs size reduction and provided a rich set of APIs to serve applications. We also adopted the Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) as an information processing paradigm for performing traffic volume prediction, where the obtained results have reached over 99% of accuracy.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
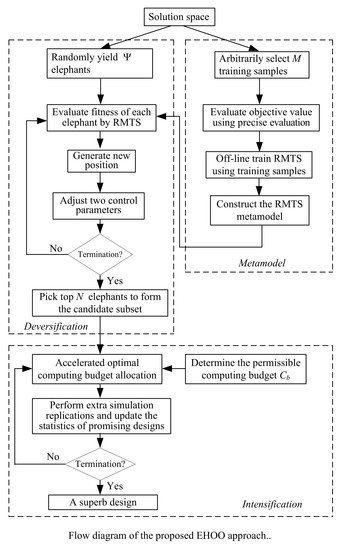
Coupling Elephant Herding with Ordinal Optimization for Solving the Stochastic Inequality Constrained Optimization Problems
by
Shih-Cheng Horng and Shieh-Shing Lin
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 2341
Abstract
The stochastic inequality constrained optimization problems (SICOPs) consider the problems of optimizing an objective function involving stochastic inequality constraints. The SICOPs belong to a category of NP-hard problems in terms of computational complexity. The ordinal optimization (OO) method offers an efficient framework for
[...] Read more.
The stochastic inequality constrained optimization problems (SICOPs) consider the problems of optimizing an objective function involving stochastic inequality constraints. The SICOPs belong to a category of NP-hard problems in terms of computational complexity. The ordinal optimization (OO) method offers an efficient framework for solving NP-hard problems. Even though the OO method is helpful to solve NP-hard problems, the stochastic inequality constraints will drastically reduce the efficiency and competitiveness. In this paper, a heuristic method coupling elephant herding optimization (EHO) with ordinal optimization (OO), abbreviated as EHOO, is presented to solve the SICOPs with large solution space. The EHOO approach has three parts, which are metamodel construction, diversification and intensification. First, the regularized minimal-energy tensor-product splines is adopted as a metamodel to approximately evaluate fitness of a solution. Next, an improved elephant herding optimization is developed to find
N significant solutions from the entire solution space. Finally, an accelerated optimal computing budget allocation is utilized to select a superb solution from the
N significant solutions. The EHOO approach is tested on a one-period multi-skill call center for minimizing the staffing cost, which is formulated as a SICOP. Simulation results obtained by the EHOO are compared with three optimization methods. Experimental results demonstrate that the EHOO approach obtains a superb solution of higher quality as well as a higher computational efficiency than three optimization methods.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
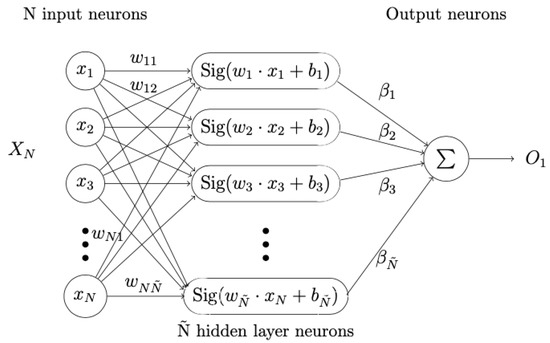
An Optimized Brain-Based Algorithm for Classifying Parkinson’s Disease
by
Rodrigo Olivares, Roberto Munoz, Ricardo Soto, Broderick Crawford, Diego Cárdenas, Aarón Ponce and Carla Taramasco
Cited by 46 | Viewed by 4465
Abstract
During the last years, highly-recognized computational intelligence techniques have been proposed to treat classification problems. These automatic learning approaches lead to the most recent researches because they exhibit outstanding results. Nevertheless, to achieve this performance, artificial learning methods firstly require fine tuning of
[...] Read more.
During the last years, highly-recognized computational intelligence techniques have been proposed to treat classification problems. These automatic learning approaches lead to the most recent researches because they exhibit outstanding results. Nevertheless, to achieve this performance, artificial learning methods firstly require fine tuning of their parameters and then they need to work with the best-generated model. This process usually needs an expert user for supervising the algorithm’s performance. In this paper, we propose an optimized Extreme Learning Machine by using the Bat Algorithm, which boosts the training phase of the machine learning method to increase the accuracy, and decreasing or keeping the loss in the learning phase. To evaluate our proposal, we use the Parkinson’s Disease audio dataset taken from UCI Machine Learning Repository. Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects over 10 million people. Although its diagnosis is through motor symptoms, it is possible to evidence the disorder through variations in the speech using machine learning techniques. Results suggest that using the bio-inspired optimization algorithm for adjusting the parameters of the Extreme Learning Machine is a real alternative for improving its performance. During the validation phase, the classification process for Parkinson’s Disease achieves a maximum accuracy of 96.74% and a minimum loss of 3.27%.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
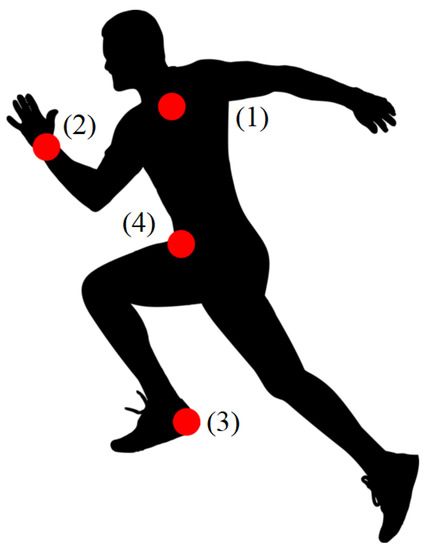
Adapted Binary Particle Swarm Optimization for Efficient Features Selection in the Case of Imbalanced Sensor Data
by
Dorin Moldovan, Ionut Anghel, Tudor Cioara and Ioan Salomie
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 4582
Abstract
Daily living activities (DLAs) classification using data collected from wearable monitoring sensors is very challenging due to the imbalance characteristics of the monitored data. A major research challenge is to determine the best combination of features that returns the best accuracy results using
[...] Read more.
Daily living activities (DLAs) classification using data collected from wearable monitoring sensors is very challenging due to the imbalance characteristics of the monitored data. A major research challenge is to determine the best combination of features that returns the best accuracy results using minimal computational resources, when the data is heterogeneous and not fitted for classical algorithms that are designed for balanced low-dimensional datasets. This research article: (1) presents a modification of the classical version of the binary particle swarm optimization (BPSO) algorithm that introduces a particular type of particles called sensor particles, (2) describes the adaptation of this algorithm for data generated by sensors that monitor DLAs to determine the best positions and features of the monitoring sensors that lead to the best classification results, and (3) evaluates and validates the proposed approach using a machine learning methodology that integrates the modified version of the algorithm. The methodology is tested and validated on the Daily Life Activities (DaLiAc) dataset.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
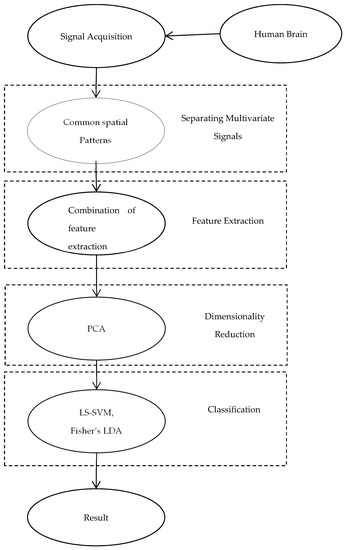
Classification of Motor Imagery Using a Combination of User-Specific Band and Subject-Specific Band for Brain-Computer Interface
by
Vacius Jusas and Sam Gilvine Samuvel
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 3173
Abstract
The essential task of a Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) is to extract the motor imagery features from Electro-Encephalogram (EEG) signals for classifying the thought process. It is necessary to analyse these obtained signals in both the time domain and frequency domains. It is observed
[...] Read more.
The essential task of a Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) is to extract the motor imagery features from Electro-Encephalogram (EEG) signals for classifying the thought process. It is necessary to analyse these obtained signals in both the time domain and frequency domains. It is observed that the combination of multiple algorithms increases the performance of the feature extraction process. This paper identifies combinations that have not been attempted previously and improves the accuracy of the overall process, although other authors implemented different combinations of the techniques. The focus is given more on the feature extraction process and frequency bands, which are user-specific and subject-specific frequency bands. In both time and frequency domains, after analysing EEG signals with the time domain parameter, we select the frequency band and the timing while using the Fisher ratio of the time domain parameter (TDP). We used Fisher discriminant analysis (FDA)-type F-score to simultaneously select the frequency band and time segment for multi-class classification. We extracted subject-specific TDP features from the training trials to train the classifier when optimal time-frequency areas were selected for each subject. In this paper, various methods are explored for obtaining the features, which are Time Domain Parameters (TDP), Fast Fourier Transform (FFT), Principal Component Analysis (PCA), R
2, Fast Correlation Based Filter (FCBF), Empirical Mode Decomposition (EMD), and Intrinsic time-scale decomposition (ITD). After the extraction process, PCA is used for dimensionality reduction. An efficient result was obtained with the combination of TDP, FFT, and PCA. We used the multi-class Fisher’s linear discriminant analysis (LDA) as the classifier, which was in line with the FDA-type F-score. It is observed that the combination of feature extraction techniques to the frequency bands that were selected by the Fisher ratio and FDA type F-score along with Fisher’s LDA classifier had higher accuracy than the results obtained other researches. A kappa coefficient accuracy of 0.64 is obtained for the proposed technique. Our method leads to better classification performance when compared to state-of-the-art methods. The novelty of the approach is based on the combination of frequency bands and two feature extraction methods.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures