-
 Fisher Information in Helmholtz–Boltzmann Thermodynamics of Mechanical Systems
Fisher Information in Helmholtz–Boltzmann Thermodynamics of Mechanical Systems -
 Relation Between Diffusion Equations and Boundary Conditions in Bounded Systems
Relation Between Diffusion Equations and Boundary Conditions in Bounded Systems -
 Mathematical Formalism and Physical Models for Generative Artificial Intelligence
Mathematical Formalism and Physical Models for Generative Artificial Intelligence -
 Probabilistic Multiple-Integral Evaluation of Odd Dirichlet Beta and Even Zeta Functions and Proof of Digamma-Trigamma Reflections
Probabilistic Multiple-Integral Evaluation of Odd Dirichlet Beta and Even Zeta Functions and Proof of Digamma-Trigamma Reflections
Journal Description
Foundations
Foundations
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on mathematics, physics and chemistry published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 37.3 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.7 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Foundations is a companion journal of Molecules, Entropy and Mathematics.
Latest Articles
The Extended Uncertainty Principle from a Projector-Valued Measurement Perspective
Foundations 2025, 5(3), 30; https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations5030030 - 1 Sep 2025
Abstract
We revisit the Extended Uncertainty Principle (EUP) from an operational viewpoint, replacing wavefunction-based widths with apparatus-defined position constraints such as a finite slit of width
We revisit the Extended Uncertainty Principle (EUP) from an operational viewpoint, replacing wavefunction-based widths with apparatus-defined position constraints such as a finite slit of width
(This article belongs to the Section Mathematical Sciences)
Open AccessArticle
Incorporating Finite Particle Number and Heat-Temperature Differences in the Maxwell–Boltzmann Speed Distribution
by
Everett M. Criss and Anne M. Hofmeister
Foundations 2025, 5(3), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations5030029 - 25 Aug 2025
Abstract
The often used analytical representation of the Maxwell–Boltzmann classical speed distribution function (F) for elastic, indivisible particles assumes an infinite limit for the speed. Consequently, volume and the number of particles (n) extend to infinity: Both infinities contradict assumptions
[...] Read more.
The often used analytical representation of the Maxwell–Boltzmann classical speed distribution function (F) for elastic, indivisible particles assumes an infinite limit for the speed. Consequently, volume and the number of particles (n) extend to infinity: Both infinities contradict assumptions underlying this non-relativistic formulation. Finite average kinetic energy and temperature (T) result from normalization of F removing n: However, total energy (i.e., heat of the collection) remains infinite because n is infinite. This problem persists in recent adaptations. To better address real (finite) systems, wherein T depends on heat, we generalize this one-parameter distribution (F, cast in energy) by proposing a two-parameter gamma distribution function (F*) in energy which reduces to F at large n. Its expectation value of kT (k = Boltzmann’s constant) replicates F, whereas the shape factor depends on n and affects the averages, as expected for finite systems. We validate F* via a first-principle, molecular dynamics numerical model of energy and momentum conserving collisions for 26, 182, and 728 particles in three-dimensional physical space. Dimensionless calculations provide generally applicable results; a total of 107 collisions suffice to represent an equilibrated collection. Our numerical results show that individual momentum conserving collisions in three-dimensions provide symmetrical speed distributions in all Cartesian directions. Thus, momentum and energy conserving collisions are the physical cause for equipartitioning of energy: Validity of this theorem for other systems depends on their specific motions. Our numerical results set upper limits on kinetic energy of individual particles; restrict the n particles to some finite volume; and lead to a formula in terms of n for conserving total energy when utilizing F* for convenience. Implications of our findings on matter under extreme conditions are briefly discussed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Physical Sciences)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Knots in Polymer Molecules Under Poiseuille Flow
by
Maurice P. Schmitt and Andrey Milchev
Foundations 2025, 5(3), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations5030028 - 13 Aug 2025
Abstract
Knots are ubiquitous in polymers and biological macromolecules such as DNA and proteins, yet their behavior and functionality are still not sufficiently explored. Here we investigate the impact of Poiseuille flow on simple knots in flexible polymers placed in a quasi-rectangular micro-channel by
[...] Read more.
Knots are ubiquitous in polymers and biological macromolecules such as DNA and proteins, yet their behavior and functionality are still not sufficiently explored. Here we investigate the impact of Poiseuille flow on simple knots in flexible polymers placed in a quasi-rectangular micro-channel by systematically varying the flow strength for different chain lengths. Hydrodynamic interactions are accounted for by means of Multi-Particle Collision Dynamics (MPCD). We find that initially loosely localized knots in polymer coils typically tighten under shear to several segments beyond a certain body force threshold. At higher shear rates, intermittent transition from chain stretching to tumbling is observed which correlates with strong fluctuations in the knot size. Somewhat unexpectedly, our results indicate that the influence of channel width on tightening steadily increases with growing width even at equal mean shear rate
(This article belongs to the Section Physical Sciences)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Probabilistic Multiple-Integral Evaluation of Odd Dirichlet Beta and Even Zeta Functions and Proof of Digamma-Trigamma Reflections
by
Antonio E. Bargellini, Daniele Ritelli and Giulia Spaletta
Foundations 2025, 5(3), 27; https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations5030027 - 11 Aug 2025
Abstract
The aim of this work was to construct explicit expressions for the summation of Dirichlet Beta functions with odd arguments and Zeta functions with even arguments. In the established literature, this is typically done using Fourier series expansions or Bernoulli numbers and polynomials.
[...] Read more.
The aim of this work was to construct explicit expressions for the summation of Dirichlet Beta functions with odd arguments and Zeta functions with even arguments. In the established literature, this is typically done using Fourier series expansions or Bernoulli numbers and polynomials. Here, instead, we achieve our goal by employing tools from probability: specifically, we introduce a generalisation of a technique based on multiple integrals and the algebra of random variables. This also allows us to increase the number of nested integrals and Cauchy random variables involved. Another key contribution is that, by generalising the exponent of Cauchy random variables, we obtain an original proof of the reflection formulae for the Digamma and Trigamma functions. These probabilistic proofs crucially utilise the Mellin transform to compute the integrals needed to determine probability density functions. It is noteworthy that, while understanding the presented topic requires knowledge of the rules for calculating multiple integrals (Fubini’s Theorem) and the algebra of continuous random variables, these are concepts commonly acquired by second-year university students in STEM disciplines. Our study thus offers new perspectives on how the mathematical functions considered relate and shows the significant role of probabilistic methods in promoting comprehension of this research area, in a way accessible to a broad and non-specialist audience.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Editorial Board Members’ Collection Series: Feature Papers in Mathematical Sciences)
Open AccessOpinion
Relation Between Diffusion Equations and Boundary Conditions in Bounded Systems
by
Fabio Sattin and Dominique Franck Escande
Foundations 2025, 5(3), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations5030026 - 31 Jul 2025
Abstract
Differential equations need boundary conditions (BCs) for their solution. It is widely acknowledged that differential equations and BCs are representative of independent physical processes, and no correlations between them are required. Two recent studies by Hilhorst, Chung et al. argue instead that, in
[...] Read more.
Differential equations need boundary conditions (BCs) for their solution. It is widely acknowledged that differential equations and BCs are representative of independent physical processes, and no correlations between them are required. Two recent studies by Hilhorst, Chung et al. argue instead that, in the specific case of diffusion equations (DEs) in bounded systems, BCs are uniquely constrained by the form of transport coefficients. In this paper, we revisit how DEs emerge as fluid limits out of a picture of stochastic transport. We point out their limits of validity and argue that, in most physical systems, BCs and DEs are actually uncorrelated by virtue of the failure of diffusive approximation near the system’s boundaries. When, instead, the diffusive approximation holds everywhere, we show that the correct chain of reasoning goes in the direction opposite to that conjectured by Hilhorst and Chung: it is the choice of the BCs that determines the form of the DE in the surroundings of the boundary.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Physical Sciences)
Open AccessHypothesis
Beyond Classical Multipoles: The Magnetic Metapole as an Extended Field Source
by
Angelo De Santis and Roberto Dini
Foundations 2025, 5(3), 25; https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations5030025 - 14 Jul 2025
Abstract
We introduce the concept of the magnetic metapole—a theoretical extension of classical multipole theory involving a fractional j pole count (related to the harmonic degree n as j = 2n). Defined by a scalar potential with colatitudinal dependence and no radial
[...] Read more.
We introduce the concept of the magnetic metapole—a theoretical extension of classical multipole theory involving a fractional j pole count (related to the harmonic degree n as j = 2n). Defined by a scalar potential with colatitudinal dependence and no radial variation, the metapole yields a magnetic field that decays as 1/r and is oriented along spherical surfaces. Unlike classical multipoles, the metapole cannot be described as a point source; rather, it corresponds to an extended or filamentary magnetic distribution as derived from Maxwell’s equations. We demonstrate that pairs of oppositely oriented metapoles (up/down) can, at large distances, produce magnetic fields resembling those of classical monopoles. A regularized formulation of the potential resolves singularities for the potential and the field. When applied in a bounded region, it yields finite field energy, enabling practical modeling applications. We propose that the metapole can serve as a conceptual and computational framework for representing large-scale magnetic field structures particularly where standard dipole-based models fall short. This construct may have utility in both geophysical and astrophysical contexts, and it provides a new tool for equivalent source modeling and magnetic field decomposition.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Physical Sciences)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Fisher Information in Helmholtz–Boltzmann Thermodynamics of Mechanical Systems
by
Marco Favretti
Foundations 2025, 5(3), 24; https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations5030024 - 4 Jul 2025
Abstract
In this paper, we review Helmholtz–Boltzmann thermodynamics for mechanical systems depending on parameters, and we compute the Fisher information matrix for the associated probability density. The divergence of Fisher information has been used as a signal for the existence of phase transitions in
[...] Read more.
In this paper, we review Helmholtz–Boltzmann thermodynamics for mechanical systems depending on parameters, and we compute the Fisher information matrix for the associated probability density. The divergence of Fisher information has been used as a signal for the existence of phase transitions in finite systems even in the absence of a thermodynamic limit. We investigate through examples if qualitative changes in the dynamic of mechanical systems described by Helmholtz–Boltzmann thermodynamic formalism can be detected using Fisher information.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Physical Sciences)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Mathematical Formalism and Physical Models for Generative Artificial Intelligence
by
Zeqian Chen
Foundations 2025, 5(3), 23; https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations5030023 - 24 Jun 2025
Abstract
This paper presents a mathematical formalism for generative artificial intelligence (GAI). Our starting point is an observation that a “histories” approach to physical systems agrees with the compositional nature of deep neural networks. Mathematically, we define a GAI system as a family of
[...] Read more.
This paper presents a mathematical formalism for generative artificial intelligence (GAI). Our starting point is an observation that a “histories” approach to physical systems agrees with the compositional nature of deep neural networks. Mathematically, we define a GAI system as a family of sequential joint probabilities associated with input texts and temporal sequences of tokens (as physical event histories). From a physical perspective on modern chips, we then construct physical models realizing GAI systems as open quantum systems. Finally, as an illustration, we construct physical models realizing large language models based on a transformer architecture as open quantum systems in the Fock space over the Hilbert space of tokens. Our physical models underlie the transformer architecture for large language models.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Physical Sciences)
Open AccessArticle
Cross-Analysis of Magnetic and Current Density Field Topologies in a Quiescent High Confinement Mode Tokamak Discharge
by
Marie-Christine Firpo
Foundations 2025, 5(2), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations5020022 - 17 Jun 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
In axisymmetric fusion devices like tokamaks, the winding of the magnetic field is characterized by its safety profile
In axisymmetric fusion devices like tokamaks, the winding of the magnetic field is characterized by its safety profile
(This article belongs to the Section Physical Sciences)
►▼
Show Figures
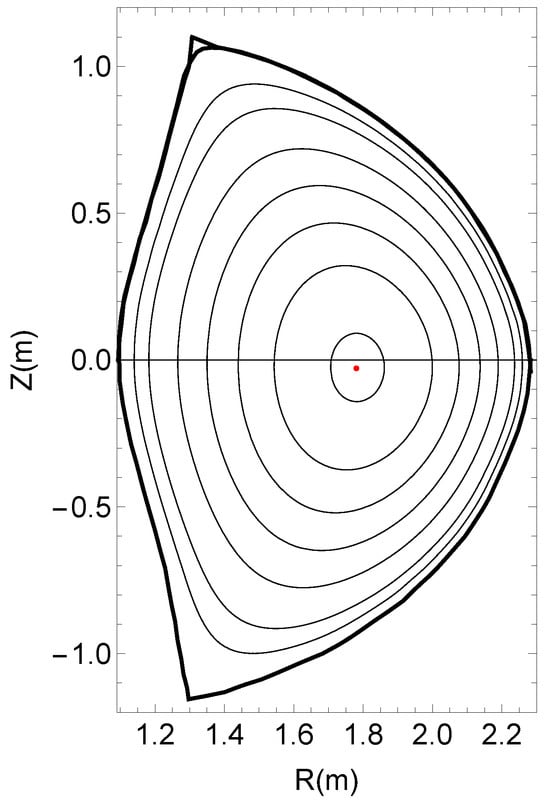
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Foreground Emission Randomization Due to Dynamics of Magnetized Interstellar Medium: WMAP and Planck Frequency Bands
by
Alexander Bershadskii
Foundations 2025, 5(2), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations5020021 - 10 Jun 2025
Abstract
Using the results of numerical simulations and astrophysical observations (mainly in the WMAP and Planck frequency bands), it is shown that Galactic foreground emission becomes more sensitive to the mean magnetic field with the frequency, resulting in the appearance of two levels of
[...] Read more.
Using the results of numerical simulations and astrophysical observations (mainly in the WMAP and Planck frequency bands), it is shown that Galactic foreground emission becomes more sensitive to the mean magnetic field with the frequency, resulting in the appearance of two levels of its randomization due to the chaotic/turbulent dynamics of a magnetized interstellar medium dominated by magnetic helicity. The galactic foreground emission is more randomized at higher frequencies. The Galactic synchrotron and polarized dust emissions have been studied in detail. It is shown that the magnetic field imposes its level of randomization on the synchrotron and dust emission. The main method for the theoretical consideration used in this study is the Kolmogorov–Iroshnikov phenomenology in the frames of distributed chaos notion. Despite the vast differences in the values of physical parameters and spatio-temporal scales between the numerical simulations and the astrophysical observations, there is a quantitative agreement between the results of the astrophysical observations and the numerical simulations in the frames of the distributed chaos notion.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Physical Sciences)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comparing Different Specifications of Mean–Geometric Mean Linking
by
Alexander Robitzsch
Foundations 2025, 5(2), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations5020020 - 6 Jun 2025
Abstract
Mean–geometric mean (MGM) linking compares group differences on a latent variable
Mean–geometric mean (MGM) linking compares group differences on a latent variable
(This article belongs to the Section Mathematical Sciences)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Numerical Evidence for a Bipartite Pure State Entanglement Witness from Approximate Analytical Diagonalization
by
Paul M. Alsing and Richard J. Birrittella
Foundations 2025, 5(2), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations5020019 - 4 Jun 2025
Abstract
We show numerical evidence for a bipartite
We show numerical evidence for a bipartite
(This article belongs to the Section Mathematical Sciences)
►▼
Show Figures
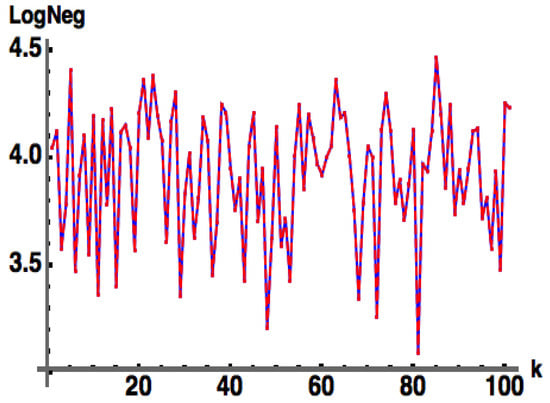
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Advances in Fractional Lyapunov-Type Inequalities: A Comprehensive Review
by
Sotiris K. Ntouyas, Bashir Ahmad and Jessada Tariboon
Foundations 2025, 5(2), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations5020018 - 27 May 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
In this survey, we have included the recent results on Lyapunov-type inequalities for differential equations of fractional order associated with Dirichlet, nonlocal, multi-point, anti-periodic, and discrete boundary conditions. Our results involve a variety of fractional derivatives such as Riemann–Liouville, Caputo, Hilfer–Hadamard,
In this survey, we have included the recent results on Lyapunov-type inequalities for differential equations of fractional order associated with Dirichlet, nonlocal, multi-point, anti-periodic, and discrete boundary conditions. Our results involve a variety of fractional derivatives such as Riemann–Liouville, Caputo, Hilfer–Hadamard,
(This article belongs to the Section Mathematical Sciences)
Open AccessArticle
Entropy Production Assumption and Objectivity in Continuum Physics Modelling
by
Angelo Morro
Foundations 2025, 5(2), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations5020017 - 22 May 2025
Abstract
This paper revisits some aspects connected with the methods for the determination of thermodynamically consistent models. While the concepts apply to the general context of continuum physics, the details are developed for the modelling of deformable dielectrics. The symmetry condition arising from the
[...] Read more.
This paper revisits some aspects connected with the methods for the determination of thermodynamically consistent models. While the concepts apply to the general context of continuum physics, the details are developed for the modelling of deformable dielectrics. The symmetry condition arising from the balance of angular momentum is viewed as a constraint for the constitutive equations and is shown to be satisfied by sets of objective fields that account jointly for deformation and electric field. The second law of thermodynamics is considered in a generalized form where the entropy production is given by a constitutive function possibly independent of the other constitutive functions. Furthermore, a representation formula is applied for solving the Clausius–Duhem inequality with respect to the chosen unknown fields.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Physical Sciences)
Open AccessArticle
Maxwell’s Demon Is Foiled by the Entropy Cost of Measurement, Not Erasure
by
Ruth E. Kastner
Foundations 2025, 5(2), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations5020016 - 22 May 2025
Abstract
I dispute the conventional claim that the second law of thermodynamics is saved from a “Maxwell’s demon” by the entropy cost of information erasure and show that instead it is measurement that incurs the entropy cost. Thus, Brillouin, who identified measurement as savior
[...] Read more.
I dispute the conventional claim that the second law of thermodynamics is saved from a “Maxwell’s demon” by the entropy cost of information erasure and show that instead it is measurement that incurs the entropy cost. Thus, Brillouin, who identified measurement as savior of the second law, was essentially correct, and putative refutations of his view, such as Bennett’s claim to measure without entropy cost, are seen to fail when the applicable physics is taken into account. I argue that the tradition of attributing the defeat of Maxwell’s demon to erasure rather than to measurement arose from unphysical classical idealizations that do not hold for real gas molecules, as well as a physically ungrounded recasting of physical thermodynamical processes into computational and information-theoretic conceptualizations. I argue that the fundamental principle that saves the second law is the quantum uncertainty principle applying to the need to localize physical states to precise values of observables in order to effect the desired disequilibria aimed at violating the second law. I obtain the specific entropy cost for localizing a molecule in the Szilard engine and show that it coincides with the quantity attributed to Landauer’s principle. I also note that an experiment characterized as upholding an entropy cost of erasure in a “quantum Maxwell’s demon” actually demonstrates an entropy cost of measurement.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Physical Sciences)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Physical and Logical Synchronization of Clocks: The Ramsey Approach
by
Edward Bormashenko
Foundations 2025, 5(2), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations5020015 - 28 Apr 2025
Abstract
Ramsey analysis is applied to the problem of the relativistic and quantum synchronization of clocks. Various protocols of synchronization are addressed. Einstein and Eddington special relativity synchronization procedures are considered, and quantum synchronization is discussed. Clocks are seen as the vertices of the
[...] Read more.
Ramsey analysis is applied to the problem of the relativistic and quantum synchronization of clocks. Various protocols of synchronization are addressed. Einstein and Eddington special relativity synchronization procedures are considered, and quantum synchronization is discussed. Clocks are seen as the vertices of the graph. Clocks may be synchronized or unsynchronized. Thus, introducing complete, bi-colored, Ramsey graphs emerging from the lattices of clocks becomes possible. The transitivity of synchronization plays a key role in the coloring of the Ramsey graph. Einstein synchronization is transitive, while general relativity and quantum synchronization procedures are not. This fact influences the value of the Ramsey number established for the synchronization graph arising from the lattice of clocks. Any lattice built of six clocks, synchronized with quantum entanglement, will inevitably contain the mono-chromatic triangle. The transitive synchronization of logical clocks is discussed. Interrelation between the symmetry of the clock lattice and the structure of the synchronization graph is addressed. Ramsey analysis of synchronization is important for the synchronization of computers in networks, LIGO, and Virgo instruments intended for the registration of gravitational waves and GPS tame-based synchronization.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Physical Sciences)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Bayesian Nonparametric Inference in Elliptic PDEs: Convergence Rates and Implementation
by
Matteo Giordano
Foundations 2025, 5(2), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations5020014 - 23 Apr 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
Parameter identification problems in partial differential equations (PDEs) consist in determining one or more functional coefficient in a PDE. In this article, the Bayesian nonparametric approach to such problems is considered. Focusing on the representative example of inferring the diffusivity function in an
[...] Read more.
Parameter identification problems in partial differential equations (PDEs) consist in determining one or more functional coefficient in a PDE. In this article, the Bayesian nonparametric approach to such problems is considered. Focusing on the representative example of inferring the diffusivity function in an elliptic PDE from noisy observations of the PDE solution, the performance of Bayesian procedures based on Gaussian process priors is investigated. Building on recent developments in the literature, we derive novel asymptotic theoretical guarantees that establish posterior consistency and convergence rates for methodologically attractive Gaussian series priors based on the Dirichlet–Laplacian eigenbasis. An implementation of the associated posterior-based inference is provided and illustrated via a numerical simulation study, where excellent agreement with the theory is obtained.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Mathematical Sciences)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Fault-Tolerant Metric Dimension in Carbon Networks
by
Kamran Azhar, Asim Nadeem and Yilun Shang
Foundations 2025, 5(2), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations5020013 - 16 Apr 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
In this paper, we study the fault-tolerant metric dimension in graph theory, an important measure against failures in unique vertex identification. The metric dimension of a graph is the smallest number of vertices required to uniquely identify every other vertex based on their
[...] Read more.
In this paper, we study the fault-tolerant metric dimension in graph theory, an important measure against failures in unique vertex identification. The metric dimension of a graph is the smallest number of vertices required to uniquely identify every other vertex based on their distances from these chosen vertices. Building on existing work, we explore fault tolerance by considering the minimal number of vertices needed to ensure that all other vertices remain uniquely identifiable even if a specified number of these vertices fails. We compute the fault-tolerant metric dimension of various chemical graphs, namely fullerenes, benzene, and polyphenyl graphs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Mathematical Sciences)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessPerspective
Revisiting the Definition of Vectors—From ‘Magnitude and Direction’ to Abstract Tuples
by
Reinout Heijungs
Foundations 2025, 5(2), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations5020012 - 15 Apr 2025
Abstract
Vectors are almost always introduced as objects having magnitude and direction. Following that idea, textbooks and courses introduce the concept of a vector norm and the angle between two vectors. While this is correct and useful for vectors in two- or three-dimensional Euclidean
[...] Read more.
Vectors are almost always introduced as objects having magnitude and direction. Following that idea, textbooks and courses introduce the concept of a vector norm and the angle between two vectors. While this is correct and useful for vectors in two- or three-dimensional Euclidean space, these concepts make no sense for more general vectors, that are defined in abstract, non-metric vector spaces. This is even the case when an inner product exists. Here, we analyze how several textbooks are imprecise in presenting the restricted validity of the expressions for the norm and the angle. We also study one concrete example, the so-called ‘vector-based sustainability analytics’, in which scientists have gone astray by mistaking an abstract vector for a Euclidean vector. We recommend that future textbook authors introduce the distinction between vectors that have and that do not have magnitude and direction, even in cases where an inner product exists.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Mathematical Sciences)
Open AccessArticle
Introducing an Evolutionary Method to Create the Bounds of Artificial Neural Networks
by
Ioannis G. Tsoulos, Vasileios Charilogis and Dimitrios Tsalikakis
Foundations 2025, 5(2), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/foundations5020011 - 25 Mar 2025
Abstract
Artificial neural networks are widely used in applications from various scientific fields and in a multitude of practical applications. In recent years, a multitude of scientific publications have been presented on the effective training of their parameters, but in many cases overfitting problems
[...] Read more.
Artificial neural networks are widely used in applications from various scientific fields and in a multitude of practical applications. In recent years, a multitude of scientific publications have been presented on the effective training of their parameters, but in many cases overfitting problems appear, where the artificial neural network shows poor results when used on data that were not present during training. This text proposes the incorporation of a three-stage evolutionary technique, which has roots in the differential evolution technique, for the effective training of the parameters of artificial neural networks and the avoidance of the problem of overfitting. The new method effectively constructs the parameter value range of the artificial neural network with one processing level and sigmoid outputs, both achieving a reduction in training error and preventing the network from experiencing overfitting phenomena. This new technique was successfully applied to a wide range of problems from the relevant literature and the results were extremely promising. From the conducted experiments, it appears that the proposed method reduced the average classification error by 30%, compared to the genetic algorithm, and the average regression error by 45%, as compared to the genetic algorithm.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Mathematical Sciences)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics

Conferences
Special Issues
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Foundations
Editorial Board Members’ Collection Series: Feature Papers in Mathematical Sciences
Collection Editors: Ravi P. Agarwal, Dimplekumar N. Chalishajar
Topical Collection in
Foundations
Editorial Board Members’ Collection Series: Theory and Its Applications in Problems of Mathematical Physics and of Mathematical Chemistry
Collection Editors: Ioannis K. Argyros, Lorentz Jäntschi



