Journal Description
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health
is a transdisciplinary, peer-reviewed, open access journal published monthly online by MDPI. It covers Global Health, Healthcare Sciences, Behavioral and Mental Health, Infectious Diseases, Chronic Diseases and Disease Prevention, Exercise and Health Related Quality of Life, Environmental Health and Environmental Sciences. The International Society Doctors for the Environment (ISDE) and Italian Society of Environmental Medicine (SIMA) are affiliated with IJERPH and their members receive a discount on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, PubMed, MEDLINE, PMC, Embase, GEOBASE, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q1 (Public Health, Environmental and Occupational Health)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 25.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.3 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2024).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Testimonials: See what our editors and authors say about IJERPH.
- Sections: published in 7 topical sections.
- Companion journal: Air.
Latest Articles
RETRACTED: Wee et al. Triaging Medical Referrals Based on Clinical Prioritisation Criteria Using Machine Learning Techniques. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7384
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22(5), 700; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050700 (registering DOI) - 29 Apr 2025
Abstract
The journal retracts and remove the article Triaging Medical Referrals Based on Clinical Prioritisation Criteria Using Machine Learning Techniques [...]
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Post-Traumatic Growth in Volunteers Following the 2023 Kahramanmaraş Earthquakes
by
Kader Demiröz, Mehtap Kılıç and Sevda Demiröz Yıldırım
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22(5), 699; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050699 (registering DOI) - 28 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The 6 February 2023 Kahramanmaraş earthquakes were devastating events that caused widespread destruction. This mixed-methods study examined post-traumatic growth (PTG) in volunteers who participated in the relief efforts. A total of 169 volunteers participated in the quantitative phase, completing a standardized PTG measure.
[...] Read more.
The 6 February 2023 Kahramanmaraş earthquakes were devastating events that caused widespread destruction. This mixed-methods study examined post-traumatic growth (PTG) in volunteers who participated in the relief efforts. A total of 169 volunteers participated in the quantitative phase, completing a standardized PTG measure. In-depth interviews were conducted with 14 volunteers during the qualitative phase. The study found that gender had a significant effect on total PTG scores. Additionally, gender, earthquake experience, and volunteer organization were significant factors in the “change in self-concept” sub-dimension. Gender was the only significant factor in the “change in philosophy of life” sub-dimension. Qualitative analysis revealed that participants experienced trauma symptoms after the earthquake but also reported positive changes in self-concept and life philosophy. This study suggests that disasters can lead to PTG, despite the presence of trauma symptoms. Further research is needed to explore PTG in different disaster response groups.
Full article
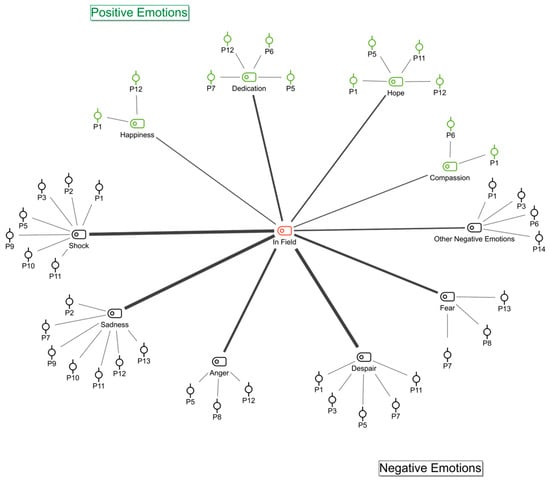
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Ability of the Hopkins Symptom Checklist-5 to Identify Generalized Anxiety Disorder and Major Depressive Disorder in the General Population
by
Benedicte Kirkøen, Ragnhild Elise Ørstavik, Anne Reneflot, Jens Christoffer Skogen, Børge Sivertsen and Ann Kristin Skrindo Knudsen
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22(5), 698; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050698 (registering DOI) - 28 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: The Hopkins Symptom Checklist (HSCL) is a widely used measure of anxiety and depression symptoms. The short form HSCL-5 is especially suitable for large population-based studies, but its ability to detect mental disorders in the general population remains unknown. The aim of
[...] Read more.
Background: The Hopkins Symptom Checklist (HSCL) is a widely used measure of anxiety and depression symptoms. The short form HSCL-5 is especially suitable for large population-based studies, but its ability to detect mental disorders in the general population remains unknown. The aim of the study was to assess how well the HSCL-5 identified cases of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) and major depressive disorder (MDD) measured by the Composite International Diagnostic Interview (CIDI) 5.0 and to find the optimal sex-specific cut-off levels of the HSCL-5. Methods: Participants from the population-based Trøndelag Health Study (HUNT) in Norway were recruited for the current study. Between April and September 2020, 1343 participants (64% women) aged 20–65 years completed the CIDI, followed by the HSCL-5. The overall agreement between the HSCL-5 and GAD or MDD measured by CIDI was examined with Receiver Operator Characteristics (ROC) analysis. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive values (NPV) for different cut-off levels were assessed. Results: The area under the curve for GAD or MDD was 0.90 (CI 95% = 0.85–0.95) for women and 0.85 (CI 95% = 0.68–1.00) for men. For women, a cut-off level of ≥ 1.80 had the best balance between sensitivity (85%) and specificity (84%), while the corresponding numbers were ≥2.00, 73%, and 93% for men. The global PPV was 21%, while the NPV was 99%. Conclusions: The HSCL-5 has high sensitivity and specificity for identifying cases of GAD or MDD. In the current study, the positive predictive value of HSCL-5 was low.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Behavioral and Mental Health)
Open AccessArticle
Factors Associated with the Enjoyment of Physical Education Class for Children with Special Educational Needs
by
Julie Dalgaard Guldager, Laura Mørk Emtoft, Line Nørgaard Remmen and Anette Lisbeth Bentholm
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22(5), 697; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050697 (registering DOI) - 28 Apr 2025
Abstract
Enjoying physical education class (PE) is important for children with special educational needs (SEN) due to its impact on their physical and mental health. However, there is a research gap concerning children with SEN and their enjoyment of PE. This exploratory study investigated
[...] Read more.
Enjoying physical education class (PE) is important for children with special educational needs (SEN) due to its impact on their physical and mental health. However, there is a research gap concerning children with SEN and their enjoyment of PE. This exploratory study investigated how school children with and without SEN report enjoyment of physical education class and explored associated factors. A cross-sectional survey was conducted among school children with and without SEN. Both groups reported very high enjoyment of PE, but children without SEN had higher enjoyment. Among children with SEN, boys, those attending schools in East Denmark, and those engaged in leisure physical activity reported higher enjoyment levels, while children from larger schools consistently reported lower enjoyment levels. Understanding the differences in PE enjoyment between children with and without SEN is crucial for educators and policymakers to develop inclusive practices that ensure equitable experiences for all children, fostering a positive and supportive environment in school PE programs. Our findings highlight nuanced differences in PE enjoyment perceptions between children with and without SEN, emphasizing the need to consider diverse student characteristics when designing PE programs to enhance overall enjoyment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Child Physical Activity and Health)
Open AccessReview
What Is the Impact of Unemployment as an Adverse Experience? Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Complex Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: A Meta-Analysis
by
Marcelo Nvo-Fernandez, Valentina Miño-Reyes, Carlos Serrano, Hedy Acosta-Antognoni, Fabiola Salas, Claudio Vásquez Wiedeman, Francisco Ahumada-Méndez and Marcelo Leiva-Bianchi
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22(5), 696; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050696 (registering DOI) - 28 Apr 2025
Abstract
This meta-analysis examined how unemployment, a psychosocial stressor, influences post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and complex PTSD (CPTSD). It specifically explores unemployment as a risk factor for trauma, with emphasis on CPTSD, and investigates economic variables, including the GINI coefficient, as potential moderators. A
[...] Read more.
This meta-analysis examined how unemployment, a psychosocial stressor, influences post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and complex PTSD (CPTSD). It specifically explores unemployment as a risk factor for trauma, with emphasis on CPTSD, and investigates economic variables, including the GINI coefficient, as potential moderators. A systematic search in Web of Science, Scopus, and PubMed yielded 33 studies comprising more than 57,000 participants. Odds ratios (OR) were computed, and a random-effects model was used to synthesize the findings. Meta-regression analyses were conducted to evaluate the effects of economic inequality (GINI) and nominal gross domestic product (NGDP), but neither moderator reached statistical significance; this is addressed in detail in the Discussion. The results revealed that unemployment significantly elevated the risk for PTSD (OR = 1.500; logOR = 0.3826; PI: 0.457–4.702) and CPTSD (OR = 2.180; logOR = 0.7430; PI: 0.501–8.808), with a stronger impact on CPTSD. These findings emphasize unemployment as a pivotal predictor of trauma, especially CPTSD, broadening the traditional focus on interpersonal factors. They also highlight the importance of integrating psychosocial and economic variables into clinical assessments and public health policies. Addressing both unemployment and economic inequality could be critical for effective interventions and prevention efforts, underscoring the need for further multidisciplinary research.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Behavioral and Mental Health)
►▼
Show Figures
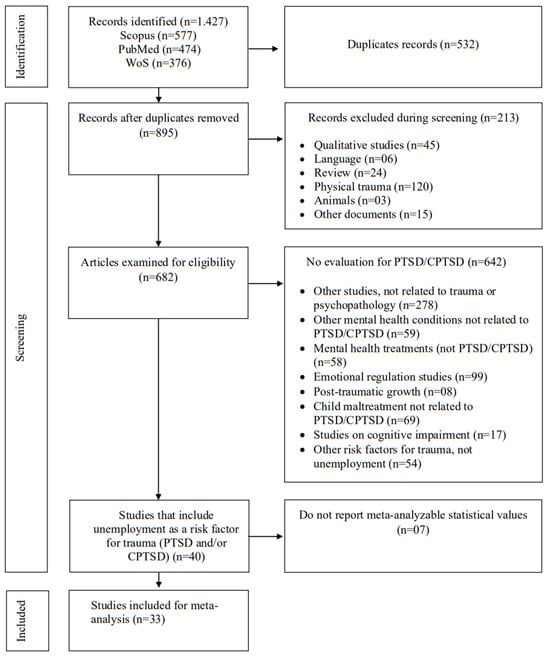
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Learning from COVID-19: A Systematic Review of the IHR-SPAR Framework’s Role in the Pandemic Response
by
Ida Santalucia, Michele Sorrentino, Claudio Fiorilla, Sabrina Tranquilli, Giordana Strazza, Paolo Montuori, Raffaele Palladino, Maria Fiore, Margherita Ferrante and Maria Triassi
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22(5), 695; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050695 (registering DOI) - 27 Apr 2025
Abstract
The International Health Regulations (IHR) provide a global framework for health security, requiring annual reporting on 35 indicators across 15 core capacities via the State Parties Annual Reporting (SPAR) tool. The COVID-19 pandemic exposed gaps in the IHR framework and monitoring systems, prompting
[...] Read more.
The International Health Regulations (IHR) provide a global framework for health security, requiring annual reporting on 35 indicators across 15 core capacities via the State Parties Annual Reporting (SPAR) tool. The COVID-19 pandemic exposed gaps in the IHR framework and monitoring systems, prompting calls for reform. This systematic review analyzed the correlations between IHR-SPAR scores and pandemic outcomes across nine studies (2020–2024), selected using the PRISMA guidelines. The study quality was assessed using the Joanna Briggs Institute’s tool for cross-sectional studies. Of 1019 screened studies, nine met the inclusion criteria. Higher SPAR scores generally correlated with lower COVID-19 incidence and mortality, although some high-scoring countries experienced severe outbreaks. Middle-income countries showed the greatest improvement, particularly in risk communication and emergency response, while zoonotic disease capacities saw little progress. While the SPAR tool aids monitoring, it requires revisions to better reflect real-world pandemic responses. High SPAR scores do not always indicate effective crisis management. This study recommends integrating more dynamic, operational, and context-sensitive indicators to enhance the global preparedness for future health emergencies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Pandemic Preparedness: Lessons from COVID-19, Arboviral Outbreaks, and Other Emerging Infectious Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
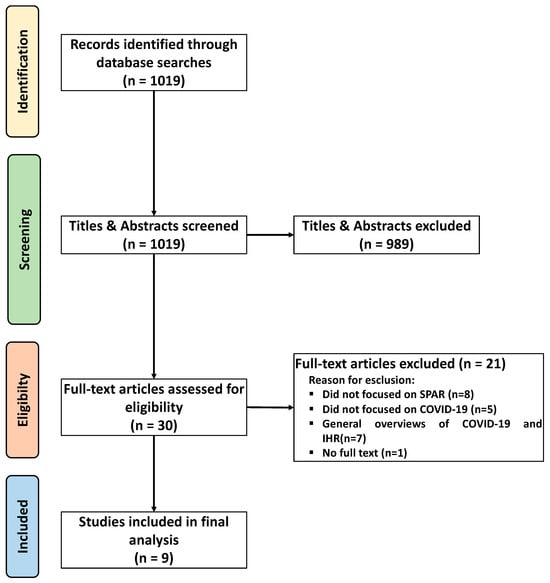
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Depressive Symptoms Among South African Construction Workers: Associations with Demographic, Social and Work-Related Factors, and Substance Use
by
Rita Peihua Zhang, Paul Bowen and Peter Edwards
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22(5), 694; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050694 (registering DOI) - 27 Apr 2025
Abstract
The construction industry exhibits higher rates of depression in its workforce compared to other industries. This study investigates the association between the prevalence of depressive symptoms and various demographic (e.g., age, ethnicity, education), social, and work-related factors (e.g., relationship status, living environment, work
[...] Read more.
The construction industry exhibits higher rates of depression in its workforce compared to other industries. This study investigates the association between the prevalence of depressive symptoms and various demographic (e.g., age, ethnicity, education), social, and work-related factors (e.g., relationship status, living environment, work situation) and behavioural factors (e.g., alcohol and drug use). Survey data collected from 496 male construction workers working in the Western Cape were analysed using binomial logistic regression to determine the associations. The results showed that ‘Black African’ construction workers exhibited lower levels of depressive symptoms than ‘Other’ ethnic groups, and workers with at least secondary education had the highest levels of depressive symptoms compared to workers with other levels of education. Workers who were single or living with other adults without children had a significantly higher risk of depression compared to those in other forms of family relationships. Substance use was found to be associated with lower levels of depressive symptoms, suggesting that construction workers use alcohol and drugs as a coping strategy for short-term depressive symptom reduction. Construction organisations should develop strategies to protect the mental health of construction workers, particularly those who are prone to depression.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Substance Use Disorder and Other Mental Health Comorbidities: Evidence-Based Approaches to Prevention and Treatment)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Quality of Life and Associated Factors Among Older Adults in Central Nepal: A Cross-Sectional Study Using the WHOQOL-OLD Tool
by
Rubisha Adhikari, Rajani Shah, Kamal Ghimire, Birat Khanal, Sunil Baral, Anisha Adhikari, Dinesh Kumar Malla and Vishnu Khanal
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22(5), 693; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050693 (registering DOI) - 27 Apr 2025
Abstract
Ensuring people’s quality of life (QOL) has become increasingly challenging due to population aging. This study aimed to investigate the QOL among older people and factors associated with it in an urban setting of Central Nepal using the World Health Organization Quality of
[...] Read more.
Ensuring people’s quality of life (QOL) has become increasingly challenging due to population aging. This study aimed to investigate the QOL among older people and factors associated with it in an urban setting of Central Nepal using the World Health Organization Quality of Life (WHOQOL-OLD) tool. A cross-sectional study was conducted in Central Nepal. The association between QOL and independent variables was first examined using a univariate analysis of variance followed by multiple linear regressions. The mean age of the 366 participants was 70 years (standard deviation [SD]: 8.2 years). The mean of the overall QOL scores was 74.37 (SD: 7.82). Older people who were literate (regression coefficient (β): 1.909; 95% confidence interval (CI): 3.771 (1.986, 5.556)), who had an annual household income of NPR 40,000 (Nepalese Rupees) or more (β: 1.909: 95% CI: 0.337, 3.480), who reported health services as accessible (β: 4.019; 95% CI: 0.666, 7.371) and affordable (β: 3.176; 95% CI: 1.327, 5.025), and who reported partaking in physical activity (β: 2.107; 95% CI: 0.607, 3.606) had higher QOL scores compared to their respective counterparts. A holistic model of service using the social determinants of health framework is essential to improve the well-being of older people in Nepal.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Global Health)
Open AccessArticle
The Socio-Environmental Impact in the Adjacent Settlements of a Former Foundry
by
Griselda Vázquez-Quintero, Daniel Lira-Hernández, César Damián Pérez-Olmos, María Cecilia Valles-Aragón, Leonor Cortes-Palacios, César Guillermo García-González, Ireyli Zuluamy Iracheta-Lara, Myrna Concepción Nevárez-Rodríguez and Gilberto Sandino Aquino-de los Ríos
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22(5), 692; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050692 (registering DOI) - 27 Apr 2025
Abstract
Mining has caused major pollution, especially in poorly regulated areas. The former Ávalos Foundry in Chihuahua, Mexico left toxic contamination after its closure in 1997, affecting the nearby settlements. This study examines the socio-environmental impact on residents adjacent to the site. A total
[...] Read more.
Mining has caused major pollution, especially in poorly regulated areas. The former Ávalos Foundry in Chihuahua, Mexico left toxic contamination after its closure in 1997, affecting the nearby settlements. This study examines the socio-environmental impact on residents adjacent to the site. A total of 5773 dwellings were considered, with 4634 inhabited by 14,187 persons. A survey to 465 residents assessed sociodemographic aspects, environmental perceptions, and disposition to community participation. Tap water samples from 70 homes were analyzed for metals and compared to Mexican, American and European regulatory standards. Water pollutant dispersion was modeled using ArcGIS interpolation. Residents face economic, social, environmental, and health issues from ongoing contamination. Several suffer respiratory and skin diseases linked to excessive dust from the proximity to mining waste and unpaved streets. While the majority consider their lives comfortable or very comfortable, many would not have moved there if aware of the risks before moving. Despite concerns, most residents are reluctant to engage in community efforts to address the pollution. Tap water tests revealed levels above the regulatory standards of arsenic, copper, chromium, iron, manganese, and nickel, posing serious health risks. This study calls for immediate action, including awareness and health campaigns, environmental remediation, and intersectoral collaboration to secure funding for long-term solutions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Collection Environmental Risk Assessment)
►▼
Show Figures
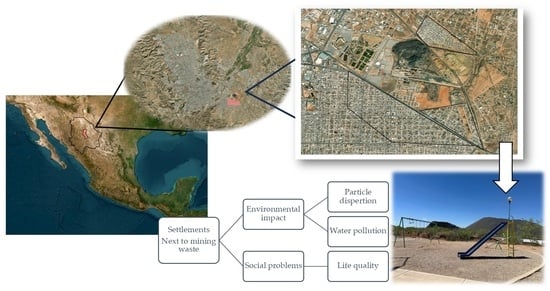
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
My Pillow Is Filled with Tears… Syrian Refugees’ Journey to Australia: Narratives of Human Courage and Resilience
by
Rosemary Qummouh, Sheridan Linnell, Shameran Slewa-Younan and Sera Harris
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22(5), 691; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050691 (registering DOI) - 27 Apr 2025
Abstract
This article showcases Syrian refugees’ narratives of trauma and survival, through a phenomenological approach to in-depth research, with refugees who have resettled in Australia. It explores their journey towards resettlement, highlighting the nexus between displacement in the home–transit–host countries and the biopsychosocial determinants
[...] Read more.
This article showcases Syrian refugees’ narratives of trauma and survival, through a phenomenological approach to in-depth research, with refugees who have resettled in Australia. It explores their journey towards resettlement, highlighting the nexus between displacement in the home–transit–host countries and the biopsychosocial determinants of mental health. Since the 2011 uprising, over 12 million Syrians have been displaced, both internally and worldwide. A refugee’s journey to safety often involves multiple displacements and exposure to dangerous, life-threatening, and dehumanising experiences. We have therefore adopted a qualitative approach that counters this dehumanisation by honouring the unique humanity in the voice of each of our research participants. This article aims to portray the nuanced interdependence between the individual, social, and political contexts of seven Syrian refugees’ lived experiences through an in-depth consideration of what they have told us, how they narrate their stories, and the meanings they ascribe to what they have experienced. The findings of this small yet eloquent study reinforce the insight that the journey to resettlement is far from linear and that resettlement itself is a process marked by recurrent and persistent complexities. The article suggests that the resilience of these refugees is best understood as an ethical and altruistic commitment to collective well-being, transcending notions of individual fortitude.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Refugee Health and Well-Being: Psychological, Behavioral and Biochemical Insights)
Open AccessSystematic Review
Green Environments for Sustainable Brains: Parameters Shaping Adaptive Neuroplasticity and Lifespan Neurosustainability—A Systematic Review and Future Directions
by
Mohamed Hesham Khalil
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22(5), 690; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050690 (registering DOI) - 26 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
As global urbanisation is rising and public health challenges intensify, this systematic review is conducted at a critical time to explore and explain the associations between the parameters of green environments and nuanced adaptive neuroplasticity in the human brain to advance the development
[...] Read more.
As global urbanisation is rising and public health challenges intensify, this systematic review is conducted at a critical time to explore and explain the associations between the parameters of green environments and nuanced adaptive neuroplasticity in the human brain to advance the development of health-focused sustainable cities and buildings in line with the concept of neurosustainability. This review includes studies involving participants of all ages and genders, with no restrictions on health conditions, exposed to green environments regardless of built environment comparisons. A systematic search of Scopus, PubMed, and Web of Science identified relevant studies published up to November 2024. The risk of bias was assessed using the PEDro scale and ROBINS-I domains, and data were analysed narratively due to heterogeneity. Twenty-three studies were included, conducted across the USA, UK, Germany, Spain, Bulgaria, the Netherlands, Japan, and South Korea. Findings reveal that green environments are associated with positive, region-specific brain changes across the lifespan, surprisingly from before birth to late adulthood. While forests showed more significant effects than blue spaces or urban green spaces, residential greenness emerged as a consistently effective exposure, especially within a 300–500 m buffer around home addresses, provided that sky visibility is present. Notably, no studies have examined green architecture or biophilic interiors, although they are more proximal, are associated with greater exposure time, have antagonistic effects, and may potentially limit sky visibility, highlighting a key gap for future research. Limitations include heterogeneity in exposure definitions, methodologies, and targeted brain regions. Still, this review offers a novel synthesis, providing insight into how greening the built environment may sustain not only the planet but also the plasticity of the brain. This review is registered with INPLASY (INPLASY2024110103) and forms part of a doctoral research project funded by the Cambridge Trust in partnership with the Jameel Education Foundation.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Dietary Fluoride Exposure During Early Childhood and Its Association with Dental Fluorosis in a Sample of Mexican Adolescents
by
Gina A. Castiblanco-Rubio, Emily C. Hector, Jose Urena-Cirett, Alejandra Cantoral, Howard Hu, Karen E. Peterson, Martha M. Tellez-Rojo and E. Angeles Martinez-Mier
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22(5), 689; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050689 (registering DOI) - 26 Apr 2025
Abstract
Dental fluorosis indicates past fluoride intake. People living in Mexico City are exposed to fluoridated salt, which contributes significantly to fluoride intake. This study aimed to (1) estimate fluoride intake during early childhood and fluorosis prevalence in permanent teeth in adolescence and (2)
[...] Read more.
Dental fluorosis indicates past fluoride intake. People living in Mexico City are exposed to fluoridated salt, which contributes significantly to fluoride intake. This study aimed to (1) estimate fluoride intake during early childhood and fluorosis prevalence in permanent teeth in adolescence and (2) identify intake windows associated with higher fluorosis scores in upper central incisors (UCIs). We included 432 participants from the ELEMENT project (Early-Life Exposures in Mexico to Environmental Toxicants), with data on fluoride intake at ages 1–5 and fluorosis (TFI) at adolescence. Median intakes ranged from 0.56 at age 1 to 1.14 mg/day at age 5, exceeding recommendations. All adolescents had some level of fluorosis, predominantly mild (62% with TFI 2). For every 0.1 mg of daily fluoride intake at age 1, the odds of higher TFI in UCIs were 1.08 [95% CI: 1.00–1.17]. At age 2, the odds were marginally significant [OR: 1.07; 95% CI: 1.00–1.16]. In conclusion, for participants of ELEMENT: (1) fluoride intake during early childhood exceeded recommendations and the prevalence of mild fluorosis in adolescence was high, and (2) fluorosis in UCIs was associated with dietary exposure during the first two years of life and may be used in future ELEMENT studies as exposure biomarkers.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Influence of Population Exposure to Fluoride on Oral Health)
►▼
Show Figures
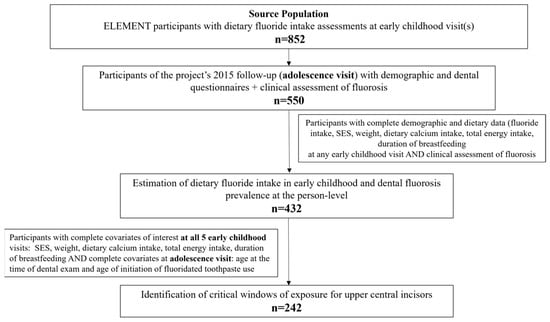
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
What Guides Organizations’ Current Dementia-Related Practices Across Four Canadian Provinces?
by
Maria Baranowski, Nancy Jokinen, Leslie Udell, Sandy Stemp, Tracey Berman and Shahin Shooshtari
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22(5), 688; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050688 (registering DOI) - 26 Apr 2025
Abstract
We conducted a survey to learn what guides current dementia-related practice to support community-dwelling adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities who may be experiencing dementia in Canada. We invited organizations working in health, disability, or senior sectors in 4 Canadian provinces to complete
[...] Read more.
We conducted a survey to learn what guides current dementia-related practice to support community-dwelling adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities who may be experiencing dementia in Canada. We invited organizations working in health, disability, or senior sectors in 4 Canadian provinces to complete an online cross-sectional survey between April and July 2023. A total of 173 people completed the survey, representing 125 unique organizations, and nearly half resided in Ontario. The most common support and services provided to adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities and their families were related to residential care, day programming, and group home living. Half of our survey respondents reported that they followed dementia-related practice guidelines. The most common guideline followed and early detection tool used were from the National Task Group on Intellectual Disabilities and Dementia Practices and the National Task Group-Early Detection and Screen for Dementia, respectively. Lack of awareness about guidelines and detection tools, challenges to implement the same, and organizational needs for future training and service provision were identified. Commitment to resources to monitor adults with IDD who may be experiencing dementia is recommended to provide meaningful support and service to them and their families.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Promoting Mentation: Assessment and Support for Dementia, Depression and Delirium)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Where Muscle Matters: How Regional Differences, Pain, and Gender Define Gamer Health
by
Joanne DiFrancisco-Donoghue, Min-Kyung Jung, Matteo J. Balentine and Hallie Zwibel
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22(5), 687; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050687 (registering DOI) - 26 Apr 2025
Abstract
Competitive gaming presents unique musculoskeletal challenges due to prolonged sitting and repetitive hand and arm movements. This study explores gender-specific regional lean body mass (LBM) differences and their associations with musculoskeletal discomfort in competitive gamers. Sixty participants (30 gamers and 30 matched controls;
[...] Read more.
Competitive gaming presents unique musculoskeletal challenges due to prolonged sitting and repetitive hand and arm movements. This study explores gender-specific regional lean body mass (LBM) differences and their associations with musculoskeletal discomfort in competitive gamers. Sixty participants (30 gamers and 30 matched controls; 15 males and 15 females in each group) underwent DXA scans to assess total and regional LBM, handgrip strength tests, and self-reported musculoskeletal pain surveys. Controls were matched for age and BMI and reported comparable academic and screen time but were not engaged in competitive gaming. Male gamers exhibited significantly reduced forearm (p < 0.05) and upper body LBM (p < 0.001), alongside lower grip strength (p < 0.001), compared to controls. Female gamers demonstrated lower upper body LBM (p = 0.01) but showed no significant differences in forearm lean mass or grip strength. In male gamers, negative correlations were observed between forearm LBM and lower back pain (r = −0.59, p < 0.01), highlighting the protective role of regional LBM against discomfort. Extended gaming duration was associated with increased musculoskeletal pain in both sexes (p < 0.05). These findings emphasize the need for targeted ergonomic interventions and physical conditioning programs to address muscle imbalances and reduce injury risk in esports athletes. Future research should focus on longitudinal and interventional designs to optimize musculoskeletal health and performance in this growing population.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Physical Fitness and Injury Prevention in Athletes)
►▼
Show Figures
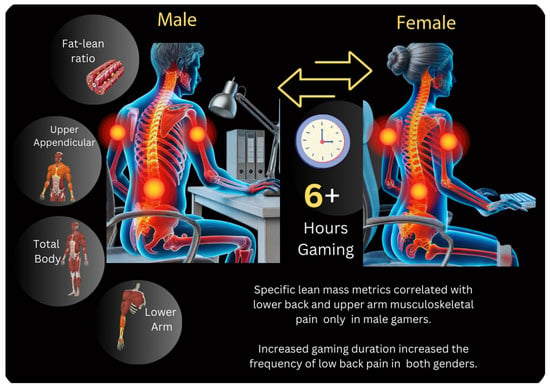
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exploring How Rheumatic Fever Is Portrayed on TikTok: A Descriptive Content Analysis
by
Siobhan Tu’akoi, Malakai Ofanoa, Samuela Ofanoa, Maryann Heather, Hinamaha Lutui and Felicity Goodyear-Smith
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22(5), 686; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050686 (registering DOI) - 26 Apr 2025
Abstract
TikTok is a popular social media platform offering educational opportunities for health issues such as rheumatic fever, which primarily affects 4–19-year-olds globally. This content analysis aimed to explore the type of rheumatic fever content available and popular on TikTok and the role that
[...] Read more.
TikTok is a popular social media platform offering educational opportunities for health issues such as rheumatic fever, which primarily affects 4–19-year-olds globally. This content analysis aimed to explore the type of rheumatic fever content available and popular on TikTok and the role that rheumatic fever representation may play in shaping public understanding and attitudes. The top 100 TikTok video posts under the hashtag #rheumaticfever were examined. Descriptive statistics were used to summarize video metrics and deductive thematic analysis enabled the coding of video content. The majority of TikTok users creating rheumatic fever content were patients or family members of people suffering from rheumatic fever (42%), followed by health professionals (30%). Forty-three percent of videos had negative connotations and personal stories were the most commonly coded type of video (42%). In terms of rheumatic fever content, symptoms (n = 59), medications/treatment (n = 37) and disease pathogenesis (n = 36) were the most common themes. Misinformation was identified in 3% of videos. This study provides a unique insight into who is making rheumatic fever-related content on TikTok and the primarily negative framing of narratives people are exposed to. There are opportunities for future health promotion strategies to focus on the gaps identified in this study, including information on where to seek health services, primordial prevention and stories of recovery.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Global Health)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Illegal Dumping Sites in Bloemfontein, South Africa: Respiratory Symptoms, Risk Factors, and Community Perspectives
by
Botle Maluleka, Phoka C. Rathebe and Busisiwe Shezi
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22(5), 685; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050685 (registering DOI) - 25 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Illegal waste dumping is a significant global issue, particularly in low- and middle-income countries such as South Africa. This study aimed to investigate the risk factors for acute respiratory symptoms among residents living near illegal domestic waste dumping sites. The study also explored
[...] Read more.
Illegal waste dumping is a significant global issue, particularly in low- and middle-income countries such as South Africa. This study aimed to investigate the risk factors for acute respiratory symptoms among residents living near illegal domestic waste dumping sites. The study also explored community perceptions regarding illegal dumping and its health effects. This cross-sectional study was conducted in Rocklands, Free State, South Africa, with 200 participants: 117 living within 0–5 km of a dumping site and 83 residing ≥5–10 km away. Data were collected using a structured questionnaire. Generalized linear models were employed to explore the relationship between proximity to illegal dumping sites and respiratory symptoms, adjusting progressively for confounders in successive models. Respiratory symptoms were more prevalent among those within 5 km of illegal dumping sites: cough (48.0% vs. 27.0%), shortness of breath (23.0% vs. 18.0%), wheezing (20.0% vs. 7.0%), and chest tightness (20.0% vs. 7.0%). Proximity was significantly associated with wheezing (PR: 2.77; 95% CI: 1.10–6.98) and chest tightness (PR: 2.86; 95% CI: 1.19–6.84). Community-driven initiatives, such as awareness campaigns and recycling, were strongly supported as solutions. These findings highlight the need for education on waste management. Collaborative efforts are essential to reduce illegal dumping and improve waste management.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Perinatal Multisite Psychiatry Databank: A Cohort Update
by
Mariane Aumais, Francois Freddy Ateba, Rahel Wolde-Giorghis, Kathelijne Keeren, Barbara Hayton, Sawsan Kalache, Isabelle Collin, Hannah Schwartz, Kirsten Gust, Marie-Josée Poulin, Andréanne Wassef, Katherine Tardif, Martin St-André, Irena Stikarovska, Phyllis Zelkowitz, Catherine M. Herba and Eszter Szekely
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22(5), 684; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050684 - 25 Apr 2025
Abstract
The Perinatal Multisite Databank (PMD) aims at facilitating research on perinatal mental health by collecting clinical information of patients referred for evaluations at perinatal mental health clinics across the province of Quebec, Canada with the potential to improve patient care and support evidence-based
[...] Read more.
The Perinatal Multisite Databank (PMD) aims at facilitating research on perinatal mental health by collecting clinical information of patients referred for evaluations at perinatal mental health clinics across the province of Quebec, Canada with the potential to improve patient care and support evidence-based practice. This study provides a detailed description of the first 693 participants concerning psychosocial risk characteristics, the prevalence of psychiatric disorders and comorbidity during the perinatal period, the evolution of perinatal depression and anxiety symptoms over time, and the treatments received. Data were collected using clinical reports and well-validated questionnaires at multiple timepoints (from pregnancy to 6 months postpartum). Results are discussed within the context of improving patient care and disease prevention strategies in the perinatal period.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Behavioral and Mental Health)
Open AccessSystematic Review
The Impact of Domiciliary Dental Care and Oral Health Promotion in Nursing Homes of Older Adults: A Systematic Review
by
Cibelle Cristina Oliveira dos Santos, Izabelle Muller Lessa Miranda, Katherine Thuller, Karoline Reis Silva, Leonardo Santos Antunes, Fernanda Signorelli Calazans and Bruna Lavinas Sayed Picciani
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22(5), 683; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050683 - 25 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: The global increase in the population older than 80 years has led to a paradigm shift centered in the hospital environment, with the inclusion of domiciliary oral health actions improving quality of life. This review evaluates the effects of domiciliary dental care
[...] Read more.
Background: The global increase in the population older than 80 years has led to a paradigm shift centered in the hospital environment, with the inclusion of domiciliary oral health actions improving quality of life. This review evaluates the effects of domiciliary dental care and oral health promotion in nursing homes of older adults. Methods: Seven databases were searched without date restrictions from 15 September to 21 November 2024. A manual search was also performed in the reference lists of the included articles. This research included studies evaluating older adults aged ≥80 years, regardless of sex, who received domiciliary dental care associated or not with oral health promotion, evaluating periodontal condition, dental caries, and the dental and denture plaque index. Regarding data collection and analysis, a risk of bias assessment was performed using RoB 2.0 and RoB 1.0, according to the study design. The level of evidence was assessed using the GRADE tool. Results: Of the 2415 studies found, 5 met the eligibility criteria. After quality assessment, one randomized clinical trial presented a moderate risk of bias, and one presented a low risk. Also, two non-randomized studies presented a high risk and one a low risk. The certainty of evidence was classified as low for all outcomes assessed. One study demonstrated a reduction in the caries level of participants. Regarding periodontal and gingival conditions, although the occurrence of deep pockets (greater than 3.5 mm) decreased over time, there was no significant difference between the control and intervention groups. The level of dental and denture plaque showed a slight reduction. Conclusion: There is limited evidence that domiciliary dental care in nursing homes for older adults can lead to a reduction in caries levels and that oral health programs can reduce dental and denture plaque in evaluations conducted over periods of up to two years. Although the results show a limited magnitude, this does not diminish the importance of promoting domiciliary oral health care.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Oral Health and Quality of Life in Older Adults)
►▼
Show Figures
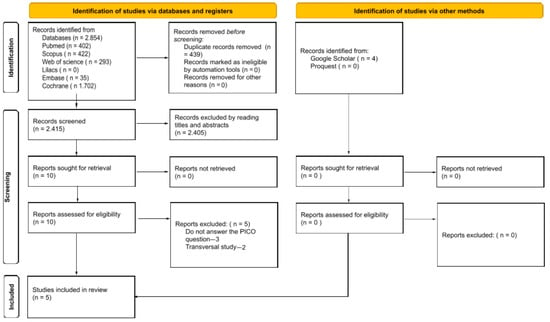
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Double Burden of Distress: Exploring the Joint Associations of Loneliness and Financial Strain with Suicidal Ideation During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Canada
by
Fahima Hassan, Lihui Liu and Cindy Feng
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22(5), 682; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050682 (registering DOI) - 25 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic, coupled with social distancing measures and economic disruptions, has been associated with increased experiences of loneliness and financial strain. While prior research has examined their separate associations with suicidal ideation, limited attention has been given to their joint relationship.
[...] Read more.
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic, coupled with social distancing measures and economic disruptions, has been associated with increased experiences of loneliness and financial strain. While prior research has examined their separate associations with suicidal ideation, limited attention has been given to their joint relationship. Methods: We used data from the 2022 Mental Health and Access to Care Survey (MHACS) (n = 9861; ages 15+ in Canada) to assess whether financial strain modifies the association between loneliness or emotional distress and suicidal ideation. Multivariable survey-weighted logistic regression was conducted, adjusting for sociodemographic, economic, psychosocial, and health-related characteristics, including mental health and substance use conditions. Results: Among the 9743 respondents who answered the question on suicidal ideation, 355 (3.65%) reported suicidal ideation. Compared to individuals with neither stressor, those who experienced loneliness or emotional distress alone had 1.54 times higher odds of suicidal ideation (aOR = 1.54, 95% CI: 1.29–1.84, p < 0.001), while those who reported financial strain alone had 0.58 times the odds (aOR = 0.58, 95% CI: 0.43–0.80, p = 0.001). The highest odds were observed among individuals who experienced both loneliness/emotional distress and financial strain, with an adjusted odds ratio of 2.05 (95% CI: 1.71–2.45, p < 0.001), indicating an interaction between these stressors. Conclusion: The co-occurrence of loneliness or emotional distress and financial strain was associated with higher odds of suicidal ideation during the COVID-19 pandemic, compared to individuals experiencing neither stressor. These findings highlight the importance of considering both social and economic stressors when assessing mental health risks. Given the cross-sectional nature of this study, further longitudinal research is needed to explore the temporal relationships and potential causal pathways linking these experiences to suicidal ideation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Depression and Suicide: Current Perspectives)
►▼
Show Figures
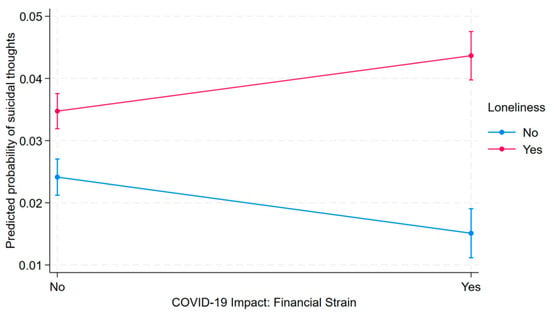
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Private Sector Engagement for Tuberculosis Services in Latin America: A Systematic Review
by
Carlos Podalirio Borges de Almeida, Leonid Lecca and Courtney M. Yuen
Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22(5), 681; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050681 - 25 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Objectives: Private sector engagement has been shown to improve tuberculosis diagnosis and treatment outcomes in Asia and Africa, but systematic reviews in 2015 and 2017 identified only two reports from Latin America. We conducted a systematic review to identify descriptions of private sector
[...] Read more.
Objectives: Private sector engagement has been shown to improve tuberculosis diagnosis and treatment outcomes in Asia and Africa, but systematic reviews in 2015 and 2017 identified only two reports from Latin America. We conducted a systematic review to identify descriptions of private sector engagement interventions for tuberculosis in Latin America. Methods: We systematically searched for reports on private sector engagement for tuberculosis services in Spanish- and Portuguese-speaking countries of the Western Hemisphere. On 1 November 2024, we searched PubMed, Embase, LILACS, and SciELO, with terms related to tuberculosis, the private sector, and eligible countries. We double-reviewed abstracts and full-text articles and classified private sector engagement mechanisms according to an established framework. Results: We identified seven documents describing five distinct interventions for private sector engagement in 10 countries. The most common engagement mechanism was technical support to increase awareness, knowledge, or capacity in the private sector. Intervention goals included promoting collaboration, ensuring adherence to national guidelines, increasing referrals to the public sector, and reducing tuberculosis drug sales in private pharmacies. Three impact evaluations found evidence of improved referral to the public sector. Conclusions: We found few reports of private sector engagement interventions for tuberculosis in Latin America, suggesting missed opportunities for collaborations to expand and improve tuberculosis service delivery. A lack of impact assessments suggests a dearth of evidence on the best models for private sector engagement to advance tuberculosis elimination in the Latin American region.
Full article
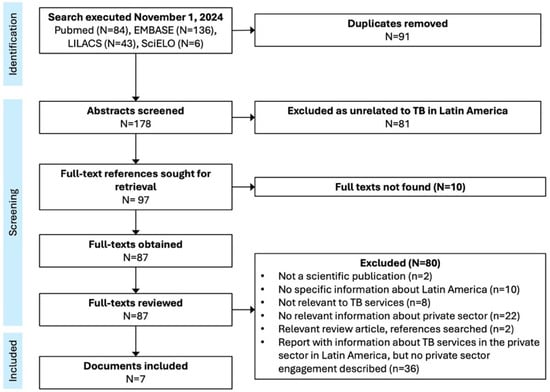
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- IJERPH Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal Browser-
arrow_forward_ios
Forthcoming issue
arrow_forward_ios Current issue - Vol. 22 (2025)
- Vol. 21 (2024)
- Vol. 20 (2023)
- Vol. 19 (2022)
- Vol. 18 (2021)
- Vol. 17 (2020)
- Vol. 16 (2019)
- Vol. 15 (2018)
- Vol. 14 (2017)
- Vol. 13 (2016)
- Vol. 12 (2015)
- Vol. 11 (2014)
- Vol. 10 (2013)
- Vol. 9 (2012)
- Vol. 8 (2011)
- Vol. 7 (2010)
- Vol. 6 (2009)
- Vol. 5 (2008)
- Vol. 4 (2007)
- Vol. 3 (2006)
- Vol. 2 (2005)
- Vol. 1 (2004)
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Environments, Forests, IJMS, Molecules, IJERPH
Molecules We Breathe: Volatile Phytocompounds for Forest Medicine
Topic Editors: Giovanni N. Roviello, Francesco MeneguzzoDeadline: 11 June 2025
Topic in
Healthcare, IJERPH, JCM, Nutrients, Sports
Effects of Exercise Behavior and Amount of Exercise on Public Health: How to Overcome Barriers to Increase Adherence
Topic Editors: Joao Gustavo Oliveira Claudino, Paula Alves Monteiro, Ana Carolina Paludo, Helder Fonseca, Enrico Fuini Puggina, Romulo Fernandes, Sílvia Rocha-Rodrigues, Julio Cerca SerraoDeadline: 1 July 2025
Topic in
Behavioral Sciences, Children, Healthcare, IJERPH, JFMK, Obesities
The Effect of Physical Activity on the Population's Health
Topic Editors: Stefania Paduano, Federica ValerianiDeadline: 31 July 2025
Topic in
Healthcare, IJERPH, JCM, Safety, Toxics
New Research in Work-Related Diseases, Safety and Health
Topic Editors: Alicja Bortkiewicz, Małgorzata KurpesaDeadline: 31 August 2025

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
IJERPH
The Lifelong Impact of Adverse Childhood Experiences on Health
Guest Editors: Ângela Rosa Pinho Costa Maia, Mariana GonçalvesDeadline: 30 April 2025
Special Issue in
IJERPH
Social Inequalities in Later Life: Care Services in the Future
Guest Editor: Ann LiljasDeadline: 30 April 2025
Special Issue in
IJERPH
Research on Emotional and Cognitive Development in Children
Guest Editor: Noemi FaeddaDeadline: 30 April 2025
Special Issue in
IJERPH
Understanding and Addressing Factors Related to Health Inequalities
Guest Editor: Nadav DavidovitchDeadline: 30 April 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
IJERPH
Health Behaviors, Risk Factors, NCDs and Health Promotion
Collection Editor: Stefano Campostrini
Topical Collection in
IJERPH
Outbreak of a Novel Coronavirus: A Global Health Threat
Collection Editor: Jianyong Wu









