Journal Description
Journal of Clinical & Translational Ophthalmology
Journal of Clinical & Translational Ophthalmology
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on ophthalmology published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: first decisions in 19 days; acceptance to publication in 4 days (median values for MDPI journals in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Journal of Clinical & Translational Ophthalmology is a companion journal of JCM.
subject
Imprint Information
Open Access
ISSN: 2813-1053
Latest Articles
MIGS, Cataract Surgery, or Both? An Analysis of Clinical Trial Data to Compare Efficacy and Outcomes on Glaucoma Patients
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(4), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3040020 - 28 Sep 2025
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Background: Glaucoma is the leading cause of irreversible blindness around the world and is characterized as a group of irreversible optic neuropathies with multiple risk factors such as age, race/ethnicity, sex, and intraocular pressure (IOP), amongst many others that play a role in
[...] Read more.
Background: Glaucoma is the leading cause of irreversible blindness around the world and is characterized as a group of irreversible optic neuropathies with multiple risk factors such as age, race/ethnicity, sex, and intraocular pressure (IOP), amongst many others that play a role in disease etiology. However, IOP is the only modifiable risk factor, with higher IOP often causing increased damage to the optic nerve, resulting in the vast majority of medical and surgical treatments aiming to reduce IOP. There are a number of interventions available to treat glaucoma including micro-invasive glaucoma surgery (MIGS), whose usage has drastically increased due to its safety and efficacy. Studies also highlight the IOP-reducing effect of cataract surgery, which is the most common procedure performed globally. However, other, more targeted therapies and surgeries have been shown to have a more significant effect on IOP reduction. The objective of this study is to compare the IOP and medication reduction between cataract surgery (CS), MIGS, and MIGS and cataract surgery (MACS) clinical trials. Methods: This analysis consisted of publicly available data on CS, MIGS, and MACS clinical trials from 2005 to 2017 using ClinicalTrials.gov. Data reporting and synthesis adhered to PRISMA guidelines. MIGS interventions studied in this analysis include iStent®, CyPass® Micro-Stent, Ex-PRESS®, Hydrus®, PRESERFLO™ MicroShunt, and XEN® Gel Stent. The main variables of interest are the mean IOP and mean number of glaucoma medications used. The primary outcomes were the baseline, post-procedure, and reduction in IOP and glaucoma medication use. Cohorts were further subdivided by the follow-up period (6, 12, and 24 months), as well as their medicated or unmedicated status for pre-op IOP measurement. PROSPERO CRD42025102892. Results: A total of 21 trials were included in this review, comprising 3330 clinical trial participants: 7 CS trials (N = 570), 13 MIGS trials (N = 1577), and 9 MACS trials (N = 1183). All interventions studied resulted in a decrease in both the IOP and medication usage with varying degrees. At 12 months, the wash-out baseline IOP reduction (mmHg) was 6.9 (27.5%) for CS, 8.8 (34.0%) for MIGS, and 8.2 (32.6%) for MACS. The medication reduction was 0.8 (56.1%) following CS, 1.0 (39.5%) for MIGS, and 1.3 (86.4%) for MACS. At 24 months, the wash-out baseline IOP reduction was 6.3 (25.1%) for CS, 8.4 (33.1%) for MIGS, and 7.6 (30.1%) for MACS. At 24 months, the medication reduction was 0.9 (58.3%) for CS, 1.5 (79.8%) for MIGS, and 1.3 (86.1%) for MACS. Conclusions: The results indicate that CS, MIGS, and MACS all result in a decrease in the IOP and glaucoma medications; however, MIGS and MACS outperform CS in IOP and medication reduction. Adopting MIGS and MACS for patients with ocular hypertension or mild-to-moderate glaucoma will help improve patient outcomes through reducing the IOP and medication burden. Given that glaucoma affects certain populations to a greater degree, future research analyzing racial representation is critical in ensuring the appropriate applicability of clinical trial results toward diverse populations.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Assessing Eye Care Needs Among Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease on Hemodialysis
by
Priya Agrawal, Ami Patel, Janet Alexander and Ramya Swamy
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(4), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3040019 - 27 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The prevalence of vision impairment and eye disease is higher among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), yet there are no standardized guidelines for this vulnerable population. We hypothesized that there are self-reported unmet ophthalmic care needs among patients receiving hemodialysis. We also
[...] Read more.
The prevalence of vision impairment and eye disease is higher among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), yet there are no standardized guidelines for this vulnerable population. We hypothesized that there are self-reported unmet ophthalmic care needs among patients receiving hemodialysis. We also hypothesized that limited awareness of the connection between eye health and CKD is a significant barrier to receiving eye care. Methods: From June 2022 to July 2022, patients on dialysis were recruited in-person at two Independent Dialysis Foundation sites in Baltimore, Maryland. Participants completed a survey assessing recent eye exam history, barriers to care, and health literacy. Results: Of 82 participants, 43 (52%) had not received a complete eye exam within the past year. The most common reasons were scheduling conflicts (15 [35%]), not wanting an eye exam (12 [28%]), and costs (6 [14%]). Less than half of respondents (40, 41%) were unaware of a relationship between kidney disease and eye health. Conclusions: Results suggest potential unmet eye care needs and low awareness of CKD-related ocular risks among dialysis patients. Interventions to enhance provider recommendations, improve health literacy, and reduce logistical barriers may help prevent avoidable vision loss in this high-risk population.
Full article
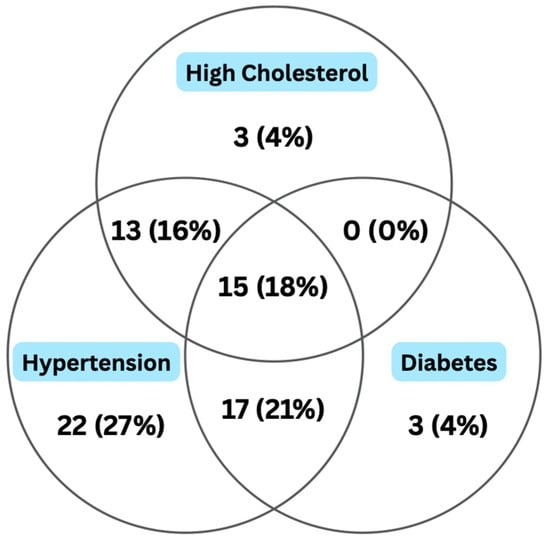
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Presbyopia-Correcting Intraocular Lens with Butterfly-Shaped Central Area Implanted in a Large Angle Kappa Patient: A Case Report
by
Camille Bosc, Sandra Delaunay, Anne Barrucand and Irene Martínez-Alberquilla
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(3), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3030018 - 11 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Intraocular lens (IOL) alignment is crucial for optimal performance in presbyopia-correcting designs. The aim was to report a case of a patient with a high angle kappa implanted with the continuous transitional focus (CTF) Precizon Prebyopic NVA IOL. Case presentation: A 51-year-old
[...] Read more.
Background: Intraocular lens (IOL) alignment is crucial for optimal performance in presbyopia-correcting designs. The aim was to report a case of a patient with a high angle kappa implanted with the continuous transitional focus (CTF) Precizon Prebyopic NVA IOL. Case presentation: A 51-year-old patient presenting large angle kappa values (0.6/0.8 mm) was implanted with the Precizon Prebyopic NVA IOL and followed-up 1 and 10 months post-surgery. This IOL is designed with a butterfly-shaped central area that allows the orientation of the lens so that the visual axis passes through the wider diameter of the optic zone. Postoperative refraction was −0.25D of cyl at 80° for the right eye and +0.25D −0.50D cyl at 170°. Corrected distance visual acuity (CDVA) at the last visit was −0.1 logMAR monocularly and −0.2 logMAR binocularly. Binocular uncorrected distance (UDVA), intermediate (UIVA) and near visual acuities (UNVA) were −0.1, 0.1 and 0.1 logMAR, respectively. The corrected binocular defocus curve exhibited outstanding vision at the 0.00D defocus level and showed a continuous range of functional vision from distance to near. Overall excellent satisfaction was reported, along with low levels of photopic phenomena. Conclusions: Precizon Presbyopic NVA IOL provided satisfactory vision and low levels of photic phenomena in a high angle kappa patient who would potentially be excluded from presbyopia-correcting IOL implantation.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Effect of Netarsudil 0.02% on a Patient with Fuchs Corneal Dystrophy and Radial Keratotomy
by
Praneetha Thulasi, Shae Chambers and Soroosh Behshad
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(3), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3030017 - 15 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study reports an unusual case of dramatic change in visual acuity, pachymetry, and corneal topography in a patient with a history of Fuchs dystrophy and radial keratotomy following the use of Rho-kinase (ROCK) inhibitor. A patient with a history of 8-cut radial
[...] Read more.
This study reports an unusual case of dramatic change in visual acuity, pachymetry, and corneal topography in a patient with a history of Fuchs dystrophy and radial keratotomy following the use of Rho-kinase (ROCK) inhibitor. A patient with a history of 8-cut radial keratotomy (RK), astigmatic keratotomy (AK), and Fuchs dystrophy showed dramatic changes in visual acuity, pachymetry, and corneal topography after using one drop of netarsudil 0.02%. The dramatic effect of netarsudil in our patient may be due to increased penetration of a rho-kinase inhibitor from the corneal incisions, facilitating the effect on corneal endothelium, resulting in a dramatic improvement in corneal pachymetry. This suggests a potential role for corneal incisions to improve the effectiveness of rho-kinase inhibitors in patients with Fuchs dystrophy.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Racial and Gender Disparities in Clinical Trial Representation for Age-Related Macular Degeneration Treatments: A Scoping Review
by
Amirmohammad Shafiee, Taylor Juran, Iza Zabaneh, Deepkumar Patel and Karen Allison
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(3), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3030016 - 13 Aug 2025
Abstract
Background/Objective: Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a leading cause of irreversible vision loss. Intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) therapy is the primary treatment for neovascular AMD. This study aimed to assess racial, ethnic, and gender representation in U.S.-based randomized controlled trials (RCTs)
[...] Read more.
Background/Objective: Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a leading cause of irreversible vision loss. Intravitreal anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) therapy is the primary treatment for neovascular AMD. This study aimed to assess racial, ethnic, and gender representation in U.S.-based randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of anti-VEGF therapies. Methods: A systematic PubMed search identified 19 eligible RCTs. Titles and abstracts were screened, and demographic data were independently extracted and cross-verified. Chi-squared analysis was used to evaluate disparities in participant representation. Risk of bias was assessed using the ROBIS checklist. Results: Among 8003 participants across 19 trials, 92.3% were Caucasian. Asian, African American, Hispanic/Latino, and American Indian participants collectively comprised just over 5%. This underrepresentation of non-Caucasian groups was statistically significant (p < 0.01, df = 4) and not associated with study sponsorship. Gender analysis showed 59% female and 41% male participation, which was not statistically significant (p = 0.83, df = 1). Conclusions: Non-Caucasian populations remain significantly underrepresented in anti-VEGF RCTs for AMD. This raises concerns about the generalizability of trial findings to diverse populations. Future clinical trials must prioritize inclusive recruitment to ensure equitable, evidence-based care for all patients.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Retinal Diseases: Recent Advances in Diagnosis and Treatment)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
An Insight into Current and Novel Treatment Practices for Refractory Full-Thickness Macular Hole
by
Chin Sheng Teoh
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(3), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3030015 - 1 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Refractory full-thickness macular holes (rFTMHs) present a significant challenge in vitreoretinal surgery, with reported incidence rates of 4.2–11.2% following standard vitrectomy with internal limiting membrane (ILM) peeling and gas tamponade. Risk factors include large hole size (>400 µm), chronicity (>6 months), high myopia,
[...] Read more.
Refractory full-thickness macular holes (rFTMHs) present a significant challenge in vitreoretinal surgery, with reported incidence rates of 4.2–11.2% following standard vitrectomy with internal limiting membrane (ILM) peeling and gas tamponade. Risk factors include large hole size (>400 µm), chronicity (>6 months), high myopia, incomplete ILM peeling, and post-operative noncompliance. Multiple surgical techniques exist, though comparative evidence remains limited. Current options include the inverted ILM flap technique, autologous ILM transplantation (free flap or plug), lens capsular flap transplantation (autologous or allogenic), preserved human amniotic membrane transplantation, macular subretinal fluid injection, macular fibrin plug with autologous platelet concentrates, and autologous retinal transplantation. Closure rates range from 57.1% to 100%, with selection depending on hole size, residual ILM, patient posturing ability, etc. For non-posturing patients, fibrin plugs are preferred. Residual ILM cases may benefit from extended peeling or flap techniques, while large holes often require scaffold-based (lens capsule, amniotic membrane) or fibrin plug approaches. Pseudophakic patients should avoid posterior capsular flaps due to lower success rates. Despite promising outcomes, the lack of randomized trials necessitates further research to establish evidence-based guidelines. Personalized surgical planning, considering anatomical and functional goals, remains crucial in optimizing visual recovery in rFTMHs.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Seven-Year Outcomes of Aflibercept in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration in a Teaching Hospital Setting
by
Antoine Barloy, Florent Boulanger, Benjamin Jany and Thi Ha Chau Tran
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(3), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3030014 - 30 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background: In clinical practice, visual outcomes with anti-VEGF therapy may be worse than those observed in clinical trials. In this study, we aim to investigate the long-term outcomes of neovascularization treated with intravitreal aflibercept injections (IAI) in a teaching hospital setting. Methods: This
[...] Read more.
Background: In clinical practice, visual outcomes with anti-VEGF therapy may be worse than those observed in clinical trials. In this study, we aim to investigate the long-term outcomes of neovascularization treated with intravitreal aflibercept injections (IAI) in a teaching hospital setting. Methods: This is a retrospective, single-center study including 81 nAMD patients (116 eyes), those both newly diagnosed and switched from ranibizumab. All patients had a follow-up duration of at least seven years. Treatment involved three monthly injections followed by either a pro re nata (PRN) or treat and extend regimen. Follow-up care was primarily conducted by training physicians. The primary endpoint was the change in best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) over seven years. Secondary endpoints included central retinal thickness changes, qualitative OCT parameters, macular atrophy progression, injection frequency, and treatment adherence. Results: Among the 116 eyes, 52 (44.8%) completed the seven-year follow-up. Visual acuity improved by +2.1 letters in the overall population (+6.3 letters in treatment-naive eyes) after the loading phase but gradually declined, resulting in a loss of −12.3 letters at seven years. BCVA remained stable (a loss of fewer than 15 letters) in 57.7% of eyes. Central retinal thickness (CRT) decreased significantly during follow-up in both naive and switcher eyes. Macular atrophy occurred in 94.2% of eyes, progressing from 1.42 mm2 to 8.55 mm2 over seven years (p < 0.001). The mean number of injections was 4.1 ± 1.8 during the first year and 3.7 per year thereafter. Advanced age at diagnosis was a risk factor for loss to follow-up, with bilaterality being a protective factor against loss to follow-up (p < 0.05). Conclusions: This study highlights the challenges faced by a retina clinic in a teaching hospital. Suboptimal functional and anatomical outcomes in real life may derive from insufficient patient information and inconsistent monitoring, which contributes to undertreatment and affects long-term visual outcomes. It also raises concerns about supervision in a teaching hospital which needs to be improved.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Multimodal Ophthalmic Imaging and Therapeutic Advances in Retinal Diseases: Real-World Insights and Clinical Outcomes)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comparative Analysis of Cycloplegic and Non-Cycloplegic Refraction in Children and Adolescents: Implications for Accurate Assessment of Refractive Errors
by
Ana Maria Varošanec, Leon Marković and Zdenko Sonicki
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(3), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3030013 - 16 Jul 2025
Abstract
Purpose: This retrospective study aimed to compare the efficacy of cycloplegic (CR) versus non-cycloplegic refraction (NCR) methods in detecting refractive errors among children and adolescents. Methods: Electronic data from pediatric ophthalmology clinics at the University Hospital “Sveti Duh”; Zagreb, Croatia, from January 2008
[...] Read more.
Purpose: This retrospective study aimed to compare the efficacy of cycloplegic (CR) versus non-cycloplegic refraction (NCR) methods in detecting refractive errors among children and adolescents. Methods: Electronic data from pediatric ophthalmology clinics at the University Hospital “Sveti Duh”; Zagreb, Croatia, from January 2008 to July 2023, were analyzed. Comprehensive eye examinations, including Logarithmic Visual Acuity tests, subjective refraction, cycloplegic retinoscopy, slit lamp, and fundus examinations, were conducted. Results: The dataset included 1075 individuals, with 180 undergoing NCR and 895 undergoing CR. In premyopes, the NCR group had a longer follow-up (5.04 vs. 3.45 years; p < 0.001) with similar SE progression. In low myopia, NCR showed more negative first visit SE (−1.86 D vs. −1.35 D; p < 0.001) and faster progression (p = 0.01). In high myopia, follow-up was longer in NCR (5.08 vs. 2.08 years; p = 0.03) with no other significant differences. SE progression was highest in 4–6-year-olds and significantly faster in NCR (−0.61 vs. −0.40 D/year; p = 0.05). Conclusions: Cycloplegic refraction is essential for accurately assessing refractive status, especially in cases of low myopia, as it prevents misclassification and ensures precise evaluation in children and adolescents, thereby facilitating the appropriate diagnosis and treatment of refractive errors.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Does Keratoconus Follow Rundle’s Curve?
by
Srujana Sahebjada, Adam A. Moktar, Sara Vogrin, Elsie Chan, Paul N. Baird and Mark Daniell
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(3), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3030012 - 26 Jun 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Rundle’s curve describes the natural progression of disease as gradually worsening before reaching a peak and stabilizing. This study aimed to investigate whether Rundle’s curve could be applied to keratoconus over a five-year follow-up period. Methods: Longitudinal study. Patients with keratoconus who
[...] Read more.
Background: Rundle’s curve describes the natural progression of disease as gradually worsening before reaching a peak and stabilizing. This study aimed to investigate whether Rundle’s curve could be applied to keratoconus over a five-year follow-up period. Methods: Longitudinal study. Patients with keratoconus who underwent Pentacam tomography imaging from the Australian Study of Keratoconus were included in this study. Patients who received surgical treatment for keratoconus were excluded. Latent class analysis was performed for five parameters: Kmean front, Kmean back, pachymetry pupil, pachymetry minimum and pachymetry apex. A total of 522 patients and 1041 eyes were included for analysis. Most parameters were stable. However, worsening keratoconus in a minority of patients (less than 5% of the population) was observed across the last year of follow-up. The patients that showed progression in the final year were younger in age and had higher baseline parameters. Results: This study suggests keratoconus does not conform to the classic Rundle’s curve of disease progression. Instead, keratoconus exhibits a distinct course characterized by an increased risk of progression among younger individuals and eyes with higher baseline parameter values. Conclusions: These findings underscore the importance of considering treatments that halt disease progression, such as corneal collagen crosslinking, particularly in this specific subgroup of patients.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Prevalence of Foveal Hypoplasia in Inherited Retinal Diseases
by
Rebhi Abuzaitoun, Kari Branham, Dana Schlegel, K. Thiran Jayasundera and Abigail T. Fahim
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(3), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3030011 - 26 Jun 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: The prevalence of foveal hypoplasia in different inherited retinal diseases (IRDs) has not been compared in a large patient cohort. We aimed to investigate the prevalence and visual significance of foveal hypoplasia in IRDs. Methods: Participants included patients with IRDs and control
[...] Read more.
Background: The prevalence of foveal hypoplasia in different inherited retinal diseases (IRDs) has not been compared in a large patient cohort. We aimed to investigate the prevalence and visual significance of foveal hypoplasia in IRDs. Methods: Participants included patients with IRDs and control subjects. All patients had macular optical coherence tomography (OCT). Results: Among our 357 patients, 123 had rod-cone dystrophy (34.5%), 22 had cone/cone-rod dystrophy (6.2%), 30 had macular dystrophy (8.4%), and 182 (51%) were controls. Having a phenotype of rod-cone (OR = 12.9, p < 0.001) or cone/cone-rod dystrophy (OR = 10.2, p < 0.001) was associated with higher odds of having foveal hypoplasia. Males had higher odds of having foveal hypoplasia (OR = 2.4, p = 0.006). The prevalence of foveal hypoplasia in the retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator (RPGR) group (8/15 (53.3%)) was significantly higher than in matched controls (0/15, 0.0%) (p = 0.002). Atypical foveal hypoplasia had the highest LogMAR of 0.50 (±0.37), which was higher than grade one 0.16 (±0.17) (p = 0.038). Grade one LogMAR was not different from normal fovea 0.20 (±0.28) (p = 0.572). Conclusions: We report that rod-cone and cone/cone-rod IRDs are associated with foveal hypoplasia. Based on our findings, detection of foveal hypoplasia in a patient with reduced vision should prompt consideration of an IRD.
Full article
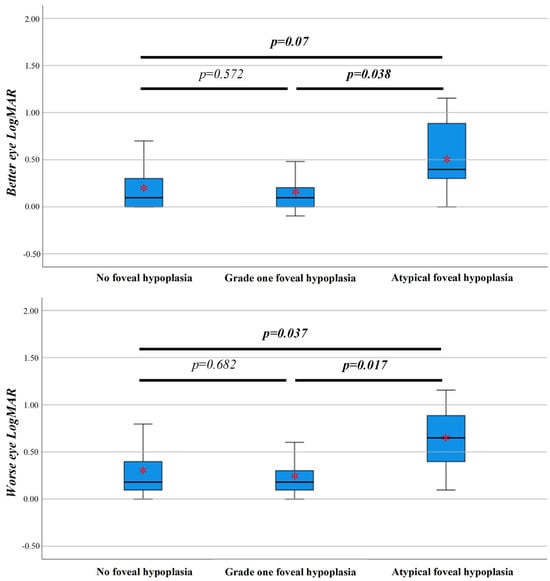
Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Iatrogenic Posterior Polar Cataract with Capsular Cystic Formation Following Lens Touch During Intravitreal Injection: A Case Report and Literature Review
by
Filomena Palmieri, Lorenzo Fabozzi, Christopher Leak and Vincenzo Maurino
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(2), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3020010 - 27 May 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This case report describes a unique ocular finding in a 64-year-old male with a history of central serous chorioretinopathy with choroidal neovascular membrane, treated with intravitreal injections of Aflibercept. The patient was found to have an iatrogenic retro-lenticular non-pigmented cystic formation in the
[...] Read more.
This case report describes a unique ocular finding in a 64-year-old male with a history of central serous chorioretinopathy with choroidal neovascular membrane, treated with intravitreal injections of Aflibercept. The patient was found to have an iatrogenic retro-lenticular non-pigmented cystic formation in the left eye, an anomaly not previously documented in the literature. Comprehensive imaging included ultrasound biomicroscopy and anterior segment optical coherence tomography. This report emphasises a rare ocular finding and the significance of recognising iatrogenic cataracts following intravitreal injections. It also highlights the necessity of individualised patient management and preoperative evaluations to prevent surgical complications.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Use of Ologen Collagen Matrix in Combination with XEN45 Microstent for the Treatment of Glaucoma: A Retrospective Chart Review
by
Catherine Johnson, Michael Jensen, John A. Musser, Neil Kelkar, Kevin Eid, Ryan T. Wallace, Cole Swiston, Ben J. Brintz, Austin Nakatsuka, Brian C. Stagg and Craig J. Chaya
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(2), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3020009 - 14 May 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: In this study, we compare the 12-month results of eyes that underwent ab externo, open-conjunctival XEN45 gel stent placement with mitomycin C (MMC) with and without the intraoperative addition of Ologen collagen matrix (XEN45 and XEN45 + Ologen groups, respectively). Methods: Intraocular
[...] Read more.
Background: In this study, we compare the 12-month results of eyes that underwent ab externo, open-conjunctival XEN45 gel stent placement with mitomycin C (MMC) with and without the intraoperative addition of Ologen collagen matrix (XEN45 and XEN45 + Ologen groups, respectively). Methods: Intraocular pressure (IOP) measurements were recorded postoperation at 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, and 9 months, and 12 months, and IOP reduction, reduction in number of IOP-lowering medications, and success rate were compared between XEN45 and XEN45 + Ologen groups. A complete success was defined as a ≥20% drop from baseline IOP at 12 months without the use of medications and without any of the following: an additional procedure (e.g., needling), a recorded IOP ≥ 21 mm Hg at two consecutive visits, or the occurrence of catastrophic events (e.g., no light perception (NLP)). A qualified success was defined as an IOP reduction of ≥20% from baseline with the use of medications. We included 145 eyes with at least 1 month of follow-up data, 46 in the XEN45 group and 99 in the XEN45 + Ologen group. Of these, 113 eyes had 12 months of follow-up data comprising 41 XEN45 eyes and 72 XEN45 + Ologen eyes. Results: There were no significant differences in the IOP change from baseline between XEN45 and XEN45 + Ologen groups except at the 3-month postop timepoint (p < 0.05). At the 12-month follow-up, 41.5% (17/41) of XEN45 eyes and 52.8% (38/72) of XEN45 + Ologen eyes met complete or qualified success criteria. Conclusions: No significant differences in success rate and decrease in the number of IOP-lowering medications from baseline were identified between XEN45 and XEN45 + Ologen groups.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
AI-Powered Smartphone Diagnostics for Convergence Insufficiency
by
Ahmad Khatib, Shmuel Raz, Haia Nasser, Haneen Jabaly-Habib and Ilan Shimshoni
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(2), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3020008 - 22 Apr 2025
Abstract
Background: This study innovatively combines Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms with smartphone technology, automatically detecting the Near Point of Convergence (NPC) and diagnosing Convergence Insufficiency (CI) without the need for extra diagnostic tools and, notably, without having to rely on the subject’s vocal response,
[...] Read more.
Background: This study innovatively combines Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms with smartphone technology, automatically detecting the Near Point of Convergence (NPC) and diagnosing Convergence Insufficiency (CI) without the need for extra diagnostic tools and, notably, without having to rely on the subject’s vocal response, marking an unprecedented approach in the field to the best of our knowledge. Methods: This was a prospective study that enrolled 86 participants. The real-time tracking of eye structures and movements was conducted using AI technologies integrated with a mobile application (MobileS). Participants brought the smartphone closer, focusing on a target displayed on the screen. The system calculated pupillary distance (PD) and phone-to-face distance, incorporating a unique feature called the exodeviation episode’s counter (ExoCounter) to determine the NPC. Additionally, participants underwent testing using the RAF Ruler test (RulerT), considering the ground truth. Results: MobileS demonstrated significant correlation with the RulerT, as evidenced by a Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.74 (p < 0.001) and an Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC) of 0.73 (p < 0.001), highlighting its reliability and consistency with conventional ophthalmic testing. Additionally, the system exhibited notable sensitivity and specificity in diagnosing CI. Notably, user feedback indicated a preference for the MobileS, with 71% of participants favouring it for its ease of use and comfort. Conclusions: MobileS is a precise, user-friendly tool for independent NPC measurement, applicable in tele-ophthalmology and home-based care. Its versatility extends beyond CI diagnosis, marking a significant advancement in ophthalmic diagnostics for accessible and efficient eye care.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Augmented and Artificial Intelligence in Ophthalmology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Reactivation of Ocular Toxoplasmosis in Immunosuppressed Neurosarcoidosis: A Case Report
by
Antonio Salvelli, Alba Chiara Termite, Pasquale Viggiano, Silvana Guerriero, Giacomo Boscia, Mariapia Laterza, Enrico Settimo and Francesco Boscia
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(2), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3020007 - 21 Apr 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Objective: To report a case of ocular toxoplasmosis reactivation in a patient with neurosarcoidosis undergoing immunosuppressive therapy. Methods: Case report and literature review. Results: A 34-year-old male with neurosarcoidosis, treated with Infliximab and Mycophenolate Mofetil, presented with sudden visual decline in his left
[...] Read more.
Objective: To report a case of ocular toxoplasmosis reactivation in a patient with neurosarcoidosis undergoing immunosuppressive therapy. Methods: Case report and literature review. Results: A 34-year-old male with neurosarcoidosis, treated with Infliximab and Mycophenolate Mofetil, presented with sudden visual decline in his left eye. Multimodal imaging revealed active chorioretinitis. Serological tests showed elevated Toxoplasma IgG levels with normal IgM levels. Treatment with oral corticosteroids and antibiotics led to significant improvements in vitreous turbidity and lesion inactivity at follow-up, despite unchanged visual acuity. Conclusions: This case highlights the risk of toxoplasmosis reactivation in immunosuppressed sarcoidosis patients. It emphasizes the importance of considering ocular toxoplasmosis even with normal IgM levels, and demonstrates the value of multimodal imaging in diagnosis and follow-up.
Full article
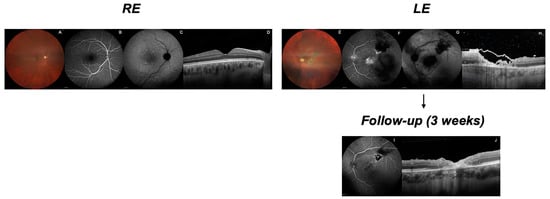
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Three-Dimensional Printing for Accessible and Personalized Ophthalmic Care: A Review
by
Mina Mina, Ajay Kumar Goel, Fady Mina, Doris Goubran and Nand Goel
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(2), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3020006 - 26 Mar 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Over 2.2 billion people across the globe face significant barriers to accessing essential ophthalmic care, with elderly, rural, and refugee populations being disproportionately affected, deepening existing disparities in eye care. Three-dimensional printing is a novel technology that has the potential to transform the
[...] Read more.
Over 2.2 billion people across the globe face significant barriers to accessing essential ophthalmic care, with elderly, rural, and refugee populations being disproportionately affected, deepening existing disparities in eye care. Three-dimensional printing is a novel technology that has the potential to transform the field and improve access by alleviating many patient-specific barriers. This article delves into the evolution of 3D printing within ophthalmology, highlighting its current applications and future potential. It explores various 3D printing techniques and numerous biomaterials discussing their effectiveness in creating advanced solutions such as bioengineered corneas, ocular prosthetics, and innovative treatments for dry eye syndrome, from punctal plugs to lacrimal gland models. Additionally, 3D printing has revolutionized drug delivery systems for conditions like glaucoma, retinal diseases, and ocular brachytherapy. Whether through 3D printed contact lens-based drug delivery systems or polycaprolactone implants that biodegrade and provide sustained drug release without adverse effects, these systems hold immense potential in the field. Despite its promise, the integration of 3D printing into clinical practice presents challenges, which the article addresses alongside strategies for overcoming them. By mapping out the technological advancements and challenges, this review offers a roadmap for enhancing global eye care accessibility and improving patient outcomes on a global scale.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessPerspective
Imaging the Anterior Segment in Spaceflight: Understanding and Preserving Astronaut Ocular Health for Long-Duration Missions
by
Joshua Ong, Ritu Sampige, Ryung Lee, Hamza Memon, Nicholas Panzo, Cihan Mehmet Kadipasaoglu, Yannie Guo, Baltaj S. Sandhur, Benjamin Soares, Daniela Osteicoechea, Ethan Waisberg, Alex Suh, Tuan Nguyen, Mouayad Masalkhi, Prithul Sarker, Nasif Zaman, Alireza Tavakkoli, John Berdahl, Patricia Chévez-Barrios and Andrew G. Lee
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3010005 - 18 Mar 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In light of the potential effects of spaceflight on the anterior segment of the eye, there is a pressing need for anterior segment imaging to be available and accessible to monitor astronauts’ ocular health, including alterations to the cornea and lens. We aim
[...] Read more.
In light of the potential effects of spaceflight on the anterior segment of the eye, there is a pressing need for anterior segment imaging to be available and accessible to monitor astronauts’ ocular health, including alterations to the cornea and lens. We aim to highlight the clinical basis and need for anterior segment imaging for astronauts. We explore the impacts of spaceflight-associated hazards, including microgravity and radiation, on astronauts’ risk of developing anterior segment pathology including risk of ocular trauma, infection, dry eye symptoms, cataracts, and possibly additional pathologies from increased radiation exposure. Such risks highlight the potential value that longitudinal assessment of anterior ocular structures would offer in future spaceflight missions. Specifically, anterior segment imaging would enable evaluations of corneal morphology, including longitudinal monitoring for microgravity-induced changes, and evaluation of interventions that aim to preserve anterior segment health during spaceflight. Lastly, non-invasive anterior segment imaging allows for unique insights into astronaut ocular health and can be performed routinely through modalities such as anterior segment optical coherence tomography (AS-OCT) and ultrasound biomicroscopy (UBM). We discuss these modalities and their implications for astronaut health during future spaceflight.
Full article
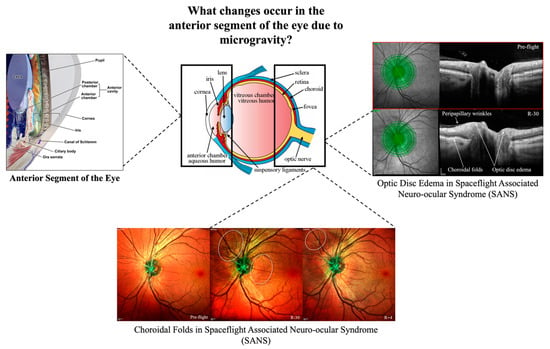
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Corneal Graft Dehiscence in Patients on Oral Angiotensin-Inhibiting Medications: Plausible Relationship and Review of the Literature
by
Jie Zhang and Jay J Meyer
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3010004 - 27 Feb 2025
Abstract
Wound dehiscence is a rare complication after penetrating keratoplasty (PK) that may occur with or without prior trauma. Multiple factors may influence corneal wound healing, including patient factors, corneal wound characteristics, and other external factors. There is also the possibility that systemic medications
[...] Read more.
Wound dehiscence is a rare complication after penetrating keratoplasty (PK) that may occur with or without prior trauma. Multiple factors may influence corneal wound healing, including patient factors, corneal wound characteristics, and other external factors. There is also the possibility that systemic medications could impact corneal wound healing. Possible factors that may predispose a cornea to experience wound dehiscence are discussed. We propose a hypothesis that oral angiotensin-inhibiting medications could play a role in reduced corneal wound healing. A literature review was conducted to investigate the effect of angiotensin inhibitors on corneal wound healing. Five patients on systemic oral angiotensin-inhibiting medications at the time of PK developed dehiscence of the graft–host wound junction following removal of sutures. The dehiscence required resuturing in all cases and resulted in an expulsive choroidal hemorrhage and complete loss of vision in one eye. Age, diabetes, lack of corneal neovascularization, early suture removal, underlying epithelial basement membrane dystrophy, corneal oedema, slower tapering of topical corticosteroid dosage, and glaucoma medication with preservatives were possible predisposing factors for some of these instances of wound dehiscence. However, oral angiotensin-inhibiting medications were taken by all patients in this series, and the literature suggests that ACE inhibitors and ARBs can reduce corneal fibrosis, resulting in inadequate healing. Oral angiotensin-inhibiting medications could have played an anti-fibrotic role in these corneae and predisposed them to wound dehiscence with minimal trauma. Despite limited evidence, these medications warrant further investigation as potential modulators of corneal wound healing.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advancements in Cornea Transplantation)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
A Novel Combined Technique to Assist with the Removal of Orbital Cavernous Venous Malformation of the Orbit Using High-Resolution Cone Beam Computed Tomography (Hr-Cbct) Imaging-Guided Embolization—Two Case Reports and a Literature Review
by
Luigi Caretti, Pietro Amistà, Cristina Monterosso and Martina Formisano
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3010003 - 5 Feb 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Orbital cavernous venous malformations (CVMs) are the most common primary lesions in the orbit, characterized by slow growth and benign nature. CVMs that become symptomatic require intervention. Surgical management is guided by the expertise of the operating surgeon. Common surgical techniques include anterior
[...] Read more.
Orbital cavernous venous malformations (CVMs) are the most common primary lesions in the orbit, characterized by slow growth and benign nature. CVMs that become symptomatic require intervention. Surgical management is guided by the expertise of the operating surgeon. Common surgical techniques include anterior orbitotomy (transconjunctival and transcutaneous), lateral and transcranial orbitotomy, and endoscopic transnasal approaches. Liquid agent embolization aids in easier lesion resection with reduced blood loss and potential prevention of recurrence. Our case reports detail the advantages and disadvantages of this approach, showcasing collaboration between neuroradiologists and orbital surgeons.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
A Review of Ocular and Systemic Side Effects in Glaucoma Pharmacotherapy
by
Xiaole Li, Michael Balas and David J. Mathew
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3010002 - 23 Jan 2025
Cited by 3
Abstract
Glaucoma, the second leading cause of irreversible blindness globally, encompasses a heterogeneous group of ocular disorders characterized by the progressive degeneration of retinal ganglion cells. Pharmacotherapy remains the cornerstone of treatment, primarily aimed at reducing intraocular pressure (IOP) by decreasing aqueous humor production
[...] Read more.
Glaucoma, the second leading cause of irreversible blindness globally, encompasses a heterogeneous group of ocular disorders characterized by the progressive degeneration of retinal ganglion cells. Pharmacotherapy remains the cornerstone of treatment, primarily aimed at reducing intraocular pressure (IOP) by decreasing aqueous humor production or enhancing its outflow. The therapeutic classes employed include carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, β-blockers, α-adrenergic agonists, prostaglandin analogs, parasympathomimetics, Rho kinase inhibitors, and hyperosmotic agents. Despite their efficacy, these medications are associated with a range of ocular and systemic side effects, influenced by their mechanisms of action, formulation, and dosage. Ocular adverse effects, such as irritation, dry eye, allergic reactions, and infections, are common, while systemic absorption may lead to more severe outcomes, including organ dysfunction, exacerbation of comorbid conditions, or life-threatening cardiovascular events. Given these potential risks, it is critical for clinicians to understand and monitor these adverse effects as they significantly affect patient adherence, quality of life, and treatment outcomes. Ongoing research is essential to develop novel therapeutic regimens, agents, or delivery methods that minimize side effects and improve compliance. Incorporating patient-reported outcomes in clinical practice may further enhance the assessment of treatment impact, facilitating more tailored and effective management of glaucoma.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Immunotherapy in Ophthalmic Oncology: Current Trends and Future Directions
by
Mouayad Masalkhi, Noura Wahoud, Bridget Moran and Ezzat Elhassadi
J. Clin. Transl. Ophthalmol. 2025, 3(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/jcto3010001 - 7 Jan 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Immunotherapy represents a revolutionary approach in cancer treatment, where it leverages the body’s immune system to target and destroy malignant cells. In ophthalmic oncology, immunotherapeutic agents offer potential for managing traditionally challenging ocular malignancies, such as melanoma and retinoblastoma. In this literature
[...] Read more.
Background: Immunotherapy represents a revolutionary approach in cancer treatment, where it leverages the body’s immune system to target and destroy malignant cells. In ophthalmic oncology, immunotherapeutic agents offer potential for managing traditionally challenging ocular malignancies, such as melanoma and retinoblastoma. In this literature review, we aim to provide a comprehensive and up-to-date review of all current research and trends in this field. Methods: This literature reviews data from recent clinical trials, peer-reviewed articles, and meta-analyses focused on immunotherapeutic interventions for eye-related cancers. Emphasis is placed on the types of immunotherapies being tested, including checkpoint inhibitors, vaccine therapies, and adoptive cell transfer therapies. Results: Recent advancements indicate a growing and significant improvement in survival rates and tumor reduction with minimal adverse effects. Clinical trials focusing on melanoma show significant promise with targeted therapies, while early-stage investigations into retinoblastoma and conjunctival melanoma explore innovative approaches to harness the immune system without harming visual function. Conclusions: Immunotherapy in ophthalmic oncology is evolving rapidly and has demonstrated a remarkable potential as a primary treatment strategy. Although results from various clinical trials are promising, further research is needed to refine these therapies, minimize side effects, and improve overall patient outcomes. The future directions involve more comprehensive clinical trials that integrate immunotherapy with existing treatment modalities to establish more robust treatment protocols.
Full article

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics

Special Issues
Special Issue in
JCTO
Advancements in Cornea Transplantation
Guest Editors: Giulia Coco, Davide RomanoDeadline: 30 November 2025
Special Issue in
JCTO
Advances in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Ocular Surface Tumors and Diseases
Guest Editors: Sotiria Palioura, Carolina L. Mercado, Jaime D. MartinezDeadline: 30 November 2025
Special Issue in
JCTO
Augmented and Artificial Intelligence in Ophthalmology
Guest Editors: Edsel B. Ing, Tina Felfeli, David Jose Mathew, Michael BalasDeadline: 30 December 2025
Special Issue in
JCTO
Clinical Challenges and Advances in Dry Eye Disease and Meibomian Gland Dysfunction
Guest Editors: Salvatore Troisi, Livio VitielloDeadline: 31 December 2025






