Sensors and Sensing Technology for Industry 4.0
A topical collection in Sensors (ISSN 1424-8220). This collection belongs to the section "Industrial Sensors".
Viewed by 67468Editors
Interests: maritime transport and logistics
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: Industry 4.0; IoT; AI/CI; big data analysis; cloud manufacturing
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
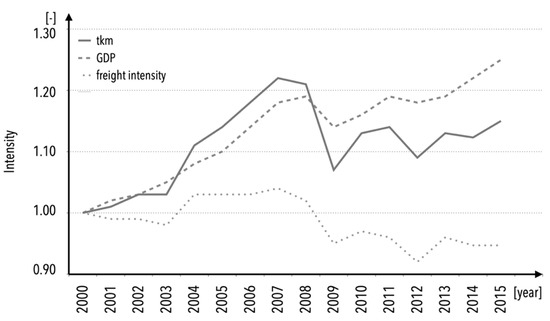
The year 2021 is the 10th anniversary of the coining of the term “Industry 4.0”. For the past decade, Industry 4.0 has been addressed as one of the megatrends in production/manufacturing, and in other fields of industry. Although certain industrial sectors benefit from it more than others, the crucial impact of Industry 4.0 on the global economy is undisputed. This is especially true since companies have been able to collect and analyze unprecedented quantities of data, owing to the use of sensors (particularly smart sensors), monitoring instrumentation, accompanying devices and equipment (e.g., microprocessors or communication units), which make it possible to convert measurements into a readable signal simply by means of sensing technology. Measurements obtained by traditional sensors are interpreted entirely by humans, whereas the use of smart sensors facilitates network connections and the use of algorithms for big data analyses. As such, (smart) sensors and technical actuators are significant components of Industry 4.0, as they support control processes, provide analyses which contribute to processes’ improvement, and offer unmatched asset protection. Such possibilities are especially important due to unprecedented levels of volatility, uncertainty, complexity, and ambiguity in actual production, logistics and other fields of human activities.
The Guest Editor invites researchers and industry representatives in the global communities of IT, transportation, logistics, and production to contribute original research papers, review articles, and empirical studies to stimulate the debate within the scope of examinations on the application of sensors and sensing technologies, robotics, and automation, addressed in the keywords below.
Dr. Mariusz Kostrzewski
Prof. Dr. Jorn Mehnen
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sensors is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Automation in design, construction, manufacturing, etc.
- Additive manufacturing (3D printing)
- Manufacturing Executions System (MES)
- Hybrid and smart manufacturing
- Sensors and Internet of Things
- Smart factory/smart manufacturing
- Smart logistics/Logistics 4.0
- Smart manufacturing systems design and engineering
- Improving quality by detecting damages, cracks, and defects
- Implementation of Industry 4.0 in different sectors
- Improving the resilience of supply chain management
- Improving safety and managing risks and hazards
- Digital transformation, digitization
- Visualization of digital information and services
- Robotics and manipulator arms
- Data acquisition and sensor fusion
- Sensor, MEMS, smart devices, and IoT applications
- Unmanned aerial vehicles/drones
- Artificial intelligence
- Big data analytics
- BIM advances and standards
- Computer vision
- Deep convolutional neural networks (DCNNs)
- Digital twin
- Digital shadow
- Mixed reality and immersive technologies
- Networking applications
- Numerical methods
- Simulation methods
- Education of the Industry 4.0 generation