Waste Valorization and Management to Increase the Resources Sustainability
A special issue of Sustainability (ISSN 2071-1050). This special issue belongs to the section "Sustainable Materials".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: 31 January 2025 | Viewed by 715
Special Issue Editors
Interests: Waste management, Waste recycling, Circular economy, Sustainability
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
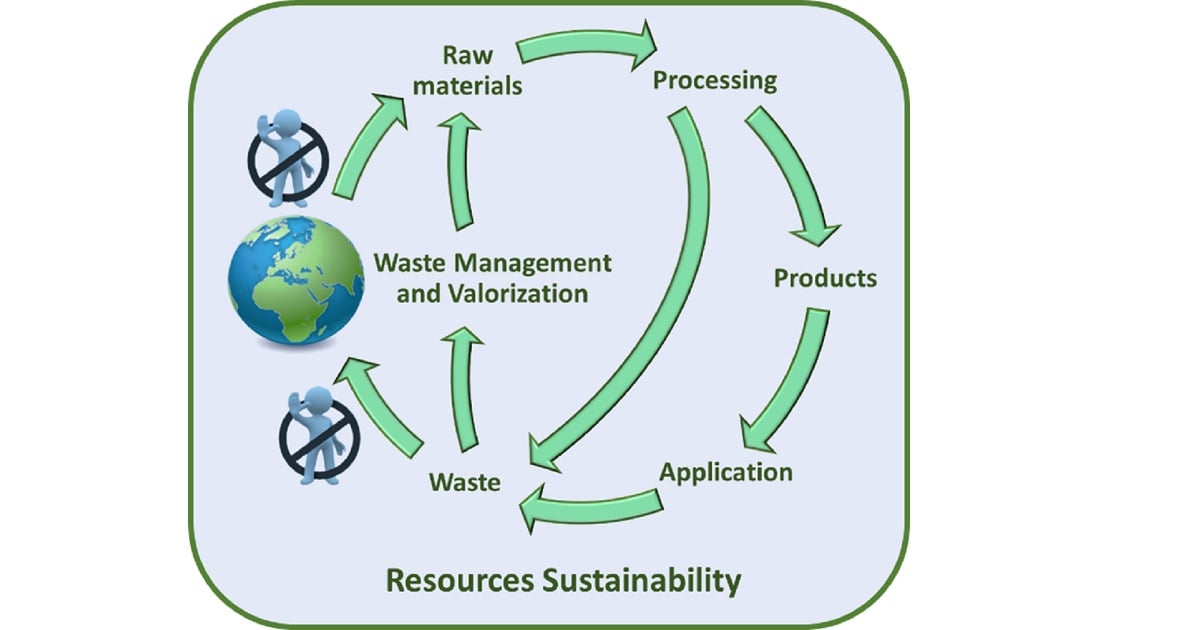
Sustainable development has been increasingly discussed due to climate change and the other environmental impacts of various production processes regarding waste generation, effluents, and emissions. The extraction of raw materials for the most diverse production sectors has become a significant environmental problem, not only due to the recurring environmental impacts of the extraction process but also due to the inadequate disposal of waste generated in the respective production processes. Waste valorization attempts to reuse and give a more noble destination to these materials that can, depending on their chemical and mineralogical compositions, replace traditional raw materials that are commonly sold, including gains in the product’s properties. In the same way, efficient resource and waste management can reduce the quantities of materials sent to landfills.
This Special Issue aims to collect new ideas of research on the topic of “Waste Valorization and Management to Increase the Resources Sustainability”. In this sense, works that involve waste characterization and the development of programs and actions aimed at waste management are included in this special edition. In this Special Issue, original research articles and reviews are welcome. Research areas may include (but not limited to) the following:
- New strategies and guidelines to improve waste management systems;
- Chemical and physical waste characterization;
- Waste valorization in new sustainable materials;
- Implement data analytics to study recycling patterns in waste management;
- Innovative approaches for the recovery of landfilled wastes;
- Life cycle and carbon footprint analysis of waste.
We look forward to receiving your contributions.
Prof. Dr. Lisandro Simão
Prof. Dr. Marcelo Tramontin Souza
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- waste management
- waste recycling
- circular economy
- sustainability
- life cycle
- carbon footprint






