- 3.3Impact Factor
- 7.7CiteScore
- 18 daysTime to First Decision
Dry Port Management and Sustainable Regional Development
This special issue belongs to the section “Sustainable Transportation“.
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
The concept of dry ports has gained significant attention from researchers around the globe (Figure 1), which has been promptly followed by practitioners, and today there are numerous dry ports established in different forms in countries such as Sweden, Finland, Spain, Holland, Germany, Russia, India, China, Vietnam, Malaysia, Australia, New Zealand, USA, Brazil, and Ethiopia to name the most researched countries. In the last 13 years, the number of publications on dry ports in the Scopus database (title and/or abstract) has grown from 2 to over 100 ((Khaslavskaya and Roso, 2020), Figure 2). The term “dry port” has been in use sporadically since the 1990s, but in the late 2000s the popularity of the dry port concept skyrocketed mainly due to its environmental perspective as recognized by Roso et al. (2009). The authors defined the concept as “an inland intermodal terminal directly connected to seaport(s) with high capacity transport mean(s), where customers can leave/pick up their standardised units as if directly to a seaport.” Still, after almost two decades, a recurring issue in research papers is different efforts to find other definitions for dry ports, such as extended gates, advanced intermodal terminals, inland ports, etc. (Witte et al., 2020).
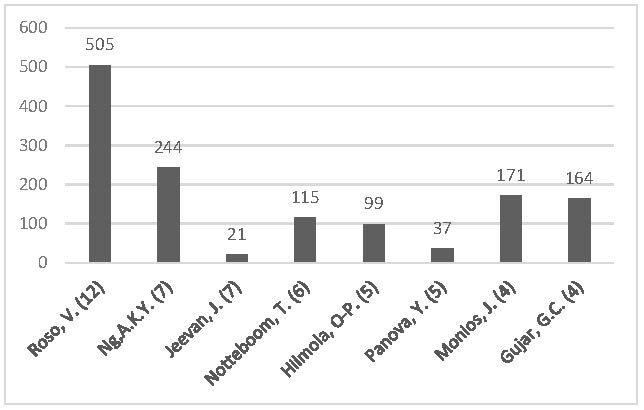
Figure 1. Top-contributing authors (number of publications in the brackets) and the Scopus citations of these authors’ dry port publications (from January 2020).
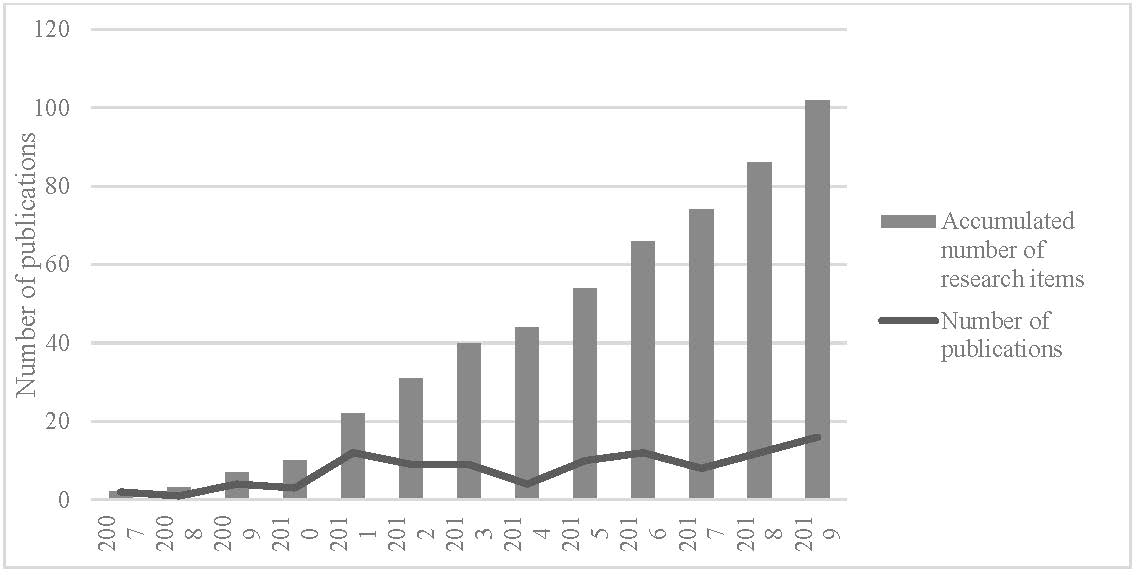
Figure 2. Number of research items published per year (Khaslavskaya and Roso, 2020).
Therefore, with this Special Issue we would like to invite papers dealing with dry ports in any form or notion in use, as long as high-capacity transport modes are in use. In particular, we would like to receive papers researching real-life cases of dry ports. The implications of this Special Issue will be a much better understanding of the impact of dry ports on regional development, considering environmental, social, and economic sustainability. It will hopefully give significant inputs to practitioners and decision-makers dealing with the planning, design, and establishment of dry ports worldwide.
The aim of this Special Issue is to publish high-quality papers addressing emerging sustainability issues related to dry ports. We welcome the submission of original and high-quality research fitting the Special Issue’s theme that have neither been published nor are currently under review by other journals. Papers selected for this Special Issue will be subject to a peer-review procedure and careful editorial scrutiny.
References:
- Khaslavskaya, A., Roso, V. 2020. Dry ports: research outcomes, trends, and future implications. Maritime Economics and Logistics (2020). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41278-020-00152-9)
- Roso, V; Woxenius, J; Lumsden, K (2009) The dry port concept: connecting container seaports with the hinterland. Journal of Transport Geography, 17 (5) pp. 338-345.
- Witte, P., Wiegmans, B., Roso, V. and Hall, P. (2020) Critical review: Moving beyond land and water: Understanding the development and spatial organization of inland ports. Journal of Transport Geography. SI Volume 84, April 2020, 102676.
This SI is intended to present the latest research in the area of dry ports. We encourage papers on all aspects of qualitative and quantitative research related to dry ports, such as:
- Dry ports for sustainable regional development;
- Dry ports from environmental, social, and economic perspectives;
- Dry port network design for sustainable transport;
- Regulatory issues related to dry ports implementation, operations and ownership;
- Policy measures concerning the dry ports;
- Sustainable hinterland transport via dry ports/inland ports;
- Hinterland transport actors and their roles for dry ports/ports;
- Stakeholders and their role in dry port management;
- Rail and inland waterway development and involvement in intermodal transportation via dry ports;
- Information technological solutions related to dry ports;
- Seaport expansions and infrastructure connections to dry ports;
- Optimization of dry port functions;
- Design and development of dry ports (subsystems, physical characteristics, layout);
- Tools for dry port location optimization;
- Dry port efficiency evaluation;
- Dry port establishment in developing economies;
- Dry port market segmentation;
- Dry port influence on the supply chain management;
- Issues related to the operationalization of dry ports.
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Violeta Roso
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Snežana Tadić
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Nikolina Brnjac
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- dry port
- inland port
- sustainability
- regional development
- efficiency
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- Reprint: MDPI Books provides the opportunity to republish successful Special Issues in book format, both online and in print.


