Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity Effects of a Magnetic Zeolite Composite in Daphnia magna (Straus, 1820)
Abstract
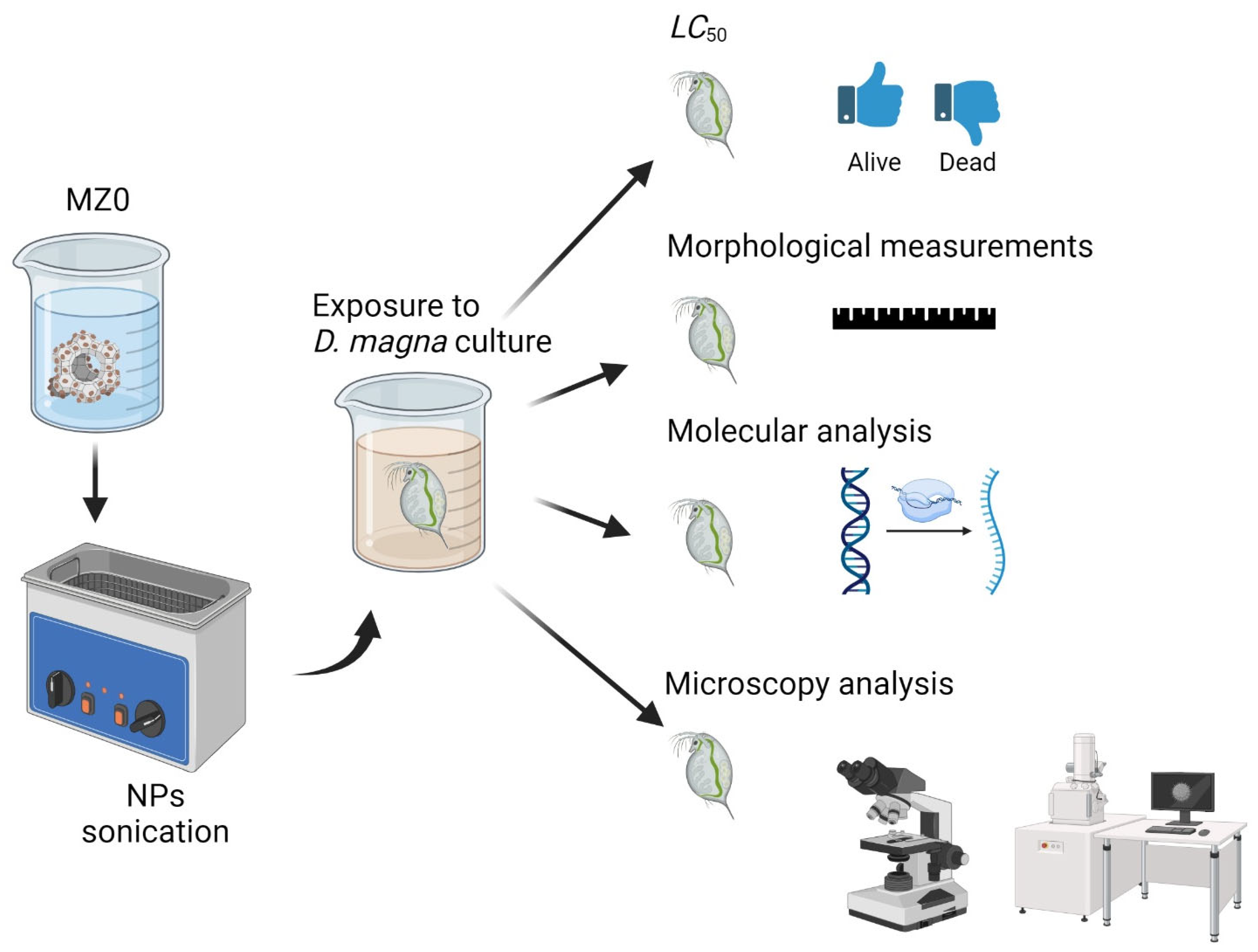
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
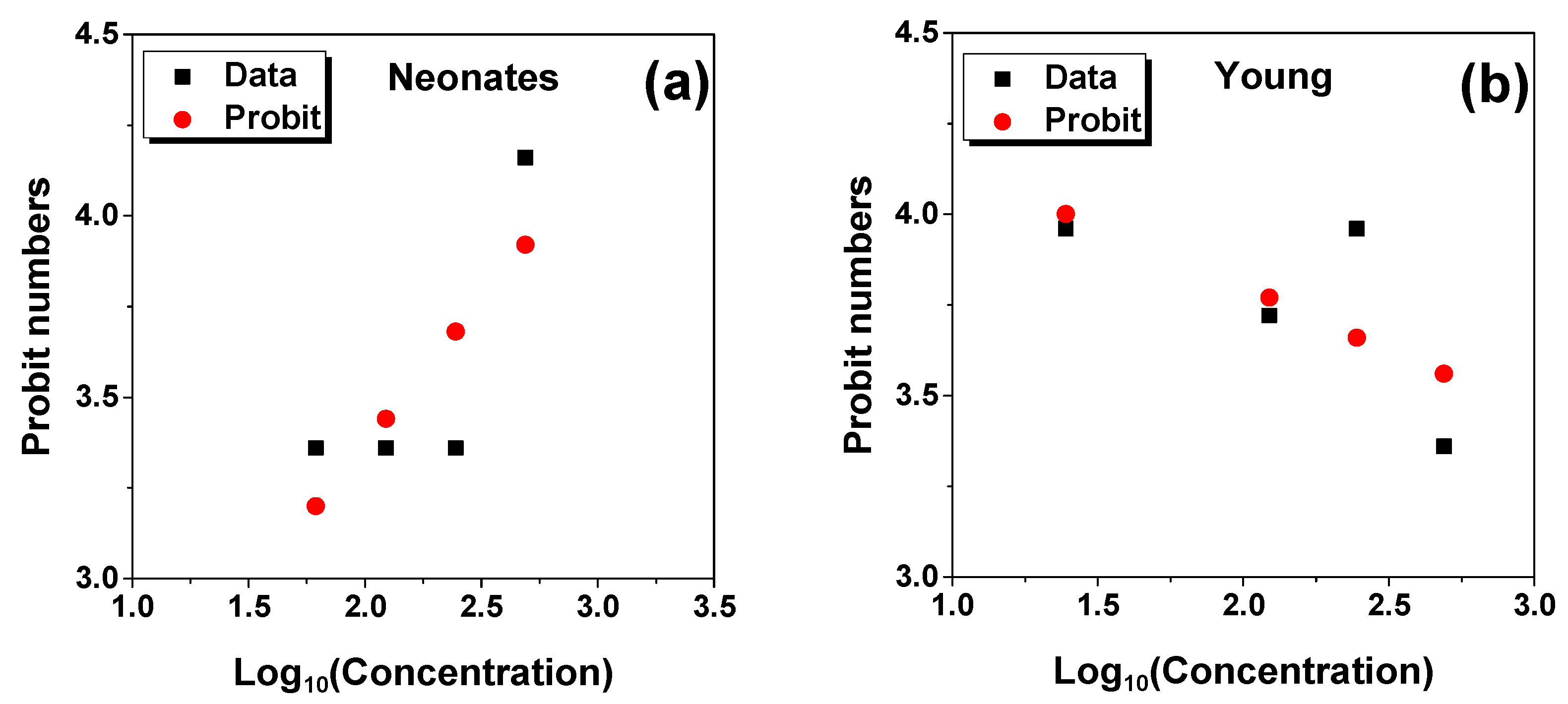
2.1. LC50 Analysis
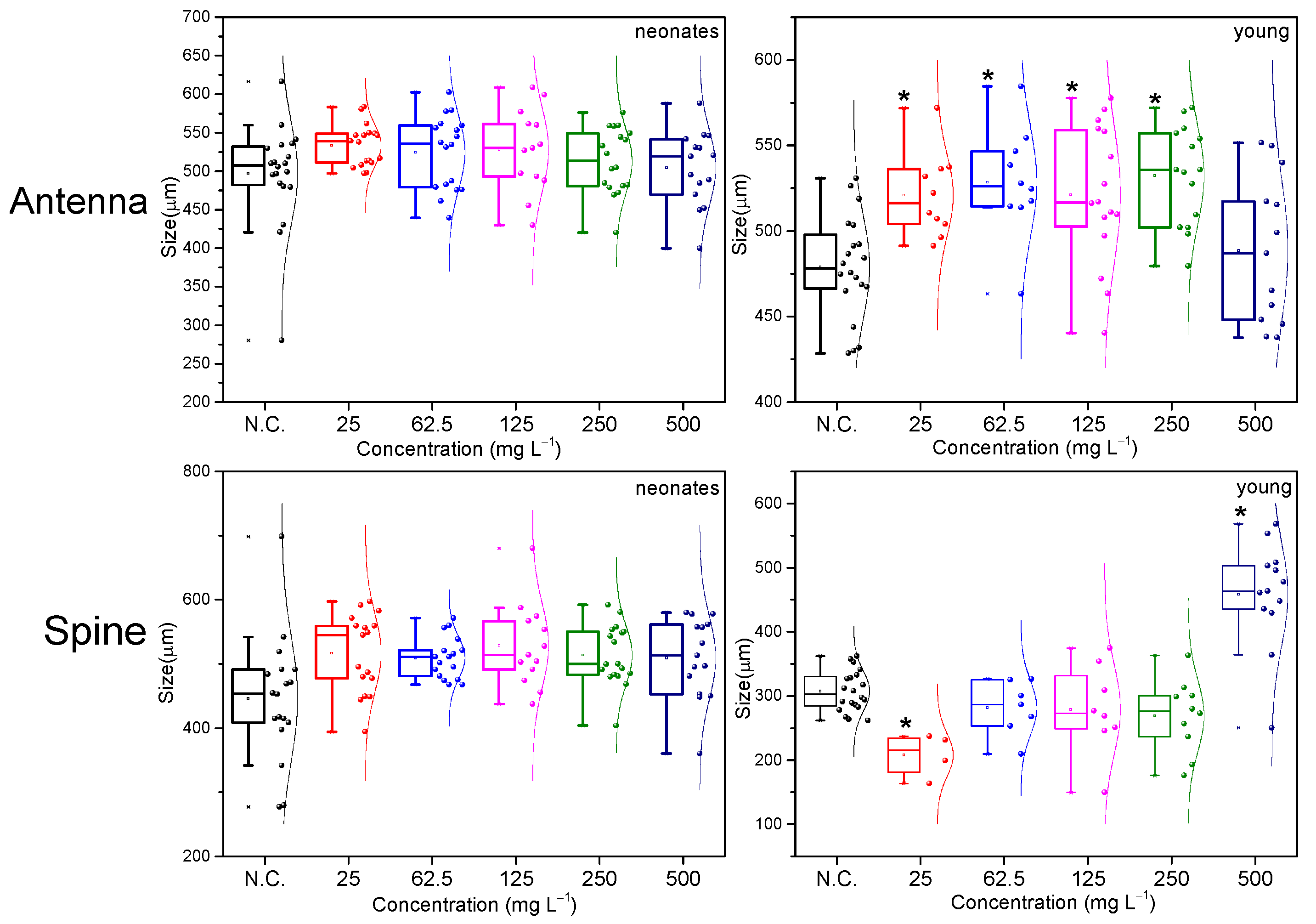
2.2. Morphological Evaluation Analysis
2.3. Reproductive Rate
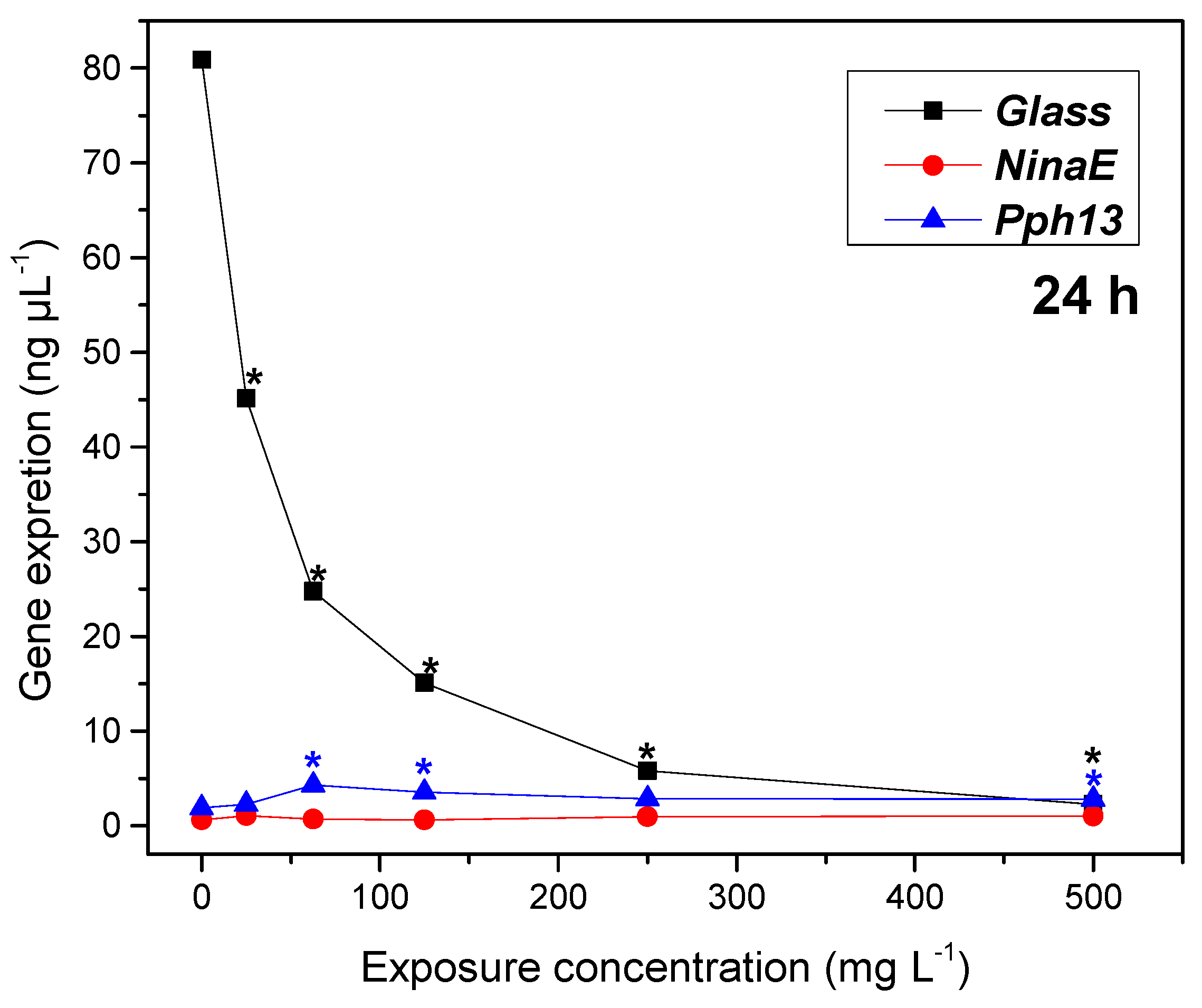
2.4. Gene Expression
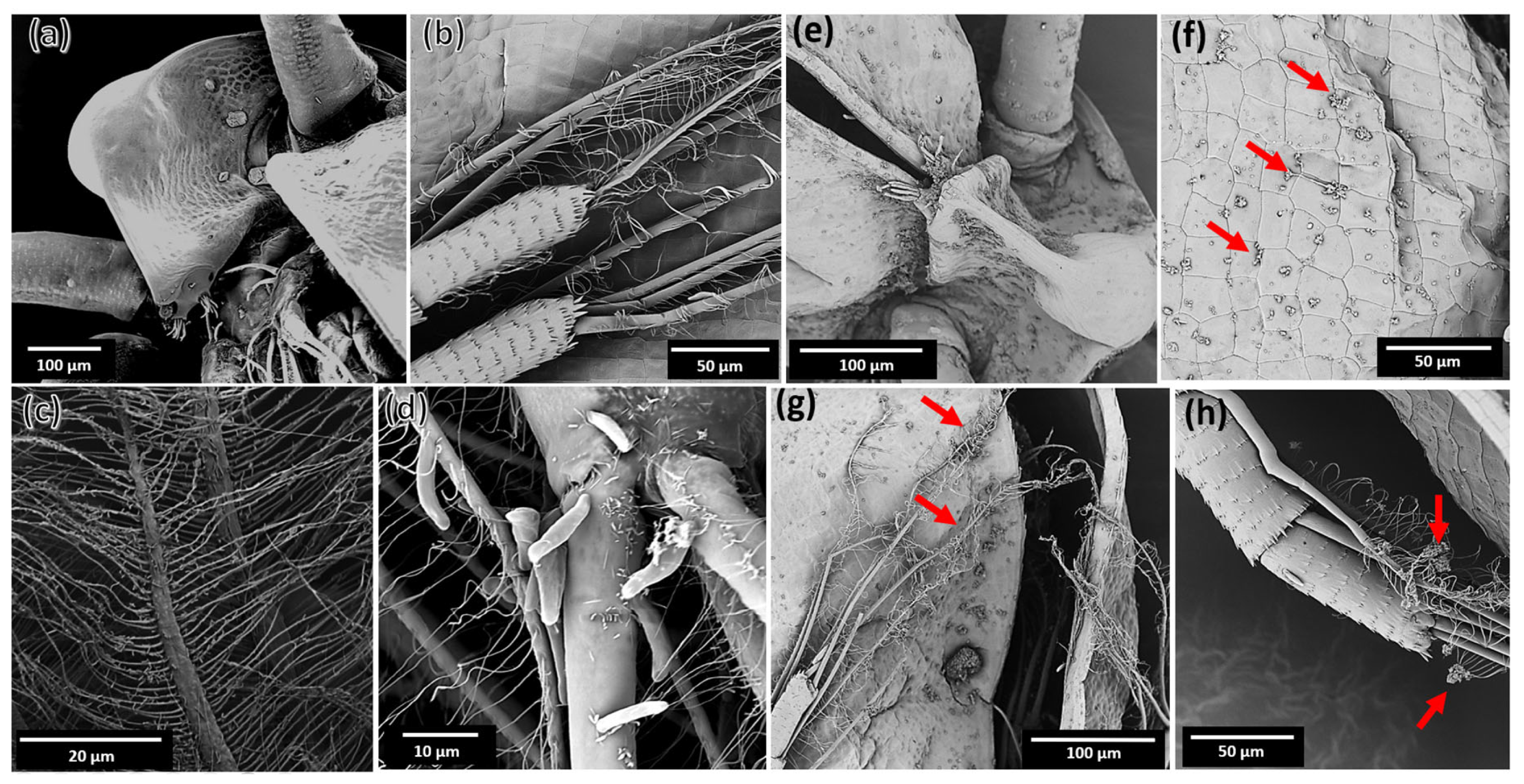
2.5. Interaction of MZ0 with D. magna
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. MZ0 Synthesis and Physicochemical Characterization
3.2. D. magna Culture and Ecotoxicological Assays
3.3. Lethal Concentration (LC50) Determination
3.4. Morphology of Daphnia and Data Analysis
3.5. Gene Expression by Conventional Electrophoresis Technique
3.6. Microscopic Analysis of the Interaction of MZ0 Sample with D. magna
3.6.1. Light Microscopy
3.6.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Serena, P.A.D. ¿Qué Sabemos de la Nanotecnología? CSIC, Ed.; Catarata: Madrid, Spain, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Argueta-Figueroa, L.; Torres-Gómez, N.; Scougall-Vilchis, R.J.; García-Contreras, R. Biocompatibilidad y toxicidad de nano-partículas de dióxido de titanio en la cavidad oral: Revisión sistemática. Investig. Clin. 2018, 59, 352–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Guivar, J.A.; Zarria-Romero, J.Y.; Canchanya-Huaman, Y.; Guerra, J.A.; Checca-Huaman, N.-R.; Castro-Merino, I.-L.; Passamani, E.C. Raman, TEM, EELS, and Magnetic Studies of a Magnetically Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanohybrid following Exposure to Daphnia magna Biomarkers. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrzyńska, M.M.; Gajowik, A.; Radzikowska, J.; Lankoff, A.; Dušinská, M.; Kruszewski, M. Genotoxicity of Silver and Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Bone Marrow Cells of Rats in Vivo. Toxicology 2014, 315, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stix, G. Little big science. Sci. Am. 2001, 285, 32–37. Available online: https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/little-big-science-2001-09/ (accessed on 7 July 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, G.; Na, J.; Song, J.; Jung, J. Chronic toxicity of biodegradable microplastic (Polylactic acid) to Daphnia magna: A comparison with polyethylene terephthalate. Aquat. Toxicol. 2024, 266, 106790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Andrés, V.; Diez-Ortiz, M.; Delpivo, C.; Janer, G.; Fritzsche, A.; Vázquez-Campos, S. Acute Ecotoxicity of Coated Colloidal Goethite Nanoparticles on Daphnia magna: Evaluating the Influence of Exposure Approaches. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Q. ZnO, TiO2, SiO2, and Al2O3 Nanoparticles-Induced Toxic Effects on Human Fetal Lung Fibroblasts. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2011, 24, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumar, N.; Sharma, P.K.; Sood, N.; Bhalla, N. Designing Magnetic Nanoparticles for in Vivo Applications and Understanding Their Fate inside Human Body. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 445, 214082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamuna, B.A.; Ravishankar, R.V. Chapter 31: Environmental Risk, Human Health, and Toxic Effects of Nanoparticles. In Nanomaterials for Environmental Protection; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Gupta, H.; Singh, Z. Daphnia magna as a model animal for assessing microplastic toxicity. Environ. Sci. Arch. 2023, 2, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Guivar, J.A.; Checca-Huaman, N.R.; Litterst, F.J.; Passamani, E.C. Synergetic effect between zeolite 5A and maghemite nanoparticles for fast lead uptake from the Peruvian river Cumbaza: Study of surface adsorption mechanism using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2023, 18, 100489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariati, F.; Poordeljoo, T.; Zanjanchi, P. The Acute Toxicity of SiO2 and Fe3O4 Nano-Particles on Daphnia magna. Silicon 2020, 12, 2941–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, W.; Xu, Z.; Peng, W.; Luo, S. Transgenerational effects of reduced graphene oxide modified by Au, Ag, Pd, Fe3O4, Co3O4 and SnO2 on two generations of Daphnia magna. Carbon 2017, 122, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Guivar, J.A.; Alca-Ramos, Y.V.; Manrique-Castillo, E.V.; Mendoza-Villa, F.; Checca-Huaman, N.R.; Rueda-Vellasmin, R.; Passamani, E.C. Pyroclastic Dust from Arequipa-Peru Decorated with Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and Their Ecotoxicological Properties in Water Flea D. magna . Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarria-Romero, J.Y.; Ocampo-Anticona, J.A.; Pinotti, C.N.; Passamani, E.C.; Checca-Huaman, N.R.; Castro-Merino, I.L.; Pino, J.; Shiga, B.; Ramos-Guivar, J.A. Ecotoxicological properties of functionalized magnetic graphene oxide and multiwall carbon nanotubes in Daphnia magna. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 15200–15212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaiser, B.K.; Fernandes, T.F.; Jepson, M.A.; Lead, J.R.; Tyler, C.R.; Baalousha, M.; Biswas, A.; Britton, G.J.; Cole, P.A.; Johnston, B.D.; et al. Interspecies Comparisons on the Uptake and Toxicity of Silver and Cerium Dioxide Nanoparticles. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Albee, B.; Alemayehu, M.; Diaz, R.; Ingham, L.; Kamal, S.; Rodriguez, M.; Whaley Bishnoi, S. Comparative Toxicity Study of Ag, Au, and Ag–Au Bimetallic Nanoparticles on Daphnia magna. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, A.; Espinosa, R.; Delgado, L.; Casals, E.; González, E.; Puntes, V.; Barata, C.; Font, X.; Sánchez, A. Acute Toxicity of Cerium Oxide, Titanium Oxide and Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Using Standardized Tests. Desalination 2011, 269, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulaby Dezfuly, Z.; Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz; Alishahi, M. Department of Clinical Sciences Faculty of Veterinary, Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz, Ahvaz, Iran; Aramoon, A.; Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz, Ahvaz, Iran; Mashjoor, S.; Department of Marine Biology, Faculty of Marine Science and Technology, Hormozgan University, Bandar Abbas, Iran. Evaluation of Silver Nanoparticles Toxicity in Daphnia magna: Comparison of Chemical and Green Biosynthetic Productions. Iran. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2017, 3, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Bortvedt, A.; Harper, B.J.; Crandon, L.E.; Harper, S.L. Uptake and Toxicity of CuO Nanoparticles to Daphnia magna Varies between Indirect Dietary and Direct Waterborne Exposures. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 190, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhu, L.; Li, Y.; Duan, Z.; Chen, W.; Alvarez, P.J.; Wang, J. Comparative toxicity of several metal oxide nanoparticle aqueous suspensions to Zebrafish (Danio rerio) early developmental stage. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2010, 45, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, J.; Köser, J.; Arndt, D.; Filser, J. The Coating Makes the Difference: Acute Effects of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles on Daphnia magna. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 484, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Tian, S.; Cai, Z. Toxicity Assessment of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Early Life Stages. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taştan, B.E.; Durukan, İ.K.; Ateş, M. Ecotoxicity study of iron oxide nanoparticles on Chlorella sp. Daphnia magna. Politek. Derg. 2019, 23, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; Lv, Y.; Kou, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X.; Yang, F.; Luo, J.; Yang, X. Silver Nanoparticles Induce Developmental Toxicity via Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 243, 113993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Tabakman, S.; Welsher, K.; Dai, H. Carbon Nanotubes in Biology and Medicine: In Vitro and in Vivo Detection, Imaging and Drug Delivery. Nano Res. 2009, 2, 85–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reagen, S.; Zhao, J.X. Analysis of Nanomaterials on Biological and Environmental Systems and New Analytical Methods for Improved Detection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrica-González, P.; Balderas-López, J.A.; Zumelzu-Delgado, E.; Nimptsch-Maass, J. Nanopartículas de oro y sus efectos sobre microorganismos acuáticos, un estudio sobre “Daphnia pulex.” In Avances de investigación en Nanociencias, Micro y Nanotecnologías. OmniaScience 2020, 2, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Wei, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y. Acute Toxicity and Responses of Antioxidant Systems to Dibutyl Phthalate in Neonate and Adult Daphnia magna. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberny, K.A. Ontogeny of the N-Methyl-D-Aspartate (NMDA) Receptor System and Susceptibility to Neurotoxicity. Toxicol. Sci. 2002, 68, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesela, S.; Vijverberg, J. Effect of Body Size on Toxicity of Zinc in Neonates of Four Differently Sized Daphnia Species. Aquat. Ecol. 2007, 41, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, Z.; Xie, Z.; Dupont, S.; Huang, W.; Wu, F.; Kong, H.; Liu, L.; Sui, Y.; Lin, D.; et al. Oxidative Stress Induced by Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Increases under Seawater Acidification in the Thick Shell Mussel Mytilus Coruscus. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 137, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Alonso, J.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, N.; Misra, S.K.; Valsami-Jones, E.; Croteau, M.-N.; Luoma, S.N.; Rainbow, P.S. Toxicity and Accumulation of Silver Nanoparticles during Development of the Marine Polychaete Platynereis Dumerilii. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 476–477, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.E.; Kim, S.; Ahn, J.H.; Youn, P.; Kang, J.S.; Park, K.; Yi, J.; Ryu, D.-Y. Induction of Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis by Silver Nanoparticles in the Liver of Adult Zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 100, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lead, J.R.; Batley, G.E.; Alvarez, P.J.J.; Croteau, M.; Handy, R.D.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Judy, J.D.; Schirmer, K. Nanomaterials in the Environment: Behavior, Fate, Bioavailability, and Effects—An Updated Review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 2029–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackevica, A.; Skjolding, L.M.; Gergs, A.; Palmqvist, A.; Baun, A. Chronic Toxicity of Silver Nanoparticles to Daphnia magna under Different Feeding Conditions. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 161, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandon, C.S.; Dudycha, J.L. Ecological Constraints on Sensory Systems: Compound Eye Size in Daphnia Is Reduced by Resource Limitation. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2014, 200, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovern, S.B.; Strickler, J.R.; Klaper, R. Behavioral and Physiological Changes in Daphnia magna When Exposed to Nanoparticle Suspensions (Titanium Dioxide, Nano-C 60, and C 60 HxC 70 Hx). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 4465–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Park, C.G.; Sung, B.; Lee, Y.O.; Ryu, C.S.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, Y.J. Acute Adverse Effects of Metallic Nanomaterials on Cardiac and Behavioral Changes in Daphnia magna. Environments 2022, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, I.H.; Kim, I.Y.; Heo, M.B.; Park, J.W.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, T.G. Real-time heart rate monitoring system for cardiotoxicity assessment of Daphnia magna using high-speed digital holographic microscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffitt, R.J.; Luo, J.; Gao, J.; Bonzongo, J.-C.; Barber, D.S. Effects of particle composition and species on toxicity of metallic nanomaterials in aquatic organisms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miner, B.E.; De Meester, L.; Pfrender, M.E.; Lampert, W.; Hairston, N.G. Linking Genes to Communities and Ecosystems: Daphnia as an Ecogenomic Model. Proc. R. Soc. B 2012, 279, 1873–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Des Roches, S.; Brans, K.I.; Lambert, M.R.; Rivkin, L.R.; Savage, A.M.; Schell, C.J.; Correa, C.; De Meester, L.; Diamond, S.E.; Grimm, N.B.; et al. Socio-eco-evolutionary Dynamics in Cities. Evol. Appl. 2021, 14, 248–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brans, K.I.; De Meester, L. City Life on Fast Lanes: Urbanization Induces an Evolutionary Shift towards a Faster Lifestyle in the Water Flea Daphnia. Funct. Ecol. 2018, 32, 2225–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarska, A. Food Quantity and Quality Shapes Reproductive Strategies of Daphnia. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e9163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrow, M.R.; Irvine, K. The Relationship between Cladoceran Body Size and the Growth of Underyearling Roach (Rutilus rutilus) (L.) in Two Shallow Lowl. Lakes: A Mech. Density-Depend. Hydrobiologia 1992, 241, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, E.; Baun, A.; Behra, R.; Hartmann, N.B.; Filser, J.; Miao, A.-J.; Quigg, A.; Santschi, P.H.; Sigg, L. Environmental Behavior and Ecotoxicity of Engineered Nanoparticles to Algae, Plants, and Fungi. Ecotoxicology 2008, 17, 372–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanpradit, P.; Byeon, E.; Lee, J.; Peerakietkhajorn, S. Ecotoxicological, Ecophysiological, and Mechanistic Studies on Zinc Oxide (ZnO) Toxicity in Freshwater Environment. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 273, 109720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshnood, R.; Jaafarzadeh, N.; Jamili, S.; Farshchi, P.; Taghavi, L. Nanoparticles Ecotoxicity on Daphnia magna. Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2016, 18, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, D.A.; Chen, J.; Moua, M.; Klaper, R.D. Multigeneration Impacts on Daphnia magna of Carbon Nanomaterials with Differing Core Structures and Functionalizations. Environ. Toxic. Chem. 2014, 33, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrunz, A.; Duester, L.; Prasse, C.; Seitz, F.; Rosenfeldt, R.; Schilde, C.; Schaumann, G.E.; Schulz, R. Biological Surface Coating and Molting Inhibition as Mechanisms of TiO2 Nanoparticle Toxicity in Daphnia magna. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalobos, M.J.; González, E.J. Estudios sobre la biología y ecología de Ceriodaphnia cornuta SARS: UNA REVISIÓN. Interciencia 2006, 31, 351–357. Available online: http://ve.scielo.org/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0378-18442006000500006&lng=es&tlng=es (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- Dodson, S.; Hanazato, T. Commentary on Effects of Anthropogenic and Natural Organic Chemicals on Development, Swimming Behavior, and Reproduction of Daphnia, a Key Member of Aquatic Ecosystems. EHP 1995, 103 (Suppl. S4), 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Barata, C.; Campos, B.; Rivetti, C.; LeBlanc, G.A.; Eytcheson, S.; McKnight, S.; Tobor-Kaplon, M.; De Vries Buitenweg, S.; Choi, S.; Choi, J.; et al. Validation of a Two-Generational Reproduction Test in Daphnia magna: An Interlaboratory Exercise. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, T.C.; Klaine, S.J. Influence of organism age on metal toxicity to Daphnia magna. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2007, 26, 1198–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scanlan, L.D.; Reed, R.B.; Loguinov, A.V.; Antczak, P.; Tagmount, A.; Aloni, S.; Nowinski, D.T.; Luong, P.; Tran, C.; Karunaratne, N.; et al. Silver Nanowire Exposure Results in Internalization and Toxicity to Daphnia magna. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 10681–10694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Wang, W.-X. Modification of Metal Bioaccumulation and Toxicity in Daphnia magna by Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 186, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.-Y.; Lin, A.Y.-M.; McKittrick, J.; Meyers, M.A. Structure and Mechanical Properties of Crab Exoskeletons. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roer, R.; Abehsera, S.; Sagi, A. Exoskeletons across the Pancrustacea: Comparative Morphology, Physiology, Biochemistry and Genetics. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2015, 55, 771–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raabe, D.; Romano, P.; Sachs, C.; Fabritius, H.; Al-Sawalmih, A.; Yi, S.-B.; Servos, G.; Hartwig, H.G. Microstructure and Crystallographic Texture of the Chitin–Protein Network in the Biological Composite Material of the Exoskeleton of the Lobster Homarus Americanus. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 421, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari, S.; Johari, S.A.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Jeon, Y.B.; Choi, H.J.; Moon, M.C.; Yu, I.J. Toxicity of Various Silver Nanoparticles Compared to Silver Ions in Daphnia magna. J. Nano. Biotechnol. 2012, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökçe, D.; Köytepe, S.; Özcan, İ. Assessing Short-Term Effects of Magnetite Ferrite Nanoparticles on Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 31489–31504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, D.; Nho, H.W.; Yoon, T.H. Transmission Electron Microscopy and Scanning Transmission X-ray Microscopy Studies on the Bioaccumulation and Tissue Level Absorption of TiO2 Nanoparticles in Daphnia magna. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 4229–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magro, M.; De Liguoro, M.; Franzago, E.; Baratella, D.; Vianello, F. The Surface Reactivity of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as a Potential Hazard for Aquatic Environments: A Study on Daphnia magna Adults and Embryos. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aarts, A.; Berends, A.; Boeije, G.; Calcinai, D.; Cerbelaud, E.; Certa, H.; van Egmond, R.; Elsmore, R.; Fox, K.; Koch, V.; et al. Members of the HERA Environmental Task Force. HERA. 2004. Available online: https://conama.mma.gov.br/index.php?option=com_sisconama&task=documento.download&id=14388 (accessed on 7 July 2024).
- Poynton, H.C.; Lazorchak, J.M.; Impellitteri, C.A.; Blalock, B.J.; Rogers, K.; Allen, H.J.; Loguinov, A.; Heckman, J.L.; Govindasmawy, S. Toxicogenomic Responses of Nanotoxicity in Daphnia magna Exposed to Silver Nitrate and Coated Silver Nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6288–6296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artells, E.; Issartel, J.; Auffan, M.; Borschneck, D.; Thill, A.; Tella, M.; Brousset, L.; Rose, J.; Bottero, J.-Y.; Thiéry, A. Exposure to Cerium Dioxide Nanoparticles Differently Affect Swimming Performance and Survival in Two Daphnid Species. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lekamge, S.; Miranda, A.F.; Ball, A.S.; Shukla, R.; Nugegoda, D. The Toxicity of Coated Silver Nanoparticles to Daphnia Carinata and Trophic Transfer from Alga Raphidocelis Subcapitata. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondikas, A.P.; Morris, A.; Reinsch, B.C.; Marinakos, S.M.; Lowry, G.V.; Hsu-Kim, H. Cysteine-Induced Modifications of Zero-Valent Silver Nanomaterials: Implications for Particle Surface Chemistry, Aggregation, Dissolution, and Silver Speciation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7037–7045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranmadugala, D.; Ebrahiminezhad, A.; Manley-Harris, M.; Ghasemi, Y.; Berenjian, A. The Effect of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles on Bacillus Subtilis Biofilm, Growth and Viability. Process Biochem. 2017, 62, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamanaha-Vegas, C.A.; Zarria-Romero, J.Y.; Greneche, J.-M.; Passamani, E.C.; Ramos-Guivar, J.A. Surface Magnetic Properties of a Ternary Nanocomposite and Its Ecotoxicological Properties in Daphnia magna. Adv. Powder Technol. 2022, 33, 103395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauridsen, T.L.; Lodge, D.M. Avoidance by Daphnia magna of Fish and Macrophytes: Chemical Cues and Predator-mediated Use of Macrophyte Habitat. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1996, 41, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawidowicz, P.; Pijanowska, J. Diel Vertical Migration of Aquatic Crustaceans—Adaptive Role, Underlying Mechanisms, and Ecosystem Consequences. Nat. Hist. Crustac. Life Hist. 2018, 5, 232–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Nanomaterial | Specie | Diameter (nm) | LC50 (mg L−1) | Exposure Time (h) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag NPs | D. magna | 20–30 | 2.4 | 48 | [17] |
| CeO2 NPs | D. magna | 5–10 | 15.8 | 48 | [17] |
| Au NPs | D. magna | 21 | 70 | 48 | [18] |
| CeO2 NPs | D. magna | 6.5 | 12 | 48 | [19] |
| Fe2O3 NPs | D. magna | 6 | 2.4 | 48 | [19] |
| Ag NPs | D. magna | 8 ± 0.78 | 0.03 | 48 | [20] |
| CuO NPs | D. magna | <50 | 0.15 | 48 | [21] |
| CuO NPs | Danio rerio | - | 16.4 | 96 | [22] |
| Iron oxide NPs | D. magna | 5–6 | 82.1 | 48 | [23] |
| Iron oxide NPs | D. magna | <20 | 654.65 | 96 | [13] |
| Iron oxide NPs | Danio rerio | 30 | 10 | 96 | [24] |
| Iron oxide NPs | D. magna | 33.91 | 50 | 72 | [25] |
| MZ0 | D. magna | 12 nm for maghemite NPs diameter zeolite 5A (~4 µm) | Neonates 11,314 Young 0.0310 | 24 | This work |
| Pph13 | F | GCTTTGAGACGCAAAGCGGCTATACTGGAA |
| R | GGTAACGATGGCTAATTTGCACGGCCTGTC | |
| Glass | F | TGGATCCTCATGTGCTTGGTAAGTGTTGAA |
| R | CTTATCCTTCTGCGGAAGCTTATGCCATCC | |
| NinaE | F | GTCAGCCTTGATGGGCTCGTTGATGCAGAA |
| R | TCGGTCGTTACATTCCAGAAGGAATTTTGG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zarria-Romero, J.Y.; Ramos-Guivar, J.A. Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity Effects of a Magnetic Zeolite Composite in Daphnia magna (Straus, 1820). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25147542
Zarria-Romero JY, Ramos-Guivar JA. Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity Effects of a Magnetic Zeolite Composite in Daphnia magna (Straus, 1820). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2024; 25(14):7542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25147542
Chicago/Turabian StyleZarria-Romero, Jacquelyne Y., and Juan A. Ramos-Guivar. 2024. "Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity Effects of a Magnetic Zeolite Composite in Daphnia magna (Straus, 1820)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25, no. 14: 7542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25147542
APA StyleZarria-Romero, J. Y., & Ramos-Guivar, J. A. (2024). Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity Effects of a Magnetic Zeolite Composite in Daphnia magna (Straus, 1820). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 25(14), 7542. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25147542







