Topic Menu
► Topic MenuTopic Editors


Application of Graphene-Based Materials
Topic Information
Dear Colleagues,
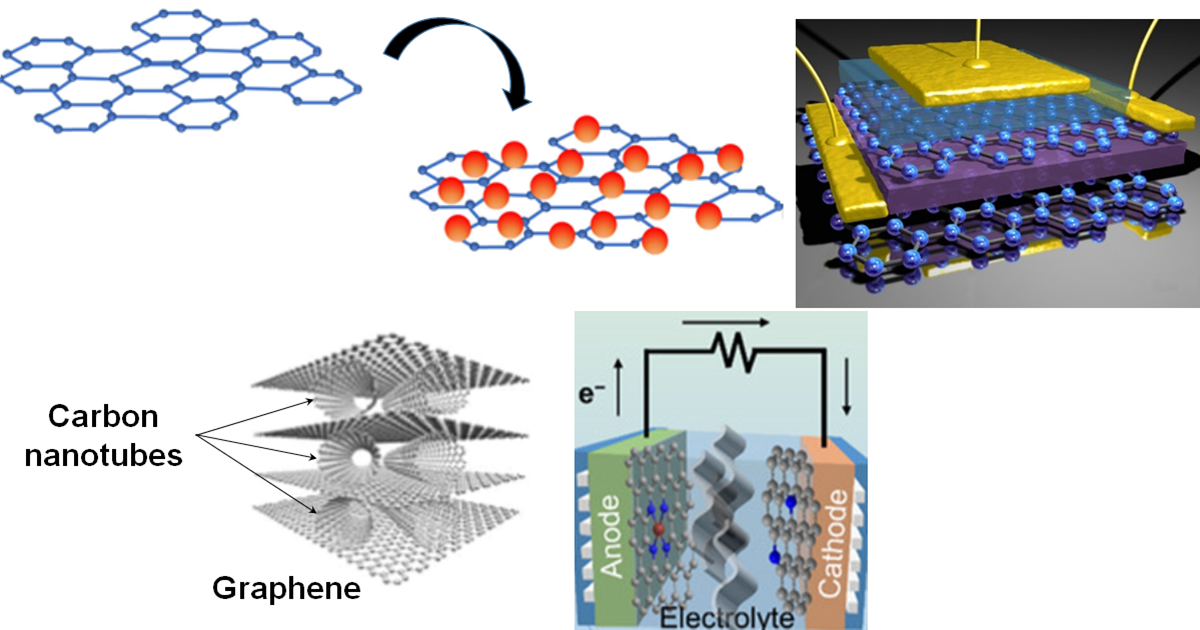
Graphene has attracted widespread attention as one of the main representatives of new nanosized carbonaceous materials. Graphene is formed by a single layer of carbon atoms, arranged as a two-dimensional honeycomb crystal. Graphene has recently become a research hotspot in the field of composite materials. The two-dimensional plane structure of graphene enables a very high in-plane thermal/electrical conductivity, making it one of the most ideal materials for improving the thermal/electrical conductivity of common insulating polymers. Since then, it has broad application prospects in electronic devices, biological and chemical sensors, energy storage devices and polymer-based composite materials. This Special Issue, entitled "Application of Graphene-Based Materials", will introduce not only the polymer fields that have recently become a hot issue, but also applications through basic research, processing, post-treatment, and fields across all materials. Papers that summarize selected areas (reviews) or discuss the latest field research (original articles) are sought. The scope of the Special Issue includes the synthesis and characterization of graphene nanocomposites used for several applications, including polymer nanocomposites containing graphene, graphene-based materials and hybrid nano-assemblies. This Topic seeks high-quality works focusing on the following topics:
- Graphene, RGO, and GO-based hybrids;
- Functionalized graphene-based hybrids;
- Nanocomposite: synthesis, morphology, and characterization;
- Processing/applications;
- Graphene hybrid materials in engineering applications;
- Electrical conductivity in composites;
- Theoretical and experimental methods;
- New technological trends of graphene;
- Paradigms of modern manufacturing systems
Prof. Dr. Jin-Hae Chang
Dr. Marcelo Antunes
Topic Editors
Participating Journals
| Journal Name | Impact Factor | CiteScore | Launched Year | First Decision (median) | APC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Polymers
|
4.9 | 9.7 | 2009 | 14 Days | CHF 2700 |

Nanomaterials
|
4.3 | 9.2 | 2010 | 15.4 Days | CHF 2400 |

Applied Sciences
|
2.5 | 5.5 | 2011 | 19.8 Days | CHF 2400 |
C
|
2.9 | 3.4 | 2015 | 24.3 Days | CHF 1600 |
Electronic Materials
|
- | 3.9 | 2020 | 26.6 Days | CHF 1200 |

Preprints.org is a multidisciplinary platform offering a preprint service designed to facilitate the early sharing of your research. It supports and empowers your research journey from the very beginning.
MDPI Topics is collaborating with Preprints.org and has established a direct connection between MDPI journals and the platform. Authors are encouraged to take advantage of this opportunity by posting their preprints at Preprints.org prior to publication:
- Share your research immediately: disseminate your ideas prior to publication and establish priority for your work.
- Safeguard your intellectual contribution: Protect your ideas with a time-stamped preprint that serves as proof of your research timeline.
- Boost visibility and impact: Increase the reach and influence of your research by making it accessible to a global audience.
- Gain early feedback: Receive valuable input and insights from peers before submitting to a journal.
- Ensure broad indexing: Web of Science (Preprint Citation Index), Google Scholar, Crossref, SHARE, PrePubMed, Scilit and Europe PMC.
Related Topic
- Application of Graphene-Based Materials, 2nd Edition (9 articles)

