Recent Sedimentation Rates of Shallow Lakes in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River: Patterns, Controlling Factors and Implications for Lake Management
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Region
2.2. Field and Laboratory Methods
2.3. Data Analyses
2.4. Reference Conditions for Sediment Accumulation Rates
3. Results
3.1. Dating Results
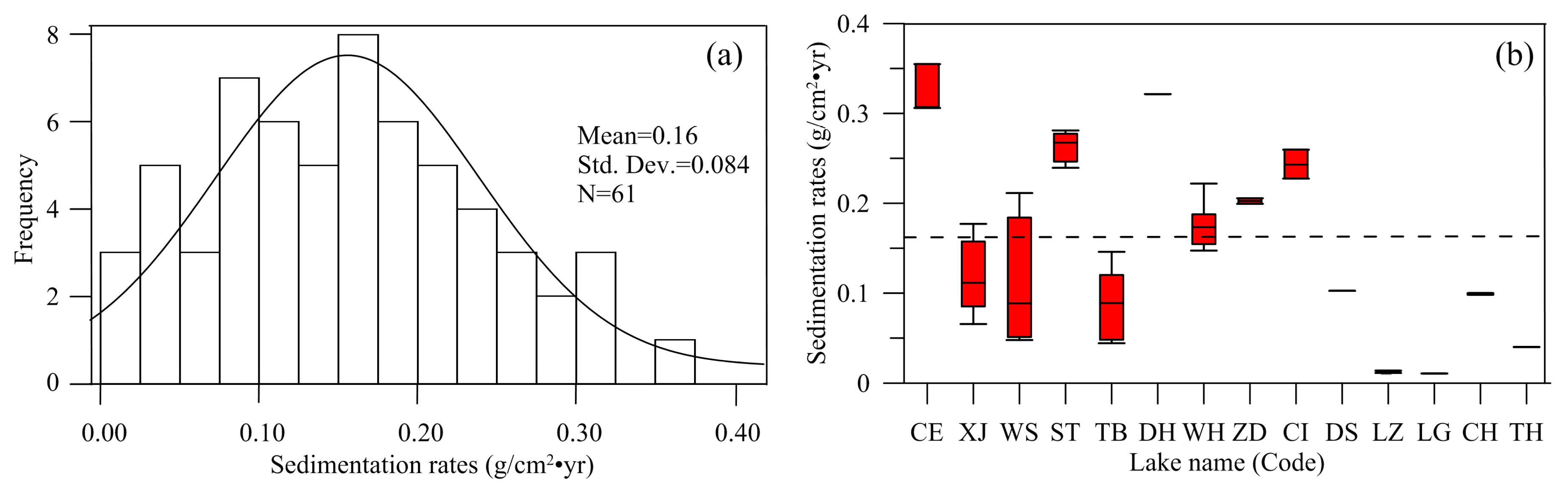
3.2. Spatiotemporal Pattern of Sedimentation Rates Among Lakes
3.3. Sedimentation Rates in Multicores of an Individual Lake
3.4. Factors Controlling Sedimentation Rates Variability
3.5. Reference Conditions for Sedimentation Rates
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatiotemporal Pattern in Sedimentation Rates in MLYB Lakes
4.2. Factors Controlling Sedimentation Rate Variability
4.3. Implications for Lake Management
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.M.; Dou, H.S. Lakes in China; Science press: Beijing, China, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Moss, B. Engineering and biological approaches to the restoration for eutrophication of shallow lakes in which aquatic plant communtities are important components. Hydrobiologia 1990, 200, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, E.M.; Carpenter, S.R.; Caraco, N.F. Human impact on erodable phosphorus and eutrophication: A global perspective increasing accumulation of phosphorus in soil threatens rivers, lakes, and coastal oceans with eutrophication. Am. Inst. Biol.Sci. 2001, 51, 227–234. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, E.; Yang, X.; Shen, J.; Dong, X.; Zhang, E.; Wang, S. Environmental response to climate and human impact during the last 400 years in Taibai Lake catchment, middle reach of Yangtze River, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 385, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiefer, E.; Reid, K.; Burt, A.; Luce, J. Watershed assessment in the Southern Interior of British Columbia. In Assessing Natural Sedimentation Patterns and Impacts of Land Use on Sediment Yield: A Lake-Sediment–Based Approach; Toews, D., Chatwin, S., Eds.; Ministry of Forests Research Program: Columbia, UK, 2001; pp. 209–236. [Google Scholar]
- Blais, J.M.; France, R.L.; Kimpe, L.E.; Cornett, R.J. Climatic changes in Northwestern Ontario have had a greater effect on erosion and sediment accumulation than logging and fire Evidence from 210Pb chronology in lake sediments. Biogeochemistry 1998, 43, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Peder Jensen, J.; Søndergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.; Landkildehus, F. Trophic structure, species richness and biodiversity in Danish lakes: Changes along a phosphorus gradient. Freshw. Biol. 2000, 45, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Gao, G.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Y.; Tang, X.; Xu, H.; Deng, J. Lake eutrophication and its ecosystem response. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, J.A.; Williams, R.J.; Martinez, N.D. Network structure and biodiversity loss in food webs: Robustness increases with connectance. Ecol. Lett. 2002, 5, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brothers, S.; Vermaire, J.C.; Gregory-Eaves, I. Empirical models for describing recent sedimentation rates in lakes distributed across broad spatial scales. J. Paleolimnol. 2008, 40, 1003–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearing, J.A.; Jones, R.T. Coupling temporal and spatial dimensions of global sediment flux through lake and marine sediment records. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2003, 39, 147–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, N.L.; Morley, D.; Appleby, P.G.; Battarbee, R.W.; Alliksaar, T.; Guilizzoni, P.; Jeppesen, E.; Korhola, A.; Punning, J.-M. Sediment accumulation rates in European lakes since AD 1850: Trends, reference conditions and exceedence. J. Paleolimnol. 2010, 45, 447–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, N.; Bennion, H.; Lotter, A. Lake eutrophication and its implications for organic carbon sequestration in Europe. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 2741–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiefer, E.; Petticrew, E.L.; Immell, R.; Hassan, M.A.; Sonderegger, D.L. Land use and climate change impacts on lake sedimentation rates in western Canada. Anthropocene 2013, 3, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Ma, R.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, J.; Yao, S.; Zhang, M.; Zeng, H. Lake status, major problems and protection strategy in China. J. Lake Sci. 2010, 22, 799–810. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Xue, H.; Wu, S.; Ling, F.; Xiao, F.; Wei, X. Lake area changes in the middle Yangtze region of China over the 20th century. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flower, R.; Appleby, P.; Thompson, J.; Ahmed, M.; Ramdani, M.; Chouba, L.; Rose, N.; Rochester, R.; Ayache, F.; Kraiem, M. Sediment distribution and accumulation in lagoons of the Southern Mediterranean Region (the MELMARINA Project) with special reference to environmental change and aquatic ecosystems. Hydrobiologia 2009, 622, 85–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Vicente, M.; Navas, A. Relating soil erosion and sediment yield to geomorphic features and erosion processes at the catchment scale in the Spanish Pre-Pyrenees. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 61, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, E.; Meerhoff, M.; Davidson, T.A.; Trolle, D.; Sondergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Beklioglu, M.; Brucet, S.; Volta, P.; Gonzalez-Bergonzoni, I.; et al. Climate change impacts on lakes: An integrated ecological perspective based on a multi-faceted approach, with special focus on shallow lakes. J. Limnol. 2014, 73, 84–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, J.F.; Plater, A.J.; Mayers, C.; Turner, S.D.; Stroud, R.W.; Weber, J.E. Land use, soil erosion, and sediment yield at Pinto Lake, California: Comparison of a simplified USLE model with the lake sediment record. J. Paleolimnol. 2011, 45, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Cai, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y. Interpretation of the environmental change of Dongting Lake, middle reach of Yangtze River, China, by 210Pb measurement and satellite image analysis. Geomorphology 2001, 41, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engstrom, D.R.; Almendinger, J.E.; Wolin, J.A. Historical changes in sediment and phosphorus loading to the upper Mississippi River: Mass-balance reconstructions from the sediments of Lake Pepin. J. Paleolimnol. 2009, 41, 563–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Masri, M.S.; Aba, A.; Khalil, H.; Al-Hares, Z. Sedimentation rates and pollution history of a dried lake: Al-Oteibeh Lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 293, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odhiambo, B.K.; Ricker, M.C. Spatial and isotopic analysis of watershed soil loss and reservoir sediment accumulation rates in Lake Anna, Virginia, USA. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 65, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M. Ecology of Shallow Lakes; Springer Science & Business Media: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Yi, C.; Xie, P.; Xing, Y.; Ni, L. Sedimentation rates, nitrogen and phosphorus retentions in the largest urban Lake Donghu, China. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2006, 267, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, E.; Bing, H.; Yang, X.; Xue, B.; Xia, W. Geochronology of recent lake sediments from Longgan Lake, middle reach of the Yangtze River, influenced by disturbance of human activities. Sci. Chin. Earth Sci. 2010, 53, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Lu, X.X.; Higgitt, D.L.; Wang, S.M. Recent lake sedimentation in the middle and lower Yangtze basin inferred from from 137Cs and 210Pb measurements. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2002, 21, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Yao, S. Recent sedimentation rates in lakes in lower Yangtze River basin. Quat. Int. 2011, 244, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Xue, B. Sedimentary geochemical record of human-induced environmental changes in Huanggaihu Lake in the middle reach of the Yangtze River, China. J. Limnol. 2015, 74, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Dong, X.; Liu, Q. Nutrient dynamics linked to hydrological condition and anthropogenic nutrient loading in Chaohu Lake (Southeast China). Hydrobiologia 2011, 661, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankman, D.; Davis, L.; De Leeuw, J. River management, landuse change, and future flood risk in China’s Poyang Lake region. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2009, 7, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Xu, H.; McCarthy, M.J.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Li, Y.; Gardner, W.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): The need for a dual nutrient (N & P) management strategy. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bennion, H.; Battarbee, R.W.; Sayer, C.D.; Simpson, G.L.; Davidson, T.A. Defining reference conditions and restoration targets for lake ecosystems using palaeolimnology: A synthesis. J. Paleolimnol. 2010, 45, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoddard, J.L.; Larsen, D.P.; Hawkins, C.P.; Johnson, R.K.; Norris, R.H. Setting Expectations for the Ecological Condition of Streams: The Concept of Reference Condition. Ecol. Appl. A Publ. Ecol. Soc. Am. 2006, 16, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.K. Bioassessment of Freshwater Ecosystems: Using the Reference Condition Approach. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 50, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 on establishing a framework for community action in the field of water policy. In Official Journal of the European Union; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2000; Volume L327, pp. 1–72. [Google Scholar]
- Battarbee, R.W.; Bennion, H. Palaeolimnology and its developing role in assessing the history and extent of human impact on lake ecosystems. J. Paleolimnol. 2010, 45, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Yang, X.; Chen, X.; Liu, Q.; Yao, M.; Wang, R.; Xu, M. Using sedimentary diatoms to identify reference conditions and historical variability in shallow lake ecosystems in the Yangtze floodplain. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2016, 67, 803–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Shen, J.; Birch, G.F.; Yang, X.; Wu, Y.; Xue, B. Human-induced change in sedimentary trace metals and phosphorus in Chaohu Lake, China, over the past half-millennium. J. Paleolimnol. 2012, 47, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Liu, G.; Pi, J.; Chen, G.; Li, C. On the river–lake relationship of the middle Yangtze reaches. Geomorphology 2007, 85, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Yang, G.; Duan, H.; Jiang, J.; Wang, S.; Feng, X.; Li, A.; Kong, F.; Xue, B.; Wu, J.; et al. The quantity, size and spatial distributions of lakes in China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleby, P.G. Chronostratigraphic Techniques in Recent Sediments. In Tracking Environmental Change Using Lake Sediments: Basin Analysis, Coring, and Chronological Techniques; Last, W.M., Smol, J.P., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 171–203. [Google Scholar]
- Robbins, J.A. Geochemical and Geophysical Applications of Radioactive Lead; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1978; Volume 1, pp. 285–393. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, E.; Bin, X.; Xiangdong, Y.; Yanhong, W.; Weilan, X. 137Cs and 210Pb Chronology for modern lake sediment: A case study of Chaohu lake Taibai Lake. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2009, 29, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Anderson, N.J.; Yang, X.; Chen, X.; Shen, J. Carbon burial by shallow lakes on the Yangtze floodplain and its relevance to regional carbon sequestration. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 2205–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, E.; Yao, S.; Zhu, Y.; Xia, W. Recent heavy metal accumulation in Dongjiu and Xijiu lakes, East China. J. Paleolimnol. 2009, 43, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.L.; Qin, B.Q. Study on 137Cs and 210Pb Dating and Sedimentation Rates of Wanghu Lake, Hubei Province. J. Ningbo Univ. (Nat. Sci. Eng. Ed.) 2008, 3, 418–422. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Lücke, A.; Wang, S. Assessment of nutrient sources and paleoproductivity during the past century in Longgan Lake, middle reaches of the Yangtze River, China. J. Paleolimnol. 2007, 39, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Liu, E.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, S.; Qu, W. Distribution and chemical fractionation of heavy metals in recent sediments from Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 2007, 581, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanjing Institute of Geography and Limnology Chinese Academy of Sciences. Technical Specification Lake Survey; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Kuang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X. Spatiaotemporal characteristics, patterns and causes of land-use changes in China since the late 1980s. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, B.; Verdin, K.; Jarvis, A. New Global Hydrography Derived From Spaceborne Elevation Data. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2008, 89, 93–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Storch, H.; Chen, X.; Zorita, E.; Zheng, J.; Wang, S. Simulated and reconstructed winter temperature in the Eastern China during the last millennium. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2005, 50, 2872–2877. [Google Scholar]
- Editorial Committee of chronicles in Wuhan. Wuhan Local Chronicles; Wuhan University Press: Wuhan, China, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Dong, X.; Liu, E. Environmental changes in Chaohu Lake (Southeast, China) since the mid 20th century: The interactive impacts of nutrients, hydrology and climate. Limnol.-Ecol. Manag. Inland Waters 2013, 43, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S. Water Balance of Zhangdu Lake in Yangtze River Basin. Exp. Water Res. Hydropower Inf. 2006, 27, 72–79. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Gao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Paerl, H.W.; Carmichael, W.W. A drinking water crisis in Lake Taihu, China: Linkage to climatic variability and lake management. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, N.; Korsman, T.; Renberg, I. Spatial heterogeneity of diatom stratigraphy in varved and non-varved sediments of a small, boreal-forest lake. Aquat. Sci. 1994, 56, 40–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto, P.; Walling, D.E.; Callegari, G. Using 137Cs measurements to establish catchment sediment budgets and explore scale effects. Hydrol. Proc. 2011, 25, 886–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanmaercke, M.; Poesen, J.; Govers, G.; Verstraeten, G. Quantifying human impacts on catchment sediment yield: A continental approach. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2015, 130, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.E.; Collins, A.L. The catchment sediment budget as a management tool. Environ. Sci. Policy 2008, 11, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Dong, X.; Yao, M.; Shiyue, C.; Yang, X. Historical information on aquatic vegetation revealed by sedimentary diatom: A case study on Liangzi Lake. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2014, 38, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar]
- Chunhua, H.; Peimin, P. Downward flux of suspended substance and organic decomposition rate in Wulihu Bay, Taihu Lake. Oceanol. Et Limnol. Sin. 2000, 31, 327–333. [Google Scholar]
- Maetens, W.; Vanmaercke, M.; Poesen, J.; Jankauskas, B.; Jankauskien, G.; Ionita, I. Effects of land use on annual runoff and soil loss in Europe and the Mediterranean: A meta-analysis of plot data. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2012, 36, 599–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.R. Soil erosion and agricultural sustainability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13268–13272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, C.; Reidy, C.A.; Dynesius, M.; Revenga, C. Fragmentation and flow regulation of the world’s large river systems. Science 2005, 308, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Milliman, J.D. Seasonal variations of sediment discharge from the Yangtze River before and after impoundment of the Three Gorges Dam. Geomorphology 2009, 104, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattel, G.R.; Dong, X.; Yang, X. A century-scale, human-induced ecohydrological evolution of wetlands of two large river basins in Australia (Murray) and China (Yangtze). Hydrol. Earth Syst.Sci. 2016, 20, 2151–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likens, G.E. Lake Ecosystem Ecology: A Global Perspective; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Le, C.; Zha, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, D.; Lu, H.; Yin, B. Eutrophication of lake waters in China: Cost, causes, and control. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, N.; Ruan, X.; Xu, J.; Pan, Z. Estimating the optimal width of buffer strip for nonpoint source pollution control in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Ecol. Model. 2014, 276, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battarbee, R.W.; Morley, D.; Bennion, H.; Simpson, G.L.; Hughes, M.; Bauere, V. A palaeolimnological meta-database for assessing the ecological status of lakes. J. Paleolimnol. 2011, 45, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WWF. WWF China Programme Annual Report; WWF: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
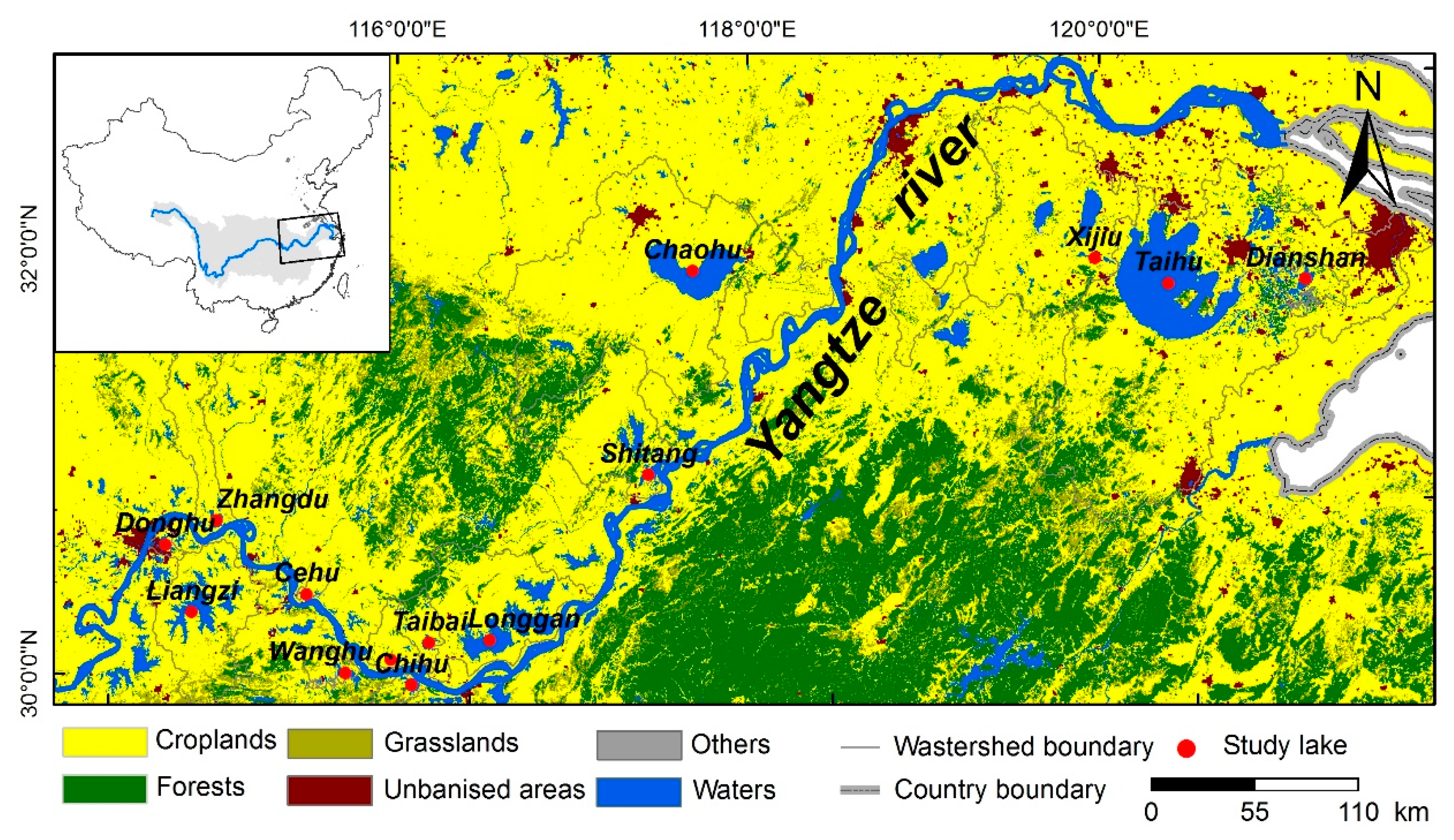
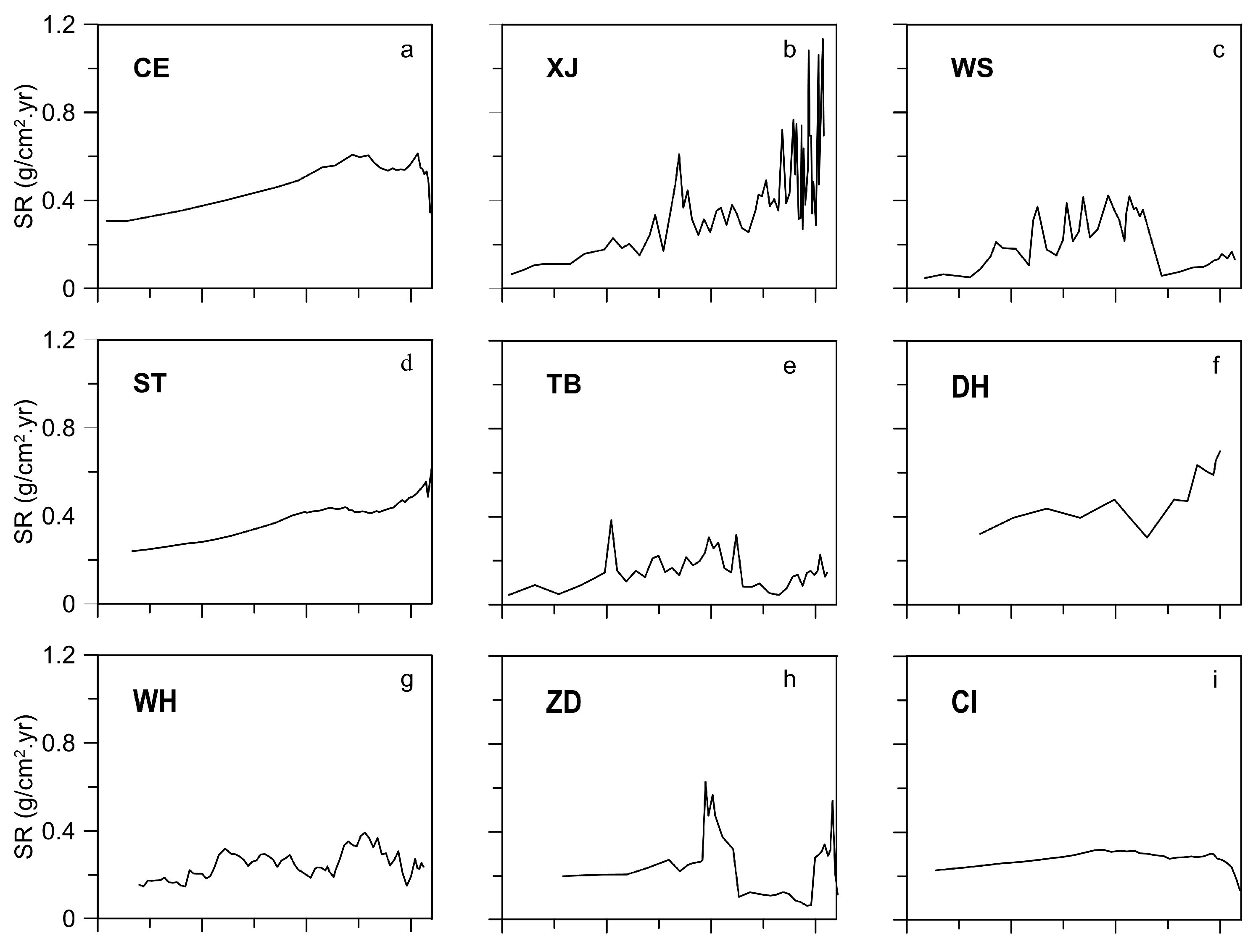

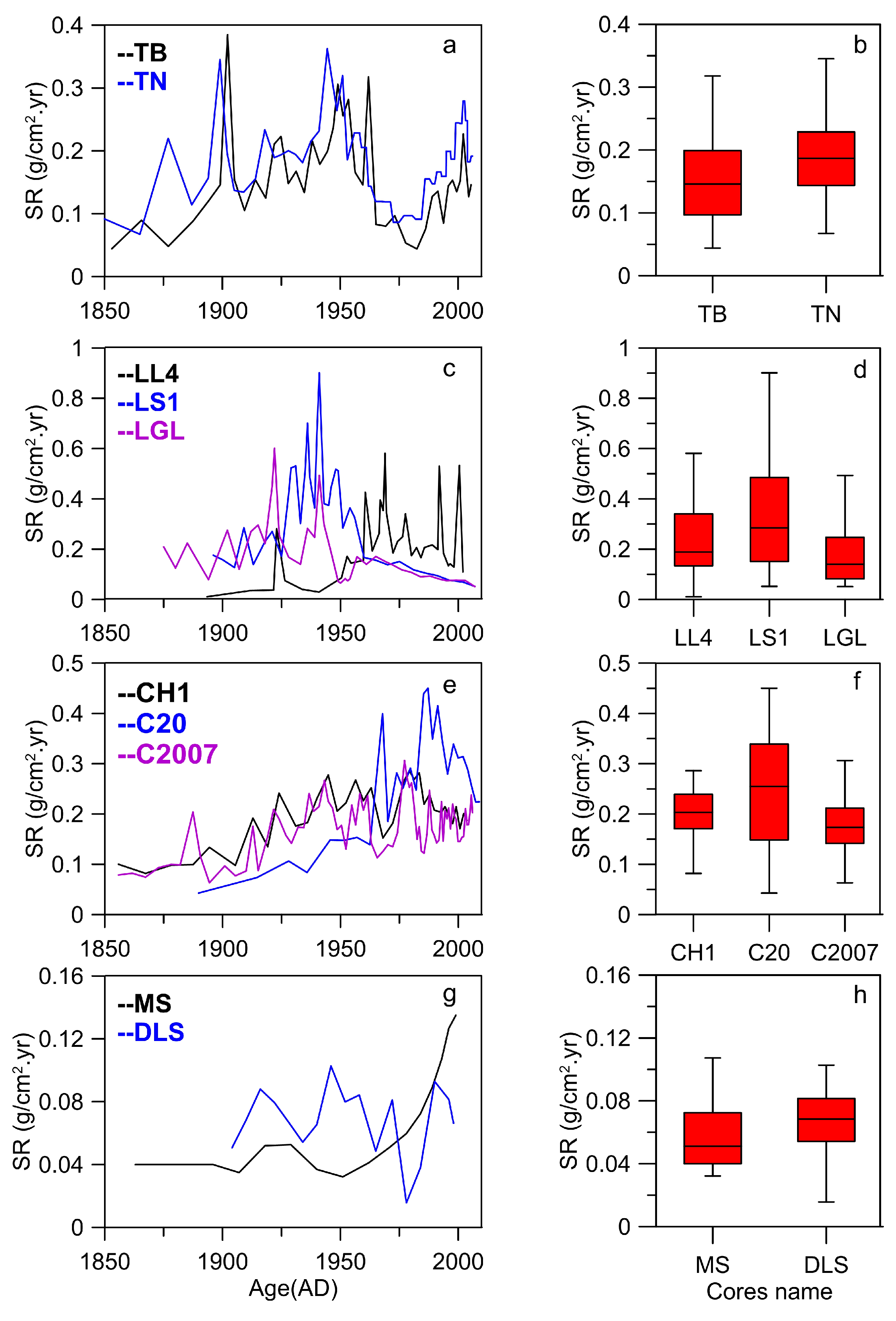
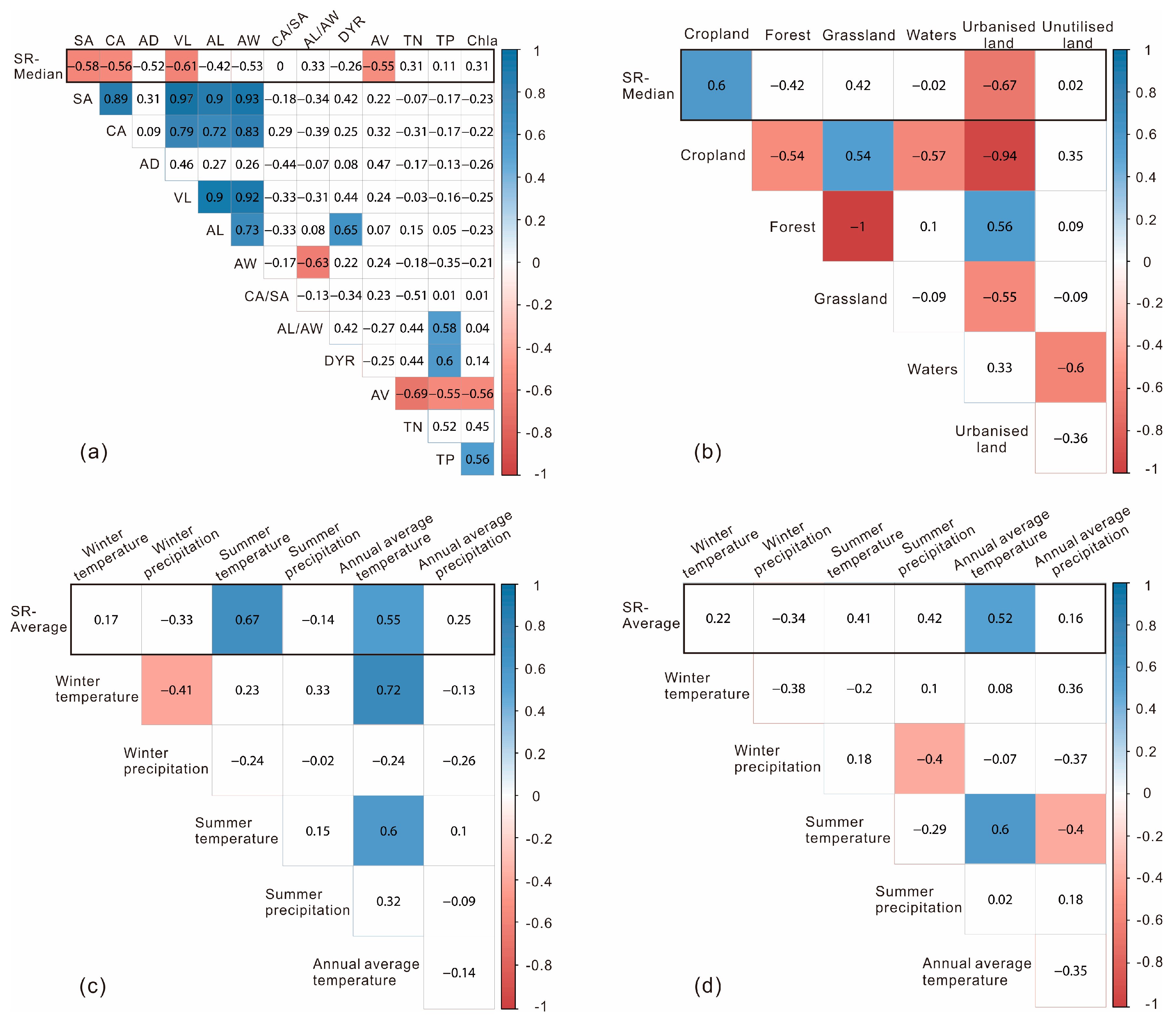
| Lake Name | Code | Location | SA (km2) | CA (km2) | AD (m) | VL (109 m3) | AL (km) | AW (km) | DYR (km) | AV | TN (mg/L) | TP (mg/L) | Chl-a (µg/L) | Core Names in Each Lake |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cehu | CE | N 30°14′–30°16′ E 115°08′–115°10′ | 11.8 | 232 | 2.1 | 0.03 | 7.1 | 1.7 | 0.95 | 1 | 0.77 | 0.04 | 4.35 | CE |
| Xijiu | XJ | N 31°22′–31°24′ E 119°42′–119°42′ | 12.4 | 97 | 1.9 | 0.04 | 20.6 | 0.87 | 125.58 | 1 | 2.76 | 0.22 | 14.26 | XJ |
| Wushan | WS | N 29°53′–29°57′ E 115°31′–115°37′ | 16.1 | 469 | 2.1 | 0.05 | 7.4 | 2.2 | 3.62 | 1 | 1.14 | 0.23 | 40.62 | WS |
| Shitang | ST | N 30°18′–30°39′ E 117°04′–117°07′ | 23.3 | 364 | 1.5 | 0.09 | 12.0 | 5.0 | 11.63 | 1 | 1.00 | 0.07 | 10.40 | ST |
| Taibai | TB | N 29°56′–30°01′ E 115°46′–115°50′ | 26.0 | 960 | 2.5 | 0.08 | 10.8 | 2.3 | 11.66 | 2 | 1.43 | 0.13 | 4.72 | TB,TN |
| Donghu | DH | N 30°31′–30°36′ E 114°21′–114°28′ | 33.7 | 650 | 2.2 | 0.09 | 11.8 | 2.9 | 9.27 | 1 | 1.53 | 0.24 | 51.53 | DH |
| Wanghu | WH | N 29°51′–29°54′ E 115°20′–115°25′ | 35.2 | 514 | 3.6 | 0.16 | 9.2 | 4.6 | 4.26 | 2 | 0.96 | 0.04 | 24.80 | WH |
| Zhangdu | ZD | N 30°37′–30°42′ E 114°40′–114°48′ | 42.3 | 5310 | 1.2 | 0.04 | 9.3 | 3.8 | 1.81 | 3 | 0.56 | 0.03 | 13.35 | ZD |
| Chihu | CI | N 29°45′–29°48′ E 115°41′–115°44′ | 61.2 | 360 | 2.5 | 0.23 | 12.0 | 6.7 | 0.44 | 2 | 1.54 | 0.01 | 7.50 | CI |
| Dianshan | DS | N 31°04′–31°12′ E 120°54′–121°01′ | 63.7 | 446 | 2.1 | 0.16 | 12.8 | 5.0 | 84.98 | 1 | 2.09 | 0.16 | 31.61 | DS |
| Liangzi | LZ | N 30°05′–30°18′ E 114°21′–114°39′ | 304.3 | 3265 | 4.2 | 1.27 | 31.7 | 9.6 | 47.38 | 5 | 0.49 | 0.04 | 3.18 | LZ |
| Longgan | LG | N 29°52′–30°05′ E 115°19′–116°17′ | 316.2 | 5511 | 3.2 | 1.20 | 29.5 | 10.7 | 4.40 | 4 | 0.77 | 0.05 | 4.82 | LL4,LS1,LGL |
| Chaohu | CH | N 31°25′–31°43′ E 117°16′–117°51′ | 769.6 | 9258 | 2.7 | 2.07 | 61.7 | 12.5 | 62.40 | 1 | 1.57 | 0.14 | 17.58 | CH1,C20,C2007 |
| Taihu | TH | N 30°55′–31°33′ E 119°52–′120°36′ | 2425.0 | 36,500 | 1.9 | 5.14 | 68.0 | 35.7 | 88.56 | 1 | 1.54 | 0.06 | 9.17 | MS,DLS |
| Lake | Code | Croplands (%) | Forests (%) | Grasslands (%) | Waters (%) | Urbanized Lands (%) | Unutilized Lands (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cehu | CE | −1.45 | −18.62 | 19.03 | 0.93 | 0.10 | 0.00 |
| Xijiu | XJ | −5.16 | −9.46 | 9.40 | 0.68 | 4.54 | 0.00 |
| Wushan | WS | −0.34 | −18.34 | 18.34 | 0.10 | 0.23 | 0.00 |
| Shitang | ST | −0.26 | −24.69 | 24.60 | −0.01 | 0.35 | 0.00 |
| Taibai | TB | −0.01 | −23.87 | 23.84 | −0.17 | 0.20 | 0.02 |
| Donghu | DH | −1.57 | −7.51 | 7.32 | −0.86 | 2.61 | 0.00 |
| Wanghu | WH | −0.19 | −29.53 | 29.52 | −0.22 | 0.26 | 0.17 |
| Zhangdu | ZD | −0.54 | −37.14 | 37.16 | 0.28 | 0.21 | 0.03 |
| Liangzi | LZ | −0.38 | −11.93 | 11.74 | −0.46 | 0.18 | 0.86 |
| Chaohu | CH | −1.36 | −12.93 | 12.92 | 0.05 | 1.32 | 0.00 |
| Xijiu | XJ | −5.16 | −9.46 | 9.40 | 0.68 | 4.54 | 0.00 |
| Wushan | WS | −0.34 | −18.34 | 18.34 | 0.10 | 0.23 | 0.00 |
| Shitang | ST | −0.26 | −24.69 | 24.60 | −0.01 | 0.35 | 0.00 |
| Wanghu | WH | −0.19 | −29.53 | 29.52 | −0.22 | 0.26 | 0.17 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, M.; Dong, X.; Yang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Wang, R.; Yao, M.; Davidson, T.A.; Jeppesen, E. Recent Sedimentation Rates of Shallow Lakes in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River: Patterns, Controlling Factors and Implications for Lake Management. Water 2017, 9, 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9080617
Xu M, Dong X, Yang X, Chen X, Zhang Q, Liu Q, Wang R, Yao M, Davidson TA, Jeppesen E. Recent Sedimentation Rates of Shallow Lakes in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River: Patterns, Controlling Factors and Implications for Lake Management. Water. 2017; 9(8):617. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9080617
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Min, Xuhui Dong, Xiangdong Yang, Xu Chen, Qinghui Zhang, Qian Liu, Rong Wang, Min Yao, Thomas A. Davidson, and Erik Jeppesen. 2017. "Recent Sedimentation Rates of Shallow Lakes in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River: Patterns, Controlling Factors and Implications for Lake Management" Water 9, no. 8: 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9080617
APA StyleXu, M., Dong, X., Yang, X., Chen, X., Zhang, Q., Liu, Q., Wang, R., Yao, M., Davidson, T. A., & Jeppesen, E. (2017). Recent Sedimentation Rates of Shallow Lakes in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River: Patterns, Controlling Factors and Implications for Lake Management. Water, 9(8), 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9080617






