Scandium and Titanium Recovery from Bauxite Residue by Direct Leaching with a Brønsted Acidic Ionic Liquid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
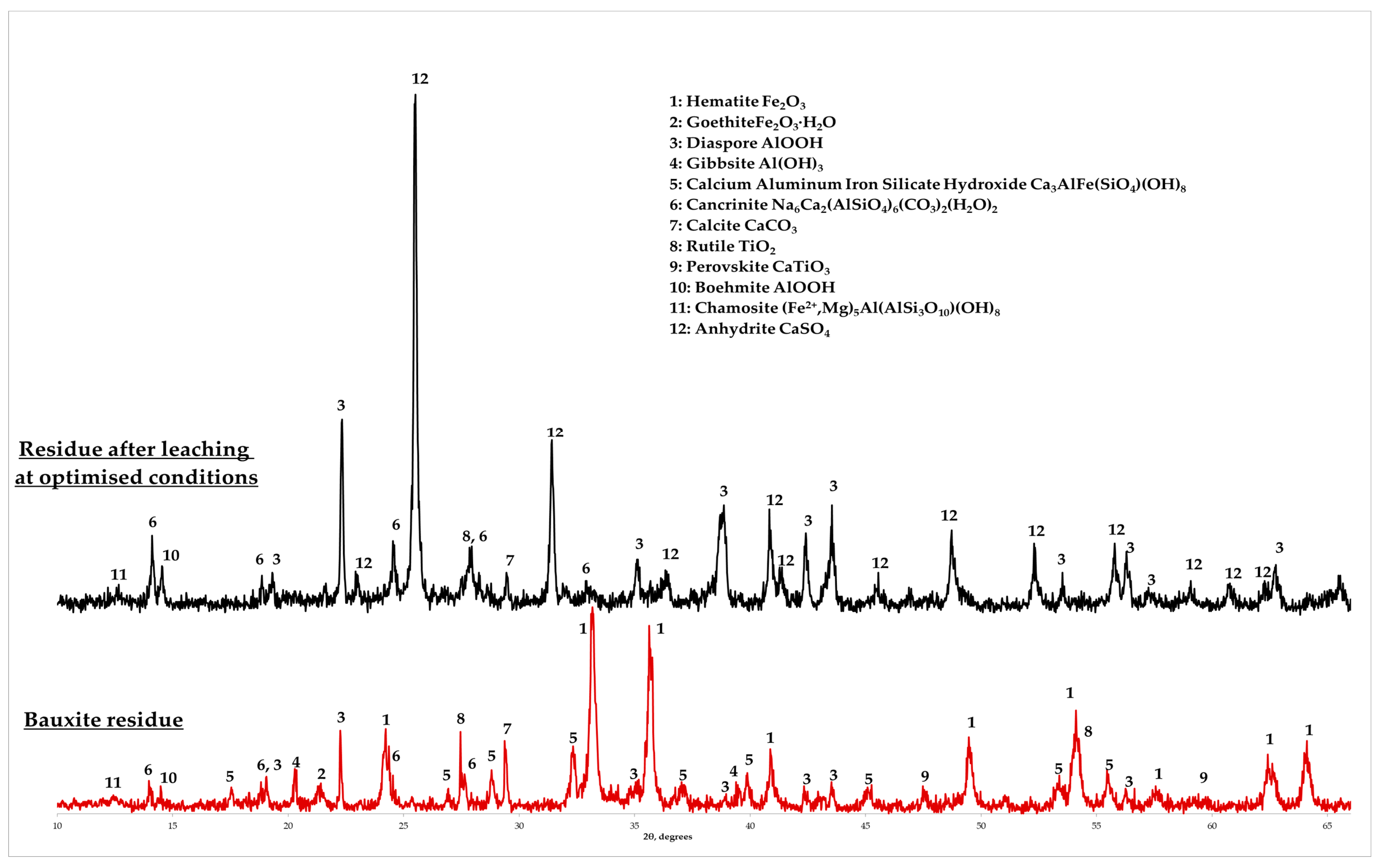
3.1. Bauxite Residue Characterization
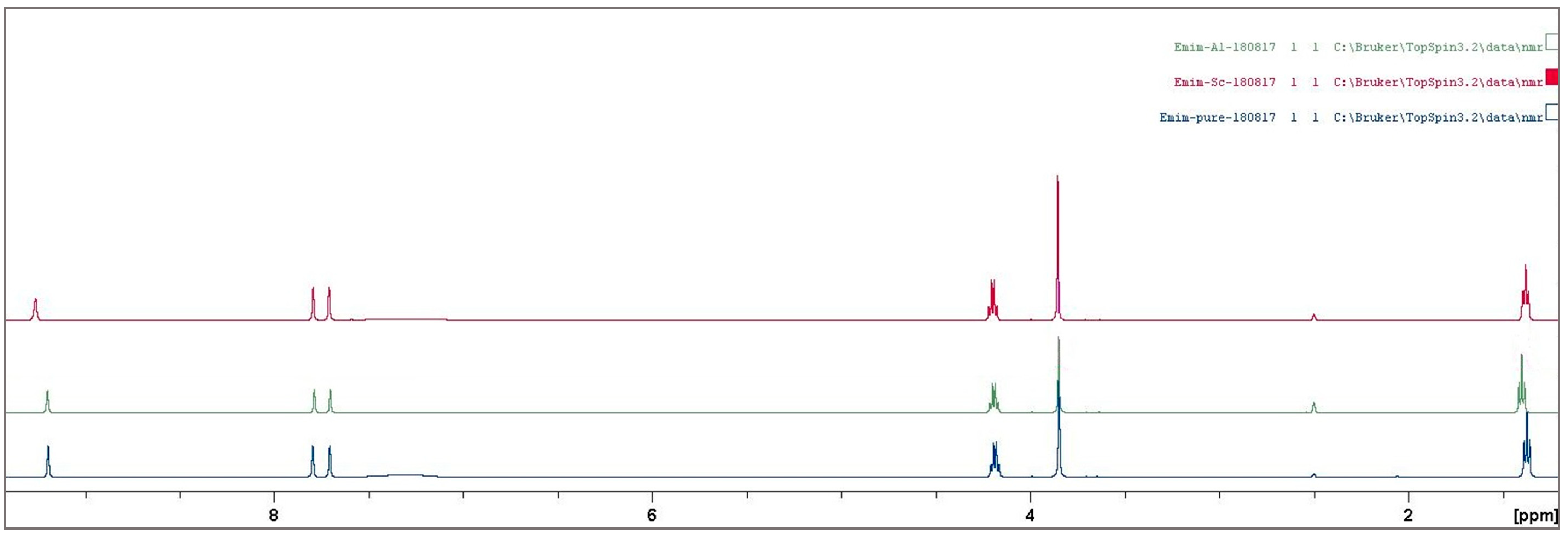
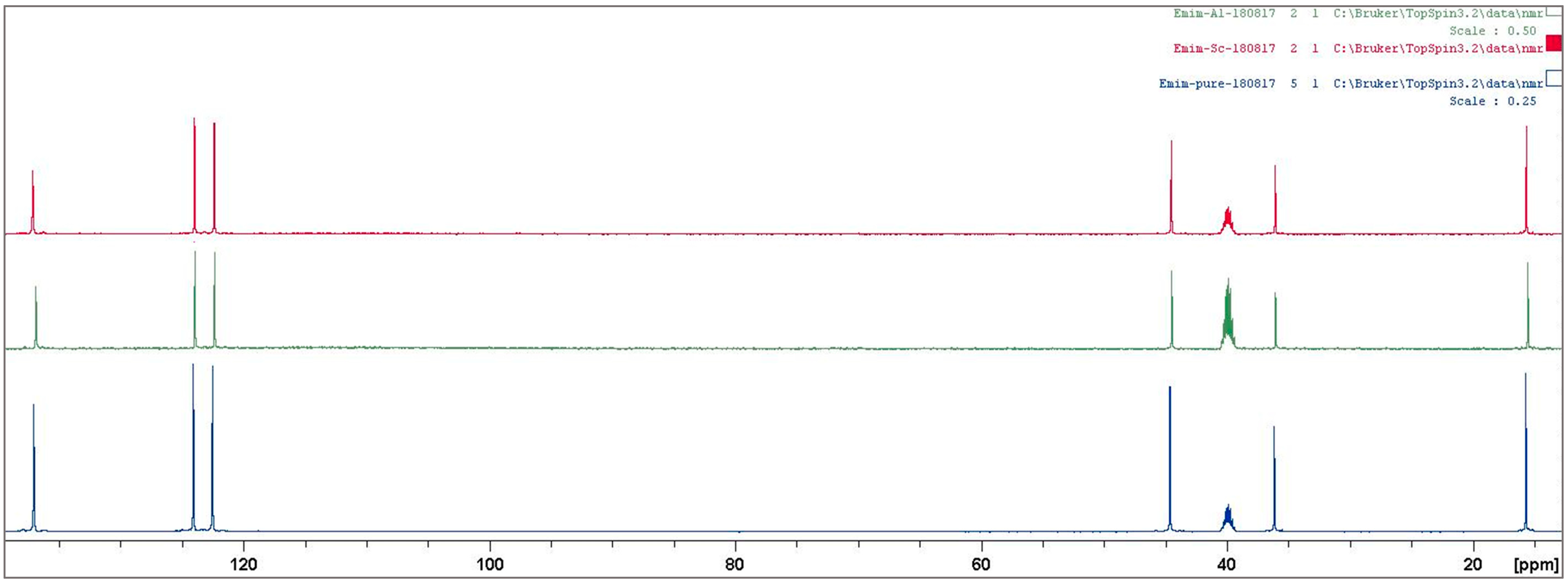
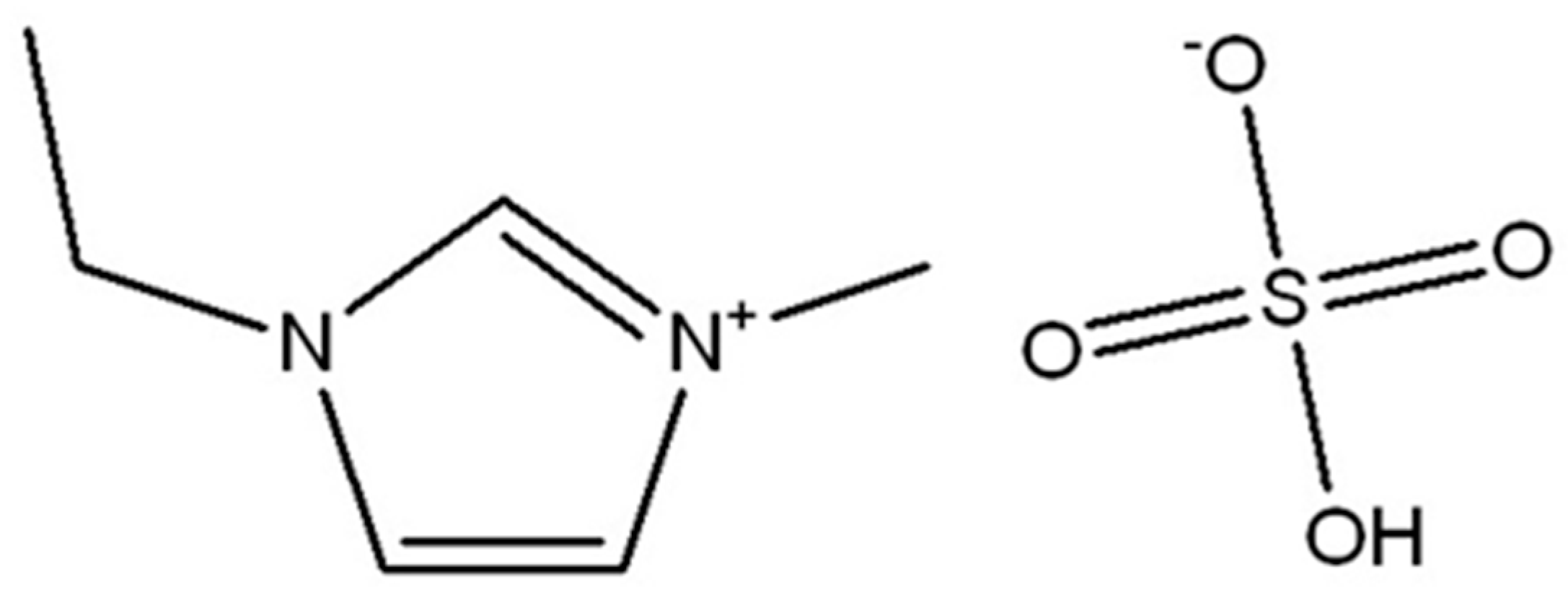
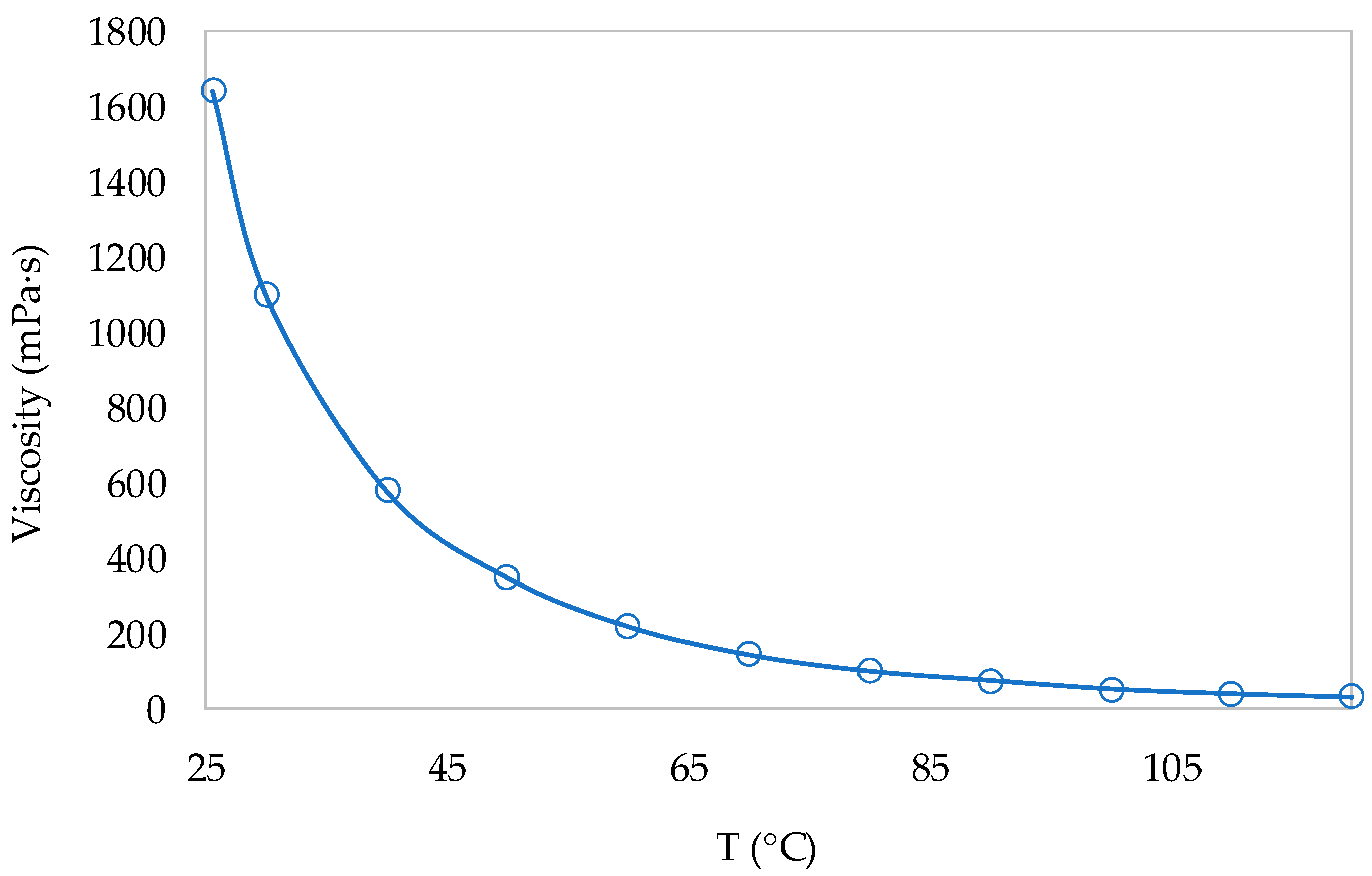
3.2. Ionic Liquid Characterization
Reaction Mechanism
3.3. Leaching Process Optimization: Parameters Affecting the System
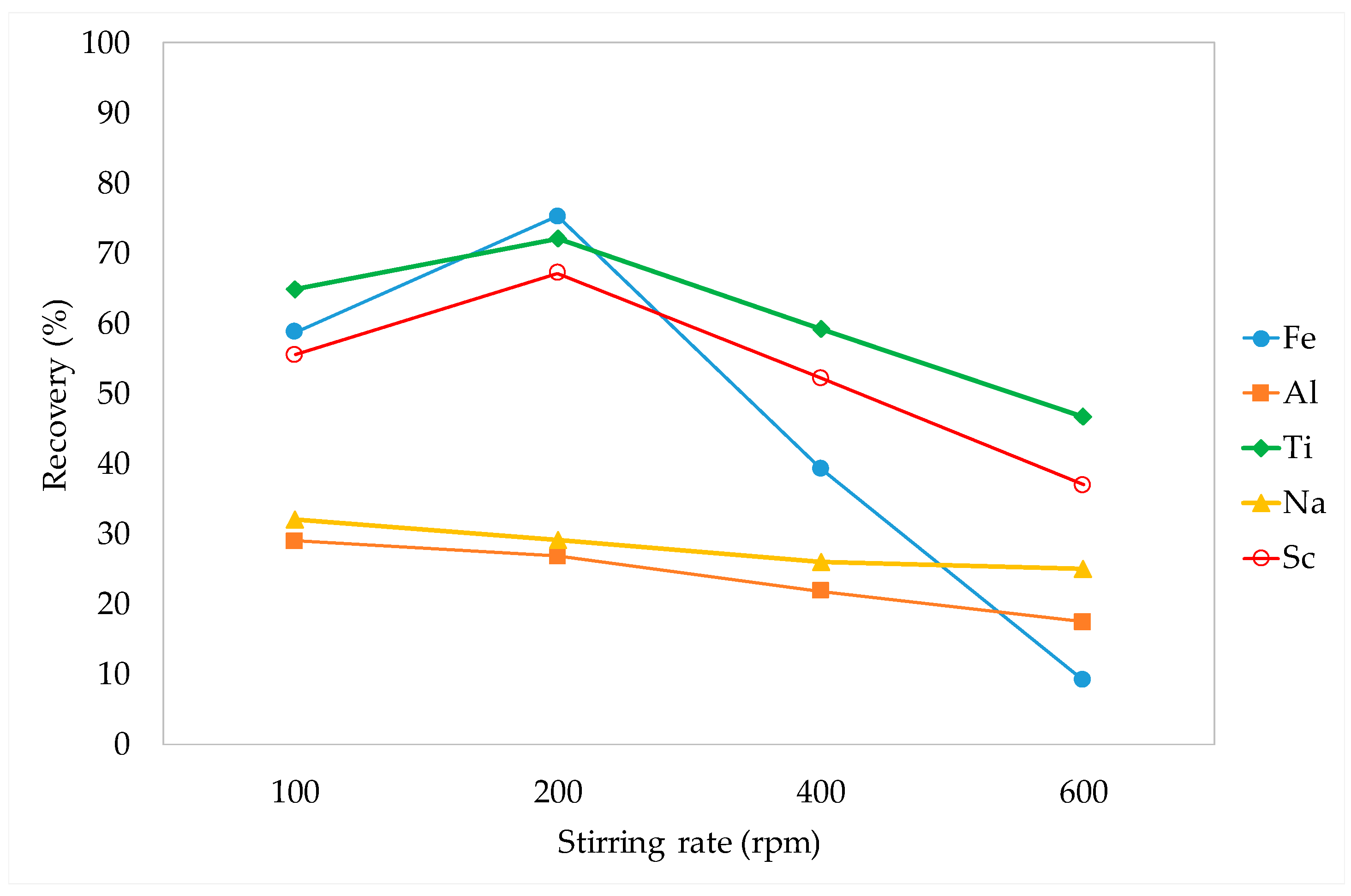
3.3.1. Stirring Rate
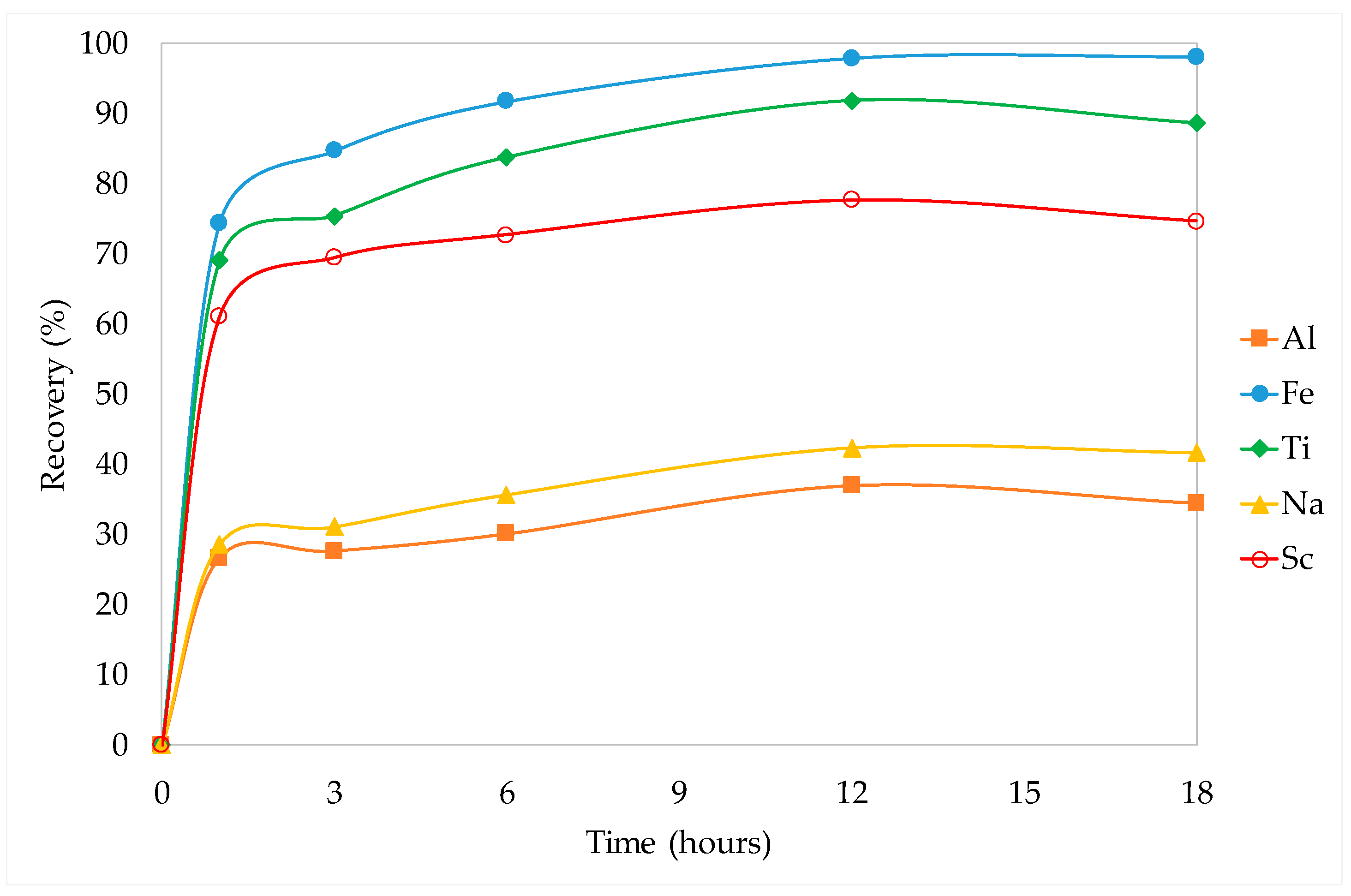
3.3.2. Kinetic Studies
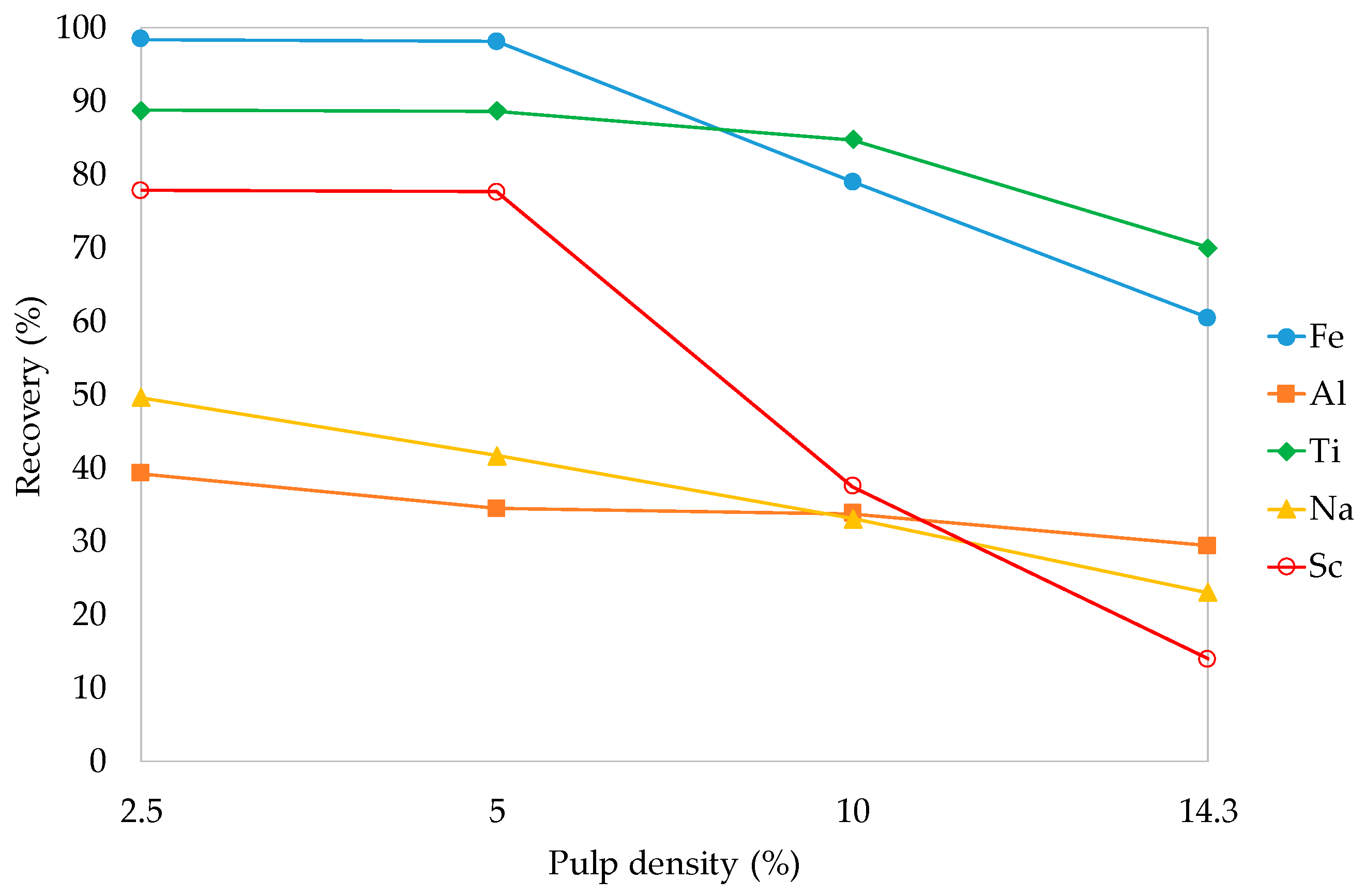
3.3.3. Pulp Density
3.4. Characterization of the Solid Residue after Leaching
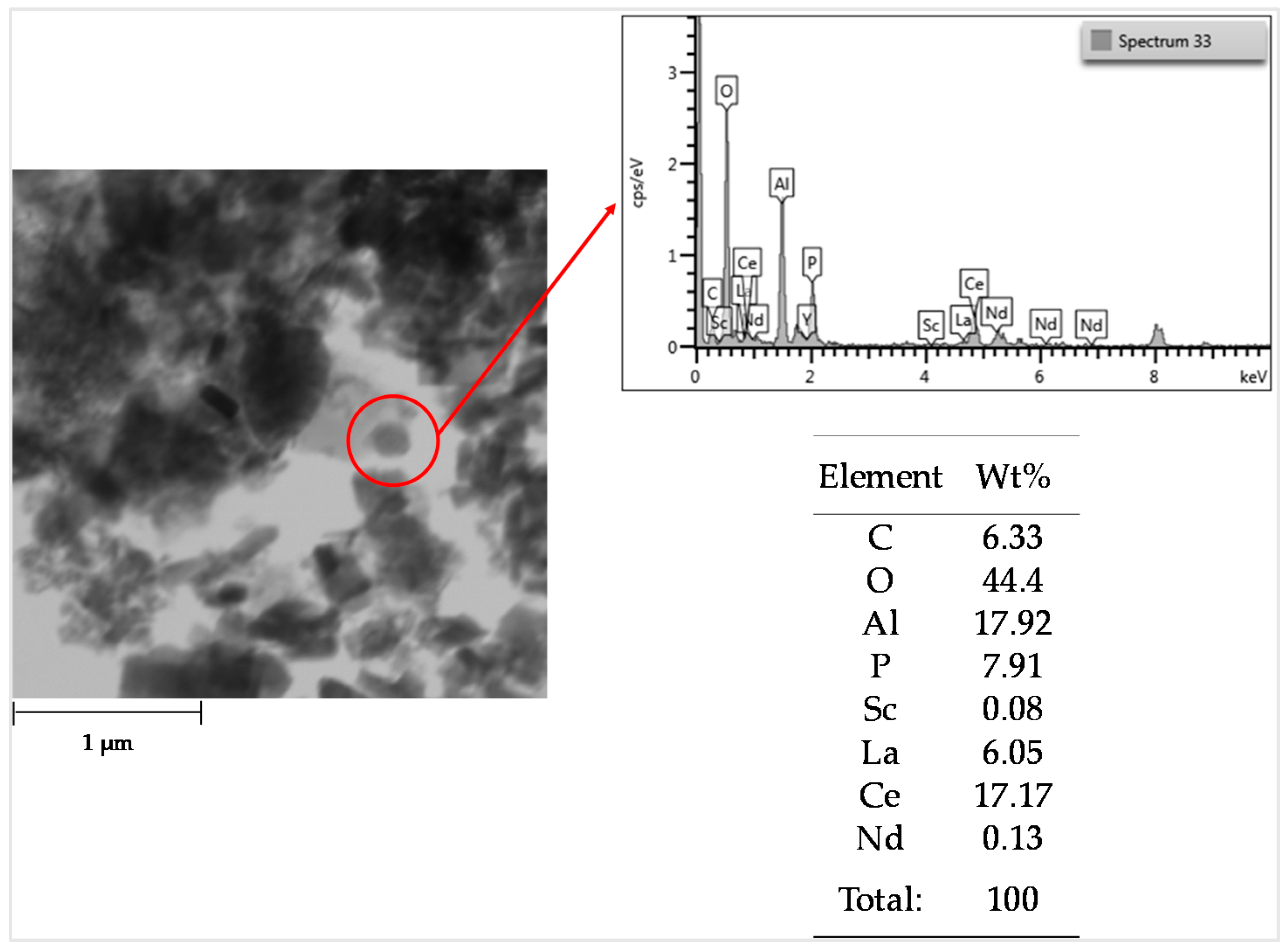
3.5. REEs in the Solid Residue
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Evans, K. The History, Challenges, and New Developments in the Management and Use of Bauxite Residue. J. Sustain. Metall. 2016, 2, 316–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Zheng, S.; Ma, S.; Zhang, Y. Recovery of Alumina and Alkali in Bayer Red Mud by the Formation of Andradite-Grossular Hydrogarnet in Hydrothermal Process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 189, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klauber, C.; Gräfe, M.; Power, G. Bauxite Residue Issues: II. Options for Residue Utilization. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 108, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräfe, M.; Power, G.; Klauber, C. Bauxite Residue Issues: III. Alkalinity and Associated Chemistry. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 108, 60–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Naidu, R. Hidden Values in Bauxite Residue (Red Mud): Recovery of Metals. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 2662–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochsenkühn-Petropulu, M.; Lyberopulu, T.; Parissakis, G. Direct Determination of Landthanides, Yttrium and Scandium in Bauxites and Red Mud from Alumina Production. Anal. Chim. Acta 1994, 296, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vind, J.; Alexandri, A.; Vassiliadou, V.; Panias, D. Distribution of Selected Trace Elements in the Bayer Process. Metals (Basel) 2018, 8, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, R.L.; Gao, S. Composition of the Continental Crust. In Treatise on Geochemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- Gambogi, J. Mineral Commodity Summaries, Scandium; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2017; pp. 146–147.
- Balomenos, E.; Davris, P.; Pontikes, Y.; Panias, D. Mud2Metal: Lessons Learned on the Path for Complete Utilization of Bauxite Residue Through Industrial Symbiosis. J. Sustain. Metall. 2017, 3, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deloitte Sustainability; British Geological Survey; Bureau de Recherches Géologiques et Minières; TNO. Study on the Review of the List of Critical Raw Materials; EU Law and Publications: Luxembourg, 2017; ISBN 978-92-79-47937-3. [Google Scholar]
- Borra, C.R.; Blanpain, B.; Pontikes, Y.; Binnemans, K.; Van Gerven, T. Recovery of Rare Earths and Other Valuable Metals From Bauxite Residue (Red Mud): A Review. J. Sustain. Metall. 2016, 2, 365–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ochsenkühn-Petropulu, M.; Lyberopulu, T.; Parissakis, G. Selective Separation and Determination of Scandium from Yttrium and Lanthanides in Red Mud by a Combined Ion Exchange/Solvent Extraction Method. Anal. Chim. Acta 1995, 315, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T.; Blanpain, B.; Van Gerven, T.; Pontikes, Y. Towards Zero-Waste Valorisation of Rare-Earth-Containing Industrial Process Residues: A Critical Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 99, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonomi, C.; Cardenia, C.; Yin, P.T.W.; Panias, D. Review of Technologies in the Recovery of Iron, Aluminium, Titanium and Rare Earth Elements from Bauxite Residue (Red Mud). In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Enhanced Landfill Mining, Lisboa, Portugal, 8–10 February 2016; pp. 259–276. [Google Scholar]
- Alkan, G.; Schier, C.; Gronen, L.; Stopic, S.; Friedrich, B. A Mineralogical Assessment on Residues after Acidic Leaching of Bauxite Residue (Red Mud) for Titanium Recovery. Metals 2017, 7, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agatzini-Leonardou, S.; Oustadakis, P.; Tsakiridis, P.E.; Markopoulos, C. Titanium Leaching from Red Mud by Diluted Sulfuric Acid at Atmospheric Pressure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 157, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkan, G.; Yagmurlu, B.; Cakmakoglu, S.; Hertel, T.; Kaya, Ş.; Gronen, L.; Stopic, S.; Friedrich, B. Novel Approach for Enhanced Scandium and Titanium Leaching Efficiency from Bauxite Residue with Suppressed Silica Gel Formation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Li, H. Metallurgical Process for Valuable Elements Recovery from Red Mud—A Review. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 155, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochsenkühn-Petropoulou, M.T.; Hatzilyberis, K.S.; Mendrinos, L.N.; Salmas, C.E. Pilot-Plant Investigation of the Leaching Process for the Recovery of Scandium from Red Mud. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2002, 41, 5794–5801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochsenkühn-Petropulu, M.; Lyberopulu, T.; Ochsenkühn, K.M.; Parissakis, G. Recovery of Lanthanides and Yttrium from Red Mud by Selective Leaching. Anal. Chim. Acta 1996, 319, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borra, C.R.; Blanpain, B.; Pontikes, Y.; Binnemans, K.; Van Gerven, T. Smelting of Bauxite Residue (Red Mud) in View of Iron and Selective Rare Earths Recovery. J. Sustain. Metall. 2016, 2, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borra, C.R.; Pontikes, Y.; Binnemans, K.; Van Gerven, T. Leaching of Rare Earths from Bauxite Residue (Red Mud). Miner. Eng. 2015, 76, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonomi, C.; Davris, P.; Balomenos, E.; Giannopoulou, I.; Panias, D. Ionometallurgical Leaching Process of Bauxite Residue: A Comparison between Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Ionic Liquids. In Proceedings of the 35th International ICSOBA Conference, Hamburg, Germany, 2–5 October 2017; pp. 557–564. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, A.P.; Frisch, G.; Hartley, J.; Ryder, K.S. Processing of Metals and Metal Oxides Using Ionic Liquids. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Hoogerstraete, T.; Onghena, B.; Binnemans, K. Homogeneous Liquid–Liquid Extraction of Rare Earths with the Betaine—Betainium Bis(Trifluoromethylsulfonyl)Imide Ionic Liquid System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 21353–21377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellens, S.; Thijs, B.; Möller, C.; Binnemans, K. Separation of Cobalt and Nickel by Solvent Extraction with Two Mutually Immiscible Ionic Liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 9663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wasserscheid, P.; Keim, W. Ionic Liquids—New “Solutions” for Transition Metal Catalysis. Angew. Chemie 2000, 39, 3772–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welton, T. Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids. Solvents for Synthesis and Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2071–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourbos, E.; Giannopoulou, I.; Karantonis, A.; Paspaliaris, I.; Panias, D. Electrodeposition of Rare Earth Metals from Ionic Liquids. In Rare Earths Industry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 199–207. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, A.P.; McKenzie, K.J. Application of Ionic Liquids to the Electrodeposition of Metals. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, R.G. Emerging Technologies in Extraction and Processing of Metals. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2003, 34, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Shikotra, P. Processing Metal Oxides Using Ionic Liquids. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. 2006, 115, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davris, P.; Balomenos, E.; Panias, D.; Paspaliaris, I. Selective Leaching of Rare Earth Elements from Bauxite Residue (Red Mud), Using a Functionalized Hydrophobic Ionic Liquid. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 164, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K.; Jones, P.T. Solvometallurgy: An Emerging Branch of Extractive Metallurgy. J. Sustain. Metall. 2017, 3, 570–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajó, I.E. X-Ray Diffraction Quantitative Phase Analysis of Bayer Process Solids. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference of ICSOBA, Bhubaneshwar, India, 23–30 November 2008; pp. 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Sajò, I.E. XDB Powder Diffraction Phase Analytical System; Version 3.107; Computer Software: Budapest, Hungary, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Vind, J.; Malfliet, A.; Bonomi, C.; Paiste, P.; Sajó, I.E.; Blanpain, B.; Tkaczyk, A.H.; Vassiliadou, V.; Panias, D. Modes of Occurrences of Scandium in Greek Bauxite and Bauxite Residue. Miner. Eng. 2018, 123, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vind, J.; Malfliet, A.; Blanpain, B.; Tsakiridis, P.; Tkaczyk, A.; Vassiliadou, V.; Panias, D. Rare Earth Element Phases in Bauxite Residue. Minerals 2018, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Unit | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 | SiO2 | TiO2 | CaO | Na2O | REO | LOI | Others | Sum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt.% | 42.34 | 16.25 | 6.97 | 4.27 | 11.64 | 3.83 | 0.19 | 12.66 | 1.85 | 100.00 |
| Mineralogical Phase | Formula | wt.% |
|---|---|---|
| Hematite | Fe2O3 | 30 |
| Calcium aluminum iron silicate hydroxide | Ca3AlFe(SiO4)(OH)8 | 17 |
| Cancrinite | Na6Ca2(AlSiO4)6(CO3)2 | 15 |
| Diaspore | α-AlOOH | 9 |
| Goethite | Fe2O3·H2O | 9 |
| Perovskite | CaTiO3 | 4.5 |
| Chamosite | (Fe2+,Mg)5Al(AlSi3O10)(OH)8 | 4 |
| Calcite | CaCO3 | 4 |
| Boehmite | γ-AlOOH | 3 |
| Gibbsite | Al(OH)3 | 2 |
| Rutile | TiO2 | 0.5 |
| Anatase | TiO2 | 0.5 |
| Sum | 98.5 |
| Metal Oxide | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 | SiO2 | TiO2 | CaO | Na2O | REO | SO3 | LOI | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt.% | 3.71 | 27.44 | 14.51 | 1.46 | 24.73 | 2.75 | 0.19 | 18.69 | 6.00 | 0.52 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bonomi, C.; Alexandri, A.; Vind, J.; Panagiotopoulou, A.; Tsakiridis, P.; Panias, D. Scandium and Titanium Recovery from Bauxite Residue by Direct Leaching with a Brønsted Acidic Ionic Liquid. Metals 2018, 8, 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8100834
Bonomi C, Alexandri A, Vind J, Panagiotopoulou A, Tsakiridis P, Panias D. Scandium and Titanium Recovery from Bauxite Residue by Direct Leaching with a Brønsted Acidic Ionic Liquid. Metals. 2018; 8(10):834. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8100834
Chicago/Turabian StyleBonomi, Chiara, Alexandra Alexandri, Johannes Vind, Angeliki Panagiotopoulou, Petros Tsakiridis, and Dimitrios Panias. 2018. "Scandium and Titanium Recovery from Bauxite Residue by Direct Leaching with a Brønsted Acidic Ionic Liquid" Metals 8, no. 10: 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8100834
APA StyleBonomi, C., Alexandri, A., Vind, J., Panagiotopoulou, A., Tsakiridis, P., & Panias, D. (2018). Scandium and Titanium Recovery from Bauxite Residue by Direct Leaching with a Brønsted Acidic Ionic Liquid. Metals, 8(10), 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8100834






