The Water Extract of Rhubarb Prevents Ischemic Stroke by Regulating Gut Bacteria and Metabolic Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of RR and Dosage Calculation
2.3. Chemical Characterization of RR Extract
2.4. Animals and Experimental Design
2.4.1. Experimental Animals and Ethics Statement
2.4.2. Neurobehavioral Assessment
2.4.3. Cerebral Edema Rate
2.4.4. Evaluation of Cerebral Infarction Volume by TTC
2.4.5. Regional Cerebral Blood Flow (rCBF) Measurements
2.4.6. Histopathological Staining
2.5. Gut Microbiota Determination and Data Analysis
2.6. H-NMR Spectroscopy and NMR Data Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
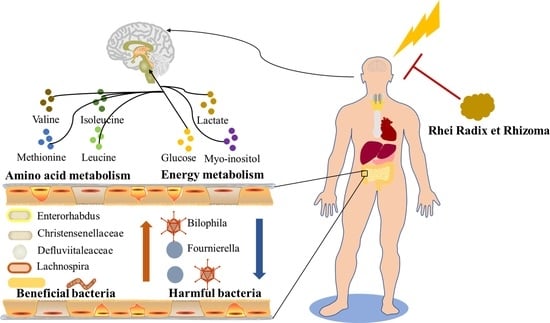
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Compositions of RR
3.2. RR Pretreatment Significantly Attenuated Cerebral Ischemic Injury
3.3. RR Pretreatment Alleviated Brain Edema Induced by MCAO
3.4. RR Pretreatment Significantly Alleviated the Changes in Regional Cerebral Blood Flow
3.5. RR Pretreatment Significantly Alleviated Neuronal Injury
3.6. Changes in Gut Microbiota Composition Induced by RR
3.7. H-NMR Analysis and Multivariate Analyses
3.8. Metabolic Pathway Analysis
3.9. Intestinal Microbes—Serum Metabolites Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Bejot, Y.; Delpont, B.; Giroud, M. Rising stroke incidence in young adults: More epidemiological evidence, more questions to be answered. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e003661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, V.L.; Go, A.S.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Benjamin, E.J.; Berry, J.D.; Borden, W.B.; Bravata, D.M.; Dai, S.; Ford, E.S.; Fox, C.S.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2012 update a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2012, 125, e2–e220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.J.; Ran, Y.Y.; Qie, S.Y.; Gong, W.J.; Gao, F.H.; Ding, Z.T.; Xi, J.N. Melatonin protects against ischemic stroke by modulating microglia/macrophage polarization toward anti-inflammatory phenotype through STAT3 pathway. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2019, 25, 1353–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, T.; Li, Z.; Liu, N.; Yan, Y.; Liu, B. Role of mitophagy in cardiovascular disease. Aging Dis. 2020, 11, 419–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, A.S.; Mozaffarian, D.; Roger, V.L.; Benjamin, E.J.; Berry, J.D.; Blaha, M.J.; Dai, S.; Ford, E.S.; Fox, C.S.; Franco, S.; et al. Executive summary: Heart disease and stroke statistics—2014 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2014, 129, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Huang, Q.; Wang, J.Q.; Deng, Q.Q.; Gu, W.P. Effect of ephrin-B2 on the expressions of angiopoietin-1 and -2 after focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Neural Regen. Res. 2016, 11, 1784–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musuka, T.D.; Wilton, S.B.; Traboulsi, M.; Hill, M.D. Diagnosis and management of acute ischemic stroke: Speed is critical. CMAJ 2015, 187, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Qin, Y.; Li, D.; Cai, N.; Wu, J.; Jiang, L.; Jie, L.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, J.; Wang, H. Inhibition of PDE4 protects neurons against oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress through activation of the Nrf-2/HO-1 pathway. Redox Biol. 2020, 28, 101342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Gu, J.; Xu, C.; Qian, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, B.; Jin, Y.; Sun, Y. Dl-NBP (Dl-3-N-Butylphthalide) treatment promotes neurological functional recovery accompanied by the upregulation of white matter integrity and HIF-1alpha/VEGF/Notch/Dll4 expression. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghi, S.; Boehme, A.K.; Dibu, J.; Leon Guerrero, C.R.; Ali, S.; Martin-Schild, S.; Sands, K.A.; Noorian, A.R.; Blum, C.A.; Chaudhary, S.; et al. Treatment and outcome of thrombolysis-related hemorrhage: A multicenter retrospective study. JAMA Neurol. 2015, 72, 1451–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jiang, X.F.; Yang, F.H.; Hu, Y.J.; Fan, H.J.; Zhang, W.; Fu, Y.C.; Lai, Y.G. Reaearch on the theory of unblocking Fu-organs in the treatment of stroke. Chin. Med. Mod. Distance Educ. China 2023, 21, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.J.; Xu, Y.P.; Gu, Z.Y.; Xiao, D. Clinical observation of therapy of resolving phlegm and relaxing bowels on the acute phase of stroke with syndrome of phlegm heat and bowel excess. J. Basic. Chin. Med. 2015, 21, 616–618. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, M.L. Study on law using Chinese herbs of Tongfu method to stroke. Chin. J. Basic. Med. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2006, 12, 602–604. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.Z.; Wang, X.Z.; Yang, H.Y. Discussion on the laws of medicine application when treating apoplexy by dredging Fu therapy. J. Beijing Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. (Clin. Med.) 2003, 10, 45–47. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.D.; He, Q.S.; Hu, F.R.; Guo, Q.; Li, Y.H. Exploration of core drugs for the treatment of ischemic stroke in traditional Chinese medicine based on the theory of Tong Fu and experimental research. J. Guizhou Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2021, 43, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Liu, T.; Li, P.; He, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Cui, H.; Luo, J.; Wang, Y.; Tang, T. iTRAQ-based proteomics analysis reveals the effect of rhubarb in rats with ischemic stroke. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 6920213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.T.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.H.; Fu, H.; Xu, Z.; Xu, Q.Q.; Zheng, G.Q. Herbal compatibility of ginseng and rhubarb exerts synergistic neuroprotection in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury of rats. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.J.; Song, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.G.; Chen, Z.X.; Huang, L.B.; Zhang, H.F.; Zheng, G.Q. Active compounds of rhubarb root and rhizome in animal model experiments of focal cerebral ischemia. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2015, 2015, 210546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Deng, Y.; Yang, A.; Lu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Han, L.; Zou, C. Rhubarb enema improved colon mucosal barrier injury in 5/6 nephrectomy rats may associate with gut microbiota modification. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Cui, M.; Li, Y.; Deng, Y.; Wu, H. Effects of rhubarb on intestinal flora and toll-like receptors of intestinal mucosa in rats with severe acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 2015, 44, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Bonder, M.J.; Cenit, M.C.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Maatman, A.; Dekens, J.A.; Brandsma, E.; Marczynska, J.; Imhann, F.; Weersma, R.K.; et al. The gut microbiome contributes to a substantial proportion of the variation in blood lipids. Circ. Res. 2015, 117, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, J.M.; Yu, K.; Donaldson, G.P.; Shastri, G.G.; Ann, P.; Ma, L.; Nagler, C.R.; Ismagilov, R.F.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Hsiao, E.Y. Indigenous bacteria from the gut microbiota regulate host serotonin biosynthesis. Cell 2015, 161, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ahn, E.H.; Kang, S.S.; Liu, X.; Alam, A.; Ye, K. Gut dysbiosis contributes to amyloid pathology, associated with C/EBPbeta/AEP signaling activation in Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba0466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; d’Aigle, J.; Atadja, L.; Quaicoe, V.; Honarpisheh, P.; Ganesh, B.P.; Hassan, A.; Graf, J.; Petrosino, J.; Putluri, N.; et al. Gut Microbiota-Derived Short-Chain fatty acids promote poststroke recovery in aged mice. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, C.F.; Pan, C.W.; Zhang, Y.X.; Zhu, X.H.; Zhang, Y.H. Metabolomics facilitates the discovery of metabolic biomarkers and pathways for ischemic stroke: A systematic review. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidorov, E.; Sanghera, D.K.; Vanamala, J.K.P. Biomarker for Ischemic stroke using metabolome: A clinician perspective. J. Stroke. 2019, 21, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Li, X.; Feng, X.J.; Wei, M.P.; Luo, Y.F.; Zhao, T.T.; Xiao, B.; Xia, J. Phenylacetylglutamine, a novel biomarker in acute ischemic stroke. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 798765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wang, J.; Liao, S.; Lv, Y.; Xu, D.; Yang, M.; Kong, L. (1)H NMR-based metabolomics reveals Refined-Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Decoction (BBG) as a potential ischemic stroke treatment drug with efficacy and a favorable therapeutic window. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Wan, J.; Yang, Q.; Xiang, Y.; Ni, L.; Long, Y.; Cui, M.; Ci, Z.; Tang, D.; et al. Preparation, characterization and in vivo study of borneol-baicalin-liposomes for treatment of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 5977–5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xue, X.; Zhang, H.; Che, X.; Luo, J.; Wang, P.; Xu, J.; Xing, Z.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Y.; et al. Neuronal-targeted TFEB rescues dysfunction of the autophagy-lysosomal pathway and alleviates ischemic injury in permanent cerebral ischemia. Autophagy 2019, 15, 493–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longa, E.Z.; Weinstein, P.R.; Carlson, S.; Cummins, R. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 1989, 20, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, L.; Li, P.; Zhu, W.; Cai, W.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Luo, W.; Stetler, R.A.; Leak, R.K.; Yu, W.; et al. Regulatory T cells ameliorate tissue plasminogen activator-induced brain haemorrhage after stroke. Brain 2017, 140, 1914–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Bai, P.; Li, Y.Y.; Li, J.Z.; Jia, C.X.; Wang, T.S.; Zhao, H.B.; Si, Y.C.; Chen, J.X. Metabolomic profiling of the synergistic effects of ginsenoside Rg1 in combination with neural stem cell transplantation in ischemic stroke rats. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 2676–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagana Gowda, G.A.; Gowda, Y.N.; Raftery, D. Expanding the limits of human blood metabolite quantitation using NMR spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagana Gowda, G.A.; Djukovic, D.; Bettcher, L.F.; Gu, H.; Raftery, D. NMR-guided mass spectrometry for absolute quantitation of human blood metabolites. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 2001–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, T.; Wei, P.; Li, N.; Zhang, W.; Ding, X.; Li, J. (1)H NMR-based metabolomics reveals the antitumor mechanisms of triptolide in BALB/c mice bearing CT26 tumors. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Rezeng, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Li, Z. Toxicological risks of renqingchangjue in rats evaluated by (1)H NMR-based serum and urine metabolomics analysis. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 2169–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.W.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wu, L.; Shu, S.; Xia, C.; Xu, C.; Zheng, J.S. (1)H-Nuclear magnetic resonance-based plasma metabolic profiling of dairy cows with clinical and subclinical ketosis. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 1552–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, W.; Long, Z.; Zeng, J.; Zhu, X.; Yuan, M.; Wu, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, L. Mechanism of radix rhei et rhizome intervention in cerebral infarction: A research based on chemoinformatics and systematic pharmacology. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2021, 2021, 6789835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Wu, J.; Gao, Y.; Luo, Y.; Yang, D.; Wang, P. The pharmacological properties of chrysophanol, the recent advances. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 110002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chu, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, N. Neuroprotective effects of anthraquinones from rhubarb in central nervous system diseases. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2019, 2019, 3790728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Chu, S.; Yang, S.; Peng, Y.; Ren, S.; Wen, B.; Chen, N. Physcion and physcion 8-O-beta-glucopyranoside: A review of their pharmacology, toxicities and pharmacokinetics. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 310, 108722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Huang, R.; Shetty, R.A.; Thangthaeng, N.; Liu, R.; Chen, Z.; Sumien, N.; Rutledge, M.; Dillon, G.H.; Yuan, F.; et al. Transient focal cerebral ischemia induces long-term cognitive function deficit in an experimental ischemic stroke model. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013, 59, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluri, F.; Schuhmann, M.K.; Kleinschnitz, C. Animal models of ischemic stroke and their application in clinical research. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2015, 9, 3445–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Tian, T.; Gong, S.X.; Huang, W.Q.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Wang, A.P.; Tian, Y. Microglia-associated neuroinflammation is a potential therapeutic target for ischemic stroke. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Li, T.; Ji, T.; Yi, W.; Yang, Z.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Gu, C. AMPK: Potential therapeutic target for ischemic stroke. Theranostics 2018, 8, 4535–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashayekh, A.; Pham, D.L.; Yousem, D.M.; Dizon, M.; Barker, P.B.; Lin, D.D. Effects of Ginkgo biloba on cerebral blood flow assessed by quantitative MR perfusion imaging: A pilot study. Neuroradiology 2011, 53, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, F.; Su, N.; Li, X.; Fei, Z. Neuroprotection mediated by natural products and their chemical derivatives. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 2008–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Kong, X.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Luo, Y. Ischemic stroke and intestinal flora: An insight into brain-gut axis. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2022, 27, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaram, S.B.; Rathipriya, A.G.; Mahalakshmi, A.M.; Sharma, S.; Hediyal, T.A.; Ray, B.; Sunanda, T.; Rungratanawanich, W.; Kashyap, R.S.; Qoronfleh, M.W.; et al. The influence of gut dysbiosis in the pathogenesis and management of ischemic stroke. Cells 2022, 11, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; He, P.; Cai, Z.; Zhao, J. Gut microbiota-derived melatonin from Puerariae Lobatae Radix-resistant starch supplementation attenuates ischemic stroke injury via a positive microbial co-occurrence pattern. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 190, 106714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Liu, M.; Ren, G.; Luo, G.; Wang, Z.; Ge, Z.; Pu, Q.; Ren, W.; Yang, S. Zhilong Huoxue Tongyu Capsules’ Effects on ischemic stroke: An assessment using fecal 16S rRNA gene sequencing and untargeted serum metabolomics. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1052110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Chen, J.; Shang, W.; Shi, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Chen, R. Atorvastatin alleviates microglia-mediated neuroinflammation via modulating the microbial composition and the intestinal barrier function in ischemic stroke mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 162, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Liao, J.; Fang, Y.; Deng, H.; Yin, H.; Shen, B.; Hu, M. Six-week exercise training with dietary restriction improves central hemodynamics associated with altered gut microbiota in adolescents with obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 569085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Zhai, M.; Wu, Q.; Jia, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, N. Protective Effect of Tong-Qiao-Huo-Xue Decoction on inflammatory injury caused by intestinal microbial disorders in stroke rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 43, 788–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Hui, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, X. Angong Niuhuang Pill ameliorates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice partly by restoring gut microbiota dysbiosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1001422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Wu, P.; Cai, Z.; Fang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Lasanajak, Y.; Tang, L.; Ye, L.; Hou, C.; Zhao, J. Puerariae Lobatae Radix with chuanxiong Rhizoma for treatment of cerebral ischemic stroke by remodeling gut microbiota to regulate the brain-gut barriers. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 65, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Long, W.; Hao, B.; Ding, D.; Ma, X.; Zhao, L.; Pang, X. A human stool-derived Bilophila wadsworthia strain caused systemic inflammation in specific-pathogen-free mice. Gut Pathog. 2017, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natividad, J.M.; Lamas, B.; Pham, H.P.; Michel, M.L.; Rainteau, D.; Bridonneau, C.; da Costa, G.; van Hylckama Vlieg, J.; Sovran, B.; Chamignon, C.; et al. Bilophila wadsworthia aggravates high fat diet induced metabolic dysfunctions in mice. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Hiel, S.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Le Roy, T.; Potgens, S.A.; Leyrolle, Q.; Pachikian, B.D.; Gianfrancesco, M.A.; Cani, P.D.; Paquot, N.; et al. Discovery of the gut microbial signature driving the efficacy of prebiotic intervention in obese patients. Gut 2020, 69, 1975–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devkota, S.; Chang, E.B. Interactions between diet, bile acid metabolism, gut microbiota, and inflammatory bowel diseases. Dig. Dis. 2015, 33, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, L.; Lou, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Deng, J.; Guan, Y.; She, M.; You, X.; Liu, M.; et al. Gut microbiotic features aiding the diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 587284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.C.; Li, G.W.; Wang, T.T.; Gao, L.; Wang, F.F.; Shang, H.W.; Yang, Z.J.; Guo, Y.X.; Wang, B.Y.; Xu, J.D. Rhubarb extract relieves constipation by stimulating mucus production in the colon and altering the intestinal flora. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 138, 111479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wan, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, C.; Li, H.F.; Dong, Z.; Zhu, K.; Jiang, S.; Shang, E.; Qian, D.; et al. Targeting intestinal flora and its metabolism to explore the laxative effects of rhubarb. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 1615–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, T.; Wang, F.; Liu, J.; Ye, W.; Zhao, T.; Li, Z. Rhubarb alleviates acute lung injury by modulating gut microbiota dysbiosis in mice. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Zhao, H.; Yin, Z.; Han, C.; Wang, Y.; Luo, G.; Gao, X. Rheum tanguticum alleviates cognitive impairment in APP/PS1 mice by regulating drug-responsive bacteria and their corresponding microbial metabolites. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 766120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickell, Z.; Williams, A.M.; Alam, H.B.; Hsu, C.H. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: A novel strategy for neuroprotection and cardioprotection following ischemia/reperfusion injury. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e016349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iadecola, C.; Gottesman, R.F. Neurovascular and Cognitive dysfunction in hypertension. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 1025–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzig, V.; Cristofori-Armstrong, B.; Israel, M.R.; Nixon, S.A.; Vetter, I.; King, G.F. Animal toxins—Nature’s evolutionary-refined toolkit for basic research and drug discovery. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 181, 114096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Deng, Z.; Liao, J.; Song, C.; Liang, C.; Xue, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, K.; Yan, G. Leptin attenuates cerebral ischemia injury through the promotion of energy metabolism via the PI3K/Akt pathway. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidorov, E.; Bejar, C.; Xu, C.; Ray, B.; Reddivari, L.; Chainakul, J.; Vanamala, J.K.P.; Sanghera, D.K. Potential metabolite biomarkers for acute versus chronic stage of ischemic stroke: A pilot study. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 104618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yuan, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, G. Serum metabolomic patterns in young patients with ischemic stroke: A case study. Metabolomics 2021, 17, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niazi, F.; Aslam, A.; Khattak, S.; Waheed, S. Frequency of homocysteinemia in young ischemic stroke patients and its relationship with the early outcome of a stroke. Cureus 2019, 11, e5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouphael, Y.; Lucini, L.; Miras-Moreno, B.; Colla, G.; Bonini, P.; Cardarelli, M. Metabolomic responses of maize shoots and roots elicited by combinatorial seed treatments with microbial and non-microbial biostimulants. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wozniak, J.R.; Fink, B.A.; Fuglestad, A.J.; Eckerle, J.K.; Boys, C.J.; Sandness, K.E.; Radke, J.P.; Miller, N.C.; Lindgren, C.; Brearley, A.M.; et al. Four-year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial of choline for neurodevelopment in fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2020, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo-Gonzalez, I.; Friday, W.B.; Munson, C.A.; Bachleda, A.; Weiss, E.R.; Alam, N.M.; Sha, W.; Zeisel, S.H.; Surzenko, N. Low availability of choline in utero disrupts development and function of the retina. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 9194–9209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahr, N.M.; Mayer, D.; Rohlfing, T.; Hasak, M.P.; Hsu, O.; Vinco, S.; Orduna, J.; Luong, R.; Sullivan, E.V.; Pfefferbaum, A. Brain injury and recovery following binge ethanol: Evidence from in vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.E.; Niu, M.; Li, R.Y.; Feng, W.W.; Ma, X.; Dong, Q.; Ma, Z.J.; Li, G.Q.; Meng, Y.K.; Wang, Y.; et al. Untargeted metabolomics reveals dose-response characteristics for effect of rhubarb in a rat model of cholestasis. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhou, J.; Cui, H.; Li, P.; Luo, J.; Li, T.; He, F.; Wang, Y.; Tang, T. iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomics reveals the neuroprotection of rhubarb in experimental intracerebral hemorrhage. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 232, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Duan, Y.; Qin, K.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; Cai, B. A UPLC-Q-TOF-MS-Based metabolomics approach to screen out active components in prepared rhubarb for its activity on noxious heat blood stasis syndrome. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 907831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Wei, F.; Vaziri, N.D.; Cheng, X.L.; Bai, X.; Lin, R.C.; Zhao, Y.Y. Metabolomics insights into chronic kidney disease and modulatory effect of rhubarb against tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benakis, C.; Martin-Gallausiaux, C.; Trezzi, J.P.; Melton, P.; Liesz, A.; Wilmes, P. The microbiome-gut-brain axis in acute and chronic brain diseases. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2020, 61, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China, Part I; China Pharmacopoeia Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2020; p. 24. [Google Scholar]










Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Hu, J.; Liu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Xu, W.; Wang, W.; Gao, J.; Wang, T. The Water Extract of Rhubarb Prevents Ischemic Stroke by Regulating Gut Bacteria and Metabolic Pathways. Metabolites 2024, 14, 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14040216
Liu X, Wang Y, Tian Y, Hu J, Liu Z, Ma Y, Xu W, Wang W, Gao J, Wang T. The Water Extract of Rhubarb Prevents Ischemic Stroke by Regulating Gut Bacteria and Metabolic Pathways. Metabolites. 2024; 14(4):216. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14040216
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaoyao, Yuxi Wang, Yuan Tian, Jiahui Hu, Zhen Liu, Yuncheng Ma, Wenhui Xu, Weiling Wang, Jian Gao, and Ting Wang. 2024. "The Water Extract of Rhubarb Prevents Ischemic Stroke by Regulating Gut Bacteria and Metabolic Pathways" Metabolites 14, no. 4: 216. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14040216