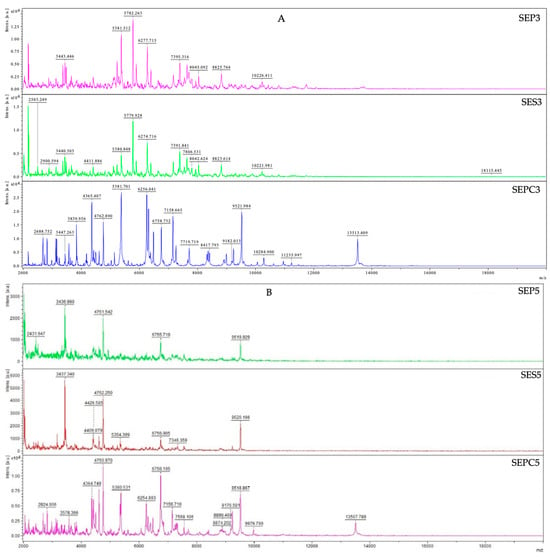
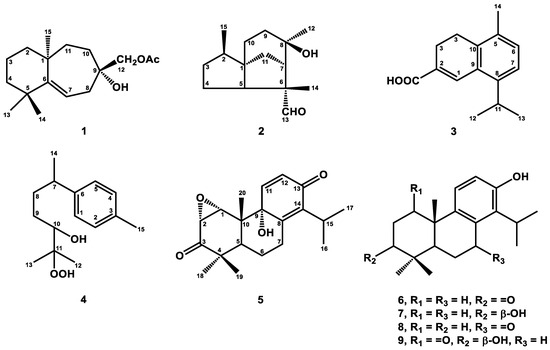
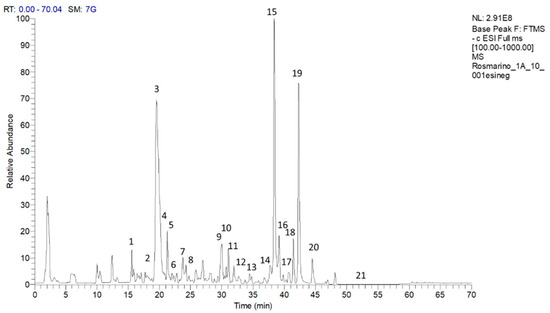
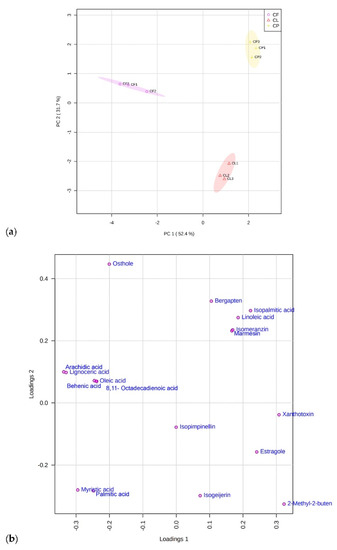
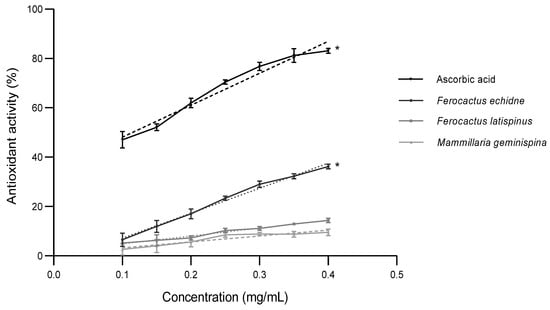
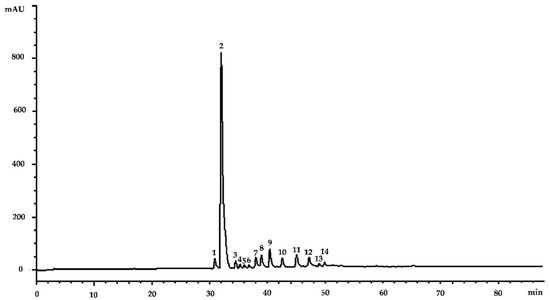
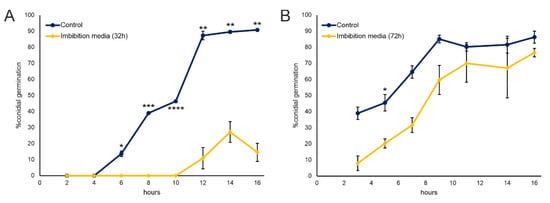
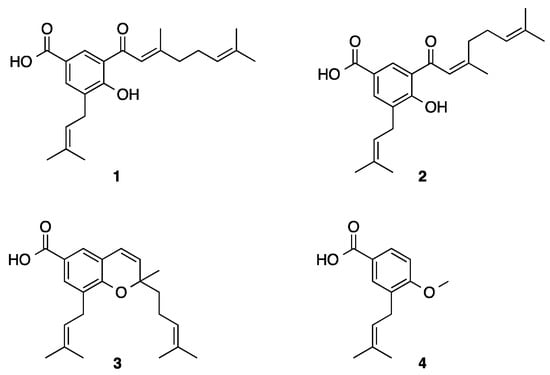
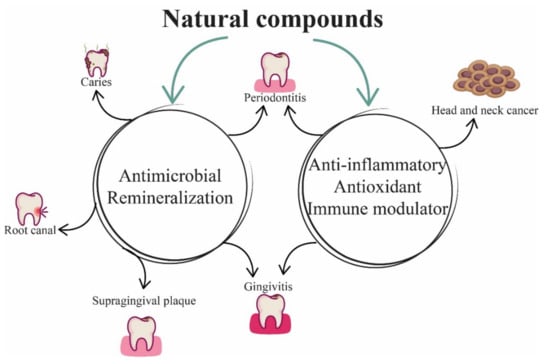
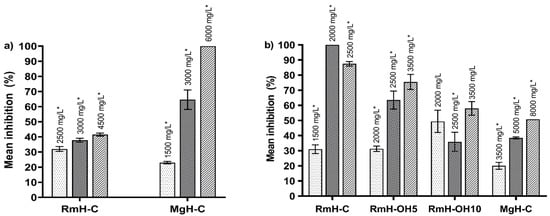
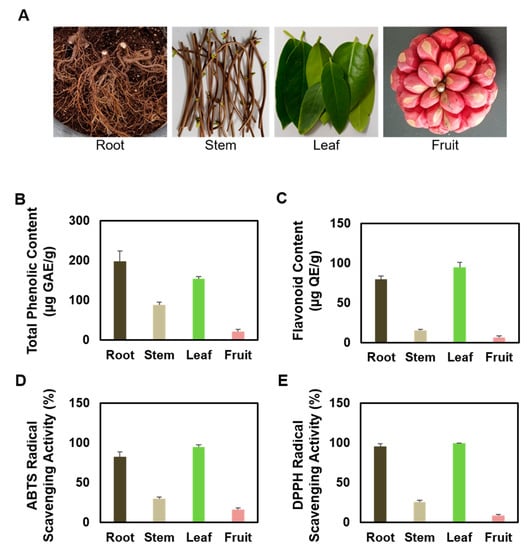
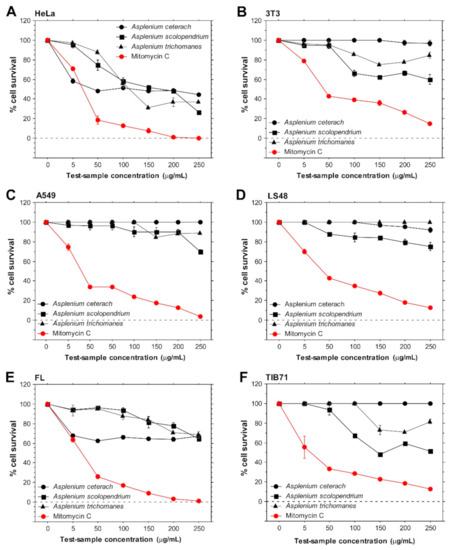
Bioactive Compounds in Plants
A topical collection in Plants (ISSN 2223-7747). This collection belongs to the section "Phytochemistry".
Viewed by 164184Editors
Interests: plant anatomy and micromorphology; medicinal plants; ethnobotany; pharmacognosy; biological activity of secondary plant metabolites
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: natural compounds; polyphenols; plant extracts; pharmacognosy; functional foods; nutraceuticals; pharmacology; toxicology; antioxidant activity; anti-inflammatory activity; cytoprotective activity; clinical studies
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
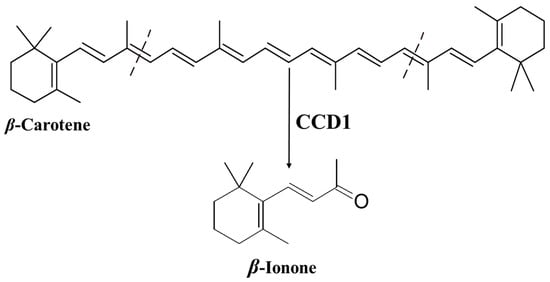
The journal Plants will jointly be publishing a Topical Collection on bioactive compounds in plants. Plant secondary metabolites are receiving ever-increasing attention due to their several health properties for a multitude of applications, not only for more common uses such as those in the pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and food industries, but also as new sources of eco-friendly biopesticides. Plant secondary metabolites play an important role as defense mechanisms in response to pathogenic organisms and predatory herbivores, and may also act as herbicides by inhibiting the growth of competing plants.
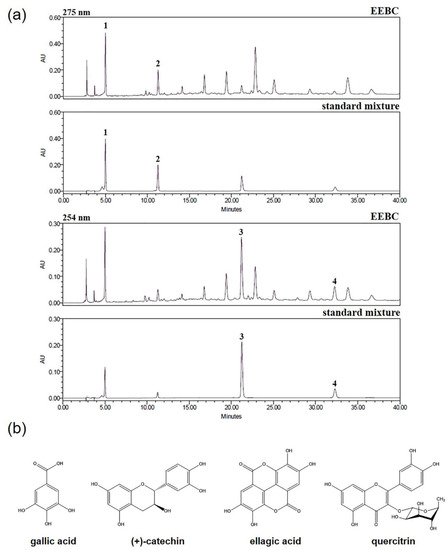
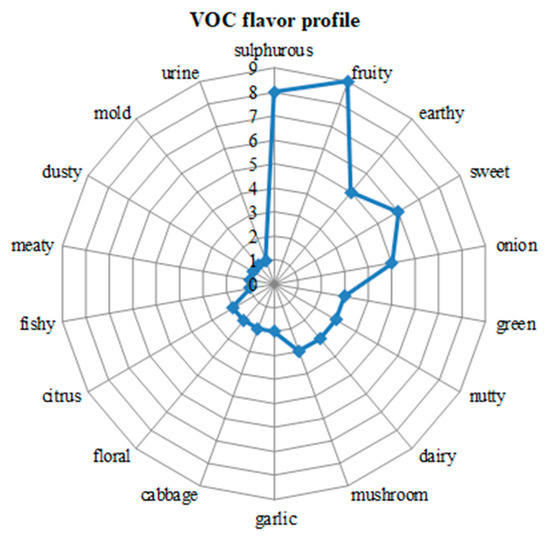
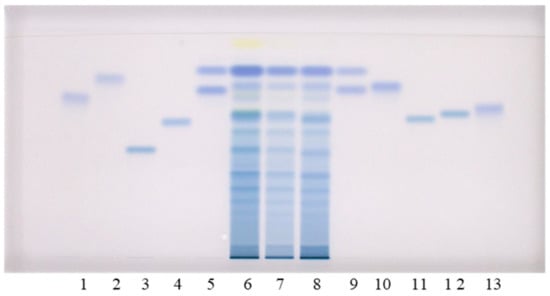
This Topical Collection will focus on a multidisciplinary approach to the study of plant secondary metabolites, including micro-morphological and histochemical studies aiming to identify and characterize the site of secretion and storage of bioactive compounds in plant tissues. Moreover, extraction and chemical characterization, as well as biological properties by in vitro cell-free and cell-based assays, of phytocomplexes or their isolated bioactive compounds, will be welcome.
Wide fields of application will be considered, including animal and human well-being as well as ecological aspects, also considering the ever-growing interest in the use of plant extracts and molecules of natural origin as biopesticides or for foodstuff management.
Moreover, studies related to the recovery of plant waste products will be also welcome, mainly from agri-food chains, including the agricultural production of medicinal plants. These studies should aim to highlight the potential use of plants and their byproducts as sources of bioactive compounds for animal or human interest, in light of the new concept of circular economy.
Dr. Laura Cornara
Dr. Antonella Smeriglio
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Plants is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- plant extracts
- essential oil
- plant byproducts
- micro-morphological features
- histochemical features
- phytochemical profile
- bioactive compounds
- health effects
- biopesticides
- circular economy