Imaging of Skull Base and Orbital Invasion in Sinonasal Cancer: Correlation with Histopathology
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. Histopathological Data
3.3. Radiohistological Correlation
3.4. Comparison of cTNM and pTNM
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Lund, V.J.; Stammberger, H.; Nicolai, P.; Castelnuovo, P.; Beal, T.; Beham, A.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Braun, H.; Cappabianca, P.; Carrau, R.; et al. European Position Paper on Endoscopic Management of Tumours of the Nose, Paranasal Sinuses and Skull Base. Rhinol. Suppl. 2010, 22, 1–143. [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd, G.; Lund, V.J.; Howard, D.; Savy, L. Optimum Imaging for Sinonasal Malignancy. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2000, 114, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castelnuovo, P.; Battaglia, P.; Turri-Zanoni, M.; Tomei, G.; Locatelli, D.; Bignami, M.; Bolzoni Villaret, A.; Nicolai, P. Endoscopic Endonasal Surgery for Malignancies of the Anterior Cranial Base. World Neurosurg. 2014, 82, S22–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolai, P.; Battaglia, P.; Bignami, M.; Villaret, A.B.; Delù, G.; Khrais, T.; Lombardi, D.; Castelnuovo, P. Endoscopic Surgery for Malignant Tumors of the Sinonasal Tract and Adjacent Skull Base: A 10-Year Experience. Am. J. Rhinol. 2008, 22, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya-Plana, A.; Bresson, D.; Temam, S.; Kolb, F.; Janot, F.; Herman, P. Development of Minimally Invasive Surgery for Sinonasal Malignancy. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2016, 133, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganly, I.; Patel, S.G.; Singh, B.; Kraus, D.H.; Bridger, P.G.; Cantu, G.; Cheesman, A.; De Sa, G.; Donald, P.; Fliss, D.M.; et al. Craniofacial Resection for Malignant Paranasal Sinus Tumors: Report of an International Collaborative Study. Head Neck 2005, 27, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.G.; Singh, B.; Polluri, A.; Bridger, P.G.; Cantu, G.; Cheesman, A.D.; deSa, G.M.; Donald, P.; Fliss, D.; Gullane, P.; et al. Craniofacial Surgery for Malignant Skull Base Tumors: Report of an International Collaborative Study. Cancer 2003, 98, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.; van der Wal, J.; van der Waal, I.; Snow, G. Studies of the Anatomy and Pathology of the Orbit in Carcinoma of the Maxillary Sinus and Their Impact on Preservation of the Eye in Maxillectomy. Head Neck 1998, 20, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moiyadi, A.V.; Pai, P.; Nair, D.; Pal, P.; Shetty, P. Dural Involvement in Skull Base Tumors--Accuracy of Preoperative Radiological Evaluation and Intraoperative Assessment. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2013, 24, 1268–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomura, N.; Hirano, H.; Sashi, R.; Hashimoto, M.; Kato, K.; Takahashi, S.; Watanabe, O.; Watarai, J. Comparison of MR Imaging and CT in Discriminating Tumor Infiltration of Bone and Bone Marrow in the Skull Base. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 1998, 22, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paling, M.R.; Black, W.C.; Levine, P.A.; Cantrell, R.W. Tumor Invasion of the Anterior Skull Base: A Comparison of MR and CT Studies. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1987, 11, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.S.; Huss, R.G.; Benson, J.E.; Kaufman, B.; Yoon, Y.S.; Morrison, S.C.; Alfidi, R.J.; Rekate, H.L.; Ratcheson, R.A. MR Imaging of the Skull Base. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 1984, 8, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, D.H.; Lanzieri, C.F.; Wanamaker, J.R.; Little, J.R.; Lavertu, P. Complementary Use of Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Assessing Skull Base Lesions. Laryngoscope 1992, 102, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, H.; Mohri, M.; Amatsu, M. Invasion of the Skull Base by Carcinomas: Histopathologically Evidenced Findings with CT and MRI. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2002, 259, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, V.J.; Howard, D.J.; Lloyd, G.A. CT Evaluation of Paranasal Sinus Tumours for Cranio-Facial Resection. Br. J. Radiol. 1983, 56, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisen, M.D.; Yousem, D.M.; Montone, K.T.; Kotapka, M.J.; Bigelow, D.C.; Bilker, W.B.; Loevner, L.A. Use of Preoperative MR to Predict Dural, Perineural, and Venous Sinus Invasion of Skull Base Tumors. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1996, 17, 1937–1945. [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre, J.B.; Perez, C.; Penta, M.; Tong, L.; Truelson, J.; Batra, P.S. Patterns of Dural Involvement in Sinonasal Tumors: Prospective Correlation of Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Histopathologic Findings. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2012, 2, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, J.; Hinton, D.R.; Segall, H.D.; Couldwell, W.T.; Stanley, R.B. Dural Invasion by Craniofacial and Calvarial Neoplasms: MR Imaging and Histopathologic Evaluation. Radiology 1993, 188, 747–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, J.; Hinton, D.R.; Segall, H.D.; Couldwell, W.T. Surgical Implications of Magnetic Resonance-Enhanced Dura. Neurosurgery 1994, 35, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.Y.; Yoon, D.Y.; Kim, E.S.; Baek, S.; Lim, K.J.; Seo, Y.L.; Yun, E.J. Diagnostic Performance of CT, MRI, and Their Combined Use for the Assessment of the Direct Cranial or Intracranial Extension of Malignant Head and Neck Tumors. Acta Radiol. 2019, 60, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerwein, C.M.; Pazahr, S.; Soyka, M.B.; Hüllner, M.W.; Holzmann, D. Diagnostic Accuracy of Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Compared to Surgical Exploration for Anterior Skull Base and Medial Orbital Wall Infiltration in Advanced Sinonasal Tumors. Head Neck 2020, 42, 2002–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisen, M.D.; Yousem, D.M.; Loevner, L.A.; Thaler, E.R.; Bilker, W.B.; Goldberg, A.N. Preoperative Imaging to Predict Orbital Invasion by Tumor. Head Neck 2000, 22, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graamans, K.; Slootweg, P.J. Orbital Exenteration in Surgery of Malignant Neoplasms of the Paranasal Sinuses. The Value of Preoperative Computed Tomography. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1989, 115, 977–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, T.H.; Lee, H.-S.; Cho, K.-S.; Roh, H.-J. Periorbita: Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings. Am. J. Rhinol. 2006, 20, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.B.; Edge, S.; Greene, F.; Byrd, D.R.; Brookland, R.K.; Washington, M.K.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Compton, C.C.; Hess, K.R.; Sullivan, D.C.; et al. (Eds.) AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th ed.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; ISBN 978-3-319-40617-6. [Google Scholar]
- Villaret, A.B.; Yakirevitch, A.; Bizzoni, A.; Bosio, R.; Bignami, M.; Pistochini, A.; Battaglia, P.; Castelnuovo, P.; Nicolai, P. Endoscopic Transnasal Craniectomy in the Management of Selected Sinonasal Malignancies. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2010, 24, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, E.; DeMonte, F.; Ibrahim, S.; Roberts, D.; Levine, N.; Kupferman, M. Endoscopic Resection of Sinonasal Cancers with and without Craniotomy: Oncologic Results. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2009, 135, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hudgins, P.A.; Baugnon, K.L. Head and Neck: Skull Base Imaging. Neurosurgery 2018, 82, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, N.; Eskander, A.; Huang, S.-H.; Curtin, H.; Bartlett, E.; Vescan, A.; Kraus, D.; O’Sullivan, B.; Gentili, F.; Gullane, P.; et al. Imaging and Resectability Issues of Sinonasal Tumors. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2013, 13, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The Measurement of Observer Agreement for Categorical Data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrari, M.; Migliorati, S.; Tomasoni, M.; Crisafulli, V.; Nocivelli, G.; Paderno, A.; Rampinelli, V.; Taboni, S.; Schreiber, A.; Mattavelli, D.; et al. Sinonasal Cancer Encroaching the Orbit: Ablation or Preservation? Oral Oncol. 2021, 114, 105185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisan, Q.; Kolb, F.; Temam, S.; Tao, Y.; Janot, F.; Moya-Plana, A. Management of Orbital Invasion in Sinonasal Malignancies: Carcinoma Invading the Orbit. Head Neck 2016, 38, 1650–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rombaux, P.; Duprez, T.; Hummel, T. Olfactory Bulb Volume in the Clinical Assessment of Olfactory Dysfunction. Rhinology 2009, 47, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carta, F.; Kania, R.; Sauvaget, E.; Bresson, D.; George, B.; Herman, P. Endoscopy Skull-Base Resection for Ethmoid Adenocarcinoma and Olfactory Neuroblastoma. Rhinol. J. 2011, 49, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziai, H.; Yu, E.; Fu, T.; Muhanna, N.; Monteiro, E.; Vescan, A.; Zadeh, G.; Witterick, I.J.; Goldstein, D.P.; Gentili, F.; et al. Impact of Dural Resection on Sinonasal Malignancies with Skull Base Encroachment or Erosion. J. Neurol. Surg. Part B Skull Base 2018, 79, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtin, H.D.; Rabinov, J.D. Extension to the Orbit from Paraorbital Disease. The Sinuses. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 1998, 36, 1201–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, C.; Ferlito, A.; Lund, V.J.; Silver, C.E.; Fagan, J.J.; Rodrigo, J.P.; Llorente, J.L.; Cantù, G.; Politi, M.; Wei, W.I.; et al. Management of the Orbit in Malignant Sinonasal Tumors. Head Neck 2008, 30, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortuaire, G.; Camous, D.; Vandenhende-Szymanski, C.; Dubrulle, F.; Chevalier, D. Local Extension Staging of Sinonasal Tumours: Retrospective Comparison between CT/MRI Assessment and Pathological Findings. Clin. Otolaryngol. Off. J. ENT-UK Off. J. Neth. Soc. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. Cervico-Facial Surg. 2017, 42, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
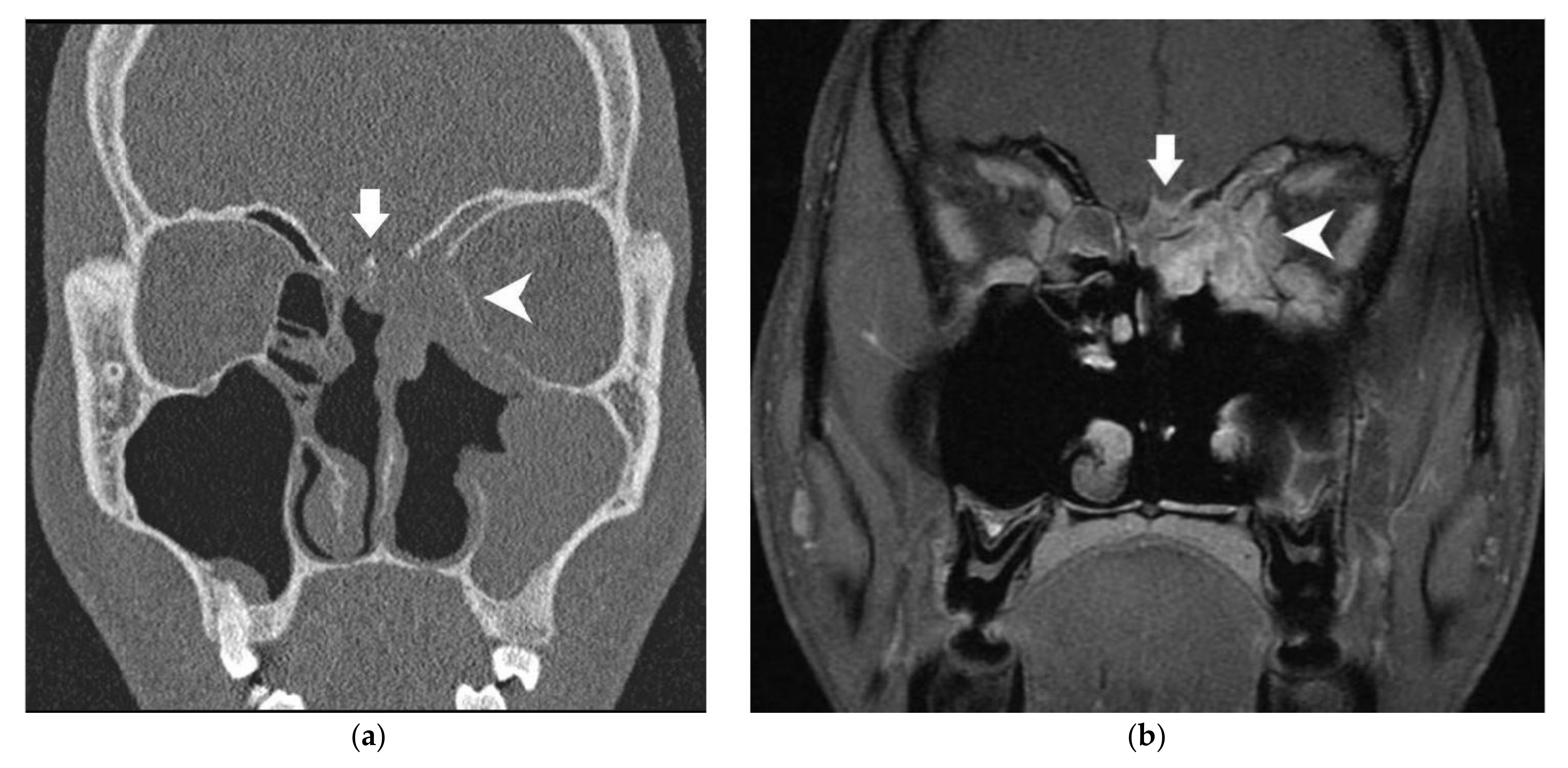
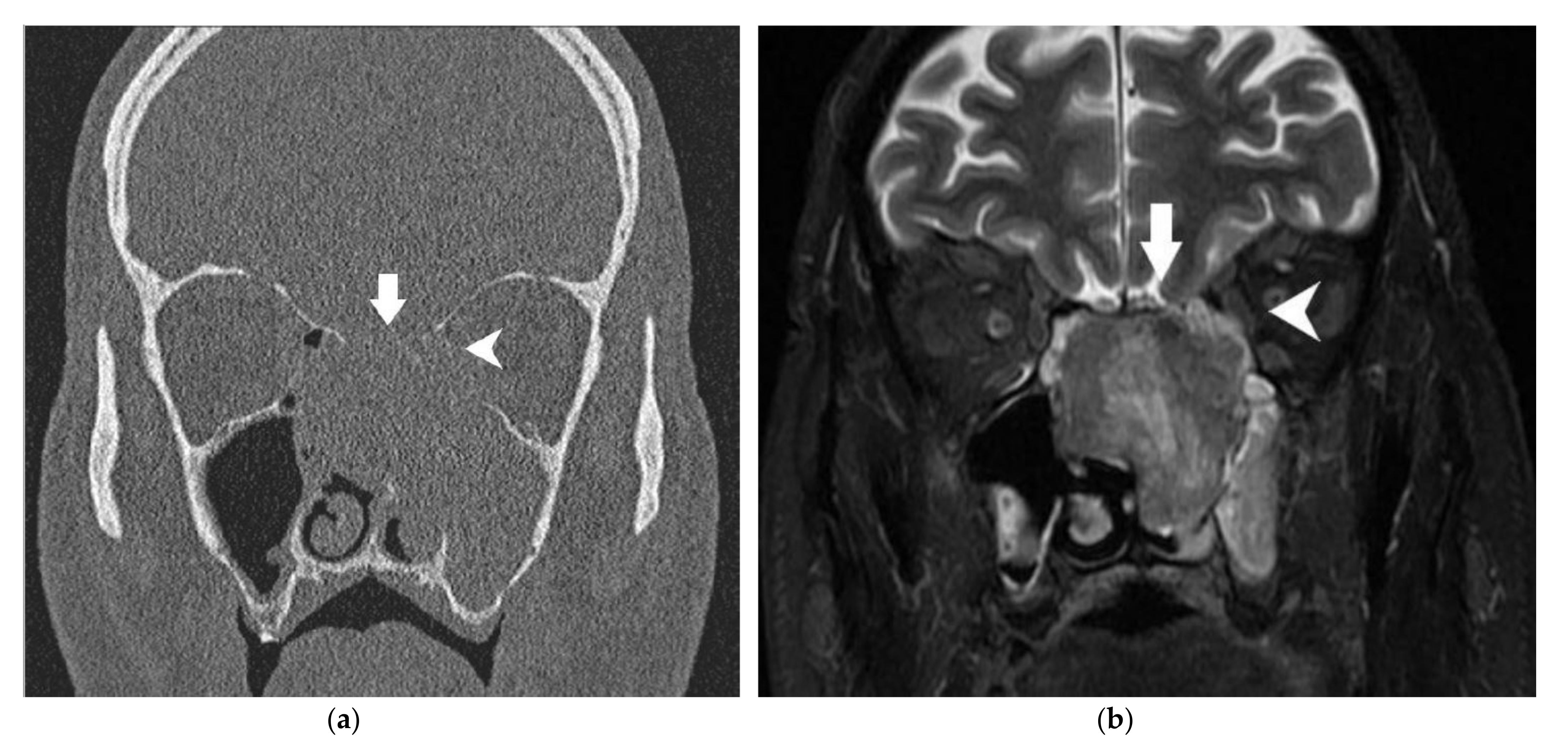
| Anatomical Structure | Imaging | Radiological Sign | Radiological Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bony skull base | CT scanner | Contact without bony modification Minor (<2 mm) erosion Major (≥2 mm) erosion | Free Invaded |
| MRI | Minor (<2 mm) modification Major (≥2 mm) modification | ||
| Dura | MRI | Linear enhancement: ≤2 mm or >2 mm Nodular enhancement: ≤2 mm or >2 mm Smooth or irregular deformation Contact angle: ≤45° or >45° | Free Invaded |
| Cerebral parenchyma | MRI | Edema Tumoral invasion | Free Invaded |
| Orbital bony walls | CT scanner | Contact without bony modification Minor (<2 mm) erosion Major (≥2 mm) erosion | Free Invaded |
| MRI | Minor (<2 mm) modification Major (≥2 mm) modification | ||
| Orbital content | MRI | Invasion of the fat between tumor and oculomotor muscle Smooth or Irregular deformation Contact angle: ≤45° or >45° Invasion of oculomotor muscle | Free Invaded |
| Patients (Number) | 176 |
|---|---|
| Mean age in years (extremes) | 57 (16–89) |
| Sex ratio (Male/Female) | 3.8 (139/37) |
| Side of the tumor (number and percentage) Bilateral Right Left | 2 (1%) 89 (51%) 85 (48%) |
| Primitive location (number and percentage) Ethmoid Olfactory cleft Nasal septum Middle turbinate Frontal Maxillary bone Orbit Sphenoid | 155 (88%) 13 (7%) 3 (2%) 1 1 1 1 1 |
| Histological type (number and percentage) Intestinal-type adenocarcinoma Esthesioneuroblastoma Non-intestinal-type adenocarcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma Mucosal melanoma Neuroendocrine carcinoma Rhabdomyosarcoma Other | 72 (41%) 36 (20%) 28 (16%) 10 (6%) 9 (5%) 6 (3%) 3 (2%) 12 |
| Pre-operative T classification Tx T1 T2 T3 T4a T4b | 8 (5%) 3 (2%) 36 (20%) 47 (27%) 23 (14%) 58 (33%) |
| Pre-operative N classification N0 N1 N2b N2c Retropharyngeal | 168 (95%) 13 (2%) 3 (2%) 1 |
| Post-operative T classification T0 T1 T2 T3 T4a T4b | 11 (6%) 5 (3%) 65 (37%) 23 (13%) 16 (9%) 56 (32%) |
| First tumor Recurrence | 169 (96%) 7 (4%) |
| Pre-operative treatments (number and percentage) Chemotherapy Radiochemotherapy | 66 (38%) 1 |
| Surgical technique (number and percentage) Craniofacial resection Endoscopic trans-nasal resection Cranio-endoscopic resection | 58 (33%) 117 (66%) 1 |
| Post-operative treatments (number and percentage) Exclusive radiotherapy Radiochemotherapy | 149 (85%) 10 (6%) |
| Histological invasion: Bony skull base Dura Olfactory bulbs Cerebral parenchyma Bony orbital walls Orbital content | 78 (44%) 46 (26%) 25 (14%) 9 (5%) 36 (20%) 15 (9%) |
| Anatomical Structure | Imaging | Radiological Sign | Number of Abnormalities | PPV (CI95) | Kappa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bony skull base | CT scanner | Contact without bony modification | 41 | 7.3% (1.5–19.9) | 0.87 | |
| Minor erosion | 32 | 50.0% (32.7–67.3) | ||||
| Major erosion | 54 | 77.8% (66.7–88.9) | ||||
| MRI | Minor modification | 40 | 45.0% (29.6–60.4) | 0.85 | ||
| Major modification | 45 | 88.9% (79.7–98.1) | ||||
| Dura | MRI | Linear enhancement | ≤2 mm | 39 | 38.5% (23.2–53.7) | 0.78 |
| >2 mm | 14 | 71.4% (41,9–91.6) | ||||
| Nodular enhancement | ≤2 mm | 5 | 40.0% (5.3–85.3) | 0.79 | ||
| >2 mm | 23 | 87.0% (66.4–97.2) | ||||
| Deformation | Smooth | 41 | 46.3% (31.1–61.6) | 0.73 | ||
| Irregular | 15 | 86.7% (59.5–98.3) | ||||
| Contact angle | ≤45° | 35 | 37.1% (21.1–53.2) | 0.84 | ||
| >45° | 21 | 85.7% (63.7–97.0) | ||||
| Cerebral parenchyma | MRI | Edema | 4 | 50.0% (6.8–93.2) | 0.52 | |
| Tumoral invasion | 1 | 100% (2.5–100) | ||||
| Orbital bony walls | CT scanner | Contact without bony modification | 47 | 0% (0–7.6) | 0.85 | |
| Minor erosion | 22 | 27.3% (10.7–50.2) | ||||
| Major erosion | 43 | 48.8% (33.9–63.8) | ||||
| MRI | Minor modification | 21 | 28.6% (11.3–52.2) | 0.90 | ||
| Major modification | 40 | 47.5% (32.0–63.0) | ||||
| Orbital content | MRI | Invasion of the fat between tumor and oculomotor muscle | 24 | 33.3%(15.6–55.3) | 0.91 | |
| Deformation | Smooth | 45 | 28.6% (13.6–43.5) | 0.75 | ||
| Irregular | 6 | 33.3% (4.3–77.7) | ||||
| Contact angle | ≤45° | 40 | 21.2% (7.3–35.2) | 0.80 | ||
| >45° | 11 | 45.5% (16.8–76.6) | ||||
| Invasion of oculomotor muscle | 3 | 33.3% (0.8–90.6) | 1 | |||
| Radiological Conclusion | Bony Skull Base | Dura | Cerebral Parenchyma | Orbital Bony Walls | Orbital Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| True positives | 60 | 33 | 1 | 29 | 4 |
| True negatives | 82 | 97 | 151 | 113 | 142 |
| False positives | 16 | 21 | 1 | 27 | 4 |
| False negatives | 18 | 9 | 7 | 7 | 10 |
| Sensitivity (CI95) | 76.9% (67.6–86.3) | 78.6% (66.2–91.0) | 12.5% (0.3–52.7) | 80.6% (67.6–93.5) | 28.6% (8.4–58.1) |
| Specificity (CI95) | 83.7% (76.4–91.0) | 82.2% (75.3–89.1) | 99.3% (98.1–100) | 80.7% (74.2–87.3) | 97.3% (94.6–99.9) |
| PPV (CI95) | 79.0% (69.8–88.1) | 61.1% (48.1–74.1) | 50.0% (1.3–98.7) | 51.8% (38.7–64.9) | 50.0% (15.4–84.7) |
| NPV (CI95) | 82.0% (74.5–89.5) | 91.5% (86.2–96.8) | 95.6% (92.4–98.8) | 94,2% (90.0–98.4) | 93.4% (89.5–97.4) |
| Accuracy (CI95) | 80.7% (74.9–86.5) | 81.3% (75.2–87,3) | 95.0 (91.6–98.4) | 76.3% (70.2–82.5) | 91.3% (86.9–95.6) |
| Kappa | 0.87 | 0.96 | 0.49 | 0.93 | 0.41 |
| Yule’s Q | 0.61 | 0.89 | 0.91 | 0.61 | 0.87 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salfrant, M.; Garcia, G.C.T.E.; Guichard, J.-P.; Bidault, F.; Reizine, D.; Aupérin, A.; Bresson, D.; Verillaud, B.; Herman, P.; Moya-Plana, A. Imaging of Skull Base and Orbital Invasion in Sinonasal Cancer: Correlation with Histopathology. Cancers 2021, 13, 4963. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13194963
Salfrant M, Garcia GCTE, Guichard J-P, Bidault F, Reizine D, Aupérin A, Bresson D, Verillaud B, Herman P, Moya-Plana A. Imaging of Skull Base and Orbital Invasion in Sinonasal Cancer: Correlation with Histopathology. Cancers. 2021; 13(19):4963. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13194963
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalfrant, Maxime, Gabriel C. T. E. Garcia, Jean-Pierre Guichard, François Bidault, Daniel Reizine, Anne Aupérin, Damien Bresson, Benjamin Verillaud, Philippe Herman, and Antoine Moya-Plana. 2021. "Imaging of Skull Base and Orbital Invasion in Sinonasal Cancer: Correlation with Histopathology" Cancers 13, no. 19: 4963. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13194963
APA StyleSalfrant, M., Garcia, G. C. T. E., Guichard, J.-P., Bidault, F., Reizine, D., Aupérin, A., Bresson, D., Verillaud, B., Herman, P., & Moya-Plana, A. (2021). Imaging of Skull Base and Orbital Invasion in Sinonasal Cancer: Correlation with Histopathology. Cancers, 13(19), 4963. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13194963






