Factors, Mechanisms, and Kinetics of Spontaneous Emulsification for Heavy Oil-in-Water Emulsions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Interfacial Tensions (IFTs) of the SE System
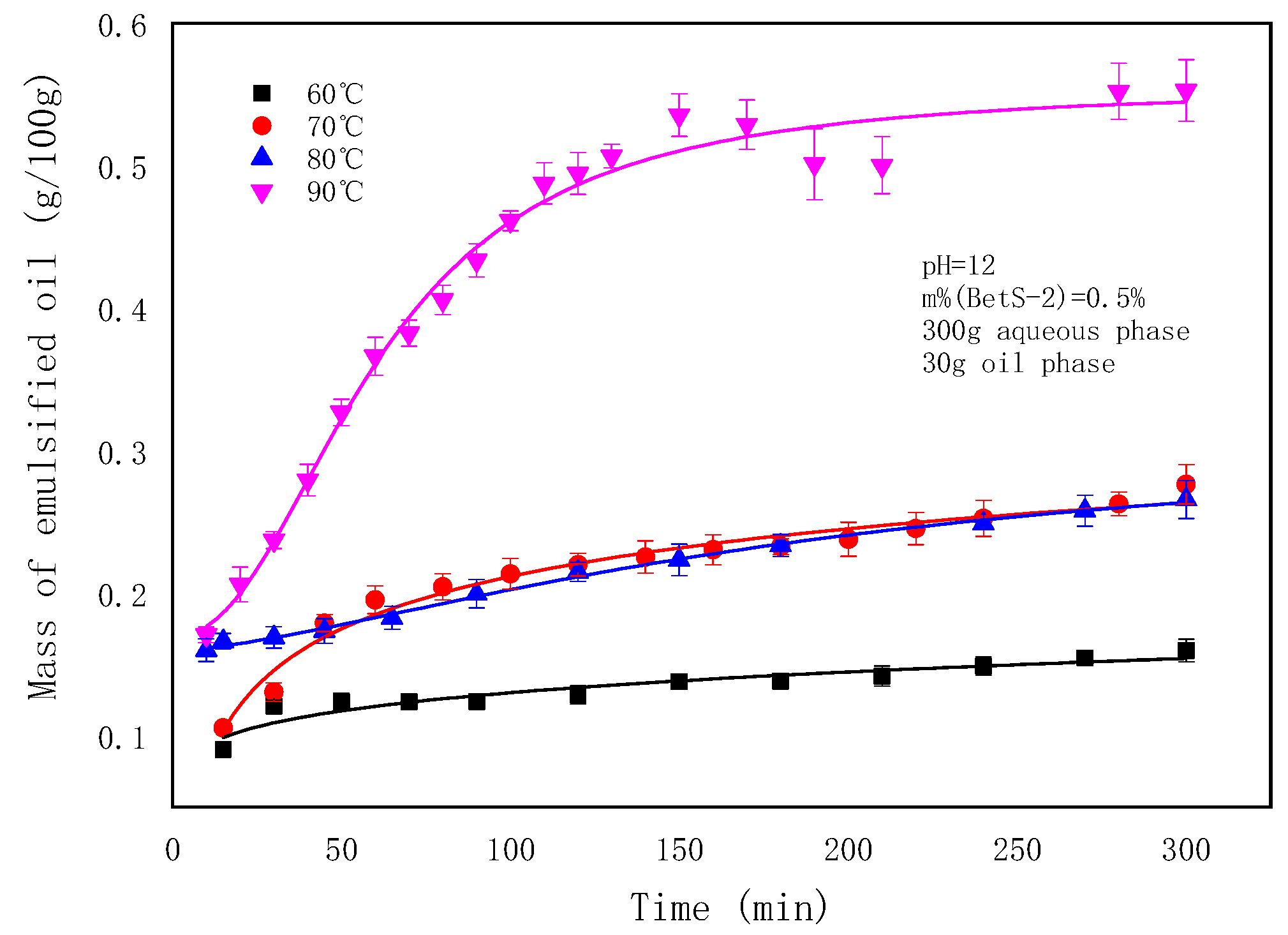
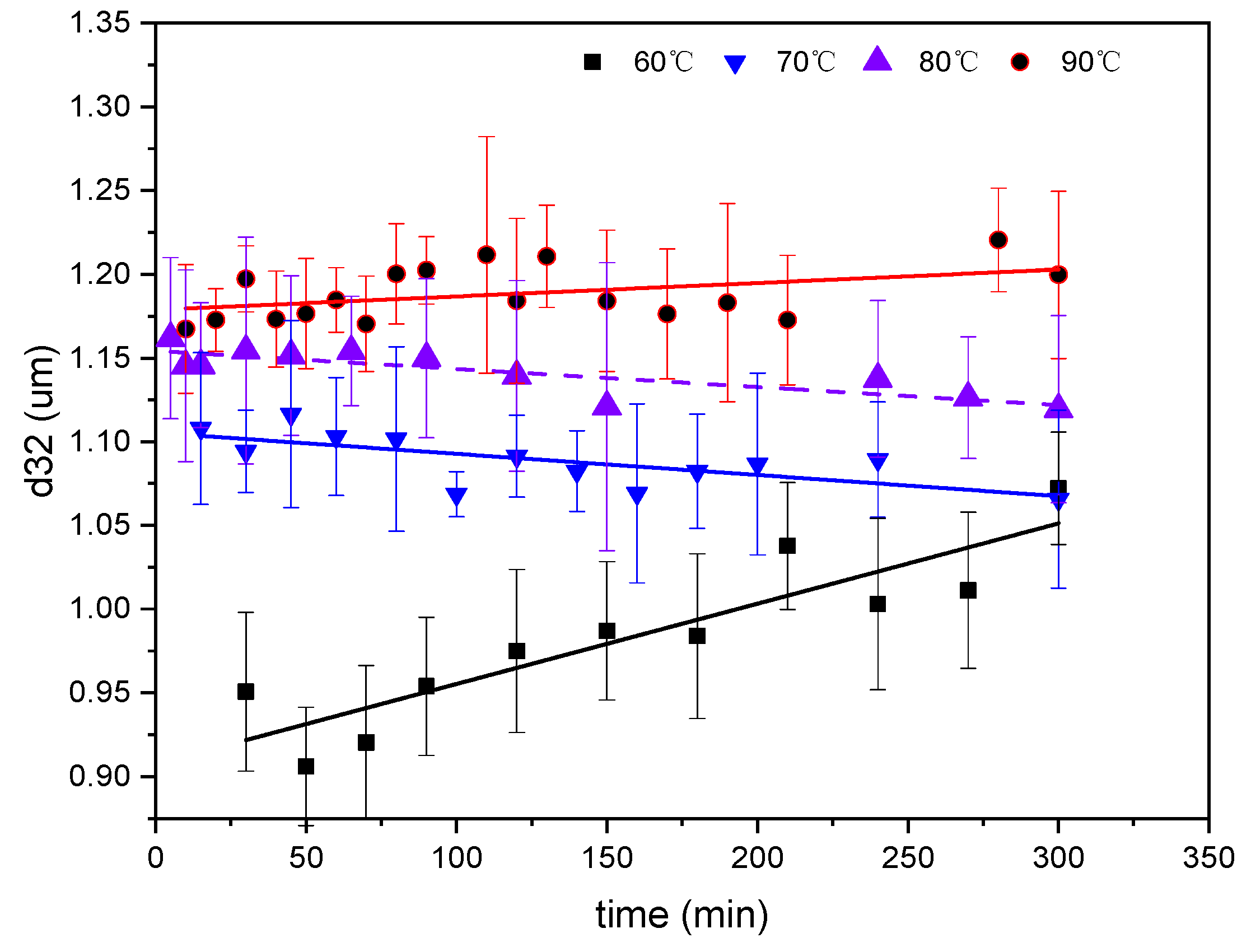
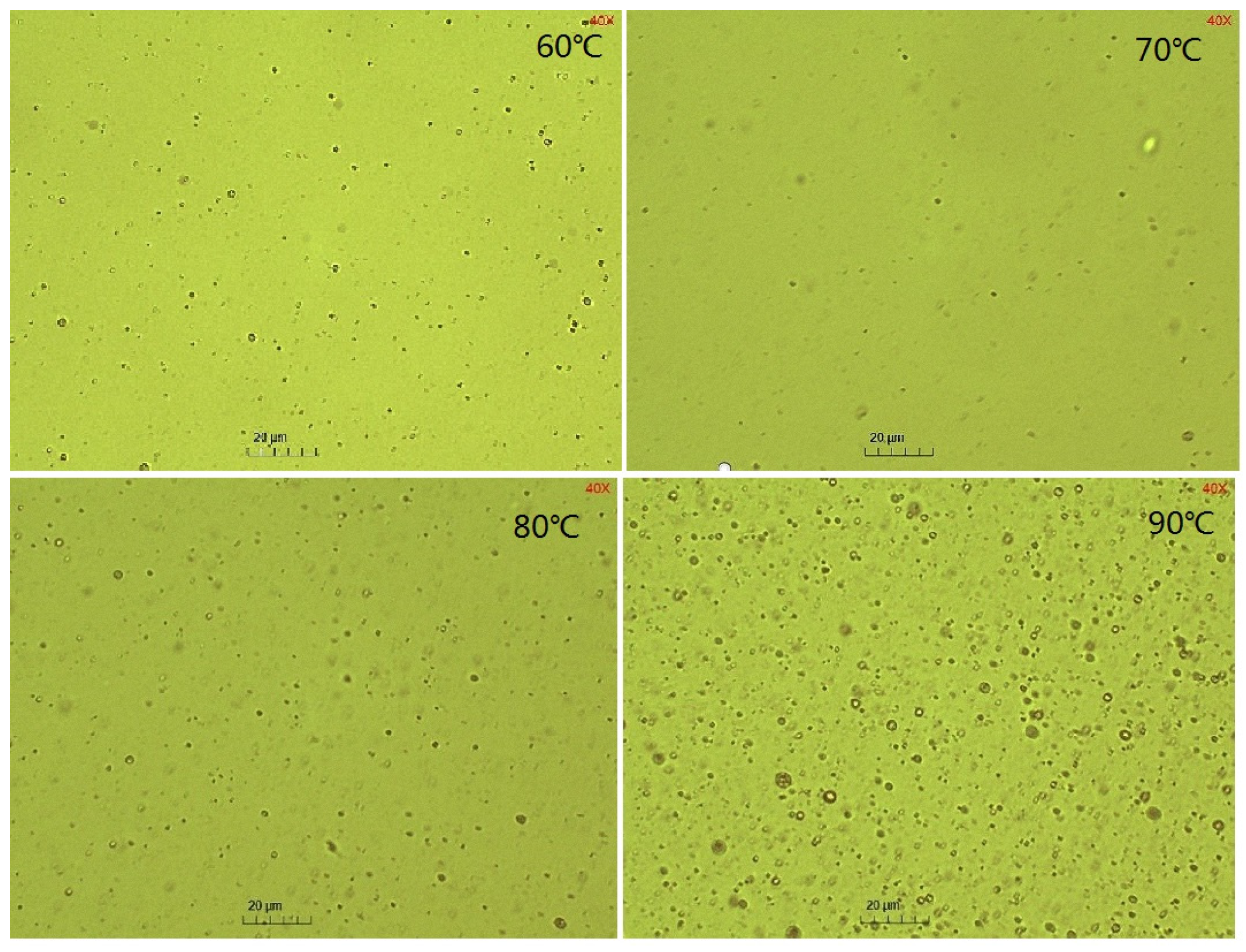
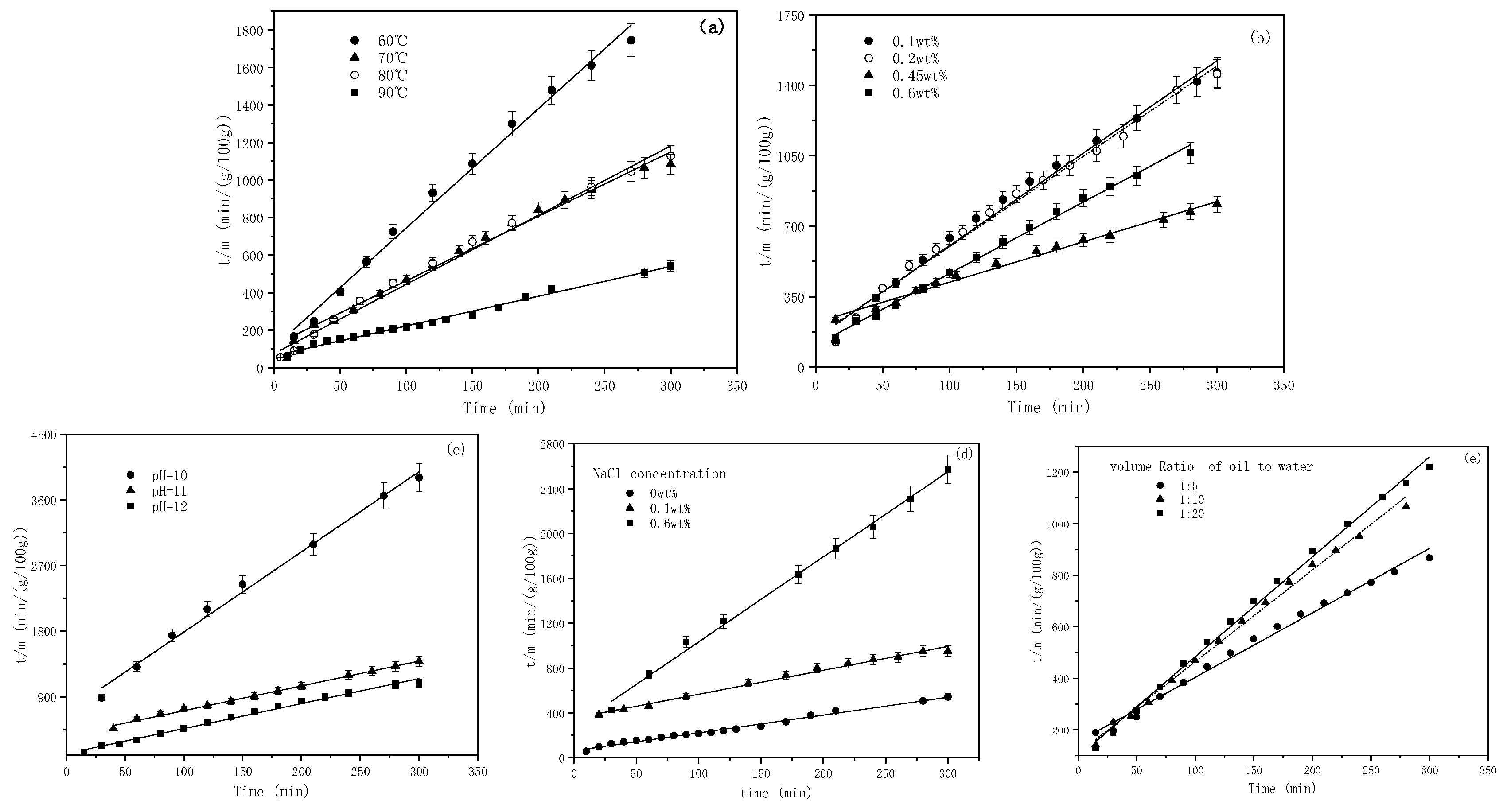
2.2. The Effect of Temperatures on the SE Process
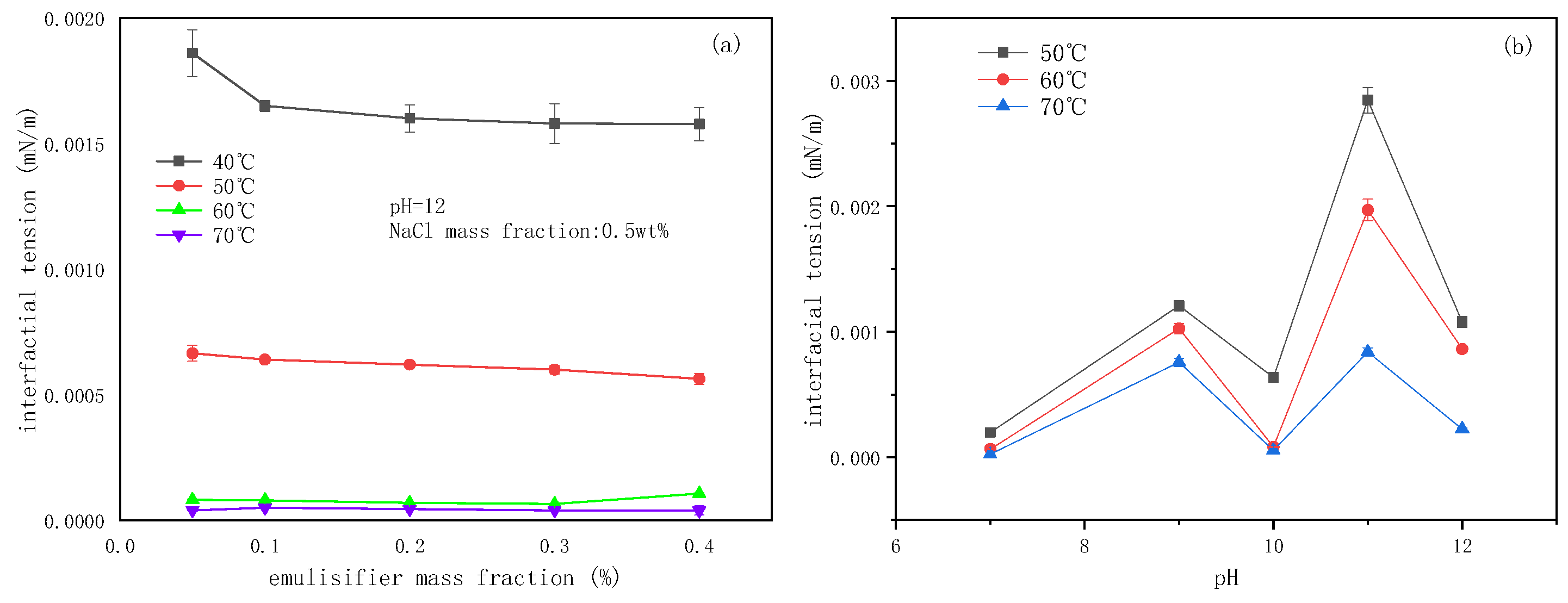
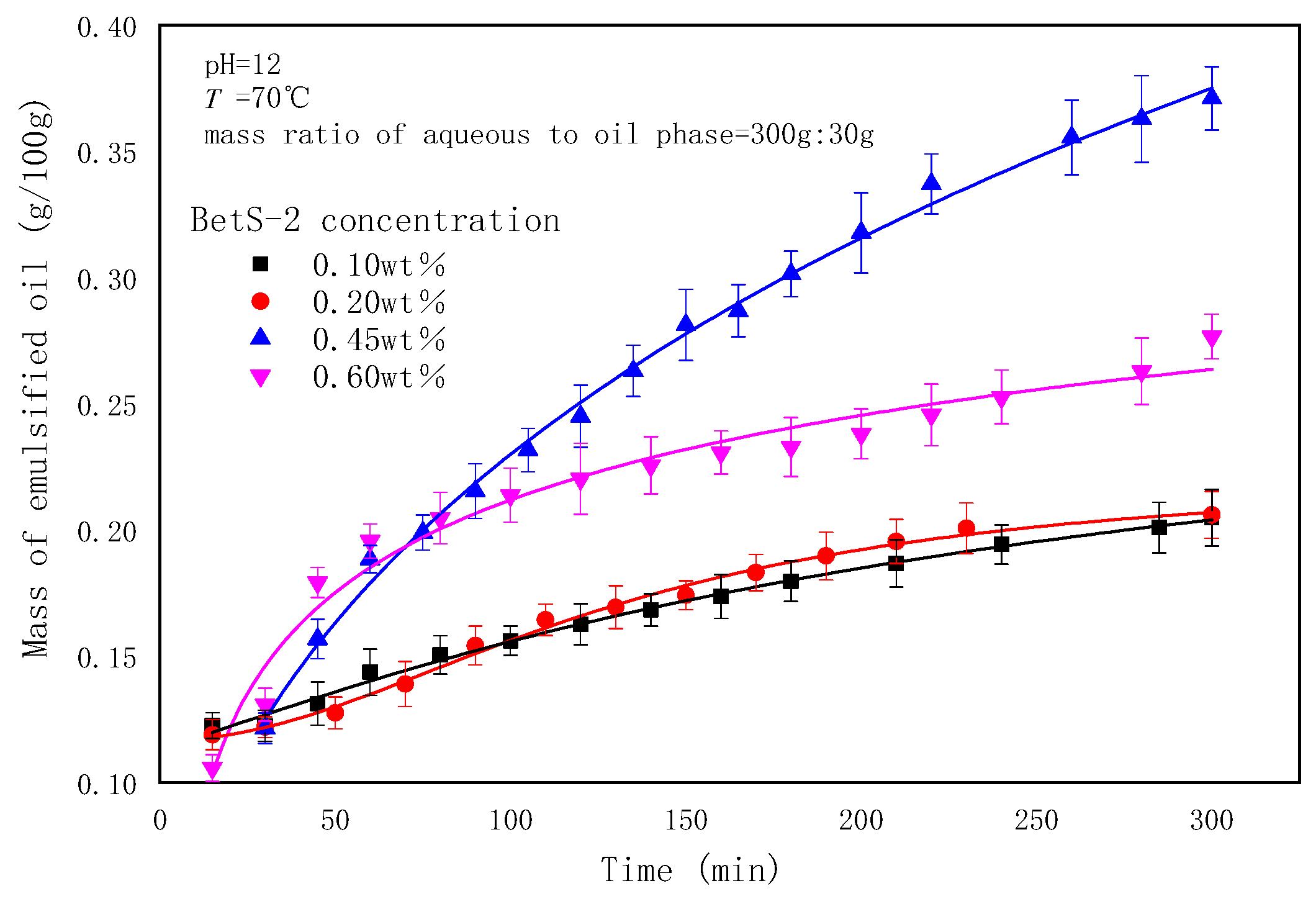
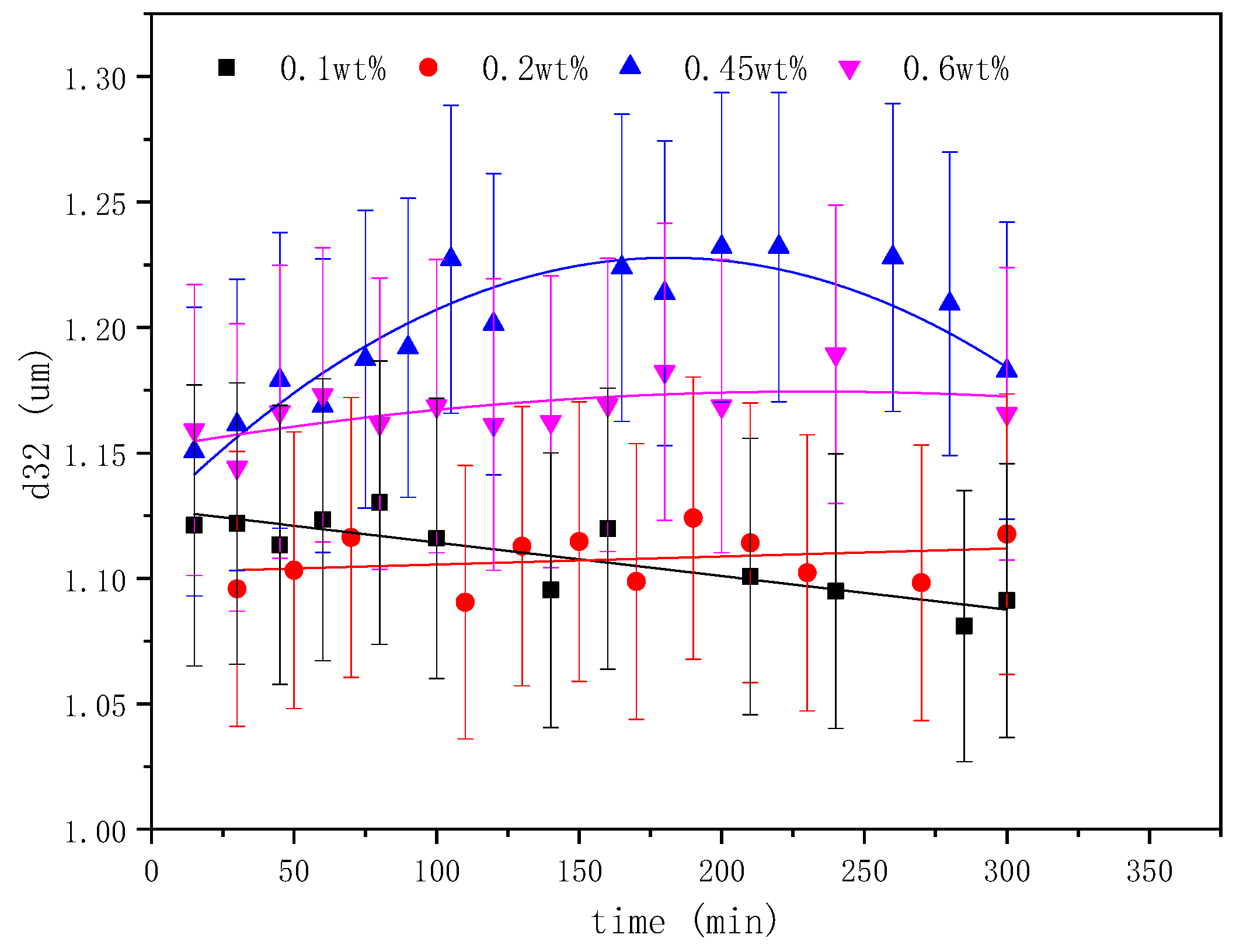
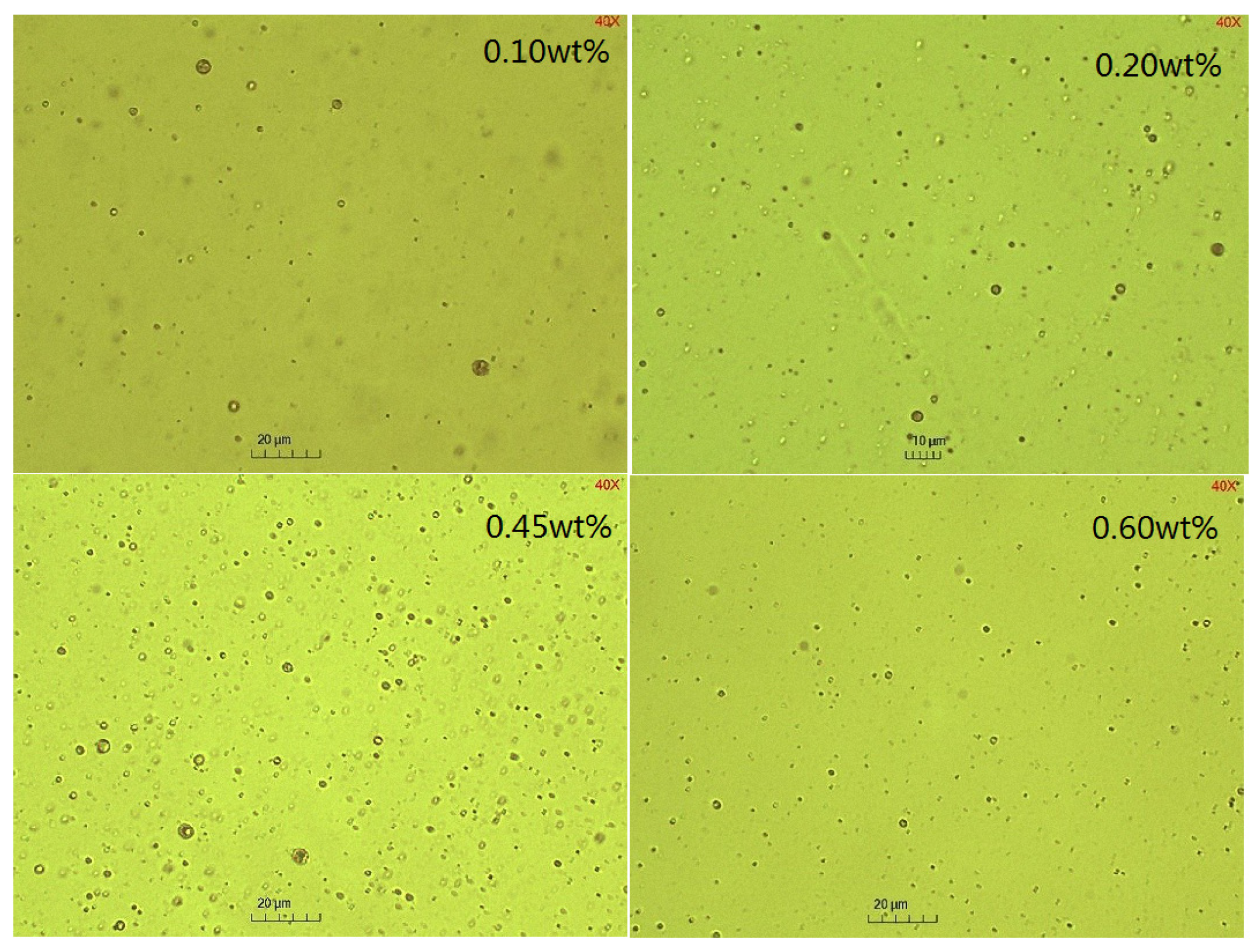
2.3. The Effect of Emulsifier Concentrations on the Emulsification Process
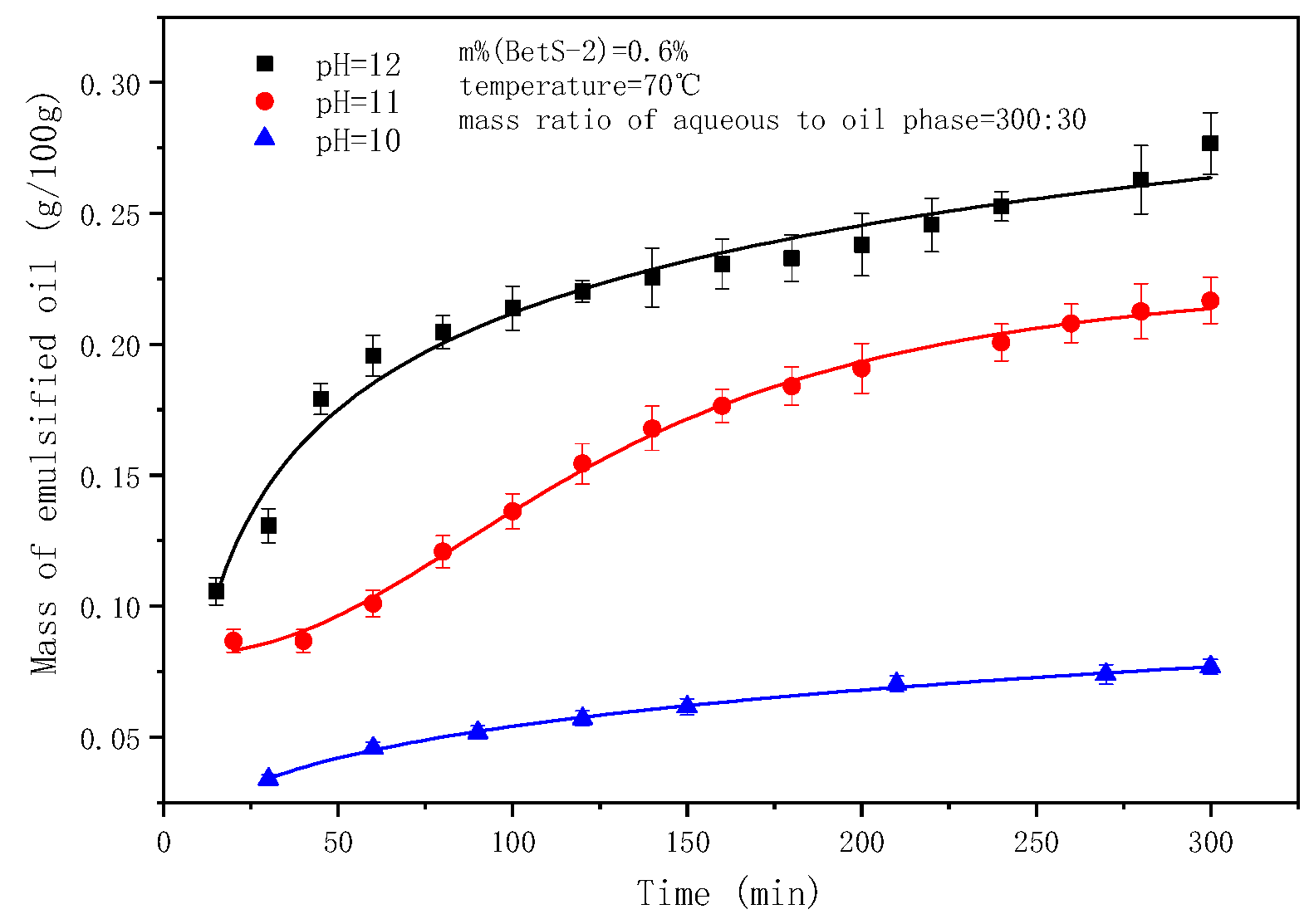
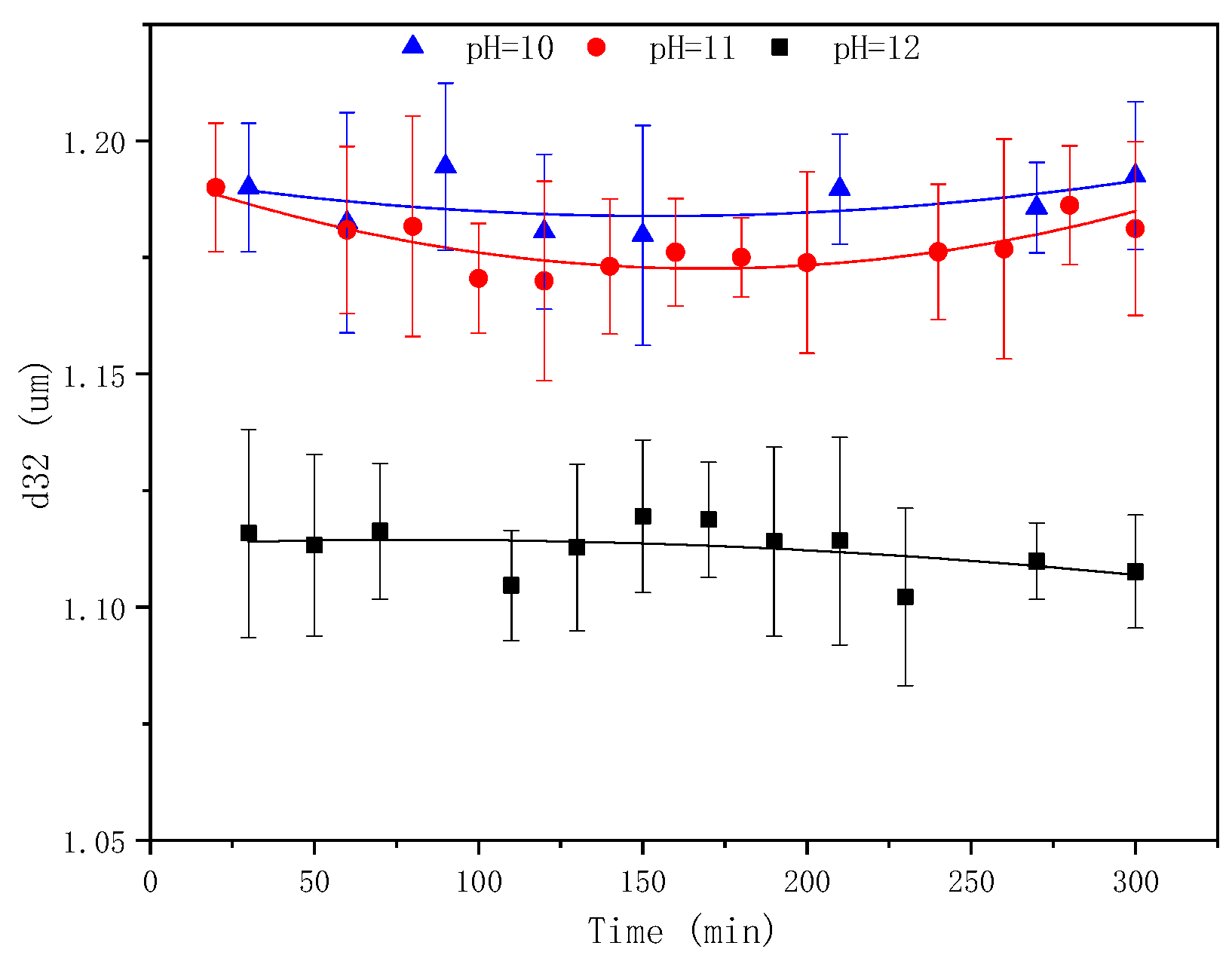
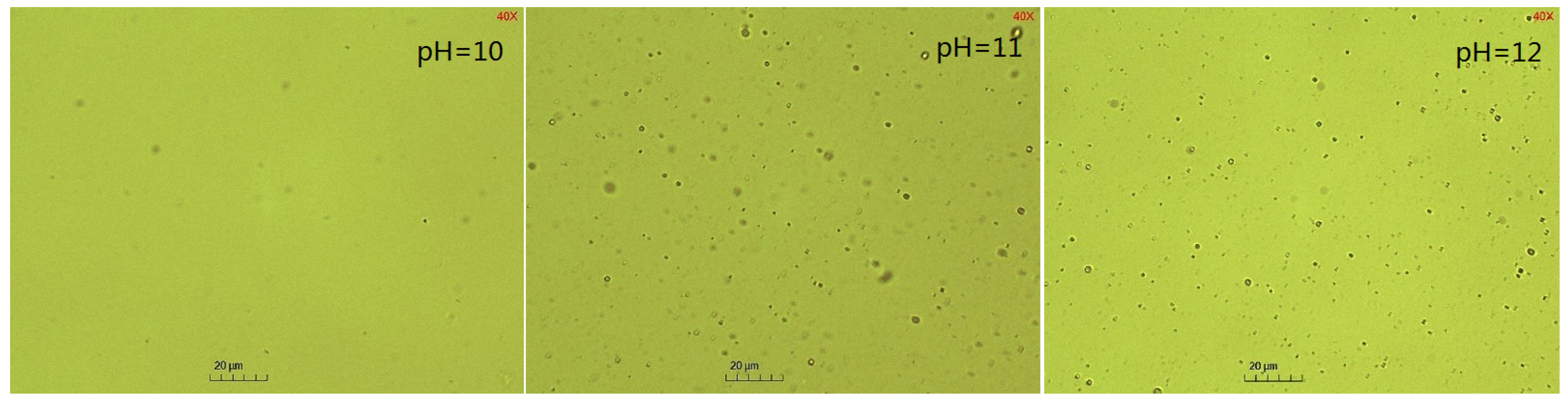
2.4. The Effect of pH on the Emulsification Process
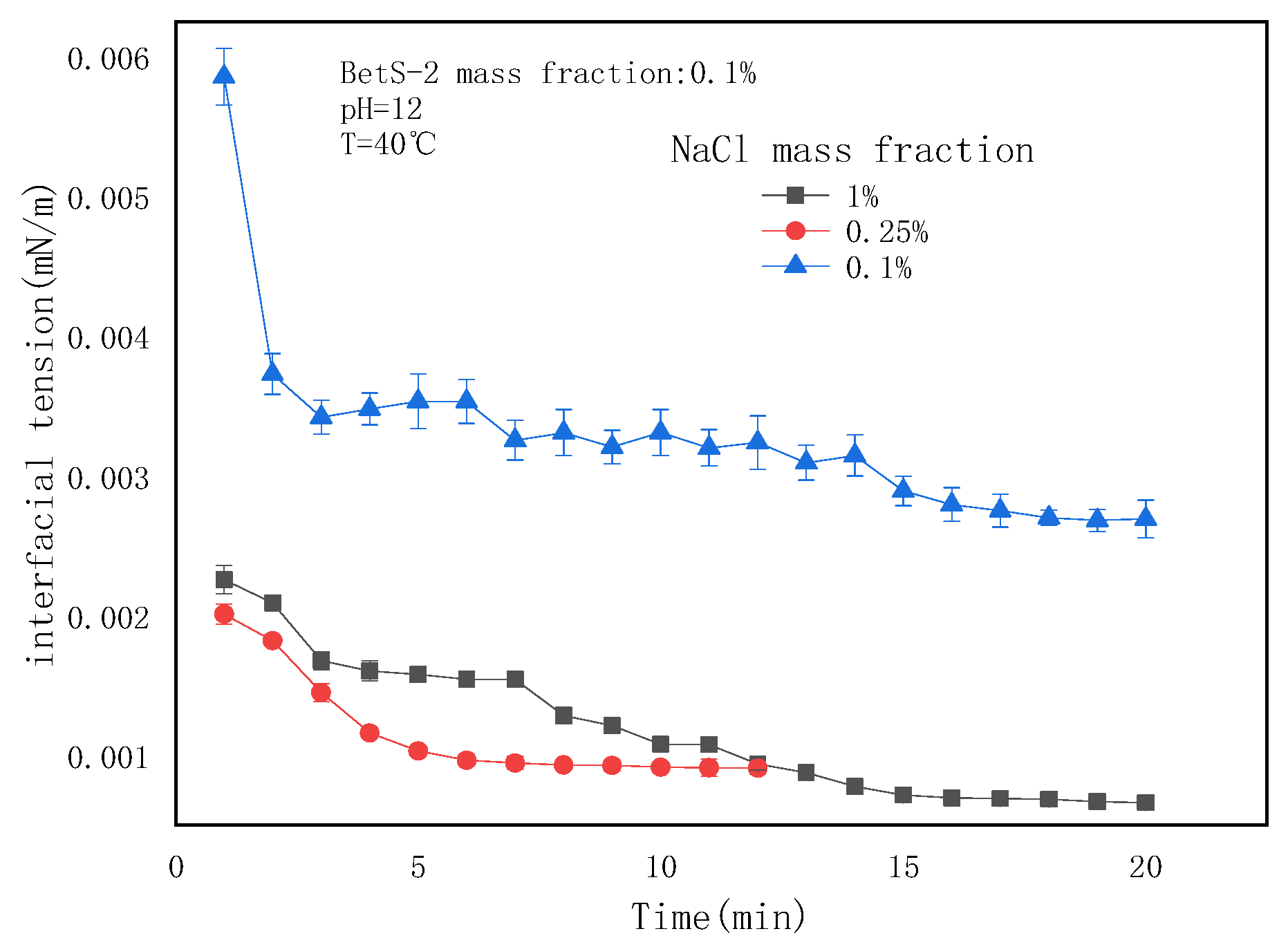
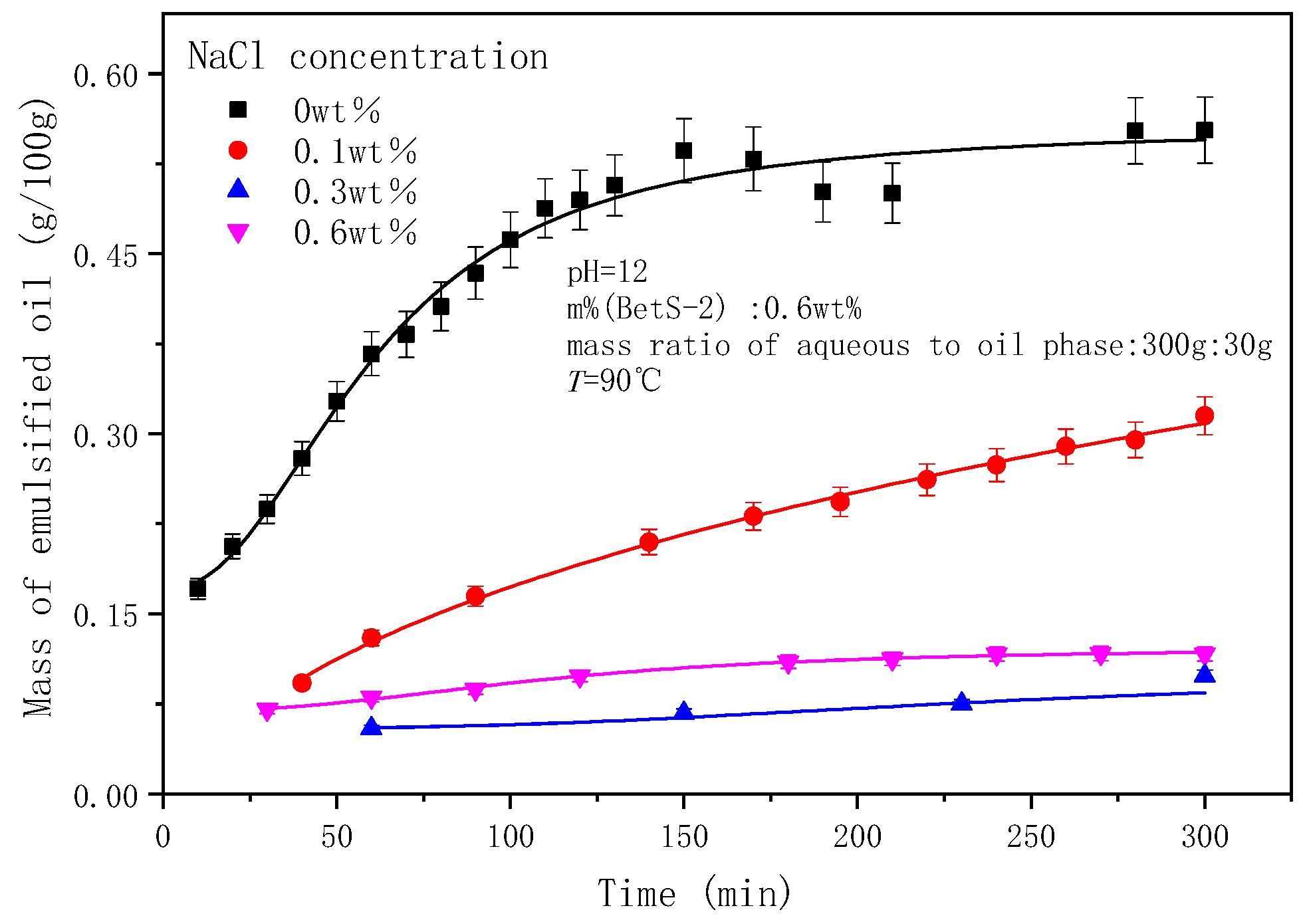
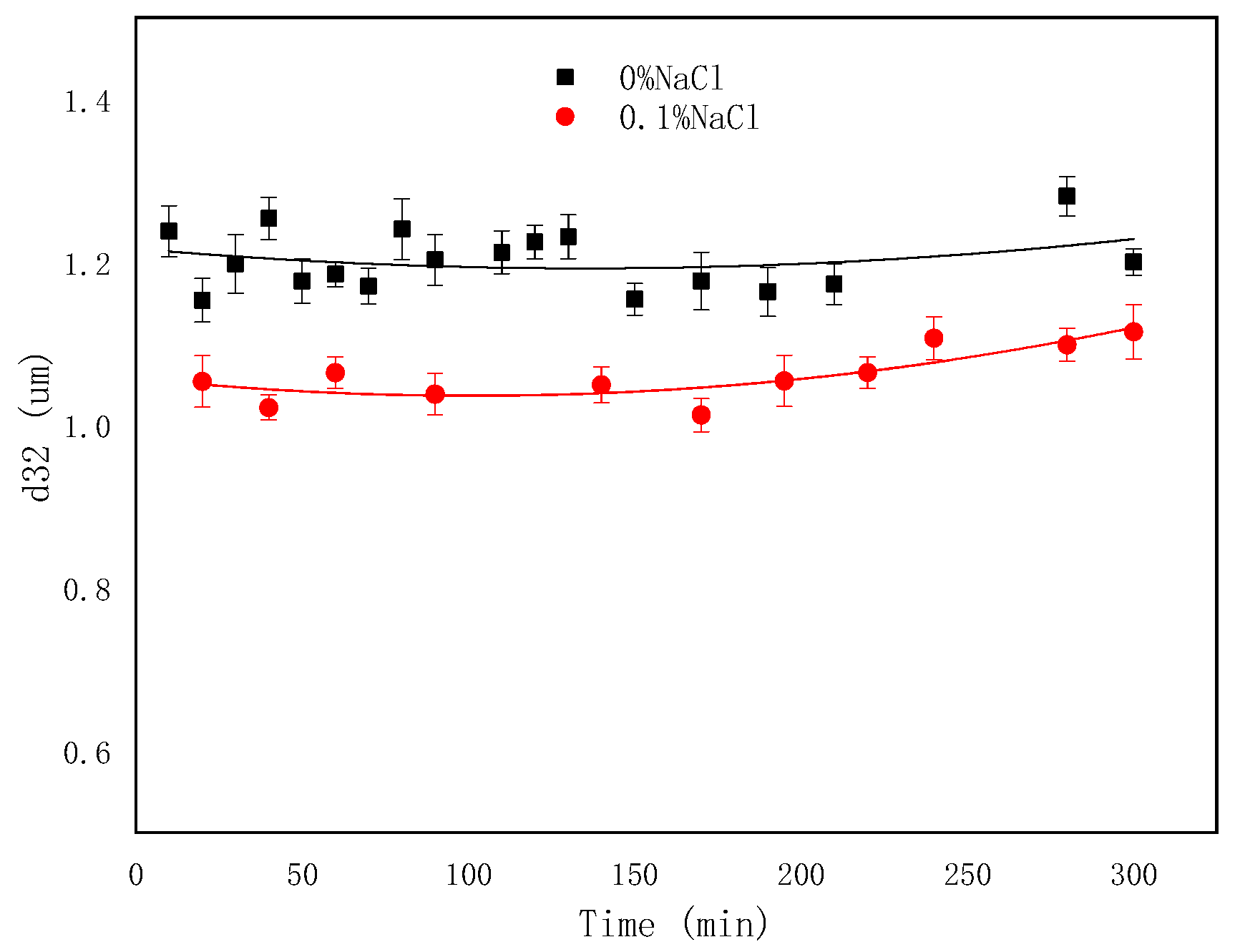
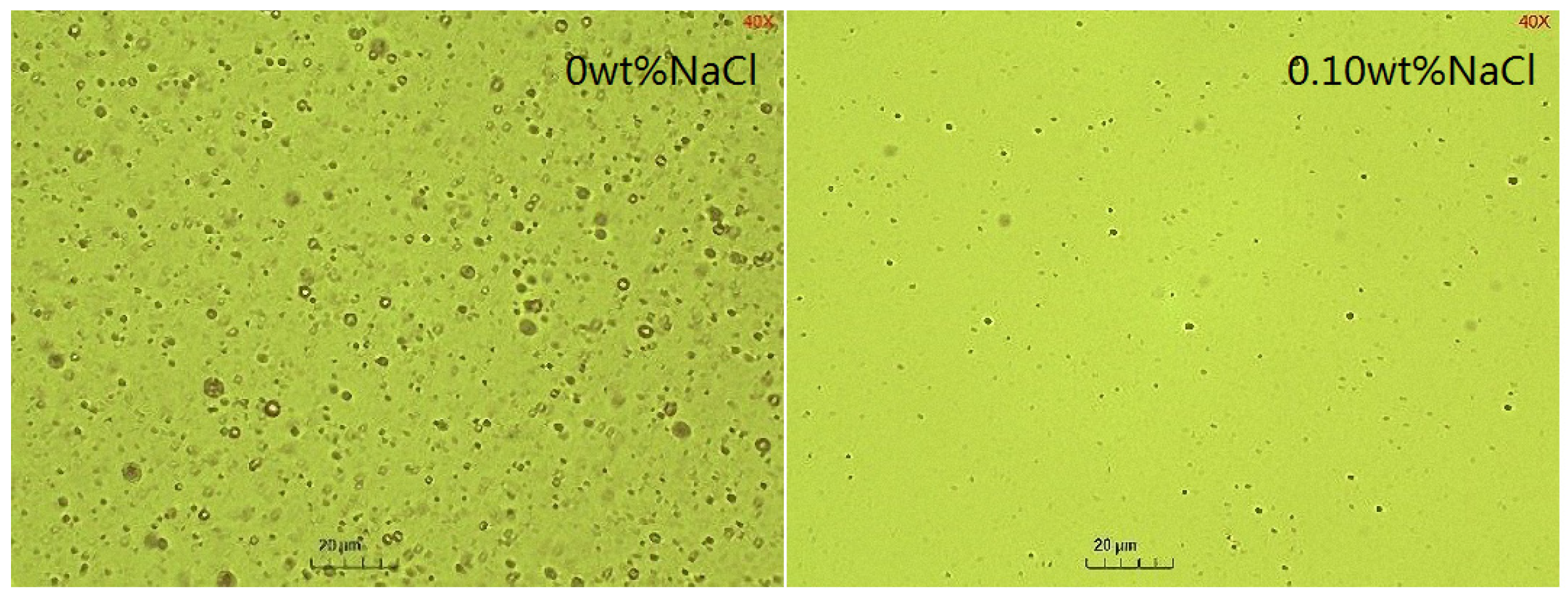
2.5. The Effect of NaCl Concentrations on the Emulsification Process
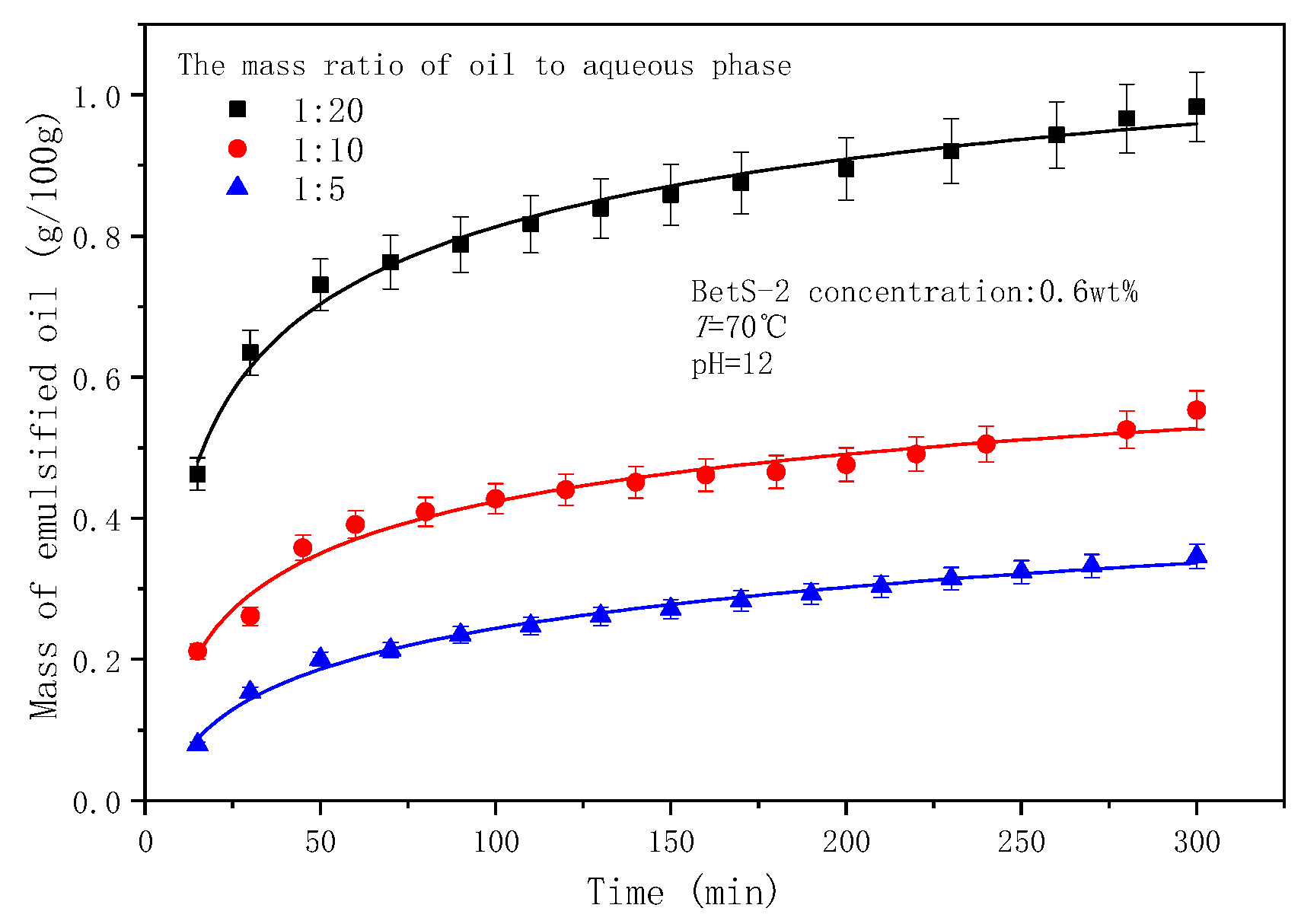
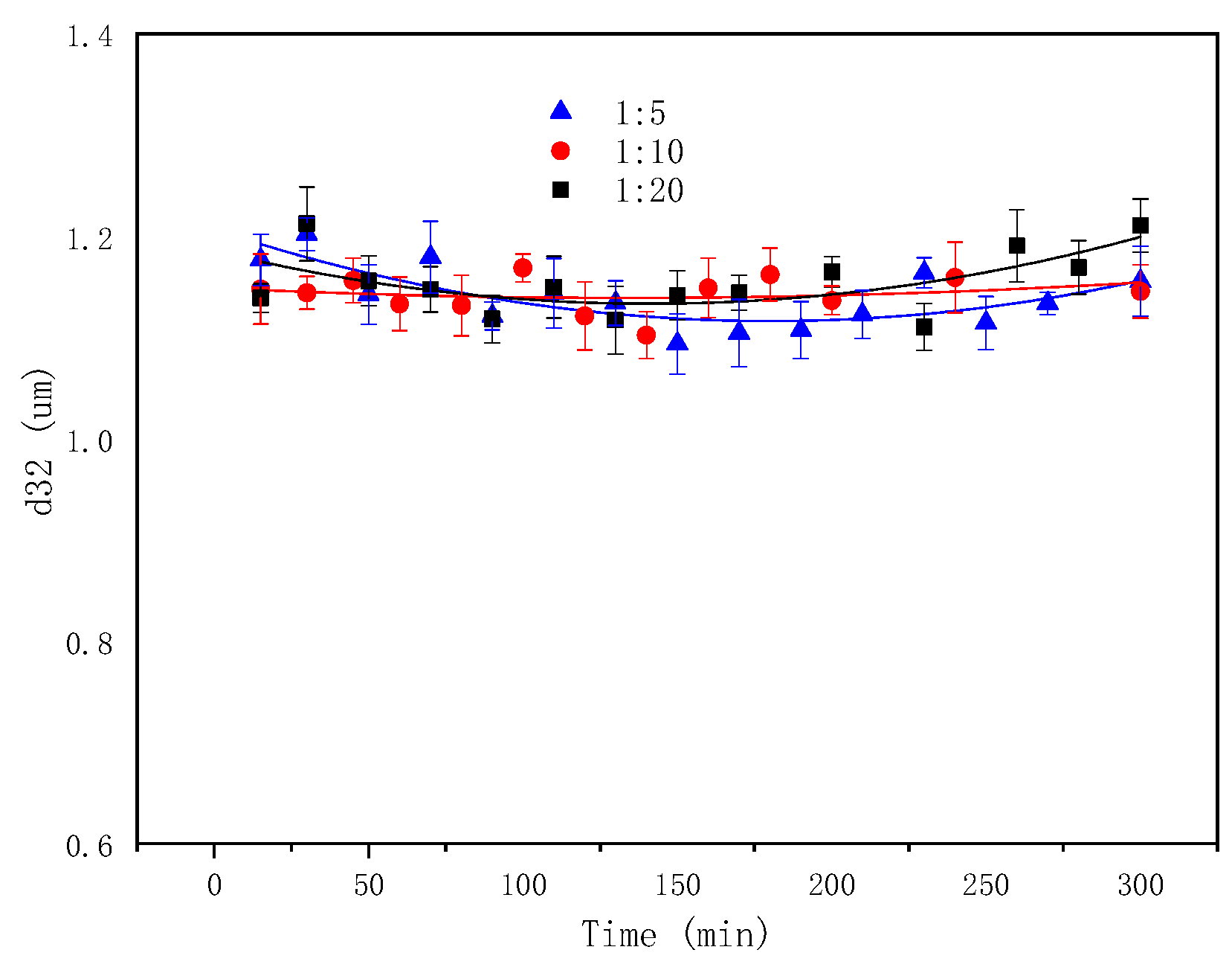
2.6. The Effect of the Mass Aqueous-to-Oil Phase Ratio on Emulsification
2.7. Mechanism of Spontaneous Emulsification
2.8. The Kinetic Equation for the SE Process
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Experimental Methods
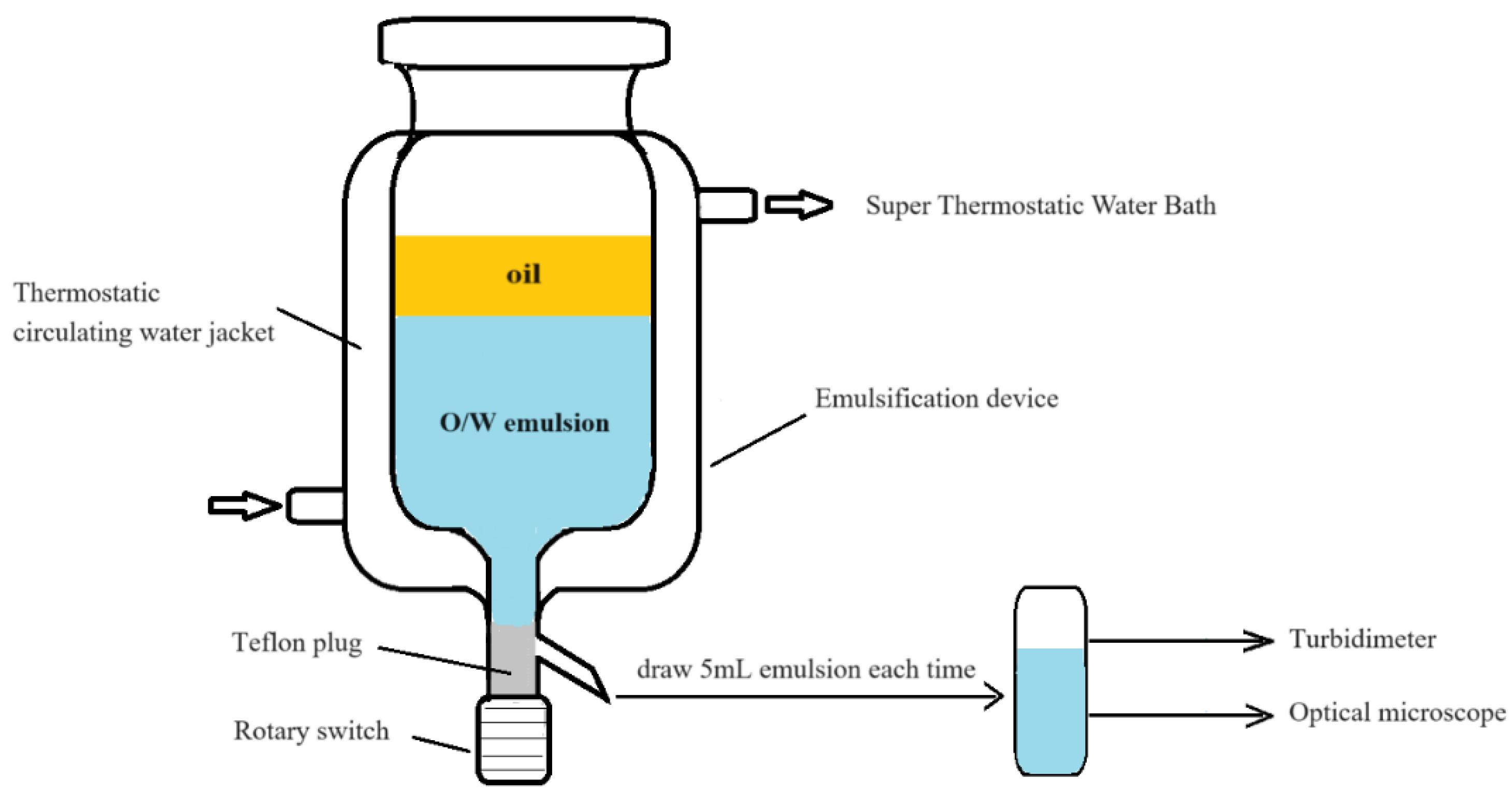
3.2.1. Spontaneous Emulsification
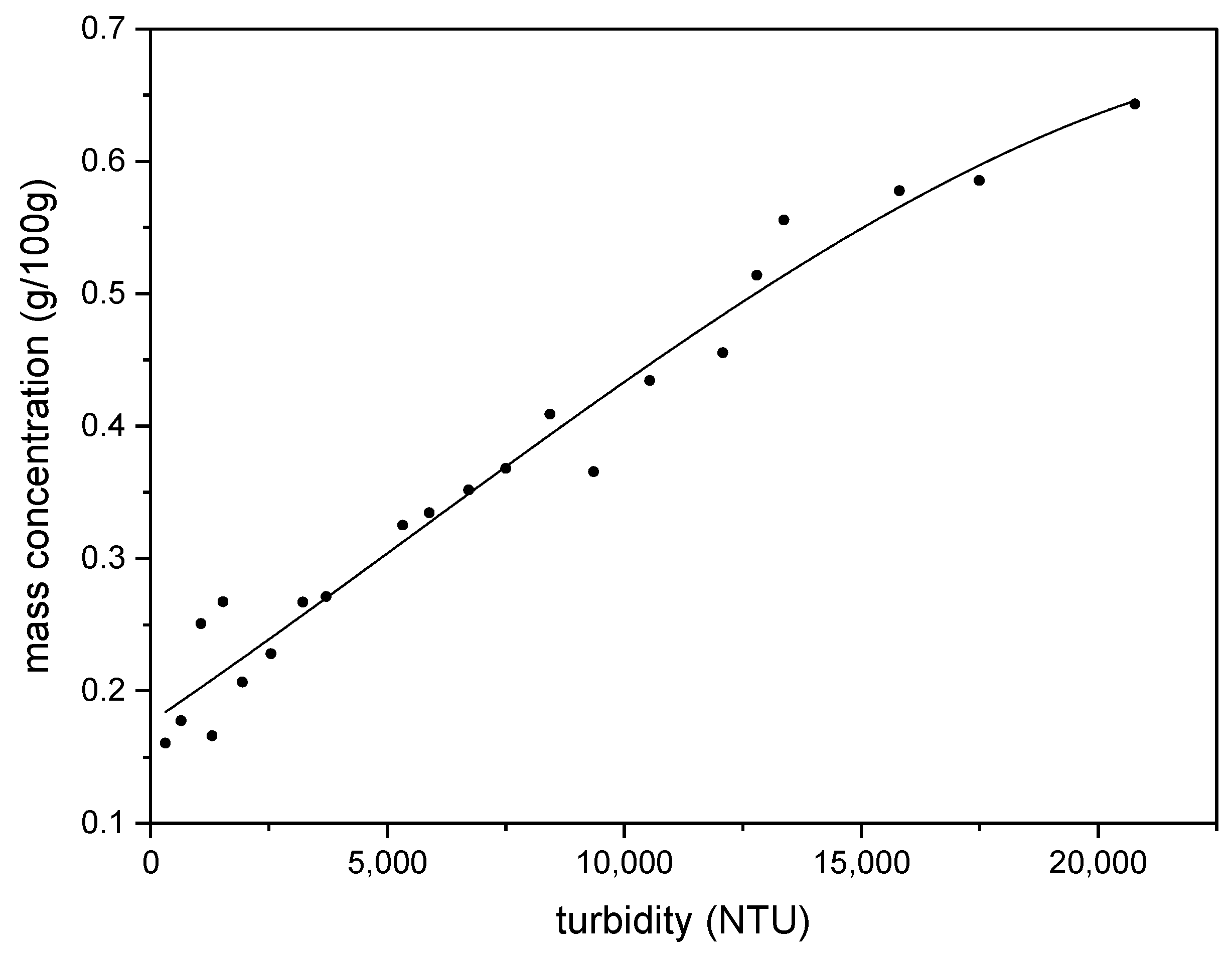
3.2.2. Emulsion Turbidity Measurement
3.2.3. Mass of oil Emulsified Measurement
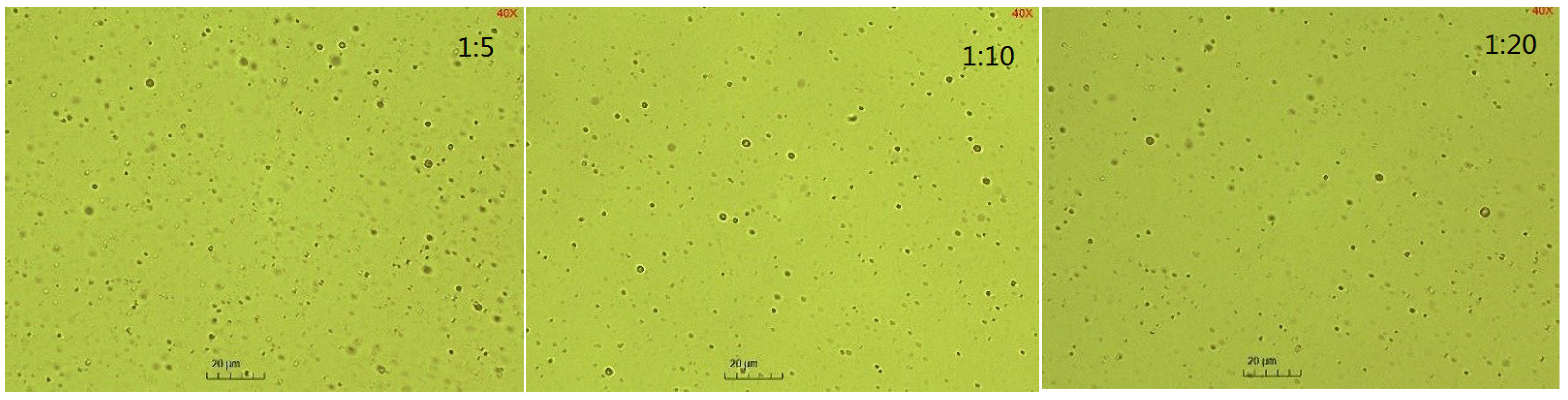
3.2.4. Droplet Size Measurement
3.2.5. Interfacial Tension (IFT) Measurement
3.2.6. Emulsification Rate and Kinetic Equation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Zhao, W.; Lun, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, P.; Li, Y.; Sun, C. Factors and Kinetics Related to the Formation of Heavy Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Energies 2023, 16, 5499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, W.; Shen, C.; Tang, X.; Pang, S.; Sun, D.; Mei, Z. Emulsification of acidic heavy oil for viscosity reduction and enhanced oil recovery. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2020, 41, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Jiang, H.; Fan, Z.; Xu, F.; Su, H.; Li, J. Formation and Flow Behaviors of in Situ Emulsions in Heavy Oil Reservoirs. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 5961–5970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borji, M.; Kharrat, A.; Ott, H. Comparability of in situ crude oil emulsification in phase equilibrium and under porous-media-flow conditions. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 615, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Xu, D.; Yuan, Y.; Wu, H.; Hou, J.; Kang, W.; Bai, B. Advances of spontaneous emulsification and its important applications in enhanced oil recovery process. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 277, 102119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Gao, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Pu, W.; Liu, R. Experimental study on self–emulsification of shale crude oil by natural emulsifiers. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2023, 45, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wei, B.; Sun, Z.; Du, Q.; Hou, J. Microfluidic study of heavy oil emulsification on solid surface. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2021, 246, 117009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, F.; Zhao, H.; Li, Z. A comparative study of the mechanism and performance of surfactant- and alkali-polymer flooding in heavy-oil recovery. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 219, 115603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Dong, M.; Yue, X.; Hou, J. Synergy of alkali and surfactant in emulsification of heavy oil in brine. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 273, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Luo, H.; Long, Z. Emulsification behaviors of crude oil-water system and its quantitative relationship with exergy loss rate. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 176, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, J.; Pinjari, D.V.; Saharan, V.K.; Pandit, A.B. Critical Review on Hydrodynamic Cavitation as an Intensifying Homogenizing Technique for Oil-in-Water Emulsification: Theoretical Insight, Current Status, and Future Perspectives. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 10587–10602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perazzo, A.; Preziosi, V.; Guido, S. Phase inversion emulsification: Current understanding and applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 222, 581–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friberg, S.E.; Corkery, R.W.; Blute, I.A. Phase Inversion Temperature (PIT) Emulsification Process. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2011, 56, 4282–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Z.; Xu, J.; Sun, D. O/W nano-emulsions with tunable PIT induced by inorganic salts. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 375, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hategekimana, J.; Chamba, M.V.; Shoemaker, C.F.; Majeed, H.; Zhong, F. Vitamin E nanoemulsions by emulsion phase inversion: Effect ofenvironmental stress and long-term storage on stability and degradation in different carrier oil types. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 483, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestro, A.; Solè, I.; González, C.; Solans, C.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Influence of the phase behavior on the properties of ionic nanoemulsions prepared by the phase inversion composition method. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 327, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldousary, S.; Kovscek, A.R. The diffusion of water through oil contributes to spontaneous emulsification during low salinity waterflooding. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 179, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carteau, D.; Bassani, D.; Pianet, I. The ‘‘Ouzo effect’’: Following the spontaneous emulsification of trans-anethole in water by NMR. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2008, 11, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sheng, J.J.; Tu, J. Effect of spontaneous emulsification on oil recovery in tight oil-wet reservoirs. Fuel 2020, 279, 118456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Jin, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, J. Potential of Spontaneous Emulsification Flooding for Enhancing Oil Recovery in High-Temperature and High-Salinity Oil Reservoir. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2015, 36, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, R.; Ayatollahi, S. Dissociation of polar oil components in low salinity water and its impact on crude oil-brine interfacial interactions and physical properties. Pet. Sci. 2019, 16, 328–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, R.B.; Sheth, N.S. A Review: Self Emulsifying Drug Delivery System. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 3 (Suppl. S2), 2328. [Google Scholar]
- Bouchemal, K.; Briançon, S.; Perrier, E.; Fessi, H. Nano-emulsion formulation using spontaneous emulsification: Solvent, oil and surfactant optimization. Pharmaceutics 2004, 280, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azodi, M.; Nazar, A.S. An experimental study on factors affecting the heavy crude oil in water emulsions viscosity. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2013, 106, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lu, Y.; Wu, H.; Yang, M.; Feng, H.; Xu, D.; Hou, J.; Kang, W.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Y.; et al. A Novel Ultra-Low IFT Spontaneous Emulsification System for Enhanced Oil Recovery in Low Permeability Reservoirs. In Proceedings of the SPE EOR Conference at Oil and Gas West Asia, Muscat, Oman, 26–28 March 2018; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Marshall-Breton, C.; Leser, M.E.; Sher, A.A.; McClements, D.J. Fabrication of ultrafine edible emulsions: Comparison of high-energy and low-energy homogenization methods. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 29, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komaiko, J.; McClements, D.J. Low-energy formation of edible nanoemulsions by spontaneous emulsification: Factors influencing particle size. Food Eng. 2015, 146, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostertag, F.; Weiss, J.; McClements, D.J. Low-energy formation of edible nanoemulsions: Factors influencing droplet size produced by emulsion phase inversion. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 388, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Kang, X.; Wu, H.; Lu, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, D.; Ma, T.; Yang, H.; Kang, W. Spontaneous emulsification induced by a novel surfactant-polymer compound system and its application to enhance oil recovery. Mol. Liq. 2021, 337, 116399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Y.; Zhang, C.; Mahardika, M.A.; Patmonoaji, A.; Hu, Y.; Matsushita, S.; Suekane, T. Pore-Scale Study of in-Situ Surfactant Flooding with Strong Oil Emulsification in Sandstone Based on X-Ray Microtomography. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 98, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Mohanty, K.K. Wettability Alteration in High-Temperature and High-Salinity Carbonate Reservoirs. SPE J. 2013, 18, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, A.; Ojha, K.; Mandal, A. Synergistic Effect of Mixed Surfactant Systems on Foam Behavior and Surface Tension. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2013, 16, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, S.I.; Chandra, M.S.; Chen, J.; Zeng, B.Y.; Zou, F.; Mapolelo, M.; Abdallah, W.; Buiting, J.J. Detection and Impact of Carboxylic Acids at the Crude Oil-Water Interface. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 4475–4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, P.; Mehraban, M.F.; Sharifi, M.; Dejam, M.; Ayatollahi, S. Effect of water salinity on oil/brine interfacial behaviour during low salinity waterflooding: A mechanistic study. Petroleum 2019, 5, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Kang, W.; Bai, B.; Wu, H.; Gou, C.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, D.; Lu, Y.; Hou, J. Fabrication and Mechanism Study of the Fast Spontaneous Emulsification of Crude Oil with Anionic/Cationic Surfactants as an Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR) Method for Low-Permeability Reservoirs. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 8279–8288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.A. Spontaneous Emulsification: Recent Developments with Emphasis on Self-Emulsification. Surfactant Sci. Ser. 2005, 132, 107–126. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Firoozabadi, A. Surfactant-Enhanced Spontaneous Emulsification Near the Crude Oil-Water Interface. Langmuir 2021, 37, 4736–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silver, B.R.; Holub, K.; Mareček, V. Spontaneous emulsification at surfactantless liquid/liquid interfaces. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 805, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solans, C.; Morales, D.; Homs, M. Spontaneous emulsification. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 22, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duboué, J.; Bourrel, M.; Carreras, E.S.; Klimenko, A.; Agenet, N.; Passade-Boupat, N.; Lequeux, F. Auto-Emulsification of Water at the Crude Oil/Water Interface: A Mechanism Driven by Osmotic Gradient. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 7020–7027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyranvand, M.K.; Rostami, B. Direct Insight into the Cause and Time Evaluation of Spontaneous Emulsification of Water in Crude Oil during Low Salinity Waterflooding Using Microfluidic Model. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 2462–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.R.; Martinez, C.J.; Howarter, J.A.; Erk, K.A. Predicting Spontaneous Emulsification in Saltwater Environments Using the HLD Model. Langmuir 2021, 37, 8866–8875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Davis, C.R.; Howarter, J.A.; Erk, K.A.; Martinez, C.J. Spontaneous Emulsions: Adjusting Spontaneity and Phase Behaviorby Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Difference-Guided Surfactant, Salt, and Oil Selection. Langmuir 2022, 38, 4276–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariyaprakai, S.; Dungan, S.R. Contribution of molecular pathways in the micellar solubilization of monodisperse emulsion droplets. Langmuir 2008, 24, 3061–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.R.; Cheong, I.W. Stimuli-triggered formation of polymersomes from w/o/w multiple double emulsion droplets containing poly(styrene)-block-poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-spironaphthoxazine methacryloyl). Langmuir 2016, 32, 9223–9228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linke, C.; Drusch, S. Turbidity in oil-in-water-emulsions—Key factors and visual perception. Food Res. Int. 2016, 89, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinoda, R.; Uchimura, T. Evaluating the Creaming of an Emulsion via Mass Spectrometry and UV-Vis Spectrophotometry. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 13752–13756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, E.J.; Le, M.A.; Harwell, J.H.; Sabatini, D.A. Coalescence and solubilization kinetics in linker-modified microemulsions and related systems. Langmuir 2003, 19, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Hert, S.C.; Rodgers, T. Continuous, recycle and batch emulsification kinetics using a high-shear mixer. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 167, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covis, R.; Marie, E.; Durand, A.; Baravian, C. Kinetics of Formation of Oil-in-Water Emulsions Using In Situ Rheo-Optical Measurements. AIChE J. 2015, 61, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Zirrahi, M.; Hassanzadeh, H. An Analytical Model for Estimation of the Self-Diffusion Coefficient and Adsorption Kinetics of Surfactants Using Dynamic Interfacial Tension Measurements. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 3206–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toor, R.; Denoyel, R.; Liggieri, L.; Schmitt, M.; Antoni, M. Influence of Surfactant Concentration on Spontaneous Emulsification Kinetics. Langmuir 2022, 38, 11521–11528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabar, M.K.; Phan, C.M.; Barifcani, A. Quantifying the spontaneous emulsification of a heavy hydrocarbon with the presence of a strong surfactant. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 656, 130425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana-Solano, J.; Quezada, C.M.; Ozuna-Chacón, S.; Arauz-Lara, J.L. Spontaneous emulsification at the water/oil interface. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 399, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitnikova, N.L.; Sprik, R.; Wegdam, G. Spontaneously Formed trans-Anethol/Water/Alcohol Emulsions: Mechanism of Formation and Stability. Langmuir 2005, 21, 7083–7089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Sharma, M.M. A family of alkyl sulfate gemini surfactants. 2. Water–oil interfacial tension reduction. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 407, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoudia, M.; Al-Shibli, M.N.; Al-Kasimi, L.H.; Al-Maamari, R.; Al-bemani, A. Novel surfactants for ultralow interfacial tension in a wide range of surfactant concentration and temperature. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2006, 9, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanshen, L. Research progress on the Marangoni instability of a drop/bubble immersed in linearly stratified liquids. Chin. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 2024, 56, 1540–1551. [Google Scholar]
- Saberi, A.H.; Fang, Y.; Mc Clements, D.J. Thermal reversibility of vitamin E-enriched emulsion-based delivery systems produced using spontaneous emulsification. Food Chem. 2015, 185, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrnia, M.-A.; Jafari, S.-M.; Makhmal-Zadeh, B.S.; Maghsoudlou, Y. Crocin loaded nanoemulsions: Factors affecting emulsion properties in spontaneous emulsification. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 84, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagala, F.; Kantzas, A.; Hethnawi, A.; Maaref, S.; Nassar, N.N. Formulation of Spontaneous In Situ Emulsification Using Sodium Lauryl Sulfate Grafted Nanopyroxene for Enhanced Heavy Oil Recovery in Sandstone Reservoirs. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 12838–12853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malzert-Fréon, A.; Schönhammer, K.; Benoît, J.P.; Boury, F. Interactions between poly(ethylene glycol) and protein in dichloromethane/water emulsions. 2. Conditions required to obtain spontaneous emulsification allowing the formation of bioresorbable poly(D,L lactic acid) microparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 73, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, H.; Yang, M.; Jiang, J.; Xu, D.; Feng, H.; Lu, Y.; Kang, W.; Bai, B.; Hou, J. Spontaneous Emulsification via Once Bottom-Up Cycle for the Crude Oil in Low-Permeability Reservoirs. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 3119–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riehm, D.A.; Rokke, D.J.; Paul, P.G.; Lee, H.S.; Vizanko, B.S.; McCormick, A.V. Dispersion of oil into water using lecithin-Tween 80 blends: The role of spontaneous emulsification. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 487, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, H.; Zhang, G.; Ge, J.; Jin, L.; Liu, X. Analysis of Microscopic Displacement Mechanisms of Alkaline Flooding for Enhanced Heavy-Oil Recovery. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 4423–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabar, M.K.; Nguyen, C.V.; Phan, C.M. Quantifying the Influence of Salinity on Spontaneous Emulsification of Hydrocarbons. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 588, 124376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.S.; Zhdanov, S.; Starov, V.M.; Holdich, R.G. Spontaneous emulsification of water in oil at appreciable interfacial tensions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 521, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.; Zhong, Q. Lemon oil nanoemulsions fabricated with sodium caseinate and Tween 20 using phase inversion temperature method. J. Food Eng. 2016, 171, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, Z.U.; Rehman, N.; Ali, F.; Khan, N.M.; Ullah, H. Physico-chemical properties of cationic surfactant cetyltrimethylammonium bromide in the presence of electrolyte. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2017, 8, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Collot, M.; Vandamme, T.F.; Anton, N. Study of the spontaneous nano-emulsification process with different octadecyl succinic anhydride derivatives. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 645, 128858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D 4124-09; Standard Test Method for Separation of Asphalt into Four Fraction Analysis of Soils. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009.
- Jewell, D.M.; Weber, J.H.; Bunger, J.W.; Plancher, H.; Latham, D.R. Ion-exchange, coordination, and adsorption chromatographic separation of heavy-end petroleum distillates. Anal. Chem. 1972, 44, 1391–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Reineccius, G.A. Factors Controlling the Turbidity of Submicron Emulsions Stabilized by Food Biopolymers and Natural Surfactant. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 71, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Density/g·cm−3 | SARA Fraction Content of GD-2 Oil/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| w (Saturates) | w (Aromatics) | w (Resins) | w (Asphaltenes) | |
| 0.9282 | 28.79 | 32.15 | 28.62 | 8.97 |
| Viscosity/mPa·s at 50 °C | Acidic–Basic Fraction Content of Asphaltenes/% | |||
| w (Acidic) | w (Basic) | w (Amphoteric) | w (Neutral) | |
| 965 | 7.69 | 5.68 | 7.57 | 76.72 |
| Components | Element Contents/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w (C) | w (H) | w (S) | w (O) | w (N) | |
| Saturates | 85.56 | 13.59 | 0.55 | 0.30 | 0 |
| Aromatics | 85.50 | 12.82 | 1.18 | 0.37 | 0.13 |
| Resins | 85.37 | 11.49 | 1.47 | 0.91 | 0.76 |
| Asphaltenes | 84.15 | 8.96 | 3.24 | 2.17 | 1.48 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Lun, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, P.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Q. Factors, Mechanisms, and Kinetics of Spontaneous Emulsification for Heavy Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Molecules 2024, 29, 2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29132998
Liu J, Li Y, Lun Z, Zhang Y, Yang P, Tang X, Zhang Q. Factors, Mechanisms, and Kinetics of Spontaneous Emulsification for Heavy Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Molecules. 2024; 29(13):2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29132998
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jinhe, Yao Li, Zengmin Lun, Yuhui Zhang, Pujiang Yang, Xinyu Tang, and Qingxuan Zhang. 2024. "Factors, Mechanisms, and Kinetics of Spontaneous Emulsification for Heavy Oil-in-Water Emulsions" Molecules 29, no. 13: 2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29132998
APA StyleLiu, J., Li, Y., Lun, Z., Zhang, Y., Yang, P., Tang, X., & Zhang, Q. (2024). Factors, Mechanisms, and Kinetics of Spontaneous Emulsification for Heavy Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Molecules, 29(13), 2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29132998






