Inhibiting Escherichia coli Growth by Optimized Low-Power Microwave Irradiation—Delivery of Ag and Au Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
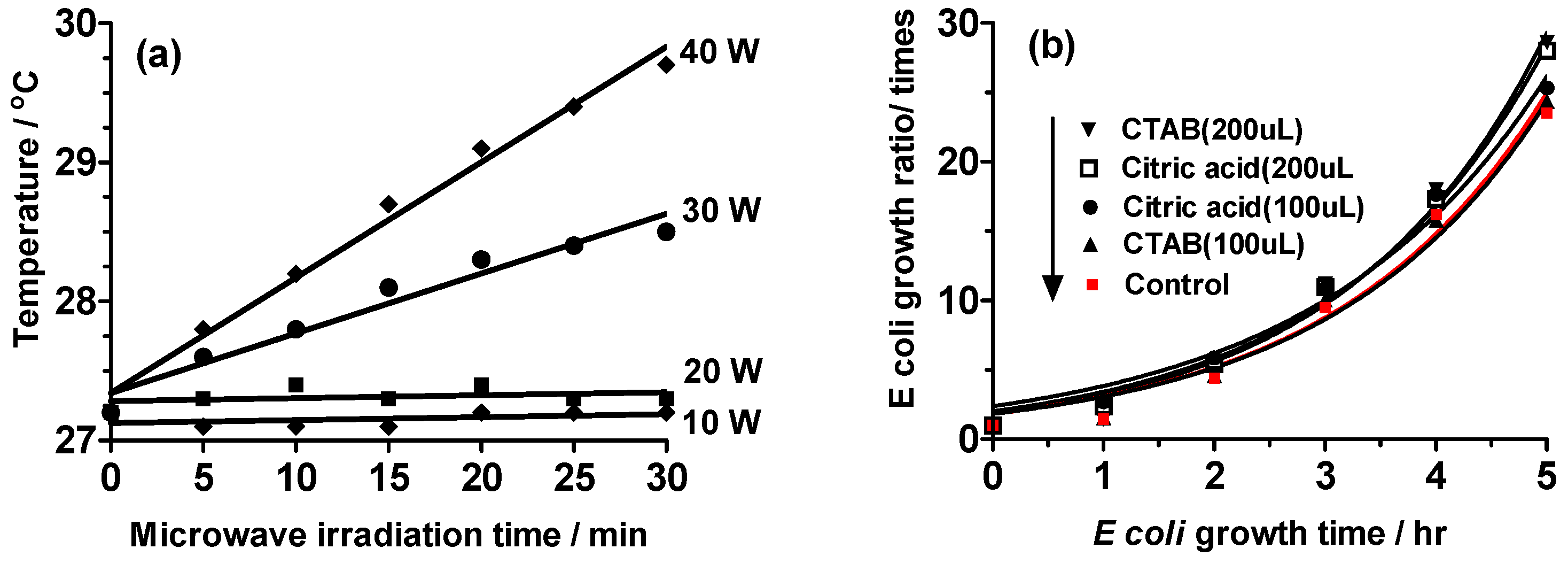
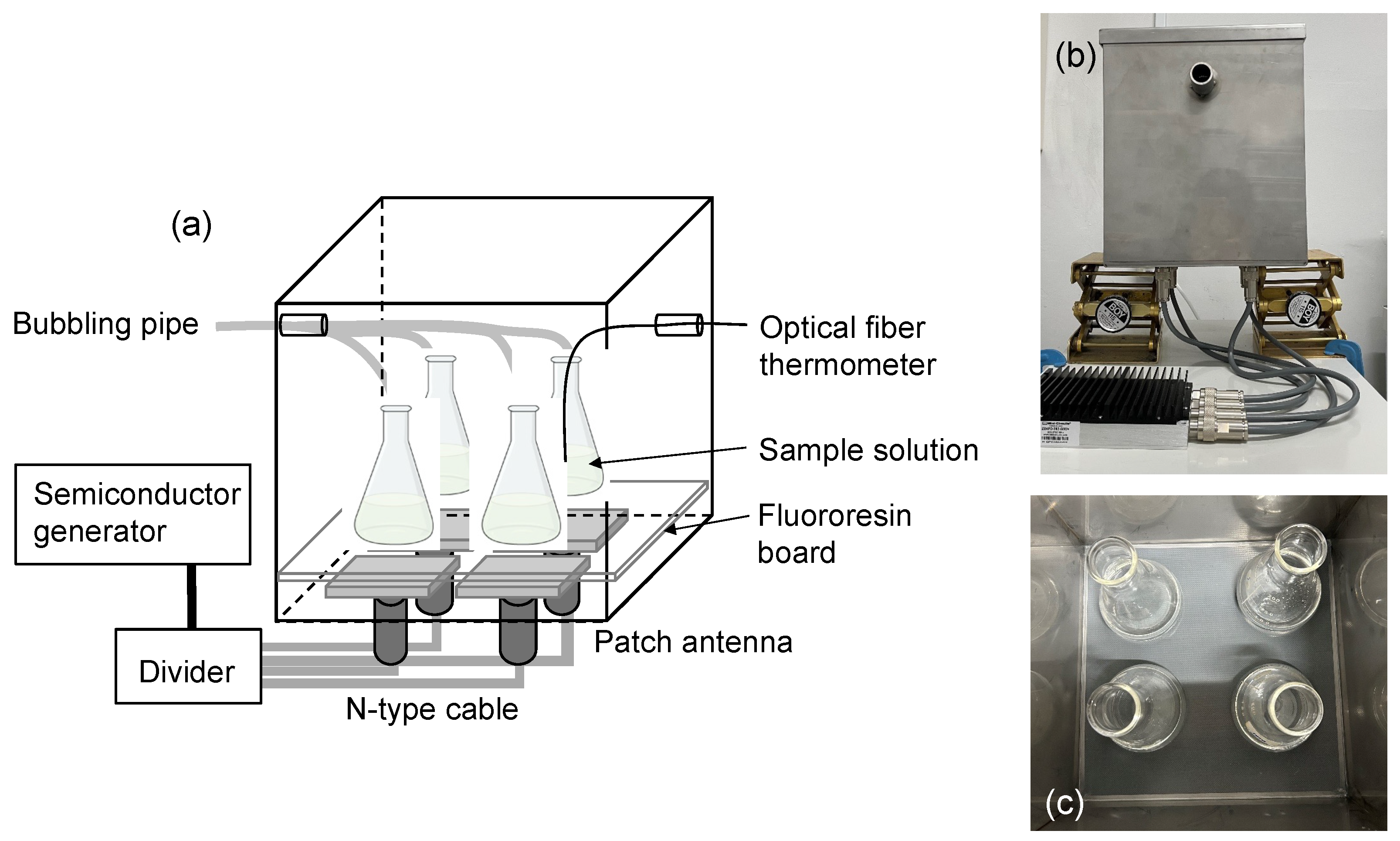
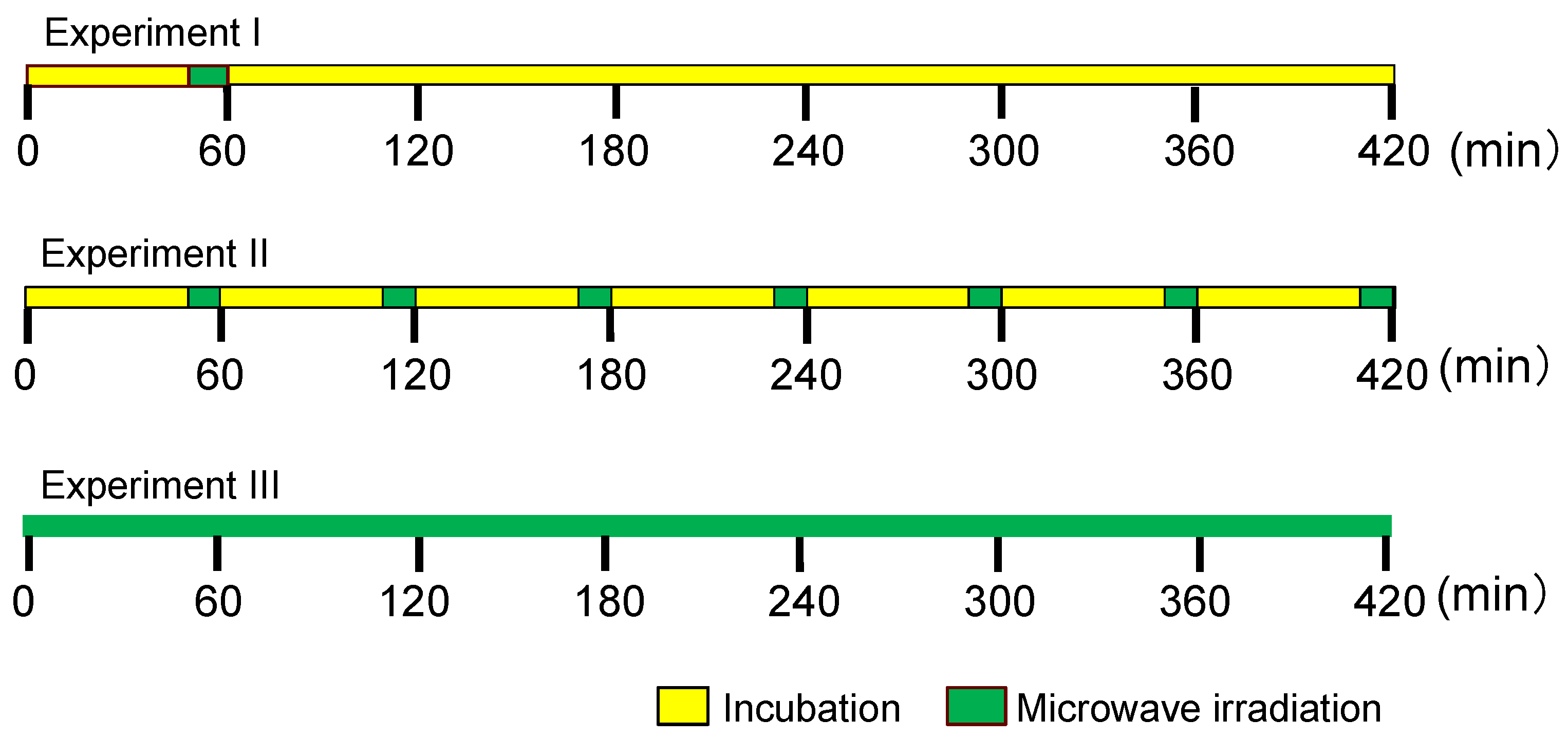
2.1. Establishing the Experimental Protocols
2.2. Experiment I
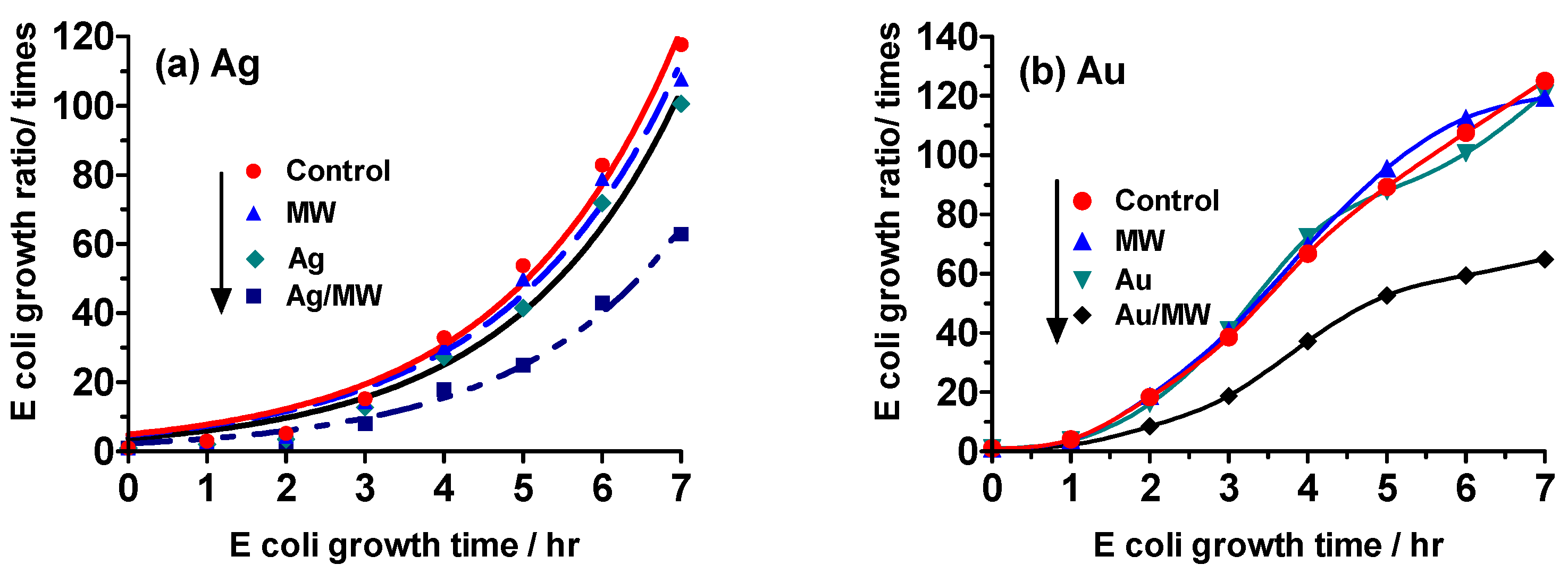
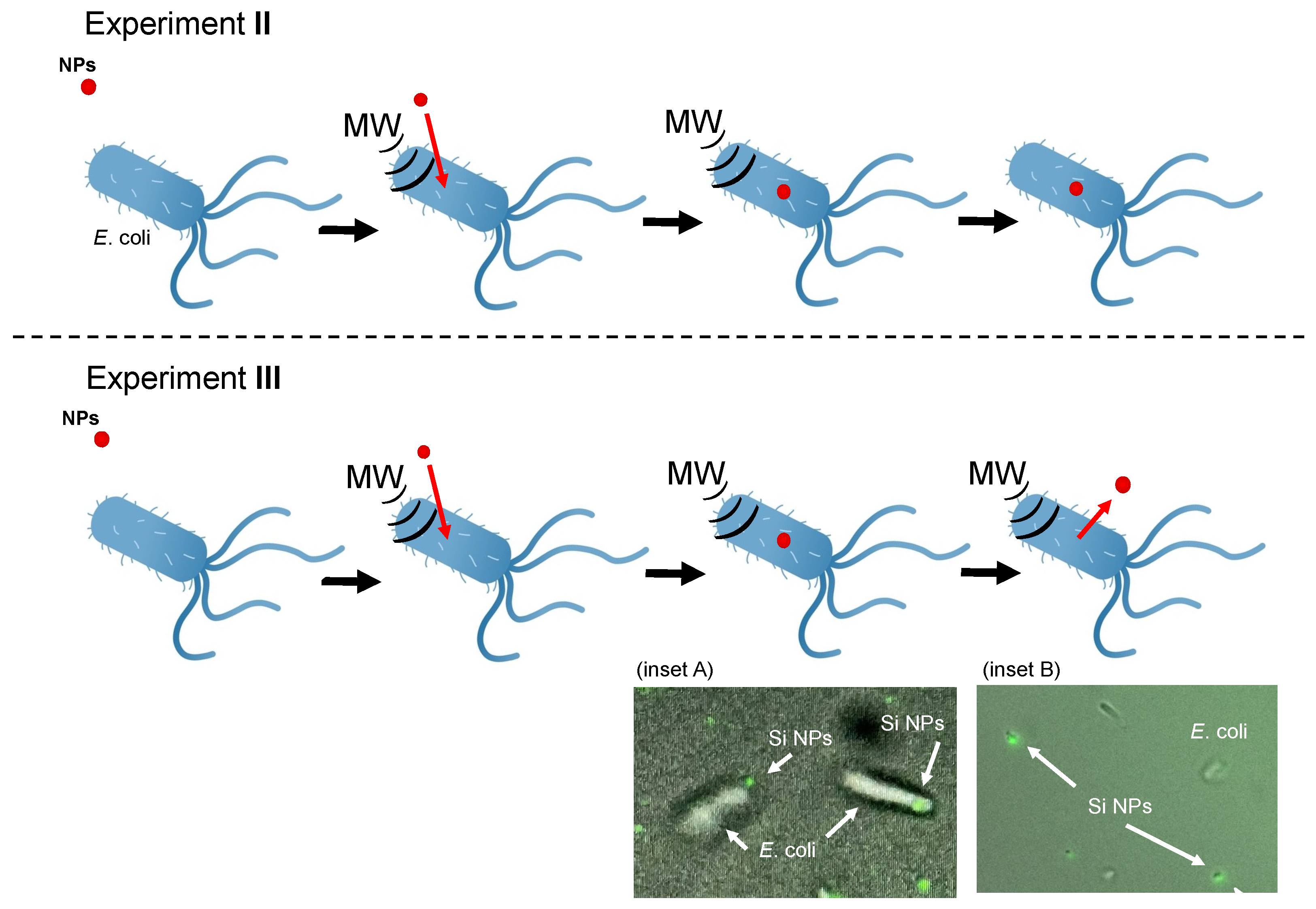
2.3. Experiment II
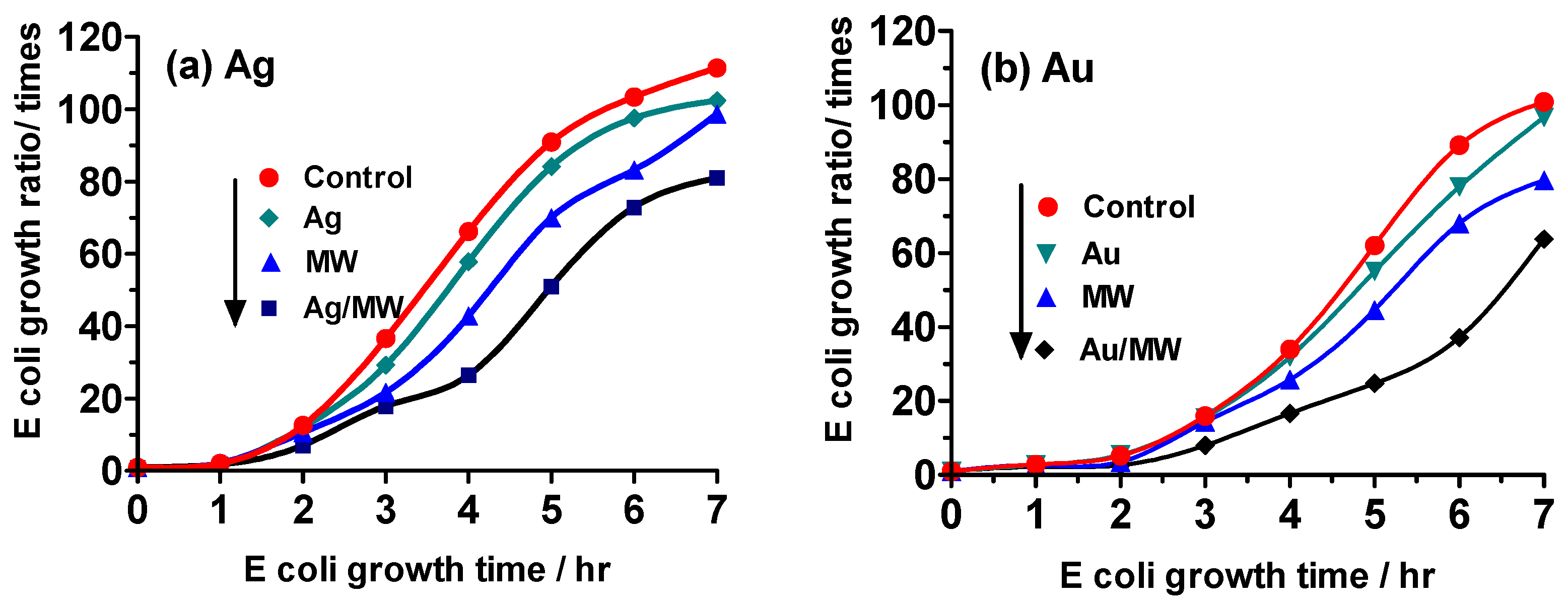
2.4. Experiment III
2.5. Mechanistic Inferences
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Escherichia coli (E. coli) Sample
3.2. Preparation of Nanoparticles
3.3. Microwave Irradiation Equipment
3.4. Experimental Protocol
3.5. Analytical Methods
4. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Horikoshi, S.; Iwabuchi, M.; Kawaguchi, M.; Yasumasu, S.; Serpone, N. Uptake of nanoparticles from sunscreen physical filters into cells arising from increased environmental microwave radiation: Increased potential risk of the use of sunscreens to human health. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2022, 21, 1819–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deruelle, F. Microwave radiofrequencies, 5G, 6G, graphene nanomaterials: Technologies used in neurological warfare. Surg. Neurol. Intern. 2024, 15, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyberg, N.R.; McCredden, J.E.; Weller, S.G.; Hardell, L. The European Union prioritizes economics over health in the rollout of radiofrequency technologies. Rev. Environ. Health 2022, 39, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization; International Agency for Research on Cancer. Press Release No. 208, 2011. International Agency for Research on Cancer. Available online: https://www.iarc.who.int/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/pr208_E.pdf (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Hardell, L.; Nyberg, R. Appeals that matter or not on a moratorium on the deployment of the fifth generation, 5G, for microwave radiation. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 12, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Hu, Y.; Wang, L. Microwaves, a potential treatment for bacteria: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 888266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, I.; Peng, C.; Khan, Z.M.; Naz, I.; Sultan, M.; Ali, M.; Abbasi, I.A.; Islam, T.; Ye, T. Overview of microbes based fabricated biogenic nanoparticles for water and wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 230, 128–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolim, W.R.; Pelegrino, M.T.; de Araújo Lima, B.; Ferraz, L.S.; Costa, F.N.; Bernardes, J.S.; Rodigues, T.; Brocchi, M.; Seabra, A.B. Green tea extract mediated biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Characterization, cytotoxicity evaluation and antibacterial activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 63, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandcolas, M.; Ye, J.; Hanagata, N. Combination of photocatalytic and antibacterial effects of silver oxide loaded on titania nanotubes. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Foldbjerg, R.; Miclaus, T.; Wang, L.; Singh, R.; Hayashi, Y.; Sutherland, D.; Chen, C.; Autrup, H.; Beer, C. Multi-platform genotoxicity analysis of silver nanoparticles in the model cell line CHO-K1. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 222, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Xiong, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Yuan, F.; Xi, T. Distribution, translocation and accumulation of silver nanoparticles in rats. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 9, 4924–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Li, B.; Han, Y.; Li, Z.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Liang, Y.; Zhu, S.; et al. Microwave-assisted antibacterial action of Garcinia nanoparticles on Gram-negative bacteria. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abhishek, K.; Bhardwaj, A.K.; Shukla, A.; Mishra, R.K.; Singh, S.C.; Mishra, V.; Uttam, K.N.; Singh, M.P.; Sharma, S.; Gopal, R. Power and time-dependent microwave assisted fabrication of silver nanoparticles decorated cotton (SNDC) fibers for bacterial decontamination. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 330–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.H.P.; Shamis, Y.; Croft, R.J.; Wood, A.; Crawford, R.L.; Ivanova, E.P. 18 GHz electromagnetic field induces permeability of Gram-positive cocci. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.X.; Wang, F.; Li, X.; Sun, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.; Ou, C.R.; Shao, X.F.; Pan, D.D.; Wang, D.I. The Influence of Microwave Sterilization on the Ultrastructure, Permeability of Cell Membrane and Expression of Proteins of Bacillus Cereus. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, P.; Kumar, N.; Mumtaz, S.; Lim, J.S.; Jang, J.H.; Sahu, B.D.; Bogaerts, A.; Choi, E.H. Evaluation of non-thermal effect of microwave radiation and its mode of action in bacterial cell inactivation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.L.; Kuo, C.-H.; Huang, M.H. Seed-mediated synthesis of gold nanocrystals with systematic shape evolution from cubic to trisoctahedral and rhombic dodecahedral structures. Langmuir 2010, 26, 12307–12313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanimoto, H.; Ohmura, S.; Maeda, Y. Size-selective formation of hexagonal silver nanoprisms in silver citrate solution by monochromatic-visible-light irradiation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 15819−15825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fus-Kujawa, A.; Prus, P.; Bajdak-Rusinek, K.; Teper, P.; Gawron, K.; Kowalczuk, A.; Sieron, A.L. An overview of methods and tools for transfection of eukaryotic cells in vitro. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. Sec. Cell Gene Ther. 2021, 9, 701031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yokota, Y.; Itabashi, N.; Kawaguchi, M.; Uchida, H.; Serpone, N.; Horikoshi, S. Inhibiting Escherichia coli Growth by Optimized Low-Power Microwave Irradiation—Delivery of Ag and Au Nanoparticles. Molecules 2025, 30, 1871. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091871
Yokota Y, Itabashi N, Kawaguchi M, Uchida H, Serpone N, Horikoshi S. Inhibiting Escherichia coli Growth by Optimized Low-Power Microwave Irradiation—Delivery of Ag and Au Nanoparticles. Molecules. 2025; 30(9):1871. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091871
Chicago/Turabian StyleYokota, Yukie, Nazuna Itabashi, Mari Kawaguchi, Hiroshi Uchida, Nick Serpone, and Satoshi Horikoshi. 2025. "Inhibiting Escherichia coli Growth by Optimized Low-Power Microwave Irradiation—Delivery of Ag and Au Nanoparticles" Molecules 30, no. 9: 1871. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091871
APA StyleYokota, Y., Itabashi, N., Kawaguchi, M., Uchida, H., Serpone, N., & Horikoshi, S. (2025). Inhibiting Escherichia coli Growth by Optimized Low-Power Microwave Irradiation—Delivery of Ag and Au Nanoparticles. Molecules, 30(9), 1871. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091871









