Abstract
Xanthomonas campestris pathovar campestris (Xcc) is a significant phytopathogen causing black rot disease in crucifers. Xcc injects a variety of type III effectors (T3Es) into the host cell to assist infection or propagation. A number of T3Es inhibit plant immunity, but the biochemical basis for a vast majority of them remains unknown. Previous research has revealed that the evolutionarily conserved XopL-family effector XopLXcc inhibits plant immunity, although the underlying mechanisms remain incompletely elucidated. In this study, we identified proton pump interactor (PPI1) as a specific virulence target of XopLXcc in Arabidopsis. Notably, the C-terminus of PPI1 and the Leucine-rich repeat (LRR) domains of XopLXcc are pivotal for facilitating this interaction. Our findings indicate that PPI1 plays a role in the immune response of Arabidopsis to Xcc. These results propose a model in which XopLXcc binds to PPI1, disrupting the early defense responses activated in Arabidopsis during Xcc infection and providing valuable insights into potential strategies for regulating plasma membrane (PM) H+-ATPase activity during infection. These novel insights enhance our understanding of the pathogenic mechanisms of T3Es and contribute to the development of effective strategies for controlling bacterial diseases.
1. Introduction
Xanthomonas is a genus of Gram-negative phytopathogens that threatens >400 plant species worldwide. Most Xanthomonas species utilize the type III secretion system to directly inject type III effector proteins (T3Es) into plant cells [1]. Once inside, T3SEs contribute to pathogenesis, where a few are required for full pathogen virulence, and promote pathogen propagation in the host. Some are perceived by pattern recognition receptors (PPRs) to suppress pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP)-triggered immunity (PTI); and others are monitored by the proteins of the host to activate strong defense responses [1,2,3].
Xanthomonas campestris pathovar campestris (Xcc) is the causal agent of black rot diseases in numerous crucifer plant genera, such as Brassica and Arabidopsis [4]. Recently, the pathogenesis mechanisms of Xcc have been studied widely, with >100 genes contributing to its pathogenicity [5,6,7,8,9]. In the Xcc 8004 genome, 34 putative genes encode T3Es [5]; yet, only a handful, including XopD, AvrXccC, XopL, XopAC, XopAM, XopN, and XopJ, have been functionally investigated [10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18]. Many of them inhibit plant immunity, but the underlying mechanisms are not fully understood.
XopLXcc (also known as XopXccLR and XopLXcc8004) is an LRR protein encoded by XC_4273 (Gene ID: 3379891) [16,19,20]. Its homologs or analogs are present in all the sequenced Xanthomonas species or pathovars. XopLs play a significant role in the virulence of Xanthomonas euvesicatoria (Xe) strain 85-10 in tomatoes [21]; X. axonopodis pv. punicae (Xap) in pomegranates [22]; and Xcc 8004 in Chinese radish, Chinese cabbage, and Arabidopsis [16,19,20]. XopLXcc is a crucial T3E that disrupts innate immunity in Arabidopsis by suppressing PTI signaling independent of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) [16,20]. Despite these findings, the specific virulence targets and underlying mechanisms of XopLXcc remain incompletely elucidated.
In plants, the plasma membrane (PM) H+-ATPase, the well-known PM H+ pump, is a central regulator in plant physiology, which mediates not only growth and development but also adaptation to diverse environmental stimuli [23,24]. In vivo, its activity is modulated by various signals, with the major regulators being 14-3-3 family proteins, which bind to the auto inhibitory domain in the C-terminus of the ATPase, thereby stimulating pump activity [25]. Limited information exists regarding the regulation of PM H+ ATPase by other effectors. Proton pump interactor 1 (PPI1) is a regulatory protein that interacts with the regulatory C-terminus of the Arabidopsis PM H+-ATPase at a site distinct from the 14-3-3 binding site, thereby stimulating its activity in vitro [24,26]. The main part of PPI1 is localized at the endoplasmic reticulum, from which it might translocate to the PM for interaction with H+-ATPase in response to as-yet-unidentified signals [27]. PPI1 is highly expressed in most plant organs [28] and has been documented in several species, including Arabidopsis [24], rice [29], potato, and tomato [30]. Additionally, previous research has revealed that PPI1 in plants responds to multiple abiotic stresses, including cold, salt, drought, and Fe deficiency stress [30,31]. However, its role in the plant immune response to pathogens remains unclear.
This study revealed that XopLXcc enhances virulence and suppresses innate immunity by targeting the proton pump interactor 1 (PPI1), a potential player in Arabidopsis immune responses. Moreover, the C-terminus of PPI1 and the LRR domains of XopLXcc play crucial roles in facilitating this interaction. These results led us to propose a model in which XopLXcc binds to PPI1, disrupting the early defense responses activated in Arabidopsis during Xcc infection and providing valuable insights into potential strategies for regulating PM H+-ATPase activity during infection. These insights shed light on the virulence strategies employed by Xcc and offer the potential for the development of novel control strategies against Xcc infections.
2. Results
2.1. Ectopic Expression of XopLXcc Inhibited PTI to Promote Xcc 8004 Proliferation in Arabidopsis
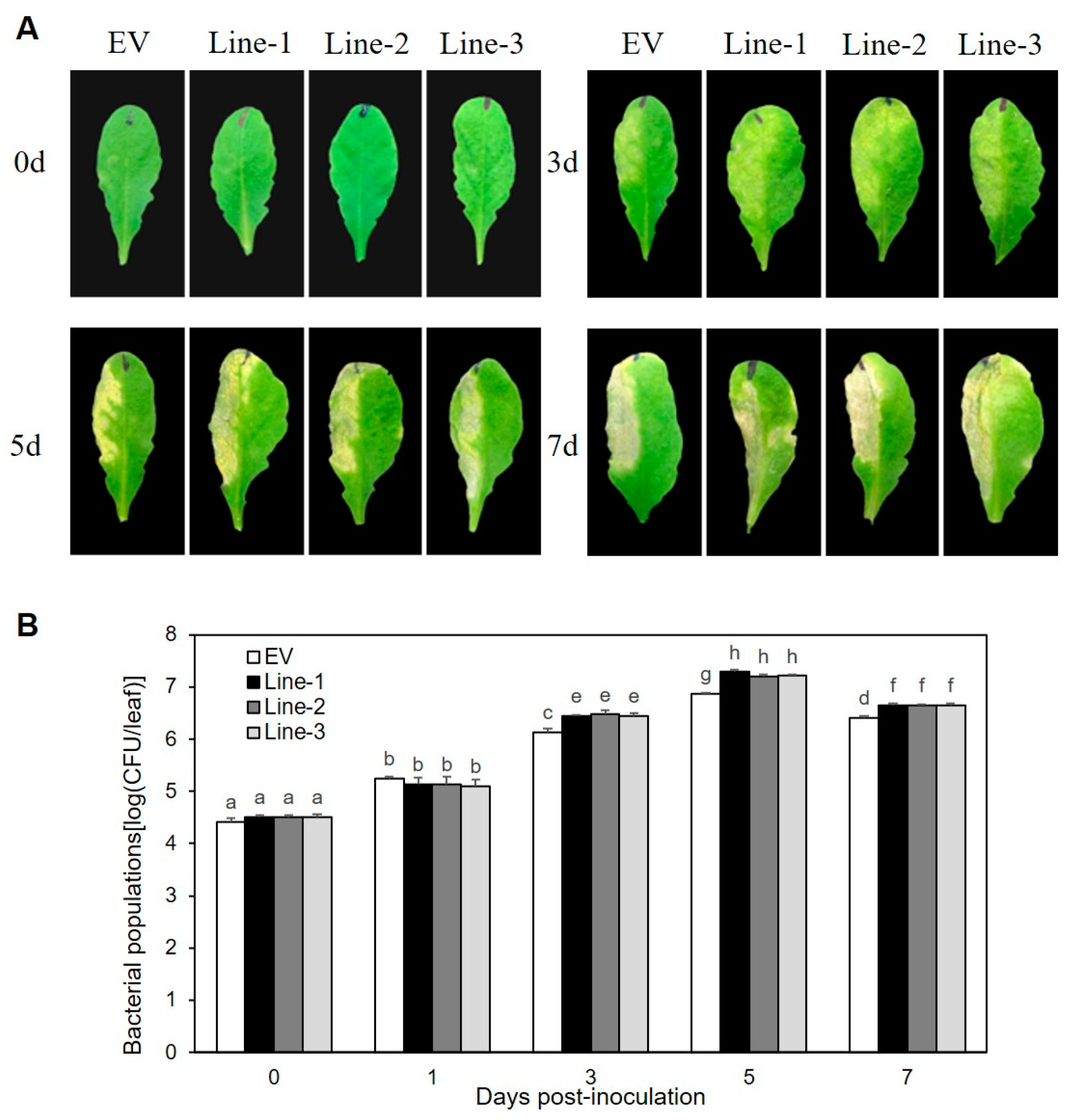
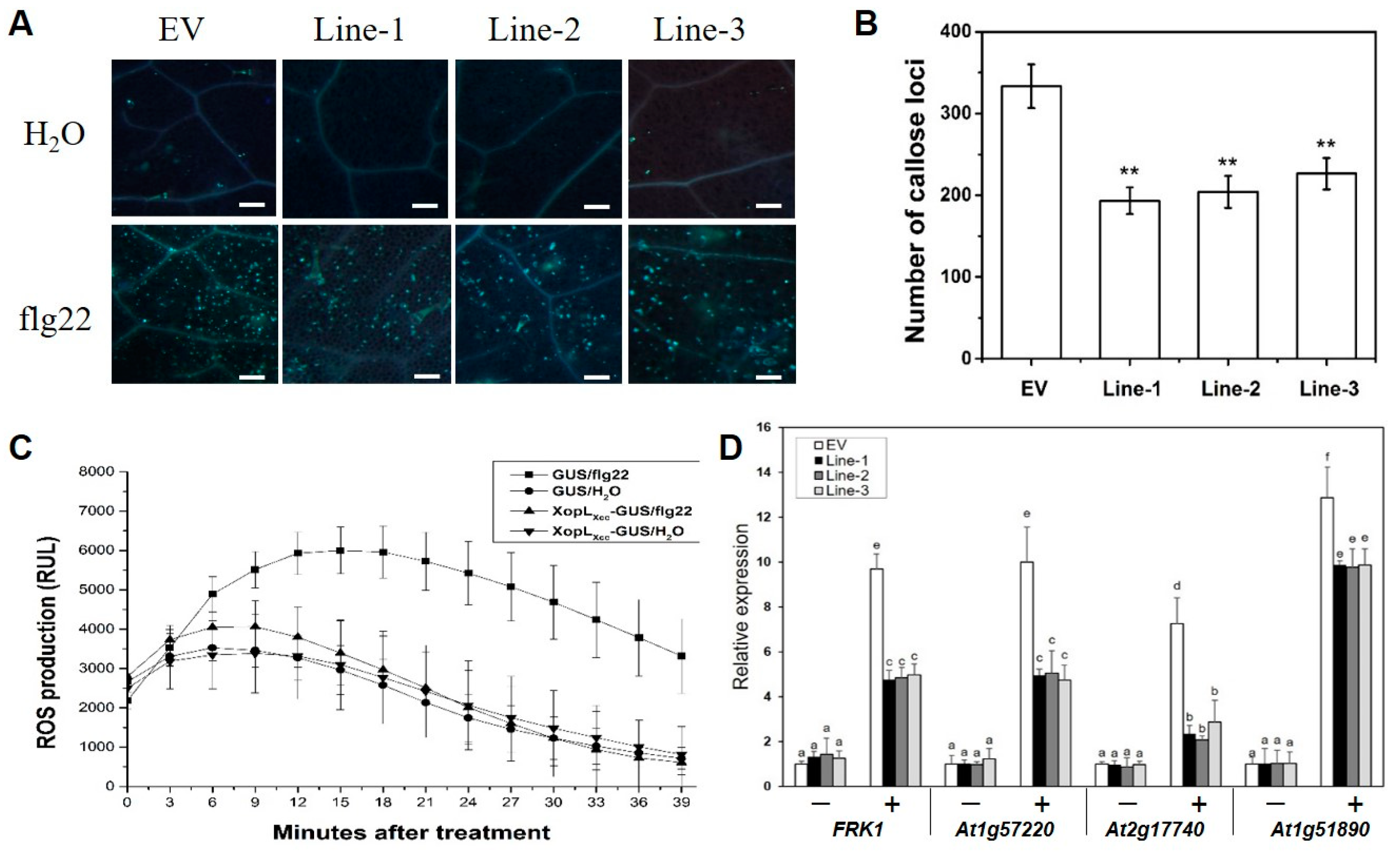
The roles of XopLXcc in the pathogenic processes of Xcc 8004 were investigated by constructing three independent transgenic lines (Line1, -2, and -3) that overexpressed 35S::XopLXcc:GUS (Figure S1). Upon exposure to Xcc 8004, all three lines exhibited more severe disease symptoms (Figure 1A) and harbored significantly larger bacterial populations compared to the control plants (Figure 1B). The flg22-induced accumulation of callose deposition (Figure 2A,B) and oxidative burst (Figure 2C) were suppressed in these lines. Additionally, the impact of XopLXcc on disease resistance in Arabidopsis was assessed by analyzing the expression of four established PTI-related genes, including FRK1. Subsequent to inoculation with Xcc 8004ΔhrcV, their transcript levels in XopLXcc transgenic plants were reduced by varying degrees (Figure 2D). In conclusion, these findings demonstrate that XopLXcc suppresses plant PTI by inhibiting the expression of PTI-related genes, the generation of flg22-induced ROS, and callose deposition in Arabidopsis.
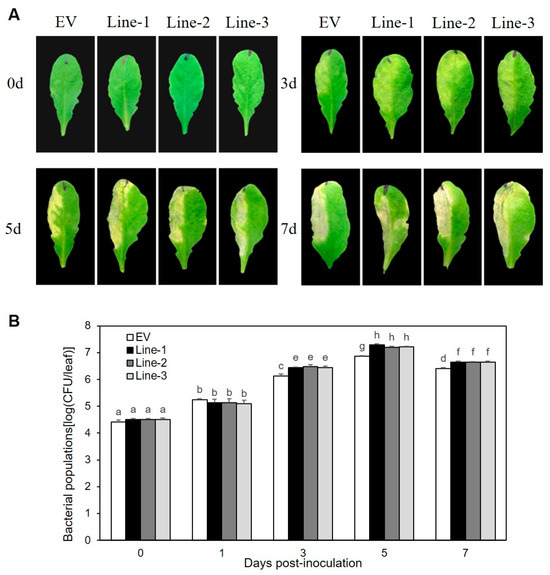
Figure 1.
XopLXcc promotes Xcc 8004 proliferation in Arabidopsis. (A) Disease symptoms. (B) Bacterial populations. Lines-1, -2, and -3 represent the three independent XopLXcc transgenic plants, and EV represents the control plants. The a–g labels on panel (B) represent significant differences (n = 30, p < 0.05; estimated by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD test). The same letters mean no statistically significant differences.
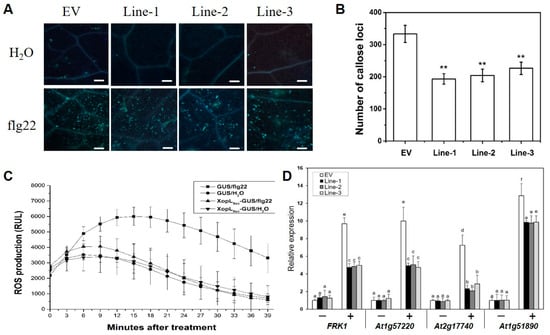
Figure 2.
XopLXcc intercepted pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP)-triggered immunity in Arabidopsis. (A) XopLXcc suppressed flg22-induced callose deposition. Scale bars = 0.1 mm. (B) Average number of callose deposits per field of view. ** p < 0.01 determined by Student’s t-test (n = 30). (C) XopLXcc impaired flg22-induced oxidative burst. RLU, relative light units. (D) Transgenic expression of XopLXcc suppressed PAMP defense response-related genes induced by ΔhrcV. ΔhrcV, T3SS-defective mutant strain. Lines-1, -2, and -3 represent the three independent XopLXcc transgenic plants, and EV represents the control plants. The a-f labels in panel D represent significant differences (n = 30, p < 0.05; estimated by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD test). The same letters mean no statistically significant differences.
2.2. XopLXcc Interacts with PPI1 in Planta and in Yeast
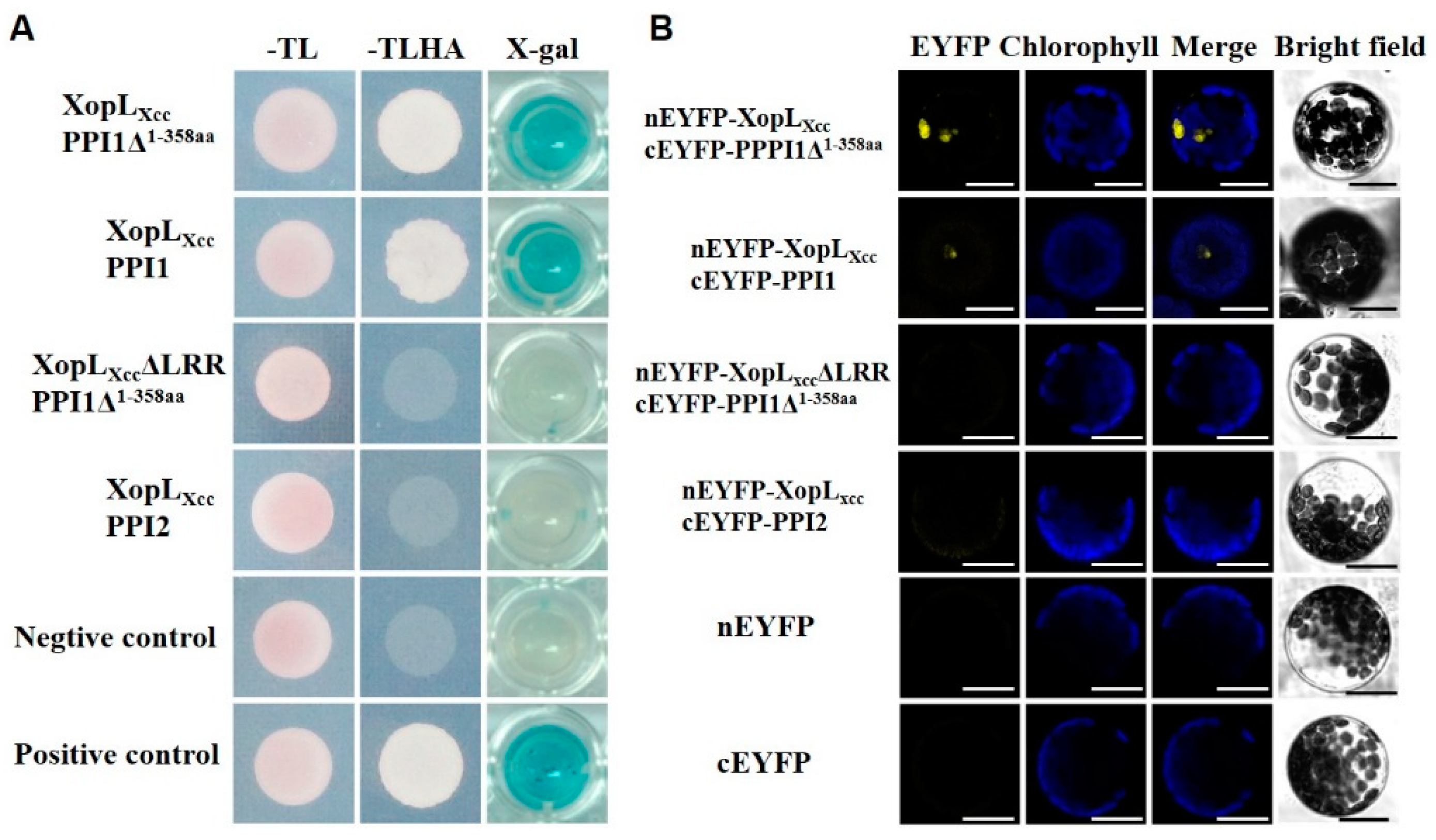
A yeast two-hybrid screen against a normalized Arabidopsis Col-0 cDNA library was conducted to identify XopLXcc interactors (Figure S2, see Methods Section 4). The yeast strain Cub-XopLXcc was utilized as bait, with the cDNA library serving as the prey. A total of 107 primary yeast transformants were screened, resulting in the identification of 30 potential candidates. From these, PPI1, comprising 612 amino acids and encoded by At4g27500, was chosen due to its consistent presence during the screening process. Both the truncated protein PPI1Δ1-358aa (lacking the N-terminal domain from 1 to 358 amino acids) and the full-length PPI1-encoding cDNA interacted with XopLXcc during the yeast two-hybrid point–point verification (Figure 3A). Conversely, no interactions were observed between XopLXcc and PPI2 (a homolog of PPI1), PPI1Δ1-358aa, and XopLXccΔLRR (lacking LRR domains) (Figure 3A).
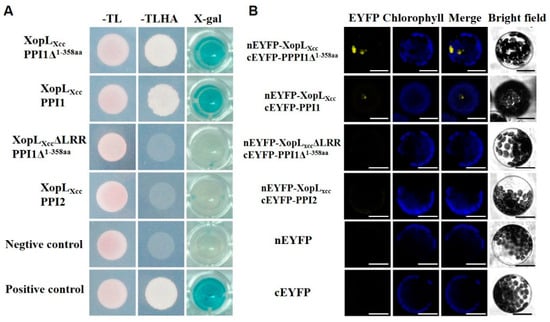
Figure 3.
XopLXcc interacted with PPI1 both in planta and in yeast. (A) Interaction of XopLXcc with PPI1 in the split-ubiquitin-based yeast two-hybrid system. –TL, yeast growth medium lacking Trp and Leu; –TLHA, yeast growth medium lacking Trp, Leu, His, and Ade; X-gal, β-galactosidase activity of yeast transformants. (B) Interaction of XopLXcc with PPI1 ascertained with a BiFC assay. Bars = 20 µm.
The BiFC assay revealed specific interactivity between cEYFP-PPI1Δ1-358aa and nEYFP-XopLXcc in Arabidopsis. As expected, PPI1 and XopLXcc also interplayed with each other in planta (Figure 3B). Consistent with the observations in the yeast two-hybrid experiments, no interaction was evident between PPI2 and XopLXcc or between PPI1Δ1-358aa and XopLXcc ΔLRR in the BiFC assay (Figure 3B). Together, these findings demonstrate that XopLXcc interacts with PPI1 in plant cells. Moreover, the data suggest that XopLXcc binds specifically to the C-terminus of PPI1, highlighting the essential role of the LRR domain in mediating this interactivity.
2.3. PPI1 Can Potentially Influence the Subcellular Localization of XopLXcc
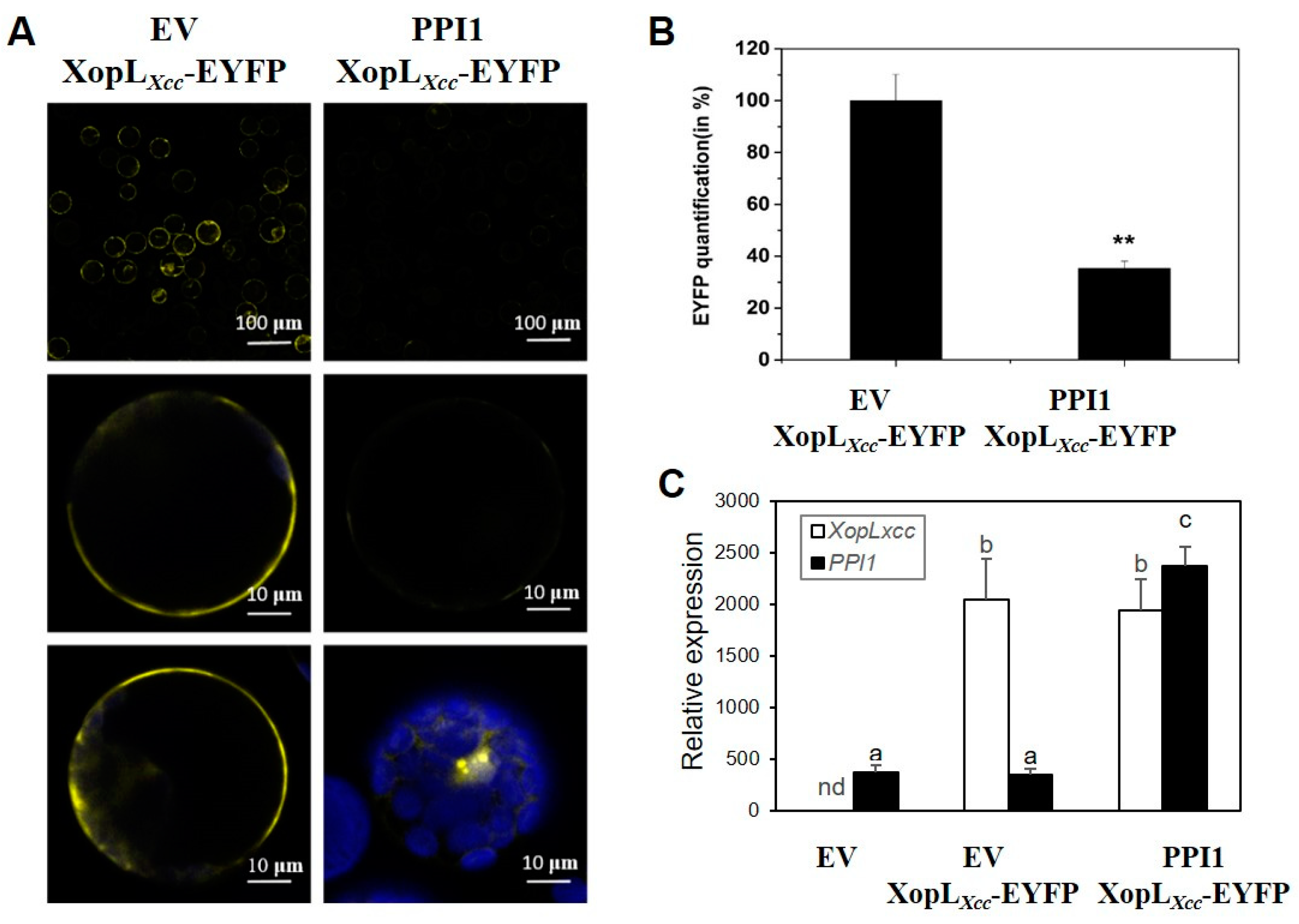
Our prior research established the subcellular localization of XopLXcc to the cell membrane and cytoplasm [20]. However, the results from the BiFC analysis were intriguing as they demonstrated a lack of interaction between XopLXcc and PPI1 in the plasma membrane (PM) (Figure 3B). Following this observation, we conducted transient co-expression experiments involving XopLXcc-EYFP with either the empty vector pXSN (EV) or PPI1 in Arabidopsis protoplasts (Figure 4C). Under consistent fluorescence excitation and detection, significantly diminished fluorescence signals of EYFP at the PM were noted upon co-expression with PPI1 compared to EV (Figure 4A,B). These findings indicate that their interaction may have modified subcellular localization.
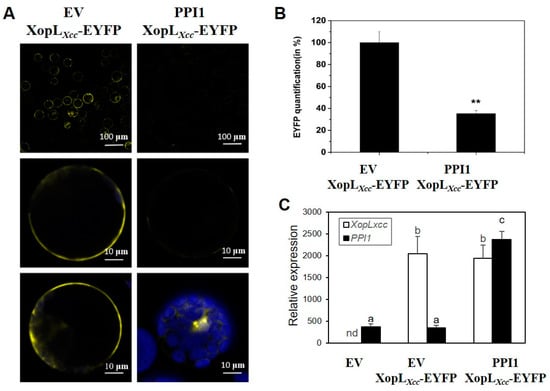
Figure 4.
PPI1 affected the subcellular localization of XopLXcc. (A) EYFP fluorescence was detected in Arabidopsis protoplasts co-expressing XopLXcc-EYFP with either the EV (the left panel) or PPI1(the right panel). Row 1 displays cell fluorescence at a 100 µm scale, while Rows 2 and 3 are shown at a 10 µm scale. Both Rows 2 and 3 were subjected to identical experimental conditions, and each presents two independent typical cells. (B) The fluorescence intensity of EYFP at the Arabidopsis protoplast membrane. ** p < 0.01 estimated by Student’s t-test (n = 50). (C) The expression levels of XopLXcc and PPI1 in Arabidopsis protoplasts. The mRNA levels of all genes were normalized with Atactin2. The a/b/c labels represent significant differences (n = 30, p < 0.05; estimated by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD test). The same letters indicate no statistically relevant differences.
2.4. PPI1 Plays a Role in Arabidopsis Immune Response to Xcc
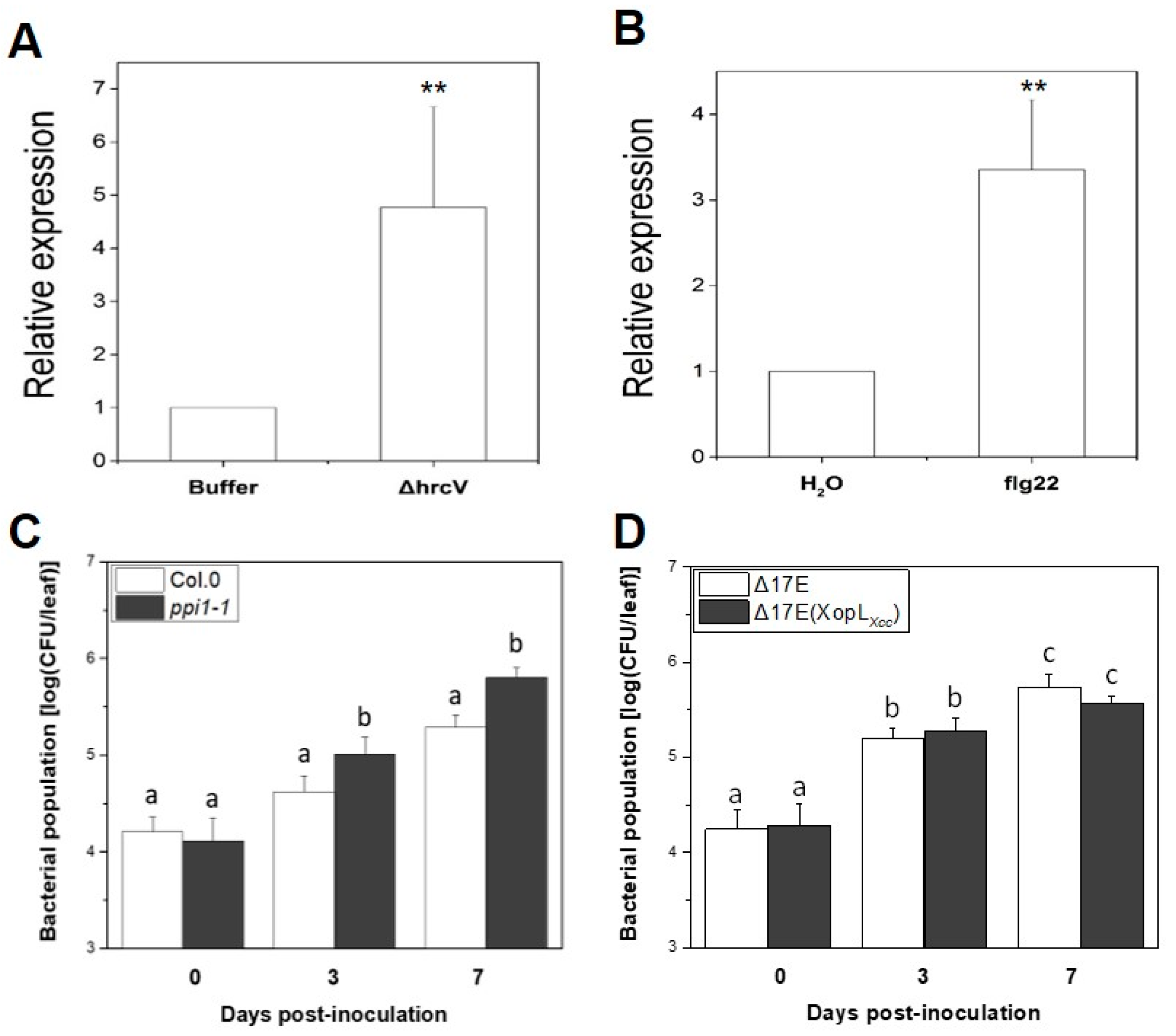
PPI1 encodes proton pump interactor 1, which can bind to the Arabidopsis PM H+-ATPase (EC 3.6.3.6) and stimulate its activity [27]. However, the function and specific signaling mechanisms to which PPI1 responds to remain unknown. Inoculation with Xcc 8004ΔhrcV or the flg22 peptide (a 22-amino-acid sequence from the N-terminal region of flagellin) led to a 3–7-fold increase in PPI1 expression in Arabidopsis Col-0 (Figure 5A,B). The role of PPI1 in the response of Arabidopsis to Xcc infection was further investigated by inoculating both the wild-type Col-0 and a PPI1 loss-of-function mutant, ppi1-1 (SALK_042646C), with 106 CFU/mL of the Xcc 8004ΔhrcV mutant (see Methods Section 4). As anticipated, ppi1-1 exhibited markedly enhanced ΔhrcV bacterial growth compared to the wild type (Figure 5C). A previous study observed that XopLXcc could amplify the pathogenicity of Δ17E (Xcc 8004 strain lacking 17 known T3Es, including XopLXcc, as described in Table S2) in the Col-0 genotype [20]. When the same experimental procedure was applied to ppi1-1, no significant variations in bacterial growth were observed, as anticipated (Figure 5D). These results indicate that PPI1 potentially plays a role in the immune response of Arabidopsis to Xcc and support the hypothesis that PPI1 is a target of XopLXcc.
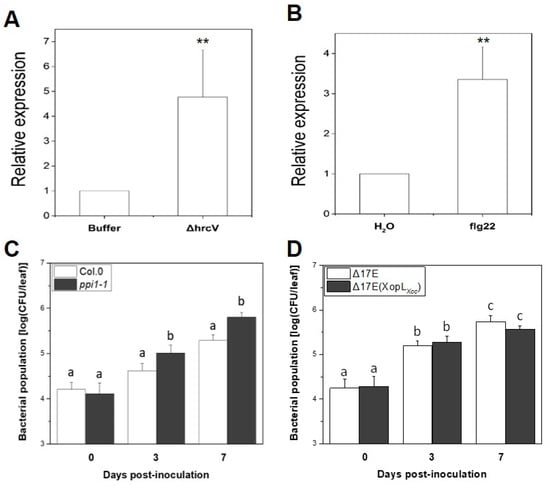
Figure 5.
PPI1 influenced the resistance of Arabidopsis to Xcc. (A,B) The expression of PPI1 was induced by XccΔhrcV (A) and flg22 (B). Statistically significant differences at ** p < 0.01 were ascertained by Student’s t-test (n = 20). (C,D) Bacterial growth was assessed at 0, 3, and 7 days post-infection. The a/b/c labels represent significant differences (n = 30, p < 0.05; estimated by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD test). The same letters indicate no statistically relevant differences.
2.5. XopLXcc Suppresses Innate Immunity in Arabidopsis by Targeting PPI1
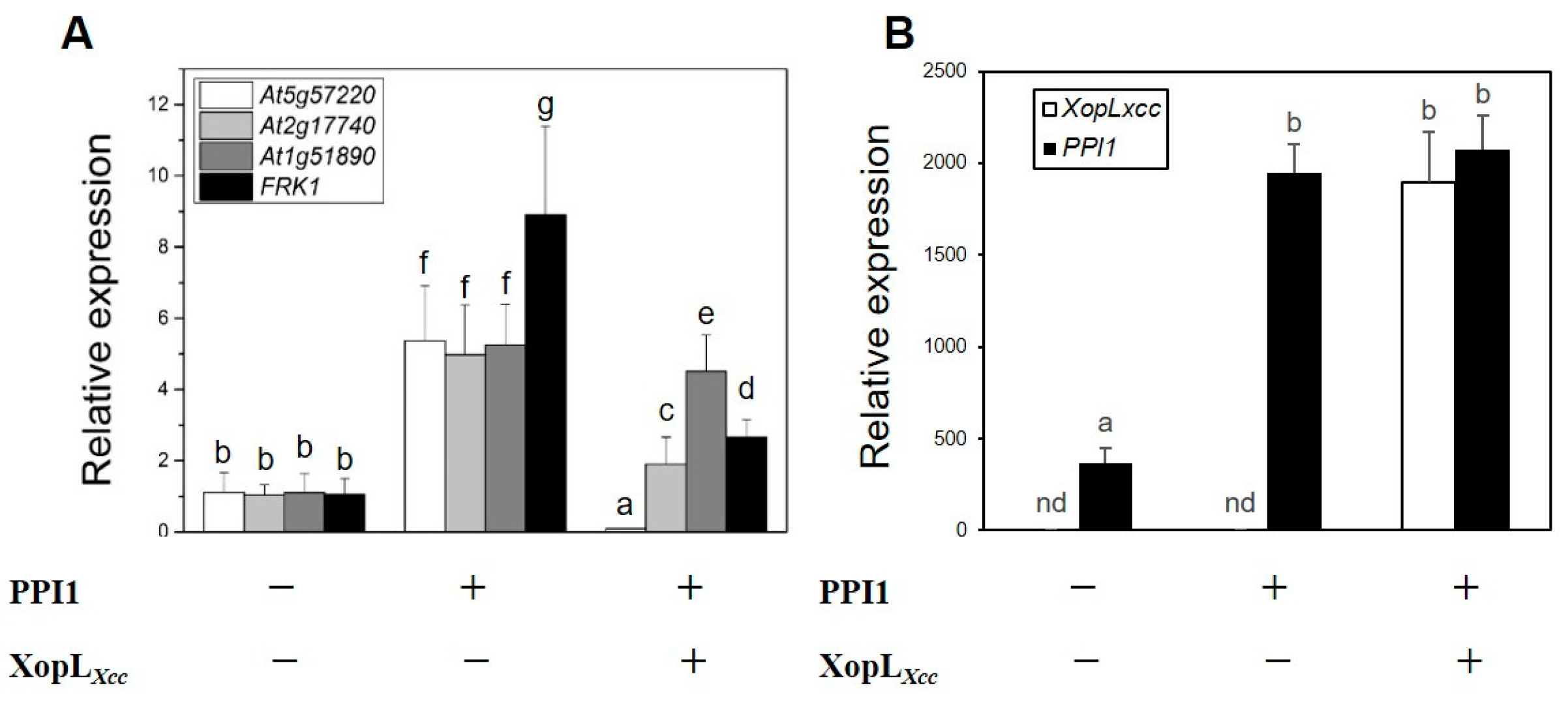
In a previous investigation, XopLXcc was demonstrated to inhibit the expression of four PTI-related genes in Arabidopsis protoplasts [20]. Hence, PPI1 was transiently co-expressed with XopLXcc or empty vector in Col-0 protoplasts (Figure 6B). The results revealed that while PPI1 induced the expression of PTI-related genes by ~5–9 fold, XopLXcc was able to suppress this response by interacting with PPI1 (Figure 6A).
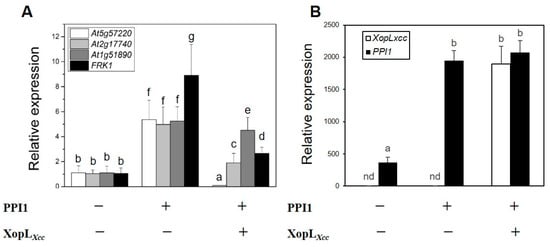
Figure 6.
XopLXcc suppresses the expression of PTI-related genes induced by PPI1. (A) The expression levels of PTI-related genes in XopLXcc or XopLXcc + PPI1-transfected protoplasts of Arabidopsis Col-0. (B) XopLXcc and PPI1 expression levels in protoplasts. The mRNA levels of all genes were normalized to those of Atactin2. The a–g labels represent statistically significant variations (n = 5, p < 0.05, two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD test). The same letters indicate no statistically relevant differences.
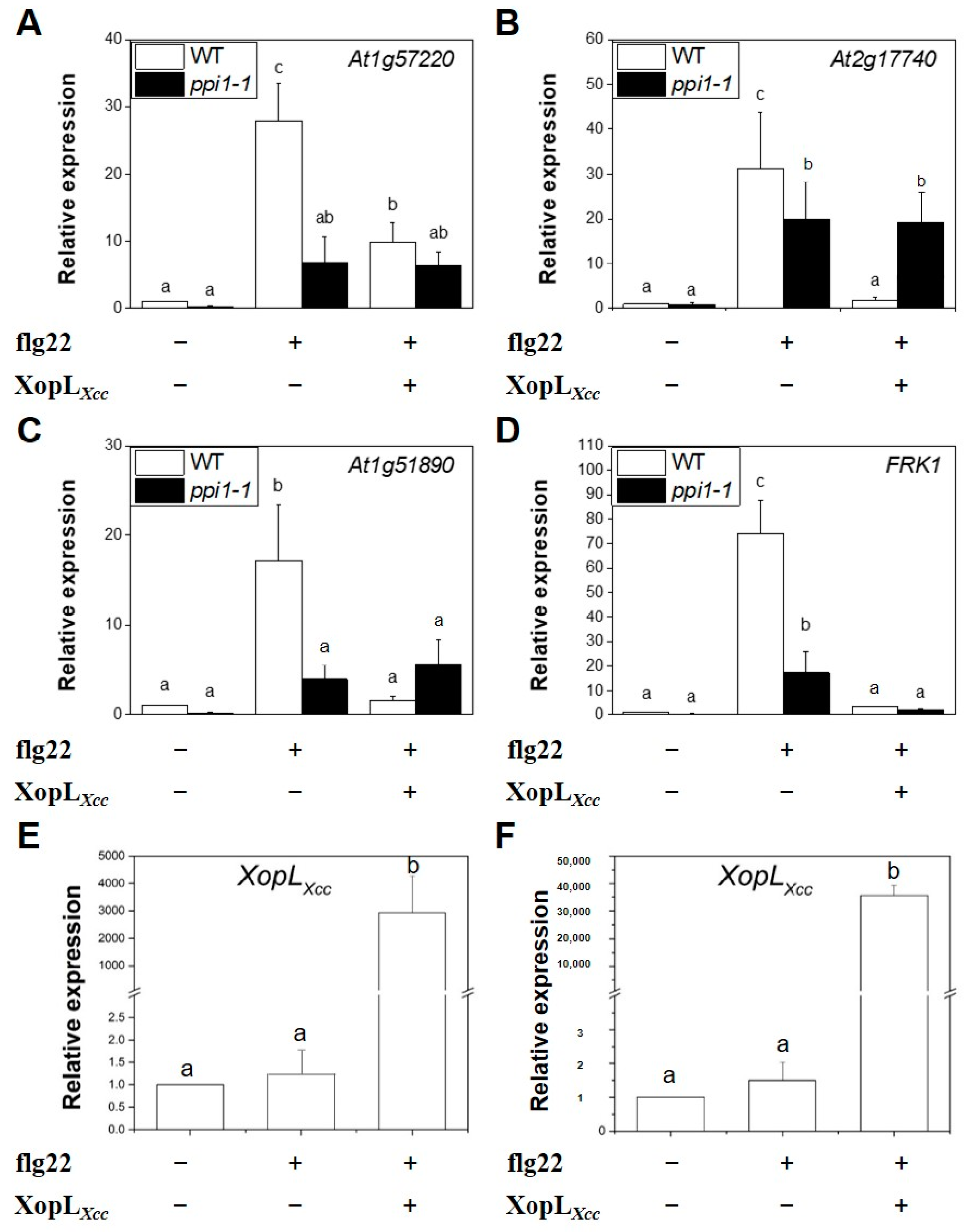
Next, XopLXcc was transiently expressed in Col-0 and ppi1-1 protoplasts (Figure 7E,F). Following treatment with flg22, the expression of the four PTI-related genes in ppi1-1 declined markedly compared to that of the wild-type Col-0 (Figure 7A–D). In Col-0, XopLXcc suppressed the expression of PTI-related genes, which was attenuated in ppi1-1 (Figure 7A–D). These findings underscore the importance of the interaction between PPI1 and XopLXcc in the immune response of Arabidopsis to Xcc.
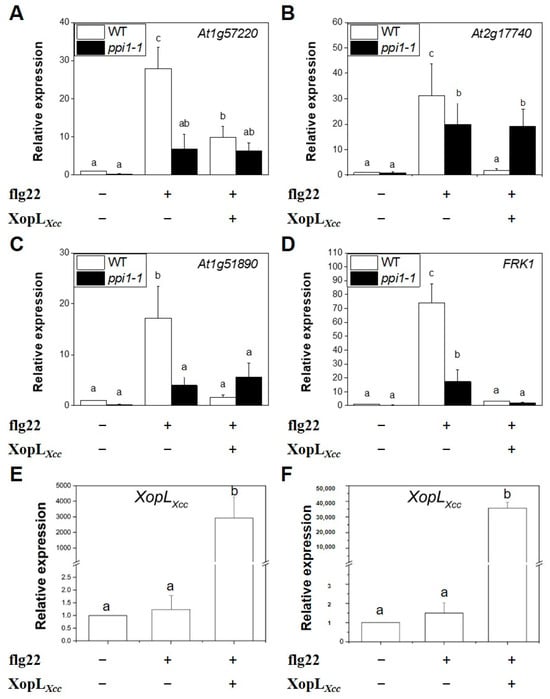
Figure 7.
XopLXcc could not suppress the expression of PTI-related genes in ppi1. (A–D) The expression levels of PTI-related genes in XopLXcc-transfected protoplasts of Arabidopsis Col-0 and ppi1-1. (E,F) The expression levels of XopLXcc in the protoplasts of Col-0 (E) and ppi1-1 (F), respectively. The mRNA levels of all genes were normalized to those of Atactin2, and the relative expression levels were determined in protoplasts transfected with the control vector. The a/b/c labels represent statistically significant variations (n = 5, p < 0.05, two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD test). The same letters indicate no statistically relevant differences.
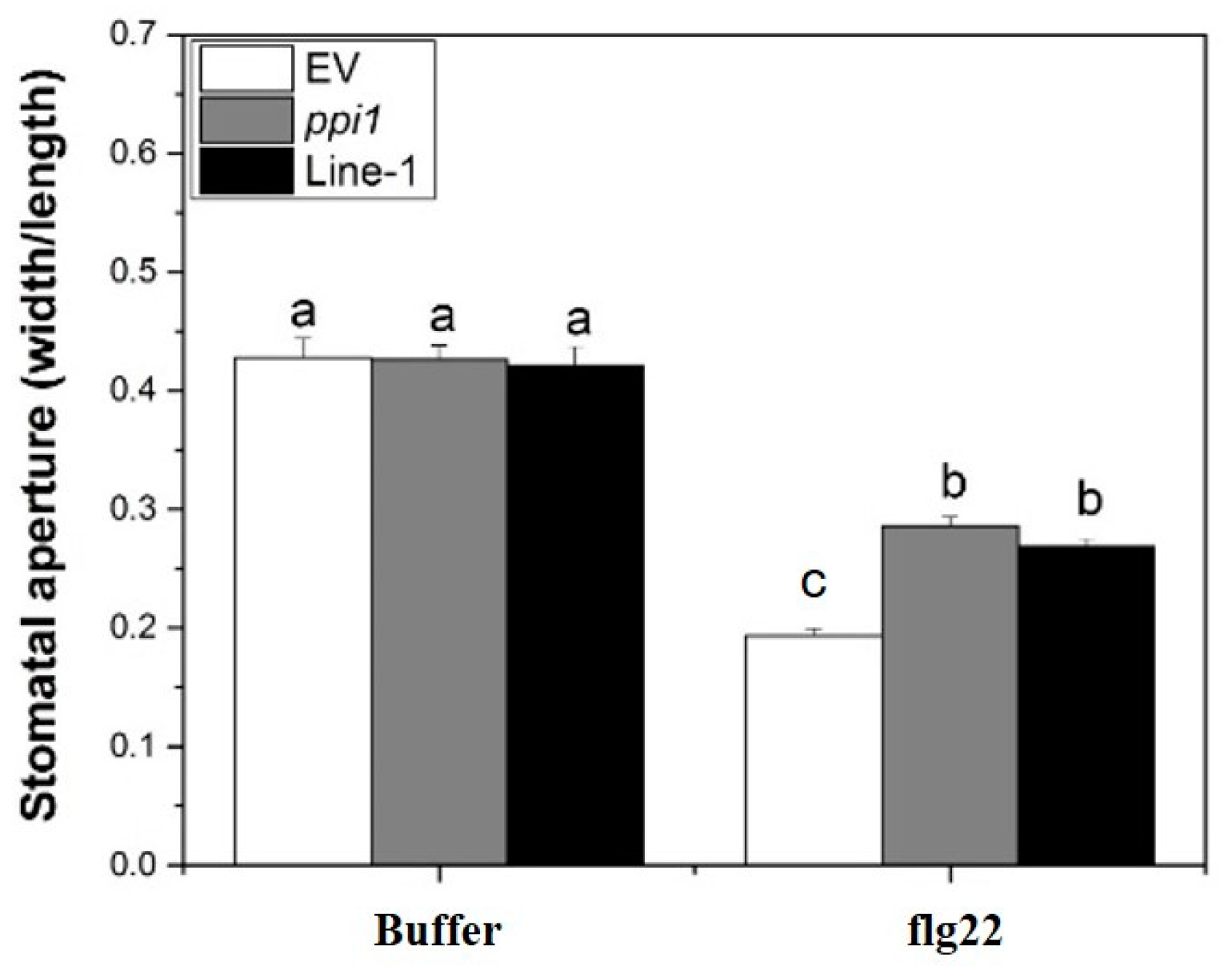
The responses of stomatal apertures to flg22 in different lines were examined to investigate the involvement of PPI1 in flg22 signaling and stomatal immunity. The stomatal apertures of XopLXcc-expressing lines resembled those of ppi1-1, exhibiting a marked increase compared to that in the control (Figure 8). In summary, these results led us to propose a model wherein XopLXcc binds to PPI1, disrupting the early defense responses activated in Arabidopsis during Xcc infection.
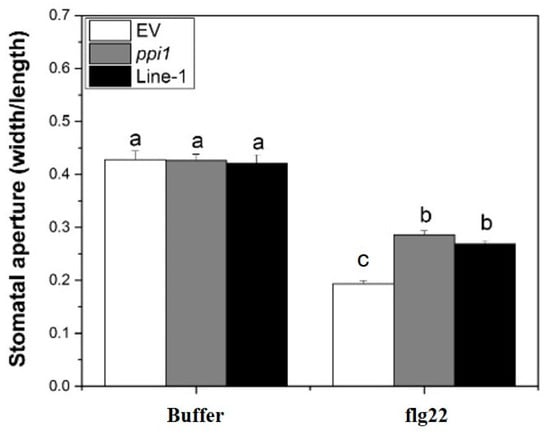
Figure 8.
The ppi1 mutant and XopLXcc-transgenic plants exhibited abolished flg22-induced stomatal closure. The a/b/c labels represent statistically significant variations (n = 50, p < 0.05, two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD test). The same letters indicate no statistically relevant differences.
3. Discussion
Plant pathogenic bacteria commonly secrete T3Es into host cells to modulate host responses, facilitating infection, establishment, and proliferation [1]. For instance, in Xcc 8004, ~12 T3Es, such as XopL, XopD, XopN, XopAC, XopK, and others, inhibited the immunity induced by flg22 in Arabidopsis [9]. Nevertheless, the specific functions and targets of many T3Es remain primarily unclear [32]. Given that Xcc 8004 is responsible for causing economically damaging black rot diseases in multiple crop species [3,4], an urgent need has arisen to identify the targets and illuminate the pathogenic mechanisms of T3Es in this specific pathogenic strain.
XopLXcc is a member of the XopL effector superfamily, which is widespread among Xanthomas species and serves as a core effector group [33]. These effectors are characterized by the presence of homologs with LRR domains and an XL box known for its E3 ligase activity. XopLXcv can suppress the expression of defense-related genes in plants, thereby undermining their immune responses. The XL box is crucial for E3 ubiquitin ligase activity and influences plastid phenotypes [33,34]. However, XopLXap (lacking the XL box) retained the ability to suppress immune responses [22]. XopL from X. euvesicatoria (XopLXe) directly associates with microtubules and causes severe cell death in N. benthamiana [22]. In this study, we observed that XopLXcc suppressed innate plant immunity by reducing the expression of PTI-related genes (Figure 2D) and the generation of flg22-induced callose deposition (Figure 2A,B), as well as reactive oxygen species (ROS) (Figure 2C) in transgenic Arabidopsis. These results are consistent with those of prior studies conducted using protoplasts or distinct transgenic platforms [16,20].
The identification of T3E targets is a fundamental question in plant pathology [35]. Our study revealed that XopLXcc could interact with both PPI1Δ1-358aa and full-length PPI1 through yeast two-hybrid and BiFC assays (Figure 3), indicating PPI1 as one of the primary targets of XopLXcc. Moreover, no interactivity was detected between PPI2 and XopLXcc or PPI1Δ1-358aa and XopLXccΔLRR, suggesting that XopLXcc engages explicitly with the C-terminus of PPI1, with the LRR domains being crucial for this interaction. All proteins containing LRR domains are believed to facilitate protein–protein associations [36]. Various invasive bacterial proteins were identified as containing multiple LRR domains [37]. Consequently, their absence could result in structural alterations that impact protein function.
Although the precise molecular mechanism remains elusive, our study indicates a potential role for PPI1 in the immune responses in Arabidopsis. Both ΔhrcV and flg22 could upregulate the expression of PPI1 in Col-0 (Figure 5A,B). Notably, the expression levels of the four PTI-related genes in ppi1-1 were significantly reduced (Figure 7A–D), aligning with the observation that ppi1-1 exhibited markedly higher ΔhrcV bacterial growth compared to the wild type (Figure 5C). In Arabidopsis protoplasts, PPI1 induced the expression of PTI-related genes, while XopLXcc counteracted this response through its interaction with PPI1 (Figure 6A). Notably, in Col-0 protoplasts, XopLXcc suppressed the expression of PTI-related genes, which was mitigated in ppi1-1 (Figure 7A–D). Moreover, the stomatal aperture of XopLXcc-expressing lines resembled those of ppi1-1 mutants, exhibiting a remarkable elevation compared to that of the control Col-0, which aligns with the phenotype observed in response to Xcc (Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 5 and Figure 8). Thus, these findings suggest a model in which XopLXcc binds to PPI1, disrupting the early defense responses elicited in Arabidopsis during Xcc infection.
PPI1 consists of 612 amino acids and is predicted to encode three coiled-coil regions and a transmembrane domain, which might be recruited to the PM for interaction with H+-ATPase [27]. Full-length PPI1 or its N-terminal domain could bind PM H+-ATPase at a site different from the known 14-3-3 binding locations and stimulate its activity [24]. PM H+-ATPase, the well-known PM H+ pump, is a central regulator in plant physiology, which mediates not only growth and development but also adaptation to diverse environmental stimuli [23,38,39]. Its activation can trigger immune responses [40], while its mutants exhibit a defective PAMP-triggered production of ROS, altered MAPK activation, malfunctioning PAMP-triggered stomatal closure, and changed bacterial infection phenotypes [41]. It is a crucial element in the defense mechanisms of plants against pathogen attack. However, it also functions as a target for pathogens that enable tissue invasion [42]. In Xcc 8004, XopLXcc did not interact with PPI1 at the PM (Figure 4), indicating a potential inhibition of PPI1 recruitment to the PM. This hindrance could disrupt the PPI1–PM H+-ATPase interactivity, ultimately affecting the activation of H+-ATPase and immune responses in plants. In contrast, XopLXcc downregulated the salicylic acid (SA)- and PTI-related genes (Figure 6A) [22], aligning with the enhancement in PM H+-ATPase activity, which could cause SA accumulation and the expression of pathogenesis-related genes in tomatoes [40]. In this context, the investigation of the possible disruption of the PPI1–H+-ATPase complex by XopLXcc via ubiquitination, as well as the intricate spatial and temporal modulation of PM H+-ATPase activity during the initial stages of pathogen recognition, will be the emphasis of forthcoming research.
In conclusion, previous research has revealed that XopLXcc interferes with the innate immunity of Arabidopsis by suppressing PTI and SA signaling, independent of MAPKs [16,20]. However, the specific virulence targets and underlying mechanisms remain incompletely elucidated. In this study, we identified proton pump interactor PPI1 as a specific virulence target of XopLXcc in Arabidopsis. Moreover, the C-terminus of PPI1 and the LRR domains of XopLXcc are pivotal for facilitating this interactivity. This novel discovery marks the first identification of PPI1’s role in conferring resistance to pathogen infection, providing valuable insights into potential strategies for regulating PM H+-ATPase activity during pathogen infection. These findings significantly enhance our understanding of the mechanisms employed by the T3Es of pathogenic bacteria and contribute to the development of effective strategies for controlling bacterial diseases.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
Xcc strains were cultured at 28 °C in a nutrient broth–yeast extract (NYG) medium. Escherichia coli and Agrobacterium tumefaciens strains were cultured in LB media at 37 °C and 28 °C, respectively. The antibiotics added were ampicillin (50 μg/mL), rifampicin (50 μg/mL), and kanamycin (50 μg/mL for E. coli and 25 μg/mL for Xcc and A. tumefaciens).
4.2. Vector Constructions
Full-length DNA fragments of XopLXcc, PPI1, and PPI2 were amplified by employing FastPfu DNA polymerase (Beijing TransGen Biotech, Beijing, China) using the primers listed in Table S1. For transient expression in protoplasts, PCR products were cloned into the pXSN-HA vector [43]. For constructing transgenic Arabidopsis plants, the PCR products were cloned into the 35S::GUS-pBI121 vector to generate the GUS-tagged constructs.
4.3. Plant Growth and Generation of the Transgenic Arabidopsis Plants
The Arabidopsis plants were grown in a mixture of vermiculite, perlite, and peat moss (1:1:2) in an environmentally controlled growth room at 22 °C and 70% relative humidity under a 12/12 h day/night light cycle. They were transformed with A. tumefaciens GV3101 carrying 35S::XopLxcc:GUS-pBI121 or 35S::GUS-pBI121 using the flower-dipping method [44]. Transgenic lines were selected using 50 μg/mL kanamycin, and homozygous lines in the T3 generation were identified.
4.4. Virulence Assays, Callose Deposition Assays, and Oxidative Burst Measurement
Virulence assays of Xcc strains were conducted utilizing mesophyll infiltration, as previously described [39]. For the callose deposition assays, the leaves of six-week-old Arabidopsis plants were infused with 1 µM flg22. They were harvested 8 h after infiltration, washed with 95% ethanol, stained for callose with 0.1% aniline blue in 7 mM K2HPO4 (pH 9.5), and then mounted in 50% glycerol. They were observed using an SZX16 fluorescence microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) under ultraviolet light, and the number of callose deposits in a 0.1 mm2 microscopic field was counted in randomly coded samples from ten leaves by applying OpenCFU Version 1.0 software [45].
For oxidative burst measurement, the leaves of six-week-old Arabidopsis plants were cut into 1 mm-long strips and incubated in 200 μL of H2O in a 96-well plate for 12 h. Next, 1 μM flg22 in 200 μL of reaction buffer supplemented with 20 mM luminol and 1 μg of horseradish peroxidase (Sigma) was added. Luminescence was recorded for 45 min using a Synergy HT plate reader luminometer (Bio-Tek).
4.5. Transient Expression in Arabidopsis Protoplasts
Mesophyll protoplasts were prepared and transfected as previously described [33]. Briefly, leaves from five–six-week-old plants were used for protoplast isolation. Enzyme solutions containing Cellulase R10 and Macerozyme R10 (Yakult, Tokyo, Japan) were utilized for leaf digestion. Plasmid DNA was purified by a HiSpeed plasmid Mini kit (QIAGEN, Dusseldorf, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
4.6. Gene Expression Analyses
Total RNA from the leaves or protoplasts was isolated using Trizol Reagent (Solarbio, Beijing, China). First-strand cDNA was synthesized from 500 ng of the total RNA utilizing a PrimeScript RT reagent kit (TaKaRa, Tokyo, Japan) per the manufacturer’s instructions. For real-time RT-qPCR, 20 ng of the cDNA was mixed with SYBR Premix Ex Taq (TaKaRa) and analyzed in triplicate by employing a LightCycler® 480 Real-Time PCR System (Roche, Basel, Switzerland). Gene expression levels were normalized to those of the reference gene Atactin2. The sequences of the primers used are listed in Table S1.
4.7. Yeast Two-Hybrid Screening
Yeast two-hybrid assays were performed by following the Yeast Protocols Handbook. The leaves of four-week-old Arabidopsis plants were infiltrated with 106 CFU/mL Xcc 8004ΔhrcV, and leaf samples were collected at 0 and 6 h. Total RNA was extracted using an RNeasy Plant Mini Kit (QIAGEN). Subsequently, reverse transcription was conducted using Switching Mechanism at 5′ End of RNA Template (SMART) technology. RT-PCR utilized the synthesized cDNA (sscDNA) as a template for dscDNA amplification. The products were purified, cleaved with SfiI, and ligated to the SfiI-digested pPR3N plasmid. Lastly, the Arabidopsis cDNA library was generated and employed to transform the Escherichia coli.
The entire XopLXcc coding region was amplified and inserted in the pDHB1 vector to generate a fusion between the membrane protein Ost4 and the C-terminal half of ubiquitin (Cub), followed by the artificial transcription factor LexA-VP1 [46]. The yeast strain NMY51 carrying the DHB1-XopLXcc vector was transformed with the Arabidopsis cDNA library. Diploid cells were selected on a medium lacking Leu, Trp, and His supplemented with 10 mM 3-aminotriazole. Then, 2 × 107 transformants were screened, of which ~300 transformants that grew on the selective medium were obtained. Cells growing on the selective medium were further tested for lacZ reporter gene activity using a β-galactosidase assay. Direct interaction of two proteins was investigated by co-transformation of the yeast strain NMY51 with the respective plasmids; followed by the selection of transformants on a medium lacking Leu and Trp at 30 °C for 3 days; with the subsequent transfer to a medium lacking Leu, Trp, and His for growth selection; and testing of the lacZ activity in the interacting clones. To generate the PPI1 or PPI2 fusions with the N-terminal half of ubiquitin (NubG), as well as the XopLXcc or XopLXccΔLRR fusion with the C-terminal half of ubiquitin (Cub), the corresponding coding regions were amplified by PCR using the primers detailed in Table S1. They were inserted into SfiI sites of the pPR3N and pDHB1 vectors, respectively, and the sequence was verified.
4.8. Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation (BiFC)
For the BiFC assay, XopLXcc, XopLXccΔLRR, and the candidate target genes were cloned in-frame with the EYFP fragments into the modified BiFC vectors derived from PSAT6-nEYFP-C1 or PSAT6-cEYFP-C1 [37]. Arabidopsis protoplasts were transfected as described previously, and the BiFC-induced YFP fluorescence was detected after 8 h by employing a TCS SP8 laser scanning confocal microscope (Leica, Solms, Germany).
4.9. Stomatal Aperture Measurement
The Arabidopsis plants were exposed to light for 2 h to ensure that most stomata were opened before treatment. Leaf peels were collected from the abaxial side of the leaves of five-week-old plants and floated in a buffer (10 mM MES [pH 6.15], 10 mM KCl, and 10 mM CaCl2). After treatment with 100 nM flg22 or the mock solution for 1 h, the stomata were observed under a microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). The stomatal aperture was measured by applying ImageJ version 1.0 software.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms25179175/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.H. and H.Z.; methodology, J.H., Y.D., N.L., Y.H. and H.Z.; validation, J.H. and H.Z.; data curation, J.H., Y.H. and H.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, J.H.; writing—review and editing, J.H. and H.Z.; project administration, Y.H. and H.Z.; funding acquisition, J.H. and H.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 32060599 and 32160079), and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province (grant no. 2021GXNSFAA075023).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data presented in this study will be available from the corresponding author upon request.
Acknowledgments
We thank the ABRC (Columbus, OH, USA) for providing the pXSN-HA, PSAT6-nEYFP-C1, and PSAT6-cEYFP-C1 plasmids. We thank the Core Facilities Center of SKLCUSA for supporting microscopic observation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Jones, J.D.G.; Dangl, J.L. The plant immune system. Nature 2006, 444, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Subramaniam, R.; Desveaux, D. Of guards, decoys, baits and traps: Pathogen perception in plants by type III effector sensors. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2016, 29, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Seto, D.; Subramaniam, R.; Desveaux, D. Oh, the places they’ll go! A survey of phytopathogen effectors and their host targets. Plant J. 2018, 93, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansfield, J.; Genin, S.; Magori, S.; Citovsky, V.; Sriariyanum, M.; Ronald, P.; Dow, M.; Verdier, V.; Beer, S.V.; Machado, M.A.; et al. Top 10 plant pathogenic bacteria in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2012, 13, 614–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Jia, Y.T.; Ren, S.X.; He, Y.Q.; Feng, J.X.; Lu, L.F.; Sun, Q.H.; Ying, G.; Tang, D.J.; Tang, H.; et al. Comparative and functional genomic analyses of the pathogenicity of phytopathogen Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris. Genome Res. 2005, 15, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.Q.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, B.L.; Zhang, Z.C.; Xu, R.Q.; Tang, D.J.; Qin, J.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, X.; Liao, J.; et al. Comparative and functional genomics reveals genetic diversity and determinants of host specificity among reference strains and a large collection of Chinese isolates of the phytopathogen Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, F.F.; Potnis, N.; Jones, J.B.; Koebnik, R. The type III effectors of Xanthomonas. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2009, 10, 749–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.P.; Vorhölter, F.J.; Potnis, N.; Jones, J.B.; Van Sluys, M.A.; Bogdanove, A.J.; Dow, J.M. Pathogenomics of Xanthomonas: Understanding bacterium-plant interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Li, T.Q.; Xu, T.; Tang, Z.Z.; Guo, J.Y.; Cai, Y. Multiple Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris 8004 type III effectors inhibit immunity induced by flg22. Planta 2020, 252, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, E.; Lautier, M.; Chabannes, M.; Roux, B.; Lauber, E.; Arlat, M.; Noël, L.D. XopAC-triggered immunity against Xanthomonas depends on Aabidopsis receptor-Like cytoplasmic kinase genes PBL2 and RIPK. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.F.; Tang, X.Y.; He, C.Z. The bifunctional effector AvrXccC of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris requires plasma membrane-anchoring for host recognition. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2007, 8, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.T.; Rong, W.; Luo, H.L.; Chen, Y.H.; He, C.Z. The Xanthomonas campestris effector protein XopDxcc8004 triggers plant disease tolerance by targeting DELLA proteins. New Phytol. 2014, 204, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Zhu, X.L.; Li, C.A.X.; Ma, Z.M.; Han, X.; Luo, Y.Y.; Yang, L.; Yu, J.; Miao, Y.S. Xanthomonas effector XopR hijacks host actin cytoskeleton via complex coacervation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.L.; He, Y.Q.; Cen, W.J.; Wei, H.Y.; Jiang, G.F.; Jiang, W.; Hang, X.H.; Feng, J.X.; Lu, G.T.; Tang, D.H.; et al. The type III secretion effector xopXccN of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris is required for full virulence. Res. Microbiol. 2008, 159, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, F.; Yang, F.; Rong, W.; Wu, X.G.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; He, C.Z.; Zhou, J.M. A Xanthomonas uridine 5′-monophosphate transferase inhibits plant immune kinases. Nature 2012, 485, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Tao, J.; Luo, H.L.; Tan, L.T.; Rong, W.; Li, H.P.; He, C.Z. A type III effector XopLxcc8004 is vital for Xanthomonas campestris pathovar campestris to regulate plant immunity. Res. Microbiol. 2019, 170, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Üstün, S.; Bartetzko, V.; Börnke, F. The Xanthomonas campestris Type III Effector XopJ Targets the Host Cell Proteasome to Suppress Salicylic-Acid Mediated Plant Defence. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.Q.; Li, X.Z.; Wei, H.Y.; Jiang, B.; Li, K.; He, Y.Q.; Feng, J.X.; Tang, J.L. Regulation of eight avr genes by hrpG and hrpX in Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris and their role in pathogenicity. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. 2006, 16, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Jiang, B.L.; Xu, R.Q.; Huang, J.D.; Wei, H.Y.; Jiang, G.F.; Cen, W.J.; Liu, J.; Ge, Y.Y.; Li, G.H.; et al. Identification of six type III effector genes with the PIP box in Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris and five of them contribute individually to full pathogenicity. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2009, 22, 1401–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, M.; Li, N.N.; Jiang, B.; He, Y.Q. Functional analysis of Type III effectors in Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris reveals distinct roles in modulating Arabidopsis innate immunity. Pathogens 2024, 13, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortmann, S.; Marx, J.; Lampe, C.; Handrick, V.; Ehnert, T.M.; Zinecker, S.; Reimers, M.; Bonas, U.; Erickson, J.L. A conserved microtubule-binding region in Xanthomonas XopL is indispensable for induced plant cell death reactions. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, M.; Mondal, K.K. Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae uses XopL effector to suppress pomegranate immunity. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2018, 60, 341–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmgren, M.G. Proton gradients and plant growth:: Role of the plasma membrane H+-ATPase. Adv. Bot. Res. 1998, 28, 1–70. [Google Scholar]
- Morandini, P.; Valera, M.; Albumi, C.; Bonza, M.C.; Giacometti, S.; Ravera, G.; Murgia, I.; Soave, C.; De Michelis, M.I. A novel interaction partner for the C-terminus of Arabidopsis thaliana plasma membrane H+-ATPase (AHA1 isoform): Site and mechanism of action on H+-ATPase activity differ from those of 14-3-3 proteins. Plant J. 2002, 31, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferl, R.J. 14-3-3 proteins: Regulation of signal-induced events. Physiol. Plant. 2004, 120, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viotti, C.; Luoni, L.; Morandini, P.; De Michelis, M.I. Characterization of the interaction between the plasma membrane H+-ATPase of Arabidopsis thaliana and a novel interactor (PPI1). FEBS J. 2005, 272, 5864–5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonza, M.C.; Fusca, T.; Homann, U.; Thiel, G.; De Michelis, M.I. Intracellular localisation of PPI1 (proton pump interactor, isoform 1), a regulatory protein of the plasma membrane H+-ATPase of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Biol. 2009, 11, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anzi, C.; Pelucchi, P.; Vazzola, V.; Murgia, I.; Gomarasca, S.; Piccoli, M.B.; Morandini, P. The proton pump interactor (Ppi) gene family of Arabidopsis thaliana: Expression pattern of Ppi1 and characterisation of knockout mutants for Ppi1 and 2. Plant Biol. 2008, 10, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirabayashi, S.; Matsushita, Y.; Sato, M.; Oh, R.; Kasahara, M.; Abe, H.; Nyunoya, H. Two proton pump interactors identified from a direct phosphorylation screening of a rice cDNA library by using a recombinant BRI1 receptor kinase. Plant Biotechnol. 2004, 21, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- García, M.N.M.; País, S.M.; Téllez-Iñón, M.T.; Capiati, D.A. Characterization of StPPI1, a proton pump interactor from Solanum tuberosum L. that is up-regulated during tuber development and by abiotic stress. Planta 2011, 233, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Sun, Q.R.; Zhai, L.M.; Zhao, D.R.; Lv, J.H.; Han, Z.H.; Wu, T.; Zhang, X.Z.; Xu, X.F.; Wang, Y. Genome-wide identification of apple PPI genes and a functional analysis of the response of MxPPI1 to Fe deficiency stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 189, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Büttner, D. Behind the lines-actions of bacterial type III effector proteins in plant cells. Fems Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 40, 894–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, A.U.; Schulze, S.; Skarina, T.; Xu, X.H.; Cui, H.; Eschen-Lippold, L.; Egler, M.; Srikumar, T.; Raught, B.; Lee, J.; et al. A Pathogen Type III Effector with a Novel E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Architecture. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, J.L.; Adlung, N.; Lampe, C.; Bonas, U.; Schattat, M.H. The Xanthomonas effector XopL uncovers the role of microtubules in stromule extension and dynamics in Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant J. 2018, 93, 856–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canonne, J.; Marino, D.; Jauneau, A.; Pouzet, C.; Brière, C.; Roby, D.; Rivas, S. The Xanthomonas type III effector XopD targets the Arabidopsis transcription factor MYB30 to suppress plant defense. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, E.; Lindblom, K.; Tillgren, V.; Aspberg, A. The leucine-rich repeat protein PRELP binds fibroblast cell-surface proteoglycans and enhances focal adhesion formation. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 1153–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitipan, S.; Sritrakul, T.; Kunjantarachot, A.; Prapong, S. Identification of epitopes in Leptospira borgpetersenii leucine-rich repeat proteins. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 14, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmore, J.M.; Coaker, G. The role of the plasma membrane H+-ATPase in plant-microbe interactions. Mol. Plant 2011, 4, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.H.; Zhu, P.; Gao, L.Y.; Chen, X.Y.; Li, M.J.; Wang, Y.H.; He, J.X.; Miao, Y.; Miao, R. Recent Advances in Understanding the Regulatory Mechanism of Plasma Membrane H+-ATPase through the Brassinosteroid Signaling Pathway. Plant Cell Physiol. 2024, pcae014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, A.; Oecking, C. Modulation of plasma membrane H+-ATPase activity differentially activates wound and pathogen defense responses in tomato plants. Plant Cell 1999, 11, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keinath, N.F.; Kierszniowska, S.; Lorek, J.; Bourdais, G.; Kessler, S.A.; Shimosato-Asano, H.; Grossniklaus, U.; Schulze, W.X.; Robatzek, S.; Panstruga, R. PAMP (Pathogen-associated Molecular Pattern)-induced Changes in Plasma Membrane Compartmentalization Reveal Novel Components of Plant Immunity. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 39140–39149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalak, A.; Wdowikowska, A.; Janicka, M. Plant Plasma Membrane Proton Pump: One Protein with Multiple Functions. Cells 2022, 11, 4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.B.; Songkumarn, P.; Liu, J.L.; Wang, G.L. A Versatile Zero Background T-Vector System for Gene Cloning and Functional Genomics. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 1111–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, S.J.; Bent, A.F. Floral dip: A simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 1998, 16, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geissmann, Q. OpenCFU, a New Free and Open-Source Software to Count Cell Colonies and Other Circular Objects. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möckli, N.; Deplazes, A.; Hassa, P.O.; Zhang, Z.L.; Peter, M.; Hottiger, M.O.; Stagljar, I.; Auerbach, D. Yeast split-ubiquitin-based cytosolic screening system to detect interactions between transcriptionally active proteins. Biotechniques 2007, 42, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).