Abstract
The study of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and SIRT1, a member of the sirtuin family with nitric oxide (NO), is emerging in depression and anxiety. As with all antidepressants, the efficacy is delayed and inconsistent. Ascorbic acid (AA) and vitamin D (D) showed antidepressant properties, while etifoxine (Etx), a GABAA agonist, alleviates anxiety symptoms. The present study aimed to investigate the potential augmentation of citalopram using AA, D and Etx and related the antidepressant effect to brain and serum ICAM-1, SIRT1 and NO in an animal model. BALB/c mice were divided into naive, control, citalopram, citalopram + etx, citalopram + AA, citalopram + D and citalopram + etx + AA + D for 7 days. On the 8th day, the mice were restrained for 8 h, followed by a forced swim test and marble burying test before scarification. Whole-brain and serum expression of ICAM-1, Sirt1 and NO were determined. Citalopram’s antidepressant and sedative effects were potentiated by ascorbic acid, vitamin D and etifoxine alone and in combination (p < 0.05), as shown by the decreased floating time and rearing frequency. Brain NO increased significantly (p < 0.05) in depression and anxiety and was associated with an ICAM-1 increase versus naive (p < 0.05) and a Sirt1 decrease (p < 0.05) versus naive. Both ICAM-1 and Sirt1 were modulated by antidepressants through a non-NO-dependent pathway. Serum NO expression was unrelated to serum ICAM-1 and Sirt1. Brain ICAM-1, Sirt1 and NO are implicated in depression and are modulated by antidepressants.
1. Introduction
Psychological stress is often associated and comorbid with depression and anxiety disorders [1]. Major depressive disorder (MDD) and anxiety are the leading causes of disability worldwide [2]. Growing lines of literature refer to the implication of neuroinflammation in MDD and anxiety [3,4]. The relationship between psychiatric disorders and neuroinflammation is well established. Neuroinflammation refers to the combined immune response and inflammation within the CNS. Increasing numbers of publications in the literature refer to the implication of neuroinflammation in depressive disorder [3,4].
Upon activation, the majority of microglia become amoeboid and induce the production of proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6) [5], which in turn increase the levels of the presynaptic transporters of monoamines, thus leading to their depletion from the synaptic space. Additionally, cytokines activate the indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase (IDO) enzyme, which breaks down tryptophan, the precursor of serotonin, to yield kynurenine, which is converted into quinolinic acid and, subsequently, into glutamate [6,7]. Furthermore, inflammatory processes and altered leukocyte trafficking play a role in the disruption of the blood–brain barrier in psychiatric disorders, supporting the hypothesis of the involvement of the central nervous system and peripheral tissues in ongoing inflammatory processes [8].
Adhesion molecules play an important role in leukocyte recruitment and their role in psychiatry is emerging. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), a marker of inflammation, is an immunoglobulin (Ig)-like transmembrane glycoprotein that is overexpressed in the endothelial lumen. ICAM-1 facilitates leukocyte transmigration across the endothelium of many cell types and plays a key role in the function of the blood–brain barrier (BBB), which helps in the migration of molecules to and from the brain [4,9]. The membrane-bound ICAM-1 is primarily expressed in several parts of the central nervous system (CNS) [10].
A soluble form of the molecule, the soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1), is found in serum and is considered a peripheral inflammatory marker associated with several inflammatory states [11]. While little evidence exists about the implications of membrane-bound ICAM-1 in the CNS, the blood levels of sICAM-1 were found to be increased in patients with depression [12].
Sirtuins are a family of NAD+-dependent deacetylases that have a crucial role in anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory balance and homeostasis [13]. SIRT1 is a member of the sirtuin family. The role of Sirt1 in depression is emerging. Two studies showed lower Sirt1 blood levels in patients with depression versus controls [14,15]. Moreover, Sirt1 activation in animal models of depression was associated with antidepressant effects [16,17]. Nitric oxide (NO) is produced from L-arginine by the enzymatic conversion of the enzyme NO synthase (NOS) [18] and is highly implicated in depression and anxiety [19,20]. Moreover, the expression of ICAM-1 and Sirt1 is thought to be, in part, dependent on NO pathways. Nitric oxide increases the expression of ICAM-1 in epithelial cells [21,22]. In addition, the inhibition of the NO synthesis reduced the levels of SIRT1 protein levels [23].
Although selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are a first-line therapy for MDD, their delayed onset and the inconsistency of antidepressant efficacy are major limitations [24]. While the need for augmenting antidepressants is critical, combining traditional antidepressants from the same or different families is not recommended due to serious adverse reactions such as asserotoni symptoms, a higher risk of weight gain and drug interactions [25].
There is emerging evidence linking depression with vitamin D. The risk of depression may be further exacerbated by low serum levels of vitamin D [26]. Some evidence indicates that vitamin D could play a role as a neuroactive molecule that enhances the expression of neurotransmitters [27]. Ascorbic acid, or vitamin C, is a known antioxidant and water-soluble vitamin that is involved in many cellular processes. In one preclinical study, ascorbic acid exerted an antidepressant effect in mice. In addition, it potentiated the effects of fluoxetine and imipramine [28]. The results of another pilot study suggest that vitamin C may be an effective adjuvant agent in the treatment of MDD in paediatric patients receiving SSRIs [29]. Etifoxine is a GABAA agonist and has an anxiolytic role that could be a potential adjuvant to depression and anxiety [30,31].
The acute restraint model involves the acute immobilisation of animals for a period of time between 6 and 8 h. This stress-induced model demonstrates anxiety and behaviour-like behaviour in animals, a model that is associated with changes in biochemical markers [8,32]. Animal models using BALB/c mice showed either no response or a very poor response to subchronic treatment with antidepressants such as citalopram. For example, the subchronic administration of citalopram failed to decrease floating immobility time in the forced swim test in BALB/c mice [33,34].
To the best of our knowledge, scattered evidence points to the possible effect of ascorbic acid and vitamin D in alleviating depressive symptoms. Furthermore, etifoxine showed non-negligible efficacy in anxiety compared to benzodiazepines. No previous studies have examined the potential adjuvant effects of ascorbic acid, vitamin D and etifoxine on the antidepressant and anxiolytic effects of citalopram with the expression of ICAM-1, Sirt1 and NO in the brain and serum of BALB/c mice. Therefore, the present study had two objectives: (1) to investigate the efficacy of ascorbic acid, vitamin D and etifoxine in potentiating the efficacy of citalopram and (2) to relate the antidepressant effect to the expressions of ICAM-1, Sirt1 and NO in the brain and serum of BALB/c mice.
2. Results
2.1. Behavioural Tests
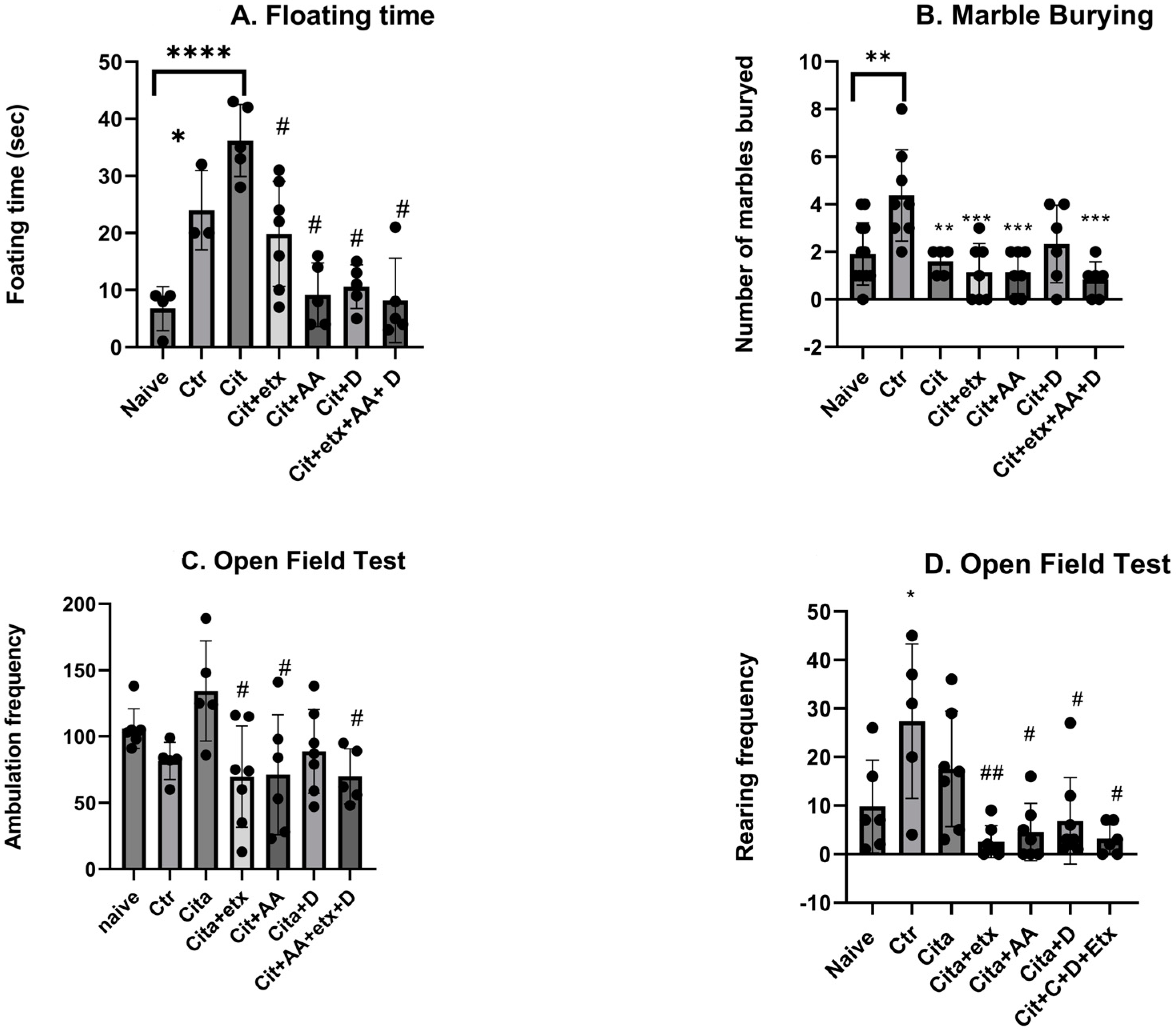
According to the forced swim test, there was a significant increase in the floating time in the naive group versus the control group (p < 0.05). The citalopram-treated group demonstrated a significantly longer floating time compared to the naive group (p < 0.05). All the adjuvants significantly reduced the floating time (p < 0.05) compared to citalopram. According to the marble burying test, the number of marbles buried by the control group was significantly higher compared to the naive group (p = 0.003), compared to the control group, where the citalopram-treated group buried significantly fewer marbles (p = 0.009). The frequency of ambulation of the open field test of the groups treated with (cita + etx, cita + AA) and (cita + etx + AA + D) showed a significant reduction (p < 0.05) in ambulation frequency compared to citalopram. Furthermore, the results of the rearing frequency showed that the control demonstrated a significantly higher (p < 0.05) rearing frequency compared to the naive group and that all the combinations (cit + etx, cita + AA, cit + D and cit + AA + D) demonstrated a significant decrease (p < 0.05) in the rearing frequency compared to citalopram. None of the adjuvants showed significant improvements compared to the citalopram group (p > 0.05) (Figure 1).
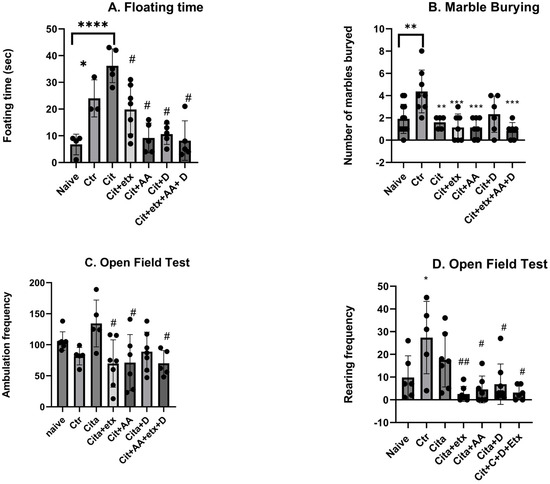
Figure 1.
(A) floating time among the different groups. ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis. Values are expressed as the mean SEM (ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test). F(6, 27) = 12.48; p < 0.0001. * p < 0.05, **** p < 0.0001 vs. naive and # p < 0.00001 vs. citalopram. Ctr: control; Cit: citalopram; etx: etifoxine; D: vitamin D; AA: ascorbic acid; SEM, standard error of the mean. (B) The number of buried marbles in the group ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis. Values are expressed as the mean SEM (ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test). F(6, 44) = 6.29; p = 0.0001. ** p <0.05; *** p < 0.001 vs. control. Ctr: control Cit: citalopram; etx: etifoxine; D: vitamin D; AA: ascorbic acid; SEM, standard error of the mean. (C) The ambulation frequency per group ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis. Values are expressed as the mean SEM (ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test). F(6, 35) = 3.19; p = 0.001; # p < 0.05 vs. citalopram. Ctr: control Cit: citalopram; etx: etifoxine; D: vitamin D; AA: ascorbic acid; SEM, standard error of the mean. (D) The rearing frequency per group ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis. Values are expressed as the mean SEM (ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test). F(6, 35) = 3.19; p = 0.001. * p < 0.05 vs. naive; ## p < 0.001 vs. Ctr; # p < 0.05 vs. Ctr. Ctr: control Cit: citalopram; etx: etifoxine; D: vitamin D; AA: ascorbic acid; SEM, standard error of the mean.
2.2. ICAM-1 and SIRT1
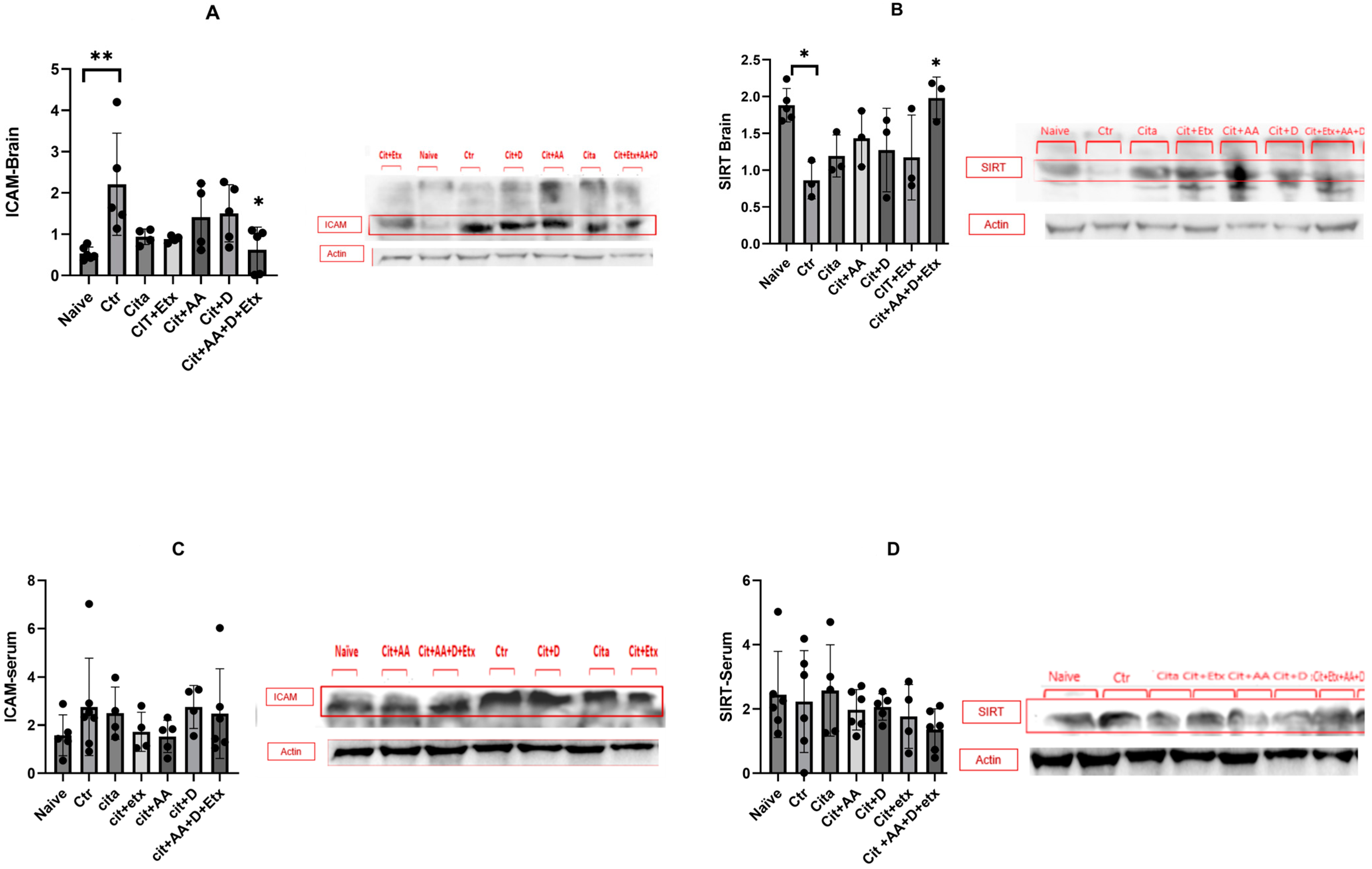
ICAM-1 expression in the brain was significantly higher in the control group compared to the naive group (p = 0.005). Citalopram did not affect ICAM-1 expression; however, the Cita + C + D + Etx group had a significantly lower ICAM-1 level (p = 0.01) than the control group. The brain Sirt1 expression of the control group was significantly lower (p = 0.02) compared to the naive group. Citalopram did not increase the Sirt1 levels; however, the Cita + C + D + Etx group had significantly higher Sirt1 expression (p = 0.02) than the control group. The serum expression of ICAM-1 and Sirt1 did not vary between the groups (p > 0.05) (Figure 2).
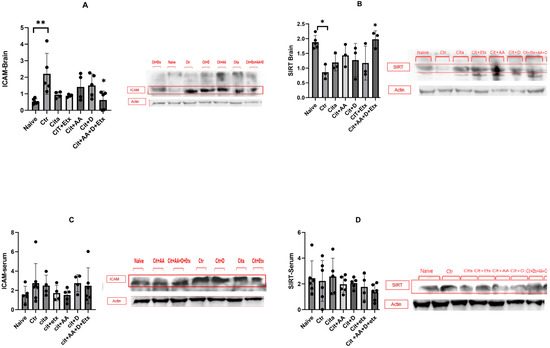
Figure 2.
(A) Brain ICAM-1 expression among the different groups ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis. Values are expressed as the mean SEM (ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test). F(6, 16) = 4.02; p = 0.005. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.005. Ctr: control; Cit: citalopram; Etx: etifoxine; D: vitamin D; AA: ascorbic acid; SEM, standard error of the mean. (B) Brain Sirt1 expression among the different groups ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis. Values are expressed as the mean SEM (ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test). F(6, 16) = 3.95; p = 0.01. * p < 0.05. Ctr: control; Cit: citalopram; etx: etifoxine; D: vitamin D; AA: ascorbic acid; SEM, standard error of the mean. (C) Serum ICAM-1 expression among the different groups ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis. Values are expressed as the mean SEM (ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test). F(6, 28) = 0.79; p = 0.58. Ctr: control; Cit: citalopram; Etx: etifoxine; D: vitamin D; AA: ascorbic acid; SEM, standard error of the mean. (D) Serum Sirt1 expression among the different groups ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis. Values are expressed as the mean SEM (ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test). F(6, 28) = 0.79; p = 0.58. Ctr: control; Cit: citalopram; etx: etifoxine; D: vitamin D; AA: ascorbic acid; SEM, standard error of the mean.
2.3. Nitric Oxide
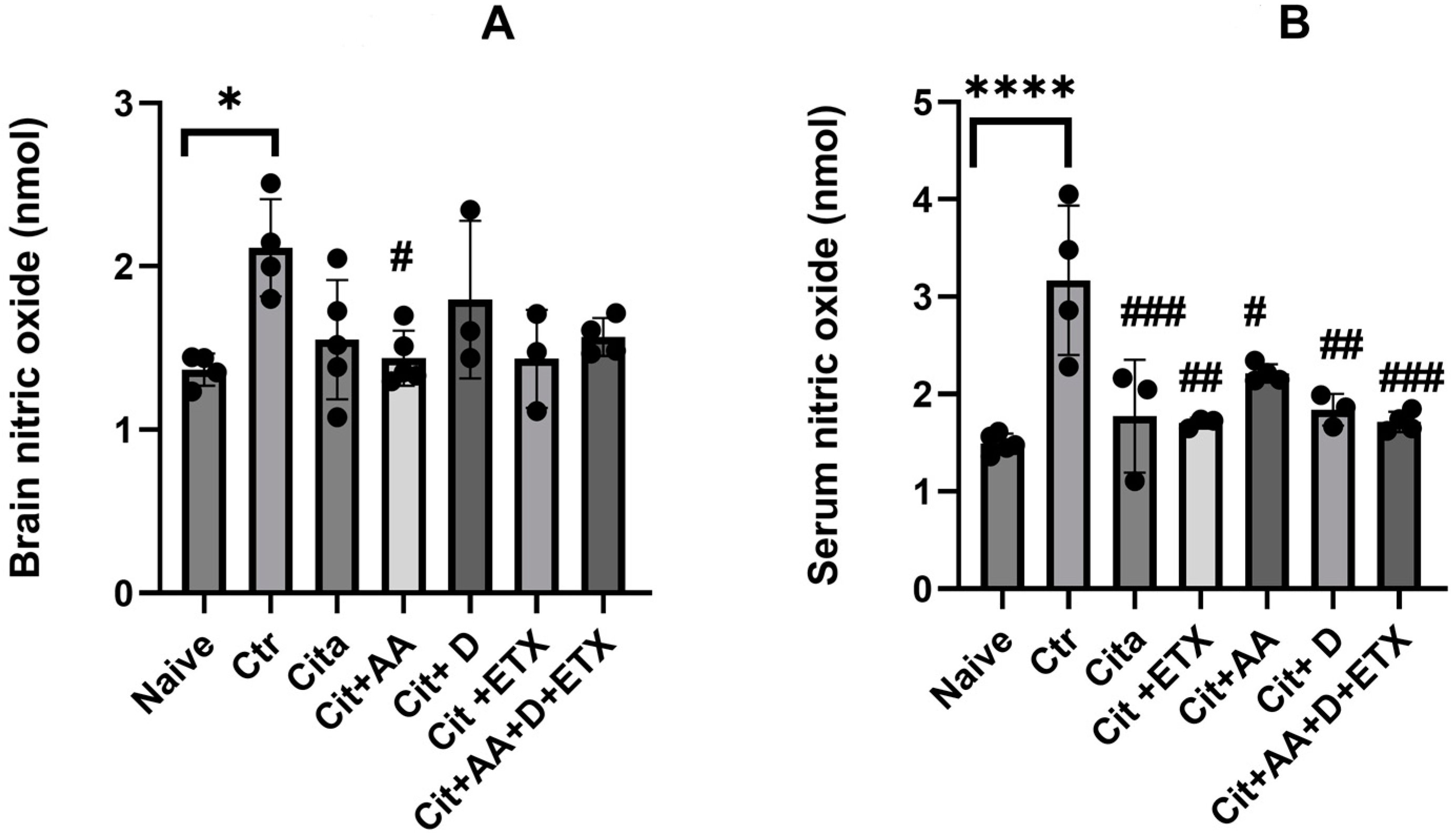
The control group demonstrated significantly higher NO brain levels compared to the naive group (p < 0.05). Only Cit + C showed a reduction in the brain NO levels compared to the control (p < 0.05). The serum NO levels were significantly higher in the control group compared to the naive group (p < 0.05). Furthermore, all the treated groups had lower serum NO levels than the control group (p < 0.05) (Figure 3).
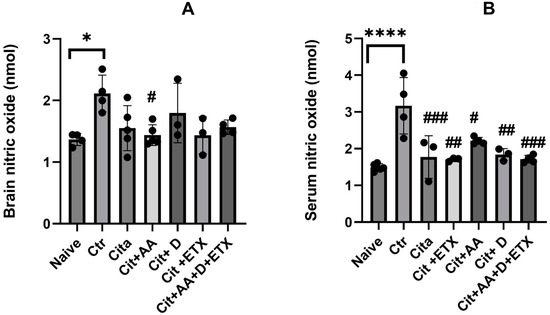
Figure 3.
(A) Brain nitric oxide expression among the different groups ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis. Values are expressed as the mean SEM (ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test). F(6, 21) = 3.47; p = 0.01. * p < 0.05, # p < 0.05 versus Ctr. Ctr: control; Cit: citalopram; Etx: etifoxine; D: vitamin D; AA: ascorbic acid; NO: nitric oxide; SEM, standard error of the mean. (B) Serum nitric oxide expression among the different groups ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis. Values are expressed as the mean SEM (ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test). F(6, 19) = 9.75; p < 0.001. **** p <0.0001 versus naive, # p < 0.05, ## p <0.001, ### p < 0.0001 versus control. Ctr: control; Cit: citalopram; Etx: etifoxine; D: vitamin D; AA: ascorbic acid NO: nitric oxide; SEM: standard error of the mean.
3. Discussion
The present study aimed to investigate neuroinflammation in psychiatric disorders. We investigated the role of vitamins C and D and etifoxine as potential adjuvants to citalopram in a B/C model of anxiety and depression. In our model, citalopram did not exert an antidepressant effect as the floating time did not decrease significantly compared to the control group; however, etifoxine, ascorbic acid and vitamin D alone and in combination were able to enhance the antidepressant effect of citalopram. The anxiolytic effect of citalopram was evaluated mainly using the marble burying test. The citalopram-treated group showed a significantly lower number of marbles buried, indicating significant anxiolytic efficacy versus the control group; however, this anxiolytic efficacy was not further enhanced by ascorbic acid, vitamin D, etifoxine, or their combination compared to citalopram alone. Furthermore, the open field test used to screen for anxiolytic and sedative effects revealed that the sedative effect of citalopram was not evident in the treated mice; however, the sedative effect was evident with citalopram in combination with etifoxine, ascorbic acid, vitamin D alone and then combined.
In our study, we used ascorbic acid, vitamin D and etifoxine as potential adjuvants due to their established antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties and their emerging antidepressant properties. Citalopram, as with other SSRIs, inhibits the serotonin carriers, therefore increasing the serotonin (a monoamine) levels at the synaptic cleft. Although it is a first-choice drug for anxiety and depression due to its safety and minimal drug interactions, about 50% of patients experience inadequate responses to SSRIs in the best conditions [35,36]. Furthermore, reviewing three decades of randomised controlled trials of antidepressants revealed that the antidepressant response rate is approximately 54% compared to a placebo response rate of 37% [37]. Therefore, the monoamine-based mechanism does not result in the optimal resolution of the patient’s symptoms. Furthermore, the use of two antidepressants could lead to detrimental effects such as serotonin syndrome, weight gain and sexual dysfunction [25]. As a result, enhancing the efficacy of SSRIs should be carried out through other strategies. In light of the literature, several potential natural and synthetic antioxidant and anti-inflammatory molecules could play an adjuvant antidepressant role. For example, vitamin D is believed to act as a neuroactive steroid [27,38] that plays a key role in the expression of neurotransmitters, the synthesis of antioxidants and neurotropic factors, thus providing a rationale for its potential antidepressant role. Although its role in depression is now still emerging, it is evident that low vitamin D levels are associated with depression [26].
Ascorbic acid, or vitamin C, is known for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and other metabolic effects, which could explain its adjuvant effect with antidepressants [29]. In a preclinical study, ascorbic acid exerted an antidepressant effect in mice. In addition, it potentiated the effects of fluoxetine and imipramine [28]. Etifoxine, a new GABAA agnostic, is believed to be a non-benzodiazepine anxiolytic with the advantage of being non-addictive [30]. Benzodiazepines such as lorazepam and bromazepam, are often co-prescribed with SSRIs to ‘bridge’ delayed SSRI effects and alleviate their symptoms of jitteriness. This is based on the immediate actions resulting from GABAA receptor activation, resulting in hyperpolarisation, which subsequently leads to a calming and anxiolytic effect. Despite the scarcity of data, etifoxine has been demonstrated to be non-inferior to benzodiazepines [39]. Also, etifoxine has never been tested as a benzodiazepine alternative along with SSRI for depression and anxiety. Moreover, the antidepressant activity of etifoxine has not been previously studied. The sedative effect could be mainly attributed to etifoxine; however, the antidepressant effects are related to the anti-inflammatory and associated mechanisms [26,30,40]. In addition, the study highlighted the implications of the central and peripheral expression of ICAM-1, SIRT1 and NO in psychiatric distress in accordance with previous research [41,42]. The acute immobility stress increased brain ICAM-1, caused a decrease in brain Sirt1 expression and increased the NO levels. The antidepressant effect of the combination (Cit + AA + D + etx) normalised both the ICAM-1 and SIRT1 brain levels but was independent of NO. The serum NO levels of NO were increased due to the acute immobility test and decreased with antidepressant treatments, which are not related to ICAM-1 and Sirt1 expression. Depression and neuroinflammation are tightly related [36]. The role of nitric oxide is established in depression. The bulk of the evidence supports an increase in NO during depression. For example, NO and its metabolites were higher in suicide attempters with respect to the controls [19,20]. Moreover, studies pointed out elevated NO levels in MDD patients, and, interestingly, NO levels were normalised after antidepressant therapy [43]. In support of the potential role in depression, a growing body of evidence has demonstrated that some antidepressants exert a NO-lowering effect. A study revealed that L-arginine antagonised the effects of the classic tricyclic antidepressant imipramine [44]. Several medications have been shown to exert antidepressant effects through NOS inhibition, including tramadol, bupropion, venlafaxine, lithium and ketamine [45,46]. Furthermore, many new investigational amino acid NOS modifiers have demonstrated interesting results, such as L-NG-nitroarginine, L-NG-monomethyl arginine and NG-propyl-L-arginine [47]. The role of ICAM-1 and Sirt1 is still emerging. Our findings showed an increase in brain ICAM-1 and a decrease in Sirt1 in the depressed group; this modulation was associated with an increase in NO. In agreement with our findings, previous studies demonstrated that ICAM-1 is upregulated via an NO-dependent mechanism, most probably via gene upregulation mechanisms involving transcriptional factors [21]. Similarly, inhibiting nitric oxide synthesis resulted in a reduction in Sirt1 protein expression [23]. The brain, but not the soluble ICAM-1 and Sirt1, was modulated, according to our findings. Moreover, the changes in the serum NO levels did not match those of ICAM-1 and Sirt1. Soluble ICAM-1 was increased in depression and in chronic inflammatory conditions, as reviewed in [4]. Our findings can be explained by the acute period of stress applied. The present study adds to the existing literature in several ways. The study tries to potentialise the effect of citalopram using a BALB/c mouse model known for its resistance to the subchronic administration of SSRI. The study recruited different safe and available ‘out of the box” adjuvants that work through a multi-mechanistic approach. Our findings will pave the road to further investigations aimed ultimately at augmenting the efficacy and fastening the onset of the action of antidepressants, thereby optimising the patient’s experience and outcomes with minimal side effects. Furthermore, our study highlighted the role of relatively new markers for neuroinflammation by focusing on the roles of ICAM-1, SIRT1 and NO in psychiatric disorders, namely stress, anxiety and depression. In addition, the study examined the expression of markers in both the central nervous system and the serum in an attempt to study the behaviour and potential effects of inflammation markers outside the central nervous system.
On the other hand, some aspects of this study can be improved in future studies. For example, the acute stress model applied to mice (8 h) can be further enhanced using chronic repeated stress; other models could also be used as models of inflammatory depression and anxiety, such as the lipopolysaccharide model. Furthermore, other antidepressants, including serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) or tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), could be used with different durations of treatment. In addition, other adjuvants could be evaluated for their antidepressant potential.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Studies
Male BALB/c mice (from the Animal House Facility of Yarmouk University, Irbid, Jordan) were used in the present study. The mice were 6–8 weeks old and weighed 25 g. The BALB/c line was selected due to its suitability for achieving the study objective of enhancing citalopram efficacy. The mice were kept in separate cages at a temperature of 25 °C with 50–60% humidity and continuous air ventilation. The research was carried out according to the international ethical standards for the care and use of laboratory animals, and the IRB committee of study was approved by Yarmouk University and the Dean of Scientific Research Project Number (51/2022).
4.2. Study Design and Treatments
After 2 days of habituation, mice were randomly allocated to the following groups (n = 6–10 per group): naive (unstressed), control (stressed), citalopram (10 mg/kg/day), citalopram + etifoxine (50 mg/kg/day), citalopram + ascorbic acid (10 mg/kg/day), citalopram + vitamin D (1200 IU/kg/week) and citalopram + ascorbic acid + vitamin D + etifoxine for 7 days, followed by acute immobilisation for 8 h on the 8th day. All the doses were chosen based on the relevant literature [33,48,49,50,51,52]. All treatments were purchased from (Santa Cruz, Santa Cruz, CA USA).
4.3. Acute Restraint Model
To induce anxiety in the mice, an acute immobility stress test was performed according to the method of Machawal and Kumar [32] with slight modifications. The mice were restrained for 8 h while breathing allowed.
4.4. Behavioural Paradigms
4.4.1. Forced Swim Test
The FST is the most commonly used behavioural model for screening antidepressant-like activity in rodents [53]. The mice were individually forced to swim for 5 min in an open glass chamber (25 × 15 × 25 cm3) containing fresh water to a height of 15 cm and maintained at 26 ± 1 °C. The floating time (FT) was defined as the time at which the mice stopped moving completely while in the water.
4.4.2. Marble Burying Test
A cage (17.5 × 10 × 5.5 inches) was filled to a depth of approximately 5 cm with husk bedding material that was evenly distributed on a flat surface across the entire cage. Twenty glass marbles (1.4 cm in diameter) were then evenly spaced in a 4 × 5 grid on the surface of the bedding. During the testing phase, each mouse was placed in the cage and allowed to explore it for 30 min. At the end of the test, the mice were removed from the cage and the number of marbles buried with bedding up to 2/3 of their depth was counted as reported in [54].
4.4.3. Open Field Test
An OFT was performed to assess locomotion, anxiety and sedation in the mice, as in [55]. Briefly, the mice were placed in a central square and allowed to move freely for 5 min. The field was located in a test room and was lit by indirect lighting. The procedure was performed in an empty room to minimise noise and distractions. The open field maze was cleaned between each mouse using 70% ethyl alcohol. The locomotion activity (represented by the number of lines crossed) and sedation (represented by the rearing frequency) were recorded.
4.5. Tissue Collection
After performing the behavioural tests, the mice were sacrificed, blood was collected and serum was obtained using standard protocols. Also, whole brains were collected and stored at −80 for further analysis.
4.5.1. Western Blots
Western blot was performed according to standard protocols as in [56] Mirzaii-Dizgah et al. (2020) with some modifications. The total protein was quantified using a bicinchoninic acid assay kit (Bioquochem, Oviedo, Spain), and an equal amount of protein was separated using a sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel and then the proteins were transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The membrane was then blocked for 1 h at room temperature using 3% bovine serum albumin (BSA) before incubating it overnight with either ICAM-1 or SIRT1 primary antibodies (Abcam, Cambridge, UK). The membrane was washed three times with washing buffer (Tween-20/Tris-buffered saline) before incubating it with the respective secondary antibody (Mybiosource, San Diego, CA, USA) for 1 h at room temperature. Then, the membrane was washed three times before incubating it with ECL substrate (ThermoScientific, USA) for one minute and imaging it using the chemiLITE Chemiluminescence Imaging System (Cleaver Scientific, Rugby, UK). Equal gel loading was determined using actin as a housekeeping gene (Mybiosource, USA). The intensity of the bands was measured using Image J software (National Institutes of Health, USA, https://imagej.net/ij/docs/index.html, accessed on 12 September 2023).
4.5.2. Nitric Oxide Assay
Blood was collected and serum was obtained using standard protocols. The accumulation of nitrate, an indicator of the production of NO, was determined using a colorimetric assay with a Griess reagent [57]. Serum nitrate was assayed using a Nitric Oxide Assay kit (Sunlong, Shanghai, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
4.6. Statistical Analysis
All the data obtained from the behavioural tests and ICAM-1, Sirt1 and NO were analysed using one-way ANOVA and a subsequent Tukey’s post hoc test. A significance threshold was established at p < 0.05. The data are presented as the mean plus the standard error of the mean.
5. Conclusions
Citalopram’s antidepressant and sedative effects are potentiated by ascorbic acid, vitamin D and etifoxine alone or in combination. The increase in NO expression in the brain NO increase was associated with an increase in ICAM-1 and a decrease in SIRT1, but only in the depression state. Antidepressants normalised the brain ICAM-1 and Sirt1 levels through a non-NO-dependent pathway. The serum levels of ICAM-1, SIRT1 and NO were not related to the psychiatric observations in mice. More studies are required to fully uncover the role of neuroinflammation in psychiatric disorders.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, O.G. and M.M.T.; Methodology, A.I., A.Y. and S.A.; Software, A.A. and S.A.; Validation, O.G. and A.A.; Formal analysis, A.I.; Investigation, A.I., E.Q. and S.A.; Resources, A.Y. and E.Q.; Data curation, A.Y. and A.A.; Writing–original draft, O.G., O.A.A. and M.M.T.; Writing–review & editing, O.G., A.A.A.A. and M.M.T.; Visualization, O.A.A.; Supervision, O.A.A. and A.A.A.A.; Project administration, O.G., A.A. and A.A.A.A.; Funding acquisition, O.G. and M.M.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Yarmouk University, grant number “51/2022”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Yarmouk University (protocol code 51/2022 approved on 15 August 2022).
Data Availability Statement
The data are available from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The corresponding author would like to thank Yasmina, Suzi, Sama and Nour for their support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Fazel, M.; Wheeler, J.; Danesh, J. Prevalence of serious mental disorder in 7000 refugees resettled in western countries: A systematic review. Lancet 2005, 365, 1309–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonadiman, C.S.C.; Malta, D.C.; Passos, V.M.d.A.; Naghavi, M.; Melo, A.P.S. Depressive disorders in Brazil: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Popul. Health Metrics 2020, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, O.; Krogh, J.; Mors, O.; Benros, M.E. Inflammation in Depression and the Potential for Anti-Inflammatory Treatment. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, N. Immunology of Major Depression. Neuroimmunomodulation 2014, 21, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FLotrich, E.; Pittsburgh, S. Inflammatory cytokine-associated depression. Brain Res. 2016, 1617, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, M.; Irwin, M.R. HHS Public Access. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 83, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, X.; Tang, Q.; Sun, W. Comparative Efficacy and Acceptability of Anti-inflammatory Agents on Major Depressive Disorder: A Network Meta-Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 691200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gammoh, O.; Mayyas, F.; Elhajji, F.D. Chlorpheniramine and escitalopram: Similar antidepressant and nitric oxide lowering roles in a mouse model of anxiety. Biomed. Rep. 2017, 6, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szarka, A.; Rigo, J., Jr.; Lázár, L.; Bekő, G.; Molvarec, A. Circulating cytokines, chemokines and adhesion molecules in normal pregnancy and preeclampsia determined by multiplex suspension array. BMC Immunol. 2010, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Benveniste, E.N. Adhesion molecule expression and regulation on cells of the central nervous system. J. Neuroimmunol. 1999, 98, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowska, A.M.; Borawska, M.H. Soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1): An overview. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2004, 15, 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Baghai, T.C.; Varallo-Bedarida, G.; Born, C.; Häfner, S.; Schüle, C.; Eser, D.; Zill, P.; Manook, A.; Weigl, J.; Jooyandeh, S.; et al. Classical Risk Factors and Inflammatory Biomarkers: One of the Missing Biological Links between Cardiovascular Disease and Major Depressive Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watroba, M.; Szukiewicz, D. Sirtuins promote brain homeostasis, preventing Alzheimer’s disease through targeting neuroinflammation. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 962769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishi, T.; Yoshimura, R.; Kitajima, T.; Okochi, T.; Okumura, T.; Tsunoka, T.; Yamanouchi, Y.; Kinoshita, Y.; Kawashima, K.; Fukuo, Y.; et al. SIRT1 gene is associated with major depressive disorder in the Japanese population. J. Affect. Disord. 2010, 126, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.-J.; Zhang, C. Down-Regulation of SIRT1 Gene Expression in Major Depressive Disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry 2016, 173, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, L.L.; Akinfiresoye, L.; Kalejaiye, O.; Tizabi, Y. Antidepressant effects of resveratrol in an animal model of depression. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 268, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.H.; Madhana, R.M.; Athira, K.V.; Kasala, E.R.; Bodduluru, L.N.; Pitta, S.; Mahareddy, J.R.; Lahkar, M. Resveratrol ameliorates depressive-like behavior in repeated corticosterone-induced depression in mice. Steroids 2015, 101, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guix, F.X.; Uribesalgo, I.; Coma, M.; Muñoz, F.J. The physiology and pathophysiology of nitric oxide in the brain. Prog. Neurobiol. 2005, 76, 126–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-K.; Paik, J.-W.; Lee, S.-W.; Yoon, D.; Han, C.; Lee, B.-H. Increased plasma nitric oxide level associated with suicide attempt in depressive patients. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 30, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.-H.; Lee, S.-W.; Yoon, D.; Lee, H.-J.; Yang, J.-C.; Shim, S.-H.; Kim, D.-H.; Ryu, S.-H.; Han, C.; Kim, Y.-K. Increased Plasma Nitric Oxide Metabolites in Suicide Attempters. Neuropsychobiology 2006, 53, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kevil, C.G.; Orr, A.W.; Langston, W.; Mickett, K.; Murphy-Ullrich, J.; Patel, R.P.; Kucik, D.F.; Bullard, D.C. Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 (ICAM-1) Regulates Endothelial Cell Motility through a Nitric Oxide-dependent Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 19230–19238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Sarna, S.K. Nitric oxide modifies chromatin to suppress ICAM-1 expression during colonic inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2012, 303, G103–G110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogacka, D.; Audzeyenka, I.; Rachubik, P.; Szrejder, M.; Typiak, M.; Angielski, S.; Piwkowska, A. Involvement of nitric oxide synthase/nitric oxide pathway in the regulation of SIRT1–AMPK crosstalk in podocytes: Impact on glucose uptake. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 709, 108985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakesh, G.; Pae, C.-U.; Masand, P.S. Beyond serotonin: Newer antidepressants in the future. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2017, 17, 777–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojo, J.E.; Ros, S.; Agüera, L.; de la Gándara, J.; de Pedro, J.M. Combined antidepressants: Clinical experience. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2005, 112, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, C.; Shaikh, A.S.; Han, W.; Chen, D.; Guo, Y.; Jiang, P. Vitamin D and depression: Mechanisms, determination and application. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr 2019, 28, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickers, N.J. Animal communication: When i’m calling you, will you answer too? Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R713–R715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binfaré, R.W.; Rosa, A.O.; Lobato, K.R.; Santos, A.R.; Rodrigues, A.L.S. Ascorbic acid administration produces an antidepressant-like effect: Evidence for the involvement of monoaminergic neurotransmission. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 33, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amr, M.; El-Mogy, A.; Shams, T.; Vieira, K.; Lakhan, S.E. Efficacy of vitamin C as an adjunct to fluoxetine therapy in pediatric major depressive disorder: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Nutr. J. 2013, 12, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, B. Etifoxine is non-inferior than clonazepam for reduction of anxiety symptoms in the treatment of anxiety disorders: A randomized, double blind, non-inferiority trial. Psychopharmacology 2020, 237, 3357–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, D.J. Etifoxine versus alprazolam for the treatment of adjustment disorder with anxiety: A randomized controlled trial. Adv. Ther. 2015, 32, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machawal, L.; Kumar, A. Possible involvement of nitric oxide mechanism in the neuroprotective effect of rutin against immobilization stress induced anxiety like behaviour, oxidative damage in mice. Pharmacol. Rep. 2014, 66, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, J.; Nitzke, A.M.; Doukas, D.G.; Seiglie, M.P.; Dulawa, S.C. Antidepressant response to chronic citalopram treatment in eight inbred mouse strains. Psychopharmacology 2011, 213, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervo, L.; Canetta, A.; Calcagno, E.; Burbassi, S.; Sacchetti, G.; Caccia, S.; Fracasso, C.; Albani, D.; Forloni, G.; Invernizzi, R.W. Genotype-Dependent Activity of Tryptophan Hydroxylase-2 Determines the Response to Citalopram in a Mouse Model of Depression. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 8165–8172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kala, M.; Nivsarkar, M. Role of cortisol and superoxide dismutase in psychological stress induced anovulation. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2016, 225, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papakostas, G.I.; Fava, M.; Thase, M.E. Treatment of SSRI-Resistant Depression: Across-Class Switches. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 63, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Undurraga, J.; Baldessarini, R.J. Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trials of Antidepressants for Acute Major Depression: Thirty-Year Meta-Analytic Review. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiraly, S.J.; Kiraly, M.A.; Hawe, R.D.; Makhani, N. Vitamin D as a Neuroactive Substance: Review. Sci. World J. 2006, 6, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coplan, J.D.; Aaronson, C.J.; Panthangi, V.; Kim, Y. Treating comorbid anxiety and depression: Psychosocial and pharmacological approaches. World J. Psychiatry 2015, 5, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahraian, A.; Ghanizadeh, A.; Kazemeini, F. Vitamin C as an adjuvant for treating major depressive disorder and suicidal behavior, a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. Trials 2015, 16, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sales, A.J.; Joca, S.R.; Del Bel, E.; Guimarães, F.S. The antidepressant-like effect of doxycycline is associated with decreased nitric oxide metabolite levels in the prefrontal cortex. Behav. Brain Res. 2024, 458, 114764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, G.; Grasso, M.; Fidilio, A.; Torrisi, S.A.; Musso, N.; Geraci, F.; Tropea, M.R.; Privitera, A.; Tascedda, F.; Puzzo, D.; et al. Antioxidant Activity of Fluoxetine and Vortioxetine in a Non-Transgenic Animal Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 809541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, E.; Yagi, G.; Nakaki, T.; Kanba, S.; Asai, M. Elevated plasma nitrate levels in depressive states. J. Affect. Disord. 2001, 63, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkin, A.J.; Bruce, K.H.; Craft, B.; Paul, I.A. Nitric oxide synthase inhibitors have antidepressant-like properties in mice 1. Acute treatments are active in the forced swim test. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 372, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesse, C.R.; Bortolatto, C.; Savegnago, L.; da Rocha, J.B.T.; Nogueira, C.W. Involvement of l-arginine–nitric oxide–cyclic guanosine monophosphate pathway in the antidepressant-like effect of tramadol in the rat forced swimming test. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 32, 1838–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhir, A.; Kulkarni, S. Involvement of l-arginine–nitric oxide–cyclic guanosine monophosphate pathway in the antidepressant-like effect of venlafaxine in mice. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 31, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegener, G.; Volke, V. Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitors as Antidepressants. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Liang, L. Vitamin D3/vitamin D receptor signaling mitigates symptoms of post-stroke depression in mice by upregulating hippocampal BDNF expression. Neurosci. Res. 2021, 170, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gammoh, O.; Ibrahim, A.; Qnais, E.; Alqudah, A.; Altaber, S.; Aljabali, A.A.A.; Tambuwala, M.M. Vitamins C and D Exhibit Similar Antidepressant Effects to Escitalopram Mediated by NOx and FKBPL in a Stress-Induced Mice Model. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koizumi, M.; Kondo, Y.; Isaka, A.; Ishigami, A.; Suzuki, E. Vitamin C impacts anxiety-like behavior and stress-induced anorexia relative to social environment in SMP30/GNL knockout mice. Nutr. Res. 2016, 36, 1379–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesmati, M.; Zadehdarvish, F.; Jelodar, Z.; Torabi, M. Vitamin C potentiate sedative effect of magnesium oxide nanoparticles on anxiety and nociception in the postpartum depression model. Nanomed. J. 2017, 4, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Verleye, M.; Dumas, S.; Heulard, I.; Krafft, N.; Gillardin, J.-M. Differential effects of etifoxine on anxiety-like behaviour and convulsions in BALB/cByJ and C57BL/6J mice: Any relation to overexpression of central GABAA receptor beta2 subunits? Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011, 21, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porsolt, R.D.; Bertin, A.; Blavet, N.; Deniel, M.; Jalfre, M. Immobility induced by forced swimming in rats: Effects of agents which modify central catecholamine and serotonin activity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1979, 57, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas, L.B.; Kolb, Y.; Prinssen, E.P. A combined marble burying–locomotor activity test in mice: A practical screening test with sensitivity to different classes of anxiolytics and antidepressants. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 547, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dishman, R.; Armstrong, R.; Delp; Graham, R.; Dunn, A. Open-field behavior is not related to treadmill performance in exercising rats. Physiol. Behav. 1988, 43, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaii-Dizgah, M.-H.; Mirzaii-Dizgah, M.-R.; Mirzaii-Dizgah, I. Serum and saliva total tau protein as a marker for relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 135, 109476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, L.C.; Wagner, D.A.; Glogowski, J.; Skipper, P.L.; Wishnok, J.S.; Tannenbaum, S.R. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal. Biochem. 1982, 126, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).